Stock Gear: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stock gear
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing stock gear efficiently can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for reliable, high-quality gears—whether for machinery repair or new equipment design—demands a strategic approach to procurement. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering an extensive range of stock gear types including spur, helical, bevel, and worm gears, alongside their applications across various industries. Additionally, it addresses critical considerations such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and logistics, enabling buyers to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence.
Understanding the nuances of stock gear specifications, material choices, and compatibility is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide empowers B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Saudi Arabia—by providing actionable insights and expert recommendations. By equipping buyers with knowledge about industry standards and supplier capabilities, this resource aims to streamline the procurement process, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime. With the right information at their fingertips, buyers can confidently select the stock gears that best meet their unique operational needs, ensuring both immediate and long-term success in their respective markets.
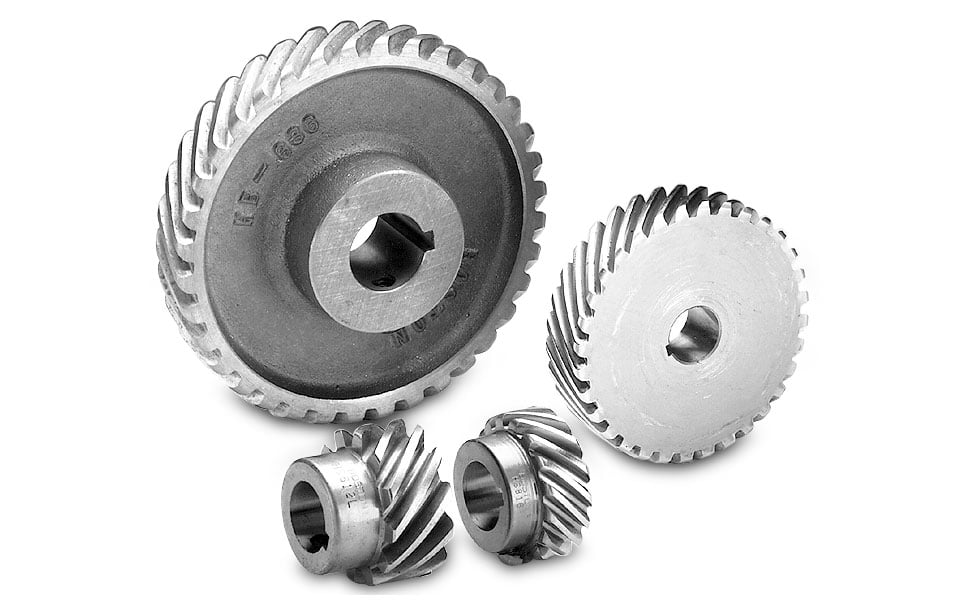
Understanding stock gear Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spur Gears | Straight teeth, high efficiency, simple design | Machine tools, conveyors, automotive | Pros: Easy to manufacture, low cost. Cons: Noisy at high speeds, limited load capacity. |
| Helical Gears | Angled teeth for smoother operation, high load capacity | Robotics, automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Quieter operation, higher load capabilities. Cons: More complex manufacturing, higher cost. |
| Worm Gears | Screw-shaped teeth, high torque reduction | Lifts, conveyors, gear reducers | Pros: Compact design, significant speed reduction. Cons: Lower efficiency, potential for overheating. |
| Bevel Gears | Conical shape, transmit motion between non-parallel axes | Automotive differentials, machinery | Pros: Versatile in direction change, high strength. Cons: Complex design, can be expensive. |
| Gear Racks | Linear gears that convert rotational motion to linear | CNC machines, steering systems | Pros: Simplifies motion conversion, customizable lengths. Cons: Requires precise alignment, limited load capacity. |
What are the characteristics of Spur Gears and their B2B relevance?
Spur gears are characterized by their straight teeth, which are parallel to the gear’s axis. They are commonly used in applications where speed and efficiency are paramount, such as in machine tools and conveyor systems. For B2B buyers, spur gears offer a cost-effective solution due to their straightforward manufacturing process. However, they can generate noise at high speeds and have limitations in load capacity, making them suitable primarily for lower-load applications.
How do Helical Gears differ from other gear types in B2B applications?
Helical gears feature angled teeth that allow for smoother engagement and operation, which results in lower noise levels compared to spur gears. This design enhances their load-carrying capacity, making them ideal for high-performance applications in robotics and industrial machinery. For B2B buyers, the investment in helical gears can yield long-term benefits due to their durability and efficiency, despite their higher initial cost and complex manufacturing requirements.
What makes Worm Gears a unique choice for specific industries?
Worm gears consist of a screw-shaped gear that meshes with a larger gear, providing significant torque reduction and compact design. They are particularly effective in applications such as lifts and conveyors, where space constraints are an issue. B2B buyers appreciate worm gears for their ability to deliver high torque in a small footprint; however, they may face challenges with efficiency and heat generation, which should be considered in high-load scenarios.
Why are Bevel Gears essential for certain mechanical designs?
Bevel gears are conical in shape and allow for the transmission of power between non-parallel shafts, making them essential in automotive differentials and various machinery applications. Their ability to change the direction of motion while maintaining strength makes them a versatile choice for B2B buyers. However, the complexity of their design can lead to higher manufacturing costs, which buyers should evaluate against their operational needs.
How do Gear Racks facilitate motion in machinery?
Gear racks are linear gears that convert rotational motion into linear motion, making them invaluable in applications like CNC machines and automotive steering systems. They can be customized in length to fit specific applications, providing flexibility for B2B buyers. However, precise alignment is crucial for optimal performance, and their load capacity may be limited compared to other gear types, requiring careful consideration during selection.
Key Industrial Applications of stock gear
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stock gear | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhances efficiency and reliability in material handling | Availability of various gear types and sizes for compatibility |
| Automotive | Steering Mechanisms | Provides precise control and responsiveness in vehicles | Compliance with international standards for quality assurance |
| Robotics | Motion Control in Automated Systems | Improves accuracy and speed of robotic operations | Customization options for specific gear ratios and materials |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbine Gearboxes | Optimizes energy conversion and operational longevity | Sourcing durable materials that withstand harsh environments |
| Mining and Heavy Duty | Hoisting and Lifting Equipment | Increases safety and productivity in material transport | Availability of heavy-duty gears with high load capacities |
How is Stock Gear Used in Manufacturing Conveyor Systems?
In manufacturing, stock gears are integral to conveyor systems, which transport materials across various stages of production. These gears facilitate smooth operation, reducing downtime caused by equipment failure. Businesses benefit from the immediate availability of replacement gears, ensuring continuous workflow. International buyers, particularly from regions with diverse industrial needs like Africa and South America, should ensure suppliers can provide a range of gear types and sizes to match their specific conveyor configurations.
What Role Do Stock Gears Play in Automotive Steering Mechanisms?
In the automotive industry, stock gears are critical for steering mechanisms, where precision and reliability are paramount. They help achieve accurate steering control, enhancing vehicle safety and performance. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing gears that comply with stringent automotive standards is essential. Additionally, buyers should consider suppliers’ ability to provide both standard and custom gear options to meet varying design specifications.
How Do Stock Gears Enhance Robotics Motion Control?
Stock gears are vital in robotics, particularly for motion control systems that require high precision and speed. These gears enable robots to execute complex tasks efficiently, making them indispensable in manufacturing and assembly lines. Companies looking to enhance their robotic systems must consider sourcing gears that offer customization for specific gear ratios and materials, ensuring optimal performance in diverse applications. Buyers should also prioritize suppliers with a track record of reliability and quality assurance.
In What Ways Do Stock Gears Optimize Wind Turbine Gearboxes?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbines, stock gears are essential for gearboxes that convert rotational energy into electrical power. They enhance the efficiency of energy conversion and extend the operational lifespan of turbines. International buyers from regions investing in renewable energy should focus on sourcing durable gears capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions. This includes considering suppliers that provide high-quality materials and robust designs tailored for renewable energy applications.
How Are Stock Gears Utilized in Mining and Heavy Duty Applications?
In mining and heavy-duty industries, stock gears are crucial for hoisting and lifting equipment, ensuring safe and efficient material transport. The reliability of these gears directly impacts productivity and safety, making it vital for businesses to have immediate access to replacements. B2B buyers in these sectors should prioritize sourcing heavy-duty gears that can handle high load capacities. Additionally, they should assess suppliers’ capabilities in delivering gears that meet industry-specific standards and regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stock gear’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Gear Specifications Leading to Compatibility Issues
The Problem: A B2B buyer tasked with sourcing stock gears often faces the challenge of inconsistent specifications between suppliers. When designing machinery, engineers rely on precise gear measurements. However, minor differences in dimensions, tooth profiles, and material specifications can lead to compatibility issues, resulting in costly delays in production. This inconsistency not only affects the assembly process but also raises concerns about the longevity and performance of the machinery in operational settings.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is crucial for buyers to establish clear communication with suppliers regarding gear specifications. Before placing orders, utilize standardized terminology and request detailed technical data sheets that include material composition, dimensions, and tolerances. Additionally, leverage industry standards such as ISO or DIN to ensure that the gears meet specific performance criteria. By carefully comparing these specifications across different suppliers, buyers can make informed decisions and select gears that will mesh perfectly with their existing machinery, thereby minimizing the risk of compatibility issues.
Scenario 2: Limited Availability of Custom Gear Sizes
The Problem: In many industries, buyers often need gears in specific sizes that are not available as stock items. This can lead to extended lead times for custom manufacturing, which can disrupt project timelines and increase costs. For example, a company may require a gear with an unusual tooth count or diameter for a specialized application, and waiting for custom production can significantly delay product launches and reduce competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should consider collaborating with suppliers who offer a wide range of stock gear options and customization capabilities. Establishing a long-term relationship with a reliable supplier can provide access to expedited services for custom orders. Additionally, buyers should maintain an inventory of commonly used gear sizes that can be readily available for quick replacements or urgent projects. Utilizing advanced inventory management systems can help track usage patterns and predict future needs, enabling timely restocking of essential gears.
Scenario 3: Overlooking Quality Standards in Gear Selection
The Problem: Many B2B buyers may prioritize cost savings over quality when selecting stock gears, leading to the procurement of subpar products. This oversight can result in premature gear failure, increased maintenance costs, and potential downtime in machinery operation. In industries where reliability is paramount, such as automotive or aerospace, choosing low-quality gears can have severe repercussions, including safety hazards and significant financial losses.

Illustrative image related to stock gear
The Solution: Buyers should conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers’ quality assurance processes. Prioritize suppliers who adhere to rigorous quality standards, such as ISO 9001, and who can provide certifications and test results for their products. Implementing a quality control checklist during the sourcing process can help ensure that all purchased gears meet specified performance and durability standards. Furthermore, engaging in regular supplier audits and maintaining open lines of communication can foster a culture of quality and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to better-performing gears and reduced operational risks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stock gear
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Stock Gears?
When selecting materials for stock gears, B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Common materials used in stock gears include steel, aluminum, plastic, and bronze. Each material possesses distinct properties that cater to various applications and operational environments.
Steel: The Standard for Durability and Strength
Steel is the most widely used material for stock gears due to its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel gears typically offer excellent wear resistance and can be heat-treated to enhance their performance.
- Pros: Steel gears are robust and can handle significant loads. They are also readily available and can be manufactured to precise specifications.
- Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can be mitigated with coatings or treatments but may increase costs. Additionally, steel gears can be heavier than alternatives, impacting the overall weight of the machinery.
- Impact on Application: Steel gears are ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, such as automotive and industrial machinery. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high humidity or corrosive media without proper treatment.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM or DIN is crucial, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to reduce lead times.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is increasingly popular for stock gears, particularly in applications where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum gears are lightweight and offer good corrosion resistance, making them suitable for various environmental conditions.
- Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum gears can lead to energy savings in applications where weight is a factor. They also resist corrosion, which is advantageous in humid or marine environments.
- Cons: While aluminum is strong, it does not match the load-bearing capacity of steel. This limitation can restrict its use in heavy-duty applications.
- Impact on Application: Aluminum gears are often used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight savings are essential. However, they may not be suitable for high-load scenarios.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum gears meet relevant standards such as JIS or ISO, especially when sourcing from different regions.
Plastic: Versatile and Cost-Effective
Plastic gears are an excellent choice for applications requiring lightweight components and lower noise levels. They are often used in consumer products and light machinery.
- Pros: Plastic gears are cost-effective and easy to manufacture. They also provide good insulation properties and can operate quietly, making them suitable for applications like home appliances.
- Cons: The primary limitation of plastic gears is their lower strength and heat resistance compared to metal gears. They may also wear out faster under heavy loads.
- Impact on Application: Plastic gears are ideal for applications where weight and noise reduction are priorities, such as in robotics or consumer electronics. However, they may not be suitable for high-stress environments.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that plastic gears comply with relevant safety and quality standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
Bronze: The Choice for High Load and Wear Resistance
Bronze is often used in applications requiring high wear resistance and the ability to withstand heavy loads. It is particularly effective in environments where lubrication is challenging.
- Pros: Bronze gears offer excellent wear resistance and can operate in high-load conditions without significant degradation. They are also resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh environments.
- Cons: The main drawback is the higher cost compared to other materials like steel and plastic. Additionally, bronze gears can be heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
- Impact on Application: Bronze gears are commonly used in marine and industrial applications where durability is critical. Their ability to operate in lubricated and non-lubricated conditions makes them versatile.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards such as ASTM is essential, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is paramount.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Stock Gears
| Material | Typical Use Case for stock gear | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery, automotive | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, lightweight applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer products, robotics | Cost-effective and quiet operation | Lower strength and heat resistance | Low |
| Bronze | Marine, industrial applications | High wear resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for stock gears, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stock gear
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stock Gears?
The manufacturing of stock gears involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing stock gears is selecting the appropriate raw materials, typically metals such as steel, aluminum, or specialized alloys. These materials must meet specific mechanical and physical properties, ensuring they can withstand the operational stresses they will encounter.
Once selected, the materials undergo a variety of processes, including cutting, heat treatment, and surface preparation. Heat treatment, for example, enhances the hardness and durability of the gears, making them suitable for high-load applications. Additionally, suppliers often employ CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining for precise cutting and shaping, ensuring that the final dimensions of the gears meet stringent specifications.
Which Techniques Are Commonly Used in Gear Forming?
Forming is a crucial stage in gear manufacturing, where the raw materials are shaped into gear profiles. Common techniques include:
-
Hobbing: A widely used method for producing spur and helical gears, hobbing involves rotating a multi-toothed cutting tool (the hob) against the workpiece, allowing for high precision and efficiency.
-
Shaping: This method is often used for producing internal gears and involves a cutting tool that moves linearly to create the desired tooth profile.
-
Forging: In high-volume applications, forging is utilized to create gears from heated metal, enhancing strength and structural integrity.
Each technique has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the gear type, required tolerances, and production volume.
How Is Gear Assembly Conducted in Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where individual gear components are brought together to form complete gear sets. This process may involve:
-
Fitting: Ensuring that each gear meshes correctly with its counterpart, which is critical for minimizing backlash and ensuring smooth operation.
-
Lubrication: Applying lubricants to reduce friction and wear during operation, prolonging the lifespan of the gears.
-
Testing: Conducting initial performance tests to verify that the assembled gears meet operational requirements before moving to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for High-Quality Stock Gears?
Finishing processes are vital for achieving the desired surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Grinding: This process is employed to refine the gear teeth and achieve precise tooth profiles. It can also enhance surface finish and reduce noise during operation.
-
Polishing: Used to improve the aesthetic appeal and reduce friction in high-speed applications, polishing can further enhance the lifespan of the gears.
-
Coating: Some manufacturers apply protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear, especially for gears exposed to harsh environments.
How Do International Standards Influence Quality Assurance for Stock Gears?
Quality assurance is a non-negotiable aspect of stock gear manufacturing. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications further guide manufacturers in establishing quality benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Gear Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets required specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. Any materials that do not meet specifications are rejected.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the production processes to catch defects early. This can involve regular measurements and inspections of gear dimensions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, FQC involves thorough testing of the finished gears. This can include dimensional checks, load testing, and noise assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for quality assurance documentation, including ISO certifications, test reports, and inspection records.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing processes and final products. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding quality.
-
Feedback from Other Clients: Connecting with other businesses that have sourced stock gears from the supplier can provide insights into their reliability and quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances when dealing with quality control across different regions. For instance, standards and regulations may vary significantly between countries. Understanding local market requirements is essential for compliance and can impact the selection of suppliers.
In regions like Germany, known for stringent engineering standards, buyers may prioritize suppliers with robust certifications and proven track records. Conversely, in emerging markets, flexibility and cost-effectiveness may be more critical, necessitating a different approach to supplier evaluation.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for stock gears is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages such as material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, and by employing rigorous quality control measures, suppliers can ensure that they deliver reliable and high-performance gears. For buyers, verifying these practices through audits, documentation, and third-party inspections can mitigate risks and enhance the integrity of their supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stock gear’
The following guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure stock gears effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process is efficient, cost-effective, and meets your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first crucial step in sourcing stock gears. This includes specifying gear type (spur, helical, bevel, etc.), material (metal or plastic), dimensions (module, pitch, and diameter), and any specific standards (ISO, JIS, DIN). Defining these parameters helps narrow down potential suppliers and ensures that the gears you procure will fit seamlessly into your machinery.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Thorough research on suppliers is essential to find reliable partners. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation in the industry, especially those who specialize in stock gears. Check their online presence, product catalogs, and customer reviews to gauge their reliability and the quality of their products.
- Key Points to Evaluate:
- Years in business and industry experience
- Product variety and availability of stock gears
- Geographic location and logistical advantages
Step 3: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Before making a bulk purchase, always request samples and technical documentation. This allows you to evaluate the quality and compatibility of the gears with your equipment. Technical documents should include detailed specifications, material certifications, and performance data.

Illustrative image related to stock gear
- What to Look For:
- Tolerance levels and manufacturing processes
- Material certifications and compliance with relevant standards
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Validating supplier certifications is critical to ensure compliance with international quality standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. This step minimizes risks associated with poor-quality components, which can lead to operational downtime.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and analyze their pricing structures. Be cautious of prices that seem too low; they may indicate inferior quality. Additionally, review payment terms to ensure they align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
- Considerations:
- Discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts
- Payment methods and credit terms
Step 6: Evaluate Delivery Times and Logistics
Understanding delivery timelines is vital for maintaining production schedules. Confirm the lead times provided by suppliers and assess their logistics capabilities, including shipping options and costs. This step ensures that you can plan your operations without unexpected delays.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Channel
Set up a clear communication channel with your selected supplier. Effective communication is crucial for resolving issues quickly, managing expectations, and maintaining a strong business relationship. Establish points of contact for technical support, order tracking, and any potential concerns during the procurement process.
By following this practical checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for stock gears, ensuring that they procure the right components for their operational needs while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.

Illustrative image related to stock gear
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stock gear Sourcing
When sourcing stock gears, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for international B2B buyers. This analysis breaks down the key cost components, price influencers, and offers actionable tips to navigate the complexities of stock gear procurement effectively.
What Are the Key Cost Components of Stock Gear Sourcing?
Materials: The primary cost driver for stock gears is the raw materials used in their manufacturing. Common materials include various grades of steel, aluminum, and plastics. The choice of material impacts both performance and price, with high-quality materials typically commanding higher costs.
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In developed markets, labor costs are higher due to skilled workforce requirements, whereas in regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, this can lower the overall price of stock gears.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, maintenance, and facility operations. Suppliers in regions with lower operational costs may offer more competitive pricing.
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial investment in molds and dies for gear production. While stock gears generally require less customization, any specific modifications can lead to increased tooling costs.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that stock gears meet industry standards is crucial, particularly for international buyers who may require certifications (e.g., ISO, AGMA). The cost of implementing quality control measures can impact the final pricing.
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and warehousing can significantly affect the total cost of ownership, especially for international buyers. The choice of logistics provider and the efficiency of the supply chain also play critical roles.
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s business model.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stock Gear Costs?
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can greatly influence pricing. Higher volume orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to balance inventory and cost.
Specifications/Customization: While stock gears are designed for standard applications, any customization required will lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials and Quality: The selection of materials and the quality certifications required can significantly affect prices. For example, high-performance gears made from specialized alloys will cost more than standard carbon steel gears.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their assurance of quality and service, while lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices but with increased risk.
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) is vital for international buyers. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting the overall price.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices?
Negotiate with Suppliers: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially if you are placing a large order. Suppliers are often willing to provide discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but all associated costs, including shipping, handling, and potential downtime if gears fail. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher overall expenses.
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that can affect prices. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and conditions.
Research Market Rates: Conduct market research to understand prevailing prices for the specific types of stock gears you need. This knowledge will empower you during negotiations and help you avoid overpaying.
In conclusion, by comprehensively analyzing the cost structure, understanding the price influencers, and utilizing strategic negotiation tips, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing of stock gears. This strategic approach not only ensures better pricing but also enhances the overall efficiency of the procurement process.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stock gear With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Stock Gears: What Are Your Options?
In the world of mechanical engineering and manufacturing, stock gears are a popular choice due to their availability and standardization. However, B2B buyers may also consider alternative solutions that could better meet their specific needs. This section explores how stock gears compare to custom gears and gear assemblies, providing insights that can guide purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Stock Gear | Custom Gears | Gear Assemblies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable and standardized; suitable for a wide range of applications. | Tailored to specific performance requirements, potentially enhancing efficiency. | Integrated solutions that can optimize space and performance through design. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to mass production and standardization. | Higher initial costs due to design and manufacturing processes. | Moderate to high costs depending on complexity and integration level. |
| Ease of Implementation | Readily available and easy to replace, reducing downtime. | Requires design time and validation, which can extend lead times. | Assembly can be complex but provides a ready-to-use solution if designed correctly. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to replace when needed. | Maintenance varies; parts may need custom solutions for replacement. | Maintenance can be simplified if designed for easy access; however, complexity may increase overall maintenance needs. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for general applications where standardization is sufficient. | Best for specialized applications requiring unique specifications. | Suitable for integrated systems where space and performance optimization is critical. |
What Are Custom Gears and Their Advantages?
Custom gears are designed and manufactured to meet specific requirements that standard stock gears cannot fulfill. One of the primary advantages of custom gears is their ability to enhance performance by matching the precise specifications needed for unique applications. However, this customization comes at a higher cost and longer lead time, which can be a disadvantage for projects with tight deadlines. Additionally, the need for validation and testing can add further complexity to their implementation.
How Do Gear Assemblies Compare?
Gear assemblies consist of multiple gears and related components designed to work together as a unit. This approach can optimize performance by integrating various gears for specific tasks, potentially improving efficiency and reducing the space required for installation. While gear assemblies can offer significant advantages in terms of performance and compactness, they also come with higher costs and can be more complex to maintain. If a gear assembly fails, it may require more extensive repairs compared to simply replacing a stock gear.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When considering the right solution for your mechanical needs, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, including performance, cost, and the complexity of implementation. Stock gears are ideal for applications that require quick replacements and cost-effectiveness, while custom gears and gear assemblies may be better suited for specialized projects with unique specifications. Ultimately, the choice should align with the operational goals, budget constraints, and timeline of the project at hand. By carefully analyzing these alternatives, buyers can ensure they select the most effective gear solution for their applications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stock gear
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stock Gears?
1. Material Grade
The material used in stock gears can significantly impact their performance and longevity. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and plastic. Each material has its own mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and wear resistance, which determine its suitability for specific applications. For instance, high-carbon steel gears offer excellent strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty machinery, while plastic gears are often used in lighter applications due to their lower weight and cost.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a gear’s dimensions. This specification is crucial for ensuring proper meshing with other gears. Tight tolerances can lead to better performance and reduced noise, but may also increase manufacturing costs. In a B2B context, understanding the required tolerance helps buyers select gears that will fit seamlessly into their existing machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance issues.
3. Pitch (Module and Diametral Pitch)
Pitch is a critical factor in gear design that defines the size of the teeth. For metric gears, the pitch is measured in “modules” (the ratio of the gear’s pitch diameter to the number of teeth), while imperial gears use “diametral pitch” (the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter). Ensuring that gears have matching pitch specifications is vital for compatibility, especially when replacing parts or designing new machinery.
4. Tooth Count
The number of teeth on a gear directly affects its diameter, gear ratio, and torque transmission capabilities. In a B2B setting, understanding tooth count helps buyers achieve specific operational goals, such as desired speed and load-bearing capacity. A higher tooth count generally results in a larger gear that can handle greater loads but may also reduce speed.
5. Hardness and Surface Finish
The hardness of a gear, often achieved through processes like quenching, influences its wear resistance and lifespan. Surface finish, which can be ground or non-ground, affects the gear’s performance in terms of noise and efficiency. Buyers should consider these factors when selecting stock gears, as they play a crucial role in the gear’s operational lifespan and maintenance requirements.
What Are Common Terms Used in the Stock Gear Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the stock gear industry, buyers often seek OEMs for reliable components that meet specific quality standards and specifications. Understanding OEM relationships can help businesses ensure they are sourcing high-quality, compatible parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers as it affects budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses gauge the feasibility of purchasing stock gears and can influence decisions on whether to maintain a larger inventory or order on demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request pricing information from suppliers for specific products. In the context of stock gears, submitting an RFQ allows businesses to compare prices and specifications from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is particularly important for B2B transactions involving stock gears. Understanding Incoterms can help businesses minimize risks and avoid unexpected costs during shipping.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In industries reliant on stock gears, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring that projects stay on schedule. Buyers should inquire about lead times when requesting quotes to effectively manage their supply chain and production timelines.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stock gears, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stock gear Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the Stock Gear Sector?
The stock gear market is experiencing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, globalization, and evolving buyer expectations. A key driver is the increasing demand for high-precision mechanical components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance operational efficiency, the need for reliable and readily available stock gears has surged.
Emerging trends reflect a strong inclination towards automation and digitalization. Technologies such as IoT and AI are being integrated into supply chain management, allowing for real-time tracking and predictive analytics. This shift not only streamlines operations but also enhances inventory management, reducing lead times for procurement. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms has made it easier for buyers to source stock gears from global suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and product variety.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving, with buyers increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer customizable solutions. The ability to quickly adapt gear specifications to meet unique project requirements is becoming a crucial consideration. Additionally, the emphasis on quality assurance and compliance with international standards, such as ISO and AGMA, is vital for buyers aiming to mitigate risks associated with product performance and reliability.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Stock Gear Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are gaining prominence within the stock gear sector, significantly influencing procurement decisions among B2B buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. Consequently, suppliers are under pressure to adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and minimizing energy consumption during production.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a critical factor for international buyers, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices, which includes the responsible sourcing of raw materials and adherence to labor rights. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 26000 (Social Responsibility) are becoming essential benchmarks for evaluating suppliers.
Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in manufacturing stock gears—such as recycled metals or bio-based plastics—is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce the carbon footprint but also align with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. By prioritizing suppliers who offer environmentally friendly options, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation while contributing positively to the planet.
How Has the Stock Gear Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the stock gear sector reflects broader trends in industrialization and technological advancements. In its early days, gear manufacturing was a labor-intensive process, characterized by bespoke production tailored to specific needs. However, the onset of mass production techniques in the early 20th century marked a significant turning point. Manufacturers began standardizing gear dimensions and specifications, leading to the development of stock gears that could be readily available for various applications.
As industries grew more complex and the demand for precision increased, advancements in materials science and engineering techniques emerged. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) revolutionized gear production, enabling manufacturers to create highly intricate designs with greater accuracy. This technological shift has facilitated the rise of stock gear catalogs, allowing buyers to quickly identify and source the components they need without the lengthy lead times associated with custom manufacturing.
Today, the stock gear market continues to evolve, driven by innovations in automation, digitalization, and sustainable practices. As international B2B buyers navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding the historical context of stock gears can provide valuable insights into current sourcing trends and future opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stock gear
-
How do I solve issues with gear compatibility in my machinery?
To address gear compatibility issues, first, ensure that the gear specifications—such as module or diametral pitch, tooth profile, and pressure angle—match those of the existing gears. Consult the manufacturer’s catalog for stock gears that align with your needs, and consider reaching out to technical support for assistance in selecting the correct gear. If custom solutions are necessary, inquire about the possibility of modifying stock gears or creating new gears that fit your machinery’s design requirements. -
What is the best type of stock gear for high torque applications?
For high torque applications, helical gears are often the best choice due to their ability to handle greater loads and operate more quietly than spur gears. Their design allows for smoother meshing and increased contact area, which translates into improved performance under high torque conditions. Additionally, consider the material and hardness of the gear, as these factors significantly influence its durability and resistance to wear in demanding applications. -
How can I ensure the quality of stock gears from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by checking their certifications (ISO, DIN, etc.), reviewing their manufacturing processes, and requesting samples. Look for suppliers with a transparent quality assurance process, including testing protocols for gear accuracy and durability. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits to verify compliance with international standards, especially when sourcing from regions with varied manufacturing practices. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for stock gears?
Minimum order quantities for stock gears can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of gear. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs, especially for common gear types, while others may require larger orders for custom or specialized gears. It’s advisable to clarify MOQ policies during initial discussions with suppliers to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities and project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering stock gears internationally?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers but commonly include options like upfront payment, net 30, or letters of credit for larger orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, as international transactions may involve currency conversion fees. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms upfront helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures a smoother transaction process. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for international gear purchases?
When managing logistics for international gear purchases, consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations. Work with suppliers who offer reliable shipping options and trackable deliveries. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in international shipping can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize stock gears to fit specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for stock gears, including modifications in size, material, or tooth design. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier to explore available customization services. Keep in mind that while customization can enhance compatibility and performance, it may also impact lead times and pricing, so plan accordingly. -
What should I look for in a supplier’s warranty for stock gears?
When evaluating a supplier’s warranty, consider the duration, coverage scope, and terms regarding defects and damages. A good warranty should provide assurance against manufacturing defects and specify the process for claims. Look for suppliers who stand behind their products with clear, comprehensive warranty terms, as this reflects their confidence in the quality and reliability of their stock gears.
Top 8 Stock Gear Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. KHK – Stock Gears for Sale
Domain: khkgears.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: KHK Stock Gears for Sale include various types of gears such as Spur Gears, Helical Gears, Gear Racks, Worm Gears, Bevel Gears, Miter Gears, Internal Gears, and Screw Gears. Each type has specific details:
– Spur Gears: Module 0.5-10, available in hardened/non-hardened, ground/non-ground, with variations in number of teeth, accuracy, hardness, material, and shaft fastening methods.
– Helical Gea…
2. Boston Gear – Open Gearing Solutions
Domain: bostongear.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Boston Gear – Open Gearing Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. AndyMark – Custom Sized Gears
Domain: andymark.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, AndyMark – Custom Sized Gears, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. KHK Gears – Precision Gear Solutions
Domain: khkgears.us
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Spur Gears”: {“description”: “Made in a variety of materials, configurations, modules and numbers.”, “buy_link”: “Buy Spur Gears”}, “Helical Gears”: {“description”: “Quiet, compact and economical, suitable for high-speed rotation.”, “buy_link”: “Buy Helical Gears”}, “Internal Gears”: {“description”: “Offered in modules 0.5 to 3 with 50 to 200 teeth, suitable for various applications.”, “buy_link…
5. QTC – Stock Metric Gears
Domain: qtcgears.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: QTC Distributor of Stock Metric Gears including Spur Gears, Helical Gears, Internal Gears, Racks, C.P. Racks, Miter Gears, Bevel Gears, Screw Gears, Worms and Worm Gears, Gearboxes, Ratchets and Pawls, Gear Couplings, Involute Spline Shafts, Gear Assembly Kits, and Rack and Pinion. Over 20,000 standard item configurations available for industrial applications, including replacement and OEM applica…
6. McMaster – Gears and Gear Racks
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Gears and Gear Racks, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Accu Components – KG Stock Anti Backlash Spur Gears
Domain: accu-components.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: The KG Stock Gears range includes high precision Anti Backlash Spur Gears designed to minimize backlash and eliminate the effects of variations in center distance, tooth dimensions, and bearing eccentricities. These gears feature a mechanism with built-in springs that pull the gears together, functioning like scissors to pinch the mating gear. The direction of the gear is reversible, and the sprin…
8. STOCK GEARS – Brass Bore Insert Spur Gear
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Quantity”: 1, “Brand”: “STOCK GEARS”, “Model”: “BRASS BORE INSERT WITH SET SCREW SPUR GEAR”, “Number Of Teeth”: 30, “Pitch”: 48, “Bore Diameter”: “3/16\””, “Material”: “Plastic”, “Condition”: “New – Open box”, “MPN”: “48-30-1875-20-BIWSS”, “Location”: “McCordsville, IN, United States”, “Shipping Cost”: “$23.99”, “Returns”: “30 days returns, buyer pays for return shipping”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stock gear
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial manufacturing, stock gears present a strategic advantage for businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By opting for stock gears, international B2B buyers can significantly reduce lead times, streamline maintenance processes, and lower costs associated with custom gear production. The availability of diverse gear types—ranging from spur to helical and worm gears—ensures that businesses can find the exact specifications needed for their applications without the delays of bespoke manufacturing.
Strategic sourcing of stock gears not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions. By establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, companies can secure a reliable source for essential components, thereby ensuring uninterrupted production lines and fostering innovation in machine design.
As we look to the future, the demand for stock gears is poised to grow, driven by advancements in automation and a focus on efficiency in manufacturing processes. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to leverage the benefits of stock gears and partner with trusted suppliers to bolster their production capabilities. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operational excellence and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.