Solar Heat Lamp: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar heat lamp
As international B2B buyers increasingly seek sustainable solutions, sourcing effective solar heat lamps presents a unique challenge. These innovative devices are not only essential for applications such as agricultural heating and aquaculture but also play a significant role in enhancing energy efficiency in diverse climates. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of solar heat lamps available in the global market, providing insights into their applications across sectors.
Buyers will find detailed analyses of different models, including their technical specifications, performance metrics, and suitability for specific environments. Additionally, the guide offers practical advice on supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reputable manufacturers who adhere to international quality standards. Cost considerations are also thoroughly examined, empowering businesses to make budget-conscious decisions without compromising on quality.
With a focus on regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Vietnam—this guide equips buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing solar heat lamps. By understanding market trends and product capabilities, B2B buyers can confidently invest in solar heat solutions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Understanding solar heat lamp Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Infrared Heat Lamp | Emits infrared radiation for targeted heating | Poultry farms, greenhouses, outdoor dining | Pros: Efficient heating, low energy costs. Cons: Limited area coverage, higher initial cost. |
| Solar Air Heater | Uses solar energy to heat air directly | Industrial spaces, livestock barns | Pros: Reduces energy bills, scalable design. Cons: Dependent on sunlight, potential installation complexity. |
| Solar Water Heater | Heats water using solar panels and heat exchangers | Aquaculture, agricultural irrigation | Pros: Cost-effective for water heating, environmentally friendly. Cons: Requires regular maintenance, initial setup cost. |
| Solar Heat Collector | Collects and stores solar energy for later use | Residential heating, commercial facilities | Pros: Versatile applications, long-term savings. Cons: Space requirements, efficiency varies by location. |
| Hybrid Solar Heat Lamp | Combines solar and electric heating sources | Greenhouses, livestock management | Pros: Reliable heating in varying conditions, versatile. Cons: Higher operational costs, complexity in maintenance. |
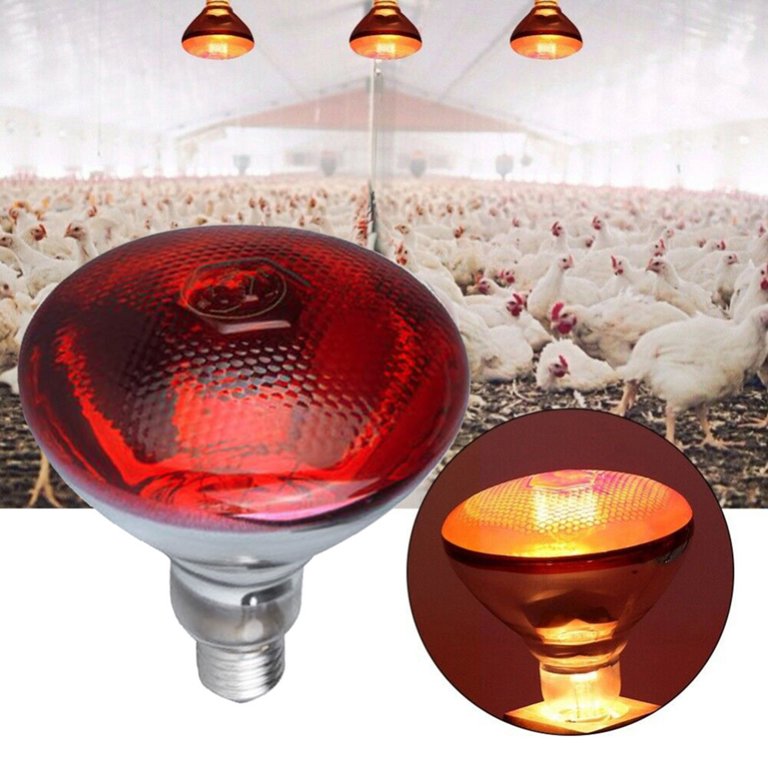
What Are the Characteristics of Solar Infrared Heat Lamps?
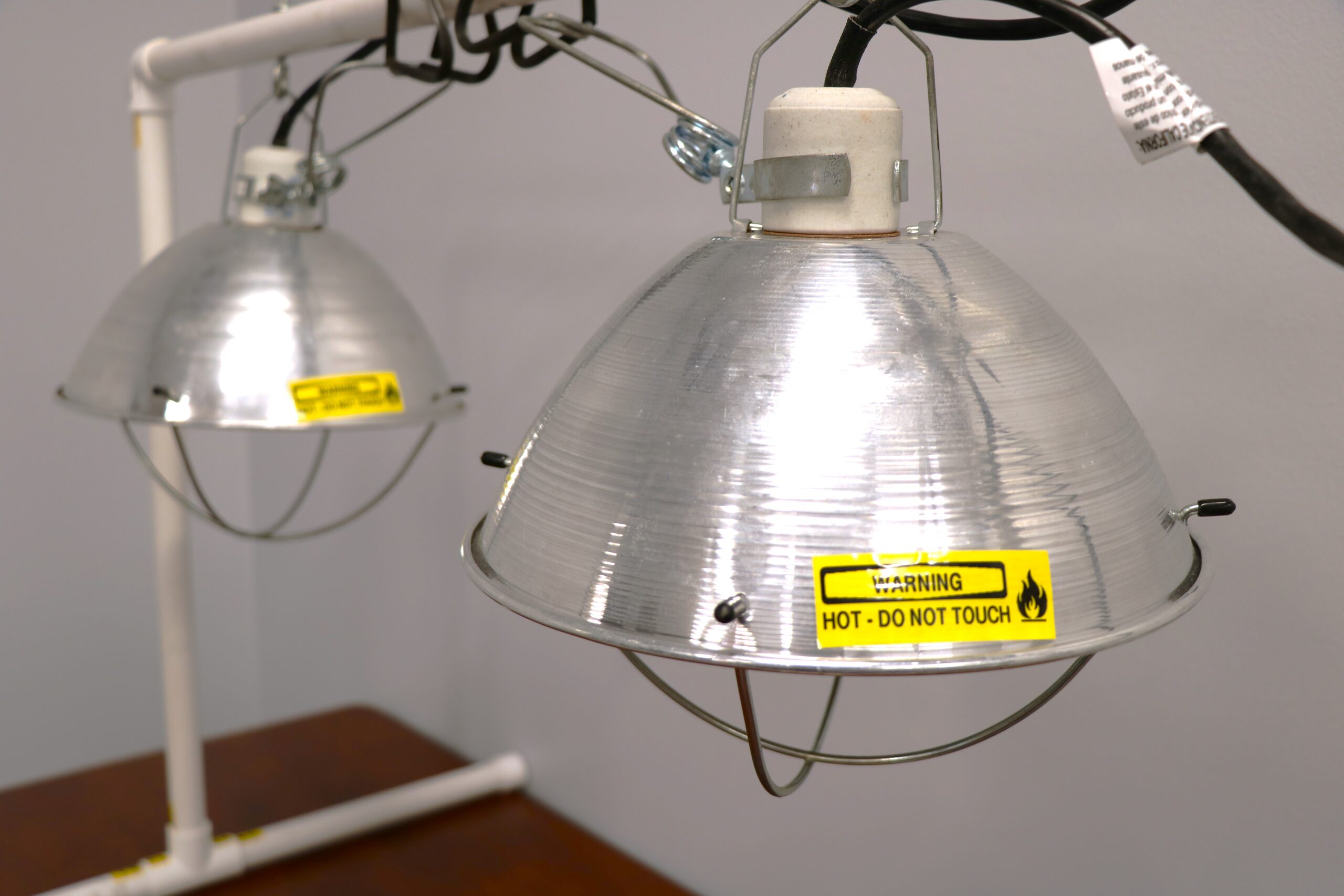
Solar infrared heat lamps are designed to emit infrared radiation, which directly warms objects rather than the air around them. This makes them particularly effective in applications like poultry farming, where targeted heating can improve animal welfare during colder months. B2B buyers should consider the efficiency of these lamps in terms of energy consumption and heating coverage. While they may have a higher initial cost, the long-term energy savings can be significant.
How Do Solar Air Heaters Operate?
Solar air heaters utilize solar energy to heat air, which is then circulated into spaces such as industrial warehouses or livestock barns. These systems can significantly reduce heating costs, making them appealing for businesses looking to lower operational expenses. When purchasing, buyers should assess the scalability of the system and the complexity of installation, as these factors can impact overall effectiveness and return on investment.
What Benefits Do Solar Water Heaters Provide?
Solar water heaters are designed to heat water through solar panels and heat exchangers, making them ideal for applications in aquaculture and agricultural irrigation. They are particularly attractive to B2B buyers due to their cost-effectiveness and minimal environmental impact. However, potential buyers should be aware of the maintenance requirements and initial setup costs, which can vary significantly based on the system’s design and location.
What Is the Function of Solar Heat Collectors?
Solar heat collectors are versatile systems that capture and store solar energy for various heating applications, including residential heating and commercial facilities. They can lead to substantial long-term savings on energy costs. B2B buyers should consider the space requirements for installation and the efficiency of the collectors in their specific geographic location, as these factors can greatly influence performance.
How Do Hybrid Solar Heat Lamps Work?
Hybrid solar heat lamps combine solar and electric heating sources to provide reliable warmth across various conditions, making them suitable for environments like greenhouses and livestock management. While they offer versatility and consistent heating, B2B buyers must consider the potential for higher operational costs and the complexity of maintenance. Understanding the balance between solar and electric components will be crucial for optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of solar heat lamp
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solar heat lamp | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Poultry Farming | Maintains optimal temperature for poultry, enhancing growth rates and reducing mortality. | Ensure UV resistance and durability against harsh weather. |
| Aquaculture | Fish Hatcheries | Provides warmth to incubate fish eggs, improving hatch rates and survival. | Look for waterproof designs and energy efficiency. |
| Greenhouses | Plant Propagation | Promotes seed germination and growth during cooler months. | Consider size, heat output, and integration with existing systems. |
| Livestock Farming | Livestock Shelters | Keeps animals warm in colder climates, improving health and productivity. | Assess energy storage capabilities for night-time use. |
| Food Processing | Drying and Curing | Utilizes solar heat for drying crops and curing meats, enhancing flavor and shelf life. | Evaluate compliance with food safety standards and materials used. |
How Are Solar Heat Lamps Beneficial in Agriculture?
In poultry farming, solar heat lamps play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures, particularly in colder climates. They help reduce mortality rates and promote faster growth by ensuring that chicks remain warm during their critical early life stages. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable, UV-resistant lamps that can withstand varying weather conditions is essential. Ensuring that these lamps are energy-efficient can significantly reduce operational costs.
What Role Do Solar Heat Lamps Play in Aquaculture?
In aquaculture, solar heat lamps are instrumental in fish hatcheries, where they provide the necessary warmth for incubating fish eggs. This application is especially relevant in regions with fluctuating temperatures, as it can lead to higher hatch rates and improved survival of young fish. Buyers should prioritize waterproof designs that can operate effectively in humid environments and assess the energy efficiency of these lamps to ensure they meet operational needs without excessive energy costs.
How Are Solar Heat Lamps Used in Greenhouses?
For greenhouse operations, solar heat lamps facilitate plant propagation by promoting seed germination and growth during cooler months. This is particularly beneficial in regions with seasonal climate variations, allowing growers to extend their growing seasons and increase yields. Buyers should consider the size and heat output of the lamps, ensuring they can adequately meet the greenhouse’s specific heating requirements while integrating seamlessly with existing systems.
What Advantages Do Solar Heat Lamps Offer for Livestock Farming?
In livestock farming, solar heat lamps provide essential warmth in shelters, particularly for young or vulnerable animals during cold weather. This application enhances animal welfare and productivity, leading to healthier livestock and improved yields. B2B buyers should evaluate the energy storage capabilities of these lamps to ensure they can provide warmth during nighttime or cloudy days, and consider the materials used to ensure durability and safety.
How Can Solar Heat Lamps Be Utilized in Food Processing?
In the food processing sector, solar heat lamps can be employed for drying and curing purposes, such as drying fruits, vegetables, and meats. This method not only enhances flavor but also extends shelf life, making it a valuable technique for businesses looking to improve product quality. Buyers must ensure that the lamps comply with food safety standards and are made from materials that do not leach harmful substances during operation, thereby safeguarding product integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solar heat lamp’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Insufficient Heating Performance in Cold Climates
The Problem:
B2B buyers, especially those operating in colder regions such as parts of Europe or South America, often find that solar heat lamps struggle to provide adequate heating during winter months. This challenge can lead to inadequate thermal comfort for livestock or crops, resulting in reduced productivity and potential financial losses. Buyers may feel frustrated when solar heat lamps fail to meet their expectations, especially after investing in what was marketed as a reliable solution.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, it is crucial for buyers to carefully assess the specifications of solar heat lamps before making a purchase. Look for models with high wattage and sufficient battery storage capacity to ensure they can operate effectively during low sunlight conditions. Consider integrating supplemental heating sources, such as thermal mass systems or insulated enclosures, to retain heat when solar output is low. Additionally, conduct a site assessment to determine solar exposure and optimize the placement of the lamps for maximum sunlight absorption. Buyers should also consider investing in smart solar heat lamps equipped with sensors that can adjust output based on temperature fluctuations.
Scenario 2: High Initial Costs and Long-Term ROI Concerns
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers are deterred by the high upfront costs associated with solar heat lamps, particularly in regions where solar technology is not yet mainstream. This initial investment can seem daunting, especially when budgets are tight. Buyers may struggle with the uncertainty of whether these products will deliver a return on investment (ROI) over time, given the fluctuating energy costs and potential maintenance needs.
The Solution:
To address these concerns, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis before purchasing solar heat lamps. This analysis should include not only the initial costs but also long-term savings on energy bills and potential subsidies or tax incentives for using renewable energy solutions. Collaborate with suppliers to identify cost-effective models that offer warranties and low maintenance requirements, thereby ensuring longevity and reliability. Additionally, consider joining a cooperative purchasing group to leverage collective buying power, which can significantly reduce costs. Engaging in educational workshops about solar technology can also help buyers understand how to maximize efficiency and savings, further justifying the investment.
Scenario 3: Limited Availability of Quality Products and Support
The Problem:
In many regions, particularly in developing countries in Africa and South America, B2B buyers often encounter a limited selection of quality solar heat lamps. They may struggle to find products that meet international standards, as well as reliable suppliers who offer customer support and after-sales services. This lack of availability can lead to frustration, as buyers fear they will invest in subpar products that could harm their operations.

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing products from reputable manufacturers with a track record of quality and service. Researching suppliers who adhere to international certification standards can ensure that products are reliable and efficient. Participating in industry trade shows or forums can also help buyers connect with trustworthy suppliers and learn about the latest innovations in solar heating technology. Establishing partnerships with local distributors who understand the regional context can provide ongoing support and maintenance services, ensuring that buyers can effectively manage their solar heat lamps over time. Furthermore, buyers can share experiences and reviews within their networks to foster a community of informed decision-makers, helping to elevate the standard of available products in their markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar heat lamp
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Solar Heat Lamps?
When selecting materials for solar heat lamps, it is essential to consider various factors such as thermal efficiency, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of solar heat lamps, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Solar Heat Lamps?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it an ideal choice for solar heat lamps. It can withstand high temperatures and has a good corrosion resistance when treated properly.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, it may require additional treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance, especially in humid environments. This can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, making it versatile for different heating applications. However, its thermal expansion can be a concern if not properly accounted for in design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, should ensure that aluminum components are anodized or treated to prevent corrosion. Compliance with international standards like ASTM for aluminum alloys is also crucial.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Solar Heat Lamp Design?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is particularly suitable for outdoor applications where environmental exposure is a concern.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and longevity, making it a preferred choice for high-quality solar heat lamps. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to work with due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various heating media, including water and oil, and is often used in applications requiring high pressure and temperature ratings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel that meet local regulations and standards. For instance, AISI 304 and 316 are commonly used grades that offer different levels of corrosion resistance.
How Does Polycarbonate Compare as a Material for Solar Heat Lamps?
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is often used for protective covers in solar applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and excellent insulation properties. However, it may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under prolonged UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring visibility and protection, such as covering heating elements. Its compatibility with various media is generally good, but care must be taken regarding temperature limits.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards for plastics, such as REACH in Europe, is essential. Buyers should also consider UV stabilization treatments to enhance the longevity of polycarbonate components in sunny regions.
What About Glass as a Material for Solar Heat Lamps?
Key Properties: Glass is an excellent insulator and has high thermal stability. It is often used in solar heat lamps for its ability to transmit sunlight effectively while providing a barrier to heat loss.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of glass is its durability and aesthetic appeal. However, it is heavier and more fragile than other materials, which can complicate shipping and installation.
Impact on Application: Glass is suitable for applications where light transmission is critical, such as in solar collectors. However, its brittleness can pose risks in high-impact environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers need to ensure that glass components meet local safety standards, especially in regions prone to extreme weather conditions. Tempered or laminated glass may be preferred to enhance safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Solar Heat Lamps
| Material | Typical Use Case for solar heat lamp | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components | Cost-effective and lightweight | Requires corrosion treatment | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-durability applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers | Lightweight and good insulation | UV degradation risk without treatment | Medium |
| Glass | Light-transmitting elements | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Heavier and more fragile | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials available for solar heat lamps, enabling informed decision-making based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar heat lamp
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solar Heat Lamps?
The manufacturing process of solar heat lamps is multifaceted and involves several critical stages, each requiring specific techniques and materials. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and reliability in their purchases.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Solar Heat Lamps?
The first stage involves the preparation of materials, which typically include solar panels, heat-conductive elements, casing materials (often aluminum or durable plastics), and insulation materials. The selection of these materials is crucial, as they influence both the efficiency and durability of the final product. For solar panels, high-quality silicon cells are preferred for their efficiency in converting sunlight to energy. Additionally, reflective coatings may be applied to enhance heat retention.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Structured?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo the forming process. This can involve cutting, molding, or extruding components to the required specifications. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are often utilized to ensure precision in the shaping of parts, particularly for the solar panels and heat elements. This stage is critical, as any inaccuracies can lead to inefficiencies in heat generation or energy conversion.
3. Assembly: How Are Solar Heat Lamps Assembled?
The assembly stage involves integrating all the components into a cohesive unit. This typically includes mounting solar panels onto the heat lamp’s casing, connecting wiring for electrical components, and installing safety features. Automated assembly lines are common, as they enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. However, manual assembly is also prevalent for complex or custom designs, ensuring that skilled workers can address any nuances in the assembly process.
4. Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Ensure Durability?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functional durability of solar heat lamps. Techniques may include powder coating, anodizing, or applying protective seals to safeguard against environmental factors. These treatments are especially important in regions with harsh climates, as they help prevent corrosion and damage from UV exposure. Quality finishing not only improves the product’s longevity but also its marketability.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Solar Heat Lamps?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process, ensuring that solar heat lamps meet both safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these measures can help in selecting reliable suppliers.

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
1. What International Standards Should Be Considered?
Manufacturers of solar heat lamps often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to maintaining high-quality processes and products. Additionally, products sold in Europe may need to meet CE marking requirements, which indicate conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
2. What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing stages, focusing on critical processes such as assembly and forming.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive evaluation of the finished product to confirm it meets all performance and safety standards before shipment.
Each checkpoint plays a vital role in preventing defects and ensuring consistent product quality.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for solar heat lamps often include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensuring that all electrical components function correctly and safely.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating the heat output efficiency and safety under various conditions.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting products to environmental conditions to assess their resilience and longevity.
These tests help manufacturers identify potential issues before products reach the market, thereby safeguarding both their reputation and the end user’s investment.

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control measures of their suppliers to mitigate risks associated with product defects. Here are some strategies to ensure supplier credibility:
1. What Steps Should Be Taken for Supplier Audits?
Conducting thorough audits of potential suppliers is essential. This can involve reviewing their manufacturing facilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Buyers should request documentation of past audits and certifications to assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
2. How Can Quality Reports and Third-Party Inspections Help?
Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insight into a supplier’s performance over time. Additionally, third-party inspections by accredited organizations can offer an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing practices. This step is crucial for international buyers, especially in regions where local regulations may vary significantly.
3. What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is vital to understand the specific regulatory requirements of their regions. This includes recognizing any additional certifications required for importing solar heat lamps, such as energy efficiency labels or safety standards mandated by local authorities. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into navigating these complexities.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for solar heat lamps are integral to ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, leading to successful partnerships and sustainable product offerings in the solar energy market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solar heat lamp’
When sourcing solar heat lamps, particularly for international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you procure quality products that meet your specific needs. This checklist will guide you through the key steps involved in the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for your solar heat lamps. This includes wattage, heating capacity, battery life, and intended use (e.g., agricultural applications, poultry heating, or outdoor heating). Defining these specifications early on will help streamline the procurement process and ensure that you communicate your needs effectively.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Understanding regional market trends and regulations is crucial for successful sourcing. Investigate local laws regarding solar energy products, safety standards, and import regulations that may affect your purchase. This knowledge will help you avoid compliance issues and ensure your products meet local safety and quality standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies from previous clients in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering quality solar heating solutions and those who offer customer support and after-sales services.
- Check for Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) that indicate adherence to industry standards. This ensures product safety and reliability.
- Assess Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your order volume and delivery timelines, especially if you require bulk purchases.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a large order, request samples of the solar heat lamps. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality, performance, and suitability of the product for your specific application. Pay attention to factors such as heat output, battery efficiency, and durability under various conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, enter negotiations to secure the best pricing and terms. Be clear about your budget constraints and discuss payment options, shipping costs, and lead times. Establishing favorable terms can lead to significant cost savings and a more beneficial long-term relationship.
Step 6: Understand Warranty and Support Options
Inquire about warranty terms and post-purchase support. A robust warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment against potential defects. Additionally, check if the supplier offers technical support and spare parts, as this can be vital for maintenance and longevity.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Logistics
After finalizing the terms, place your order and coordinate logistics for shipping. Ensure that all documentation is in order, including invoices, packing lists, and any import permits required. Maintain communication with the supplier throughout the shipping process to address any potential issues promptly.
By following these steps, you can ensure a successful procurement process for solar heat lamps that meets your operational needs while adhering to regional standards and regulations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar heat lamp Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of solar heat lamps, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of cost structures and pricing dynamics. Understanding these components is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with budgetary constraints and operational needs.
What Are the Key Cost Components of Solar Heat Lamp Production?
The cost structure of solar heat lamps comprises several components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality solar panels, durable housing, and efficient heating elements can drive up expenses. Buyers should evaluate the balance between cost and longevity to avoid frequent replacements.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the skill level required for assembly and quality assurance. In countries with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America or Southeast Asia, buyers might find more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, which may be passed on as savings to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or functionalities can add to initial costs. Buyers looking for unique features should factor these potential expenses into their budget.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with safety standards. However, rigorous testing protocols can increase costs. Buyers should assess the value of quality assurance in their purchasing decisions.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling fees are critical components, especially for international shipments. Costs can fluctuate based on shipping routes, volume, and packaging requirements.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover their risks and profit expectations. Understanding the typical margin in the solar heat lamp market can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Solar Heat Lamp Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of solar heat lamps:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider their needs and aim for bulk purchasing to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored products may incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements early in the negotiation process to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and compliance with international standards can affect pricing. Buyers in regions with stringent regulations must ensure that their suppliers meet these criteria.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and history of performance can influence costs. Researching potential suppliers thoroughly is essential for building a long-term partnership.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for calculating total landed costs. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly impact pricing depending on shipping arrangements.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Solar Heat Lamp Prices?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in discussions regarding pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can incentivize suppliers to offer better rates.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance, and lifespan when assessing value.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be cognizant of fluctuating currency rates, tariffs, and trade regulations that can influence pricing.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to a large order, request samples to evaluate quality and performance. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product meets expectations.
Conclusion
In summary, the sourcing of solar heat lamps requires a nuanced understanding of cost components and pricing dynamics. By considering factors such as material quality, volume discounts, and logistics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals. Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of the Total Cost of Ownership to ensure that investments yield long-term benefits.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solar heat lamp With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Heating
When considering heating solutions for various applications, especially in agricultural and outdoor settings, solar heat lamps are just one option among several viable alternatives. Each solution has its unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on factors such as performance, cost, and ease of implementation. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Solar Heat Lamp | Passive Solar Heating | Electric Heat Mats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate heat output | Variable; depends on design and location | High, consistent heat output |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing energy savings | Low long-term cost; higher initial design cost | Moderate to high; ongoing electricity costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install; requires sunlight | Requires thoughtful design and construction | Simple installation; requires electrical setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; check battery and connections | Minimal; periodic inspection of structure | Moderate; need to monitor electrical systems |
| Best Use Case | Small, localized heating (e.g., animal coops) | Greenhouses, passive heating in buildings | Heat-sensitive areas requiring constant warmth |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Passive Solar Heating
Passive solar heating utilizes the sun’s energy to heat spaces without mechanical assistance. This method involves designing buildings or structures to maximize sunlight exposure, using materials that absorb and retain heat.
Pros:
– Low ongoing costs due to minimal energy consumption.
– Environmentally friendly, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Cons:
– Performance varies based on geographic location and climate.
– Requires upfront investment in design and construction.
Electric Heat Mats
Electric heat mats are heated pads that can be placed under plants, animals, or other items requiring warmth. These mats provide consistent and controlled heating, making them ideal for specific applications.
Pros:
– High and consistent heat output.
– Simple installation process that can be easily integrated into existing setups.
Cons:
– Ongoing electricity costs can accumulate, especially in larger installations.
– Requires access to electrical outlets, limiting placement options.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Heating Solution
Selecting the ideal heating solution hinges on understanding the unique requirements of your application. For localized heating needs with a focus on sustainability, solar heat lamps can be effective. However, if your goals include optimizing energy efficiency and reducing long-term costs, passive solar heating may be more suitable. Conversely, for scenarios where consistent warmth is critical, such as in nurseries or animal husbandry, electric heat mats offer reliable performance. By carefully assessing these options, B2B buyers can choose a solution that not only meets their immediate needs but also aligns with their long-term operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar heat lamp
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Solar Heat Lamps for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical specifications of solar heat lamps is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in solar heat lamps—typically aluminum, polycarbonate, or tempered glass—affect durability, heat retention, and overall efficiency. Higher-grade materials ensure better performance, especially in harsh weather conditions. For buyers, selecting the right material can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans.
2. Heat Output (Wattage)
The wattage of a solar heat lamp indicates its heating capability. A higher wattage means more heat output, which is vital for applications requiring consistent warmth. When sourcing products, buyers should match wattage to their specific needs, whether for agricultural, residential, or industrial applications, to ensure optimal performance.
3. Battery Capacity (Ah)
Battery capacity, measured in amp-hours (Ah), determines how long the heat lamp can operate without sunlight. For B2B buyers, understanding battery specifications helps in assessing how well a solar heat lamp can perform during prolonged cloudy days or nighttime. A larger capacity may incur higher initial costs but can provide greater reliability.
4. Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency of the solar panel, usually expressed as a percentage, indicates how well the panel converts sunlight into usable energy. Higher efficiency panels allow for smaller installations while still meeting energy needs. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with limited sunlight, as it directly impacts the operational effectiveness of the heat lamp.

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
5. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating indicates the level of protection against dust and moisture. For solar heat lamps used outdoors, a high IP rating (e.g., IP65) is essential to ensure longevity and functionality under various environmental conditions. Buyers should prioritize products with suitable IP ratings to avoid premature failures.
6. Installation Requirements
Understanding the installation requirements, including mounting options and wiring needs, is crucial for B2B buyers. Some solar heat lamps may require professional installation, while others are designed for easy setup. Knowing these details helps in planning budgets and timelines effectively.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Solar Heat Lamp Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation for B2B buyers. Here are some essential terms:

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products based on specifications provided by another company. For buyers, partnering with OEMs can lead to customized solar heat lamps tailored to specific operational needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively, especially when entering new markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price proposals from suppliers. This process helps in comparing different suppliers and their offerings, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
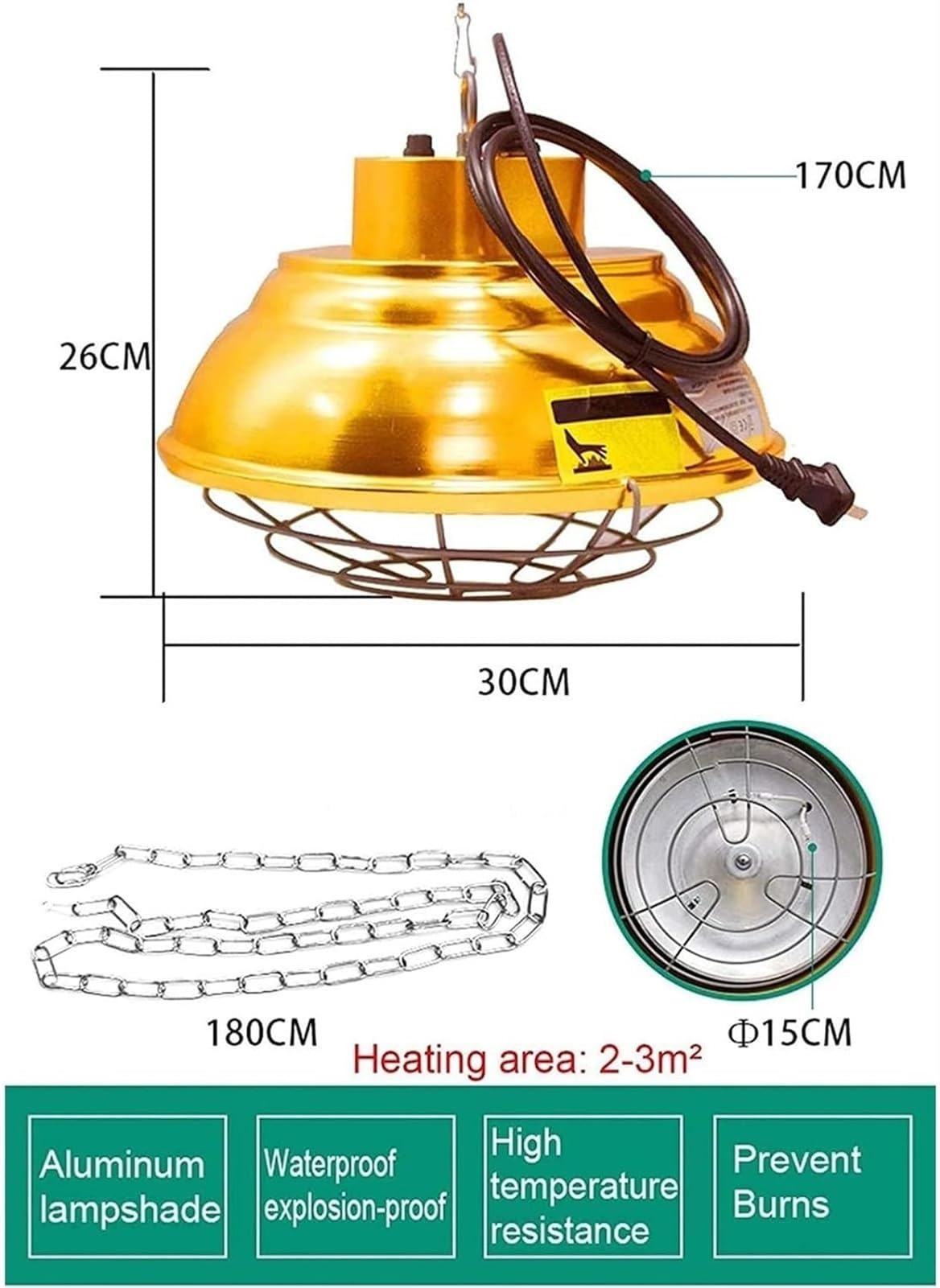
Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which are crucial for cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For solar heat lamps, understanding lead times can help buyers plan for seasonal demands or projects.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a product is guaranteed to function correctly. Knowing the warranty terms helps buyers assess the risk associated with their investment in solar heat lamps, ensuring they choose reliable products.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms enables B2B buyers to navigate the solar heat lamp market effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solar heat lamp Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Solar Heat Lamp Sector?
The solar heat lamp market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing energy costs and a global shift towards renewable energy sources. In regions such as Africa and South America, where access to reliable electricity can be sporadic, solar heat lamps offer a practical solution for heating applications, particularly in agriculture and rural settings. The Middle East and Europe are also witnessing a surge in demand due to government incentives promoting green energy solutions.
Emerging technologies such as advanced photovoltaic cells and energy-efficient designs are reshaping product offerings. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking solar heat lamps that not only provide effective heating but also integrate smart technologies, such as IoT capabilities for remote monitoring and control. Additionally, the trend towards modular and scalable solutions is appealing to businesses that require flexibility in their heating systems, allowing them to adapt to varying energy needs and environmental conditions.
Sourcing trends indicate a growing preference for local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. Buyers are also focusing on the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and energy consumption, rather than just the initial purchase price. As a result, manufacturers are encouraged to enhance product durability and reliability, ensuring that solar heat lamps can withstand diverse climatic conditions prevalent in targeted regions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Solar Heat Lamp Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of purchasing decisions in the solar heat lamp sector. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impacts of their sourcing choices and are seeking products that contribute to a lower carbon footprint. Ethical sourcing practices are crucial, as companies strive to ensure that their supply chains are free from human rights violations and environmentally harmful processes. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local communities can be significantly affected by supply chain practices.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into product offerings is becoming a vital differentiator in the market. Certifications such as Energy Star or Solar Keymark not only provide assurance of quality and efficiency but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Furthermore, utilizing sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly plastics in the manufacturing of solar heat lamps, aligns with the growing demand for responsible consumption.
B2B companies that prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing are likely to establish stronger brand loyalty and attract a customer base that values corporate responsibility. This can result in long-term partnerships and a competitive edge in an increasingly crowded market.

Illustrative image related to solar heat lamp
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of the Solar Heat Lamp Sector?
The concept of solar heating dates back several decades, but the modern solar heat lamp market has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Initially, solar heating systems were primarily used in residential settings, focusing on water heating. However, as technology advanced and the importance of renewable energy became more pronounced, solar heat lamps began to emerge as a versatile heating solution.
The introduction of photovoltaic technology allowed for the development of solar heat lamps that could effectively convert sunlight into usable energy. This innovation opened new applications in various sectors, from agriculture to urban development. Today, solar heat lamps are recognized not only for their efficiency but also for their role in promoting sustainability and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. As the market continues to grow, innovations in design and technology promise to further enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of solar heat lamps worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar heat lamp
-
How do I solve the challenge of sourcing reliable suppliers for solar heat lamps?
To effectively source reliable suppliers for solar heat lamps, start by conducting thorough market research to identify manufacturers with a solid reputation. Utilize platforms such as Alibaba or Global Sources to find verified suppliers. Request samples to evaluate product quality and assess responsiveness to inquiries. Additionally, consider attending trade shows or industry conferences in regions like Europe or the Middle East to meet suppliers in person. Always check references and reviews from other businesses to ensure credibility and reliability. -
What are the key features to look for in solar heat lamps for agricultural applications?
When sourcing solar heat lamps for agricultural use, focus on durability, efficiency, and energy output. Look for models that offer high wattage to ensure adequate heating for livestock or crops. Additionally, consider products with weather-resistant materials to withstand outdoor conditions. Features like adjustable settings and timers can enhance usability. Assess the solar panel’s efficiency and battery capacity to ensure it meets your operational needs, particularly in regions with variable sunlight exposure. -
What is the best solar heat lamp for poultry farming?
The ideal solar heat lamp for poultry farming should provide sufficient warmth without causing overheating. Look for lamps that emit a consistent heat output of around 100 watts, suitable for small to medium-sized coops. Models with automatic temperature control and energy-efficient solar panels are highly recommended. Additionally, consider lamps that are easy to install and maintain, with features like adjustable mounting options to cater to different coop designs. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing solar heat lamps?
Customization options are crucial when sourcing solar heat lamps, especially for specific applications or branding. Inquire about the possibility of customizing wattage, color, and design features to align with your operational needs. Additionally, ask suppliers if they can offer branding options, such as your company’s logo on the product. Flexibility in packaging and labeling can also enhance your product’s appeal in your target market. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect from solar heat lamp suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 50 to 500 units for solar heat lamps. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs and negotiate MOQs based on your market demand. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or samples, which is beneficial for testing the market before committing to larger orders. Always clarify the MOQ during initial discussions to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What payment terms are typically offered by solar heat lamp suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely, but most suppliers require a deposit upfront, often between 30-50%, with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer more flexible terms, including letters of credit or payment upon delivery for established relationships. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms that work for both parties, ensuring clarity to avoid disputes. Always verify the supplier’s payment security measures, especially for large transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for solar heat lamps?
To ensure quality assurance for solar heat lamps, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers, such as CE or ISO certifications. Conduct factory audits if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate production processes. Additionally, establish clear quality control protocols in your contract, including standards for testing and acceptance criteria. Regular communication and feedback loops with your supplier can also help maintain quality throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solar heat lamps?
When importing solar heat lamps, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations in your country. Evaluate whether air freight or sea freight is more cost-effective based on your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with local import duties and taxes to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the logistics process, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with all necessary regulations.
Top 3 Solar Heat Lamp Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Solar Haven – Heating Lamp Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Solar setup for heating lamps in chicken coops, specifically designed to power heating bulbs safely. User mentions a need for a simple solar solution to avoid running power to the coop during winter.
2. Backyard Chickens – Solar Powered Heat Lamp
Domain: backyardchickens.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Backyard Chickens – Solar Powered Heat Lamp, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Facebook – Solar Powered Heat Lamps
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Easy Meals | Any solar powered heat lamps
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar heat lamp
In the realm of solar heat lamps, strategic sourcing is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their investments and enhance operational efficiency. Understanding the diverse applications of solar heat lamps—from agricultural uses to residential heating—can significantly impact purchasing decisions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and innovation, ensuring that their products not only meet current energy demands but also align with environmental goals.
By leveraging local resources and fostering relationships with manufacturers in regions like Africa and South America, buyers can mitigate costs and enhance supply chain resilience. Furthermore, assessing technological advancements in solar heating solutions can provide a competitive edge in various markets, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight.
As the global focus shifts towards renewable energy, the demand for efficient solar heat lamps is set to grow. International buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships that emphasize quality, reliability, and technological advancements. Embrace this opportunity to lead in the renewable energy sector by investing in solar heat lamps that promise efficiency and sustainability, ensuring a brighter future for both business and the environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.