Stepper Gauges: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stepper gauges
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial instrumentation, sourcing the right stepper gauges can present a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These precision instruments, crucial for various applications from automotive to manufacturing, require an understanding of both technical specifications and market dynamics. This comprehensive guide aims to equip buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
We will delve into the different types of stepper gauges available, exploring their applications and performance characteristics. Additionally, we will provide insights into the supplier vetting process, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet international quality standards. Cost analysis will also be a key focus, helping buyers understand pricing structures and negotiate effectively.
By navigating this guide, you will be empowered to select the most suitable stepper gauges for your specific needs, ensuring operational efficiency and accuracy in your projects. The aim is to demystify the complexities of the global market, enabling you to make strategic decisions that enhance your competitive edge. Whether you’re sourcing for a small startup or a large enterprise, this guide serves as your essential resource for mastering the procurement of stepper gauges.
Understanding stepper gauges Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Stepper Gauges | High precision, digital readout, fast response time | Automotive diagnostics, racing applications | Pros: Accurate readings, easy integration with digital systems. Cons: Higher cost compared to analog gauges. |
| Mechanical Stepper Gauges | Analog display, mechanical movement, robust design | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment | Pros: Durable, no power required. Cons: Less precise than digital options. |
| Bi-Polar Stepper Motors | Fine step precision, bi-polar design, compact size | Automotive applications, custom projects | Pros: Smooth operation, suitable for small indicators. Cons: Limited load capacity, requires additional components for operation. |
| Waterproof Stepper Gauges | Sealed design, resistance to moisture and dust | Marine applications, outdoor equipment | Pros: Reliable in harsh environments, durable. Cons: Typically more expensive due to specialized materials. |
| Multi-Function Stepper Gauges | Combines multiple readings (e.g., temperature, pressure) | Automotive and aerospace industries | Pros: Space-saving, versatile. Cons: Complexity may lead to higher failure rates if not maintained properly. |
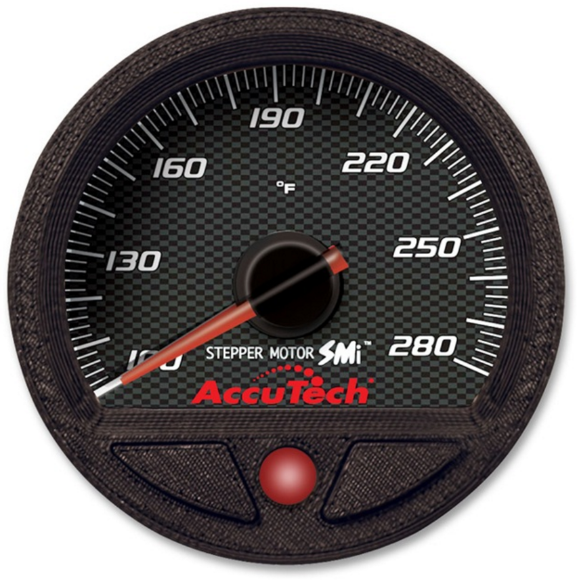
What Are Digital Stepper Gauges and Their B2B Applications?
Digital stepper gauges are characterized by their high precision and rapid response capabilities. They offer digital readouts that enhance readability and accuracy, making them ideal for automotive diagnostics and racing applications where real-time data is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the integration requirements with existing digital systems, as well as the higher upfront costs compared to traditional analog gauges.
How Do Mechanical Stepper Gauges Differ in Functionality?
Mechanical stepper gauges utilize an analog display mechanism that relies on mechanical movement. Their robust design makes them suitable for heavy machinery and industrial equipment, where durability is essential. While they do not require power, which can be a significant advantage in remote applications, their precision is inferior to digital alternatives. Buyers should weigh the importance of power-free operation against the need for accuracy.
What Are the Characteristics of Bi-Polar Stepper Motors?
Bi-polar stepper motors are known for their fine step precision, offering about 600 steps per rotation. They are compact and often used in automotive applications or for custom projects requiring precise motion. However, they have a limited load capacity and necessitate additional components like H-Bridge drivers for operation. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application needs, especially concerning the motor’s strength and required driving circuits.
Why Choose Waterproof Stepper Gauges for Harsh Environments?
Waterproof stepper gauges are designed to withstand moisture and dust, making them ideal for marine applications and outdoor equipment. Their sealed construction ensures reliability in challenging conditions. While they are generally more expensive due to the materials used, their durability can lead to long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Buyers in sectors exposed to harsh environments should prioritize these gauges for enhanced performance and longevity.
What Advantages Do Multi-Function Stepper Gauges Offer?
Multi-function stepper gauges combine various readings, such as temperature and pressure, into a single unit. This space-saving design is particularly beneficial in automotive and aerospace industries, where dashboard space is often limited. However, the complexity of these gauges can lead to higher failure rates if not maintained properly. B2B buyers should consider the trade-off between versatility and potential maintenance challenges when selecting these gauges for their operations.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
Key Industrial Applications of stepper gauges
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stepper gauges | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Digital dashboard instrumentation for vehicles | Enhanced precision and reliability in readings | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and environmental ratings. |
| Aerospace | Engine monitoring and control systems | Improved safety and operational efficiency | Look for gauges with high accuracy and resistance to extreme conditions. |
| Industrial Automation | Machine performance monitoring | Real-time data for predictive maintenance | Consider integration capabilities with existing automation systems. |
| Marine Engineering | Navigation and engine performance monitoring | Increased vessel safety and operational efficiency | Evaluate corrosion resistance and durability in marine environments. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine performance tracking | Optimized energy production and maintenance | Focus on gauges that can withstand harsh weather conditions. |
How Are Stepper Gauges Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, stepper gauges are integral to digital dashboard instrumentation. These gauges provide real-time data on various vehicle parameters such as speed, fuel levels, and engine temperature. The precision of stepper motors allows for accurate readings, which enhances vehicle performance and safety. International buyers should prioritize sourcing gauges that meet specific automotive standards and ensure compatibility with their vehicle models, especially in diverse markets like Africa and South America where vehicle types can vary widely.
What Role Do Stepper Gauges Play in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, stepper gauges are crucial for monitoring engine performance and control systems. These gauges provide vital data that can influence safety and operational efficiency, such as fuel flow and temperature readings. Buyers in this industry must consider the stringent accuracy requirements and the ability of gauges to perform reliably under extreme conditions, particularly in regions like the Middle East where operational environments can be harsh.
How Are Stepper Gauges Beneficial in Industrial Automation?
Stepper gauges are widely used in industrial automation for monitoring machine performance. They provide real-time data that helps businesses implement predictive maintenance strategies, reducing downtime and operational costs. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, sourcing gauges that can seamlessly integrate with existing automation systems is essential. Additionally, understanding the technical specifications and calibration requirements is critical to ensure optimal performance in various industrial applications.
In What Ways Are Stepper Gauges Applied in Marine Engineering?
In marine engineering, stepper gauges serve as vital components for navigation and engine performance monitoring. They help ensure vessel safety by providing accurate readings of critical parameters. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing gauges that are not only accurate but also resistant to corrosion and other marine environmental factors. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions with significant maritime activities, such as Europe and South America.
How Are Stepper Gauges Utilized in Renewable Energy?
Stepper gauges are increasingly used in renewable energy sectors, particularly for monitoring wind turbine performance. These gauges provide essential data that can lead to optimized energy production and improved maintenance schedules. When sourcing gauges for renewable energy applications, buyers should look for products that can withstand harsh weather conditions and provide high accuracy readings, as these factors directly impact energy efficiency and operational success in diverse climates across Africa and Asia.
Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stepper gauges’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Calibration Challenges with Stepper Gauges
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face calibration issues when integrating stepper gauges into their systems. The precision of stepper gauges is one of their key advantages, yet improper calibration can lead to inaccurate readings. This can be particularly problematic in industries such as automotive or manufacturing, where precise measurements are crucial for operational efficiency and safety. A miscalibrated gauge can cause delays in production or even lead to equipment failures, resulting in significant downtime and increased costs.
The Solution:
To overcome calibration challenges, buyers should invest in high-quality stepper gauges that come with comprehensive calibration instructions or software. It is essential to establish a routine calibration schedule, utilizing calibration tools that are compatible with the gauges being used. Additionally, consider partnering with suppliers who offer training or support services for calibration processes. Implementing digital solutions that allow for real-time monitoring and calibration adjustments can further enhance accuracy and reliability. Regularly reviewing calibration procedures and adapting them to any changes in operational parameters can also mitigate potential issues.
Scenario 2: Integration Issues with Existing Systems
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the difficulty in integrating stepper gauges into existing systems. Many companies operate with legacy systems or specific configurations that may not be compatible with newer gauge technologies. This incompatibility can lead to inefficient operations, increased installation costs, and frustration among engineers and technicians tasked with the integration.
The Solution:
To address integration issues, it is crucial to conduct a thorough analysis of the current systems before selecting stepper gauges. Buyers should look for gauges with flexible connectivity options, such as multiple communication protocols (CAN, RS232, etc.), which can facilitate easier integration. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customization options can also be beneficial; they can design gauges that specifically meet the existing system requirements. Additionally, investing in middleware solutions that bridge the gap between legacy systems and new technologies can streamline integration efforts. Engaging in pilot projects before full-scale implementation can help identify and resolve potential integration challenges early in the process.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
Scenario 3: Lack of Technical Support and Resources
The Problem:
Many buyers encounter difficulties due to a lack of technical support and resources when sourcing and utilizing stepper gauges. This is particularly true for businesses in regions where access to expert knowledge and customer service is limited. Without proper guidance, companies may struggle with installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, which can lead to prolonged operational interruptions and inefficiencies.
The Solution:
To combat this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing stepper gauges from reputable suppliers known for their customer service and technical support. Before making a purchase, inquire about the availability of technical resources such as installation guides, troubleshooting manuals, and dedicated support teams. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who offer on-site training or virtual workshops can also empower teams to become more proficient in gauge management. Additionally, consider joining industry forums or networks where companies share insights and solutions related to stepper gauge applications. Leveraging online resources and communities can help bridge knowledge gaps and ensure that technical support is readily available when needed.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stepper gauges
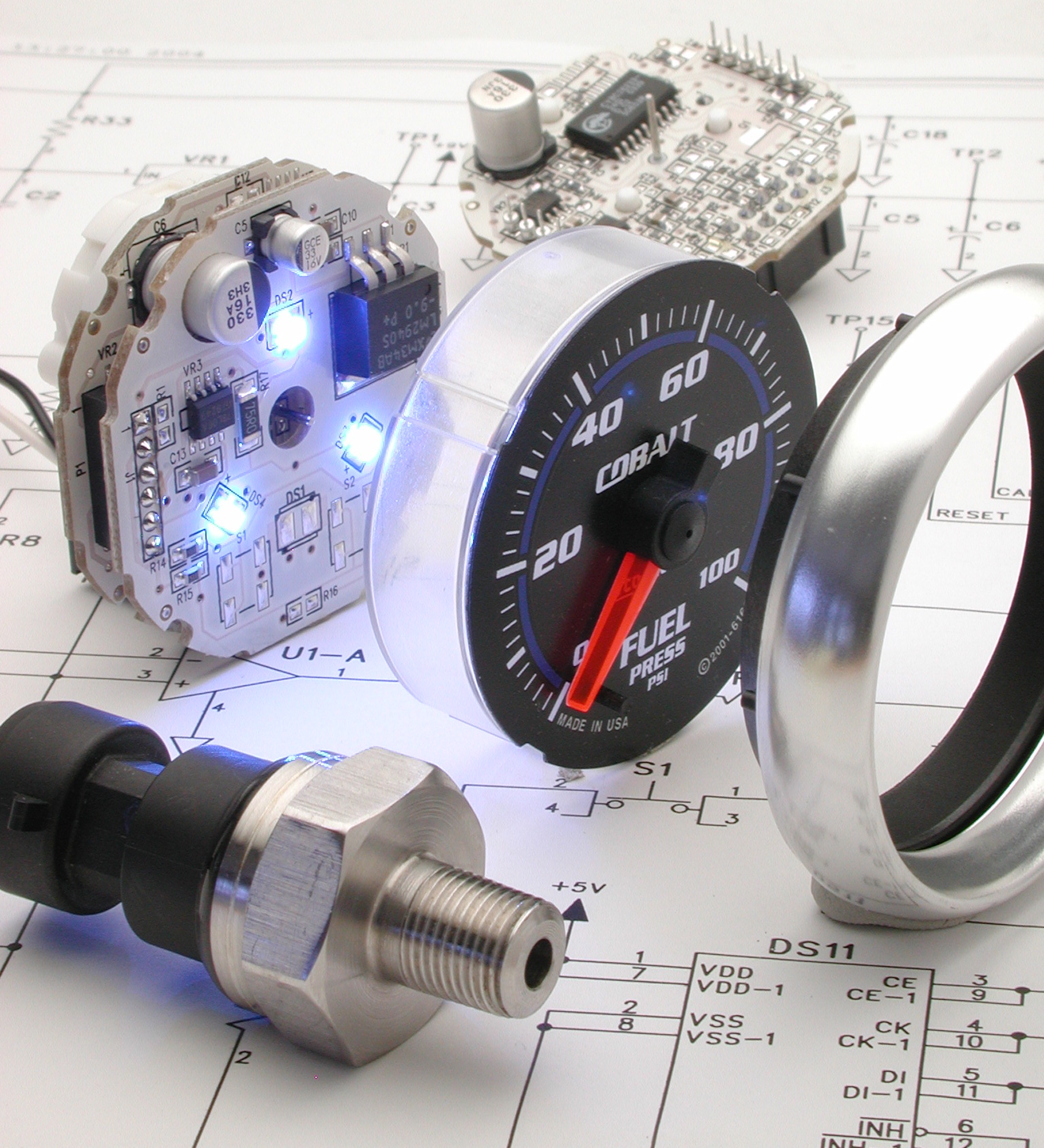
What Are the Key Materials Used in Stepper Gauges?
Stepper gauges are critical components in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. The selection of materials for these gauges significantly impacts their performance, durability, and overall suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in stepper gauges: aluminum, stainless steel, plastic, and glass.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Stepper Gauge Applications?
Aluminum is widely used in the manufacturing of stepper gauges due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and offers decent corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective and easy to machine, making it suitable for mass production. Its lightweight property enhances the overall efficiency of gauge systems, especially in automotive applications.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be less resistant to harsh chemicals compared to other metals. Its susceptibility to corrosion in certain environments may necessitate additional coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and non-corrosive fluids. However, in environments with high humidity or corrosive substances, careful consideration of protective coatings is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like the Middle East and South America should also consider local environmental factors that may affect aluminum’s performance.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Stepper Gauges?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for stepper gauges, especially in applications requiring high corrosion resistance and durability. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and offers excellent mechanical strength.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. Its robust nature ensures long-term reliability, which is critical for industries like oil and gas.
Cons: The primary drawback of stainless steel is its higher cost compared to aluminum and plastic. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where minimizing weight is crucial.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive fluids. Its durability and resistance to extreme conditions make it ideal for applications in the Middle East, where high temperatures and humidity are common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used meets specific standards, such as AISI or JIS, to guarantee quality and performance.
How Does Plastic Compare for Stepper Gauge Manufacturing?
Plastic materials, particularly engineering plastics like polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in stepper gauges due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They typically handle temperatures up to 100°C and offer good resistance to various chemicals.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to mold into complex shapes, making it ideal for custom applications. Its resistance to corrosion and chemicals is advantageous in various environments.
Cons: While plastic is suitable for many applications, it may not withstand extreme temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals. Over time, exposure to UV light can lead to degradation.
Impact on Application: Plastic is compatible with non-corrosive fluids and gases, making it suitable for automotive and consumer products. However, its limitations in high-temperature applications should be considered.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic materials is essential, especially in regions with strict waste management policies.
What Role Does Glass Play in Stepper Gauge Design?
Glass is often used in the construction of gauge faces and lenses due to its clarity and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros: Glass provides excellent visibility and is scratch-resistant, enhancing the durability of the gauge’s display. It is also chemically inert, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: Glass is heavier and more fragile than other materials, which can pose challenges in terms of durability and handling during manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for applications where visibility and aesthetic quality are paramount. However, its fragility may limit its use in rugged environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that glass components meet safety standards to prevent breakage and ensure reliability in various applications.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
Summary Table of Material Selection for Stepper Gauges
| Material | Typical Use Case for stepper gauges | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, consumer electronics | Lightweight and cost-effective | Corrosion susceptibility | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, aerospace | High corrosion resistance and strength | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Plastic | Consumer products, automotive | Lightweight and easy to mold | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Glass | Gauge faces and lenses | Excellent visibility and scratch resistance | Heavier and more fragile | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in stepper gauges, aiding in informed decision-making for diverse applications across international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stepper gauges
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stepper Gauges?
The manufacturing of stepper gauges involves several critical stages that ensure product quality and functionality. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing these components.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with material selection, typically involving high-grade metals and plastics that can withstand operational stresses. Common materials include aluminum for housings and polycarbonate for lens covers. Suppliers often conduct a preliminary inspection of raw materials, checking for defects such as corrosion or dimensional inaccuracies. This stage may also include the preparation of circuit boards, which are integral to the gauge’s electronic functions.
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, forming techniques are employed to shape components. This can involve CNC machining for precision parts, stamping for metal housings, and injection molding for plastic components. Advanced techniques like laser cutting and 3D printing may also be used, particularly for prototyping or small-batch production. Each technique has its own set of advantages, such as reduced waste or faster turnaround times, which can be crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chains.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
Assembly Process
The assembly of stepper gauges involves integrating various components, including the stepper motor, circuit boards, and display elements. This step is often performed in a clean environment to minimize contamination. Automated assembly lines may be used for high-volume production, while manual assembly could be employed for custom or low-volume orders. Quality checks are integrated at this stage to ensure that each gauge meets specified tolerances and functional requirements.
Finishing Techniques
Finishing processes such as anodizing, painting, or applying protective coatings enhance both aesthetics and durability. For example, anodizing aluminum components can improve corrosion resistance, while painting can provide branding opportunities. Additionally, final assembly may include the installation of calibration features to ensure accuracy.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Stepper Gauge Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process, ensuring that stepper gauges meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Govern Stepper Gauge Quality?
Compliance with international quality standards such as ISO 9001 is vital for manufacturers seeking to establish credibility in global markets. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system that enhances customer satisfaction through consistent product quality. In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications can be critical for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East where regulatory compliance may vary.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should verify material certifications and conduct tests to ensure compliance with specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the production stages, IPQC involves monitoring production processes and conducting regular inspections. This may include dimensional checks and functionality tests of assembled components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, FQC is performed to ensure that each stepper gauge meets all design specifications and quality standards. This final inspection often includes performance testing under simulated operational conditions.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Stepper Gauges?
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the functionality and reliability of stepper gauges. Common techniques include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that the gauge operates correctly under a range of conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Assessing performance under extreme temperatures and humidity levels to ensure durability.
- Calibration Tests: Ensuring that the gauge provides accurate readings, which is essential for applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like South America and Europe, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is essential. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality control processes, and adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed reports on past production batches, including quality metrics, defect rates, and corrective actions taken, can help assess a supplier’s reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of product quality and compliance with specifications before shipment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers must navigate various certification and quality assurance nuances when sourcing stepper gauges from international suppliers. For example, the acceptance of certain certifications may vary by region. Buyers in Europe may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on compliance with local standards.
Additionally, language barriers and different regulatory frameworks can complicate the verification process. It is advisable for buyers to establish clear communication channels with suppliers and seek assistance from local representatives or consultants who are familiar with the market landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for stepper gauges is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of production, quality checkpoints, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product reliability. As the global market continues to evolve, prioritizing quality in procurement will remain a key differentiator for businesses across various sectors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stepper gauges’
To assist B2B buyers in successfully procuring stepper gauges, this guide outlines a practical, step-by-step checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. Whether your business operates in automotive, industrial, or specialized applications, following these steps will ensure that you make informed decisions and secure high-quality products.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements of the stepper gauges you need. This includes parameters such as gauge type (digital or analog), measurement range (e.g., pressure, temperature), and compatibility with existing systems. Defining these specifications helps narrow down your options and ensures that the selected gauges meet your operational needs.
- Considerations: Look for precision levels, response times, and any specific certifications required for your industry.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Explore the current market landscape for stepper gauges. Identify potential suppliers, compare product offerings, and analyze price ranges. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry publications to gather insights about leading manufacturers and emerging technologies.
- Tools: Use online directories, industry forums, and social media to gather feedback from other businesses regarding their experiences with various suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to thoroughly vet them. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to understand their capabilities. Look for references from other buyers in your sector to gauge reliability and quality.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
- Key Indicators: Assess their experience in your industry, customer service responsiveness, and warranty or return policies.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This is particularly important for gauges used in regulated environments, where precision and safety are paramount.
- Common Certifications: Check for ISO certifications, CE markings, or any specific local certifications relevant to your region (e.g., UL for the USA, IEC for international).
Step 5: Request Samples
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the stepper gauges to evaluate their performance and compatibility with your systems. Testing samples allows you to assess the build quality, accuracy, and ease of installation.
- Testing Focus: Pay attention to gauge responsiveness, clarity of readouts, and overall functionality in real-world conditions.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and delivery timelines. A good negotiation can lead to better pricing, favorable payment terms, and assurances on lead times.
- Considerations: Be prepared to discuss bulk discounts or long-term partnership benefits, especially if you anticipate repeat orders.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
After finalizing your supplier, set up a clear communication plan to ensure smooth interactions. Regular updates on order status, shipping, and any potential issues can help prevent misunderstandings and delays.
- Best Practices: Designate a point of contact on both sides and schedule periodic check-ins, especially if you’re placing ongoing orders.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing stepper gauges more effectively, leading to better purchasing decisions and ultimately, enhanced operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stepper gauges Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Stepper Gauges?
When evaluating the sourcing of stepper gauges, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality metals and plastics used in the manufacturing of stepper motors and gauge casings can increase expenses. For example, specialized components like waterproof sensors or high-precision stepper motors may come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence overall pricing. Countries with higher labor costs may see increased prices for manufacturing stepper gauges. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can provide cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, thereby reducing the final price of the gauges.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom gauges can be significant, especially for specialized designs. Buyers should consider these upfront costs when evaluating total expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may also be required, which can further influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary significantly depending on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. International shipments may incur additional fees, including customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the final price. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers assess the fairness of quotes.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stepper Gauge Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing stepper gauges:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized gauges typically incur higher costs due to unique designs or features. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customizations against budget constraints.
-
Materials: The specific materials chosen can impact both performance and pricing. Premium materials may enhance durability but can also increase overall costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Gauges that meet specific industry standards or certifications may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential for calculating total costs. Different Incoterms can shift responsibilities and costs between the buyer and seller, affecting the final pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Stepper Gauge Sourcing?
Buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing stepper gauges:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions to negotiate better pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can incentivize suppliers to offer more competitive rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price. Factor in maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality gauges.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding currency fluctuations and local economic conditions is essential. This knowledge can aid in evaluating total costs and avoiding unexpected price increases.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to compare pricing, quality, and delivery times. Due diligence can uncover hidden costs and provide leverage during negotiations.
Conclusion
While sourcing stepper gauges, it is vital for B2B buyers to thoroughly analyze the cost components and price influencers. By understanding the underlying factors that contribute to pricing, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints and quality requirements. Keep in mind that prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stepper gauges With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Stepper Gauges
In the evolving landscape of measurement technologies, B2B buyers must evaluate various solutions to ensure they select the most effective option for their operational needs. Stepper gauges are popular due to their precision and reliability, but alternative technologies can also offer unique advantages. Below, we compare stepper gauges with two prominent alternatives: analog gauges and digital pressure sensors, providing insights into their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Comparison Aspect | Stepper Gauges | Analog Gauges | Digital Pressure Sensors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with fine steps | Moderate precision, less responsive | High accuracy and real-time data |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally low | Moderate to high |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires electronic setup | Simple installation | Requires calibration and setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Moderate, mechanical wear | Low, but requires software updates |
| Best Use Case | Automotive and robotics | Basic monitoring applications | Industrial applications needing real-time data |
How Do Stepper Gauges Compare to Analog Gauges?
Analog gauges utilize a needle that moves over a calibrated scale to display measurements. While they are generally less expensive and easier to install than stepper gauges, their performance can be inconsistent, especially under rapid changes in measurement conditions. Analog gauges can suffer from mechanical wear and may not provide the precision required for high-tech applications. Therefore, they are best suited for basic monitoring tasks where high accuracy is not critical.
What Are the Advantages of Digital Pressure Sensors Compared to Stepper Gauges?
Digital pressure sensors offer a modern approach to measurement, providing real-time data and high accuracy. These sensors convert physical measurements into digital signals, allowing for easier integration with data logging and monitoring systems. While they may require more initial calibration and setup, their low maintenance and capability to provide continuous data can significantly enhance operational efficiency in industrial settings. However, their cost can be comparable to or even exceed that of stepper gauges, depending on the specifications.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right measurement technology involves a careful assessment of specific operational requirements. B2B buyers should consider factors such as the necessary precision, cost constraints, ease of installation, and maintenance needs. Stepper gauges are ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness, particularly in automotive and robotics sectors. Conversely, if budget constraints are significant and precision is less critical, analog gauges may suffice. For industries demanding real-time data and integration with advanced monitoring systems, digital pressure sensors present a compelling alternative. Ultimately, aligning the choice of technology with the unique demands of the application will ensure optimal performance and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stepper gauges
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stepper Gauges?
Understanding the technical specifications of stepper gauges is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Stepper Motor Type
Stepper motors used in gauges can vary significantly. Common types include bi-polar and uni-polar motors. Bi-polar motors, for example, provide smoother operation and greater torque, making them suitable for applications requiring precision. Selecting the right type can influence the performance and longevity of the gauge in various environments. -
Rotation Angle
The rotation angle, typically expressed in degrees, indicates the range of motion of the gauge needle. Many stepper gauges offer a rotation angle of around 270 to 315 degrees. This specification is crucial for applications where precise readings are necessary, as a larger rotation angle allows for more granularity in measurement, which is vital in automotive and industrial applications. -
Step Resolution
Step resolution refers to the degree of movement per step, which can range from 0.5 to 1.8 degrees per step in many stepper motors. A finer step resolution allows for more precise readings and smoother transitions in needle movement. This property is particularly important in high-accuracy applications, such as racing or high-performance vehicles, where real-time data is critical. -
Coil Resistance
Coil resistance is a measure of the electrical resistance within the motor’s coils, often expressed in ohms. For example, a common value is around 200-260 ohms. This specification affects the motor’s efficiency and power consumption. Understanding coil resistance helps buyers assess the compatibility of the gauge with their existing systems and the overall energy requirements. -
Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the environmental conditions under which the stepper gauge can function effectively. A typical range might be from -40°C to 85°C. This is particularly relevant for applications in extreme climates, ensuring reliability and performance in various environments. -
Material Composition
The materials used in manufacturing stepper gauges—such as plastics, metals, and composites—play a crucial role in durability and performance. High-quality materials can enhance the gauge’s resistance to environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations, thus extending its service life.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Stepper Gauge Industry?
Navigating the terminology in the stepper gauge market can be daunting. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking reliable suppliers who provide quality components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for buyers to assess whether a supplier’s offerings align with their production needs and inventory management strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other details for specific products. This process helps buyers compare costs and terms across different suppliers, enabling better negotiation and purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks during shipping and delivery. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Calibration
Calibration is the process of adjusting the accuracy of a gauge to ensure it provides precise readings. Regular calibration is essential in maintaining the reliability of stepper gauges, especially in high-stakes environments where precision is critical.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes and ensure they select the right stepper gauges for their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stepper gauges Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Stepper Gauges Sector?
The stepper gauges sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Globally, there is a rising preference for digital over analog gauges due to their precision, ease of integration with modern automotive and industrial applications, and user-friendly interfaces. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where industries are increasingly automating processes and seeking real-time data analytics. In South America and Africa, the growing automotive and manufacturing sectors are driving demand for reliable and efficient measurement solutions, highlighting a shift towards higher-quality products that can withstand diverse environmental conditions.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT integration, are reshaping how stepper gauges are utilized. Smart gauges can now provide data remotely, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. As international B2B buyers consider sourcing, understanding the compatibility of these gauges with existing systems will be crucial. Furthermore, competition among suppliers is intensifying, leading to increased innovation and more competitive pricing. Buyers should stay informed about the latest product releases and technological advancements to leverage these developments for their operational needs.
Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Stepper Gauges Market?
Sustainability has become a central focus for many industries, including the stepper gauges sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and material sourcing is prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production methods, and waste reduction strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for products that come with certifications indicating sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence, as companies aim to ensure their supply chains are free from labor exploitation and environmental degradation. Buyers in the stepper gauges market should assess suppliers not only on product quality but also on their commitment to ethical practices. This can include transparency in sourcing, fair labor practices, and the use of recyclable materials. By choosing suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethics, businesses can enhance their corporate responsibility profiles and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Stepper Gauges?
Stepper gauges have evolved significantly since their inception, transitioning from purely mechanical designs to advanced digital technologies. Initially used in automotive applications, these gauges relied on analog mechanisms to provide measurements. As electronic components became more prevalent in the late 20th century, stepper motors began to replace traditional gauges, offering improved accuracy and responsiveness.
The integration of digital technology in the early 2000s marked a turning point, enabling features such as programmable settings and real-time data reporting. As industries continue to innovate, stepper gauges are now being integrated with IoT capabilities, allowing for enhanced data collection and analysis. This evolution reflects broader trends in automation and connectivity across various sectors, making stepper gauges a critical component in modern manufacturing and automotive applications. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and the potential for future developments in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stepper gauges
-
How do I select the right stepper gauge for my application?
Choosing the right stepper gauge depends on several factors, including the specific measurements you need, the environment in which the gauge will be used, and the compatibility with your existing systems. Assess the range of measurements (e.g., pressure, temperature) and ensure the gauge’s specifications align with your equipment. Additionally, consider the installation requirements and whether the gauge must withstand extreme conditions, such as moisture or vibration. Consulting with suppliers can provide insights into the best options available for your needs. -
What customization options are available for stepper gauges?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for stepper gauges to meet specific client requirements. Customizations can include variations in size, display type (analog vs. digital), measurement ranges, and housing materials. You can also request branding elements, such as logos or color schemes, to align with your corporate identity. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly to the supplier during the initial discussions to determine feasibility and any associated costs or lead times. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stepper gauges?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stepper gauges can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10 units, while others might require orders of 100 or more to achieve favorable pricing. When negotiating, consider asking if there are flexibility options, such as reduced MOQs for first-time orders or bulk purchasing agreements. Understanding MOQs is crucial for managing inventory and cash flow effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing stepper gauges internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing stepper gauges, request certifications and quality control documentation from suppliers. Look for ISO certification or compliance with international standards relevant to your industry. Conducting factory audits or utilizing third-party inspection services can further verify the quality of the products before shipment. Additionally, establishing clear quality expectations and testing protocols in your purchase agreement can help mitigate risks associated with overseas sourcing. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers?
Negotiating payment terms is vital for managing cash flow and mitigating risks. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%) and the balance upon delivery or after inspection. Consider negotiating for extended payment terms if your cash flow allows, as this can improve your financial flexibility. It’s also prudent to discuss options for letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to protect both parties during transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing stepper gauges?
When importing stepper gauges, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Choose a shipping method that balances cost and delivery speed; air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Understand the customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and additional fees. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with international trade can streamline the process and help navigate any potential challenges. -
How do I vet suppliers for stepper gauges effectively?
Effective supplier vetting involves researching potential manufacturers, checking references, and reviewing client testimonials. Verify their production capabilities, quality certifications, and compliance with industry standards. Engage in initial discussions to gauge responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on your specific requirements. If possible, request samples to assess product quality firsthand before committing to larger orders. Building relationships with reliable suppliers can enhance your supply chain’s stability. -
What are the common applications for stepper gauges in various industries?
Stepper gauges are widely used across several industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. In automotive applications, they provide precise measurements for dashboard indicators. In aerospace, they monitor critical system parameters under rigorous conditions. Manufacturing sectors utilize stepper gauges for machinery diagnostics and performance monitoring. Understanding the specific applications within your industry can guide you in selecting the appropriate gauge types that meet your operational needs.
Top 8 Stepper Gauges Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AutoMeter – Digital Stepper Motor Boost Gauge
Domain: autometer.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, AutoMeter – Digital Stepper Motor Boost Gauge, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Longacre Racing – Digital Elite Waterproof Gauges
Domain: longacreracing.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Gauges, Panels, & Electrical products include: Digital Elite LED Waterproof Gauges, Digital Elite LED Waterproof Gauge Panels, SMi™ Elite Waterproof Gauges, SMi™ Elite Waterproof Gauge Panels, Sportsman™ Elite Gauges, Sportsman™ Elite Gauge Panels, various types of switches and switch panels, wire harnesses, and specialty tools. Specific products listed include SMi™ Temperature Sensor, SMi™ Pressu…
3. Adafruit – Automotive Gauge Stepper Motor
Domain: adafruit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Automotive Gauge Stepper Motor [x27.168]”, “Product ID”: “2424”, “Price”: “$9.95”, “Discount Pricing”: {“1-9”: “$9.95”, “10-99”: “$8.96”, “100+”: “$7.96”}, “In Stock”: true, “Description”: “This stepper motor is used in gauges for motorcycles and cars to replace old-style fully-analog types. It has a fine step precision of about 1/2 a degree per step, 600 steps for single steppin…
4. RedLine – Fuel Pressure Gauge
Domain: quickcar.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘RedLine Gauge – Fuel Pressure’, ‘model’: ’69-005′, ‘size’: ‘2-5/8″‘, ‘range’: ‘0-100 PSI’, ‘type’: ‘Electric stepper motor gauge’, ‘features’: ‘Adjustable warning level; Back lighting changes from white to green and flashes’, ‘price’: ‘$129.95’}, {‘name’: ‘RedLine Gauge – Fuel Pressure’, ‘model’: ’69-000′, ‘size’: ‘2-5/8″‘, ‘range’: ‘0-15 PSI’, ‘type’: ‘Electric stepper motor gauge’, ‘f…
5. Longacre – AccuTech SMI Stepper Motor Gauges
Domain: hrpworld.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Longacre AccuTech SMI Stepper Motor Gauges are precision instruments designed for accurate measurement in motorsport applications. They feature a stepper motor for precise needle movement, ensuring quick and accurate readings. The gauges are available in various configurations, including oil pressure, water temperature, fuel pressure, and more. They are designed for easy installation and come with…
6. Chevy Hardcore – Mechanical Gauges
Domain: chevyhardcore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Mechanical Gauges: Use a tube filled with the monitored fluid; more accurate (+/- 2% at full deflection); direct connection to engine; can operate without electrical system; potential for fluid leaks in passenger compartment. Pros: Great accuracy, full dial-sweep, always on. Cons: Harder to install, introduces fluid into passenger compartment.
Electrical Gauges: Use a magnetic core and voltage re…
7. Arduino – Automotive Gauge Stepper Motor
Domain: forum.arduino.cc
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Automotive Gauge Stepper Motor, Price: $9.95 USD, Used in gauges for motorcycles and cars, designed to replace old-style fully-analog types.
8. Longacre Racing Products – SMi Stepper Motor Gauges
Domain: jegs.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Longacre Racing Products SMi Stepper Motor Gauges, Promo Code: BUILT for discounts, Free Shipping over $199, Same Day Shipping before 10pm, Price Match Guarantee.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stepper gauges
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and automotive industries, strategic sourcing of stepper gauges is essential for ensuring precision, efficiency, and reliability. With the increasing demand for digital and high-performance solutions, international B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who offer robust products that meet stringent quality standards. Stepper gauges, with their fine precision and rapid response capabilities, serve as critical components in various applications, from automotive to industrial equipment.
Investing in high-quality stepper gauges not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to overall product reliability and customer satisfaction. As buyers explore options, it is crucial to evaluate suppliers based on their product range, technological innovation, and after-sales support. Engaging with manufacturers who understand local market needs in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can provide a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the market for stepper gauges is poised for growth as industries increasingly adopt automation and digital solutions. Buyers should seize the opportunity to build strategic partnerships that will drive innovation and excellence in their operations. By aligning with the right suppliers, businesses can ensure they remain at the forefront of technological advancements in the gauge sector.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to stepper gauges
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.