Sachet Filling Equipment: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Sachet Filling Equipment
In today’s fast-paced B2B landscape, the global sachet packaging market is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2025, driven by surging demand in food, pharmaceuticals, and beverages. For manufacturers in the USA and Europe, this growth presents a prime opportunity to optimize production efficiency and meet consumer preferences for convenient, single-serve packaging. Yet, selecting the right sachet filling equipment amid a sea of options can be daunting—balancing cost, precision, and scalability while navigating regulatory compliance and supply chain complexities.
The core challenge lies in identifying equipment that delivers consistent performance without compromising on ROI. Many businesses struggle with outdated systems that lead to inconsistent fill volumes, increased waste, and operator fatigue. High-quality sachet fillers, like those offering 0.05-1% accuracy tolerances, are essential for handling diverse volumes from mini pouches to bulk reservoirs. Factors such as adaptability for industries (e.g., wine, chemicals, or pharma) and add-ons like steam sterilization further complicate decisions, especially for startups minimizing capital investment through rentals.
This comprehensive guide equips you with actionable insights to make informed choices:
- Market Overview: Key trends, regional regulations, and growth drivers in USA and Europe.
- Equipment Types: From manual hand fillers to semi-automatic high-volume machines.
- Selection Criteria: Evaluating dependability, precision, and customization options.
- Case Studies and Best Practices: Real-world applications for optimal integration.
By the end, you’ll be prepared to invest in sachet filling solutions that enhance efficiency and drive business growth. (248 words)
Top 10 Sachet Filling Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pouch Filling Machine | Sachet Filler – ZONESUN Technology Limited
Domain: zonesuntech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5–10 day delivery 7-day returnsSachet filling machines (also called sachet packaging machine or pouch filling machine) are ideal for packaging powders, liquids, and granules….
2. 5 Best Premade Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers in the USA
Domain: chlbpack.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Top 5 Premade Pouch Filling Machine Manufacturers in the USA · Alliedflex Technologies Inc. · Viking Masek · Massman Automation · Matrix Packaging ……
3. 5 Best Small Sachet Packaging Machines | Save Costs & Scale
Domain: spackmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Find flexible small sachet packaging machines for SMEs. SpackMachine’s FDA-compliant models with quick-change tooling reduce costs and scale ……
4. Sachet Filling Machine Supplier in China – Jochamp
Domain: jochamp.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: We are your great source of different sachet filling machines, the perfect option for pharmacy products, food elements, granules, liquids, and more….
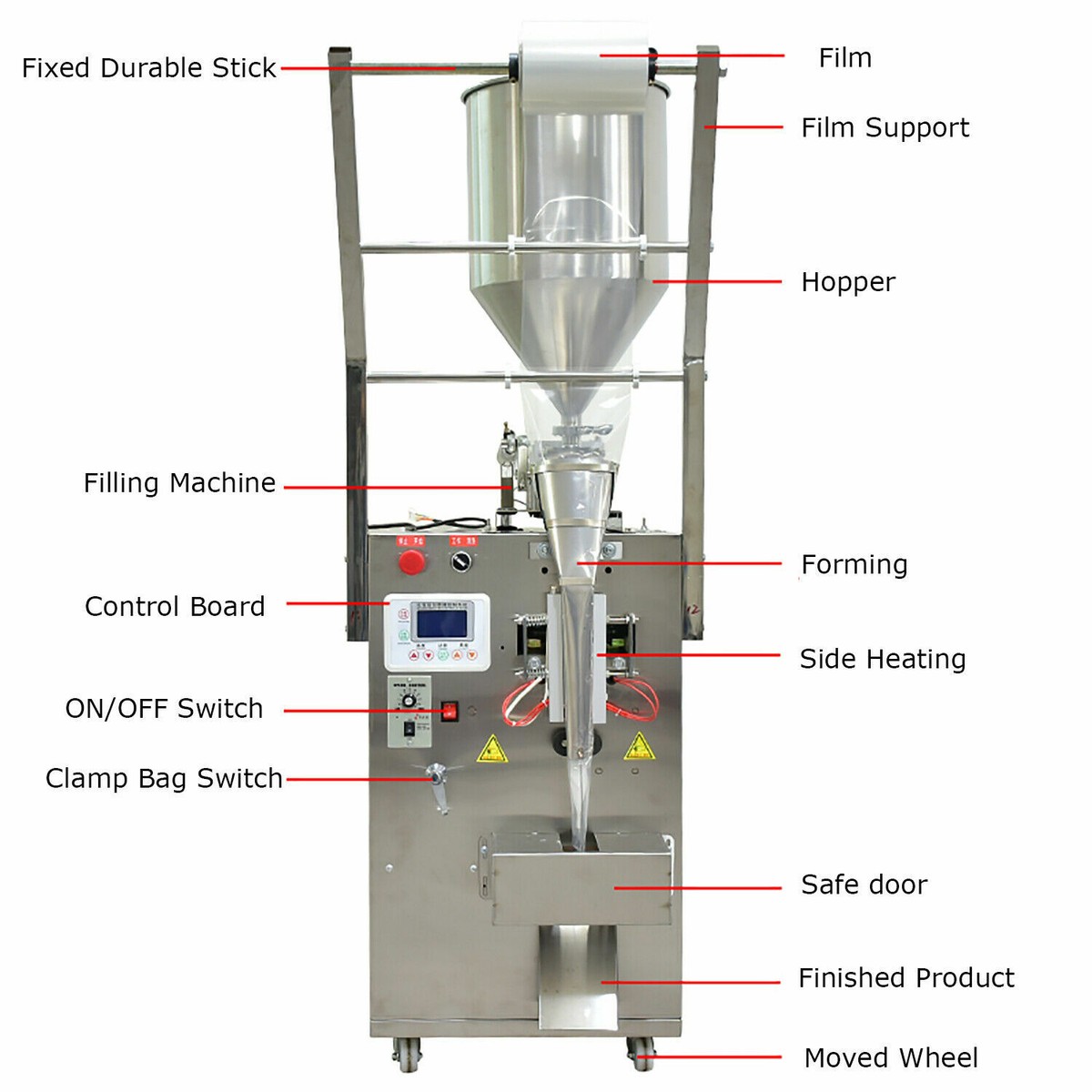
Understanding sachet filling equipment Types and Variations
Understanding Sachet Filling Equipment Types and Variations
Sachet filling equipment is essential for packaging small, single-serve portions of liquids, powders, or granules in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and beverages. Based on operational complexity, scale, and customization, we identify four key types: Manual Fillers, Semi-Automatic Fillers, Automatic Fillers, and High-Volume Production Fillers. These variations cater to businesses ranging from startups to large-scale operations, ensuring precise filling, sealing, and efficiency.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Fillers | Hand-operated; basic pumping or gravity-fed mechanisms; low-cost models like Astrofill® 90 or 100; suitable for small volumes (e.g., 187-500 ml); minimal automation. | Small-batch production in wine, beverages, or chemicals; ideal for startups or testing markets. | Pros: Affordable; easy to use; no capital investment needed via rentals. Cons: Labor-intensive; lower throughput; potential for inconsistency in fill volumes. |
| Semi-Automatic Fillers | Operator-assisted automation; features like diaphragm pumps and balance tanks; models such as Astrofill® Easy Start or HT1; consistent fill accuracy (0.05-1% tolerance); add-ons for steam sterilization. | Medium-scale operations in food, pharma, or cold brew coffee; filling pouches up to 3-5 L. | Pros: Reduces operator fatigue; high dependability; scalable with add-ons. Cons: Requires manual oversight; not suited for very high volumes; moderate initial cost. |
| Automatic Fillers | Fully automated filling and sealing; high-speed operation; models like Astrofill® 121 or 200; precise volume control for mini pouches to 9 L; integration with conversion heads. | High-throughput needs in beverages, foods, or spirits; bulk packaging for export markets. | Pros: Consistent accuracy; minimizes errors; efficient for large runs. Cons: Higher upfront cost; requires technical maintenance; less flexible for frequent product changes. |
| High-Volume Production Fillers | Advanced automation for dozens of pouches per minute; customizable with accessories like pumps or sterilization units; models such as Astrofill® Probox or HT2; supports bulk reservoirs up to 20 L or more. | Large-scale manufacturing in chemicals, beer, or wine industries; high-ROI operations. | Pros: Optimal for mass production; superior cap integrity; adaptable to changing needs. Cons: Significant investment; complex setup; overkill for small businesses. |
Manual Fillers
Manual fillers are entry-level options designed for businesses with limited production needs. These hand-operated machines, such as the Astrofill® 100, rely on simple mechanisms like manual pumps to fill sachets with precise volumes, often within a 0.05-1% tolerance. They are particularly useful for small volumes (e.g., 187-500 ml) and can be rented to minimize capital outlay. In B2B contexts, they suit USA and European startups in the beverage sector testing market viability without committing to automated systems. Key benefits include affordability and ease of integration into existing workflows, though they demand more labor and may not scale efficiently for growing operations.
Semi-Automatic Fillers
Semi-automatic fillers bridge manual and fully automated systems, offering operator-assisted efficiency for medium-scale production. Models like the Astrofill® Easy Start or HT1 incorporate features such as diaphragm pumps and balance tank systems to ensure consistent filling and sealing. These machines handle a range of sachet sizes up to 5 L and support add-ons like steam sterilization for sanitary applications in pharma or food industries. For B2B users in Europe and the USA, they provide a balance of cost-effectiveness and reliability, reducing fatigue while achieving high ROI through precise fills. However, they still require human intervention, making them less ideal for unattended high-volume runs.
Automatic Fillers
Automatic fillers deliver hands-free operation, automating the entire filling, sealing, and capping process for enhanced productivity. Equipment like the Astrofill® 121 or 200 excels in maintaining fill accuracy across various pouch sizes, from mini sachets to 9 L reservoirs. These systems are equipped for integration with additional units, such as conversion heads, to adapt to specific product requirements. In B2B environments, they are favored by established firms in the spirits or food sectors needing consistent output for distribution in USA and European markets. While they offer superior dependability and speed, the higher cost and maintenance needs should be weighed against production demands.
High-Volume Production Fillers
High-volume production fillers are engineered for industrial-scale operations, capable of processing dozens of sachets per minute with advanced automation. Models such as the Astrofill® Probox or HT2 include customizable options like pumps and sterilization features to handle bulk volumes up to 20 L or more. These machines ensure optimal cap integrity and efficiency, making them suitable for large B2B operations in chemicals or beer packaging across the USA and Europe. They maximize ROI by minimizing downtime and errors but require substantial investment and technical expertise, positioning them as a strategic choice for enterprises focused on scalability and long-term growth.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of sachet filling equipment
Key Industrial Applications of Sachet Filling Equipment
Sachet filling equipment provides precise, efficient packaging solutions for various industries, ensuring consistent fill volumes, minimal waste, and adaptability to production scales. Below is a summary of key applications and their benefits.
| Industry/Application | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|
| Food Industry (e.g., sauces, powders, condiments) | Enables high-accuracy filling within 0.05-1% tolerance for consistent portion control; reduces operator fatigue through semi-automatic options; supports volumes from mini sachets to bulk (e.g., 187 ml to 20 L), minimizing waste and ensuring hygiene compliance; adaptable add-ons like steam sterilization maintain product integrity and extend shelf life. |
| Beverage Industry (e.g., wine, spirits, beer, cold brew coffee) | Facilitates fast, efficient filling for volumes ranging from 187 ml to 300 gal, optimizing ROI with high-volume capabilities (dozens of sachets per minute); ensures superior cap integrity and dependability for leak-proof packaging; rental programs allow low-capital entry for startups, while conversion heads support evolving needs like bag-in-box formats. |
| Pharmaceutical Industry (e.g., powders, gels, single-dose medications) | Provides precise, contamination-free filling with tight tolerance levels to meet regulatory standards; semi-automatic systems reduce human error and fatigue, ensuring consistent dosing; options for sterilization and balance tank systems enhance safety and adaptability for small to high-volume production. |
| Chemical Industry (e.g., detergents, lubricants, specialty fluids) | Offers robust, dependable filling for corrosive or viscous materials across volumes from 25 oz to 55 gal; high accuracy minimizes overfill and waste, improving cost efficiency; add-ons like diaphragm pumps handle diverse viscosities, supporting scalable operations from manual to semi-automatic setups. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sachet filling equipment’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Sachet Filling Equipment & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Filling Accuracy
- Scenario: A mid-sized food manufacturer in Europe fills sachets with sauces, but variations in fill volumes lead to product waste and customer complaints.
- Problem: Manual or low-precision equipment causes overfilling or underfilling, resulting in material losses, regulatory non-compliance (e.g., FDA or EU standards), and reduced ROI within 0.05-1% tolerance levels.
- Solution: Invest in semi-automatic sachet fillers with built-in precision controls, such as those offering consistent volumes and superior cap integrity. These machines ensure accuracy, minimize waste, and support high-volume operations up to dozens of sachets per minute.
Pain Point 2: High Initial Costs for Scalability
- Scenario: A U.S. startup in the pharma sector needs to package small-batch supplements in sachets but faces budget constraints for equipment purchase.
- Problem: Upfront capital investment for filling machines limits scalability, especially for businesses transitioning from mini sachets (187-500 ml) to larger volumes (up to 9-20 L), delaying market entry and growth.
- Solution: Opt for rental programs that allow testing and use of pouch fillers with minimal or no capital outlay. Once ready, transition to owned semi-automatic models with add-ons like conversion heads for flexible scaling across volumes and product types.
Pain Point 3: Equipment Adaptability and Maintenance
- Scenario: A beverage producer in the USA switches between filling sachets for cold brew coffee and chemicals, requiring frequent equipment adjustments and cleaning.
- Problem: Rigid machines lack versatility for diverse pouch sizes, product viscosities, or sterilization needs, leading to downtime, operator fatigue, and inconsistent performance in food, pharma, or chemical applications.
- Solution: Select adaptable sachet filling systems with add-ons such as diaphragm pumps, balance tank supply systems, and steam sterilization options. These enhance dependability, reduce maintenance needs, and ensure efficient adaptation to changing production requirements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sachet filling equipment
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Sachet Filling Equipment
Selecting appropriate materials for sachet filling equipment and packaging is critical for ensuring product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. This guide analyzes key materials used in sachet films and equipment construction, focusing on compatibility with industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals. Material choices must align with USA (e.g., FDA) and European (e.g., EU Regulation 10/2011) standards, prioritizing factors like barrier properties, durability, sterility, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Materials for Sachet Packaging Films
Sachet films are typically multi-layer laminates designed for protection against moisture, oxygen, light, and contaminants. Common materials include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Low-cost, flexible option for non-barrier applications. Ideal for dry goods or low-moisture products like powders.
- Polypropylene (PP): Offers heat resistance and clarity. Suitable for hot-fill processes in food and beverages.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Provides strength and transparency. Often used in outer layers for pharma and chemical sachets requiring visibility.
- Aluminum Foil Laminates: High-barrier material for oxygen and light-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals or chemicals. Enhances shelf life but increases cost.
- Biodegradable Alternatives (e.g., PLA or Starch-Based Films): Emerging for eco-friendly packaging in Europe, compliant with sustainability directives, but limited barrier properties.
Selection depends on product type: For food and beverages, prioritize FDA-approved food-contact materials; for pharma, ensure USP Class VI compliance; for chemicals, focus on corrosion resistance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Materials for Sachet Filling Equipment
Equipment materials must withstand filling processes, cleaning, and sterilization while minimizing contamination risks. Based on available options like semi-automatic fillers (e.g., Astrofill® series), key materials include:
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304 or 316 Grade): Standard for contact surfaces in food, pharma, and beverage applications due to corrosion resistance and ease of sterilization (e.g., via steam systems).
- Food-Grade Plastics (e.g., HDPE or PTFE): Used in pumps and valves for non-corrosive environments. Compatible with diaphragm pumps for precise filling.
- Alloy Components: In high-volume machines, alloys like aluminum or titanium may be used for frames to reduce weight while maintaining durability.
- Sealing Elements (e.g., Silicone or EPDM): For gaskets and seals, ensuring leak-proof operation and tolerance to temperatures up to 200°C.
Add-ons like balance tank systems or conversion heads should use compatible materials to support adaptability, such as steam sterilization for pharma-grade hygiene.
Factors Influencing Material Selection
- Product Compatibility: Match materials to contents (e.g., acidic beverages require acid-resistant films; chemicals need inert equipment surfaces).
- Regulatory Compliance: USA requires FDA 21 CFR approval; Europe mandates REACH and migration testing.
- Operational Efficiency: Opt for materials enabling precise filling (0.05-1% tolerance) and high-volume output (dozens of sachets per minute).
- Cost and Sustainability: Balance initial investment with ROI; consider rentals for testing before committing to custom setups.
- Volume and Application: Small volumes (e.g., 187-500 ml) suit flexible films; larger or bulk (e.g., 9-20 L) may require reinforced materials.
Comparison Table of Materials by Application
| Material Type | Primary Use Cases | Advantages | Limitations | Regulatory Suitability (USA/Europe) | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Foods, Beverages (dry/low-moisture) | Low cost, flexible, recyclable | Poor barrier to oxygen/moisture | FDA-approved; EU-compliant | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Hot-fill foods, Pharma powders | Heat-resistant, durable | Less transparent than PET | FDA 21 CFR; EU 10/2011 | Medium |
| PET | Beverages, Chemicals | High strength, clarity | Not biodegradable | FDA/USP; REACH-compliant | Medium |
| Aluminum Foil Laminates | Pharma, Light-sensitive chemicals | Excellent barrier properties | Higher cost, non-recyclable in some regions | FDA-approved; EU migration-tested | High |
| Stainless Steel (Equipment) | Food/Pharma filling lines | Corrosion-resistant, sterilizable | Heavy, requires maintenance | FDA cGMP; EU hygienic design | High |
| Food-Grade Plastics (Equipment) | Beverage/chemical pumps | Lightweight, cost-effective | Limited heat tolerance | FDA 21 CFR; EU food-contact | Low-Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sachet filling equipment
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Sachet Filling Equipment
Sachet filling equipment, such as pouch fillers and semi-automatic systems, is engineered for precision, reliability, and scalability in B2B applications across food, pharmaceutical, beverage, and chemical sectors. This section outlines the key manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, drawing from industry standards to ensure equipment like AstraPouch’s Astrofill® series delivers consistent performance, with fill accuracy within 0.05-1% tolerance and adaptability for volumes from 187 ml to 300 gallons.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of sachet filling equipment involves sequential steps to create durable, efficient machines capable of high-volume operations while minimizing operator fatigue and ensuring cap integrity. These processes are optimized for semi-automatic and manual fillers, incorporating add-ons like diaphragm pumps, steam sterilization, and balance tank systems.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Preparation
- Material Selection and Sourcing: High-grade stainless steel, food-safe polymers, and corrosion-resistant alloys are selected to meet regulatory requirements for food, pharma, and chemical applications. Components are sourced from certified suppliers to ensure compatibility with diverse products, such as wines, cold brew coffee, or bulk reservoirs up to 9 liters.
- Design and Prototyping: CAD software models the equipment based on specifications for fill rates (e.g., dozens of pouches per minute) and ROI optimization. Prototypes incorporate features like precise volume control for mini pouches or bag-in-box systems.
- Pre-Processing: Raw materials undergo cutting, cleaning, and inspection to remove contaminants, preparing them for forming while adhering to hygiene standards.
Forming
- Shaping Components: Metal sheets are formed using CNC machining, laser cutting, or stamping to create frames, hoppers, and filling nozzles. For example, Astrofill® models like the HT1 or Probox feature robust housings designed for dependability in high-volume environments.
- Molding and Fabrication: Plastic and rubber parts, such as seals and gaskets, are injection-molded to ensure leak-proof operation. Heat treatment or welding is applied to enhance durability for steam sterilization add-ons.
- Integration of Electronics: Sensors for fill accuracy and control panels are embedded during this phase, enabling tolerances as low as 0.05% for consistent results.
Assembly
- Component Integration: Pre-formed parts are assembled into complete units, including pumps, conversion heads, and sealing mechanisms. Semi-automatic models like the Astrofill® 100 or 200 are built for easy scalability, with options for rental programs to test market fit.
- System Testing: Initial functional tests verify mechanical and electronic integration, ensuring features like reduced operator fatigue and adaptability for changing needs (e.g., from 750 ml to 5-gallon volumes).
- Customization: Add-ons such as balance tank supply systems or accessories for wine, beer, or chemical filling are incorporated based on client specifications.
Quality Control
- In-Process Inspections: Each stage includes dimensional checks, material integrity tests, and functionality verifications to maintain precision.
- Final Testing: Completed equipment undergoes simulated operation tests for fill consistency, speed, and tolerance levels. For instance, AstraPouch fillers are tested to exceed expectations in efficiency and cap integrity.
- Documentation: Batch records and traceability data are compiled for compliance, supporting warranty and service programs.
| Manufacturing Step | Key Activities | Benefits for B2B Users |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Material sourcing, design prototyping | Ensures regulatory compliance and customization for USA/Europe markets |
| Forming | CNC shaping, molding | Delivers durable components for long-term reliability |
| Assembly | Integration and initial testing | Supports scalable production with minimal capital investment |
| Quality Control | Inspections and final simulations | Achieves 0.05-1% accuracy, reducing waste and enhancing ROI |
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance for sachet filling equipment adheres to international benchmarks to guarantee safety, efficiency, and consistency. Manufacturers like AstraPouch prioritize ISO 9001 certification for quality management systems, ensuring processes are documented, audited, and continuously improved. Additional standards include:
- ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management): Applied to equipment handling food and beverages, focusing on hazard analysis and hygienic design.
- ISO 13485 (Medical Devices): Relevant for pharma-grade fillers, emphasizing risk management and traceability.
- CE Marking (for Europe): Confirms compliance with EU directives on machinery safety and electromagnetic compatibility.
- FDA Compliance (for USA): Ensures materials and designs meet 21 CFR standards for food contact and pharmaceutical applications.
These standards facilitate third-party audits, reducing downtime risks and supporting global supply chains. Businesses can leverage rental programs or used equipment options to validate quality before full investment. For inquiries on custom configurations, contact suppliers like AstraPouch at [email protected].
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sachet filling equipment’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Sachet Filling Equipment
This checklist provides a structured approach to sourcing sachet filling equipment for B2B operations in the USA and Europe, focusing on efficiency, compliance, and scalability for industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Identify product types (e.g., liquids, powders, or gels for food, pharma, beverages, or chemicals).
- Determine volume needs (e.g., mini sachets from 187-500 ml or larger up to 9-20 L equivalents).
- Assess production scale: Manual for low-volume startups or semi-automatic for high-volume (e.g., dozens per minute).
- Specify tolerances: Aim for 0.05-1% fill accuracy to ensure consistency and ROI.
- Consider applications: Wine/spirits, beer, cold brew, foods, or non-food items like chemicals.
Step 2: Research Suppliers and Options
- Search for reputable providers offering pouch/sachet fillers (e.g., AstraPouch or similar for high-quality, affordable models).
- Filter by type: Hand fillers (e.g., entry-level like Astrofill® 100), semi-automatic (e.g., Astrofill® HT series), or full systems.
- Explore shop categories: By volume (e.g., 187-500 ml to 55-300 gal), use (e.g., beverages or chemicals), or accessories (e.g., pumps, sterilization units).
- Check for used equipment: Inquire about availability via supplier contacts (e.g., email for details on refurbished units).
- Review compliance: Ensure equipment meets USA/EU standards for food/pharma safety and precision.
Step 3: Evaluate Features and Performance
- Prioritize dependability: Look for machines reducing operator fatigue, ensuring consistent volumes, and providing superior seal integrity.
- Assess add-ons: Options like diaphragm pumps, balance tanks, steam sterilization, or conversion heads for adaptability.
- Test efficiency: Seek models with fast, easy processes for optimal packaging and delivery.
- Consider trials: Opt for rental programs to test without capital investment, ideal for market entry.
Step 4: Analyze Costs and ROI
- Compare pricing: Entry-level (e.g., $34.99-$249.99) to advanced models; sort by low-to-high for budget alignment.
- Calculate total cost: Include accessories, maintenance, and potential upgrades.
- Evaluate ROI: Factor in precision filling to minimize waste and achieve consistent results.
- Budget for scalability: Choose adaptable equipment for evolving business needs.
Step 5: Finalize and Procure
- Request quotes and demos: Contact suppliers for customized recommendations.
- Verify support: Confirm availability of immediate shipping for components (e.g., tubes or kits).
- Place order: Select based on needs; start with starter kits if new to sachet filling.
- Plan integration: Ensure equipment fits existing workflows for seamless adoption.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sachet filling equipment Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Sachet Filling Equipment Sourcing
Sachet filling equipment, including pouch fillers and related systems, varies in price based on capacity, automation level, and customization. Entry-level manual fillers start at around $35–$250, while semi-automatic or high-volume models can range from $1,000 to $10,000 or more, depending on features like precise filling tolerances (e.g., 0.05–1% accuracy). Used or rental options can reduce upfront costs significantly. Below is a detailed breakdown of key cost components for sourcing in the USA and Europe, informed by market data from suppliers like AstraPouch.
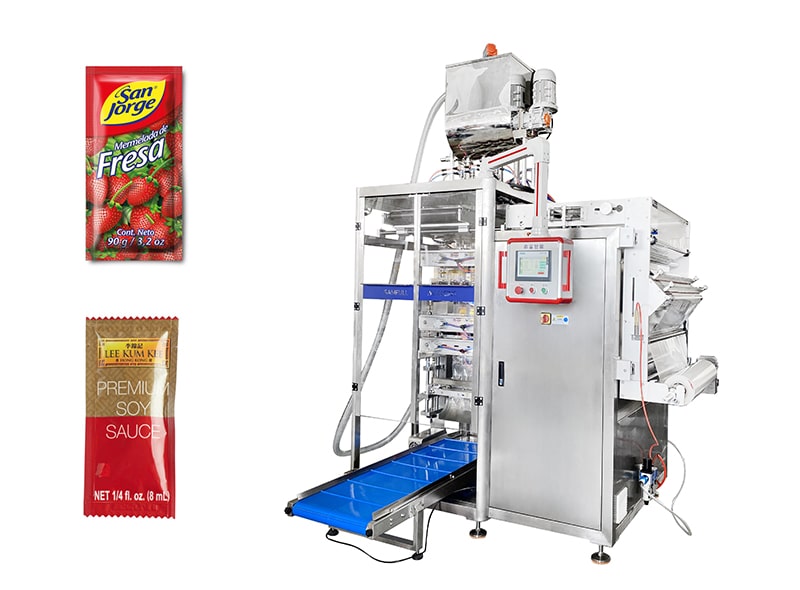

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cost Breakdown
Materials
Materials costs encompass the equipment purchase price, accessories, and consumables. These form the bulk of initial investment for sachet filling setups.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Machine | Manual or semi-automatic sachet/pouch fillers (e.g., Astrofill® 90 or 100 models for small-scale operations). High-volume units handle dozens of sachets per minute. | $35–$10,000+ (entry-level: $35–$250; advanced: $5,000–$10,000) |
| Add-Ons and Accessories | Diaphragm pumps, balance tanks, steam sterilization units, or conversion heads for adapting to different sachet sizes (e.g., mini pouches to 9L reservoirs). | $100–$2,000 per item |
| Consumables | Sachet materials, caps, and tubes (e.g., bag-in-box tubes for related applications). | $0.05–$0.50 per unit; bulk orders reduce to $0.02–$0.10 |
| Customization | Modifications for specific industries (e.g., food, pharma, chemicals) or volumes (187ml–20L). | 10–30% markup on base price |
Prices may vary by supplier and region; European sourcing often includes VAT (20–27%), adding 10–20% to totals.
Labor
Labor costs involve setup, operation, and maintenance, impacting long-term ROI through efficiency gains like reduced operator fatigue and consistent fill volumes.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation and Training | Professional setup and operator training for semi-automatic systems. | $500–$2,000 (one-time fee; lower for manual units) |
| Operational Labor | Ongoing staffing for filling processes; high-volume machines reduce needs by enabling dozens of sachets/minute. | $15–$30/hour per operator; annual total $20,000–$50,000 for small teams |
| Maintenance | Routine servicing to maintain 0.05–1% fill accuracy and cap integrity. | $200–$1,000 annually; includes parts and technician visits |
In the USA, labor rates average $25–$35/hour; in Europe, they range from €20–€40/hour, influenced by local regulations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Logistics
Logistics cover shipping, import, and distribution, which can add 10–25% to total costs, especially for international sourcing.
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD/EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Shipping and Freight | Domestic or international transport; immediate shipping available for in-stock items like bag-in-box tubes. | $100–$1,000 (domestic); $500–$3,000 (international, e.g., USA to Europe) |
| Import Duties and Taxes | Customs fees for equipment sourced outside the USA/EU; EU tariffs on non-EU goods average 5–10%. | 5–15% of equipment value; plus handling fees ($50–$200) |
| Storage and Distribution | Warehousing for bulk consumables or equipment prior to deployment. | $200–$500/month for small operations |
Factor in lead times: 1–4 weeks for in-stock items, longer for custom units.
Tips to Save Costs
- Opt for Used or Rental Equipment: Inquire about used sachet fillers (e.g., via suppliers like AstraPouch) for 30–50% savings, or use rental programs for minimal capital outlay during market testing.
- Bulk Purchasing and Negotiation: Buy consumables in bulk to lower per-unit costs; negotiate with suppliers for discounts on add-ons or bundled packages, especially for startups or high-volume needs.
- Choose Scalable Models: Start with entry-level manual fillers (e.g., $35–$250) and upgrade via modular add-ons to avoid over-investment.
- Local Sourcing: Source from USA or EU suppliers to minimize shipping and duties; check for regional incentives like tax credits for efficient packaging equipment.
- Efficiency Enhancements: Invest in semi-automatic systems to cut labor costs by reducing manual intervention and ensuring precise ROI through consistent fills.
- Supplier Programs: Leverage flexible options like starter kits or samples to test equipment without full commitment, adapting to needs in food, pharma, or beverage sectors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sachet filling equipment With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Sachet Filling Equipment With Other Solutions
This section compares sachet filling equipment—typically used for small, single-serve packets (e.g., 1-500 ml volumes for food, pharma, beverages, or chemicals)—with two common alternatives: bag-in-box filling equipment and bottling lines. Sachet systems, such as semi-automatic pouch fillers, offer precise filling (0.05-1% tolerance), scalability from manual to high-volume operations, and options like rentals for minimal capital investment. The comparison focuses on key business factors for USA and European markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sachet Filling Equipment | Bag-in-Box Filling Equipment | Bottling Lines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low to moderate (e.g., $35-$250 for entry-level models; rentals available) | Moderate (e.g., $200+ for semi-automatic units; add-ons like pumps increase costs) | High (e.g., $10,000+ for automated lines; requires significant infrastructure) |
| Production Speed | Variable (manual: 1-10 units/min; semi-automatic: dozens/min) | High for bulk (e.g., 4-20 L fills at 5-20 units/min) | Very high (e.g., 100+ bottles/min for automated setups) |
| Volume Flexibility | High (mini sachets to 500 ml; easy to adjust for small batches) | Moderate (focused on 4-300 gal; less ideal for single-serve) | Low (optimized for fixed bottle sizes; changes require retooling) |
| Precision and Consistency | Excellent (0.05-1% tolerance; reduces waste and operator fatigue) | Good (consistent for larger volumes; options like steam sterilization enhance reliability) | High (automated dosing; but prone to variations in glass/plastic tolerances) |
| Applications | Versatile (food, pharma, beverages, chemicals; single-serve convenience) | Bulk liquids (wine, beer, chemicals; extended shelf life) | Beverages, pharma (durable packaging for retail; not ideal for powders) |
| Scalability | High (from startups to high-volume; add-ons like pumps for growth) | Moderate (suits mid-to-large operations; bulk-focused) | High for large-scale (requires space and maintenance; less flexible for small runs) |
| Maintenance and Efficiency | Low maintenance; reduces fatigue with consistent fills and cap integrity | Moderate; adaptable with conversion units | High maintenance; efficient for mass production but energy-intensive |
Analysis
Sachet filling equipment provides a cost-effective entry point for businesses targeting single-serve or small-batch packaging, with superior flexibility for diverse products like powders, liquids, and gels. It outperforms bag-in-box systems in handling mini volumes and quick setup changes, making it ideal for startups or variable demand in USA and European markets. However, bag-in-box excels in bulk efficiency and shelf-life extension for liquids, offering better ROI for high-volume operations like wine or chemicals. Bottling lines, while superior for speed in mass production, involve higher upfront costs and less adaptability, often suiting established brands with stable product lines. For optimal ROI, select based on volume needs: sachets for precision and agility, bag-in-box for bulk, and bottling for high-throughput retail. Rental programs for sachets can minimize risks during market testing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sachet filling equipment
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Sachet Filling Equipment
This section outlines critical technical attributes of sachet filling equipment and defines key trade terms commonly used in B2B procurement. These elements are essential for evaluating equipment suitability in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals, ensuring precision, efficiency, and compliance with USA and European standards (e.g., FDA, EU GMP).
Key Technical Properties
Sachet filling equipment varies by model, from manual to semi-automatic systems, with features designed for accuracy, scalability, and adaptability. Core properties include:
- Filling Accuracy and Tolerance: Equipment typically achieves precision within 0.05-1% tolerance, ensuring consistent fill volumes and minimizing product waste. This is critical for high-value items like pharmaceuticals or chemicals.
- Production Speed and Capacity: Ranges from low-volume manual fillers (e.g., 10-20 sachets per minute) to high-volume semi-automatic models (dozens per minute). Select based on throughput needs, such as filling mini sachets (187-500 ml) to larger formats (up to 9L).
- Automation Level: Options include hand-operated fillers for startups and semi-automatic systems that reduce operator fatigue through automated capping and sealing for superior integrity.
- Volume and Format Compatibility: Supports diverse sachet sizes, from small pouches to bulk reservoirs (e.g., 25-96 oz or 1-5 gal). Compatibility with bag-in-box formats is common for versatile applications.
- Add-On Features and Customization: Includes diaphragm pumps for viscous liquids, balance tank supply systems for steady flow, steam sterilization for hygiene (essential in food and pharma), and conversion heads for adapting to changing needs.
- Dependability and Maintenance: Built for reliability with minimal downtime; features like rental programs allow testing without capital investment. Compliance with sanitary standards ensures suitability for sensitive products like beverages, foods, or chemicals.
| Property | Description | Typical Range/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Tolerance level for fill volume | 0.05-1% |
| Speed | Output rate | 10-50+ sachets/min |
| Volume | Supported sachet sizes | 187 ml to 9L |
| Automation | System type | Manual to semi-automatic |
| Add-Ons | Enhancements | Pumps, sterilization units |
Trade Terminology
Understanding these terms facilitates negotiations with suppliers, particularly for OEM/ODM arrangements or bulk orders in the USA and Europe.
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity a supplier will produce or sell, often 1-10 units for equipment to balance production costs.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): A company that manufactures equipment to buyer specifications, allowing branding under the buyer’s name (e.g., custom sachet fillers for pharma use).
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): Similar to OEM but includes design services; suppliers provide ready-to-brand models with modifications like add-on pumps.
- Lead Time: Time from order placement to delivery, typically 4-12 weeks for sachet equipment, depending on customization and volume.
- ROI (Return on Investment): Metric for evaluating equipment efficiency; high-accuracy fillers improve ROI by reducing waste and increasing output.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Shipping term where the seller covers costs to the destination port, common for European imports.
- FOB (Free on Board): Seller delivers goods to the port of shipment; buyer handles transport thereafter, often used in USA transactions.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice): Regulatory standard ensuring equipment meets hygiene and quality requirements for food/pharma sectors.
For procurement, prioritize suppliers offering rentals or used equipment to assess fit before full commitment. Contact manufacturers for quotes tailored to specific applications.
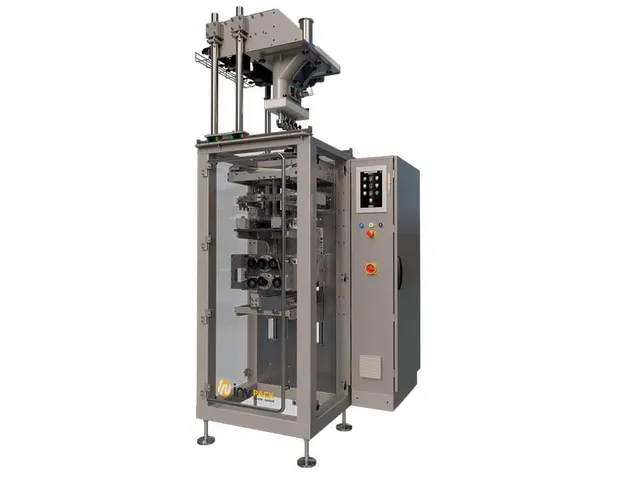

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sachet filling equipment Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Sachet Filling Equipment Sector
This section examines the evolution, current trends, and strategic considerations for sachet filling equipment in the B2B landscape, with a focus on USA and European markets. Informed by industry providers like AstraPouch, which offers a range of pouch fillers from manual to semi-automatic models, we highlight precision (0.05-1% tolerance), adaptability, and applications across food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals.
History of Sachet Filling Equipment
Sachet filling technology originated in the mid-20th century as an extension of flexible packaging innovations. Initially developed for portion-controlled food and pharmaceutical products in the 1950s, early machines focused on manual or basic mechanical filling for items like condiments and powders. By the 1970s, automation advanced with vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) systems, driven by demand from Europe (e.g., for single-serve coffee and pharma samples) and the USA (e.g., for snacks and OTC medications). The 1990s introduced digital controls and higher-speed semi-automatic fillers, enabling precise volumes from mini-sachets (187-500 ml) to larger formats (up to 20 L). Today, equipment like AstraPouch’s Astrofill® series builds on this legacy, offering dependable solutions with features such as consistent fill volumes and cap integrity to reduce operator fatigue.
Current Market Trends
The sachet filling equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5-7% through 2030, fueled by demand for convenient, portable packaging in food, pharma, and beverages. Key trends include:
- Automation and Scalability: Businesses are shifting from manual fillers (e.g., Astrofill® 100 at $249.99) to semi-automatic models capable of dozens of sachets per minute, supporting high-volume production for startups and established firms.
- Diverse Applications: Adoption spans wine & spirits, cold brew coffee, foods, and chemicals, with volume options from 187 ml to 55-300 gal. In the USA, regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA standards) drives pharma use, while Europe emphasizes EU food safety directives.
- Customization and Add-Ons: Providers offer modular upgrades like diaphragm pumps, steam sterilization, and balance tank systems to adapt to changing needs, enhancing ROI.
- Regional Dynamics: USA markets prioritize cost-efficiency and quick ROI, with rental programs minimizing capital investment. Europe focuses on high-precision equipment for premium products, amid rising e-commerce packaging demands.
| Trend | USA Focus | Europe Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Level | Semi-automatic for scalability | Fully automated for efficiency |
| Key Sectors | Food & Beverages (e.g., snacks) | Pharma & Premium Foods |
| Growth Driver | E-commerce and convenience | Regulatory compliance and exports |
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is a core driver in sachet filling, with equipment designed to minimize waste and support eco-friendly materials. Modern fillers like those from AstraPouch enable precise filling to reduce overfill (within 0.05-1% tolerance), cutting material usage by up to 10%. Trends include:
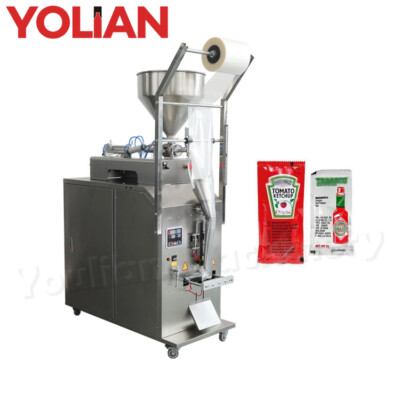

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Recyclable Materials: Integration with biodegradable or recyclable pouches, aligning with USA’s EPA guidelines and Europe’s Circular Economy Action Plan.
- Energy Efficiency: Low-energy semi-automatic models reduce operational carbon footprints, with add-ons like steam sterilization promoting reusable components.
- Waste Reduction: Features such as consistent cap integrity prevent leaks, extending shelf life and minimizing product waste in supply chains.
- Rental and Modular Models: Programs allow testing without full purchase, reducing manufacturing emissions from underutilized equipment.
Businesses sourcing equipment should prioritize suppliers offering sustainability certifications (e.g., ISO 14001) to meet stakeholder expectations and comply with regulations like the EU’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive.
Sourcing Strategies
Effective sourcing balances cost, adaptability, and reliability. Key approaches include:
- Rental Programs: Ideal for market entry with minimal capital; AstraPouch offers rentals for pouch and bag-in-box fillers, enabling quick scaling.
- Vendor Evaluation: Select based on precision, volume range (e.g., 1-5 gal for mid-sized operations), and add-ons for customization. Contact suppliers like [email protected] for used or tailored options.
- Supply Chain Integration: In the USA, focus on domestic suppliers for faster delivery; in Europe, leverage networks for compliance with REACH regulations.
- Cost Analysis: Entry-level models start at $34.99 (e.g., Astrofill® 90), scaling to high-volume units. Factor in ROI from reduced fatigue and consistent outputs.
By aligning sourcing with these trends, B2B buyers can optimize operations in dynamic markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sachet filling equipment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Sachet Filling Equipment
1. What types of sachet filling machines are available for B2B operations?
AstraPouch offers a range of sachet and pouch filling machines, including manual options like the Astrofill® 100 hand filler and semi-automatic models such as the Astrofill® HT1 and HT2. These are designed for precise filling of sachets and pouches, with options for high-volume production capable of processing dozens of units per minute.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. What volume ranges can these machines handle?
Our machines support filling from mini sachets (starting at 187 ml) up to larger pouches and reservoirs (up to 9-20 L or 55-300 gal). This flexibility accommodates various B2B needs, from small-batch sampling to bulk production.
3. Which industries are sachet filling machines suitable for?
These machines are ideal for food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, chemicals, wine & spirits, beer, cold brew coffee, and other sectors. They ensure compliant packaging for diverse products, with features like steam sterilization for sanitary applications.
4. What is the accuracy level of the filling process?
All Astrofill® models provide consistent fill volumes with an accuracy tolerance of 0.05-1%. This precision minimizes waste and ensures optimal ROI for B2B buyers focused on efficiency and quality control.
5. Are there rental or trial options for sachet filling equipment?
Yes, AstraPouch offers a rental program for pouch and sachet filling solutions, allowing businesses to test equipment with minimal or no capital investment. This is particularly useful for startups or companies entering new markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. What customization and add-on options are available?
Add-ons include diaphragm pumps, balance tank supply systems, steam sterilization units, and conversion heads for adapting machines to changing needs. These enhancements support scalability for high-volume or specialized B2B operations.
7. How much do sachet filling machines cost?
Pricing starts at $34.99 for entry-level models like the Astrofill® 90 and goes up to $249.99 for the Astrofill® 100. Higher-end semi-automatic options vary; contact sales at [email protected] for quotes on models like the Astrofill® Probox or used equipment.
8. How can I source used or additional accessories for sachet filling?
Used pouch and sachet filling machines are available; email [email protected] for details. Accessories, such as bag-in-box tubes, are in stock for immediate shipping, along with starter kits and samples to integrate into your production line.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sachet filling equipment
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Sachet Filling Equipment
In summary, strategic sourcing of sachet filling equipment delivers substantial value for B2B operations in the USA and Europe. Providers like AstraPouch offer a versatile range of solutions—from affordable hand fillers (e.g., Astrofill® 100 at $249.99) to high-volume semi-automatic systems—ensuring precise filling with 0.05-1% tolerance. Key benefits include:
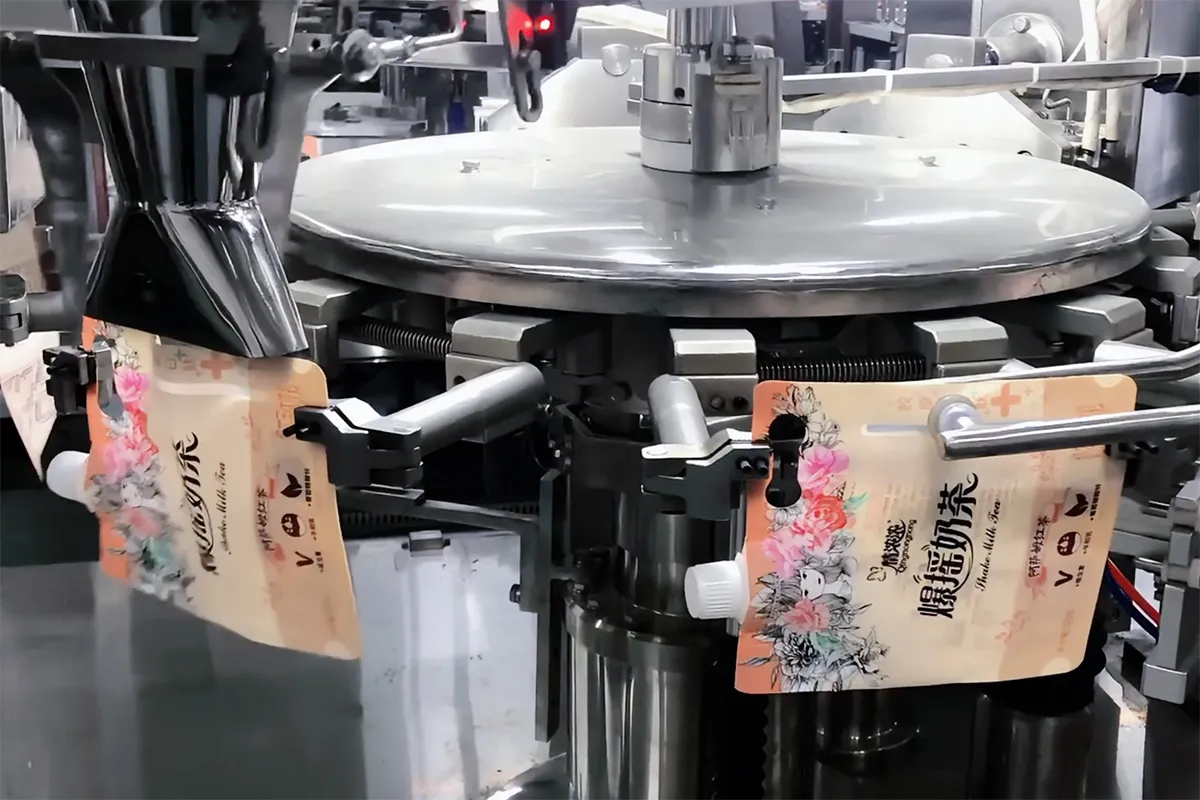

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Efficiency and ROI: Consistent fill volumes reduce waste and operator fatigue, supporting optimal returns across industries like food, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals.
- Adaptability: Rental programs minimize capital investment for startups, while add-ons (e.g., diaphragm pumps, steam sterilization) enable customization for evolving needs.
- Scalability: Equipment handles volumes from mini pouches to 9-liter reservoirs, with options for pouch and bag-in-box formats.
Looking ahead, the outlook for sachet filling equipment is promising, driven by automation advancements and sustainability demands. Expect increased integration of IoT for real-time monitoring and eco-friendly materials to align with EU regulations and US green initiatives. Businesses sourcing strategically can enhance competitiveness, with projected market growth of 5-7% annually through 2028, emphasizing precision and flexibility for long-term success.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.