Refinery Furnace Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for refinery furnace
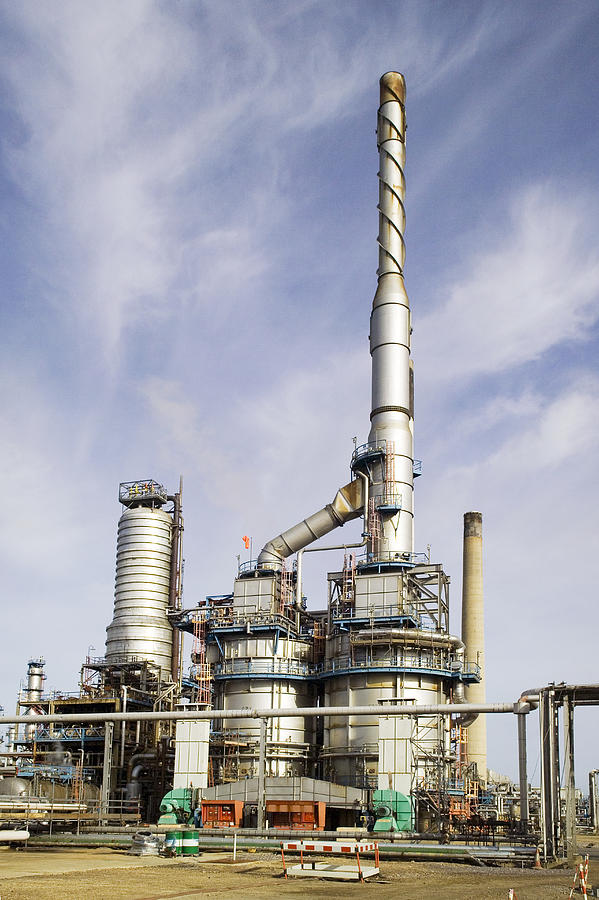
In the dynamic world of refinery operations, sourcing the right furnace is paramount for efficient production and competitive advantage. Refinery furnaces, essential for heating and vaporizing hydrocarbon fluids, are critical components in the production of fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. However, international B2B buyers often face significant challenges in identifying the ideal furnace types, applications, and suppliers that align with their operational needs and budgets.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted landscape of refinery furnaces, providing insights into various types, including fired heaters and process heaters, and their specific applications across different industries. We will also explore crucial aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and compliance with industry standards, ensuring that you have all the tools necessary for informed purchasing decisions.
Designed specifically for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global market confidently. By equipping you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, we aim to streamline your sourcing process, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately contribute to your business’s success in a competitive landscape.
Understanding refinery furnace Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cabin/Box Heater | Horizontal tube arrangement; compact design | Crude oil distillation | Pros: Space-efficient, easier maintenance. Cons: Limited heating capacity compared to cylindrical types. |
| Cylindrical Heater | Vertical tube arrangement; higher heat capacity | Heavy oil processing | Pros: Higher thermal efficiency, better suited for large-scale operations. Cons: Requires more space for installation. |
| Thermal Oxidizer | Combines combustion with heat recovery; reduces emissions | Waste gas treatment | Pros: Environmentally friendly, energy recovery. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex operation. |
| Indirect Fired Heater | Uses heat exchangers; minimizes direct contact with flame | Chemical processing | Pros: Enhanced safety, better temperature control. Cons: More expensive to install and maintain. |
| Direct Fired Heater | Direct combustion for heating; simple design | General heating applications | Pros: Cost-effective, straightforward operation. Cons: Lower energy efficiency, higher emissions. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Cabin/Box Heaters?
Cabin or box heaters are characterized by their horizontal tube arrangement, which allows for a compact design ideal for space-limited refinery environments. They are predominantly used in crude oil distillation processes where moderate heating is required. Buyers should consider the ease of maintenance and lower footprint of these heaters, making them a practical choice for smaller operations. However, their heating capacity is limited compared to other types, which may not suit larger-scale applications.
How Do Cylindrical Heaters Stand Out in Refinery Applications?
Cylindrical heaters feature a vertical arrangement of tubes, which enables them to achieve higher thermal efficiency and heat capacity. They are extensively used in heavy oil processing, making them suitable for larger refineries that require significant heating power. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate their spatial requirements and operational scale since these heaters require more installation space. The benefits of improved efficiency must be weighed against the larger footprint.
Why Choose Thermal Oxidizers for Emission Control?
Thermal oxidizers are unique in their ability to combine combustion processes with heat recovery, making them an excellent choice for waste gas treatment applications. They are particularly valued for their environmentally friendly operation, as they significantly reduce emissions while recovering energy. B2B buyers should consider the higher initial investment and complexity of operation; however, the long-term savings in energy and compliance with environmental regulations can justify the cost.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
What are the Advantages of Indirect Fired Heaters?
Indirect fired heaters utilize heat exchangers to provide thermal energy without direct contact with the flame, enhancing safety and control over the heating process. They are often used in chemical processing where temperature precision is crucial. Buyers should note the higher costs associated with installation and maintenance, but the benefits of improved safety and operational efficiency make them a worthwhile investment in sensitive applications.
When to Opt for Direct Fired Heaters?
Direct fired heaters are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for general heating applications across various industries. Their straightforward design allows for easy operation and lower upfront costs. However, buyers must be mindful of the lower energy efficiency and higher emissions associated with these heaters. This type is best for operations with less stringent environmental regulations and those prioritizing budget over efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of refinery furnace
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of refinery furnace | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Heating and vaporizing crude oil for distillation processes | Maximizes yield of high-demand fuels such as gasoline and diesel | Efficiency ratings, compliance with API standards |
| Petrochemical | Production of ethylene and propylene through steam cracking | Enhances production efficiency and lowers operational costs | Material durability, heat transfer capabilities |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Pre-heating feedstock for chemical reactions | Improves reaction rates and product quality | Temperature control, safety features, and emissions |
| Power Generation | Providing heat for combined cycle power plants | Increases overall energy efficiency and reduces fuel consumption | Fuel type compatibility, emissions control technologies |
| Renewable Energy | Biomass conversion to biofuels via thermal processes | Supports sustainable energy initiatives and reduces carbon footprint | Adaptability to different feedstocks, regulatory compliance |
How is ‘refinery furnace’ used in the Oil & Gas sector?
In the Oil & Gas industry, refinery furnaces are crucial for heating and vaporizing crude oil during the distillation process. This application is vital for maximizing the yield of high-demand fuels such as gasoline and diesel. International buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Africa, should consider sourcing furnaces that meet API standards for efficiency and safety. Additionally, understanding the local fuel types and operational conditions can help in selecting the right furnace model.
What role does the refinery furnace play in Petrochemical production?
In Petrochemical manufacturing, refinery furnaces are employed to produce ethylene and propylene through steam cracking. This process requires precise temperature control and efficient heat transfer to enhance production rates while minimizing energy costs. Buyers from South America and Europe should prioritize furnaces with advanced material durability and energy efficiency features to ensure long-term operational success and reduced downtime.
How does the refinery furnace enhance Chemical Manufacturing processes?
Refinery furnaces are utilized to pre-heat feedstock for various chemical reactions, significantly improving reaction rates and product quality. This application is essential for chemical manufacturers aiming to optimize production efficiency. For B2B buyers in Africa and Asia, selecting furnaces equipped with advanced safety features and precise temperature control mechanisms is crucial to mitigate risks associated with high-temperature operations.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
In what ways does the refinery furnace contribute to Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, refinery furnaces provide essential heat for combined cycle power plants. This application enhances overall energy efficiency and reduces fuel consumption, making it a strategic investment for energy companies. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing furnaces that are compatible with various fuel types and equipped with emissions control technologies to meet stringent environmental regulations.
How is the refinery furnace utilized in Renewable Energy initiatives?
Refinery furnaces play a significant role in converting biomass into biofuels through thermal processes. This application supports sustainable energy initiatives and helps reduce carbon footprints. International buyers, especially in regions like South America, should look for furnaces that can adapt to different feedstocks and comply with local regulations to ensure successful integration into renewable energy projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘refinery furnace’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Heat Transfer Leading to Increased Operational Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of inefficient heat transfer in refinery furnaces, which can lead to higher energy consumption and operational costs. When the heat transfer efficiency drops, it often results from issues like coking, fouling, or inadequate airflow, which can compromise the entire heating process. This inefficiency not only increases fuel costs but may also necessitate more frequent maintenance, further straining budgets and resources.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should prioritize regular maintenance and monitoring of heat transfer components. Implementing a predictive maintenance schedule, including inspections of convection and radiant sections, can help identify coking or fouling before they escalate. Additionally, investing in advanced monitoring technologies such as infrared thermography can provide real-time data on heat distribution and identify hotspots that indicate inefficiencies. By ensuring that the furnace is designed and operated according to API standards, buyers can enhance heat transfer efficiency and reduce overall operating costs.
Scenario 2: Equipment Downtime Due to Flue Gas Management Issues
The Problem: Another common pain point is the challenge of managing flue gases effectively. Poor flue gas management can lead to unsafe operating conditions, equipment downtime, and potential regulatory fines. Issues such as improper draft systems or malfunctioning exhaust stacks can create back pressure, leading to reduced furnace performance and increased emissions, which can be particularly problematic in regions with stringent environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
The Solution: To address flue gas management issues, buyers should evaluate and optimize their draft systems. This can include transitioning to a balanced draft system that utilizes both forced and induced draft fans for optimal airflow. Conducting a flue gas analysis will provide insights into the combustion process and help identify inefficiencies. It’s also vital to ensure that all components, including stacks and dampers, are correctly sized and functioning to facilitate proper exhaust flow. Investing in advanced flue gas treatment technologies can further ensure compliance with environmental standards while improving overall furnace reliability.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Specifying the Right Furnace Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate type of refinery furnace for their specific applications, such as heavy oil processing or petrochemical production. With various styles available, including cabin and cylindrical heaters, the decision can be overwhelming. An incorrect specification can lead to suboptimal performance, increased maintenance, and even safety hazards, which can compromise production schedules and profitability.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment that includes evaluating the specific characteristics of the hydrocarbons being processed, the desired output temperatures, and the operational environment. Consulting with experienced manufacturers or industry experts can provide invaluable insights into which furnace design will best meet operational needs. Additionally, buyers should consider future scalability and flexibility; opting for modular designs may allow for easier upgrades as production needs evolve. Providing detailed operational parameters during the procurement process will ensure that the selected furnace aligns with the refinery’s overall objectives, ultimately leading to improved performance and reduced risk.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for refinery furnace
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Refinery Furnaces?
Selecting the right materials for refinery furnaces is crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and maintaining compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of refinery furnaces: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steels, and ceramic materials.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Refinery Furnaces?
Carbon steel is widely used in refinery furnaces due to its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and can handle moderate pressure levels. The primary advantages of carbon steel include its durability and ease of fabrication, making it a preferred choice for many applications.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
However, carbon steel has limitations, particularly concerning corrosion resistance. In environments with high sulfur content or acidic conditions, carbon steel can degrade quickly, leading to potential failures. For international buyers, especially in regions like the Middle East and South America where high temperatures and corrosive environments are common, it is essential to consider protective coatings or linings to enhance longevity.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Refinery Furnaces?
Stainless steel is another popular material for refinery furnaces, particularly in components exposed to corrosive media. Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, stainless steel can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,800°F or 982°C) and is suitable for high-pressure applications. Its ability to maintain structural integrity in harsh environments makes it a reliable choice.
The downsides of stainless steel include higher costs and manufacturing complexities compared to carbon steel. Additionally, while it performs well in many environments, it may not be suitable for applications involving certain types of chlorides. Buyers from Europe and Africa should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 or EN 10088 to guarantee quality.
How Do Alloy Steels Compare for High-Temperature Applications?
Alloy steels, which include various combinations of elements like chromium, molybdenum, and nickel, offer enhanced performance in high-temperature applications. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 1,800°F (982°C) and provide excellent strength and toughness. The versatility of alloy steels makes them suitable for various furnace designs and operational conditions.
However, the complexity of manufacturing and higher costs can deter some buyers. Additionally, alloy steels may require specific heat treatment processes to achieve desired properties, which could complicate logistics. For international buyers, especially in regions with stringent regulations like Europe, ensuring compliance with relevant standards (e.g., ASTM A335) is critical for successful procurement.
What Role Do Ceramic Materials Play in Refinery Furnaces?
Ceramic materials are increasingly being used in furnace linings due to their exceptional thermal resistance and low thermal conductivity. They can withstand temperatures up to 2,200°F (1,200°C) and are highly resistant to corrosive environments, making them ideal for protecting steel structures from high-temperature flue gases.
The main drawback of ceramics is their brittleness, which can pose challenges during installation and operation. Additionally, the cost of ceramic materials can be high, and they may require specialized installation techniques. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of skilled labor for installation and maintenance when opting for ceramic materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Refinery Furnaces
| Material | Typical Use Case for refinery furnace | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components in furnaces | Cost-effective and durable | Poor corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Alloy Steels | High-temperature applications | Enhanced strength and toughness | Higher cost and specific heat treatment | Medium |
| Ceramic Materials | Furnace linings | Exceptional thermal resistance | Brittleness and high installation costs | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers in the refinery sector, particularly those operating in diverse and challenging environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can significantly influence purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for refinery furnace
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Refinery Furnace?
Manufacturing a refinery furnace involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the rigorous demands of the petrochemical industry. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring quality, efficiency, and durability.
How Is Material Prepared for Refinery Furnace Production?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where high-quality steel is selected for its heat resistance and structural integrity. Common materials include carbon steel and alloy steels, which are chosen based on their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
Before fabrication, the materials undergo rigorous inspection to verify their chemical composition and mechanical properties. This ensures that they meet international standards, such as ASTM specifications. Additionally, suppliers often provide certificates of compliance, which can be reviewed by B2B buyers to ensure material integrity.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming the Components of a Refinery Furnace?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This includes processes such as cutting, bending, and welding to create components like tubes, casings, and headers. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are commonly used to achieve precise dimensions and complex geometries, which are essential for optimal heat transfer and structural strength.
Welding is particularly crucial, as it connects various components and must withstand high pressure and temperature. Techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are frequently utilized due to their high-quality results.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Refinery Furnaces?
After forming, the assembly phase begins. This involves fitting together the various components, including the radiant and convection sections, and ensuring that all joints are secure and leak-proof. During this phase, it is essential to follow detailed assembly instructions and industry guidelines, such as those set by the American Petroleum Institute (API).
Quality control measures, such as visual inspections and non-destructive testing (NDT), are conducted at this stage to identify any defects or weaknesses in the assembly. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing and radiographic inspection, which help ensure the integrity of welds and joints.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Enhance the Durability of Refinery Furnaces?
The finishing stage focuses on surface treatment and coatings that enhance corrosion resistance and thermal efficiency. Common techniques include sandblasting, painting, and applying ceramic or refractory linings. These treatments not only protect the furnace from harsh operating conditions but also improve its overall efficiency by optimizing heat retention.
Additionally, quality checks are performed to ensure that the finished product meets the specifications and is free from defects. This includes dimensional checks and surface quality inspections.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Refinery Furnace Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for refinery furnaces. Implementing a robust QA program helps ensure that the furnaces meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Refinery Furnace Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO standards assures B2B buyers that manufacturers adhere to established quality protocols.
Moreover, industry-specific standards such as CE marking and API certifications are essential for refinery furnaces. These certifications verify that the product meets safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which is particularly important for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor and verify quality. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to identify and rectify defects early in the process, minimizing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the completed furnace undergoes comprehensive testing, including pressure tests and performance evaluations, to ensure it meets all design and safety requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring product reliability.
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request from Suppliers?
Buyers should request documentation such as quality management system (QMS) audits, inspection reports, and certificates of compliance. Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and practices.
Additionally, third-party inspections can be arranged to validate the manufacturing process and quality assurance measures. Engaging independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of the specific regulatory requirements and standards applicable in their regions. For instance, different countries may have varying safety and environmental standards that must be adhered to. Understanding these nuances helps buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers and negotiating contracts.
Furthermore, cultural differences in business practices may affect communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting explicit quality expectations can help bridge these gaps.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Refinery Furnace Manufacturing
Manufacturing a refinery furnace involves a meticulous process that combines advanced techniques and strict quality control measures. By understanding the stages of manufacturing and the relevant quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers. This knowledge not only helps ensure the durability and efficiency of refinery furnaces but also fosters long-term partnerships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘refinery furnace’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure a refinery furnace. Given the complexity and critical nature of these systems in refining operations, this checklist will help ensure that you make informed decisions while aligning with industry standards and best practices.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the right refinery furnace. Consider factors such as heating capacity, fuel type, and the specific processes you will be using the furnace for. This step will help you filter potential suppliers and ensure that the equipment meets your operational needs.
2. Assess Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the furnace complies with relevant industry standards, such as those set by the American Petroleum Institute (API). Compliance is essential for safety, efficiency, and regulatory adherence. Check for certifications and documentation that demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to quality and safety protocols.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s vital to conduct thorough evaluations. Look for company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or regions. This due diligence will provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and customer support.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
- Request Detailed Product Information: Ask for specifications, performance data, and maintenance requirements.
- Verify Supplier Experience: A supplier with extensive experience in refinery furnaces can better understand your unique needs.
4. Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Performing a cost-benefit analysis will help you understand the long-term value of the furnace. Consider not only the initial purchase price but also operating costs, maintenance expenses, and potential downtime. This comprehensive view will aid in determining the return on investment (ROI) for your procurement decision.
5. Inquire About After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
After-sales support can significantly impact the operational efficiency of your refinery furnace. Inquire about the availability of maintenance services, spare parts, and technical support. A supplier that offers robust support can help minimize downtime and ensure optimal performance over the furnace’s lifespan.
6. Evaluate Delivery and Installation Capabilities
The logistics surrounding delivery and installation are critical aspects of the procurement process. Confirm the supplier’s capability to deliver the furnace on time and in compliance with your operational schedule. Additionally, ensure they have qualified personnel for installation to avoid operational disruptions.
7. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, before finalizing your purchase, negotiate the terms and conditions carefully. Discuss payment terms, warranties, and any potential penalties for non-compliance. Clear contractual agreements will protect your interests and ensure a smoother transaction.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for a refinery furnace and make informed decisions that align with your operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for refinery furnace Sourcing
When sourcing a refinery furnace, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will help buyers navigate the complexities of procurement and secure competitive pricing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Refinery Furnace Sourcing?
The cost structure for a refinery furnace encompasses several components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include high-quality metals and refractory linings that can withstand extreme temperatures. The choice of materials significantly impacts the furnace’s longevity and efficiency, leading to variations in price.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and installation. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and local wage standards, influencing the overall price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower overhead costs, which may be reflected in the pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling is often required to produce custom designs. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial but may lead to cost savings in large volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the furnace meets industry standards and certifications involves rigorous quality control processes. High QC standards may increase costs but are essential for operational safety and efficiency.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary depending on the location of the supplier and the destination. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in defining responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and risk.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can be influenced by market conditions, competition, and supplier reputation.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Refinery Furnaces?
Several factors can significantly influence pricing:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to discounts. Buyers should consider their future needs to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed furnaces tailored to specific operational needs can increase costs. Buyers must balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as API standards) can lead to higher prices but offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, experience, and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but could offer superior support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is essential, as they define who is responsible for shipping costs and risks. This can significantly impact the total landed cost.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Refinery Furnaces?
To secure favorable pricing, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Engage in Strategic Negotiation: Leverage volume purchasing or long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Highlighting the potential for repeat business can incentivize suppliers to offer discounts.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and efficiency. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that can affect pricing. Collaborating with local experts can mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of refinery furnaces is vital for international B2B buyers. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. It is important to note that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional factors, so buyers should continuously assess the market landscape.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing refinery furnace With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Refinery Furnaces in Industrial Applications
In the quest for efficient and effective heating solutions in industrial settings, particularly within the refining and petrochemical sectors, various technologies can serve as alternatives to traditional refinery furnaces. Each option presents its unique benefits and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to thoroughly evaluate these alternatives based on their specific operational needs.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Refinery Furnace | Indirect Fired Heater | Electric Heater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal efficiency, robust for large-scale operations | Moderate efficiency, suitable for specific applications | High precision, low thermal inertia |
| Cost | High initial investment, ongoing fuel costs | Moderate initial cost, lower operational costs | Lower initial investment, higher energy costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation, requires skilled labor | Easier setup, less space required | Simplified installation, minimal labor needed |
| Maintenance | High maintenance due to wear and tear | Moderate maintenance needs, easier access | Low maintenance, less frequent servicing |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large refineries needing high heat output | Best for smaller operations or specific heating tasks | Optimal for precision heating in smaller applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Indirect Fired Heater
Indirect fired heaters operate by heating a medium (such as oil or water) that then transfers heat to the process fluid without direct contact with combustion gases. This method can be advantageous in applications where product purity is crucial, as it reduces the risk of contamination.
Pros: They offer a moderate initial investment and lower operational costs, especially in terms of energy consumption. They are also easier to install and require less space compared to traditional refinery furnaces.
Cons: While effective for specific applications, their performance may not match that of refinery furnaces in terms of thermal output, making them less suitable for large-scale operations.
2. Electric Heater
Electric heaters utilize electrical resistance to generate heat, providing an efficient and precise heating solution. This method is particularly advantageous for industries requiring exact temperature control and where emissions regulations are stringent.
Pros: They generally have a lower initial investment and simplified installation processes, which can be beneficial for smaller operations or facilities looking to minimize downtime. Their maintenance requirements are also significantly lower, leading to reduced operational interruptions.
Cons: The primary downside is the higher energy costs associated with electricity, which can become a significant factor in larger operations. Additionally, their heating capacity may not suffice for high-volume applications, making them less ideal for traditional refining processes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors, including the scale of their operations, budget constraints, and specific heating requirements. Refinery furnaces excel in high-demand environments, while indirect fired heaters and electric heaters offer viable alternatives for smaller, more specialized applications. Ultimately, the choice should align with operational goals, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that the selected technology optimally meets the company’s needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for refinery furnace
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Refinery Furnace?
When selecting a refinery furnace, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the furnace components, particularly tubes and casing, is vital for durability and resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Common materials include carbon steel, alloy steels, and stainless steels. Selecting the right material grade can prevent premature wear and reduce maintenance costs, making it essential for long-term operational efficiency.
2. Temperature Rating
Furnaces operate at high temperatures, often exceeding 2,200°F (1,200°C). The temperature rating indicates the maximum operational temperature a furnace can handle without risking structural integrity. Understanding temperature ratings helps buyers ensure that the furnace can meet the specific heating requirements of their refining processes, thereby maximizing productivity and safety.
3. Heat Transfer Efficiency
Heat transfer efficiency refers to how effectively a furnace converts fuel energy into usable heat for processing fluids. This efficiency is influenced by design factors such as tube arrangement and surface area. High efficiency reduces fuel consumption and operational costs, providing a competitive edge in the refining sector. Buyers should prioritize furnaces with high heat transfer capabilities to improve overall plant performance.
4. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating determines the maximum internal pressure a furnace can safely withstand. This property is crucial in processes involving volatile substances, as improper pressure management can lead to catastrophic failures. Buyers must ensure that the furnace’s pressure rating aligns with their operational requirements to enhance safety and reliability.
5. Emission Control Compliance
Compliance with environmental regulations is increasingly important in the refining industry. Furnaces must be designed to minimize emissions of flue gases and other pollutants. Understanding the emission control technologies integrated into the furnace—such as flue gas recirculation or advanced burner systems—can help buyers meet regulatory standards while maintaining operational efficiency.
Which Trade Terms Should Buyers Know When Purchasing a Refinery Furnace?
In the B2B marketplace, familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common trade terms relevant to refinery furnace procurement:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of refinery furnaces, knowing whether you are dealing directly with the OEM or a reseller can affect warranties, support, and pricing. Buyers should seek OEM partnerships for reliable quality and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their specific needs to avoid overstocking or undersupply situations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific goods or services. For refinery furnaces, an RFQ should detail technical specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. This process helps buyers compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for clarifying shipping costs and risk management. Buyers should ensure that the terms of sale align with their logistics strategies.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Knowing the lead time for a refinery furnace is essential for project planning and operational scheduling. Buyers should factor in lead times when making procurement decisions to ensure timely project execution.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing refinery furnaces, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the refinery furnace Sector
What Are the Current Global Drivers Influencing the Refinery Furnace Market?
The refinery furnace sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by several global factors. The ongoing transition towards renewable energy sources and stricter environmental regulations are reshaping market dynamics. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking efficiency and sustainability in their sourcing strategies. This shift is pushing manufacturers to innovate, leading to the development of advanced fired heaters that optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions.
Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
Another key trend is the growing adoption of digital technologies such as IoT and AI in refinery operations. These technologies enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing for improved operational efficiency. For international B2B buyers, investing in such technologies can yield significant cost savings and enhance competitiveness in an increasingly regulated market.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to diversify their sourcing strategies. Buyers are now prioritizing local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global logistics and ensure timely delivery. As a result, suppliers who can demonstrate reliability and flexibility in meeting diverse needs will have a competitive advantage.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Refinery Furnace Sector?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the refinery furnace market. The environmental impact of fossil fuel consumption is under scrutiny, prompting companies to prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing, including the use of responsibly sourced materials and energy-efficient technologies, is becoming a baseline requirement rather than a competitive differentiator.
Buyers should actively seek suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicates effective environmental management systems. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Moreover, the use of alternative materials in furnace manufacturing, such as recycled metals and low-emission fuels, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with refinery operations. By integrating sustainability into their sourcing strategies, international buyers can not only comply with regulatory standards but also position themselves favorably in the market.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
What Is the Historical Context of the Refinery Furnace Market?
The evolution of the refinery furnace market is closely linked to the broader development of the petroleum industry. Since the early 20th century, advancements in technology have transformed how crude oil is processed, with fired heaters playing a pivotal role in heating and vaporizing hydrocarbons. Early designs were rudimentary, focusing primarily on functionality, but as demand for efficiency and safety grew, so did the complexity of furnace designs.
The introduction of advanced materials and combustion technologies in the late 20th century allowed for higher operational temperatures and better energy efficiency. These developments paved the way for the modern fired heater, which now incorporates sophisticated control systems and safety features. Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing innovation in the sector and the importance of selecting suppliers who are at the forefront of these advancements.
Overall, the refinery furnace market continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and changing market dynamics, offering B2B buyers numerous opportunities to enhance their operations and align with global trends.

Illustrative image related to refinery furnace
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of refinery furnace
-
How do I solve issues with heat transfer in my refinery furnace?
To address heat transfer problems in a refinery furnace, start by ensuring that the process fluid is flowing optimally through the heating tubes. Regular maintenance checks can identify issues like coking or fouling, which can restrict flow and insulate the tube walls, leading to inefficient heating. Implementing a monitoring system to track temperature and pressure can also help identify anomalies early. Additionally, consider upgrading to finned tubes to increase heat absorption or reviewing your combustion efficiency to optimize heat transfer performance. -
What is the best type of refinery furnace for high-capacity operations?
For high-capacity operations, a cylindrical or box-fired heater is often recommended due to their ability to handle large volumes of hydrocarbon fluids efficiently. Cylindrical designs can provide better heat distribution and are often more compact, which can be advantageous in space-constrained facilities. It’s essential to assess the specific requirements of your operations, such as the type of feedstock and desired output, to select a furnace that meets both performance and efficiency standards. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for refinery furnaces?
When vetting suppliers for refinery furnaces, consider their experience and reputation in the industry, especially in your region. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record of delivering quality equipment that complies with international standards, such as those set by the American Petroleum Institute (API). Request case studies or references from previous clients to assess their reliability. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s ability to provide ongoing support and maintenance services post-installation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for refinery furnaces?
Minimum order quantities for refinery furnaces can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the equipment. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for specialized custom designs to larger quantities for standard models. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine their MOQs and negotiate terms that fit your project requirements. Be sure to also consider lead times and production schedules in your planning. -
How can I customize my refinery furnace to meet specific operational needs?
Customizing a refinery furnace involves collaborating closely with the manufacturer to define your operational specifications, such as capacity, fuel type, and heat transfer efficiency. Many manufacturers offer options for materials, burner configurations, and control systems to tailor the furnace to your unique process requirements. Engage in thorough discussions about your needs and ensure that the supplier can provide the necessary engineering support throughout the customization process to guarantee optimal performance. -
What payment terms are typically offered for refinery furnace purchases?
Payment terms for refinery furnace purchases can vary based on the supplier and the scale of the transaction. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger purchases. It’s essential to review the payment terms in detail and negotiate them to ensure they align with your budget and cash flow considerations. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from a supplier?
A reputable supplier should have robust quality assurance measures in place, including adherence to international standards such as ISO certifications. They should conduct thorough inspections and testing of the furnace components throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring compliance with specifications. Request documentation of their QA processes, including material certifications and testing reports, to ensure that the furnace will operate safely and efficiently within your facility. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing a refinery furnace?
When importing a refinery furnace, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and local infrastructure. Verify that the supplier can manage the logistics process, including transportation arrangements and documentation for customs clearance. Assess the delivery timelines to ensure they align with your project schedule. Additionally, be prepared for installation logistics, including site preparation and coordination with local contractors or engineers for safe assembly and operation.
Top 5 Refinery Furnace Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. XRG Technologies – Fired Heaters
Domain: xrgtechnologies.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Fired heaters, or process heaters, are essential in refineries and petrochemical plants for heating and vaporizing hydrocarbon fluids to produce gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. Key features include:
– Heat production through fuel combustion, transferring heat to process fluids via conduction, radiation, and convection.
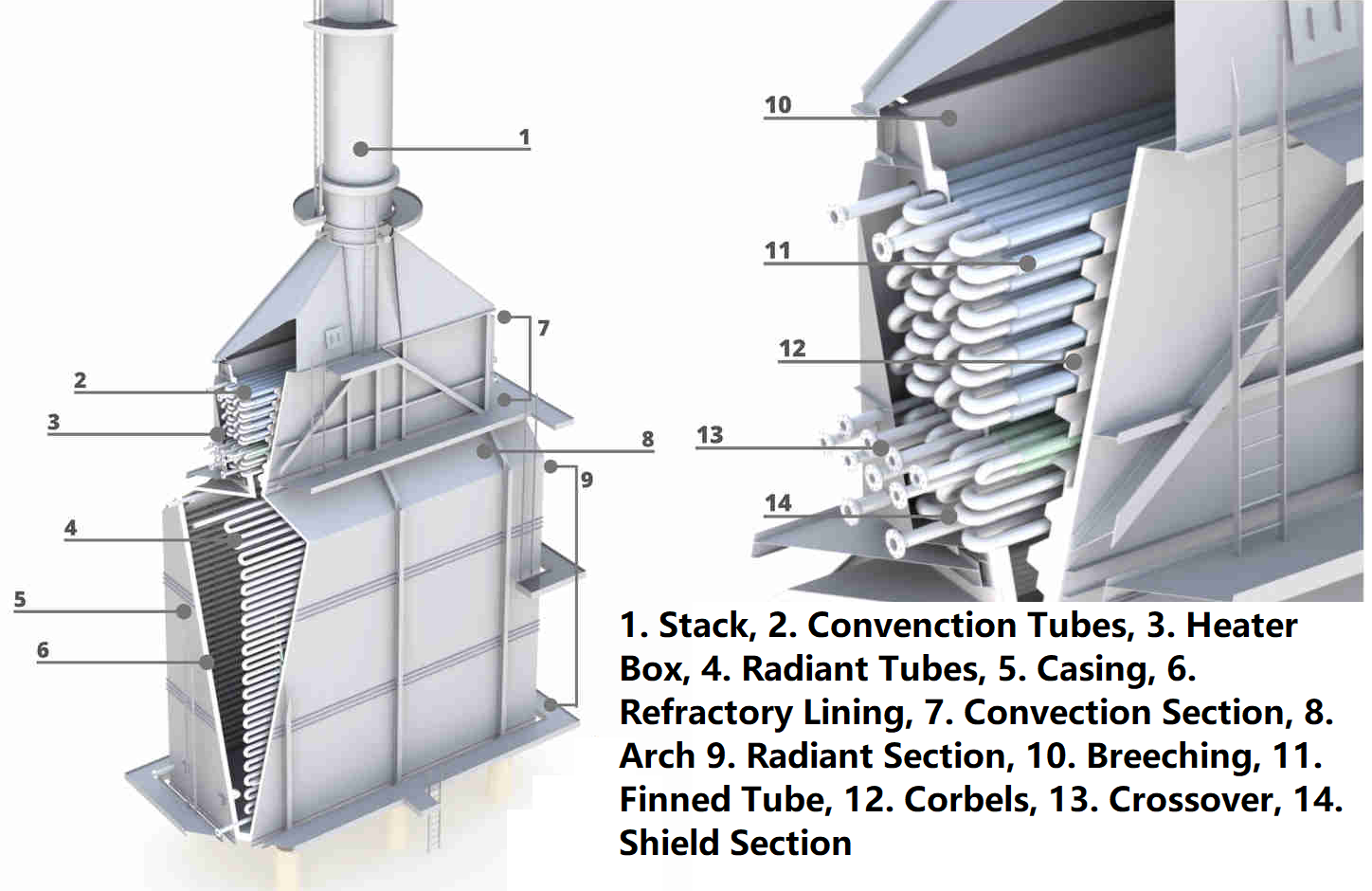
– Anatomy includes components like stacks (exhaust chimneys), convection tubes,…
2. Axens – Fired Heaters for Refining and Petrochemicals
Domain: axens.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Fired heaters designed for refining, petrochemicals, and syngas processes. Tailor-made solutions ensuring efficiency, reliability, and optimal thermal performance. Key applications include:
– Process heaters for refinery units, including crude & vacuum distillation, catalytic reforming (CCR, semi-regenerative), isomerization, catalytic cracking (FCC, RFCC), hydrodesulfurization, hydrotreating, hyd…
3. Refinery Caves – Industrial Furnace
Domain: refinerycaves.fandom.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Industrial Furnace”, “price”: “$4,500”, “location”: “Novabay Utility Convenience Store”, “version_added”: “Beta v.6”, “status”: “Obtainable”, “temperature_capacity”: “850°”, “material”: “Reinforced steel”, “features”: [“Highest temperature capacity”, “Capable of smelting tough ores”, “Ideal for high-level crafting and large-scale operations”], “smeltable_materials”: [“Scarlet Tin”, “Clou…
4. Scribd – Industrial Process Furnaces
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Industrial Process Furnaces are essential devices used in the heating of crude oil, consisting of an insulated chamber with tubes that carry the oil. Key components include burners that heat the tubes through combustion, a radiant section for intense heating via radiation, and a convection section for additional heat recovery. Other important parts are soot blowers and a stack for venting exhaust….
5. Hedhme – Process Heaters
Domain: hedhme.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Hedhme – Process Heaters, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for refinery furnace
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for refinery furnaces is pivotal for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs in the refining process. By selecting high-quality fired heaters that meet industry standards, buyers can ensure optimal heat transfer and minimize maintenance issues, such as coking or fouling, which can lead to significant downtime and safety hazards.
Furthermore, understanding the various types of heaters, their configurations, and advanced technologies will empower international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to make informed procurement decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, so too does the importance of investing in advanced refinery technologies. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability in their offerings. Engage in proactive discussions with manufacturers to explore solutions that not only meet current demands but also anticipate future challenges. By doing so, you will position your operations for long-term success in a competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.