The Definitive Guide to Big Air Compressor: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for big air compressor
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing the right big air compressor can be a formidable challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a plethora of options available, from portable models to robust stationary units, the decision-making process often becomes overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of selecting the ideal air compressor, providing insights into various types, applications, and key considerations for effective supplier vetting.
Understanding the nuances of air compressor technology is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and maximizing return on investment. Throughout this guide, we will explore the diverse applications of big air compressors across industries, from construction to manufacturing, and discuss essential factors such as performance specifications, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Additionally, we will provide a comprehensive overview of pricing structures, enabling buyers to make cost-effective choices that align with their budgetary constraints.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market for big air compressors with confidence. Whether you are based in Vietnam, Germany, or elsewhere, our expert recommendations will help you make informed purchasing decisions that meet your unique operational needs. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your procurement process and ensure your projects run smoothly with the right air compressor solution.
Understanding big air compressor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stationary Air Compressors | Fixed installation, high capacity, continuous duty | Manufacturing, automotive repair, construction | Pros: High efficiency, lower operational costs. Cons: Limited mobility, higher upfront investment. |
| Portable Air Compressors | Compact design, easy transport, versatile power options | Construction sites, outdoor events, maintenance | Pros: Flexibility, ease of use. Cons: Lower capacity, may require frequent refueling. |
| Diesel Air Compressors | Powered by diesel engines, high pressure and flow rates | Heavy-duty applications, remote locations | Pros: Long run times, suitable for harsh environments. Cons: Noise, emissions, higher fuel costs. |
| Electric Air Compressors | Powered by electricity, quieter operation, various sizes | Workshops, factories, indoor applications | Pros: Energy-efficient, lower maintenance. Cons: Dependent on power supply, limited mobility. |
| Two-Stage Air Compressors | Two compression stages for higher pressure output | Industrial applications, pneumatic tools | Pros: Increased efficiency, higher PSI. Cons: More complex design, potentially higher costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Stationary Air Compressors?
Stationary air compressors are designed for high-capacity, continuous operation, making them ideal for industries such as manufacturing and automotive repair. They typically feature larger tanks and more powerful motors, allowing for sustained air delivery. B2B buyers should consider the installation space, power requirements, and overall operational efficiency, as these compressors often represent a significant upfront investment but can lead to lower long-term costs.
How Do Portable Air Compressors Serve Various Industries?
Portable air compressors are characterized by their compact design and mobility, making them suitable for construction sites and outdoor events. They can be powered by electricity or gas, offering versatility in different environments. Buyers must assess the compressor’s capacity and ease of transport, as well as the specific air delivery needs of their applications. While they offer flexibility, their lower capacity compared to stationary models may require careful planning for extensive use.
What Makes Diesel Air Compressors Ideal for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Diesel air compressors are robust machines designed for heavy-duty use, often employed in remote locations where electricity is not readily available. They offer high pressure and flow rates, making them suitable for demanding applications in construction and mining. When purchasing, buyers should consider fuel availability, noise levels, and emissions, as these compressors can be noisy and may have higher operational costs due to fuel consumption.
Why Choose Electric Air Compressors for Indoor Use?
Electric air compressors are favored for indoor applications due to their quieter operation and energy efficiency. They come in various sizes, making them suitable for workshops and factories where space and noise are considerations. Buyers should evaluate the power supply requirements and ensure the compressor meets the air demand of their tools and equipment. While they are easier to maintain, their reliance on electrical power may limit mobility.
What Are the Benefits of Two-Stage Air Compressors?
Two-stage air compressors utilize a two-step compression process, allowing for higher pressure outputs ideal for industrial applications. They are particularly effective for powering pneumatic tools that require consistent high pressure. Buyers should consider the compressor’s efficiency and pressure ratings, as well as the complexity of the system, which may lead to higher costs. Despite this, their performance often justifies the investment for businesses requiring reliable and powerful air supply.
Key Industrial Applications of big air compressor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of big air compressor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Pneumatic tools operation | Enhances productivity and efficiency on-site | Reliability, pressure ratings, and portability |
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Streamlines production, reducing labor costs | Energy efficiency, maintenance support, and capacity |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and exploration | Increases operational uptime and safety | Durability in harsh environments, fuel type, and service intervals |
| Automotive | Paint spraying and surface preparation | Improves finish quality and reduces waste | Air quality, tank size, and compatibility with tools |
| Food & Beverage | Packaging and bottling processes | Ensures hygiene and compliance with standards | Clean air certifications, energy consumption, and ease of integration |
How is a Big Air Compressor Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, big air compressors are vital for powering pneumatic tools such as jackhammers, nail guns, and concrete vibrators. These compressors provide a consistent air supply, which enhances productivity and reduces downtime. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing a reliable compressor that can withstand diverse weather conditions is crucial. Additionally, considerations around portability and ease of maintenance are key to ensuring seamless operations on various job sites.
What Role Does a Big Air Compressor Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, big air compressors are integral to automated assembly lines, providing the necessary air pressure for tools and machinery. This application not only streamlines production processes but also reduces labor costs by automating repetitive tasks. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on energy efficiency and capacity when sourcing compressors, as these factors directly impact operational costs and sustainability efforts. Understanding the specific requirements of the production line is essential for selecting the right compressor.
How is a Big Air Compressor Essential in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas sector, big air compressors are used for drilling and exploration activities, supplying air to tools and equipment that operate under extreme conditions. The reliability of these compressors is paramount, as they contribute to safety and operational uptime. Buyers in harsh environments, such as those in the Middle East, need to consider durability, the type of fuel used, and service intervals when sourcing compressors. This ensures they can maintain operations without unexpected failures.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
What is the Importance of Big Air Compressors in Automotive Applications?
Big air compressors are crucial in the automotive industry, particularly for paint spraying and surface preparation. They provide the necessary air pressure to achieve a fine finish and reduce waste, thereby improving overall quality. When sourcing compressors, businesses should prioritize air quality and tank size, ensuring compatibility with various tools and processes. Buyers in Europe, where regulatory standards are stringent, must also consider compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
How Do Big Air Compressors Support Food & Beverage Operations?
In the food and beverage industry, big air compressors are used in packaging and bottling processes, ensuring that operations adhere to hygiene standards. Clean air is essential for preventing contamination, making it crucial for buyers to source compressors with clean air certifications. Additionally, energy consumption and ease of integration into existing systems are vital considerations for businesses looking to optimize their operations while maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘big air compressor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Downtime Due to Equipment Failure
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges B2B buyers face with big air compressors is unexpected downtime due to equipment failure. For industries reliant on continuous air supply, such as construction or manufacturing, a sudden breakdown can halt production lines and lead to costly delays. This not only affects project timelines but also impacts customer satisfaction and can result in financial penalties for late deliveries.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of equipment failure, B2B buyers should implement a proactive maintenance program that includes regular inspections and servicing based on the manufacturer’s guidelines. Establishing a partnership with a reliable supplier who offers comprehensive service contracts can provide peace of mind. Additionally, investing in smart monitoring technologies that provide real-time data on the compressor’s performance can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This data-driven approach allows for timely interventions and minimizes downtime, ensuring that operations run smoothly.
Scenario 2: Insufficient Air Pressure for Operations
The Problem: Many businesses encounter issues with insufficient air pressure generated by their compressors, leading to inadequate performance of pneumatic tools and machinery. This is particularly problematic in sectors like automotive repair or heavy construction, where precise air pressure is crucial for tasks such as painting, riveting, and powering tools. Inadequate pressure can not only reduce productivity but also affect the quality of work, resulting in rework and wasted resources.
The Solution: To address air pressure issues, buyers should assess their specific air requirements before purchasing a compressor. This involves calculating the total cubic feet per minute (CFM) needed for all tools operating simultaneously. Selecting a compressor that not only meets but exceeds these requirements can prevent pressure drops during operation. For existing compressors, consider adding a larger receiver tank to store more compressed air or upgrading to a two-stage compressor that can provide higher pressure levels. Regularly checking for leaks in the air system can also enhance overall efficiency and ensure that the tools receive adequate air pressure.
Scenario 3: High Energy Costs and Inefficiencies
The Problem: Energy costs associated with operating big air compressors can be substantial, particularly for businesses in regions where electricity prices are high. Many organizations struggle with the inefficiency of older compressor models, which consume excessive energy while providing insufficient output. This not only increases operational expenses but can also hinder the company’s profitability and sustainability efforts.
The Solution: To combat high energy costs, buyers should consider investing in energy-efficient compressors that are designed to operate at optimal efficiency. Look for models with variable speed drives (VSD) that adjust the motor speed according to air demand, significantly reducing energy consumption during low-demand periods. Additionally, incorporating an energy audit can provide insights into how much energy the current compressor uses and identify areas for improvement. Implementing energy management systems can also help monitor usage patterns and optimize operational strategies, ensuring that the compressor runs only when necessary. Upgrading to newer technology may involve a higher upfront investment but can yield significant savings in the long run, making the business more competitive in the market.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Strategic Material Selection Guide for big air compressor
When selecting materials for big air compressors, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations, as these factors significantly impact performance and durability. This guide analyzes four common materials used in the construction of big air compressors: aluminum, steel, cast iron, and composites. Each material has unique characteristics that cater to different operational needs and market preferences, particularly for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Big Air Compressors?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. The thermal conductivity of aluminum also allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial in compressor operation.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum:
– Pros: Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, and ease of manufacturing.
– Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, higher cost relative to some alternatives, and potential for fatigue under high-stress conditions.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for portable compressors where weight is a critical factor. However, it may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring high strength and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may prefer aluminum for its lightweight properties, particularly in mobile applications. Compliance with standards like ASTM and EN for material quality is essential.
How Does Steel Perform in Big Air Compressor Applications?
Steel is widely used in the construction of air compressors due to its strength and durability. It can handle high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel:
– Pros: High strength, excellent pressure and temperature resistance, and relatively low cost.
– Cons: Heavier than aluminum, susceptible to corrosion without proper treatment, and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Steel is often used in stationary compressors that require robust construction. Its ability to handle high stress makes it suitable for demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel’s compliance with various international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, makes it a preferred choice for many buyers. However, buyers in humid regions must consider corrosion resistance treatments.
What Advantages Do Cast Iron Components Offer in Big Air Compressors?
Cast iron is favored for its excellent vibration dampening and durability. It can withstand high pressures and is often used in the compressor block and cylinder components.
Pros and Cons of Using Cast Iron:
– Pros: Exceptional durability, good wear resistance, and effective vibration dampening.
– Cons: Heavy, brittle under certain conditions, and more challenging to manufacture.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is particularly effective in stationary compressors where weight is less of a concern, and durability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with stringent manufacturing standards, such as Germany, may prefer cast iron for its reliability. Ensuring compliance with relevant standards is crucial.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
How Do Composites Enhance Big Air Compressor Design?
Composite materials, often a blend of plastic and fiberglass, are increasingly used in compressor design due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Pros and Cons of Using Composites:
– Pros: Lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be molded into complex shapes.
– Cons: Generally lower strength compared to metals, higher manufacturing costs, and potential issues with heat resistance.
Impact on Application:
Composites are suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as portable compressors. However, they may not be ideal for high-stress components.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Considerations for International Buyers:
In emerging markets like Africa and South America, the cost of composite materials may be a barrier. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits versus initial costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Big Air Compressors
| Material | Typical Use Case for big air compressor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable compressors | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial stationary compressors | High strength and durability | Heavier and corrosion-prone | Low |
| Cast Iron | Stationary compressors | Exceptional durability | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
| Composites | Lightweight portable compressors | Molding flexibility and corrosion resistance | Lower strength and higher cost | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for big air compressors, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for big air compressor
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Big Air Compressors?
The manufacturing process of big air compressors involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Sourced and Prepared?
The first stage in manufacturing big air compressors involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, which typically include steel, aluminum, and various polymers. Suppliers must be vetted for material quality and compliance with international standards. Once materials are sourced, they undergo preparation processes such as cutting, machining, and surface treatment to ensure they are ready for assembly. Precision in this stage is critical, as any defects can lead to inefficiencies or failures in the final product.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Forming: What Techniques Are Used in the Fabrication of Components?
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into specific components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and welding are commonly employed. Advanced technologies like CNC machining and laser cutting enhance precision and reduce waste. The choice of technique often depends on the complexity of the part and the desired tolerances. For instance, components requiring high durability may be forged, while intricate parts may be better suited for CNC machining.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into a Complete Unit?
Once the individual components are fabricated, the assembly process begins. This involves integrating parts such as the motor, compressor unit, and control systems into a complete air compressor. Automated assembly lines are often used to increase efficiency and consistency. During this stage, each component is carefully inspected to ensure it fits correctly and functions as intended. Proper assembly is critical, as it directly affects the compressor’s performance and reliability.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure the Product Meets Aesthetic and Functional Standards?
The finishing stage encompasses various processes aimed at enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the air compressor. This may include painting, powder coating, or applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Quality checks are also performed to ensure that the finish meets industry standards. A well-finished product not only looks professional but also extends the lifespan of the compressor in various operational environments.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Big Air Compressors?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both regulatory and customer specifications.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should look for compliance with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications. These certifications demonstrate that manufacturers adhere to stringent quality control processes.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control in the manufacturing of big air compressors typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step ensures that raw materials meet specified quality standards before they enter the production process. Suppliers should provide material certifications to facilitate this verification.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, operators perform checks at various stages to catch defects early. This might involve measurements of critical dimensions or functional tests of components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the assembly line, the complete unit undergoes rigorous testing. This may include performance testing under simulated operational conditions, ensuring that the compressor meets specified output pressures and flow rates.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential to mitigate risks. Here are some actionable strategies:
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. This can include on-site visits where buyers can review documentation, observe processes, and interview staff. Buyers should check for ISO certifications and review the supplier’s quality manual, which outlines their QA procedures.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Reports and Testing Data?
Buyers should request quality reports that detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. This documentation should include pass/fail rates, detailed test results, and any corrective actions taken for non-conforming products. Transparency in reporting can significantly influence a buyer’s confidence in a supplier.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control practices. These organizations can conduct audits, verify compliance with international standards, and perform random sampling of products for testing. This additional layer of verification is particularly valuable for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance may vary.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate different regulatory environments and quality expectations. For instance, in Europe, CE marking is mandatory for many industrial products, while in other regions, different certifications may be required. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these nuances to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality standards. Establishing clear lines of communication and using standardized documentation can help mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for big air compressors is crucial for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with each stage of production, relevant international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘big air compressor’
Introduction
Sourcing a big air compressor can be a complex task, especially for B2B buyers looking to meet specific operational needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline the procurement process, ensuring you select the right equipment for your business while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it’s essential to clarify your operational requirements. Determine the necessary pressure (PSI) and airflow (CFM) ratings based on your intended applications, such as pneumatic tools or industrial processes. Knowing these specifications will help you avoid overspending on features you don’t need or underestimating your requirements.
Step 2: Research Available Compressor Types
Understand the different types of big air compressors available on the market. Options include portable, stationary, electric, and gas-powered models. Each type has unique advantages depending on your operational environment, such as mobility for construction sites or larger tank capacities for manufacturing facilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, check for industry certifications, and ask for case studies that showcase their experience in your specific sector. Look for testimonials or references from other B2B clients in similar regions to gauge reliability and service quality.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Step 4: Assess Warranty and Support Services
Inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support. A robust warranty can protect your investment, while good customer support ensures that any issues can be resolved quickly. Clarify whether the supplier provides maintenance services and how they handle parts replacement to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Be sure to consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy consumption. Additionally, explore financing options that may be available, such as leasing or installment payments, which can ease cash flow concerns.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the compressors you are considering comply with local regulations and standards, especially in regions with strict environmental guidelines. Check for necessary certifications that confirm the equipment meets safety and performance benchmarks, which can prevent costly legal issues down the line.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected a supplier and model, review the purchase agreement carefully. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, installation services, and payment conditions, are clearly defined. This will help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing a big air compressor, aligning your purchase with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for big air compressor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Big Air Compressors?
When sourcing big air compressors, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing compressors, such as metal alloys, plastics, and electrical components, significantly influence costs. High-grade materials can enhance durability and performance but may increase the initial investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of assembly. Regions with lower labor costs might offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes impact quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead and thus lower prices.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling, especially for custom designs, can be substantial. This cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making it crucial to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the compressors meet industry standards and certifications. While this may add to costs, it ultimately reduces the risk of defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties play significant roles in the overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on market competition, brand reputation, and product uniqueness. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy is vital for negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Big Air Compressor Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of big air compressors, impacting the overall cost for buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounted pricing. Suppliers may set minimum order quantities that can significantly affect unit costs. Buyers should weigh their needs against potential savings from larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized compressors tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers must evaluate whether the added features justify the increased price.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Compressors that meet industry certifications, such as ISO or CE, typically carry a premium. However, these certifications can enhance product reliability and safety, offering long-term value.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and history of performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better support and warranties.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can have a significant impact on the total cost. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears the shipping and insurance costs, affecting the overall pricing structure.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Big Air Compressor Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can yield significant savings:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may not always result in the best long-term value.
-
Leverage Competitive Quotes: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to create a competitive bidding environment. This approach can enhance your bargaining power.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can improve cash flow. Consider negotiating extended payment terms or discounts for upfront payments.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing strategies based on local market dynamics. Understanding these nuances can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Establish Long-term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, preferential treatment, and access to exclusive deals.
Conclusion and Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While the analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing structure for big air compressors, actual prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier policies, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain updated quotes to ensure accurate budgeting and forecasting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing big air compressor With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Alternatives Exist to Big Air Compressors?
When evaluating air compression solutions, businesses often consider a range of technologies that can fulfill similar roles. While big air compressors are widely recognized for their robust performance in heavy-duty applications, there are alternative solutions that may offer varying benefits depending on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. In this section, we will compare big air compressors against two viable alternatives: rotary screw compressors and gas-powered portable compressors.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Big Air Compressor | Rotary Screw Compressor | Gas-Powered Portable Compressor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High pressure (100-250 psi) | Continuous airflow, less pulsation | Moderate pressure (up to 150 psi) |
| Cost | High initial investment | Moderate to high cost | Lower initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant setup | Easier installation, compact | Highly portable, easy setup |
| Maintenance | Regular oil changes, complex | Lower maintenance frequency | Requires fuel management |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications | Manufacturing, processing | Construction, outdoor projects |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotary Screw Compressors?
Rotary screw compressors are designed to provide a continuous supply of compressed air, making them ideal for industrial applications that require sustained airflow. Their efficiency allows for lower operating costs over time, as they consume less energy compared to traditional reciprocating compressors. However, they come with a higher initial investment and may necessitate professional installation. Additionally, while they require less frequent maintenance, when maintenance is needed, it can be complex and costly.
Why Consider Gas-Powered Portable Compressors?
Gas-powered portable compressors offer the advantage of mobility, making them suitable for jobs that require flexibility, such as construction sites or remote locations. They are typically easier to set up and operate, requiring minimal infrastructure. The lower initial cost is also appealing for small to medium-sized enterprises. However, they generally provide lower pressure output and may not be suitable for applications demanding high air volumes. Furthermore, managing fuel consumption and emissions can be a drawback in terms of operational costs and environmental impact.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Air Compression Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right air compression solution involves evaluating your specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Big air compressors are optimal for high-demand industrial applications but come with higher costs and maintenance needs. On the other hand, rotary screw compressors provide efficiency and continuous airflow, suitable for manufacturing environments. Gas-powered portable compressors offer affordability and flexibility, making them ideal for construction and outdoor projects. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for big air compressor
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with big air compressors is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines essential specifications and common industry jargon that can impact the selection, pricing, and functionality of these powerful tools.
What Are the Key Technical Specifications for Big Air Compressors?
-
Maximum Pressure (PSI)
Maximum pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the highest pressure the compressor can achieve. This specification is vital for determining the compressor’s suitability for various applications, such as pneumatic tools, painting, or industrial processes. A higher PSI can accommodate a broader range of tasks, making it a critical factor for businesses with diverse operational needs. -
Air Delivery (CFM)
Cubic feet per minute (CFM) measures the volume of air delivered by the compressor. This metric is essential for understanding how quickly the compressor can supply air to tools and equipment. For businesses, selecting a compressor with adequate CFM ensures that operations run smoothly without interruptions, particularly in high-demand environments like construction or manufacturing. -
Tank Capacity (Gallons)
The tank capacity, expressed in gallons, determines how much compressed air can be stored. A larger tank capacity allows for longer operation times between refills, which can enhance productivity in a work setting. Businesses that require sustained air pressure for extended periods should prioritize compressors with higher tank capacities. -
Power Source
Big air compressors can be powered by electricity, gasoline, or diesel. The choice of power source affects portability, maintenance, and operational costs. Electric compressors are generally quieter and easier to maintain, while gasoline or diesel models provide greater mobility and are often preferred for remote job sites. Understanding the implications of the power source helps businesses select a compressor that aligns with their operational requirements. -
Compressor Type (Single Stage vs. Two Stage)
Compressors can be categorized into single-stage and two-stage types. Single-stage compressors are typically more compact and less expensive, suitable for light-duty applications. In contrast, two-stage compressors offer higher efficiency and are ideal for heavy-duty tasks, providing better performance for professional-grade applications. The choice between these types can significantly impact both upfront costs and long-term operational efficiency. -
Lubrication Type
Compressors can operate with oil-lubricated or oil-free mechanisms. Oil-lubricated compressors typically provide better performance and durability but require more maintenance. Oil-free compressors are cleaner and easier to maintain, making them suitable for applications where air purity is paramount, such as in food processing or pharmaceuticals.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Big Air Compressor Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of air compressors, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the quality and reliability of the components used in their compressors. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses negotiate better terms and ensure they meet their operational needs without excessive stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products. For buyers of big air compressors, issuing an RFQ can facilitate the procurement process by providing a structured way to compare costs and features from multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk at each stage of the shipping process, helping to avoid misunderstandings and disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers, as it impacts project timelines and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their operations to ensure they have the necessary equipment when needed. -
Warranty
A warranty is a promise made by the manufacturer regarding the performance and reliability of a product. For big air compressors, warranty terms can vary significantly, influencing long-term maintenance costs and buyer confidence. A comprehensive warranty can serve as an assurance of quality and service support, making it a critical consideration in the purchasing decision.
By familiarizing themselves with these specifications and terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of selecting a big air compressor that meets their operational needs while ensuring compliance with industry standards and practices.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the big air compressor Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Big Air Compressor Sector?
The global big air compressor market is experiencing significant growth driven by various factors, including industrialization, increasing demand for energy-efficient equipment, and advancements in technology. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are at the forefront of this growth, propelled by their expanding manufacturing and construction sectors. For instance, countries like Vietnam and Germany are investing heavily in infrastructure projects, which in turn boosts the demand for robust air compressors capable of handling heavy-duty applications.
Emerging trends in the B2B landscape include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology in air compressors, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This technology not only optimizes performance but also significantly reduces downtime, enhancing operational efficiency for businesses. Additionally, the shift towards electric and hybrid compressors is becoming prominent, driven by the need for sustainability and lower operational costs. Such innovations are crucial for B2B buyers who are increasingly looking for reliable, high-performance equipment that aligns with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is shifting as manufacturers are increasingly focusing on customized solutions tailored to specific industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and construction. This trend emphasizes the importance of strategic partnerships and relationships between buyers and suppliers, ensuring access to the latest technologies and innovations in air compressor systems.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers in the Big Air Compressor Sector?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the global marketplace, and the big air compressor sector is no exception. Environmental impact concerns have prompted many businesses to reevaluate their sourcing strategies, placing greater emphasis on eco-friendly practices and products. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, whether through energy-efficient products or sustainable manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is critical for maintaining a positive brand image and meeting regulatory standards. Buyers are more inclined to engage with manufacturers who use green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signifies adherence to effective environmental management systems. Additionally, the use of sustainable materials in the production of air compressors not only reduces the environmental footprint but also enhances product durability, which is a significant consideration for B2B buyers looking for long-term value.
Moreover, as governments across various regions tighten regulations regarding emissions and energy consumption, suppliers who can offer compliant and innovative solutions stand to gain a competitive edge. This shift is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where there is a growing emphasis on sustainable development goals (SDGs).

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
What Historical Factors Have Shaped the Big Air Compressor Market?
The evolution of the big air compressor market can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, where the need for mechanization in manufacturing processes spurred the development of air compression technology. Early models were bulky and inefficient, primarily powered by steam engines. Over the decades, technological advancements led to the introduction of electric-powered compressors, which revolutionized the industry by offering greater efficiency and versatility.
In the latter part of the 20th century, the focus shifted towards enhancing performance and reducing energy consumption, driven by the growing importance of sustainability. The introduction of variable speed drive (VSD) technology in compressors further transformed the market, allowing for more precise control of air output and energy savings.
Today, the big air compressor sector is characterized by rapid innovation, with a strong emphasis on digitalization and smart technologies. This historical context highlights the continuous evolution of the industry, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies that can impact their purchasing decisions. As the market continues to evolve, understanding these historical developments will be crucial for making informed sourcing choices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of big air compressor
-
How do I determine the right size of a big air compressor for my business needs?
Choosing the right size of a big air compressor involves assessing your specific applications and the required air output. Calculate the total SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute) needed for all tools and equipment that will be running simultaneously. Consider the pressure requirements (PSI) as well, since different applications may demand varying levels of pressure. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on your industry requirements, ensuring you select a compressor that can efficiently handle your workload. -
What is the best type of big air compressor for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, two-stage air compressors are often the best choice due to their ability to provide higher pressure and greater efficiency. They can deliver consistent air flow for heavy-duty tools and machinery, making them suitable for construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries. Additionally, consider whether a stationary or portable compressor fits your operational needs, as each offers unique advantages depending on your work environment and mobility requirements. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for big air compressors?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Look for certifications that ensure compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request references from previous clients and assess their after-sales support, warranty policies, and availability of spare parts. It’s beneficial to engage suppliers who have a solid understanding of your specific market needs, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East. -
What customization options are typically available for big air compressors?
Most manufacturers offer customization options tailored to specific industry needs, including modifications to pressure settings, tank sizes, and mobility features. You can also request specific power sources, whether electric or gas, depending on your operational environment. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of adding features such as noise reduction or enhanced filtration systems to meet your requirements. Discussing customization upfront can ensure the compressor aligns perfectly with your operational expectations. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for big air compressors?
Minimum order quantities for big air compressors can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for smaller manufacturers to several units for larger companies. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs during your initial conversations with suppliers to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities. Additionally, consider the potential for bulk discounts, which may be available if you commit to larger orders. -
What payment terms are typically available when purchasing big air compressors internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include advance payments, letters of credit, and staggered payments based on delivery milestones. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans to accommodate your budget. Ensure you understand the payment terms fully before finalizing the purchase to avoid any complications during the transaction. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for big air compressors sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, work with suppliers who have established QA processes and certifications. Request detailed specifications and performance data for the compressors you are considering. It’s advisable to conduct factory inspections or audits, if feasible, to assess the manufacturing standards. Additionally, consider negotiating for warranties or guarantees that cover performance issues, ensuring you have recourse should the product not meet the specified standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing big air compressors?
When importing big air compressors, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties that may apply. It’s essential to work with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy equipment to ensure safe and timely delivery. Additionally, plan for any necessary transportation arrangements upon arrival, such as local delivery or storage. Familiarizing yourself with the logistics process will help prevent delays and additional costs associated with your importation.
Top 3 Big Air Compressor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ingersoll Rand – Air Compressors
Domain: compressorpros.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Air Compressors with 200 + Gallon or Larger Tanks available from various brands including ABAC, BelAire, Chicago Pneumatic, C-Aire, EMAX, Industrial Gold, Ingersoll Rand, Jenny, Mi-T-M, Quincy, and Schulz. Types include Piston/Reciprocating Compressors, Rotary Screw Air Compressors, and Portable Air Compressors. Options for Single Stage, Two Stage, Duplex, and Variable Speed models. Additional fea…
2. Chicago Pneumatic – Large Mobile Air Compressors
Domain: power-technique.cp.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Large Mobile Air Compressors from Chicago Pneumatic offer high-performance diesel air compressors with the following specifications:
– Pressure Range: 100-360 psi
– Flow Rate: 575-1600 cfm
– Robust design suitable for challenging weather conditions
– Easy to service with a simple control panel
– Suitable for full 8-hour shifts
Specific Models:
1. CPS 650-250 Diesel Air Compressor:
– Flo…
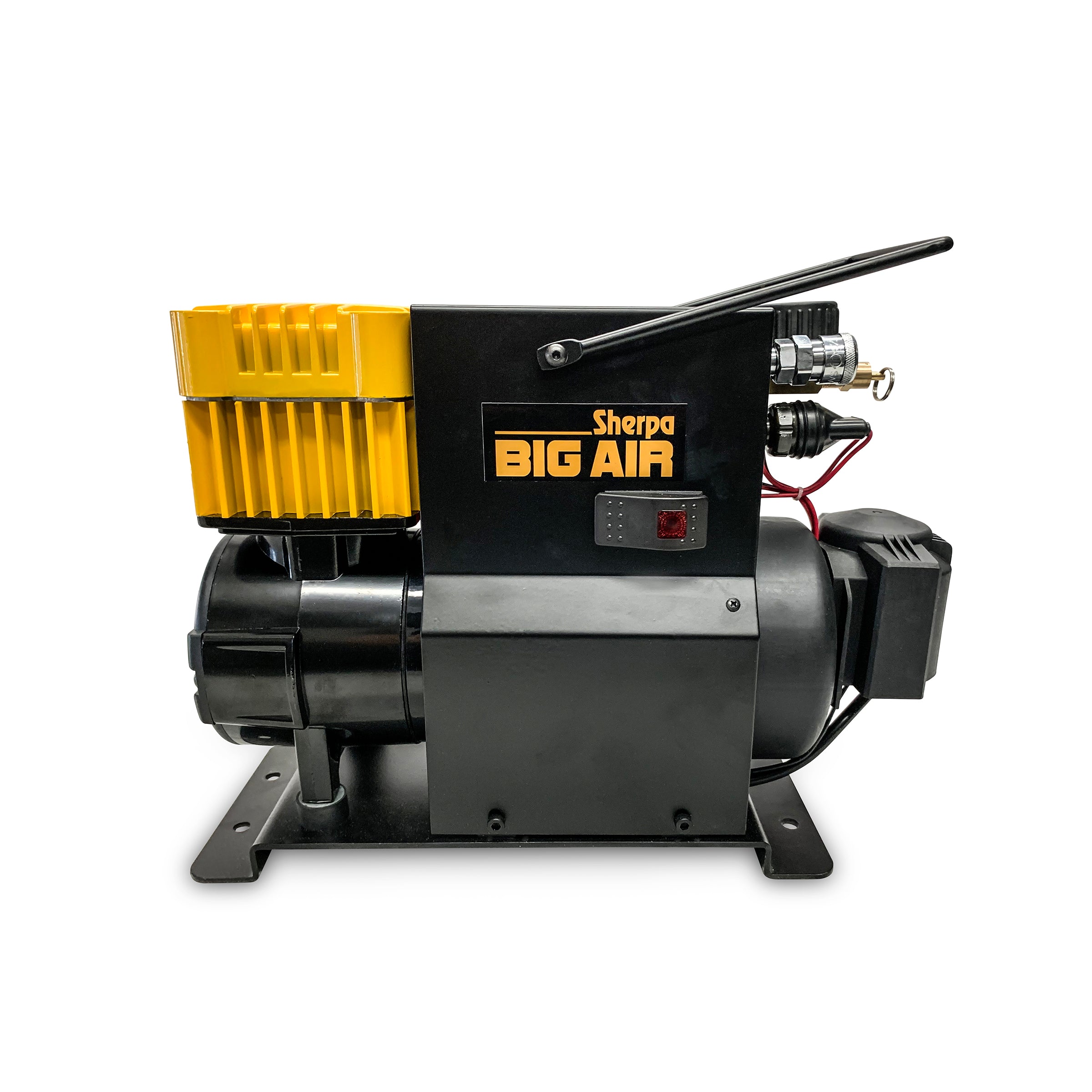
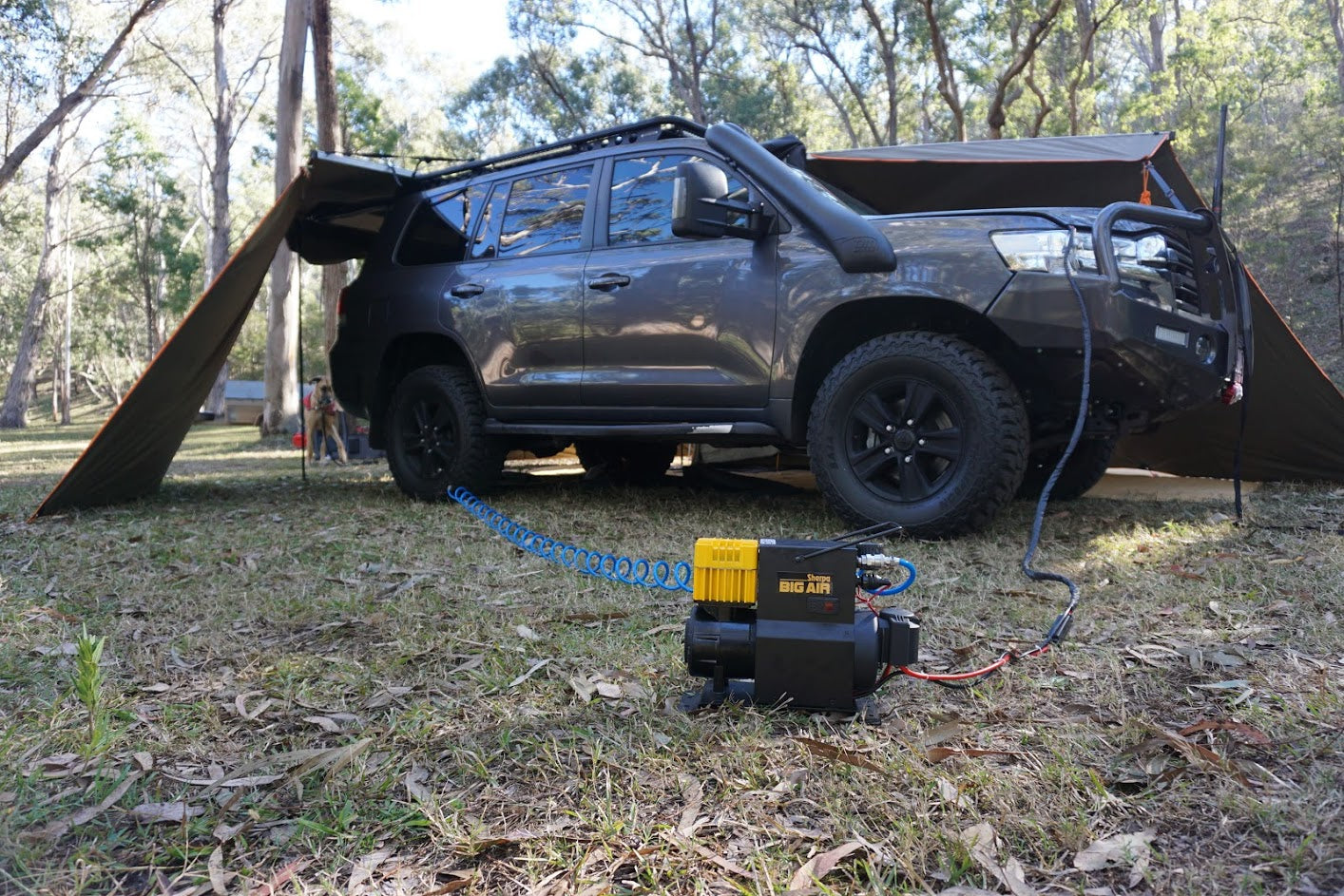
3. Sherpa – 12V Air Compressor Big Air
Domain: sherpa4x4.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Sherpa 12V Air Compressor Big Air”, “features”: [“Powerful 12V motor”, “High airflow rate”, “Compact and portable design”, “Built-in pressure gauge”, “Durable construction”], “applications”: [“Inflating tires”, “Air mattresses”, “Sports equipment”, “Camping gear”], “dimensions”: “N/A”, “weight”: “N/A”, “warranty”: “N/A”, “price”: “N/A”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for big air compressor
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of big air compressors is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and productivity. By leveraging robust supplier relationships and understanding market trends, companies can secure high-performance equipment that meets their specific needs. Key considerations include evaluating compressor specifications, maintenance support, and the total cost of ownership.
Investing in quality compressors not only reduces downtime but also optimizes energy consumption, leading to significant long-term savings. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, the demand for reliable air compression solutions will only increase.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
Looking ahead, businesses should prioritize sustainable sourcing practices and consider innovative technologies that enhance compressor efficiency and environmental performance. By doing so, they position themselves for success in a competitive landscape. We encourage buyers to engage with reputable manufacturers and distributors to explore the latest offerings, ensuring they make informed decisions that support their growth objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to big air compressor
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.