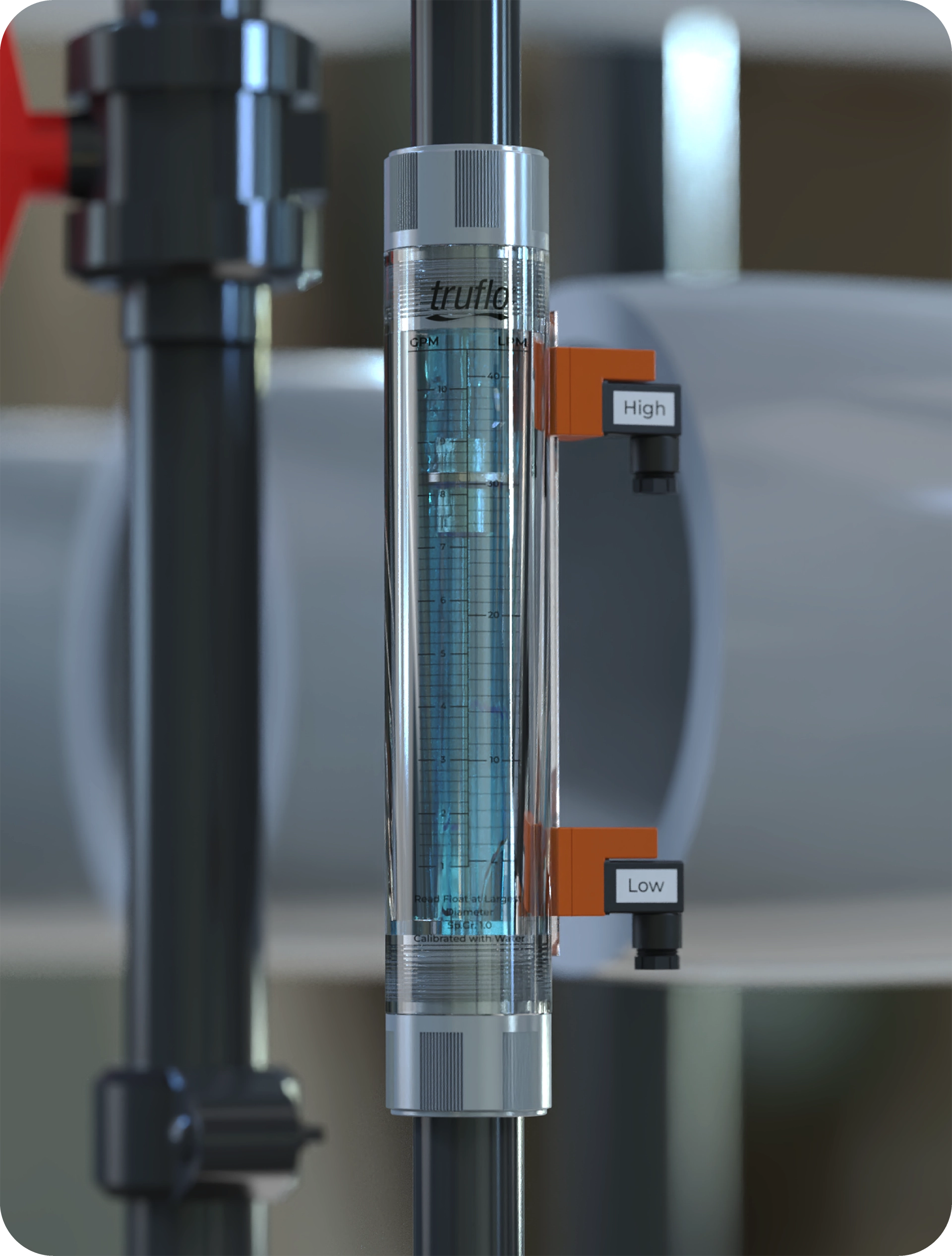
Rotameter Flow Indicator: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rotameter flow indicator
In the intricate landscape of industrial measurement, sourcing reliable rotameter flow indicators poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse markets. These essential devices, known for their simplicity and accuracy in measuring fluid flow, are pivotal in various applications, from agriculture to pharmaceuticals. However, the task of selecting the right rotameter can be daunting, especially when considering factors such as fluid compatibility, installation requirements, and regional supply chain dynamics.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of rotameter flow indicators, providing international B2B buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Vietnam and Nigeria)—with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. We explore the different types of rotameters available, their specific applications across industries, and key considerations for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will address cost factors, ensuring that buyers understand the value proposition of each option.
By equipping buyers with detailed knowledge and actionable insights, this guide empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of sourcing rotameter flow indicators effectively. Whether you are looking to enhance operational efficiency or ensure compliance with industry standards, understanding these instruments is essential to driving success in your business operations.
Understanding rotameter flow indicator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass Rotameters | Transparent tube, high visibility | Laboratory, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage | Pros: High accuracy, visual flow indication. Cons: Fragile, limited to low pressure. |
| Acrylic Rotameters | Lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion | Water treatment, chemical processing, HVAC | Pros: Cost-effective, good for corrosive fluids. Cons: Lower temperature resistance than metal. |
| Metal Rotameters | Robust construction, suitable for high-pressure use | Oil & gas, petrochemical, heavy industry | Pros: High durability, suitable for harsh conditions. Cons: Higher initial cost, heavier. |
| Low Flow Rotameters | Designed for precise measurement of small flows | Laboratory applications, microfluidics | Pros: Accurate at low flow rates. Cons: Limited to specific applications, higher cost per unit. |
| Digital Rotameters | Electronic readouts, optional connectivity | Automation, process control, data logging | Pros: Enhanced accuracy, remote monitoring capabilities. Cons: Higher complexity, requires power source. |
What are the Characteristics and Applications of Glass Rotameters?
Glass rotameters are recognized for their transparent tubes, providing a direct visual indication of flow rates. Typically used in laboratories and industries requiring high accuracy, such as pharmaceuticals and food and beverage sectors, these rotameters offer excellent precision. However, their fragility limits their application in high-pressure environments, making them less suitable for rugged industrial settings. B2B buyers should consider their installation environment and the potential for breakage when selecting glass rotameters.
How Do Acrylic Rotameters Compare in Durability and Cost?
Acrylic rotameters are favored for their lightweight and durable properties, making them ideal for applications in water treatment and chemical processing. They resist corrosion, allowing for the measurement of various fluids, including aggressive chemicals. While they are generally more cost-effective than glass or metal options, their temperature resistance is lower, which may limit their use in high-temperature applications. Buyers should evaluate the chemical compatibility and temperature requirements of their processes when considering acrylic rotameters.
What Makes Metal Rotameters Suitable for Harsh Environments?
Metal rotameters are designed for heavy-duty applications and are often employed in the oil and gas industry, petrochemical processes, and heavy manufacturing. Their robust construction allows them to withstand high pressures and harsh environmental conditions, making them reliable for critical operations. However, they come at a higher initial cost and can be heavier, which may require additional support during installation. B2B buyers need to assess their operational requirements and budget constraints when selecting metal rotameters.
Why Choose Low Flow Rotameters for Precision Measurement?
Low flow rotameters are specifically engineered to provide accurate measurements of small flow rates, making them essential in laboratory settings and microfluidic applications. Their precision is unmatched in low-flow scenarios, yet they are typically more expensive per unit than standard rotameters. The limited application range means that businesses must consider whether their processes will consistently operate within the low flow range before investing in these specialized instruments.
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Digital Rotameters?
Digital rotameters incorporate electronic readouts and often come with connectivity options for data logging and process automation. These features enhance measurement accuracy and allow for remote monitoring, making them suitable for modern industrial applications that require real-time data. However, the complexity and need for a power source can be a drawback in environments where simplicity and reliability are paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of advanced technology against the operational requirements and potential maintenance needs of digital rotameters.
Key Industrial Applications of rotameter flow indicator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rotameter flow indicator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Monitoring flow rates in filtration and treatment processes | Ensures compliance with environmental regulations and efficiency | Compatibility with water quality, pressure, and temperature ranges |
| Food and Beverage | Controlling ingredient flow in production lines | Improves product consistency and quality, reduces waste | Material compatibility with food standards, ease of cleaning |
| Oil and Gas | Measuring flow rates in pipelines and refineries | Enhances operational safety and efficiency | Resistance to high pressure and corrosive environments |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Flow monitoring for active ingredient dosing | Ensures precise dosing for product efficacy and compliance | Accuracy requirements, chemical compatibility, and calibration needs |
| Agriculture | Irrigation system flow measurement | Optimizes water usage and crop yield | Durability in outdoor conditions, measurement range for varying flow rates |
How Are Rotameter Flow Indicators Used in Water Treatment?
In water treatment facilities, rotameter flow indicators play a crucial role in monitoring flow rates during filtration and chemical treatment processes. By providing real-time flow data, these instruments help operators ensure that treatment processes remain compliant with environmental regulations. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, sourcing rotameters that can withstand varying water quality and temperature conditions is essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
What Role Do Rotameters Play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, rotameters are used to control the flow of ingredients, such as liquids and gases, during production. This application is vital for maintaining product consistency and quality while minimizing waste. Buyers in this industry must consider material compatibility with food safety standards, as well as the ease of cleaning and maintenance, to ensure compliance with health regulations.
How Are Rotameter Flow Indicators Applied in Oil and Gas?
Within the oil and gas industry, rotameters are employed to measure flow rates in pipelines and refineries. Accurate flow measurement is crucial for enhancing operational safety and efficiency, as it allows for better monitoring of fluid dynamics within these critical infrastructures. When sourcing rotameters for this application, businesses should prioritize models that can resist high pressures and corrosive materials typical in oil and gas environments.
Why Are Rotameters Important in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, rotameter flow indicators are essential for monitoring the flow of active ingredients during the dosing process. Precise flow measurement ensures product efficacy and compliance with strict regulatory standards. Buyers must pay close attention to the accuracy of these instruments, along with their chemical compatibility and calibration needs, to meet the high standards of the pharmaceutical industry.
How Do Rotameters Benefit Agricultural Irrigation Systems?
Rotameters are utilized in agricultural irrigation systems to measure water flow rates, enabling farmers to optimize water usage and enhance crop yield. Accurate flow measurement allows for better management of water resources, which is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity. Buyers should consider the durability of rotameters in outdoor conditions and their measurement range to accommodate varying flow rates typical in agricultural applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rotameter flow indicator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inaccurate Flow Measurements Leading to Operational Inefficiencies
The Problem:
A manufacturing plant in Nigeria is experiencing frequent production delays due to inaccurate flow measurements from their rotameter flow indicators. The inaccuracies stem from incorrect installation and orientation, leading to inconsistent readings that affect process control. This not only hampers production efficiency but also increases costs due to wasted materials and energy. The plant manager feels frustrated, knowing that the rotameters were supposed to provide reliable measurements but are instead causing operational chaos.
The Solution:
To address this issue, it’s crucial to ensure that rotameters are installed correctly, particularly in a vertical orientation, as specified by the manufacturer. Buyers should prioritize rotameters that are suited for their specific application—considering factors such as fluid type, flow rate, and installation environment. Moreover, conducting a thorough calibration before use can significantly enhance measurement accuracy. Regular maintenance checks should be scheduled to clean and verify the device’s accuracy, thus preventing inaccuracies from arising. Providing training for operators on proper installation and maintenance practices will also mitigate future issues.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Selecting the Right Rotameter for Specific Applications
The Problem:
A Brazilian agricultural company is tasked with monitoring water flow in irrigation systems but struggles to select the appropriate rotameter. With a variety of options available, including different materials, flow rates, and designs, the buyer feels overwhelmed and uncertain about which model will best suit their specific needs. This indecision delays the procurement process and jeopardizes the timely implementation of their irrigation strategy.
The Solution:
Buyers should begin by conducting a comprehensive needs analysis to clearly define the application requirements. This includes understanding the type of fluid being measured (e.g., clean water, chemicals), the expected flow rate, and environmental conditions such as temperature and pressure. Utilizing resources like application advisors or consulting with manufacturers can provide valuable insights into the most suitable rotameter types. It’s also beneficial to request samples or demonstrations to evaluate performance under actual operating conditions. Establishing a checklist of criteria—like chemical compatibility, maximum flow rates, and budget—will streamline the selection process and lead to a more informed purchase decision.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Integrating Rotameters with Existing Systems
The Problem:
A company in the Middle East is looking to upgrade its monitoring systems by integrating new rotameter flow indicators into existing automated processes. However, the buyer faces compatibility issues between the new rotameters and the current control systems, leading to frustration over the integration process. The inability to collect real-time data hampers decision-making and operational efficiency, creating a bottleneck in production.
The Solution:
To facilitate seamless integration, it is essential to choose rotameters that offer electronic signal outputs compatible with existing control systems. Buyers should look for models that provide options for 4-20mA output or pulse signals, which are standard in many industrial applications. Engaging with the supplier during the selection process can ensure that the rotameters chosen are compatible with the current system and that necessary adapters or interfaces are available. Additionally, involving IT or engineering teams early in the procurement process can help identify integration challenges and develop solutions proactively. Finally, consider investing in training for staff to understand the new systems and maximize their functionality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rotameter flow indicator
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rotameter Flow Indicators?
When selecting a rotameter flow indicator, the choice of material is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of rotameters: glass, acrylic, stainless steel, and PVC. Each material has unique properties that can significantly impact the application, particularly for international B2B buyers.
How Does Glass Perform in Rotameter Applications?
Glass is a traditional choice for rotameter construction, particularly in applications where visibility of the fluid is essential. Its key properties include high chemical resistance and the ability to withstand moderate pressure and temperature variations, typically up to 200°F and 150 PSI.
Pros: Glass offers excellent clarity, allowing for easy visual inspection of fluid flow. It is also resistant to many corrosive chemicals, making it suitable for various applications, including pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Cons: However, glass is fragile and can break under impact or thermal shock. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher costs compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: Glass rotameters are ideal for clean, low-viscosity fluids. Buyers in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as Europe, must consider the potential for breakage and the need for protective housing.
What Advantages Does Acrylic Offer for Rotameter Flow Indicators?
Acrylic is a lightweight alternative to glass, offering similar visibility and chemical resistance but with enhanced durability. It can typically handle temperatures up to 180°F and pressures around 100 PSI.

Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
Pros: Acrylic is less prone to breakage, making it a safer option in environments where impact is a concern. It is also more cost-effective than glass, which can appeal to budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: However, acrylic is susceptible to certain solvents and may degrade over time when exposed to UV light. This limits its use in some chemical applications.
Impact on Application: Acrylic rotameters are suitable for a wide range of applications, including water and air flow measurement. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may prefer acrylic for its lower cost and durability, especially in less controlled environments.

Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Rotameter Construction?
Stainless steel is favored for its robustness and versatility, particularly in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 300°F and pressures up to 1500 PSI.
Pros: The material is highly resistant to corrosion and mechanical wear, making it ideal for harsh environments, including oil and gas applications. Its durability ensures a long lifespan, reducing replacement costs.
Cons: The primary downside is the higher initial investment compared to plastic or glass alternatives. Manufacturing stainless steel rotameters can also be more complex, leading to increased lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel rotameters are optimal for aggressive media and high-flow applications. International buyers from the Middle East, where oil and gas industries are prevalent, will find stainless steel rotameters particularly beneficial.
How Does PVC Compare in Rotameter Applications?
PVC is a cost-effective option for rotameters, particularly in low-pressure applications. It typically handles temperatures up to 140°F and pressures around 75 PSI.
Pros: The material is lightweight and resistant to many chemicals, making it suitable for water treatment and agricultural applications. Its low cost makes it an attractive option for budget-sensitive projects.
Cons: However, PVC is not suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications, limiting its use. It also lacks the clarity of glass or acrylic, which can hinder visual flow inspection.
Impact on Application: PVC rotameters are ideal for non-corrosive liquids in less demanding environments. Buyers in developing regions may favor PVC for its affordability and ease of installation.

Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rotameter Flow Indicators
| Material | Typical Use Case for rotameter flow indicator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | Pharmaceuticals, food processing | Excellent chemical resistance | Fragile, higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Acrylic | Water and air flow measurement | Lightweight, cost-effective | Susceptible to UV and certain solvents | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas applications | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher initial investment | High |
| PVC | Water treatment, agricultural applications | Low cost, lightweight | Limited temperature and pressure range | Low |
In summary, the choice of material for rotameter flow indicators significantly influences their performance and suitability for various applications. International buyers should carefully consider these factors, including compliance with local standards and the specific requirements of their applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rotameter flow indicator
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rotameter Flow Indicators?
The manufacturing process of rotameter flow indicators involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Selecting Components
The first stage involves sourcing high-quality materials suitable for the specific application of the rotameter. Common materials include borosilicate glass, acrylic, stainless steel, and various plastics. Each material is chosen based on factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and pressure ratings. Suppliers often conduct material testing to ensure they meet industry standards.
Forming: Shaping and Molding Components
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. For glass rotameters, this may involve precision glass-blowing techniques to create the tapered flow tube. For plastic rotameters, injection molding is commonly used. This stage requires high precision to ensure the float can rise and fall accurately within the tube. Advanced technology, such as CNC machining, may also be employed to create the required parts with exceptional accuracy.
Assembly: Integrating Components for Functionality
The assembly stage is where various components come together. This typically involves assembling the flow tube, float, and measurement scale. Attention to detail is crucial here; the float must be perfectly calibrated to ensure accurate flow measurement. During assembly, manufacturers often use automated systems to enhance precision and efficiency.
Finishing: Quality Checks and Surface Treatments
Finishing processes may include polishing the glass or plastic components and applying protective coatings to metal parts to enhance durability and corrosion resistance. This stage also involves the initial quality control checks, where products are visually inspected for defects and functionality.
How is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing of Rotameter Flow Indicators?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process for rotameter flow indicators. It ensures that each unit meets both international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of rotameters often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that the manufacturer has established processes for maintaining quality throughout the production cycle. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (for European markets) and API (for petroleum and gas industries) may also be relevant. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. This includes checks for consistency, purity, and compliance with certifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random samples are tested for dimensional accuracy and performance. This can include pressure testing for leaks or flow testing to ensure accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, each rotameter undergoes rigorous testing to verify that it meets operational specifications. This may involve calibrating the flow measurement against known standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods employed during the QC process include:
-
Hydraulic Testing: This method assesses the integrity of the rotameter under pressure, ensuring there are no leaks and that it can withstand operational conditions.
-
Flow Testing: Rotameters are tested against known flow rates to ensure accuracy. This often involves using calibrated flow meters to compare results.
-
Environmental Testing: Products may be subjected to various environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive atmospheres, to test durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers have several avenues to ensure that their suppliers adhere to quality control standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request documentation that outlines the QC processes used by the supplier, including test results and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Utilizing independent third-party services to inspect products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality. This is particularly important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding product standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can differ significantly across cultures. Establishing a clear line of communication with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings related to quality expectations.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. This transparency can build trust and facilitate better cooperation.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for rotameter flow indicators are complex but essential for ensuring reliability and accuracy. B2B buyers should take the time to understand these processes and actively engage with suppliers to ensure that their products meet the required standards and specifications. By doing so, they can make informed purchasing decisions that support their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rotameter flow indicator’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure rotameter flow indicators. Given their vital role in accurately measuring fluid flow in various applications, ensuring the right selection and supplier is crucial. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing and selecting the ideal rotameter for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search, clearly outline the technical requirements for the rotameter flow indicator. Consider factors such as the type of fluid being measured (liquid or gas), flow rate, pressure, and temperature ranges. These specifications will guide you in choosing the right model and ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
- Fluid Type: Determine if you will be measuring water, air, or more corrosive substances.
- Flow Range: Specify the minimum and maximum flow rates required for your application.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Understanding the specific application for which the rotameter will be used is essential. Different industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, or oil and gas, may have unique requirements regarding accuracy, chemical compatibility, and installation conditions.
- Accuracy Needs: Identify the acceptable accuracy level for your application, as this can significantly impact process control.
- Installation Environment: Consider whether the rotameter will be installed in a cleanroom, outdoor setting, or hazardous location.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchasing decision, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients within your industry. This will help you gauge the supplier’s reliability and expertise.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and feedback from previous customers.
- Experience in Your Industry: Ensure the supplier has a proven track record in providing rotameters for your specific application.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the rotameter flow indicators meet relevant industry standards and certifications. Compliance with international standards such as ISO, CE, or ATEX can be indicative of quality and reliability.
- Quality Assurance: Check for certifications that validate the manufacturing process and product quality.
- Safety Standards: Confirm that the product adheres to safety regulations pertinent to your industry.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, lead times, and warranty information. This step is crucial for comparing different options and understanding the total cost of ownership.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the quote provides a clear breakdown of all costs, including shipping and installation if applicable.
- Warranty Terms: Review the warranty policy to understand the supplier’s commitment to product support.
Step 6: Consider After-Sales Support
Evaluate the level of after-sales support offered by the supplier. Reliable support can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs, especially in critical applications.
- Technical Assistance: Ensure that the supplier offers technical support for installation and troubleshooting.
- Training Services: Inquire if the supplier provides training for your staff on proper use and maintenance of the rotameter.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Decision
After careful consideration of all the factors outlined in this guide, finalize your purchase decision. Ensure that all terms are clearly defined in the purchase agreement, including delivery timelines, payment terms, and return policies.
- Documentation: Keep all correspondence and agreements documented for future reference.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback mechanism to communicate with the supplier regarding product performance and any issues that may arise post-purchase.
By following this checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing process for rotameter flow indicators is thorough, informed, and aligned with your operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rotameter flow indicator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Rotameter Flow Indicators?
When sourcing rotameter flow indicators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Rotameters can be made from plastic, metal, or glass, with variations in durability and chemical resistance. Higher-grade materials often lead to increased costs but may result in longer service life and reduced maintenance needs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the manufacturing process and the region of production. Regions with lower labor costs can offer more competitive pricing; however, this may come with trade-offs in quality or delivery times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, leading to cost savings that can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized rotameters can be expensive. However, once initial investments are made, the costs per unit typically decrease with higher production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential for ensuring product reliability. While these processes incur additional costs, they can prevent costly failures and enhance customer satisfaction in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, weight, and shipping method. International buyers should factor in tariffs and customs duties, which can substantially affect the overall cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin, which can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Rotameter Flow Indicators?
Several factors influence the final pricing of rotameter flow indicators:
-
Volume/MOQ: Buyers looking for bulk purchases often benefit from reduced pricing. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can also affect the cost structure; negotiating lower MOQs can help smaller businesses enter the market.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customization to meet specific application needs can increase costs. Standard models are generally more affordable, while tailored solutions may require additional engineering and manufacturing resources.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Certifications for industry standards (e.g., ISO, CE) can add to costs but are essential for ensuring compliance, especially in regulated industries. Higher quality materials typically command a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to perceived quality and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define shipping responsibilities. For instance, choosing Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) may lead to higher upfront costs but simplifies logistics and risk management.
What Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips Should Buyers Consider?
To maximize value when sourcing rotameter flow indicators, buyers should consider the following tips:
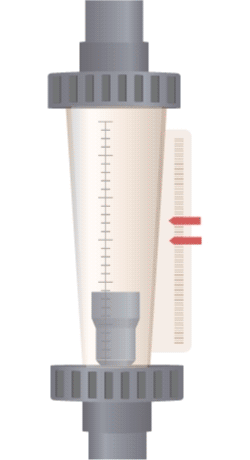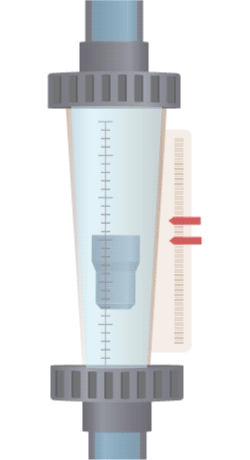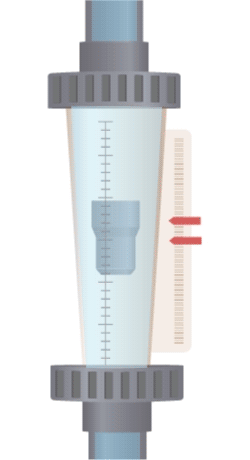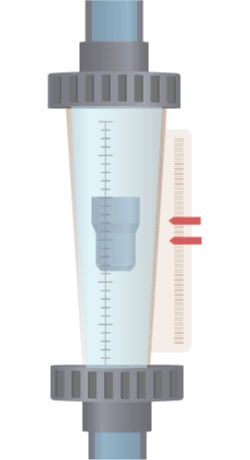
Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Leverage multiple quotes to establish a competitive environment.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, assess the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower operational expenses over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and logistics challenges. Building relationships with local distributors can help mitigate these issues.
-
Leverage Bulk Buying: Consider consolidating orders with other businesses to reach higher volume discounts, especially when dealing with suppliers that have MOQs.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor market trends and pricing fluctuations to make informed purchasing decisions. This knowledge can also provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that the prices of rotameter flow indicators can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. The pricing information provided in this analysis serves as an indicative reference and may not reflect the final costs incurred by buyers. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rotameter flow indicator With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Rotameter Flow Indicators
In the field of flow measurement, selecting the right instrument is crucial for ensuring accuracy and efficiency. While rotameter flow indicators are widely used due to their simplicity and reliability, there are alternative solutions available that may better suit specific applications. This section explores these alternatives, comparing their performance, costs, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and best-use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Rotameter Flow Indicator | Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Ultrasonic Flow Meter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate accuracy (±2-6%) | High accuracy (±0.5-2%) | High accuracy (±1-2%) |
| Cost | Low to moderate ($75-$2500) | Moderate to high ($500-$5000) | Moderate to high ($1000-$3000) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, vertical orientation required | Requires electrical supply, complex setup | Simple installation, often portable |
| Maintenance | Low, minimal moving parts | Moderate, requires calibration | Low, no moving parts |
| Best Use Case | Low to moderate flow rates, non-viscous fluids | Conductive liquids, high flow rates | Non-conductive fluids, varying temperatures |
Electromagnetic Flow Meters: Advantages and Disadvantages
Electromagnetic flow meters operate based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, making them suitable for measuring the flow of conductive liquids. They offer high accuracy and are ideal for applications involving wastewater, chemicals, and slurries. However, they tend to be more expensive than rotameters and require a stable electrical supply for operation. Maintenance can be moderate due to the need for periodic calibration, but they provide excellent performance for industrial applications where precision is critical.
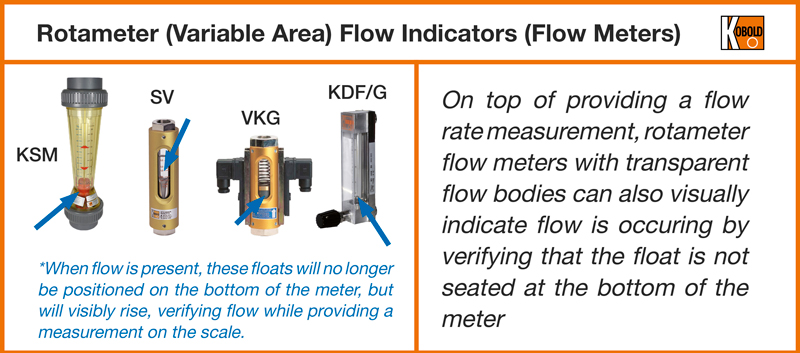
Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Pros and Cons
Ultrasonic flow meters utilize sound waves to measure the flow rate of liquids and gases. They are known for their non-invasive operation and high accuracy. These meters can be used for a variety of fluids, including clean and dirty liquids, making them versatile. Their installation is often straightforward, and they can be portable for temporary applications. However, they can be more expensive than rotameters and may not perform well with highly viscous or aerated fluids. Regular calibration may also be necessary to maintain accuracy.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Flow Measurement Solution
Choosing the right flow measurement solution depends on various factors, including the type of fluid, required accuracy, budget constraints, and installation conditions. Rotameter flow indicators are an excellent choice for straightforward applications with low to moderate flow rates. However, for more demanding environments or specific fluid types, electromagnetic or ultrasonic flow meters may offer the accuracy and versatility needed. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their unique operational requirements and consider consulting with industry experts to make an informed decision that aligns with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rotameter flow indicator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Rotameter Flow Indicator?
Understanding the essential technical properties of rotameter flow indicators is crucial for businesses looking to invest in effective flow measurement solutions. Below are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material of the rotameter can significantly impact its durability and compatibility with various fluids. Common materials include glass, plastic, and metal (like stainless steel). For example, glass rotameters are suitable for low-pressure applications and offer high visibility, while metal variants are better for high-pressure and aggressive media. Choosing the right material ensures longevity and reliability, reducing the risk of costly downtime. -
Flow Range
This specification defines the minimum and maximum flow rates that the rotameter can accurately measure. Understanding the flow range is vital for ensuring the device will meet specific operational needs. A rotameter that operates outside its designated flow range may yield inaccurate readings, leading to inefficiencies or even system failures. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the rotameter can withstand without failure. It is essential for applications where the fluid is under high pressure. Selecting a rotameter with an appropriate pressure rating ensures safety and operational efficiency, preventing leaks or bursts that could lead to significant financial and operational repercussions. -
Accuracy
Accuracy is a critical parameter that defines how closely the rotameter’s measurement aligns with the actual flow rate. Typical accuracy specifications might range from ±2% to ±6% of the full scale. High accuracy is particularly important in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, where precise flow measurements are crucial for compliance and product quality. -
Temperature Tolerance
Rotameters must be able to operate effectively within specific temperature ranges. Some applications may expose the rotameter to extreme temperatures, which can affect the performance and integrity of the device. Understanding the temperature tolerance helps in selecting a rotameter that can withstand the operational environment, ensuring reliable performance. -
Installation Orientation
Rotameters generally need to be installed vertically to function correctly, as the float relies on gravity to provide accurate readings. Failing to install the device as required can lead to inaccurate measurements, which can adversely affect processes. This consideration is particularly important in installation planning and system design.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in the Rotameter Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology enhances communication and ensures smoother transactions. Here are some common trade terms relevant to rotameter flow indicators:
Illustrative image related to rotameter flow indicator
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of rotameters, an OEM may provide custom solutions tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help businesses secure specialized equipment that meets their unique requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers looking to optimize their inventory and costs. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchasing strategies effectively, especially in regions with fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for prices and terms for specific products or services. For rotameters, an RFQ can help businesses obtain competitive quotes, allowing them to compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international B2B transactions involving rotameters, as they define who bears the costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process. -
Calibration
Calibration refers to the process of adjusting the rotameter to ensure its measurements are accurate. Regular calibration is essential for maintaining measurement integrity, especially in regulated industries. Buyers should inquire about calibration services to ensure their rotameters remain reliable over time. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For businesses requiring rotameters, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that operations run smoothly without delays.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rotameter flow indicator Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Rotameter Flow Indicator Sector?
The rotameter flow indicator sector is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. As industries increasingly adopt automation and digital solutions, the demand for reliable and precise flow measurement devices, such as rotameters, is on the rise. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly seeing heightened activity due to burgeoning industrial sectors, including oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage. These regions are investing in infrastructure development, which necessitates accurate flow measurement for process optimization and safety.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are transforming traditional flow measurement practices. Smart rotameters that integrate with digital platforms enable real-time monitoring and data analysis, enhancing operational efficiency. Furthermore, the trend towards automation in manufacturing processes is increasing the need for more sophisticated flow measurement solutions. Buyers are now looking for rotameters that not only meet basic requirements but also offer additional functionalities such as remote monitoring, which can lead to cost savings and improved decision-making.
Additionally, the competitive landscape is evolving, with manufacturers focusing on offering customizable solutions tailored to specific applications. This trend allows international buyers to source rotameters that align closely with their operational needs, thus enhancing their procurement strategies. As companies prioritize reliability and accuracy, the demand for high-quality rotameters that can withstand varying conditions will continue to grow.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends for Rotameter Flow Indicators?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of rotameter flow indicators. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, coupled with increasing regulatory pressures, is prompting companies to seek ethically sourced materials and environmentally friendly practices. For international buyers, particularly those operating in regions with stringent environmental regulations, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to sustainable practices is essential.
Ethical supply chains are gaining importance, and buyers are encouraged to collaborate with manufacturers that prioritize transparency and sustainability in their operations. This includes sourcing materials with lower environmental footprints, such as recycled or biodegradable components. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are becoming valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in rotameter production not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances product durability and performance. Buyers are increasingly recognizing the long-term benefits of investing in sustainable technologies, as they often lead to reduced operational costs and improved brand reputation. In this context, aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals can provide a competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
What Is the Historical Context of Rotameters and Their Relevance Today?
The history of rotameters dates back to the early 20th century, when they were first introduced as a simple and effective means of measuring fluid flow. Based on the principle of variable area flow measurement, these devices have evolved significantly over the decades. Initially, rotameters were primarily used in laboratories and small-scale applications; however, their reliability and cost-effectiveness have led to widespread adoption across various industries.
Today, rotameters are integral to numerous applications, from water treatment facilities to chemical processing plants. Their straightforward design and low maintenance requirements make them appealing to international buyers looking for dependable flow measurement solutions. As industries continue to evolve, the adaptability of rotameters to different fluids and conditions ensures their sustained relevance in the global market.
In summary, understanding the historical context and current trends in the rotameter flow indicator sector is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rotameter flow indicator
-
1. How do I select the right rotameter flow indicator for my application?
Choosing the right rotameter involves evaluating several factors, including the type of fluid being measured (liquid or gas), flow rate, viscosity, and pressure requirements. You should also consider whether you need a local display or electronic output. It’s essential to assess the chemical compatibility of the fluid with the wetted parts of the flow meter. Additionally, ensure that the installation environment allows for vertical mounting, as this is crucial for accurate readings. -
2. What are the common applications for rotameter flow indicators?
Rotameters are versatile instruments commonly used in various industries, including water treatment, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage processing, and petrochemical applications. They effectively measure flow rates for gases and liquids in both laboratory and industrial settings. Specific applications may include boiler feedwater, compressed air systems, and fermentation processes. Understanding the specific needs of your industry will help you select the most suitable rotameter. -
3. What are the typical lead times for ordering rotameter flow indicators?
Lead times for rotameter orders can vary significantly based on factors such as supplier location, customization requirements, and order quantity. Standard models may have shorter lead times, typically ranging from 2 to 4 weeks, while custom designs may take longer, often 6 to 8 weeks or more. It’s advisable to communicate with suppliers early in the procurement process to understand their timelines and plan accordingly, especially for international shipping. -
4. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for rotameter flow indicators?
Many manufacturers and suppliers impose a minimum order quantity (MOQ) for rotameters, especially for customized units. MOQs can vary from as low as 5 to 10 units for standard models to higher quantities for specialized designs. It’s crucial to inquire about the MOQ when negotiating with suppliers to ensure it aligns with your purchasing needs and budget. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing rotameters internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include upfront payment, 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment, or net 30/60 days post-delivery. International buyers should also consider currency exchange rates and potential bank fees. Discussing payment terms early in the negotiation process can help establish clear expectations and facilitate a smoother transaction. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing rotameters?
To ensure quality assurance, select suppliers that adhere to recognized industry standards, such as ISO certifications. Request product samples or detailed specifications before placing a bulk order. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or third-party inspections to verify manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Establishing a strong communication channel with your supplier can also help address any concerns regarding product quality. -
7. What shipping and logistics options are available for international rotameter orders?
Shipping options for international orders typically include air freight, sea freight, and courier services. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Discuss with your supplier about their logistics partners and available shipping methods. Additionally, consider customs clearance procedures and associated duties to avoid unexpected delays or costs. -
8. How do I handle issues or defects with rotameter flow indicators after purchase?
In the event of defects or issues with your rotameter, promptly contact the supplier to discuss the problem. Most reputable suppliers offer warranties or return policies, which should be outlined in your purchase agreement. Document any defects with photographs and detailed descriptions to facilitate the claims process. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can help resolve issues more efficiently and may provide access to technical support or replacements.
Top 6 Rotameter Flow Indicator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Brooks Instrument – Variable Area Flow Meters
Domain: brooksinstrument.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Variable Area Flow Meters (Rotameters) from Brooks Instrument are designed for maximum repeatability and reliability in measuring gas and liquid flow rates across various industries. Key features include:
– Reliable, easy-to-read displays for gas, fluid, and water flow meters.
– Fail-safe inline flow indication.
– Integral flow controller for pressure compensation.
– Materials and designs suitabl…
2. Yokogawa – Rotameters
Domain: yokogawa.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rotameters, also known as Variable Area Flow Meters, are used for measuring the flow rate of liquids and gases. They operate based on the principle of variable area, where the flow rate is indicated by the position of a float within a tapered tube. Yokogawa offers a range of rotameters suitable for various industries including oil & gas, chemical, power generation, water & wastewater, and food & b…
3. Blue-White – F-400N Flow Meter
Domain: blue-white.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: [{‘model’: ‘F-400N’, ‘flow_rate’: ‘0.5-5 GPM’, ‘material’: ‘ACRYLIC’, ‘connection_size’: ‘.50″ F/NPT’, ‘price’: ‘$144.00’}, {‘model’: ‘F-300’, ‘flow_rate’: ’20-120 GPM’, ‘connection_size’: ‘2.00″ PIPE’, ‘price’: ‘$155.00’}, {‘model’: ‘F-440’, ‘flow_rate’: ‘1-10 GPM’, ‘connection_size’: ‘.75″ M/NPT’, ‘type’: ‘INLINE’, ‘price’: ‘$166.00’}, {‘model’: ‘F-410N’, ‘flow_rate’: ‘2-20 GPM’, ‘material’: ‘AC…
4. DwyerOmega – Variable Area Flow Meters
Domain: dwyeromega.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Variable Area Flow Meter from DwyerOmega. Price range: $0-$49.99 (1), $50-$199.99 (17), $200-$499.99 (34), $500-$999.99 (37), $1,000-$9,999.99 (35). In Stock: Dwyer (20), Omega (47). Media Compatibility: Air (35), Alcohols (1), Alkaline solutions (1), Argon (4), Carbon dioxide (2), Helium (2), Hydraulic Oil (12), Hydrogen (2), Light Oil (11), Nitrogen (4), Oil (11), Oxygen (3), Steam (1), Water (5…
5. Bürkert – Rotameter Flow Meter
6. KROHNE – Variable Area Flowmeters
Domain: krohne.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Variable area flowmeters, also known as rotameters, are used for measuring the volumetric flow rate of conductive and non-conductive liquids and gases. They operate without auxiliary power and are suitable for low flow rates of clean liquids or gases. KROHNE offers various models including:
1. **H250 M40**: Modular design for liquids and gases, installation in any position, temperature range -196…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rotameter flow indicator
In summary, the strategic sourcing of rotameter flow indicators presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The inherent simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of rotameters make them an ideal choice for a range of applications, from agricultural processes to industrial manufacturing. Understanding the specific requirements of your fluid measurement needs—including flow rate, pressure, temperature, and compatibility—will greatly enhance your purchasing decision.
Investing in a tailored sourcing strategy not only ensures you procure the right flow meter for your application but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that can yield additional benefits, such as improved pricing and service support. As global markets continue to evolve, prioritizing strategic sourcing will empower your organization to stay competitive and responsive to industry demands.
Looking ahead, we encourage international buyers to explore the diverse offerings in the rotameter market. By leveraging local expertise and aligning with reputable suppliers, you can enhance operational efficiency and drive sustainable growth in your business. Take the next step in optimizing your flow measurement solutions today!
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.