Rubber Extruder Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber extruder
The quest for efficient rubber extrusion solutions can be daunting for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the diverse range of rubber types, applications, and specifications, sourcing reliable rubber extruders that meet specific manufacturing needs is a critical challenge. This guide addresses those complexities by providing a comprehensive overview of the rubber extruder market, detailing various rubber types such as EPDM, Neoprene, and silicone, along with their respective applications in industries ranging from automotive to medical.
Navigating the intricacies of supplier vetting, understanding cost structures, and ensuring compliance with international standards can significantly impact purchasing decisions. This guide empowers buyers by equipping them with actionable insights into selecting the right rubber extrusion equipment and materials. By breaking down the essential factors to consider, such as material properties, production capabilities, and quality control measures, this resource serves as a vital tool for making informed decisions that align with operational requirements and budget constraints.
Whether you are a manufacturer seeking to enhance production efficiency or an engineer tasked with sourcing high-quality elastomeric products, this guide provides the knowledge needed to navigate the global market effectively. Prepare to elevate your procurement strategy and ensure that your rubber extrusion needs are met with confidence.
Understanding rubber extruder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Screw Extruder | Simple design, high throughput, versatile for various rubber types | Automotive parts, seals, gaskets | Pros: Cost-effective, easy maintenance. Cons: Limited to specific rubber compounds. |
| Twin Screw Extruder | Enhanced mixing capabilities, better control over material properties | Medical devices, specialty seals | Pros: Superior homogeneity, adaptable to diverse formulations. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Ram Extruder | Uses a piston-driven mechanism, suitable for thick materials | Heavy-duty applications, rail products | Pros: Ideal for high-viscosity materials. Cons: Slower processing speed. |
| Cold Feed Extruder | Processes rubber at ambient temperatures, minimizing thermal degradation | Industrial components, custom profiles | Pros: Maintains material integrity, versatile for various compounds. Cons: Lower production rates compared to others. |
| Hot Feed Extruder | Preheats materials before extrusion, enhancing flow and shape accuracy | High-performance automotive parts | Pros: Improved material flow, reduced energy consumption. Cons: Risk of thermal degradation if not monitored closely. |
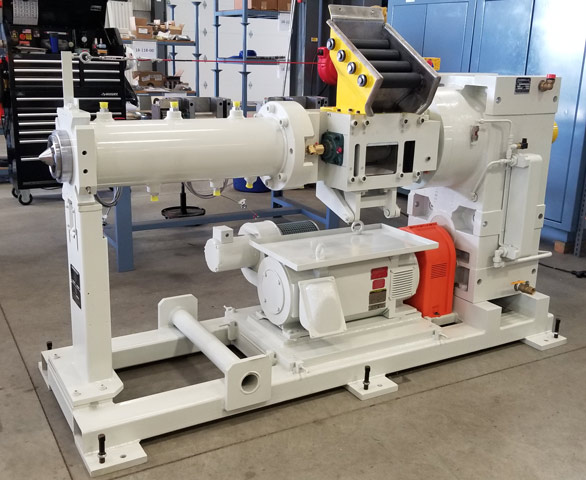
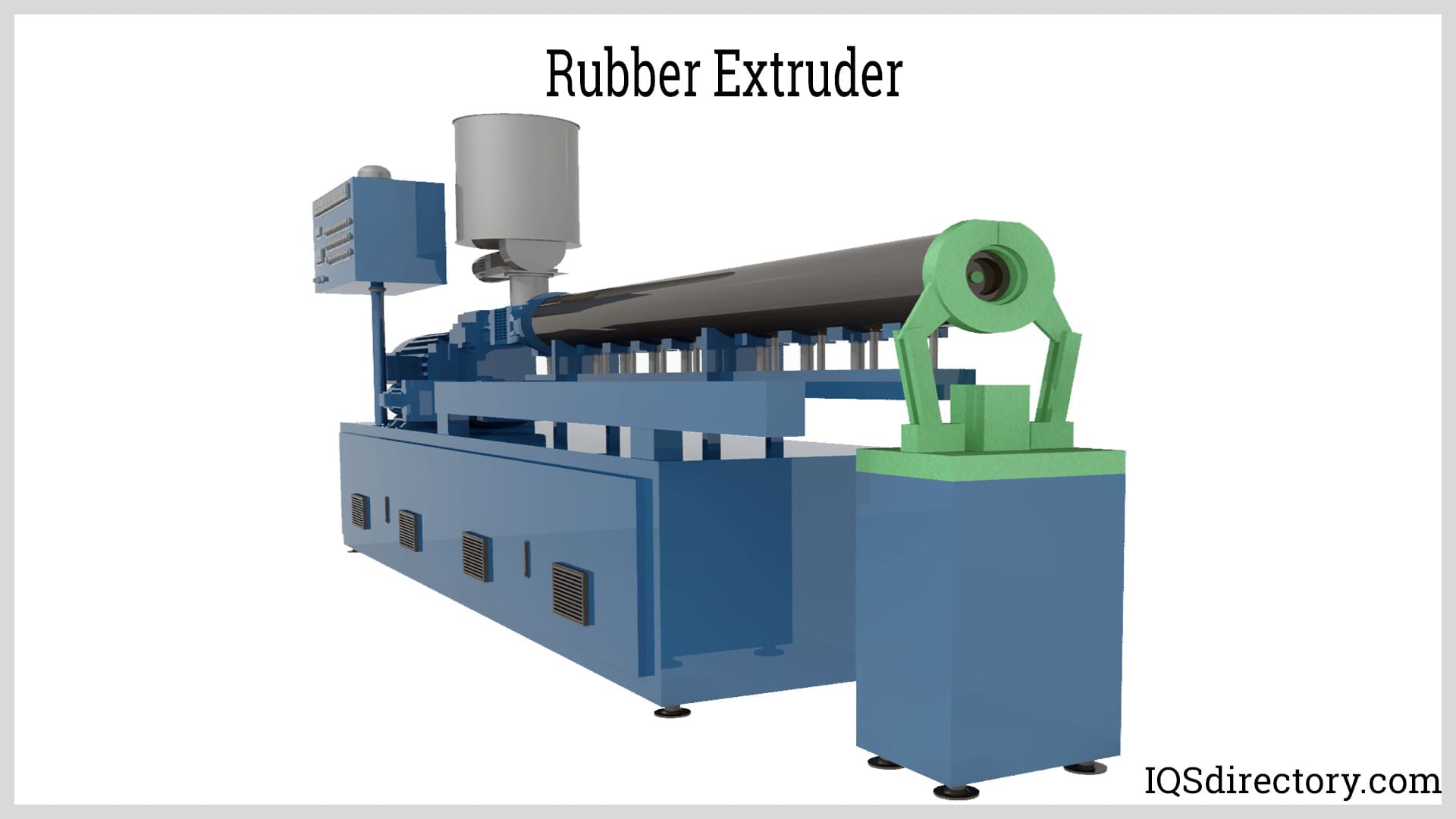
What Are the Characteristics of a Single Screw Extruder?
Single screw extruders are among the most commonly used in the rubber industry due to their straightforward design and operational efficiency. They typically feature a single screw that conveys the rubber through a heated barrel, allowing for consistent melting and shaping of the material. This type is particularly suitable for producing seals and gaskets in automotive applications. Buyers should consider the specific rubber compounds they intend to process, as single screw extruders may have limitations with certain high-viscosity materials.

Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
How Does a Twin Screw Extruder Enhance Rubber Processing?
Twin screw extruders consist of two intermeshing screws that provide superior mixing and kneading capabilities. This design is beneficial for applications requiring precise control over the material’s properties, such as in medical device manufacturing or specialty seals. The adaptability of twin screw extruders to various formulations makes them a valuable investment, despite their higher initial costs. B2B buyers should assess their production volume and product specifications to determine if the investment aligns with their operational needs.
What Makes Ram Extruders Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Ram extruders utilize a piston-driven mechanism, making them ideal for processing thick, high-viscosity rubber materials. This type is commonly employed in heavy-duty applications, such as rail products and industrial components, where durability is paramount. While ram extruders excel in handling tough materials, they may have slower processing speeds compared to other types. Buyers should weigh the benefits of material suitability against the potential for reduced throughput when considering this option.
Why Choose a Cold Feed Extruder for Custom Profiles?
Cold feed extruders operate at ambient temperatures, which helps maintain the integrity of heat-sensitive rubber compounds. This type is particularly useful for industrial components requiring custom profiles, as it allows for versatility in processing various materials without thermal degradation. While cold feed extruders can produce high-quality outputs, they may have lower production rates than their hot feed counterparts. Buyers should evaluate their specific production requirements and the types of rubber compounds they intend to use.
What Are the Advantages of Hot Feed Extruders?
Hot feed extruders preheat rubber materials before processing, which enhances flow and shape accuracy. This type is often preferred for high-performance automotive parts that demand precise tolerances and material properties. While hot feed extruders can improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption, they also carry the risk of thermal degradation if not properly monitored. B2B buyers should consider their production scale and the sensitivity of their rubber materials when deciding on this option.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber extruder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber extruder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and Gaskets | Enhanced vehicle performance and reliability | Material durability, compliance with automotive standards, custom design capabilities |
| Aerospace | Vibration Dampening Components | Improved safety and efficiency in flight | Weight considerations, temperature resistance, certification for aerospace standards |
| Construction | Weatherproofing Seals | Protection against environmental factors | UV resistance, flexibility in extreme temperatures, custom dimensions |
| Medical | Custom Rubber Tubing | Ensured safety and compliance in medical applications | Biocompatibility, sterilization capabilities, precision manufacturing |
| Railroad | Rail Boots and Crossing Pads | Increased safety and reduced maintenance costs | Compliance with rail industry standards, durability under heavy loads, custom fit solutions |
How is Rubber Extruder Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber extruders are primarily employed to produce seals and gaskets that prevent leaks and enhance vehicle performance. These extrusions must be crafted from durable materials that can withstand high temperatures and resist chemicals. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing suppliers who can provide custom designs that meet local automotive standards is crucial. Additionally, ensuring that the rubber compounds used are compliant with industry regulations helps maintain safety and reliability.
What Role Does Rubber Extrusion Play in Aerospace Applications?
Rubber extruders are vital in aerospace for manufacturing vibration dampening components, which are essential for reducing noise and enhancing passenger comfort during flights. The materials used need to be lightweight yet robust, capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures. International buyers in the aerospace sector must prioritize suppliers with certifications that align with aerospace standards, ensuring that the components will perform reliably under demanding conditions.
Why is Rubber Extrusion Important for the Construction Sector?
In construction, rubber extruders are used to create weatherproofing seals that protect structures from environmental damage. These seals must exhibit excellent UV resistance and flexibility to adapt to various weather conditions. For businesses in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing rubber extrusions that can be tailored to specific project dimensions is key. Buyers should also consider the longevity and performance of materials to minimize maintenance costs over time.
How is Rubber Extrusion Utilized in Medical Applications?
Rubber extruders manufacture custom rubber tubing for medical applications, where safety and compliance are paramount. These extrusions must be made from biocompatible materials that can be easily sterilized to prevent contamination. For buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it is essential to partner with suppliers who can provide certified products that meet stringent medical standards, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
What are the Applications of Rubber Extrusion in the Railroad Industry?
In the railroad industry, rubber extruders produce rail boots and crossing pads that enhance safety and reduce maintenance requirements. These products must be durable enough to withstand heavy loads and environmental exposure. Buyers, particularly from developing markets, should focus on suppliers who understand the specific compliance requirements of the rail industry and can deliver custom-fit solutions that improve operational efficiency and safety.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber extruder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Selection for Rubber Extrusion
The Problem: Selecting the right material for rubber extrusion can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with diverse applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical. Each application has specific requirements regarding temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and mechanical properties. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the multitude of rubber types available, such as EPDM, silicone, and neoprene, and may not fully understand the implications of their choices. This can lead to suboptimal product performance, increased production costs, or even project delays if the wrong material is selected.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, it is essential for buyers to engage closely with their extrusion suppliers during the material selection process. Conduct a thorough assessment of the application requirements, including environmental conditions and performance expectations. Suppliers often have extensive knowledge of material properties and can recommend suitable options based on their expertise. Additionally, consider conducting material testing or prototyping with small batches to evaluate performance before committing to larger production runs. This proactive approach not only ensures that the right material is chosen but also helps build a collaborative relationship with suppliers, leading to more tailored solutions in the future.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality and Tolerances in Extruded Products
The Problem: Quality control is a critical concern for B2B buyers who rely on rubber extruders to produce components with precise specifications. Variability in product quality can result from inconsistent manufacturing processes, leading to issues such as incorrect dimensions, surface imperfections, or material defects. Such inconsistencies can jeopardize the integrity of the final product and may cause costly rework or replacements, ultimately affecting timelines and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who have robust quality control measures in place. This includes verifying that the extruder manufacturer holds relevant certifications (such as ISO or ASTM) that demonstrate adherence to industry standards. Buyers should also request documentation on quality assurance processes, including testing protocols and tolerances for the specific products they intend to order. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and conducting regular audits or evaluations of the supplier’s operations can further enhance product reliability. By fostering a culture of quality and transparency, buyers can significantly reduce the risk of inconsistencies in their extruded rubber products.
Scenario 3: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Extrusion Processes
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges with production costs that escalate due to inefficient rubber extrusion processes. Factors such as equipment downtime, excessive material waste, and prolonged lead times can contribute to financial strain, particularly for businesses operating on thin margins. Buyers often struggle to balance the need for high-quality products with the demands of cost-effectiveness, which can lead to compromises in either area.
The Solution: To address these cost-related challenges, buyers should consider investing in suppliers who utilize advanced extrusion technology and processes that optimize efficiency. This can include automation, which minimizes human error and speeds up production times, or the use of specialized machinery designed to reduce material waste. Additionally, buyers can explore value-added services offered by suppliers, such as pre-assembly or additional machining, which can streamline the supply chain and reduce overall costs. Engaging in a detailed cost analysis with potential suppliers can also highlight areas for improvement, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that enhance both quality and cost-efficiency. By taking a strategic approach to supplier partnerships and production processes, buyers can achieve a more sustainable balance between cost and quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber extruder
What Are the Key Properties of Common Rubber Extrusion Materials?
When selecting materials for rubber extrusion, it is essential to consider their unique properties that directly impact product performance. The following materials are commonly used in rubber extrusion, each with distinct characteristics that cater to various applications.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
EPDM is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent weather resistance, high elasticity, and thermal stability. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -50°C to 150°C and is resistant to UV, ozone, and aging.
Pros: EPDM is highly durable and cost-effective, making it suitable for outdoor applications such as seals and gaskets. Its resistance to water and steam also enhances its longevity.
Cons: While EPDM has good mechanical properties, it is not suitable for use with petroleum-based oils and solvents, which can limit its applications.
Impact on Application: EPDM is ideal for applications requiring high weather resistance, such as roofing membranes and automotive seals. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. EPDM is widely accepted in Europe and North America, but specific grades may be required in other regions.
Neoprene
Neoprene, also known as polychloroprene, is a synthetic rubber characterized by its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability. It can operate effectively in temperatures from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros: Neoprene is resistant to oils, chemicals, and ozone, making it suitable for harsh environments. Its high tensile strength and flexibility allow for a wide range of applications.
Cons: The cost of Neoprene can be higher than that of other rubber materials, and its performance may degrade when exposed to certain solvents.
Impact on Application: Neoprene is commonly used in automotive applications, electrical insulation, and medical devices due to its superior chemical resistance and durability.

Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards such as ASTM D2000 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should verify local regulations regarding the use of Neoprene in specific applications.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is known for its exceptional heat resistance, flexibility, and biocompatibility. It can withstand temperatures from -60°C to 230°C, making it ideal for high-temperature applications.
Pros: Silicone is highly versatile, with excellent resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. It is also non-toxic, making it suitable for food and medical applications.
Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
Cons: Silicone can be more expensive than other rubber materials, and its mechanical strength is generally lower, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Silicone is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries for seals, gaskets, and molds due to its high-temperature stability and chemical resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for silicone grades that meet FDA and other international standards, especially in the food and medical sectors. Compliance with specific certifications is essential in Europe and North America.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
SBR is a synthetic rubber that combines the properties of styrene and butadiene. It is known for its excellent abrasion resistance and is commonly used in tire manufacturing.
Pros: SBR is cost-effective and provides good performance in a wide range of applications, particularly in automotive and industrial uses.
Cons: SBR has limited resistance to oil and solvents, which may restrict its use in specific applications.
Impact on Application: SBR is primarily used in tires, conveyor belts, and various automotive parts due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
Considerations for International Buyers: SBR is widely accepted across various markets, but buyers should ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM and JIS for specific applications.
Summary Table of Rubber Extrusion Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber extruder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) | Automotive seals, roofing membranes | Excellent weather resistance | Not suitable for petroleum-based oils | Medium |
| Neoprene | Electrical insulation, automotive applications | High chemical resistance | Higher cost, solvent sensitivity | High |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices, high-temperature seals | Exceptional heat resistance | More expensive, lower mechanical strength | High |
| Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Tires, conveyor belts | Cost-effective, good abrasion resistance | Limited oil resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when sourcing rubber extrusion materials tailored to specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber extruder
What Are the Key Stages of the Rubber Extrusion Manufacturing Process?
Rubber extrusion is a complex process that transforms raw rubber materials into various usable products. Understanding the manufacturing stages is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers. The primary stages involved in rubber extrusion include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
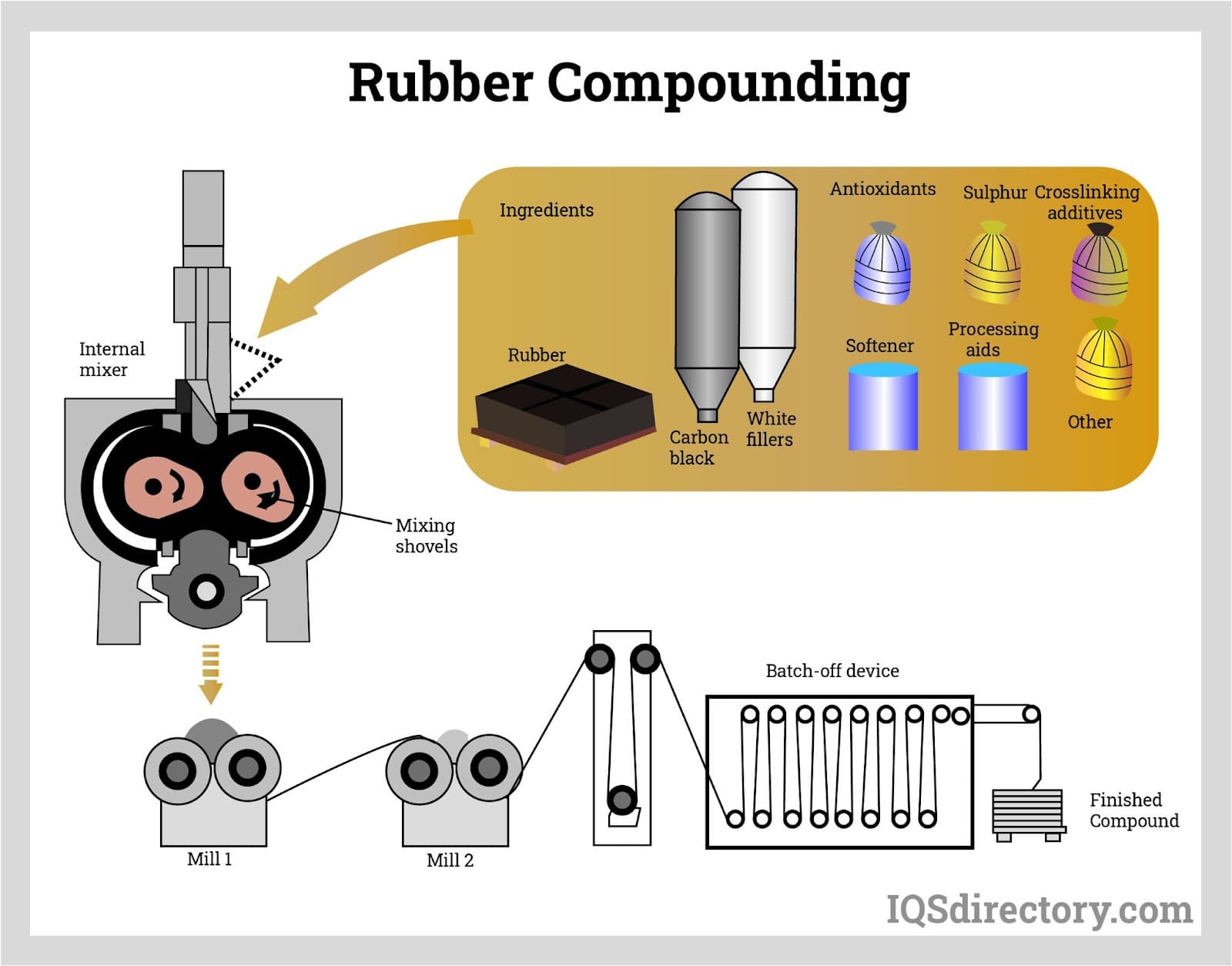
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Extrusion?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate rubber type—be it natural or synthetic—and mixing it with additives. Common additives include sulfur for vulcanization, carbon black for reinforcement, and accelerators to speed up the curing process. The rubber compound is then processed into sheets or pellets through milling, which ensures a uniform distribution of materials and prepares it for extrusion.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Rubber Extrusion?
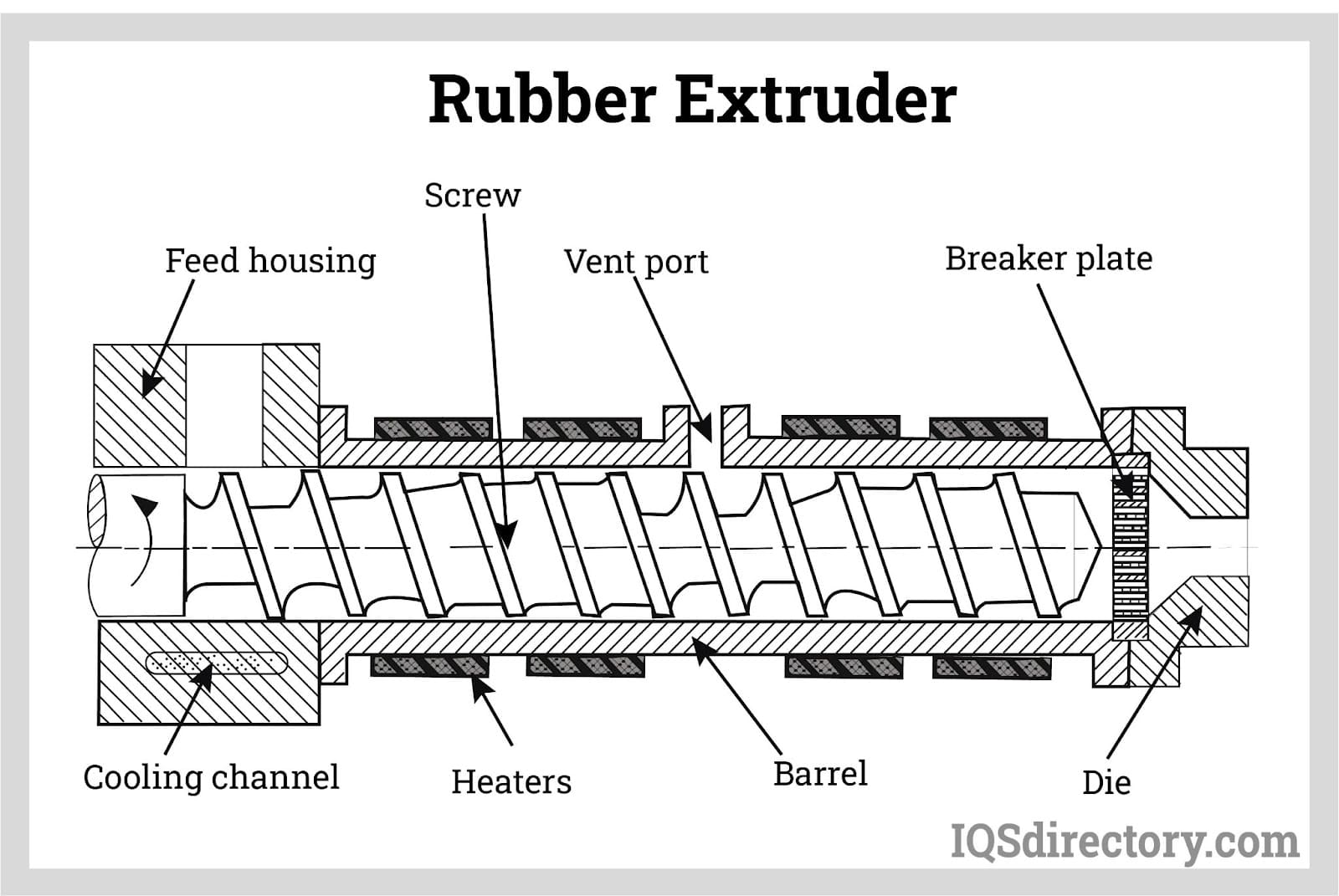
The forming stage is where the prepared rubber is transformed into its desired shape. The rubber compound is fed into an extruder, which utilizes a screw mechanism to push the material through a die, creating a continuous profile. The design of the die is critical, as it dictates the final shape and dimensions of the extruded product. Techniques such as hot and cold extrusion may be employed, depending on the application and material characteristics. Post-extrusion, the product usually undergoes a curing or vulcanization process to enhance its mechanical properties and durability.
What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly and Finishing Processes?
After forming, the extruded rubber may require assembly and finishing processes. This can involve cutting the extruded material to length, adding components (such as metal reinforcements), or applying secondary operations like adhesive backing or surface treatments. Finishing touches may also include surface texturing or coloring to meet specific customer requirements. These steps are essential to ensure that the final product meets the design specifications and functional needs of various applications, such as sealing or vibration dampening.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Rubber Extrusion?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of rubber extrusion, ensuring that the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations. A robust QC process typically follows international standards, such as ISO 9001, and may include industry-specific certifications like CE or API.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Rubber Extrusion?
Quality control in rubber extrusion is generally segmented into three main checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should verify the quality and specifications of rubber and additives to ensure they meet predefined standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the extrusion process, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and material flow rate are continuously monitored. Regular checks are performed to ensure that the extruded profiles conform to dimensional tolerances and material properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the extrusion and finishing processes, final inspections are conducted. This includes visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional testing of the finished products to ensure they meet customer specifications and industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This firsthand observation helps ensure that the supplier adheres to international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including inspection reports and compliance certificates. This transparency builds trust and provides assurance of quality.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These agencies can conduct random inspections and testing, offering additional assurance of product quality.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
-
Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and ensure their suppliers comply with these regulations.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is crucial in ensuring that quality expectations are understood and met. Buyers should establish clear communication channels to overcome potential barriers.
-
Logistical Challenges: Shipping and transportation may introduce variables that affect product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who understand these challenges and implement measures to mitigate risks during transit.
How Do International Certifications Impact Quality Assurance in Rubber Extrusion?
International certifications play a vital role in ensuring quality assurance in rubber extrusion. Certifications like ISO 9001 not only demonstrate a commitment to quality but also indicate that the supplier has established a systematic approach to managing processes and improving performance. For B2B buyers, partnering with certified suppliers can reduce risks associated with product quality and compliance, leading to enhanced trust and reliability in the supply chain.
Conclusion: Why Quality Assurance Matters in Rubber Extrusion
In the competitive landscape of rubber extrusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, implementing thorough quality control practices, and verifying supplier standards, businesses can ensure they receive high-quality rubber products tailored to their specific needs. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers in the global market.
Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber extruder’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of rubber extruders can be complex, particularly for B2B buyers in diverse global markets. This guide serves as a practical checklist to help you identify and source the right rubber extruder that meets your technical and business needs. By following these steps, you can ensure that your investment aligns with industry standards and operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your technical requirements before reaching out to suppliers. This includes identifying the types of rubber you will be extruding (such as EPDM, silicone, or SBR) and the specific dimensions and tolerances needed for your products. Knowing these details upfront will help suppliers provide accurate solutions and prevent costly adjustments later.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers specializing in rubber extrusion equipment. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and positive customer reviews. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to gather a list of reputable suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the capabilities of each supplier to ensure they can meet your specific production needs. Inquire about their technology, manufacturing processes, and material handling. Pay attention to their ability to produce custom profiles and whether they have the necessary certifications (like ASTM or ISO) to comply with industry standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a final decision, request samples or prototypes of the extruded products. This step is crucial to verify the quality, elasticity, and durability of the rubber compounds they can produce. Evaluate these samples against your specifications to ensure they meet your performance requirements.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications that demonstrate their adherence to quality standards. Look for certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific material compliance certifications. This verification will give you confidence in their manufacturing processes and product reliability.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Costs
Engage in discussions about lead times, production capacity, and pricing structures. Understanding these factors will help you align your production schedule with supplier capabilities and budget constraints. Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that can lead to more favorable pricing or improved delivery timelines.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Once you have selected a supplier, establish clear communication channels for ongoing support and feedback. This includes setting up regular check-ins and discussing any potential issues that may arise during production. Effective communication is vital for maintaining a strong supplier relationship and ensuring product quality over time.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process for rubber extruders and make informed decisions that contribute to your business’s success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber extruder Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Extruder Sourcing?
When sourcing rubber extruders, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of rubber, whether natural or synthetic (like EPDM, Neoprene, or SBR), significantly influences costs. Prices can vary based on quality and availability, which is especially pertinent for international buyers who may face fluctuating shipping costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing rubber extrusions. The labor costs can vary widely depending on the location of the manufacturing facility, with regions like Southeast Asia generally offering lower labor costs compared to Europe or North America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs, making it important to assess a supplier’s operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific rubber profiles can be a significant upfront cost. It’s essential to consider the tooling lifespan and the amortization of these costs over production runs when evaluating total expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the extruded products meet industry standards, which is vital for applications in sectors like automotive and aerospace. This can add to the overall cost but is often necessary to avoid costly defects.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the chosen shipping methods. Incoterms play a critical role here, influencing who bears the shipping costs and risks, which can affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to the base costs. Understanding the market rates can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Rubber Extruder Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of rubber extruders, and understanding these can lead to more strategic purchasing decisions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can impact pricing, so negotiating these terms is critical for cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs can increase costs due to additional tooling and labor. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Selection: The specific type of rubber and any additives required for the extrusion process can significantly impact costs. Higher-grade materials typically command higher prices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with industry standards (such as ASTM or ISO) can elevate costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of certifications based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Rubber Extruder Sourcing?
International B2B buyers can leverage several strategies to optimize their sourcing processes:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing structures, volume discounts, and payment terms. Building a relationship can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime. Assessing TCO can provide a clearer picture of long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and local tariffs that can affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies or negotiating fixed prices can mitigate this risk.
-
Supplier Diversity: Explore multiple suppliers to compare costs and quality. This not only provides leverage in negotiations but also ensures a better fit for specific needs.
-
Local Regulations: Understand local import regulations and compliance requirements, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where these can vary significantly.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for rubber extruders can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and economic factors. The information provided here serves as a general guideline; actual prices may vary. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber extruder With Other Solutions
When considering the best methods for rubber processing, it is crucial to explore various alternatives to rubber extruders. Each solution offers unique benefits and drawbacks that can significantly impact production efficiency, cost, and product quality. Below, we compare rubber extruders with other viable methods, including compression molding and injection molding, to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Extruder | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; ideal for continuous production of uniform profiles | Good for complex shapes; slower cycle times | Excellent precision; fast production for small parts |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs for high volumes | Lower equipment cost; higher labor costs | Higher initial setup cost; cost-effective for large runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized knowledge and equipment; training needed | Easier setup; less specialized knowledge required | Complex machinery setup; requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | High maintenance due to wear on parts; requires regular checks | Generally lower maintenance; simpler machinery | Moderate maintenance; requires specific parts replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for producing long, continuous profiles like seals and gaskets | Best for larger parts and lower volume production | Optimal for high-volume production of small, intricate components |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a widely used alternative to rubber extrusion, particularly for producing larger, more complex parts. The process involves placing a rubber compound into a heated mold, where it is compressed and cured. One of the primary advantages of compression molding is its lower initial equipment cost compared to rubber extruders. It is particularly effective for small production runs and offers flexibility in part design. However, the cycle times are slower, making it less efficient for high-volume production. Additionally, while the machinery is simpler, it may require more labor input, which can increase overall costs in a high-volume setting.
How Does Injection Molding Compare to Rubber Extruders?
Injection molding offers a different approach to rubber processing, utilizing a process where molten rubber is injected into a mold. This method is renowned for its precision and ability to produce intricate shapes at high speeds. One significant advantage of injection molding is its efficiency in producing large quantities of small parts, making it cost-effective for manufacturers focusing on high volumes. However, the initial setup cost is typically higher than that of rubber extrusion, and the machinery can be complex, requiring skilled operators for effective implementation. While maintenance is moderate, specific parts may need frequent replacement, impacting operational costs.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right rubber processing solution hinges on various factors, including production volume, part complexity, and cost considerations. For companies focusing on high-volume production of uniform profiles, rubber extruders may offer the best efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Conversely, if the primary need is for larger, more complex parts or low-volume production, compression molding could be the ideal choice. Injection molding stands out for those needing high precision and speed for smaller components but requires careful consideration of the initial investment and operational complexity. Understanding these nuances will empower B2B buyers to make the most informed decision tailored to their specific operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber extruder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Extruders?
Understanding the technical properties of rubber extruders is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right equipment and materials for their specific applications. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of rubber compounds based on their performance characteristics, such as elasticity, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance. Common grades include Ethylene Propylene (EPDM), Neoprene, and Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). Selecting the appropriate grade is vital as it directly affects the durability and functionality of the final product, particularly in industries such as automotive and construction.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the extruded product. Tight tolerances are critical for applications requiring precise fits, such as seals and gaskets. Inadequate tolerance can lead to product failure or increased costs due to rework. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers that can guarantee the required tolerances to ensure product reliability.
3. Durometer Hardness
Durometer hardness measures a material’s resistance to indentation, often expressed on a Shore scale (e.g., Shore A for softer materials). This property is essential for determining the flexibility or rigidity of the rubber. For example, softer materials are preferred for seals, while harder materials are suitable for structural components. Understanding durometer specifications helps buyers select the right material for their application needs.
4. Shrinkage Rate
The shrinkage rate refers to the amount a rubber product may contract during the cooling process after extrusion. This property can vary significantly based on the rubber compound used and the extrusion process. Buyers must consider shrinkage rates to ensure the final product meets design specifications and tolerances, particularly in high-precision applications.

Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
5. Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance defines a material’s ability to withstand exposure to various substances without degrading. Different rubber types exhibit varying levels of resistance to oils, solvents, and other chemicals. B2B buyers in industries like oil and gas or food processing must evaluate chemical resistance to avoid premature failure of components.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Rubber Extrusion?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and enhance decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the rubber extrusion industry, OEMs provide custom extrusions designed to meet specific customer specifications. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for tailored solutions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For rubber extrusions, MOQs can significantly affect procurement strategies and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about MOQs to ensure they can meet their project needs without excessive surplus.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the rubber extrusion sector, submitting an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and understand lead times. Clear RFQs can facilitate better supplier responses and more favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects like shipping costs, risks, and delivery points. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases of rubber extrusions, as they impact overall costs and logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. In rubber extrusion, lead times can vary based on material availability and production schedules. Recognizing lead times is vital for effective project planning, especially in industries where timing is critical.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing rubber extruders, ensuring they meet their operational and product requirements effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber extruder Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Rubber Extruder Market?
The rubber extruder market is witnessing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality, customized rubber products. The demand for specialized rubber compounds, such as Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) and Neoprene, is on the rise due to their superior performance in various applications including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Emerging technologies, such as Industry 4.0 and IoT, are revolutionizing rubber extrusion processes. Automated systems and smart machinery enable manufacturers to improve production efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality. Additionally, the adoption of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is streamlining supply chains, allowing buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and materials. The growing emphasis on customization is pushing manufacturers to invest in flexible production capabilities, enabling them to meet unique customer specifications quickly.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and economic conditions. Buyers from developing regions are increasingly looking for cost-effective solutions while ensuring compliance with international quality standards. As a result, suppliers that can demonstrate agility in production and a commitment to quality assurance will be well-positioned to capture market share.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Rubber Extruder Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the rubber extruder sector. The environmental impact of rubber production, particularly in terms of deforestation and pollution, has prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. This includes sourcing raw materials from certified suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices, such as using recycled rubber or bio-based materials.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important as buyers seek to align their purchasing decisions with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC for sustainable forestry are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers. Additionally, the push for ‘green’ materials is leading to innovations in rubber formulations that minimize environmental impact while maintaining performance standards.
As buyers prioritize sustainability, they are also looking for suppliers who can provide transparency in their operations. This includes clear documentation of material sourcing, production methods, and waste management practices. By partnering with suppliers that prioritize sustainability, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
How Has the Rubber Extruder Sector Evolved Over Time?
The rubber extruder sector has undergone significant evolution over the past century, transitioning from basic manual processes to highly automated and technologically advanced operations. In the early days, rubber extrusion was primarily a labor-intensive process, relying on simple machinery and basic techniques. However, as industries expanded and the demand for diverse rubber products grew, manufacturers began to invest in more sophisticated equipment capable of producing complex shapes and profiles.
The introduction of synthetic rubbers in the mid-20th century further transformed the industry, providing manufacturers with a wider range of materials tailored for specific applications. Today, advancements in materials science and engineering continue to drive innovation in rubber extrusion, enabling the production of high-performance products that meet stringent industry standards. This evolution reflects the sector’s adaptability and responsiveness to changing market needs, positioning it well for future growth in a competitive global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber extruder
-
How do I choose the right rubber extruder for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate rubber extruder involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as the type of rubber (natural or synthetic), desired product specifications, and production volume. Evaluate the machine’s capabilities, including temperature control, speed, and adaptability for different rubber grades. Additionally, consider the manufacturer’s reputation, customer support, and technological advancements. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive consultations can help clarify your needs and ensure you select a machine that aligns with your operational goals. -
What types of rubber are suitable for extrusion processes?
Common types of rubber suitable for extrusion include Ethylene Propylene (EPDM), Neoprene, Silicone, and Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). Each type has unique properties that cater to various applications, such as resistance to temperature, chemicals, and weathering. It’s essential to match the rubber type with your intended use, whether for automotive, industrial, or consumer products. Consulting with suppliers can provide insights into which rubber formulations would best meet your performance and durability requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for rubber extrusions?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among manufacturers and depend on factors such as production capabilities and material costs. Typically, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It is crucial to communicate your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a small or medium-sized enterprise. Some manufacturers may offer flexible solutions or allow for smaller trial orders to establish a working relationship. -
What should I consider when vetting rubber extruder suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience, certifications, and customer testimonials. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and those that comply with international quality standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support. Establishing direct communication can also help you gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on your specific requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing rubber extruders internationally?
Payment terms vary by supplier and can include options like upfront deposits, net 30/60/90 days, or letters of credit. It’s crucial to clarify these terms early in negotiations to ensure alignment with your budget and cash flow. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders. Be aware of any additional costs, such as shipping and import duties, which can affect the overall expense of your procurement. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my rubber extrusions?
Quality assurance in rubber extrusions can be ensured by selecting manufacturers that implement rigorous quality control processes. Look for suppliers that conduct regular testing of materials and finished products against established industry standards. Request documentation of their quality certifications and inquire about their testing procedures for durability, elasticity, and other critical attributes. Establishing a clear quality agreement can also facilitate compliance with your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing rubber extruders?
When importing rubber extruders, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. It’s vital to understand the total landed cost, which includes shipping, insurance, and duties. Engage with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial equipment to facilitate smoother transportation and compliance with import regulations. Additionally, plan for potential delays and have contingency measures in place to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
What customization options are available for rubber extruded products?
Customization options for rubber extruded products can include variations in material composition, color, dimensions, and specific design features such as profiles or surface textures. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions to meet unique application requirements. Discuss your needs with suppliers, as they may provide design assistance and prototyping services to ensure the final product aligns with your specifications. Understanding the customization capabilities of your supplier can significantly enhance your product’s performance and marketability.
Top 1 Rubber Extruder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Daextrusion – Custom Rubber Extrusion Solutions
Domain: daextrusion.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Rubber processing requires specialized knowledge and custom extrusion equipment designed for the elastic properties of rubber compounds. Suitable types of rubber for extrusion include Ethylene Propylene (EPR or EPDM), Neoprene, Silicone, and Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). Different grades of rubber are available, including commercial and specific grades such as MIL, ASTM, and SAE. The extrusion p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber extruder
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for rubber extruders is essential for companies aiming to enhance their production capabilities and meet diverse market demands. By prioritizing quality materials and advanced manufacturing processes, businesses can ensure the production of high-performance rubber products tailored to specific applications across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must leverage the unique properties of rubber materials—such as their elasticity and resistance to environmental factors—when selecting suppliers. Establishing partnerships with experienced manufacturers can provide access to cutting-edge technology and custom solutions, ultimately resulting in cost-effective, high-quality products that meet rigorous industry standards.
As the global market continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements in rubber extrusion technology and best practices in sourcing will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Embrace the opportunities that strategic sourcing offers and connect with reputable suppliers who can help you achieve your business objectives. Let’s pave the way for innovation and excellence in your rubber extrusion needs!

Illustrative image related to rubber extruder
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.