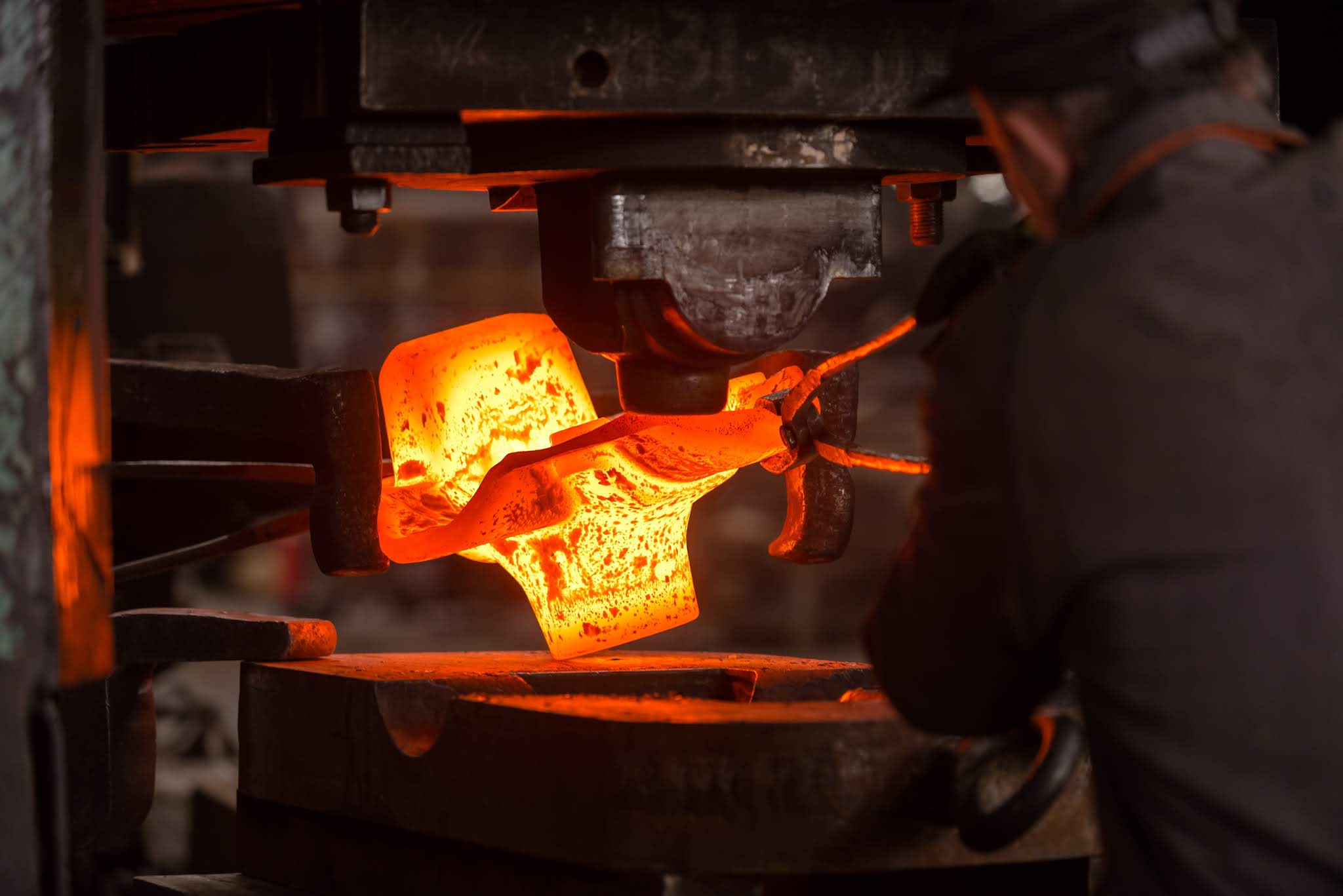
The Definitive Guide to Closed Die Forging: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for closed die forging
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable closed die forging solutions can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries demand higher precision and durability in metal components, understanding the nuances of closed die forging becomes essential. This guide aims to demystify the closed die forging process, exploring its various types, applications, and the critical factors influencing cost and quality.
From automotive to aerospace, closed die forging serves diverse sectors, offering advantages such as enhanced strength and tailored designs. As you navigate this global market, our comprehensive resource will empower you to make informed purchasing decisions by detailing how to effectively vet suppliers, evaluate material options, and understand the implications of different forging techniques.
With insights into the latest technological advancements and industry best practices, this guide is designed to help you identify reputable partners and optimize your procurement strategy. By addressing key considerations and providing actionable insights, we aim to equip B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to harness the full potential of closed die forging in their operations. Whether you are looking to enhance product quality or reduce lead times, this guide will serve as your roadmap in the intricate world of closed die forging.
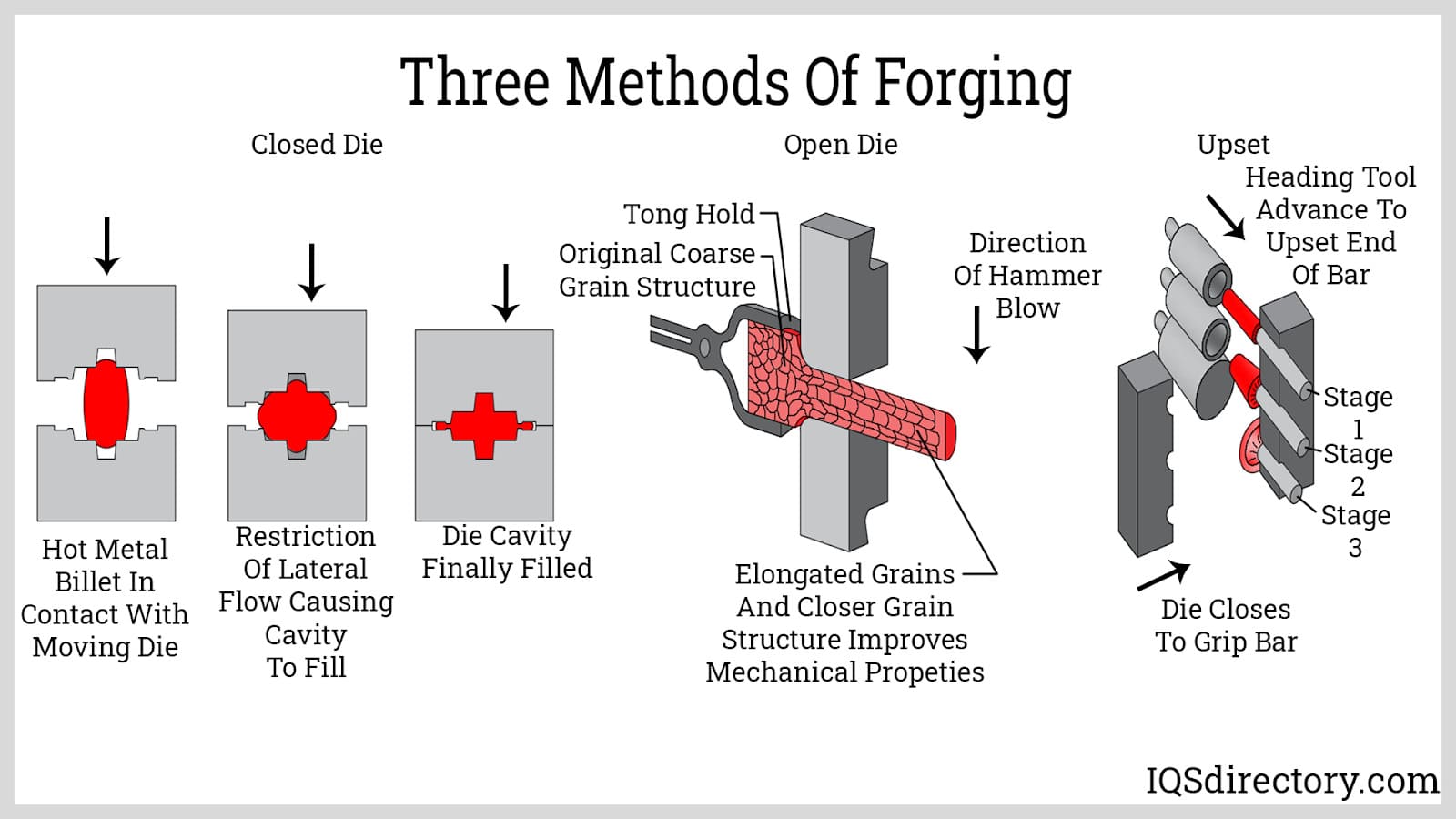
Understanding closed die forging Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impression Die Forging | Uses custom-shaped dies to create complex geometries. | Automotive components, aerospace parts | Pros: High precision, excellent surface finish. Cons: Higher tooling costs, longer lead times. |
| Flashless Forging | Minimal or no flash produced; close tolerance achieved. | Precision engineering, medical devices | Pros: Reduces material waste, enhances dimensional accuracy. Cons: Limited to simpler shapes. |
| Multi-Stage Forging | Involves multiple forging steps to achieve complex shapes. | Gears, crankshafts, and other intricate components | Pros: Improved mechanical properties, tailored designs. Cons: Increased complexity in tooling and process management. |
| Upset Forging | Increases the diameter of the workpiece while shortening its length. | Fasteners, bolts, and bushings | Pros: Efficient material use, strong structural integrity. Cons: Limited to specific applications, requires precise control. |
| Ring Forging | Specifically designed for producing rings or circular shapes. | Bearings, rings for machinery | Pros: High strength and uniformity, ideal for rotating components. Cons: Specialized tooling, potentially higher costs. |
What are the Characteristics of Impression Die Forging?
Impression die forging is characterized by the use of custom-shaped dies that allow for the production of complex geometries. This method is particularly suitable for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision and surface finish are critical. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment in tooling, which can be significant, but the resulting high-quality components often justify the cost.
Illustrative image related to closed die forging
How Does Flashless Forging Enhance Precision?
Flashless forging minimizes or eliminates the flash produced during the forging process, enabling manufacturers to achieve close tolerances. This method is ideal for precision engineering applications, including medical devices, where exact dimensions are crucial. Buyers should weigh the advantages of reduced material waste and enhanced accuracy against the limitation of producing simpler shapes.
What Advantages Does Multi-Stage Forging Offer?
Multi-stage forging involves several sequential forging processes to create intricate shapes. This technique is advantageous for producing components like gears and crankshafts, where enhanced mechanical properties are essential. For B2B buyers, the ability to customize designs is a significant benefit; however, the increased complexity in tooling and process management should be considered.
When is Upset Forging the Right Choice?
Upset forging focuses on increasing the diameter of a workpiece while simultaneously shortening its length. It is commonly used for manufacturing fasteners and bolts. This method offers efficient material use and strong structural integrity, making it appealing for buyers in the fastener industry. However, its applications are somewhat limited, requiring precise control during the forging process.
What is the Role of Ring Forging in Manufacturing?
Ring forging is specialized for producing rings or circular shapes, which are critical in various machinery components such as bearings. This method provides high strength and uniformity, making it ideal for rotating parts. B2B buyers should be aware of the specialized tooling requirements and potentially higher costs associated with this type of forging, but the benefits of improved performance often outweigh these drawbacks.
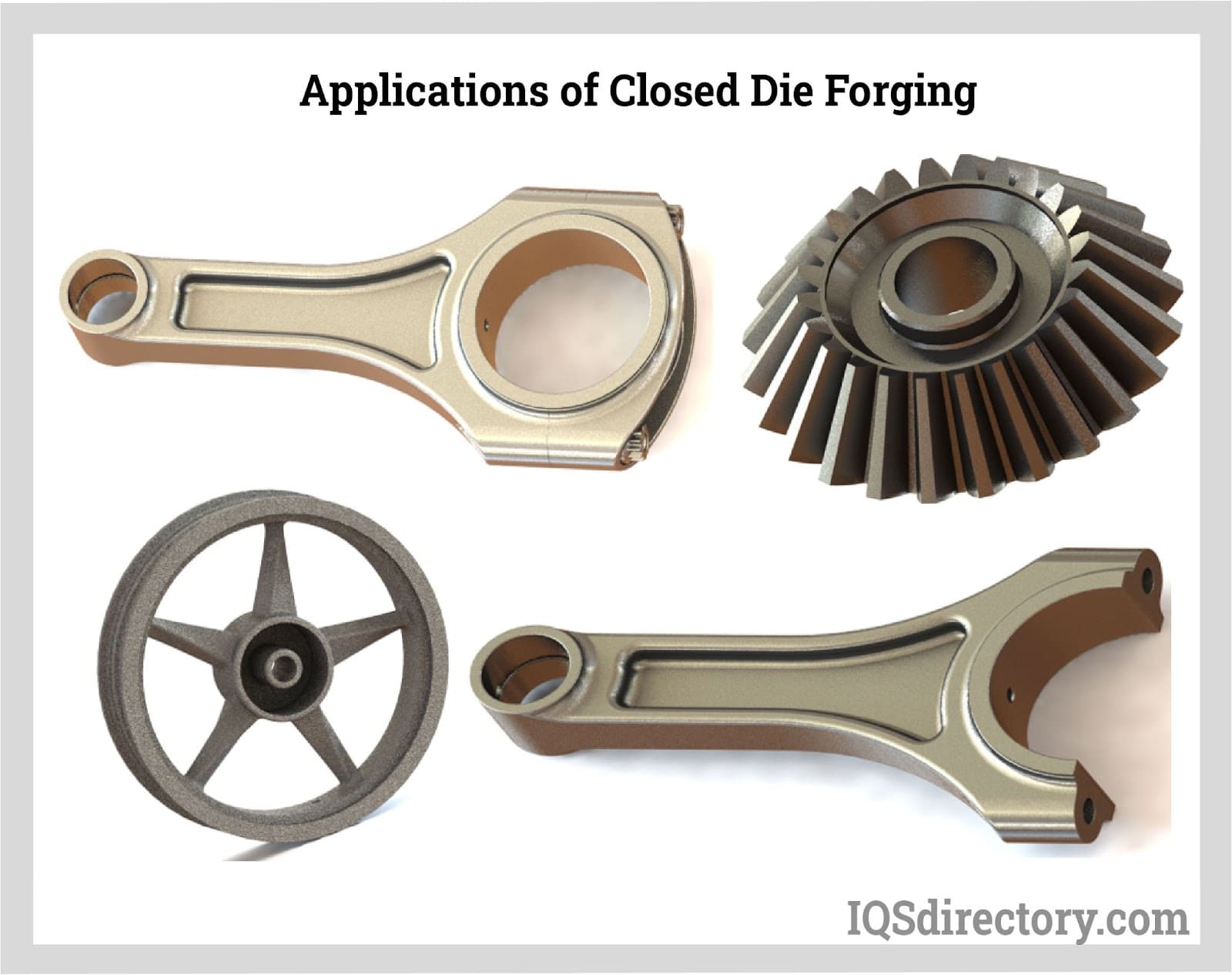
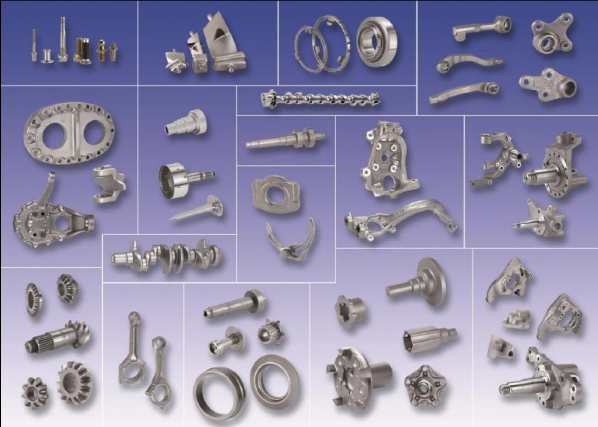
Key Industrial Applications of closed die forging
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of closed die forging | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of drivetrain components | Enhanced strength and durability of parts | Material specifications, precision tolerances, lead times |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of aircraft structural components | Lightweight yet robust parts for improved fuel efficiency | Compliance with industry standards, quality certifications |
| Energy | Creation of turbine components | High-performance parts that withstand extreme conditions | Material selection, heat treatment requirements |
| Heavy Machinery | Forging of gears and shafts | Improved mechanical properties and longevity | Custom die design, volume production capabilities |
| Construction Equipment | Production of high-strength fasteners | Increased reliability and safety in construction | Sourcing of specialized materials, dimensional accuracy |
How is Closed Die Forging Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, closed die forging is critical for producing drivetrain components such as gears, axles, and crankshafts. These parts require high strength and precision to ensure optimal performance and safety. Closed die forging enhances the mechanical properties of these components, making them more durable and capable of withstanding rigorous operational conditions. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, it is vital to consider material specifications and precision tolerances to ensure compatibility with existing automotive systems.
What Are the Aerospace Applications of Closed Die Forging?
Closed die forging plays a pivotal role in the aerospace industry, specifically in the manufacturing of structural components like wing spars and fuselage frames. The process allows for the creation of lightweight yet robust parts that contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance. Aerospace components must meet stringent industry standards, making compliance and quality certifications essential for sourcing. Buyers from Europe, particularly Germany, should focus on suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to these rigorous quality benchmarks.
How is Closed Die Forging Used in the Energy Sector?
In the energy industry, closed die forging is utilized to produce turbine components such as blades and rotors that operate in extreme conditions. The high-performance requirements of these parts necessitate materials that can withstand intense pressure and temperature fluctuations. Buyers must consider the specific heat treatment requirements and material selection to ensure the longevity and reliability of these components. This is particularly important for buyers in the Middle East, where energy production plays a significant economic role.
What Are the Benefits of Closed Die Forging in Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery relies on closed die forging for the production of critical components like gears and shafts. The enhanced mechanical properties achieved through this forging process lead to increased longevity and reduced maintenance costs. For businesses in this sector, sourcing considerations include the need for custom die designs and the ability to meet volume production demands. International buyers must also evaluate the supplier’s capacity to deliver high-quality products within specified lead times to maintain operational efficiency.
How Does Closed Die Forging Enhance Construction Equipment Reliability?
In the construction equipment sector, closed die forging is essential for producing high-strength fasteners and structural components. These parts are crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of construction machinery. The forging process significantly improves the mechanical properties of the materials used, making them less prone to failure under heavy loads. Buyers should focus on sourcing specialized materials and ensuring dimensional accuracy to meet the demanding requirements of construction applications, particularly in regions with challenging operating conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘closed die forging’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection Challenges in Closed Die Forging
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in selecting the right material for closed die forging. With various options like aluminum, carbon steel, and titanium, each material presents unique properties that influence the final product’s strength, weight, and durability. Buyers may struggle to understand how these properties will perform under specific conditions, leading to potential failures in application, increased costs, or extended lead times. This can be particularly challenging for industries such as automotive or aerospace, where precision and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: To overcome material selection challenges, buyers should conduct thorough assessments of their project requirements, considering factors such as mechanical properties, application conditions, and cost implications. Collaborating closely with suppliers who have expertise in metallurgy can provide valuable insights into which materials are best suited for specific applications. Additionally, utilizing simulation software can help predict how different materials will perform during the forging process, allowing for more informed decisions. Establishing a clear communication channel with the manufacturer regarding material expectations will help ensure that the right choice is made from the outset, thus avoiding costly mistakes later in production.
Scenario 2: Managing Production Efficiency and Lead Times
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers in closed die forging is managing production efficiency and lead times. As the complexity of designs increases, so too does the time required for tooling and setup, which can lead to delays in product delivery. Buyers may find themselves in situations where their production schedules are disrupted, affecting their supply chain and ultimately customer satisfaction. This is particularly critical in fast-paced industries like automotive, where time-to-market can significantly impact competitiveness.
Illustrative image related to closed die forging
The Solution: To enhance production efficiency and minimize lead times, buyers should consider investing in advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation and predictive maintenance. By partnering with suppliers who utilize state-of-the-art equipment and techniques, buyers can reduce setup times and improve overall production flow. Furthermore, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can help align production schedules with market demand, reducing the risk of overproduction and associated costs. Regularly reviewing and optimizing the forging process based on data analytics will also enable continuous improvements and quicker response times to market changes.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality Control and Consistency in Forged Products
The Problem: Quality control and consistency are significant concerns for buyers of closed die forging products. Variations in die design, material properties, and process parameters can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, which may result in rejected parts, increased scrap rates, and warranty claims. These issues can be particularly costly in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace and defense, where even minor defects can have serious repercussions.
The Solution: To ensure high-quality outcomes, buyers should implement robust quality control measures throughout the forging process. This includes conducting thorough inspections of dies and materials before production, as well as establishing clear quality benchmarks for the finished product. Engaging suppliers that adhere to stringent quality standards, such as ISO certifications, can provide additional assurance of consistency and reliability. Utilizing non-destructive testing methods can also help identify potential defects early in the production process, allowing for timely interventions. Finally, fostering a collaborative relationship with manufacturers to share feedback on product performance can lead to continuous improvements and higher quality standards over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for closed die forging
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Closed Die Forging?
Aluminum is a widely used material in closed die forging due to its favorable properties. It boasts a low density, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. Aluminum can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors. However, its low yield strength necessitates careful control during the forging process to prevent overstressing, which can lead to defects.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which contributes to fuel efficiency in automotive applications. Additionally, its corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of forged components. However, aluminum’s lower strength compared to steel and its susceptibility to deformation under high loads can limit its use in high-stress applications. Furthermore, the manufacturing complexity associated with aluminum forging can increase production costs.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Closed Die Forging?
Carbon steel is another popular choice for closed die forging, known for its good forgeability and ability to be heat-treated for enhanced strength. It offers a balance of ductility and hardness, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Carbon steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it versatile for both structural and mechanical components.
Pros and Cons of Using Carbon Steel
The cost-effectiveness of carbon steel is a significant advantage, as it is generally cheaper than many alloys. Its mechanical properties can be tailored through heat treatment, allowing for a wide range of applications. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, which may necessitate additional surface treatments. Moreover, its brittleness at low temperatures can limit its use in certain environments.
What Are the Benefits of Alloy Steel in Closed Die Forging?
Alloy steel is often selected for closed die forging when high strength and wear resistance are critical. This material is engineered to withstand high-stress applications, making it ideal for components like gears and crankshafts. Alloy steel can endure elevated temperatures and pressures, ensuring durability and reliability in demanding environments.

Illustrative image related to closed die forging
Pros and Cons of Using Alloy Steel
The key advantage of alloy steel is its enhanced mechanical properties, which improve performance in high-stress applications. It also offers improved corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel. However, alloy steel can be more expensive due to the alloying elements used, and its forging process may require more complex tooling and techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Why Choose Titanium for Closed Die Forging Applications?
Titanium is a premium material for closed die forging, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is particularly suitable for applications requiring high precision and complex shapes, such as aerospace components. Titanium can withstand high temperatures and is highly resistant to oxidation, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Pros and Cons of Using Titanium
The primary advantage of titanium is its lightweight nature combined with high strength, which is essential for aerospace and high-performance applications. Its corrosion resistance further enhances its suitability for demanding environments. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than other metals, and its forging process is more complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Summary Table of Materials for Closed Die Forging
| Material | Typical Use Case for closed die forging | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive components | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Structural and mechanical parts | Cost-effective and versatile | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Alloy Steel | Gears and high-stress components | High strength and wear resistance | More expensive and complex tooling | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace and high-performance parts | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex processing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of commonly used materials in closed die forging. By understanding these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for closed die forging
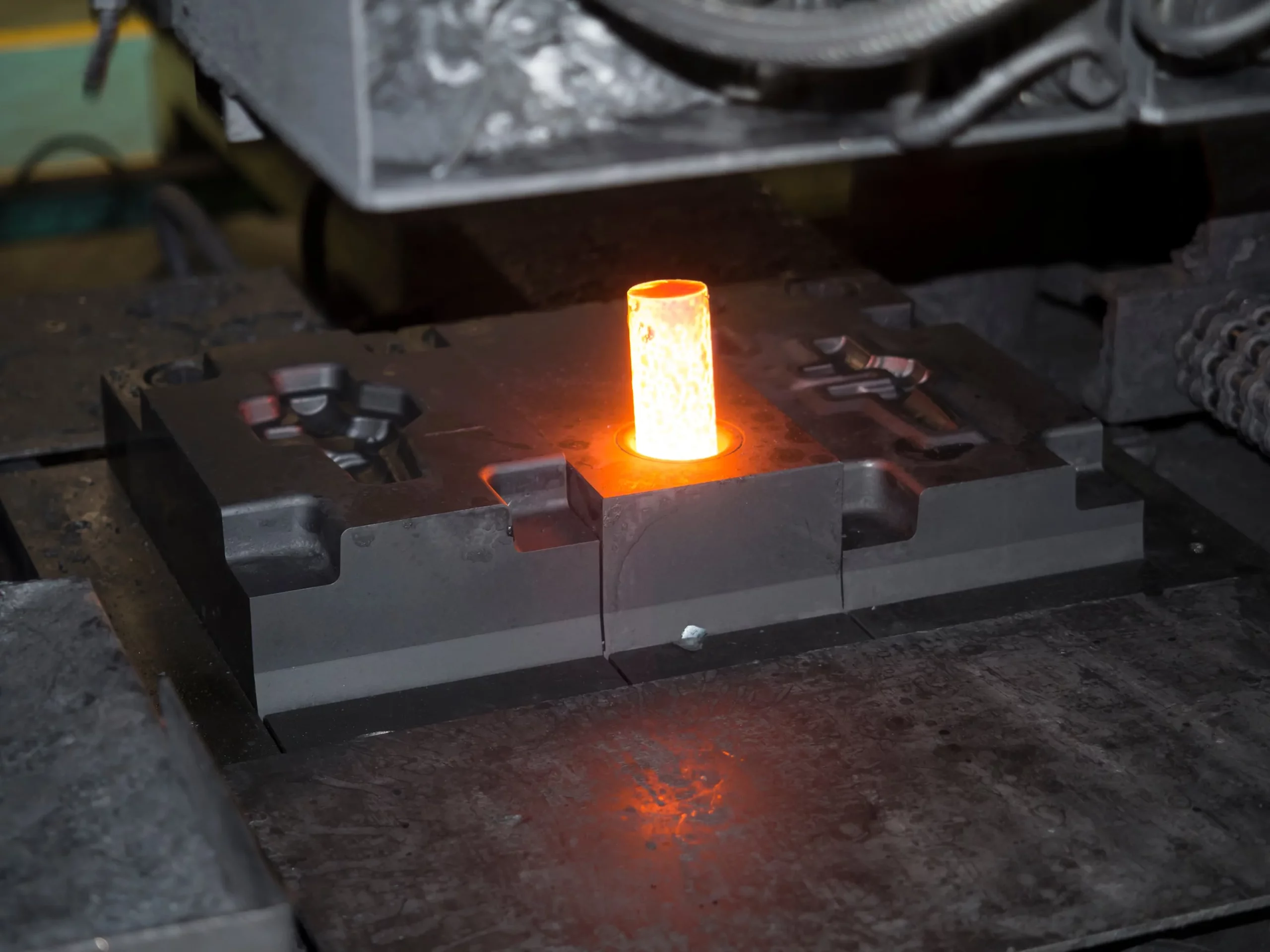
What Are the Main Stages of the Closed Die Forging Manufacturing Process?
Closed die forging is a highly specialized manufacturing process that involves several critical stages to produce high-quality forged components. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is the Raw Material Processed Before Forging?
The first stage involves selecting and preparing the raw material, which is typically a metal alloy suited for forging, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, or titanium. The metal is cut into pre-determined lengths and shapes, often in the form of billets or bars, which are then heated to a specific temperature range to enhance malleability. This heating process is crucial, as it allows the metal to be easily shaped without cracking.
Once heated, the material is transferred to the forging area, where it is inspected for consistency in temperature and quality. This ensures that the material’s properties are optimal for the subsequent forming process.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Metal?
The forming stage is where the actual shaping of the metal occurs. In closed die forging, the heated workpiece is placed between two dies that carry the negative impression of the desired shape. The top die descends to apply high pressure, forcing the metal to fill the die cavities completely. This process can involve multiple blows or stages, particularly for complex geometries, which allows for controlled grain flow and improved mechanical properties.
Key techniques in this stage include:
- Multi-Stage Forging: This involves a series of sequential operations to gradually shape the metal, which is essential for achieving intricate designs.
- Die Design and Engineering: The dies must be meticulously designed to match the desired specifications and material characteristics, ensuring precision in the final product.
Assembly: How Are Forged Components Joined Together?
Following the forging process, components may require assembly, particularly if they are part of a larger system or machinery. This could involve welding, machining, or other joining techniques to combine multiple forged parts into a single assembly. The assembly stage is critical, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Quality of the Forged Parts?
The finishing stage includes several operations to enhance the mechanical properties and surface quality of the forged components. Common finishing processes include:
- Heat Treatment: This process alters the microstructure of the material to improve strength and hardness.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as shot peening, coating, or polishing are employed to enhance wear resistance and surface finish.
- Machining: Some components may require additional machining to achieve tight tolerances and specific surface finishes.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Closed Die Forging?
Quality assurance in closed die forging is paramount for ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations. Buyers must be aware of the various quality control measures that suppliers implement throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Closed Die Forging?
Adhering to international standards is crucial for maintaining quality and consistency in manufacturing processes. The most common standards include:

Illustrative image related to closed die forging
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management system standard that outlines requirements for consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet specific safety and health standards to be sold, which is indicated by the CE mark.
- API Standards: For products used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is often required.
These standards provide a framework for continuous improvement and ensure that suppliers are committed to delivering high-quality products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Forging Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the forging process to ensure compliance with quality standards. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify their compliance with specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, inspections are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and material flow.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After finishing, the final products undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet dimensional and performance specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Verify Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality of forged components. These methods may include:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and dye penetrant testing are used to detect surface and subsurface defects without damaging the component.
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile tests, impact tests, and hardness tests are conducted to assess the material’s mechanical properties and ensure they meet specified requirements.
- Dimensional Inspection: Precision measurement tools are used to verify that the forged parts conform to design specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to strict quality control measures is vital. Here are some strategies to verify supplier QC practices:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess their quality control practices. These audits can be scheduled regularly or conducted as part of the supplier selection process. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the supplier’s quality management systems, production processes, and adherence to international standards.
Additionally, requesting quality reports that document the results of inspections and tests can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality assurance.
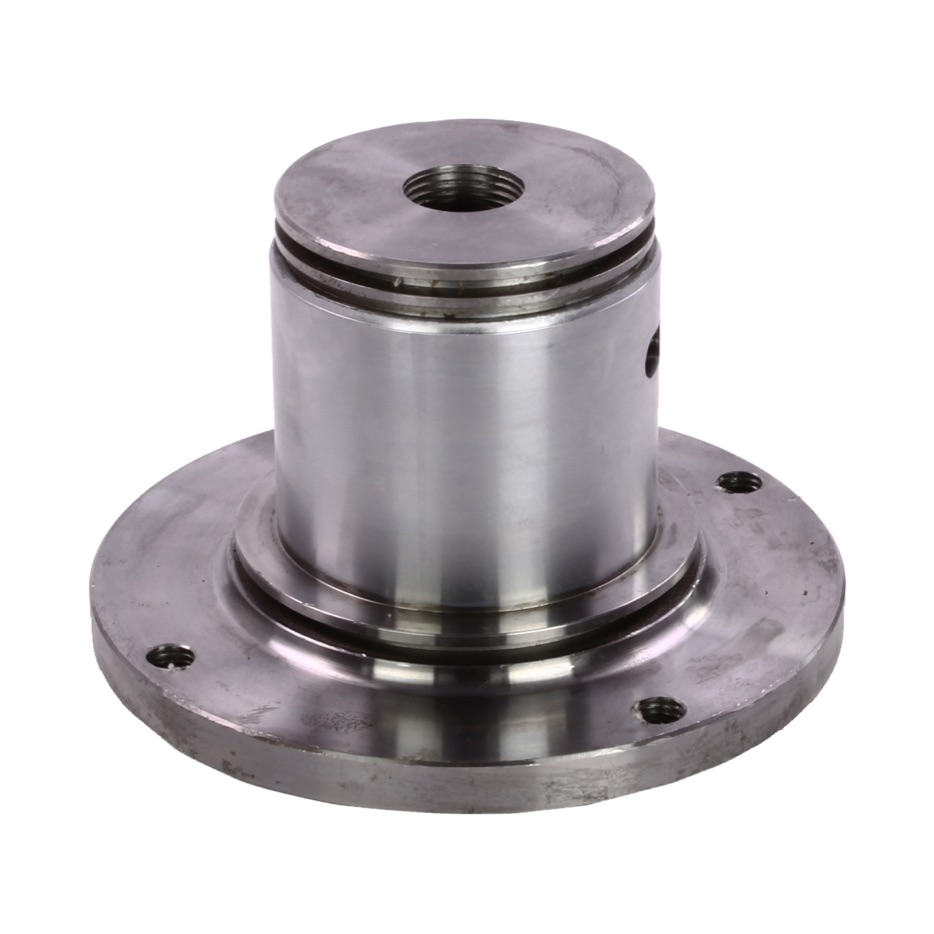

Illustrative image related to closed die forging
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These independent inspections can be particularly valuable for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where local suppliers may not always meet international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from different regions may encounter unique quality control challenges due to varying local regulations and standards. It’s crucial for buyers to:
- Understand Regional Standards: Familiarize themselves with the quality standards applicable in their region, as well as those of their suppliers’ countries.
- Evaluate Supplier Certifications: Verify that suppliers possess relevant certifications and comply with both local and international standards.
- Maintain Open Communication: Establish clear communication channels with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in closed die forging, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘closed die forging’
When sourcing closed die forging services, a systematic approach can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of the components you procure. This checklist is designed to guide international B2B buyers through essential steps in the sourcing process, ensuring that you find a supplier who meets your technical and business requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly define your project’s technical specifications. Include details such as the material type, dimensions, tolerances, and any specific mechanical properties required.
– Why It Matters: Precise specifications help suppliers provide accurate quotes and timelines, minimizing misunderstandings later in the process.
– What to Look For: Ensure your specifications align with industry standards relevant to your sector, such as automotive or aerospace.
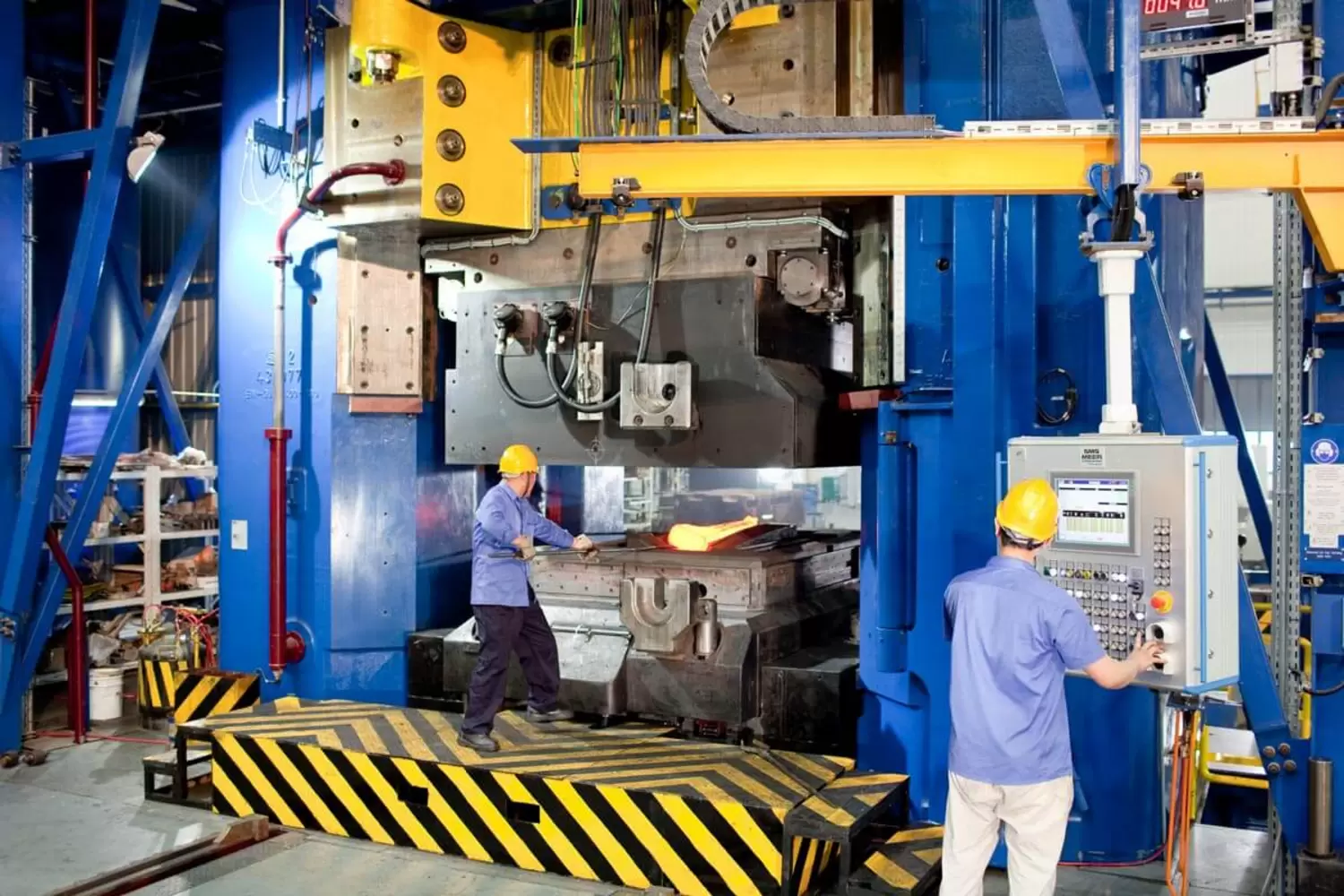

Illustrative image related to closed die forging
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential closed die forging suppliers. Use online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of candidates.
– Why It Matters: A diverse pool of suppliers increases your chances of finding one that meets both your quality and budgetary needs.
– What to Look For: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and positive customer reviews.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the technical capabilities of each supplier on your shortlist. Request detailed information about their forging processes, equipment, and quality control measures.
– Why It Matters: Understanding a supplier’s capabilities ensures they can meet your specific requirements and produce high-quality parts.
– What to Look For: Look for suppliers who utilize advanced technology and maintain high standards in their production processes.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Check that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. This ensures they adhere to quality management principles and regulatory compliance.
– Why It Matters: Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and reliability, which is critical in industries like automotive and aerospace.
– What to Look For: Ask for documentation and audit reports to verify their certifications are current and applicable to your needs.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Solicit quotes from your shortlisted suppliers, ensuring you provide the same specifications to each. This allows for a fair comparison of pricing and services.
– Why It Matters: Obtaining multiple quotes helps you understand the market rate and ensures you are not overpaying for your components.
– What to Look For: Pay attention to the breakdown of costs, including tooling, labor, and lead times, and consider the total value rather than just the lowest price.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If possible, conduct site visits or virtual tours of the suppliers’ facilities to observe their operations firsthand. This can provide insight into their production capabilities and work environment.
– Why It Matters: Seeing the operation in action helps you assess the supplier’s quality standards, equipment, and overall professionalism.
– What to Look For: Evaluate cleanliness, organization, and the technology used in production, as these factors can impact the quality of your forged components.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Ensure that there are clear communication channels between you and your chosen supplier. Discuss how you will handle updates, changes, and any potential issues that may arise.
– Why It Matters: Effective communication is crucial for addressing challenges promptly and maintaining a smooth workflow throughout the project.
– What to Look For: Choose a supplier that demonstrates a willingness to collaborate and communicate openly, which can foster a long-term partnership.
By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing closed die forging services effectively, ensuring that you partner with a reliable supplier capable of meeting your technical and quality demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for closed die forging Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Closed Die Forging?
Understanding the cost structure of closed die forging is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metal significantly affects costs. Common materials like aluminum, carbon steel, and titanium vary in price due to their availability and processing requirements. Specialty alloys may incur higher costs due to their enhanced properties and production complexities.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for operating forging machinery and managing quality control. Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographical location and the complexity of the forging process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as equipment maintenance, utilities, and facility management. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the overall cost per unit.
-
Tooling: Closed die forging requires custom dies that can be expensive to design and manufacture. The cost of tooling is a significant upfront investment but can be amortized over large production runs, making it more economical for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final product meets industry standards necessitates robust QC measures, which can add to the overall cost. Certifications and testing (e.g., ISO standards) may also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs vary based on the origin and destination of the forged components. International shipping can introduce additional complexities, including tariffs and duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Closed Die Forging Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of closed die forging:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it crucial to assess your long-term needs against current pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components or intricate designs can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and longer production times. Clearly defined specifications can help avoid unexpected cost escalations.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material not only affects base costs but also impacts the processing complexity and tooling requirements. Understanding the material properties can help in making cost-effective choices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that require specific quality certifications will generally be more expensive due to the additional testing and compliance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and geographical location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect the total landed cost of the product. Buyers should understand the implications of terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) on their overall pricing strategy.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices in Closed Die Forging?
To maximize value when sourcing closed die forging, consider these negotiation tips:
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQ requirements. This can lead to better pricing and terms from suppliers.
-
Explore Alternative Materials: Assess if alternative materials can meet your specifications at a lower cost, particularly if the application allows for some flexibility.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, performance, and replacement of forged components.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Familiarize yourself with local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors that can impact costs.
-
Build Strong Supplier Relationships: Establishing a reliable partnership with suppliers can facilitate better pricing and favorable terms over time.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing in closed die forging can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. The information provided here serves as a guideline and may not reflect real-time market conditions. For precise quotations, it is advisable to engage directly with suppliers and request tailored proposals that align with your specific requirements.
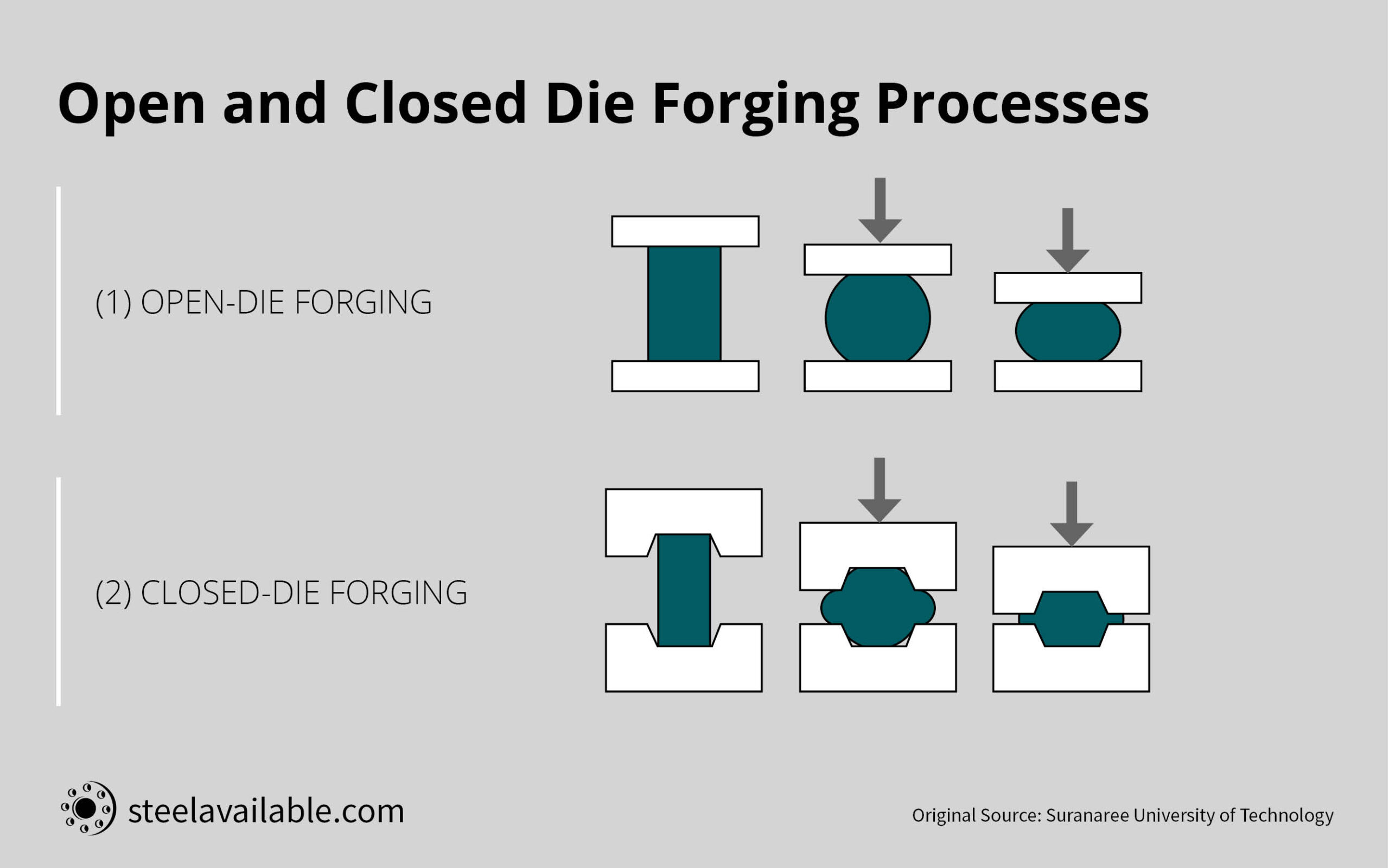
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing closed die forging With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Metal Forming Solutions
When evaluating metal forming techniques, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider various methods that can meet their production needs while balancing performance, cost, and implementation ease. Closed die forging is a well-established technique known for producing high-strength, precise components. However, alternatives such as open die forging and machining may offer advantages in specific applications. Understanding these alternatives can help buyers make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Closed Die Forging | Open Die Forging | Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; excellent mechanical properties | Lower precision; best for simpler shapes | Very high precision; complex geometries achievable |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling costs; cost-effective for large volumes | Lower tooling costs; economical for small runs | High operational costs; cost-effective for low volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized dies; longer setup time | Simple tooling; faster setup | Requires skilled labor; variable setup time |
| Maintenance | Regular die maintenance needed; longer lifespan | Minimal maintenance; dies can wear faster | Tool wear requires regular replacement; maintenance-intensive |
| Best Use Case | Complex, high-stress components (e.g., automotive, aerospace) | Simple, large components (e.g., shafts, rings) | High-precision components (e.g., intricate parts, prototypes) |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Open Die Forging: What Are Its Strengths and Weaknesses?
Open die forging, also known as free forging, utilizes simple dies that do not completely encase the workpiece. This method is ideal for producing large and straightforward shapes, such as shafts and rings. The primary advantage of open die forging is its lower tooling costs and faster setup times, making it an attractive option for small production runs. However, the downside lies in its lower precision and the potential need for additional machining to achieve the desired dimensions. This method is not suitable for complex parts that require tight tolerances.
Machining: When Is It the Right Choice?
Machining involves removing material from a solid block to create parts with high precision. This method excels in producing intricate geometries that other methods may struggle with. Machining provides exceptional control over dimensions and surface finishes, making it ideal for prototypes and low-volume production of complex components. However, the operational costs can be high, particularly for large parts, and skilled labor is often required. Buyers should consider machining when precision is paramount, and the production volume is low.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Metal Forming Solution
Selecting the appropriate metal forming solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your project. Closed die forging stands out for high-volume production of complex and high-strength components. In contrast, open die forging may be more suitable for simpler shapes and lower volumes due to its cost-effectiveness. Machining is the go-to option for high-precision parts, especially when complexity is a factor. By carefully assessing performance needs, cost constraints, and production volumes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and product specifications.
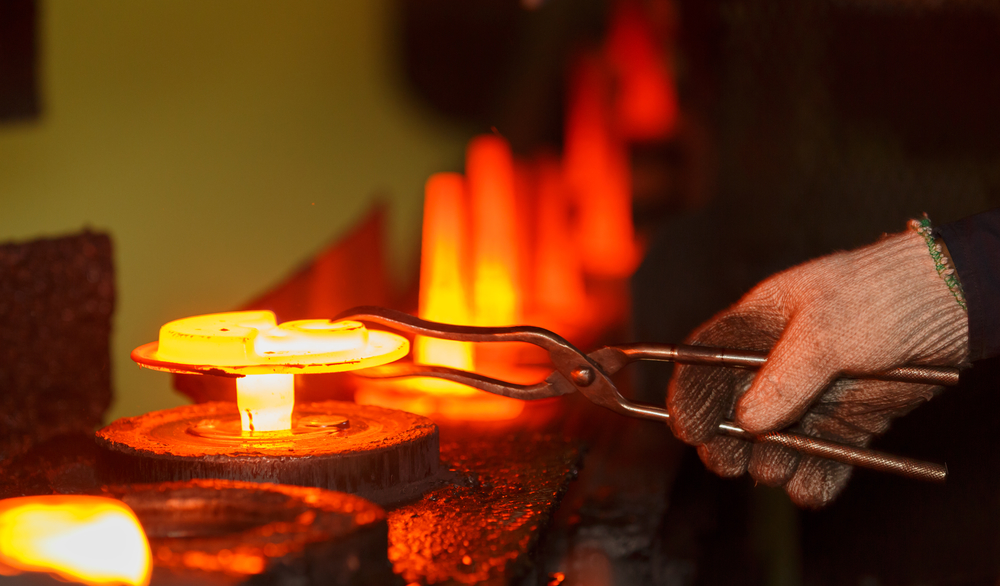

Illustrative image related to closed die forging
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for closed die forging
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Closed Die Forging?
When evaluating closed die forging, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring the production of high-quality components. Understanding these specifications can enhance decision-making for B2B buyers looking for reliable forging solutions.
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific composition and properties of the metal being forged. Common materials include aluminum, carbon steel, alloy steel, copper alloys, and titanium. Each material offers distinct advantages, such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for achieving desired mechanical properties and ensuring the longevity of the final product.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the permissible limits of variation in a component’s dimensions. In closed die forging, tight tolerances are essential to meet the precise specifications required by industries such as aerospace and automotive. The ability to maintain tight tolerances directly impacts the performance and functionality of the forged part, making it a key consideration for buyers.
3. Forging Load
Forging load refers to the amount of pressure applied during the forging process. This parameter is critical because an insufficient load may result in incomplete shaping, while excessive load can lead to material failure, such as cracking or warping. Understanding the required forging load helps manufacturers optimize their processes, ensuring the production of durable and reliable components.
4. Grain Flow Orientation
Grain flow orientation describes the direction of the metal’s internal structure after forging. Proper grain flow is essential for maximizing strength and toughness in the final product. A well-controlled forging process can enhance mechanical properties by aligning the grain structure with the expected load paths. Buyers should consider the implications of grain flow on the performance of their components, especially in high-stress applications.
5. Heating Temperature
The heating temperature is crucial for achieving malleability in the metal before forging. Each material has an optimal temperature range for forging, and maintaining this range is essential to prevent defects. A precise heating cycle ensures that the material can flow adequately into the die, leading to a high-quality finished product.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Closed Die Forging?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the closed die forging sector. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In closed die forging, OEMs often collaborate with forging companies to create custom components tailored to specific needs. Recognizing OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and establish strong partnerships.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQs is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and control costs. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production efficiency, so buyers should negotiate terms that align with their operational needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of closed die forging, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, lead times, and capabilities of different manufacturers. This process is vital for informed decision-making and cost management.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms cover aspects such as shipping, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers engaged in global sourcing to ensure clarity and minimize disputes in contracts.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the final product. In closed die forging, lead times can vary based on factors such as the complexity of the dies and production schedules. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their projects and manage timelines effectively.
Illustrative image related to closed die forging
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions in the closed die forging market, ensuring that they select the right materials and partners for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the closed die forging Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Closed Die Forging?
The closed die forging sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global market dynamics. Key drivers include the rising demand for high-performance components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy. These sectors require forged parts that offer superior strength and precision, thus making closed die forging an attractive option. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can deliver high-quality products with rapid turnaround times.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends within this sector. Automation and digital solutions are enhancing production efficiency and reducing lead times, making it essential for buyers to partner with manufacturers who invest in advanced technologies. Moreover, the adoption of Industry 4.0 practices is allowing for real-time monitoring and data analytics, which can optimize manufacturing processes and improve product quality. Buyers must consider suppliers who are not only technologically adept but also capable of providing customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
Additionally, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions due to global events are prompting buyers to diversify their sourcing strategies. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can mitigate risks associated with dependency on a single source. As the market matures, international buyers will benefit from a keen understanding of local market conditions and supplier capabilities to drive their sourcing decisions effectively.
Illustrative image related to closed die forging
How Is Sustainability Reshaping the Closed Die Forging Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the closed die forging sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and companies are increasingly pressured to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials. Buyers are now looking for suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through transparent practices and measurable outcomes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential benchmarks in supplier evaluation. These certifications not only enhance a supplier’s credibility but also assure buyers that their procurement processes align with their corporate sustainability goals.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in closed die forging is gaining traction. This includes sourcing recycled metals and utilizing eco-friendly lubricants during the forging process. By prioritizing sustainability, buyers can contribute to a circular economy while also enhancing their brand image. As the global market continues to evolve, integrating sustainable and ethical considerations into sourcing strategies will be pivotal for maintaining competitiveness in the closed die forging sector.
What Is the Historical Context of Closed Die Forging?
The roots of closed die forging can be traced back to ancient metalworking practices where artisans used simple dies to shape metal. Over centuries, the process has evolved significantly, transitioning from manual hammering techniques to sophisticated machinery capable of producing complex geometries with high precision. The industrial revolution marked a turning point, as advancements in technology allowed for mass production and increased efficiency.
In the latter half of the 20th century, closed die forging gained prominence in sectors demanding high-strength components, particularly in automotive and aerospace applications. The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining further refined the process, allowing for intricate designs and tighter tolerances. Today, closed die forging stands at the intersection of innovation and tradition, offering manufacturers and buyers alike a reliable method for producing durable, high-performance components while adapting to modern technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of closed die forging
-
How do I choose the right material for closed die forging?
Choosing the right material is crucial for the success of closed die forging. Consider the mechanical properties required for your application, such as strength, ductility, and toughness. Common materials include aluminum for lightweight applications, carbon steel for cost-effectiveness, and titanium for high-precision components. Always consult with your supplier to understand how different materials behave during the forging process, as this will impact the quality and performance of the final product. -
What are the key factors to consider when evaluating closed die forging suppliers?
When evaluating suppliers for closed die forging, consider their industry experience, technical capabilities, and quality certifications. Assess their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demands. Additionally, inquire about their previous projects and client testimonials to gauge their reliability. A good supplier should also be open to communication and willing to collaborate on design and material specifications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for closed die forging?
Minimum order quantities for closed die forging can vary significantly based on the complexity of the part and the supplier’s capabilities. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to accommodate smaller orders, especially for prototypes or initial production runs. Keep in mind that higher MOQs often lead to lower per-unit costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in closed die forging?
Quality assurance in closed die forging can be ensured through several methods. First, select suppliers with ISO certifications or other relevant quality management systems. Request detailed inspection reports and material certifications for each batch. Additionally, consider implementing in-process inspections during production to catch any defects early. Collaborating with suppliers on establishing clear quality standards and expectations will also help maintain product integrity. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by closed die forging suppliers?
Payment terms for closed die forging suppliers can vary widely, but they often include options such as upfront deposits, net 30, or net 60 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments. It’s important to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in your commitment. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable payment arrangements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing closed die forging?
Logistics play a vital role in sourcing closed die forging, particularly for international buyers. Consider shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with transporting heavy forged parts. Ensure that your supplier has reliable logistics partners and can manage customs clearance efficiently. Additionally, it’s wise to discuss packaging options to prevent damage during transit and to understand the insurance coverage for your shipments. -
How can I customize my closed die forging components?
Customization of closed die forging components is achievable through collaboration with your supplier. Begin by clearly defining your specifications, including dimensions, tolerances, and material requirements. Many suppliers offer design assistance and can create custom dies to meet your unique needs. Be prepared for potential additional costs and longer lead times associated with custom projects, but ensure that the resulting products align perfectly with your application. -
What industries commonly use closed die forging?
Closed die forging is widely utilized across various industries due to its ability to produce high-strength, precise components. Key sectors include automotive for parts like gears and axles, aerospace for structural components, and energy for turbine and valve applications. Additionally, industries such as agriculture, construction, and heavy machinery also benefit from closed die forging due to its efficiency in producing durable parts tailored to specific operational requirements.
Top 6 Closed Die Forging Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cornell Forge – Closed Die Forging Solutions
Domain: cornellforge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Closed die forging is a specialized metal forming process that uses dies to shape metal into desired forms, offering advantages like increased strength and precision. Key considerations include: 1. Material: Suitable metals include Aluminum (versatile, low yield strength), Carbon Steel (good forgeability, heat-treatable), Alloy Steel (high strength for high-stress applications), Copper Alloy (high…
2. Canton Drop Forge – Open Die Forging Solutions
Domain: cantondropforge.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Open Die Forging:
– Also known as free forging or smith forging.
– Involves striking a hammer to deform metal on a stationary anvil or using compression with simple dies.
– Dies are typically flat, semi-round, or V-shaped.
– Not suitable for complex shapes; often requires precision machining.
– Pros: Little or no tooling cost, reduced lead time, variety of size options (from a few centimeters…
3. ScienceDirect – Closed-Die Forging
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Closed-die forging is a metal forming process where metal is restricted in lateral flow and filled into a cavity between a punch and die. It involves stages of upsetting, die filling, and end-stage filling, with some material flowing out as flash. This process minimizes production costs and material waste. Closed-die forgings are also known as impression forgings and are categorized into blocker-t…
4. Ferralloy – Closed Die Forging Solutions
Domain: ferralloy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Closed die forging, also known as impression-die forging, is a process where metal is placed between customized shapes and then pressed and hammered to fill the cavities of the dies. It is frequently used for forging steel components and offers several advantages: minimal machining required, ability to create near net shapes and sizes, accurate impressions, tight tolerances, superior mechanical pr…
5. Walker Forge – Closed Die Steel Forgings
Domain: walkerforge.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Walker Forge specializes in closed die steel forgings, also known as impression-die forgings, produced through a multi-step process involving heated special bar quality (SBQ) steel. Key capabilities include:
– Presses up to 4,000 tons
– Parts weighing up to 75 lbs
– Production volumes ranging from a few thousand to 750,000 units per year
– In-house heat treating and precision machining services
– …
6. Laube – Custom Closed Die Forgings
Domain: laube.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Closed Die Forgings Manufacturing Custom Parts, Mass Production. Laube has over 75 years of experience in delivering high-strength, high-precision components across various industries. Capabilities include custom metal forgings, castings, stampings, and screw machined parts. Materials used include carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and titanium alloys. Applications span a…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for closed die forging
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Closed Die Forging Operations?
In the competitive landscape of closed die forging, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for success. By prioritizing the selection of high-quality materials and leveraging advanced forging technologies, international B2B buyers can enhance product strength and precision. Understanding the diverse material properties—such as the advantages of aluminum and alloy steel—allows for informed decisions that align with specific application needs, from automotive to aerospace.
Moreover, engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive services, including heat treatment and assembly, can streamline the production process and reduce lead times. This approach not only ensures superior product quality but also fosters strong supplier relationships that are essential for navigating global markets.
As the demand for high-performance forged components continues to grow across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, proactive buyers should seize the opportunity to innovate and optimize their supply chains. By focusing on strategic sourcing, businesses can not only meet current market demands but also position themselves for future growth. Connect with reputable suppliers today to explore how closed die forging can elevate your manufacturing capabilities and contribute to your long-term success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to closed die forging
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.