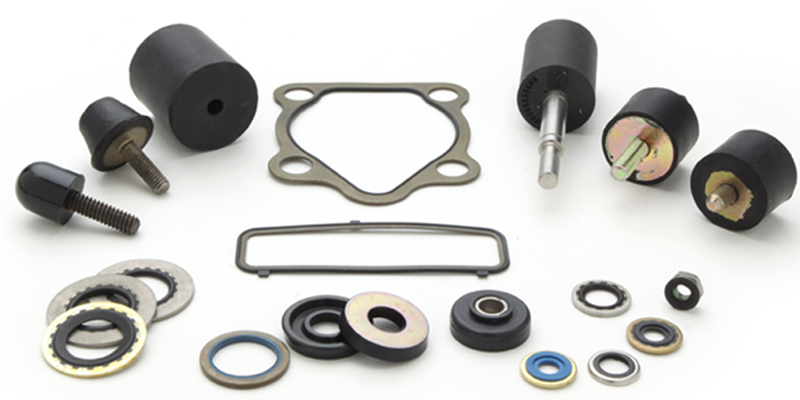
Rubber Bonded Metal Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber bonded metal
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality rubber bonded metal components presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The unique properties of rubber bonded to metal, such as enhanced durability and vibration reduction, make it an essential material for various applications across industries, including automotive, construction, and medical sectors. However, the complexities of selecting the right materials, understanding manufacturing processes, and navigating supplier capabilities can complicate procurement decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of rubber bonded metal, providing insights into different types of materials, bonding methods, and practical applications. We will explore key factors such as cost considerations, supplier vetting processes, and best practices for ensuring optimal performance and safety in your projects. By equipping you with actionable knowledge and strategic insights, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
As you navigate the global market for rubber bonded metal, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to leverage this versatile material to achieve superior performance in your applications. Whether you’re looking to optimize production processes or enhance product quality, this guide serves as your essential resource for success in the evolving landscape of rubber bonded metal procurement.
Understanding rubber bonded metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overmolded Rubber | Rubber is molded directly over a visible metal substrate | Automotive mounts, seals, gaskets | Pros: High durability, customizable shapes. Cons: Potential for higher production costs. |
| Encapsulated Rubber | Metal insert is fully encapsulated in rubber | Medical devices, electrical components | Pros: Enhanced protection, reduced wear. Cons: Limited visibility of metal, may require specific design considerations. |
| Anti-Vibration Mounts | Designed for shock absorption and vibration isolation | Industrial machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Effective in noise reduction, long-lasting. Cons: Requires precise engineering to ensure effectiveness. |
| Bonded Seals | Rubber seals bonded to metal for leak prevention | Plumbing, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Excellent sealing capabilities, reliable. Cons: May require specific adhesives for optimal performance. |
| Composite Materials | Combination of various rubber and metal types | Aerospace, construction, automotive | Pros: Tailored properties for specific applications. Cons: More complex material selection process. |
What Are the Characteristics of Overmolded Rubber Products?
Overmolded rubber involves the process of molding rubber directly over a visible metal substrate, creating a strong bond that enhances durability. This method is particularly suitable for applications requiring high resilience, such as automotive mounts and seals. B2B buyers should consider production costs and the complexity of design, as overmolding allows for intricate shapes that can accommodate specific mechanical requirements.
Why Choose Encapsulated Rubber for Your Projects?
Encapsulated rubber features a metal insert that is fully surrounded by rubber, providing excellent protection against environmental factors. This type is commonly used in medical devices and electrical components where exposure to contaminants is a concern. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced protection against the design limitations, as the metal is not visible and may require unique considerations in the product design phase.
How Do Anti-Vibration Mounts Benefit Industrial Applications?
Anti-vibration mounts are engineered specifically for shock absorption and vibration isolation, making them ideal for industrial machinery and automotive applications. These mounts effectively reduce noise and prolong the lifespan of equipment. However, precise engineering is crucial to ensure that they perform as intended, which may involve additional costs for specialized designs and testing.
What Advantages Do Bonded Seals Offer in Various Industries?
Bonded seals consist of rubber components that are securely attached to metal surfaces to prevent leaks, commonly used in plumbing, automotive, and aerospace industries. Their sealing capabilities are exceptional, providing reliability in critical applications. Buyers should consider the compatibility of adhesives and materials, as the effectiveness of the bond can significantly impact performance.
How Are Composite Materials Used in Aerospace and Construction?
Composite materials combine various types of rubber and metal to achieve tailored properties suitable for demanding applications in aerospace and construction. This versatility allows for the optimization of performance characteristics, such as weight reduction and enhanced strength. However, the complexity of selecting the right materials can pose challenges, necessitating careful consideration during the purchasing process to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber bonded metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber bonded metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine mounts and suspension components | Enhanced vibration dampening and noise reduction | Material compatibility, temperature resistance, and durability |
| Agriculture | Isolation mounts for machinery | Improved equipment longevity and reduced operational noise | Resistance to environmental factors and ease of installation |
| Medical | O-rings and seals for pumps | Ensured reliability and safety in critical medical applications | Compliance with health regulations and chemical resistance |
| Mass Transit | Vibration isolation for rail systems | Increased passenger comfort and reduced wear on infrastructure | Load-bearing capacity and environmental durability |
| Construction | Conveyor belt components | Enhanced efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Material strength, resistance to wear, and customization options |
How is Rubber Bonded Metal Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, rubber bonded metal is primarily used in engine mounts and suspension components. These parts are crucial for minimizing vibrations and noise (NVH), enhancing the overall driving experience. International buyers, especially from regions like Europe and the Middle East, should prioritize materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and road conditions. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for elastomers and metals can lead to better performance and longevity of these components, ultimately reducing maintenance costs.
What Role Does Rubber Bonded Metal Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, rubber bonded metal is utilized for isolation mounts in various machinery, such as tractors and harvesters. This application helps to dampen vibrations, thereby prolonging equipment life and reducing noise levels during operation. Buyers from South America and Africa should consider sourcing products that offer resistance to harsh environmental conditions, such as moisture and temperature fluctuations, which can affect performance. Ensuring that these parts are easy to install can also improve operational efficiency.
Why is Rubber Bonded Metal Critical in Medical Applications?
Rubber bonded metal finds significant applications in the medical sector, particularly in O-rings and seals for pumps. These components are essential for maintaining sterile environments and ensuring the safe operation of medical devices. Buyers must ensure that the materials used comply with stringent health regulations and possess chemical resistance to various substances encountered in medical settings. This focus on safety and reliability is vital for maintaining operational integrity in healthcare environments.
How Does Rubber Bonded Metal Enhance Mass Transit Systems?
In mass transit, rubber bonded metal is used for vibration isolation in rail systems, contributing to passenger comfort and the longevity of infrastructure. This application reduces wear on tracks and rolling stock, leading to lower maintenance costs and improved service reliability. International buyers should evaluate the load-bearing capacity of these components, ensuring they meet the demands of high-frequency transit systems. Environmental durability is also a key factor, particularly in regions with varying climate conditions.
What Advantages Does Rubber Bonded Metal Offer in Construction?
In the construction industry, rubber bonded metal is commonly found in conveyor belt components. This application enhances operational efficiency by reducing friction and wear, leading to lower maintenance costs. Buyers should focus on the strength and durability of materials used in these components, as they must withstand heavy loads and abrasive environments. Customization options can also provide significant benefits, allowing businesses to tailor solutions to specific operational needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber bonded metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Material Combination for Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in selecting the appropriate elastomer and metal combination for their rubber bonded metal components. This decision is critical, as it can significantly affect performance, durability, and cost. For example, a company manufacturing automotive parts may struggle to choose between natural rubber and synthetic alternatives, leaving them unsure about which will withstand the specific environmental conditions of their application.
The Solution: To effectively source and specify rubber bonded metal, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements, including temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Engaging with material suppliers to request samples and performance data can also help in making informed choices. Additionally, employing the expertise of engineers who understand the nuances of rubber and metal bonding will ensure the right material synergy is achieved. Buyers should always prioritize suppliers that offer customization capabilities to tailor the materials to their unique needs, thereby optimizing both performance and longevity.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Quality Assurance and Consistency of Bonding
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter issues with the quality and consistency of rubber bonded metal products. Variability in the bonding process can lead to weak bonds, resulting in product failure and increased warranty claims. This inconsistency often stems from inadequate quality control measures during the manufacturing process, such as improper surface preparation or incorrect curing times, which can vary significantly between suppliers.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement stringent quality assurance protocols throughout the rubber to metal bonding process. This includes verifying that the metal surfaces are properly cleaned and treated, as well as ensuring that the bonding agents used are compatible with the chosen materials. Buyers can also request documentation of the manufacturing process, including test results from load/deflection testing, to ensure that the components meet the specified standards. Establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers who are committed to continuous improvement and who can demonstrate a history of reliability will also help mitigate these quality concerns.
Scenario 3: High Costs Associated with Overmolding and Production Inefficiencies
The Problem: B2B buyers may find that the costs associated with overmolding processes for rubber bonded metal components can escalate quickly, particularly when production volumes are low. This situation is exacerbated by the need for specialized equipment and tooling, which can result in long lead times and increased operational costs, making it challenging for companies to maintain competitive pricing.
The Solution: To overcome these cost challenges, buyers should consider leveraging alternative manufacturing methods, such as transfer molding, which can be more cost-effective for smaller production runs. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who offer flexible manufacturing solutions can provide access to advanced technologies without the burden of upfront investments. Buyers should also explore bulk purchasing agreements that can reduce unit costs and optimize inventory management. By actively engaging with suppliers to understand their capabilities and exploring innovative production strategies, buyers can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber bonded metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Rubber Bonded Metal?
When selecting materials for rubber bonded metal applications, it is crucial to understand the specific properties of both the rubber and metal components. This ensures optimal performance and durability of the final product.
1. Natural Rubber (NR) and Mild Steel
Natural rubber is renowned for its excellent elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility. When bonded to mild steel, it can withstand varying temperatures (up to 70°C) and provides good resistance to abrasion. However, it is not suitable for extreme temperatures or exposure to oils and solvents.
Pros: Cost-effective, excellent flexibility, and good wear resistance.
Cons: Limited temperature range and susceptibility to chemical degradation.
Impact on Application: Ideal for automotive and agricultural components where flexibility is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure compliance with ASTM standards for rubber materials, especially in regions with strict regulations like Europe and the Middle East.
2. Ethylene-Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) and Aluminum
EPDM is a synthetic rubber that excels in weather resistance and can operate effectively in a temperature range from -50°C to 120°C. When bonded with aluminum, it offers excellent durability against UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: Exceptional weather and ozone resistance, good thermal stability.
Cons: Higher cost compared to natural rubber and potential manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in seals and gaskets for construction and automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Familiarity with JIS standards is important, particularly in Japan and other Asian markets.
3. Nitrile Rubber (NBR) and Stainless Steel
Nitrile rubber is particularly effective in applications requiring oil and fuel resistance, making it a popular choice in automotive and industrial sectors. When bonded to stainless steel, it can withstand temperatures up to 100°C and offers excellent chemical resistance.
Pros: High resistance to oils and fuels, good mechanical properties.
Cons: Limited temperature range compared to other synthetic rubbers.
Impact on Application: Ideal for fuel system components and hydraulic seals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry-specific standards, such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials, is essential, especially in the oil and gas sector.
4. Silicone Rubber (VMQ) and Brass
Silicone rubber is known for its high-temperature resistance (up to 200°C) and flexibility. When bonded with brass, it provides excellent thermal stability and is suitable for applications involving extreme temperatures or environmental conditions.
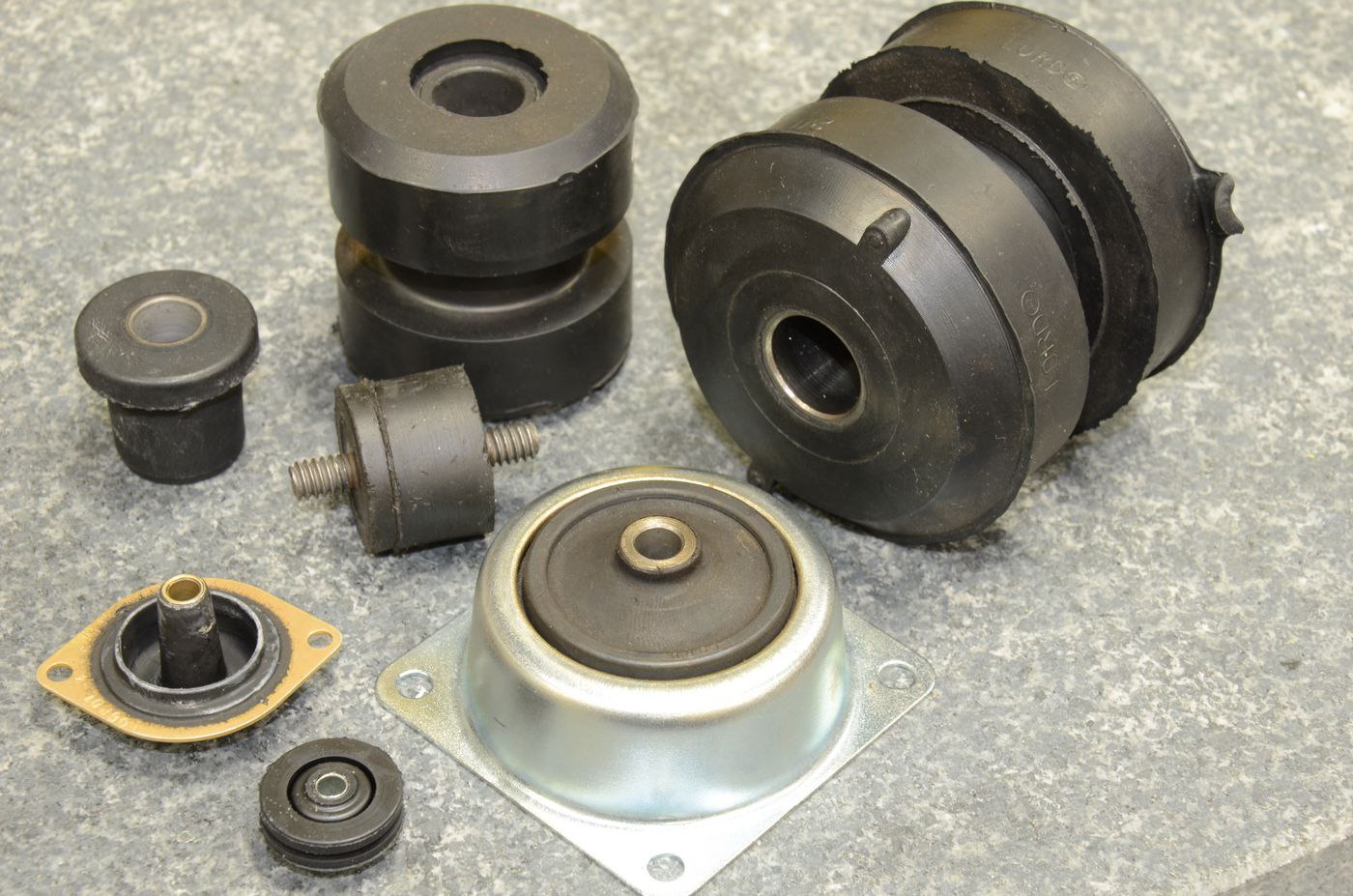

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
Pros: Outstanding temperature range, good electrical insulation properties.
Cons: Generally more expensive and may have lower mechanical strength compared to other rubbers.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in medical devices and high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure compliance with ISO standards, particularly in the medical and food industries, prevalent in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rubber Bonded Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber bonded metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) + Mild Steel | Automotive components, agricultural machinery | Cost-effective and flexible | Limited temperature range, chemical susceptibility | Low |
| Ethylene-Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) + Aluminum | Outdoor seals and gaskets | Exceptional weather resistance | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) + Stainless Steel | Fuel system components, hydraulic seals | High oil and fuel resistance | Limited temperature range | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber (VMQ) + Brass | Medical devices, high-temperature applications | Outstanding temperature resistance | Higher cost, lower mechanical strength | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in rubber bonded metal applications, tailored for B2B buyers across diverse international markets. Understanding these materials’ properties and implications will enable informed decision-making and enhance product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber bonded metal
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rubber Bonded Metal?
The manufacturing process of rubber bonded metal involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets the necessary specifications for durability and functionality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers and their capabilities effectively.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Rubber and Metal Prepared for Bonding?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is the preparation of the materials. For metal components, this typically involves cleaning and surface treatment to ensure optimal adhesion. Common practices include degreasing and blast-cleaning to remove contaminants such as oil, grease, and dust. This step is vital as any residue can compromise the bond’s integrity.

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
For rubber, selection is based on application requirements, including temperature resistance, flexibility, and environmental factors. Common elastomers used include natural rubber, EPDM, and nitrile. The choice of rubber type will significantly influence the performance characteristics of the final product.
2. What Techniques Are Used for Forming Rubber Bonded Metal Components?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming the rubber bonded metal components. Two primary techniques are employed in this process: overmolding and encapsulation.
-
Overmolding involves molding rubber directly over a metal substrate. This method allows for complex geometries and is often used for parts that require visible metal, such as seals and gaskets.
-
Encapsulation, or insert molding, places a metal insert into a mold before adding the rubber. This technique is ideal for applications where the metal is not intended to be visible, such as in electrical connectors.
Both methods can utilize transfer molding and injection molding techniques, each with its advantages. Transfer molding is often preferred for its cost-effectiveness and suitability for complex shapes, while injection molding is known for precision and efficiency in high-volume production.
3. How Is the Assembly of Rubber Bonded Metal Components Executed?
After the forming stage, the assembly of rubber bonded metal components may involve additional processes, particularly if multiple parts are being combined. This may include mechanical fastening or additional bonding steps to ensure that components are securely held together.
During assembly, it’s crucial to maintain cleanliness to avoid contamination that could affect the bond. All parts should be inspected for defects before final assembly to ensure quality and reliability.
4. What Finishing Techniques Are Used to Ensure Quality?
The finishing stage includes processes such as trimming, surface treatment, and additional curing, which may be necessary to enhance the product’s characteristics. Trimming ensures that excess material is removed, while surface treatments can improve adhesion properties or aesthetics.
Final curing processes may involve additional heat treatment to ensure that the rubber achieves its desired hardness and elasticity. This step is particularly important for applications requiring specific performance characteristics, such as vibration dampening.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Rubber Bonded Metal Production?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of rubber bonded metal manufacturing. International standards and industry-specific certifications play a significant role in ensuring that products meet quality benchmarks.
1. Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to recognized international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates a supplier’s commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Other certifications may be relevant depending on the industry, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for oil and gas applications. These certifications ensure that products meet specific regulatory and safety requirements.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints should be integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting incoming materials for compliance with specifications, ensuring that only quality materials are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections should be conducted to monitor adherence to process parameters and specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection verifies that the finished products meet all quality standards before shipment.
Testing methods may include mechanical testing, environmental exposure testing, and adhesion tests to ensure that the rubber and metal bond is robust and reliable.
3. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers. This includes:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help verify that the supplier adheres to established quality management systems and processes.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, defect rates, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing rubber bonded metal products from suppliers in different regions, international buyers must consider various quality control nuances.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements is crucial. Suppliers in regions like Africa and South America may have different standards compared to those in Europe or the Middle East.
-
Communication Barriers: Clear communication regarding quality expectations is essential. Language differences can lead to misunderstandings, so providing detailed specifications and guidelines can mitigate risks.
-
Logistical Considerations: Supply chain logistics can impact quality. Ensure that suppliers have robust logistics systems to maintain product integrity during transportation.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing rubber bonded metal products, ensuring they receive high-quality components that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber bonded metal’
In the competitive landscape of industrial components, sourcing rubber bonded metal parts requires a strategic approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure high-quality rubber bonded metal components, ensuring optimal performance and durability for their applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of the rubber bonded metal components you need. Consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, temperature range, and environmental conditions. This step is vital as it sets the foundation for selecting appropriate materials and manufacturing processes that align with your application.
Step 2: Identify Suitable Materials
Evaluate the types of rubber and metal that will best suit your needs. Common rubber materials include Natural Rubber (NR), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone, while metals may range from mild steel to aluminum. Understanding the properties of these materials, such as chemical resistance and flexibility, is crucial for ensuring a successful bond and longevity of the product.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in rubber bonded metal components. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and request case studies or references from similar projects. This step is essential to ensure that the supplier possesses the necessary expertise and quality assurance measures.
Step 4: Evaluate Manufacturing Processes
Inquire about the manufacturing processes used by potential suppliers, such as overmolding or encapsulation. Understanding the methods they employ, like transfer or injection molding, can impact the quality and cost-effectiveness of your order. Assess how these processes align with your technical specifications and production volume needs.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the rubber bonded metal components for testing. This will allow you to evaluate the bond strength, durability, and overall performance in real-world conditions. It’s critical to validate that the products meet your requirements and expectations.
Step 6: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the supplier complies with relevant industry standards and certifications. This includes checking for ISO certifications, material safety data sheets, and compliance with regional regulations. Verification of these credentials is crucial for ensuring product quality and safety, particularly when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 7: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Finally, discuss after-sales support and warranty options with your supplier. A reputable supplier should provide assistance in case of defects or performance issues. Understanding warranty terms and support services can safeguard your investment and ensure long-term reliability of the components.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for rubber bonded metal components, minimizing risks and optimizing their procurement strategies.
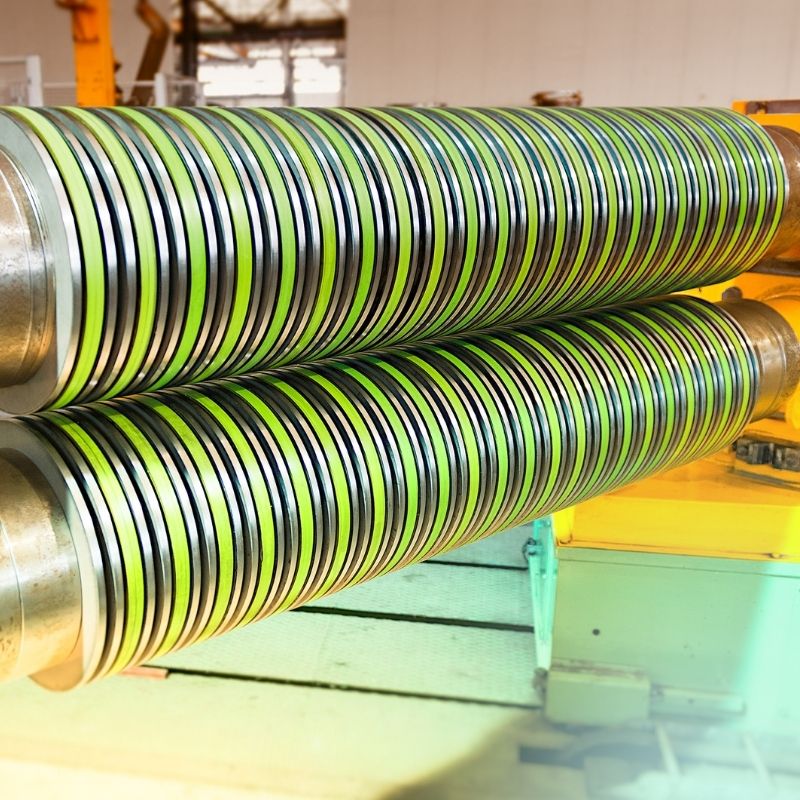

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber bonded metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Rubber Bonded Metal Sourcing?
When sourcing rubber bonded metal components, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The cost components typically include:
-
Materials: The choice of rubber and metal significantly influences costs. Common rubbers like natural rubber and EPDM are often more economical compared to specialty elastomers like silicone. Metals such as mild steel are cost-effective, while options like aluminum or brass may drive up material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the bonding process and the region of production. Skilled labor is often required for quality assurance in the bonding process, especially in regions with stringent manufacturing standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, maintenance, and indirect labor costs associated with running production facilities. Efficient operations can reduce overhead, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and tooling can be substantial, particularly for customized parts. This cost is amortized over production runs, making it critical to consider volume when assessing overall costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the rubber bonded components meet industry standards requires rigorous QC processes. This includes testing for bond strength and durability, adding to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transporting materials and finished products can vary widely in cost based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Understanding these logistics is essential for accurate pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin based on their operational costs, market conditions, and competition. Margins can vary significantly based on the supplier’s position in the market.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Rubber Bonded Metal Components?
Several factors influence the pricing of rubber bonded metal components, particularly for international B2B transactions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often come with discounts, so buyers should assess their needs against MOQ requirements to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions, while offering enhanced performance, can lead to increased costs. Standard parts typically have lower pricing due to established production processes.
-
Materials Used: The choice of rubber and metal not only affects performance but also cost. Specialty materials will increase the price, whereas more common materials can help keep costs down.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and capabilities of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should consider who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, as these can add hidden costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Rubber Bonded Metal Sourcing?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing rubber bonded metal components effectively, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Always engage in negotiation with suppliers. Understanding the cost components can provide leverage in discussions to secure better pricing or terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the upfront price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and lifecycle costs when assessing the total expenditure associated with the component.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to reach higher volumes, which can lead to significant savings per unit.
-
Investigate Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer lower logistics costs and shorter lead times, contributing to overall cost efficiency.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Be aware of fluctuating material prices and changes in supplier capabilities to better anticipate costs and make informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost and pricing landscape for rubber bonded metal components requires a nuanced understanding of various cost components and pricing influencers. By leveraging strategic buying practices and considering the total cost of ownership, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement efficiency and drive better value from their sourcing activities.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber bonded metal With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Rubber Bonded Metal: Key Comparisons
When evaluating solutions for applications requiring durability, strength, and vibration dampening, it is essential to consider alternatives to rubber bonded metal. This section explores two viable alternatives: polyurethane bonding and mechanical fastening, providing insights into their performance, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for various applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Bonded Metal | Polyurethane Bonding | Mechanical Fastening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for NVH applications; provides superior vibration and noise reduction. | Good flexibility and resistance to wear; suitable for various environmental conditions. | High strength; effective in load-bearing applications but less effective in vibration dampening. |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs; long-term savings due to durability. | Generally lower initial cost; can require more frequent replacements. | Low initial costs; however, may incur higher installation and maintenance costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized processes for bonding; can be complex. | Easier to implement; often involves straightforward application techniques. | Simple installation with readily available tools; however, may require precise alignment. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durability and resistance to environmental factors. | Moderate maintenance; may need frequent checks for wear and tear. | Requires regular checks for tightness and alignment; can be labor-intensive. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automotive, construction, and medical applications needing vibration isolation. | Suitable for general industrial applications and where flexibility is needed. | Best for structural applications where high strength is critical, such as in heavy machinery. |
Understanding Polyurethane Bonding as an Alternative
Polyurethane bonding is a viable alternative, known for its elasticity and resistance to wear and tear. This method offers good performance in various environmental conditions, making it suitable for industrial applications. While the initial costs are generally lower than rubber bonded metal, the longevity may not match that of rubber bonded components, potentially leading to more frequent replacements. This option is particularly effective in applications where flexibility is required, but it lacks the noise and vibration dampening properties of rubber bonded metal.
Evaluating Mechanical Fastening: Pros and Cons
Mechanical fastening utilizes bolts, screws, or rivets to connect components. This method is straightforward and often cost-effective due to the low initial investment required. However, while mechanical fasteners provide high strength for load-bearing applications, they do not offer the same level of vibration dampening as rubber bonded metal. Additionally, mechanical fasteners require regular maintenance checks to ensure tightness and alignment, which can lead to increased labor costs over time. This method is best suited for structural applications where strength is paramount, but it may fall short in applications requiring noise and vibration control.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best solution for your specific application, consider the unique requirements of your project. Rubber bonded metal excels in applications requiring durability and effective noise and vibration dampening, making it ideal for sectors like automotive and medical. Polyurethane bonding offers flexibility and lower initial costs, suitable for less demanding environments, while mechanical fastening provides straightforward assembly for structural integrity but may require more maintenance. By assessing the performance, cost, implementation ease, and maintenance needs of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber bonded metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Bonded Metal?
Understanding the essential technical properties of rubber bonded metal is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when selecting materials for demanding applications. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the rubber and metal components based on their composition and performance characteristics. Common grades for rubber include Natural Rubber (NR), Nitrile (NBR), and Silicone (VMQ), while metals can range from mild steel to aluminum. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures that the final product meets specific performance criteria such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the maximum amount of tensile (stretching) stress that a material can withstand before failing. For rubber bonded metal applications, high tensile strength is critical to ensure that components can endure operational stresses without deforming or breaking. This is particularly important in automotive and heavy machinery applications, where safety and reliability are paramount. -
Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance indicates the ability of rubber and metal components to perform under varying thermal conditions. Different elastomers have specific temperature ranges in which they can operate effectively. Buyers must consider this property to prevent material degradation in environments that experience extreme heat or cold, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs. -
Bonding Adhesion
The quality of the adhesive bond between rubber and metal is vital for performance. Strong adhesion prevents delamination and ensures that the rubber component performs as intended in applications such as vibration isolation. Understanding the bonding process and the type of adhesive used can help buyers make informed decisions about material compatibility and product durability. -
Hardness
Hardness, measured on the Shore durometer scale, indicates the resistance of rubber to indentation. The hardness of rubber affects its flexibility and ability to absorb shock. In applications where vibration dampening is crucial, selecting the right hardness level ensures optimal performance and user comfort. -
Chemical Resistance
This property evaluates how well rubber and metal can withstand exposure to various chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids. For industries such as automotive and chemical processing, ensuring chemical resistance is vital to prevent material degradation, which could lead to component failure and safety hazards.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Rubber Bonded Metal Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms:
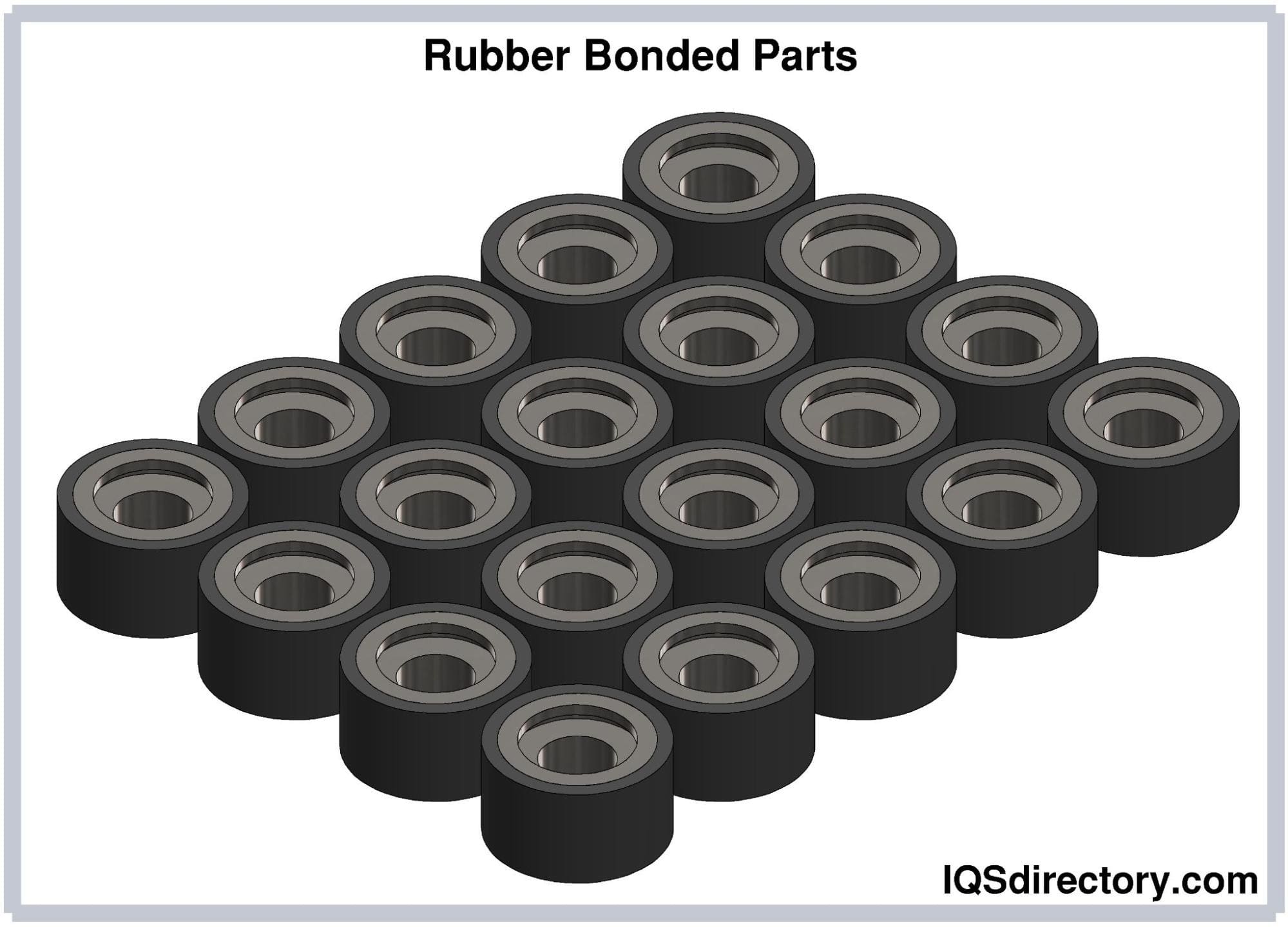

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that parts meet the required quality and compatibility standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers to know as it can affect inventory management and overall costs. Negotiating MOQs can lead to more favorable purchasing terms. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ ensures that buyers receive accurate and competitive pricing, which is essential for budgeting and project planning. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms helps buyers navigate global trade complexities. -
Vulcanization
Vulcanization is a chemical process that involves heating rubber with sulfur to improve its properties, making it more durable and elastic. Knowledge of this term is vital for buyers to understand the production process and the quality of the rubber components they are purchasing. -
Curing
Curing refers to the process of hardening rubber after it has been molded or shaped. This term is essential for buyers to comprehend the final product’s performance characteristics, including flexibility and thermal resistance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right rubber bonded metal components for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber bonded metal Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Rubber Bonded Metal Sector?
The rubber bonded metal market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increased demand for noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) solutions in automotive and industrial applications is propelling this sector forward. Key trends include the rise of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as injection and transfer molding, which enhance product precision and reduce waste. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and automation, is streamlining production processes and enabling real-time quality control. International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should pay attention to local market demands, as each region exhibits unique preferences for rubber and metal combinations based on environmental and application-specific requirements.
Furthermore, the evolving landscape of global supply chains is influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer customizable solutions and fast turnaround times. The shift towards digital platforms for procurement is also significant; many companies are adopting e-commerce solutions to facilitate easier ordering and enhance supplier visibility. For instance, markets in Brazil and Saudi Arabia are witnessing a surge in local manufacturing capabilities, which can provide cost-effective sourcing options for rubber bonded metal products.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Rubber Bonded Metal Industry?
Sustainability has become a focal point for B2B buyers in the rubber bonded metal sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly the carbon footprint associated with rubber production and metal extraction, is prompting companies to seek out greener alternatives. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is also crucial, as businesses are held accountable for their supply chain practices. This includes ensuring that raw materials are sourced from suppliers who engage in responsible environmental and labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and various eco-labels for rubber materials are gaining traction among B2B buyers. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also foster consumer trust in an increasingly eco-conscious market.

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
In addition, the use of recycled materials in rubber bonding is on the rise. This trend is particularly appealing to companies looking to reduce waste and promote circular economy practices. By investing in suppliers that utilize sustainable materials and processes, businesses can align their procurement strategies with global sustainability goals while meeting the growing demand for environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context of Rubber Bonded Metal Applications in B2B?
The evolution of rubber bonded metal applications can be traced back to the early 20th century when the automotive industry began exploring innovative ways to enhance vehicle performance and comfort. Initially, rubber was used primarily for seals and gaskets, but as technology progressed, manufacturers recognized the advantages of bonding rubber to metal for various applications, including anti-vibration mounts and shock absorbers.
Over the decades, advancements in bonding techniques, such as vulcanization and various molding processes, have significantly improved the strength and durability of rubber bonded components. This evolution has enabled the development of high-performance parts used in diverse sectors, including automotive, agriculture, medical, and construction. As the demand for specialized applications continues to grow, the rubber bonded metal sector is positioned for further innovation, with a strong focus on customization and sustainability in response to market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber bonded metal
-
How do I select the right rubber and metal materials for bonding?
Choosing the appropriate materials for rubber bonded metal applications involves understanding the specific requirements of your project. Factors such as environmental conditions, temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and mechanical properties must be considered. Common rubber types include natural rubber, EPDM, and silicone, while metals often include mild steel, aluminum, and brass. Collaborate with suppliers who can offer insights into material compatibility to ensure optimal performance and durability for your application. -
What are the advantages of rubber bonded metal in industrial applications?
Rubber bonded metal provides numerous benefits, including enhanced durability, superior resistance to vibration and shock, and improved noise reduction. These characteristics make it ideal for applications in automotive, medical, construction, and agricultural sectors. The strong bond between rubber and metal ensures longevity and reliability, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. By leveraging rubber bonded solutions, businesses can achieve higher operational efficiency and improved safety for their equipment. -
What is the typical lead time for rubber bonded metal products?
Lead times for rubber bonded metal products can vary significantly based on factors such as customization, order volume, and the manufacturing process employed. Generally, standard products may take a few weeks, while custom orders could require several weeks to months for design, prototyping, and production. It is advisable to discuss timelines with suppliers upfront and factor in potential delays due to logistics or material sourcing, especially when dealing with international shipments. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rubber bonded metal products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rubber bonded metal products often depend on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Standard components may have lower MOQs, while custom parts usually require larger quantities to justify production costs. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and explore options for flexibility, especially if you are a smaller buyer or entering a new market. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in rubber bonded metal products?
To ensure quality assurance in rubber bonded metal products, consider suppliers who implement rigorous testing and quality control processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, request documentation of material specifications, bonding techniques, and performance testing results. Establishing a strong partnership with your supplier and maintaining open communication can also help address any quality concerns promptly. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international orders?
Payment terms for international orders of rubber bonded metal products can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s important to discuss payment options early in negotiations and understand any currency exchange implications. Establishing clear terms can help mitigate risks associated with international transactions, ensuring a smoother purchasing process. -
How do I vet suppliers for rubber bonded metal products?
Vetting suppliers involves evaluating their experience, reputation, and capabilities in producing rubber bonded metal products. Start by checking customer reviews, case studies, and references from previous clients. Assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible or requesting virtual tours to gain insights into their operations and commitment to quality. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing internationally?
When sourcing rubber bonded metal products internationally, consider factors such as shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier is well-versed in international logistics and can handle export documentation and compliance. It’s also wise to evaluate the reliability of shipping methods and carriers, as well as potential tariffs or duties that may apply. Establishing a solid logistics plan can help minimize delays and additional costs in the supply chain.
Top 5 Rubber Bonded Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. RD Rubber – Durable Rubber to Metal Bonding
Domain: rdrubber.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rubber to metal bonding forms a permanent, durable connection between rubber and metal components, offering superior resistance to vibration damage and mechanical stress. The process involves five key steps: 1) Identifying the right elastomer (natural and synthetic rubbers), 2) Preparing the metal surface (cleaning and moisture control), 3) Applying primer and adhesive (using vulcanization bonding…
2. GMT Rubber – Bonding Solutions for Diverse Industries
Domain: gmtrubber.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: GMT Rubber specializes in bonding rubber to metal for various applications, including anti-vibration mounts and shock mounts. Key product details include: 1. Industries served: Aerospace, Automotive, Agriculture, Construction, Defence, Marine, Material Handling, Railway, Renewable Energy. 2. Types of products: Anti Vibration Mounts, Machine Feet, Rubber Bobbins, Cone Mounts, Compactor Mounts, Isol…
3. Bonded to Metal Rubber – Rubber to Metal Bonding Solutions
Domain: bondedtometalrubber.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Rubber to metal bonding is a specialized engineering process used to permanently adhere rubber compounds to metal substrates. It combines the flexibility, vibration absorption, and sealing capabilities of rubber with the structural integrity, durability, and load-bearing capacity of metal. This results in high-performance components that endure mechanical stresses, temperature extremes, chemicals,…
4. Trelleborg – Bonded Sealing Solutions
Domain: trelleborg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Rubber-to-Metal and Rubber-to-Plastic Bonded Parts from Trelleborg Sealing Solutions offer advantages in technical robustness, quality, performance, and total cost of ownership. The bonding of standard or specialized elastomers, including Isolast®, is feasible with a variety of metals and thermoplastics. Trelleborg acts as a development partner to design and develop products tailored to specific a…
5. Apple Rubber – Bonded Parts Solutions
Domain: applerubber.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Rubber-to-metal bonded parts require careful selection of materials and adhesives. Key metals include stainless steel for corrosive applications, brass for propane/natural gas, and common steel for cost reduction. Rubber types must meet performance criteria, with options like silicone and natural rubber for vibration absorption, FKM/Viton™ for aerospace, and NBR/HNBR for automotive. Adhesive syste…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber bonded metal
In the evolving landscape of rubber bonded metal applications, strategic sourcing remains pivotal for businesses seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and product performance. By understanding the diverse materials, processes, and applications, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific industry needs. Key takeaways include the significance of selecting suitable rubber and metal combinations, the advantages of various bonding techniques, and the importance of quality control to ensure durability and reliability.
As companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly prioritize innovation and sustainability, the demand for high-performance rubber bonded metal solutions is expected to rise. Embracing strategic sourcing not only fosters competitive advantages but also opens avenues for collaboration with leading manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions.
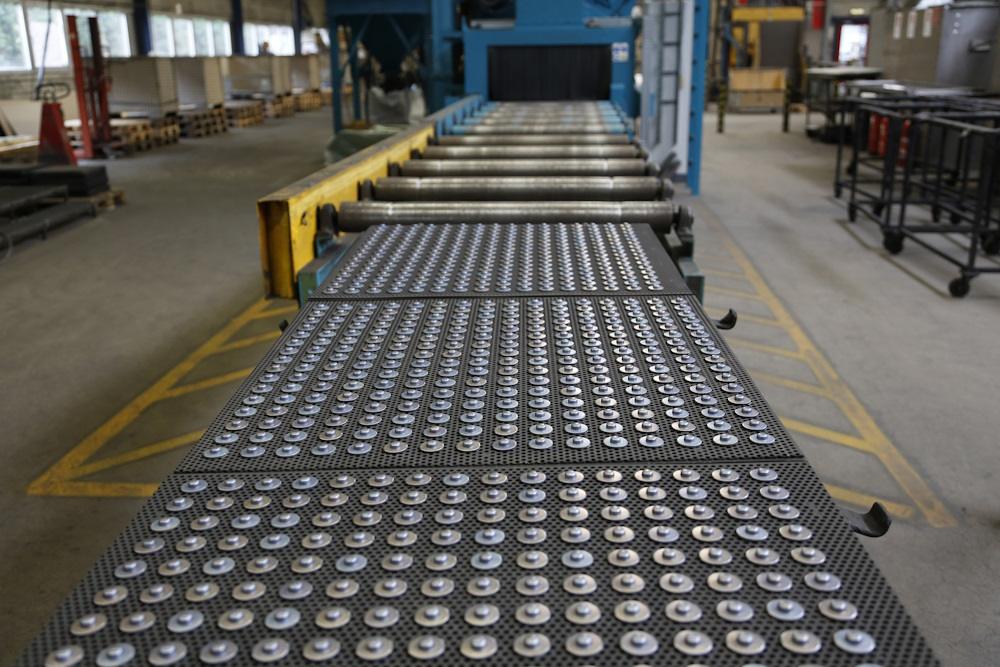

Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with reputable suppliers that offer customized services and robust quality assurance. By doing so, you can position your business to thrive in a dynamic market, ensuring that your products meet the highest standards of performance and reliability. Engage with industry experts today to capitalize on the opportunities within the rubber bonded metal sector.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to rubber bonded metal
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.