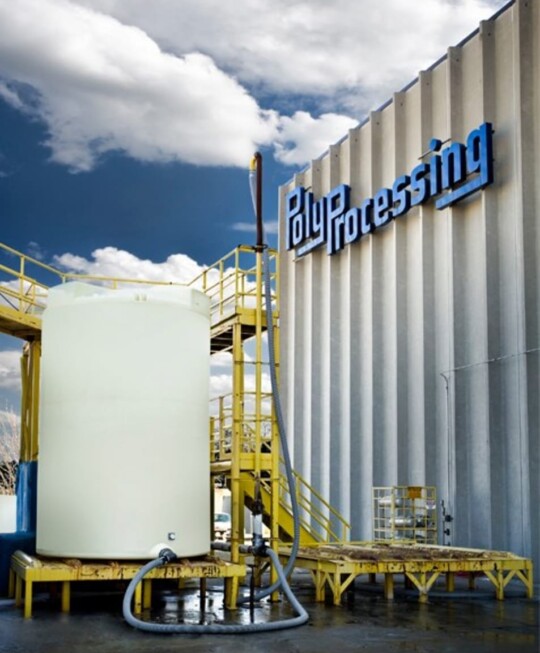
Poly Processing Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for poly processing
Navigating the complexities of sourcing polyethylene processing solutions can be daunting for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in identifying the right suppliers but also in understanding the diverse applications and specifications of poly processing systems. This comprehensive guide addresses critical aspects such as types of tanks, their applications in various industries, effective supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions.
As the demand for safe and efficient chemical storage continues to rise, understanding the nuances of polyethylene processing becomes essential for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and safety standards. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into selecting high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) tanks, including innovative designs like the SAFE-Tank® and IMFO® systems. With a focus on safety, environmental compliance, and long-term performance, this resource serves as your roadmap to navigating the global market for poly processing.
By leveraging the information presented here, international buyers from Nigeria to Saudi Arabia can confidently assess their options and partner with reputable manufacturers. Whether you’re in the chemical processing, water treatment, or industrial sectors, this guide equips you with the knowledge to secure the best solutions for your specific needs.
Understanding poly processing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE) | Exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and impact strength | Chemical storage, water treatment, industrial applications | Pros: Long lifespan, robust performance; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to standard materials. |
| SAFE-Tank® Double Wall System | “Tank within a tank” design for enhanced safety and containment | Hazardous chemical storage, environmental compliance | Pros: Minimizes risk of leaks; Cons: Requires more space for installation. |
| Integrally Molded Flanged Outlet (IMFO) | Seamless design with full drain capability, no sump area | Wastewater treatment, chemical processing | Pros: Reduces maintenance needs; Cons: Limited to specific tank configurations. |
| Cone-Bottom Tanks | Designed for complete drainage and sediment control | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Efficient for viscous materials; Cons: May require specialized handling. |
| Open-Top Tanks | Facilitates easy access for filling and cleaning | Bulk storage, temporary storage solutions | Pros: Versatile application; Cons: Increased risk of contamination if not properly covered. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE) Tanks?
High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE) tanks are engineered for durability, making them suitable for storing a wide range of chemicals, including corrosive substances. Their exceptional chemical resistance and UV stability are critical for industries like water treatment and chemical manufacturing. When considering HDXLPE tanks, buyers should evaluate their chemical compatibility and the tank’s capacity to withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and safety in their operations.
Why Choose the SAFE-Tank® Double Wall System for Hazardous Chemical Storage?
The SAFE-Tank® double wall system offers a robust solution for hazardous chemical storage, featuring a “tank within a tank” design that provides secondary containment. This design significantly reduces the risk of leaks and spills, making it ideal for industries focused on environmental compliance. Buyers should assess the space requirements and installation logistics, as the double wall design may necessitate more room than single-wall tanks.
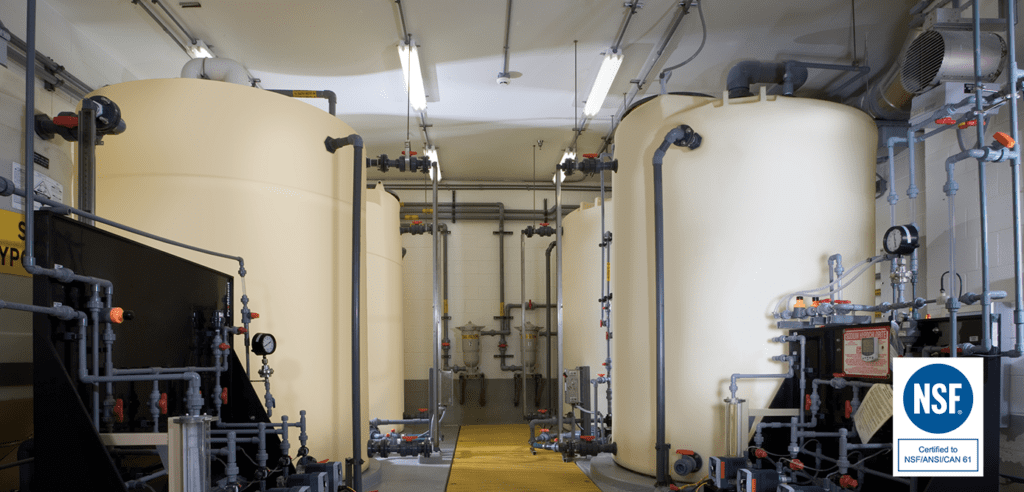
Illustrative image related to poly processing
How Does the Integrally Molded Flanged Outlet (IMFO) Enhance Chemical Processing?
The IMFO design is characterized by its seamless construction, allowing for full drainage without the complications of a sump area. This feature is particularly beneficial in wastewater treatment and chemical processing, where complete drainage is essential. When purchasing, businesses should consider their specific drainage needs and whether the IMFO’s configuration aligns with their operational requirements.
What Advantages Do Cone-Bottom Tanks Offer for Viscous Materials?
Cone-bottom tanks are specifically designed for applications that require complete drainage and sediment control, making them ideal for food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their sloped bottoms facilitate the efficient handling of viscous materials, ensuring that no residue remains in the tank. Buyers should evaluate the tank’s compatibility with their specific materials and consider the potential need for specialized handling equipment.
When Should Open-Top Tanks Be Considered for Bulk Storage?
Open-top tanks are versatile solutions for bulk storage and temporary applications, allowing for easy access for filling and cleaning. However, they come with an increased risk of contamination if not properly managed. Businesses looking for flexibility in their storage solutions should assess the operational protocols in place to mitigate contamination risks and ensure that the open-top design meets their specific needs.
Key Industrial Applications of poly processing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of poly processing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Storage of corrosive chemicals like Sodium Hypochlorite | Enhanced safety and compliance with environmental regulations | Certification standards (NSF/ANSI), tank compatibility, delivery times |
| Chemical Processing | Storage of acids such as Sulfuric and Hydrochloric Acid | Durability and resistance to chemical corrosion | Material specifications, tank design (e.g., IMFO), local regulations |
| Agriculture | Fertilizer and pesticide storage | Improved shelf life and reduced risk of contamination | Bulk purchasing options, tank sizes, and transport logistics |
| Food and Beverage | Storage of ingredients like fats and oils | Compliance with food safety standards | Certification (FDA), material safety, and tank accessibility |
| Waste Management | Leachate and condensate storage | Environmental protection and regulatory compliance | Secondary containment requirements, tank integrity assessments |
How is Poly Processing Used in Water Treatment?
In the water treatment sector, poly processing is crucial for the safe storage of corrosive chemicals such as sodium hypochlorite. These chemicals are essential for disinfection processes but pose significant risks if not stored properly. Polyethylene tanks, specifically designed with the SAFE-Tank® double-wall system, provide superior safety and compliance with environmental regulations. International buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East must ensure that the tanks meet NSF/ANSI certification standards to guarantee safety and reliability.
What Role Does Poly Processing Play in Chemical Processing?
Poly processing is integral in the chemical processing industry, particularly for storing hazardous acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid. The high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) tanks offer unparalleled resistance to chemical corrosion, thereby extending the lifespan of storage solutions. Buyers should focus on the material specifications and tank design features, such as the IMFO® (Integrally Molded Flanged Outlet) for full drainage. Understanding local regulations is also crucial, especially in Europe, where compliance standards can be stringent.

Illustrative image related to poly processing
How is Poly Processing Beneficial for Agriculture?
In agriculture, poly processing is utilized for the storage of fertilizers and pesticides, which are often volatile and sensitive to environmental conditions. The robust construction of polyethylene tanks ensures that these substances maintain their efficacy while minimizing contamination risks. Buyers should consider bulk purchasing options and the availability of various tank sizes to meet their storage needs. Logistics, including transport and installation, are also key factors for agricultural businesses, particularly in remote areas of South America and Africa.
What Are the Applications of Poly Processing in Food and Beverage?
The food and beverage industry relies on poly processing for the safe storage of ingredients such as fats and oils. These tanks must comply with food safety standards, which necessitates certification from relevant authorities like the FDA. The use of high-quality polyethylene ensures that the stored materials remain uncontaminated and stable. Buyers should prioritize material safety and tank accessibility to facilitate easy handling and compliance with health regulations.
How Does Poly Processing Contribute to Waste Management?
In waste management, poly processing is essential for storing leachate and condensate, which can pose environmental hazards if not contained properly. The double-wall containment systems provide an extra layer of protection, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Buyers need to consider secondary containment requirements and conduct integrity assessments of the tanks to ensure they can withstand harsh waste materials. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions with strict environmental laws, such as those in Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘poly processing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Chemical Compatibility
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the right poly processing tanks for storing various chemicals. A common issue arises when a company chooses a tank without fully understanding the chemical compatibility, leading to potential leaks, contamination, and safety hazards. For instance, a buyer may select a tank based on size and cost, neglecting to verify whether the tank material can withstand the corrosive nature of chemicals like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid. Such oversights not only jeopardize workplace safety but can also result in costly cleanup and regulatory fines.
The Solution:
To ensure optimal chemical compatibility, buyers should conduct thorough research on the chemical properties of the substances they intend to store. Utilize resources such as compatibility charts provided by manufacturers or consult with technical experts from poly processing companies. When specifying a tank, consider options like High Density Cross-Linked Polyethylene (HDXLPE), which offers exceptional resistance to a wide range of chemicals. Additionally, leveraging tools such as tank configurators can help buyers select the most suitable tank based on their specific chemical storage needs. Always request material safety data sheets (MSDS) and ensure that the chosen tank complies with relevant industry standards, such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61, to guarantee safety and reliability.
Scenario 2: Concerns About Environmental Compliance
The Problem:
International buyers, particularly from regions with stringent environmental regulations, often struggle with ensuring that their chemical storage solutions meet legal compliance. The fear of non-compliance can stem from a lack of knowledge regarding local regulations or uncertainty about the environmental impact of the materials used in their storage solutions. This can lead to significant risks, including legal penalties, forced shutdowns, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution:
To navigate these complexities, buyers should engage with suppliers who prioritize environmental compliance and sustainability. Look for poly processing companies that provide double-wall containment systems, such as the SAFE-Tank® system, which offers added security against leaks and spills. Furthermore, ensure that the tanks are constructed from materials that comply with local environmental standards. Regular audits and assessments of storage practices can also help identify potential compliance gaps. Collaborating with local regulatory bodies and industry associations can provide valuable insights into evolving regulations and best practices, ensuring that your operations remain compliant and environmentally responsible.
Scenario 3: Long Lead Times Affecting Project Timelines
The Problem:
In the competitive landscape of chemical processing, delays in sourcing and receiving poly processing tanks can severely impact project timelines. B2B buyers may encounter extended lead times, especially when ordering customized tanks or during periods of high demand. This can lead to project setbacks, increased costs, and strained relationships with clients who expect timely delivery of services or products.
The Solution:
To mitigate lead time issues, buyers should establish strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide transparent timelines and proactive communication. When placing orders, consider standard tank sizes and configurations that are readily available, as these typically have shorter lead times than custom solutions. Additionally, consider working with manufacturers that have multiple production facilities, as this can enhance supply chain resilience and expedite delivery. Implementing a just-in-time inventory strategy can also help manage storage space and reduce costs, allowing companies to maintain flexibility while ensuring they have the necessary equipment on hand when needed. Regularly reviewing and optimizing procurement processes can also help identify potential bottlenecks and improve overall efficiency.
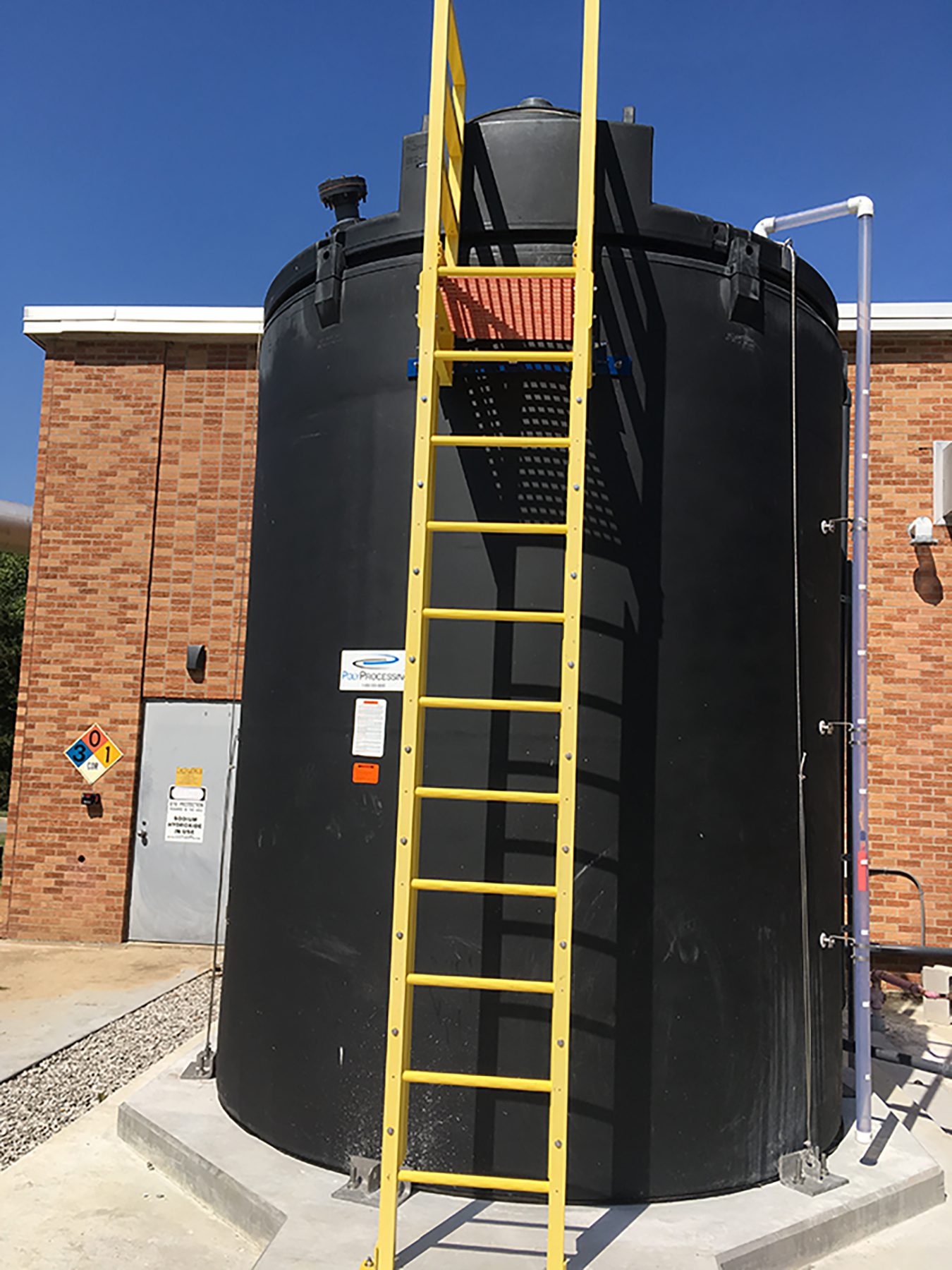

Illustrative image related to poly processing
Strategic Material Selection Guide for poly processing
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Poly Processing?
In the realm of poly processing, selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of chemical storage tanks. Below, we analyze four common materials used in poly processing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Perform in Chemical Storage?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a widely used material in the manufacture of chemical storage tanks. It boasts excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for storing a variety of substances, including acids and alkalis. HDPE has a temperature rating of up to 120°C and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros: HDPE is known for its durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. It is also cost-effective, which is a significant advantage for businesses looking to minimize expenses.
Cons: However, HDPE can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light unless properly treated. Its lower temperature tolerance compared to other materials may limit its application in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: HDPE is compatible with a wide range of chemicals, but users must ensure that the specific chemical does not exceed the material’s temperature and pressure ratings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D1998 and NSF/ANSI Standard 61 is essential for HDPE tanks. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should also consider UV protection due to high sun exposure.
What Advantages Does Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Offer?
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) is an advanced form of polyethylene that exhibits superior chemical resistance and structural integrity. XLPE can withstand temperatures up to 100°C and offers enhanced durability against physical stress.

Illustrative image related to poly processing
Pros: The primary advantage of XLPE is its ability to handle aggressive chemicals without degrading, making it suitable for applications involving sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. Its resistance to cracking and environmental stress makes it a long-lasting option.
Cons: The manufacturing process for XLPE is more complex and costly compared to HDPE, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, XLPE is not as widely available, which could lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: XLPE is particularly well-suited for chemical storage in industries such as water treatment, where chemical compatibility is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as Europe.
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Compare for Chemical Storage Solutions?
Polypropylene (PP) is another material used in poly processing, known for its excellent chemical resistance and lower density compared to polyethylene. It can handle temperatures up to 80°C and is suitable for various applications, including food-grade storage.
Pros: PP is lightweight and offers a good balance of strength and flexibility. It is also resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it versatile for different storage needs.
Cons: However, PP has a lower impact resistance than HDPE and XLPE, which may lead to concerns in high-stress environments. Additionally, its cost can be higher than that of HDPE.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is particularly effective for storing less aggressive chemicals and is often used in the food and beverage industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety regulations is crucial for buyers in the food sector. Buyers should also check for local standards like DIN or JIS.
What Role Does Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Play in Poly Processing?
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) combines plastic with glass fibers to enhance strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: FRP offers excellent corrosion resistance and can be tailored for specific chemical storage requirements. Its strength makes it ideal for large-scale industrial applications.
Cons: The primary drawback is its high cost and complexity in manufacturing. Additionally, FRP can be susceptible to UV degradation if not properly coated.
Impact on Application: FRP is often used in applications involving aggressive chemicals, such as chlorinated solvents.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure FRP tanks meet local regulations and standards, especially in regions with strict environmental laws.
Summary of Material Selection for Poly Processing
| Material | Typical Use Case for poly processing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | General chemical storage | Durable and cost-effective | Brittle with UV exposure | Low |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) | Aggressive chemical storage | Superior chemical resistance | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food-grade storage | Lightweight and versatile | Lower impact resistance | Medium |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) | Industrial chemical storage | Excellent strength and corrosion resistance | High cost and UV susceptibility | High |
This guide aims to provide actionable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions in material selection for poly processing applications across various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for poly processing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Poly Processing?
The manufacturing process of poly processing involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality polyethylene chemical storage tanks. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage begins with the selection of high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) or other suitable materials. These materials are chosen for their chemical resistance, durability, and ability to withstand harsh environments. Prior to processing, the materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards. Suppliers often utilize advanced techniques such as pellet drying and blending to prepare the materials for the subsequent manufacturing processes.
2. Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins, predominantly utilizing rotational molding. This technique allows for the creation of seamless, hollow structures that can be tailored to various shapes and sizes. During rotational molding, the powdered resin is heated in a mold while being rotated, which ensures even distribution and thickness. This method minimizes weak points in the final product, enhancing structural integrity. Some manufacturers may also employ blow molding for specific applications, especially when producing smaller components.
3. Assembly
After the components are formed, the assembly stage takes place. This involves integrating various parts such as lids, manways, and outlet systems into the tanks. Advanced assembly techniques, including the use of heat fusion or mechanical fastening, ensure that all components are securely attached, preventing leaks and enhancing safety. The assembly process is often executed in controlled environments to maintain cleanliness and prevent contamination.
4. Finishing Touches
The final stage of manufacturing includes surface finishing and additional quality checks. Tanks may receive treatments to enhance UV stability or chemical resistance. Finishing also involves labeling, installation of safety features, and preparation for shipment. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Poly Processing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of poly processing, ensuring that products meet stringent safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA measures is essential for ensuring product reliability.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
Manufacturers in the poly processing industry adhere to several international standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking, API specifications, and NSF/ANSI standards are critical for ensuring safety and quality in chemical storage applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is systematically integrated into the manufacturing process through various checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor critical parameters and identify defects early in the process. This includes assessing the temperature and duration of the molding process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the tanks are assembled, final inspections are performed to ensure that products meet all specifications and safety standards. This includes pressure testing and visual inspections for any surface defects.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
To validate the quality of poly processing products, several testing methods are employed:
- Hydrostatic Pressure Testing: Ensures that tanks can withstand internal pressures without leaking.
- Chemical Compatibility Testing: Assesses how well the tank material can hold various chemicals over time.
- Impact Resistance Testing: Evaluates the tank’s durability against physical impacts, ensuring it can withstand handling and environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control measures. Here are actionable strategies:
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. During these audits, buyers should assess the supplier’s adherence to international standards, review QC documentation, and observe production practices.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks. These reports provide transparency into the supplier’s commitment to quality and can reveal patterns or concerns that may affect product reliability.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can enhance trust in the supplier’s quality assurance processes. Independent inspectors can validate that the products meet specified standards and provide unbiased reports on the quality of the manufactured tanks.
Illustrative image related to poly processing
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is crucial. Buyers should be aware of:
- Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding chemical storage. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards.
- Cultural and Logistical Challenges: Language barriers and logistical issues may affect communication about quality assurance practices. Establishing clear lines of communication and expectations is vital.
- Certification Validity: Buyers should verify the validity of certifications and ensure that they are recognized in their home countries. This may involve checking the issuing body’s credibility and the relevance of the certification to the specific product.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in poly processing enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet international standards and provide safe, durable chemical storage solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘poly processing’
In the ever-evolving landscape of chemical storage, ensuring the right procurement process for poly processing systems is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. This guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to facilitate informed sourcing decisions for polyethylene processing solutions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by identifying the specific requirements for your chemical storage needs. Consider factors such as the type of chemicals being stored, their specific gravity, and the volume required. This clarity will help you select the right tank design and material, ensuring compatibility with the substances involved and compliance with safety standards.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Understanding the relevant industry standards is essential for compliance and safety. Familiarize yourself with regulations such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61, ASTM D1998, and API 650 that pertain to chemical storage tanks. This knowledge will guide you in selecting suppliers who adhere to these standards, ultimately safeguarding your operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Look for company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or regions. Key aspects to consider include:
– Experience in Poly Processing: Choose suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) tanks.
– Product Range: Ensure they offer a variety of tank configurations, such as vertical, horizontal, and cone-bottom tanks, to meet your specific needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your chosen supplier holds relevant certifications, which validate their compliance with industry standards. Certifications like NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 demonstrate that their products are safe for chemical storage. Additionally, inquire about any quality assurance processes they implement during manufacturing.
Step 5: Assess Customization Capabilities
Explore whether the supplier can customize tank designs to suit your specific operational requirements. Customization may include modifications for unique chemical properties or integration with existing systems. Discuss your needs openly to gauge their willingness and capability to provide tailored solutions.
Step 6: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Before finalizing your decision, request samples or detailed technical documentation of the tanks you are considering. This allows you to assess the quality of materials used and understand the operational guidelines. Pay attention to:
– Installation Instructions: Ensure you can easily integrate the tanks into your current setup.
– Maintenance Guidelines: Understand the upkeep required to extend the life of the tanks and ensure safe operations.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, engage in discussions regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty terms. Ensure you understand the total cost of ownership, including shipping and installation. A transparent negotiation will help establish a mutually beneficial relationship, leading to successful long-term collaboration.
By following this checklist, you can enhance your sourcing strategy for poly processing systems, ensuring that you select the most suitable solutions for your chemical storage needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for poly processing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Poly Processing?
When engaging in poly processing sourcing, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of polyethylene (HDPE or XLPE) significantly affects costs. High-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) is preferred for its durability and chemical resistance, but it typically comes at a higher price point than standard materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards. Skilled labor is necessary for the manufacturing and installation processes, particularly for specialized tanks that require precise engineering.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor. High-capacity production facilities may benefit from economies of scale, reducing overhead per unit.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom tank designs. Investing in high-quality molds can lead to better finished products and lower defect rates, impacting long-term costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring tanks meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Regular testing and compliance with certifications (e.g., NSF/ANSI/CAN 61) are crucial for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs should not be overlooked, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs can add to the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers often include a margin that reflects their operational costs and profit expectations. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers gauge if the margin is reasonable.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Poly Processing Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the poly processing sector:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to bulk pricing. Buyers should negotiate for volume discounts when feasible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tanks designed for specific chemical storage needs can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can justify increased prices. Buyers in regulated industries must prioritize compliance, potentially increasing initial costs but ensuring long-term safety and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and service quality, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect total landed costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Poly Processing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand standard pricing and terms within the industry. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the complete cost of ownership, including maintenance, potential downtime, and replacement costs. This analysis can justify higher upfront costs for superior products that offer long-term savings.
-
Flexible Payment Terms: Negotiate for favorable payment terms that may include staggered payments based on delivery milestones or discounts for early payment.
-
Build Relationships: Cultivating strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals and more favorable terms in the long run. Trust and communication often yield benefits beyond price.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If negotiations do not meet your budgetary constraints or quality expectations, be ready to explore alternative suppliers. This mindset can often lead to improved offers from your current supplier.
Conclusion and Pricing Disclaimer
While the information provided offers a comprehensive overview of cost structures and pricing influencers in poly processing, prices can vary widely based on specific circumstances. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes directly from suppliers to get a clear picture of current market conditions and potential pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing poly processing With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Chemical Storage Solutions
When considering chemical storage solutions, businesses must evaluate various options to ensure safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Poly processing, particularly through high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) tanks, offers unique advantages. However, alternative solutions like fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) tanks and stainless steel tanks also provide viable options. This analysis will compare these alternatives against poly processing to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Poly Processing | Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) | Stainless Steel Tanks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent chemical resistance; long lifespan; integrally molded for full drainage | Good chemical resistance; can be customized; generally less durable than HDXLPE | Superior strength; high resistance to corrosion; versatile |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; low long-term maintenance | Higher initial cost; can vary based on customization | High upfront cost; long-term ROI through durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick to install; lightweight; available in various configurations | Moderate; requires skilled labor for installation | Complex installation; heavy and may need specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to UV and impacts | Moderate maintenance; can be prone to cracking | Low maintenance; corrosion-resistant but may require periodic inspections |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for corrosive chemicals and water treatment | Suitable for a variety of chemicals; often used in custom applications | Best for high-pressure applications and industries requiring stringent safety standards |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Tanks
FRP tanks are constructed using a combination of fiberglass and resin, offering good chemical resistance and customization options. They can be tailored for specific applications and environments, making them versatile. However, while they are less expensive than stainless steel tanks, they are generally more costly than poly processing solutions. Maintenance can be moderate, as FRP tanks may be prone to cracking under stress, necessitating careful handling and installation by skilled labor.
Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless steel tanks are renowned for their durability and strength, making them suitable for high-pressure applications and industries that require robust safety standards, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Although they offer excellent corrosion resistance, the initial investment is significantly higher than poly processing or FRP tanks. Installation can also be complex and may require specialized equipment, which can add to overall project costs. However, their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements can lead to significant long-term cost savings.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Chemical Storage Solution
Selecting the right chemical storage solution involves weighing various factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. For B2B buyers, poly processing tanks provide a balanced approach, particularly for corrosive chemicals, thanks to their innovative design and lower maintenance needs. However, if specific customization or extreme durability is paramount, alternatives like FRP or stainless steel tanks may be more suitable. Ultimately, the decision should align with the unique operational requirements and budget constraints of the business.

Illustrative image related to poly processing
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for poly processing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Poly Processing?
In the world of poly processing, understanding the technical properties of materials used in chemical storage tanks is crucial for international buyers. Here are several essential specifications that impact performance, safety, and compliance:
1. Material Grade (HDPE and XLPE)
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) are the primary materials used in poly processing tanks. HDPE offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, while XLPE enhances structural integrity and thermal stability. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the tanks will withstand harsh chemicals and environmental conditions, reducing the risk of leaks and failures.
2. Specific Gravity
Specific gravity measures the density of a substance compared to water. Poly processing tanks often accommodate specific gravities up to 2.2, particularly when using engineered materials like OR-1000 resin. Understanding specific gravity is vital for buyers as it affects tank design, capacity, and the type of chemicals that can be safely stored, ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and specifications during manufacturing. Accurate tolerances are essential for ensuring that tanks fit correctly with other system components, minimizing the risk of leaks or operational failures. For B2B decision-makers, understanding tolerance levels can guide the selection of tanks that will integrate seamlessly into existing systems.
4. Certification Standards
Certifications such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 indicate that a product meets safety and health standards for drinking water system components. For international buyers, especially in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks, ensuring that tanks have the appropriate certifications is paramount for compliance and safety assurance.
5. Resistance to Oxidation
Oxidation resistance is a critical property for tanks storing chemicals that can corrode materials over time. The OR-1000 oxidation-resistant system is designed to extend the life of tanks in aggressive chemical environments. Buyers should prioritize tanks with this property to reduce maintenance costs and extend service life.
6. UV Stability
Ultraviolet (UV) stability refers to a material’s ability to withstand degradation from sunlight exposure. Tanks designed with UV-stable materials are essential for outdoor installations. B2B buyers need to consider this property to ensure that their storage solutions remain effective and reliable, regardless of environmental conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Poly Processing?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in poly processing. Here are key terms that every buyer should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In poly processing, buyers often source tanks from OEMs that specialize in chemical storage solutions, ensuring quality and reliability.

Illustrative image related to poly processing
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers to manage inventory effectively and meet production needs without incurring unnecessary costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products. B2B buyers should use RFQs to compare pricing, terms, and conditions from different suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk, and responsibility, ensuring smoother cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. Knowing the lead time is essential for buyers to plan their operations and avoid disruptions in their supply chain.
6. Secondary Containment
Secondary containment refers to systems designed to prevent leaks or spills from primary storage tanks. This term is particularly relevant for buyers focused on safety and environmental compliance, as it ensures that any accidental releases are contained effectively.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions in the poly processing industry, enhancing operational efficiency and compliance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the poly processing Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Impacting the Poly Processing Market?
The global poly processing market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for chemical storage solutions across various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, and manufacturing. As international regulations become stricter regarding the storage and handling of hazardous materials, businesses are seeking reliable and safe solutions, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Emerging technologies, such as advanced rotational molding and high-density cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) innovations, are enhancing the durability and safety of storage tanks, making them more attractive to B2B buyers.
In addition to technological advancements, the market is witnessing a shift towards integrated supply chain solutions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide comprehensive services, including tank design, manufacturing, and installation. This trend is particularly relevant in developing markets where logistical challenges can hinder the timely delivery of products. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce and digital platforms is simplifying the sourcing process, allowing buyers to compare products and suppliers more efficiently.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in Poly Processing?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the poly processing sector, as businesses increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their operations. Ethical sourcing practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, are now essential for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements. Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are particularly focused on sustainable solutions, as environmental regulations tighten and public awareness grows.
Green certifications, such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 for drinking water system components, are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. These certifications not only ensure product safety but also affirm a commitment to environmental responsibility. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who adhere to these standards, as this can lead to long-term partnerships built on trust and shared values. Moreover, investing in sustainable solutions can reduce operational costs in the long run, making it a strategic choice for businesses.
What Is the Historical Context of Poly Processing That Influences Current Market Dynamics?
The poly processing industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially focused on agricultural distribution, the sector transitioned to address the growing need for safe storage solutions for corrosive chemicals in the 1970s. Pioneering companies, such as Poly Processing, began utilizing rotational molding techniques to create robust, cross-linked polyethylene tanks as alternatives to traditional materials like stainless steel and fiberglass.
This shift not only improved the safety and longevity of chemical storage tanks but also led to the development of innovative containment systems, such as the SAFE-Tank double-wall system. Today, the legacy of these early innovations continues to shape the market, driving advancements in technology and sustainability while addressing the evolving needs of B2B buyers across the globe. Understanding this historical context is essential for stakeholders looking to navigate the complexities of the current poly processing landscape effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of poly processing
-
How do I select the right poly processing tank for my chemical storage needs?
Selecting the right tank involves understanding the specific properties of the chemicals you plan to store, such as their density, corrosiveness, and temperature requirements. Consider tanks made from high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE), which offers superior chemical resistance and durability. Evaluate tank configurations—vertical, horizontal, or cone-bottom—based on your space and operational needs. Consulting with a supplier’s technical team can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific applications and compliance requirements. -
What are the benefits of using high-density polyethylene tanks for chemical storage?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) tanks are highly resistant to corrosion, UV radiation, and impact, making them ideal for storing a wide range of chemicals. Their structural integrity ensures a longer lifespan compared to traditional materials like steel or fiberglass. Additionally, HDPE tanks are lightweight, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. Many manufacturers also offer innovative features, such as double-wall systems for enhanced safety and containment. -
What customization options are available for poly processing tanks?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options, including tank size, shape, and additional features like manway covers, fittings, and secondary containment solutions. Customization allows you to tailor tanks to specific chemical properties, operational needs, and space constraints. It’s essential to engage with your supplier early in the process to discuss your requirements and ensure that the final product aligns with your operational objectives. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering poly processing tanks?
Lead times can vary based on the manufacturer’s production capacity and the complexity of your order. Generally, you can expect most orders to be shipped within 8 to 10 weeks after the order approval. For customized tanks, the timeline may extend, so it’s advisable to communicate your project deadlines with your supplier early on to avoid any disruptions in your operations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for poly processing tanks?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between manufacturers and depend on the type of tank and customization options selected. Some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard models, while custom tanks might require larger quantities to justify production costs. Always discuss your needs with potential suppliers to find options that align with your purchasing capabilities. -
How do I ensure the quality of poly processing tanks?
To ensure quality, select suppliers who adhere to industry standards and certifications, such as NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 for potable water applications. Request documentation of quality assurance processes and inquire about testing methods used during production. Engaging in thorough supplier vetting, including reviews of previous client feedback and case studies, can also help ensure that you choose a reputable manufacturer. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing poly processing tanks?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the size of your order. Common terms include a percentage upfront with the balance due upon delivery or a net 30- or 60-day payment plan. When negotiating terms, consider factors such as order size, your company’s credit history, and any potential discounts for early payment. Always clarify payment methods accepted by the supplier, especially for international transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing poly processing tanks?
When importing tanks, consider factors such as shipping costs, customs duties, and compliance with local regulations. Ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Additionally, factor in the logistics of transporting the tanks from the port to your facility. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in handling large and sensitive shipments can help streamline the process and mitigate potential delays.
Top 4 Poly Processing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Polyprocessing – Polyethylene Chemical Storage Tanks
Domain: polyprocessing.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Polyethylene Chemical Storage Tanks including SAFE-Tank® Double Wall Tank System, Sloped Bottom Vertical Tanks with IMFO®, Vertical Tanks, Cone-Bottom Tanks, Open-Top Tanks, Secondary Containment Basins, Polyspheres, Horizontal Tanks, Lined Steel Vessels, Non-Standard Tanks & Custom Molded Products. Key features include: 15,500-Gallon Tank Series, High-Density Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE), NSF…
2. Poly Processing – Innovative Tank Systems
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Poly Processing – Innovative Tank Systems, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. PolyProcessing – HDXLPE Chemical Storage Tanks
Domain: texasprocess.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: PolyProcessing manufactures large rotational molded high density crosslinked polyethylene (HDXLPE) chemical storage tanks. Key features include the SAFE-TANK® double-wall containment system, IMFO® full drain vertical storage poly tank, and OR-1000™ oxidation resistant system. Tanks are available in various configurations: vertical, horizontal, cone bottom, and open top, with secondary containment …
4. SCG Process – Polyethylene Chemical Storage Tanks
Domain: scgprocess.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Polyethylene Chemical Storage Tanks from SCG Process represent Poly Processing’s storage systems and custom parts. Key features include: robust corrosion resistance, broad chemical compatibility, minimal field maintenance, and long life. Typical markets served include municipal water treatment, industrial chemical storage and distribution, oil and gas, pulp and paper, and pharmaceuticals. Features…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for poly processing
In the realm of poly processing, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and innovative chemical storage solutions. By prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers like Poly Processing, businesses can access high-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE) tanks that offer unparalleled durability, safety, and compliance with stringent industry standards. The integration of advanced technologies, such as the SAFE-Tank® double-wall containment system and IMFO® full drain capabilities, underscores the importance of investing in modern, efficient storage solutions that mitigate risk and enhance operational efficiency.
As global markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable chemical storage systems is expected to rise. B2B buyers must focus on sourcing suppliers that not only provide quality products but also offer expert guidance and support tailored to specific chemical storage challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of poly processing will be shaped by ongoing innovation and collaboration. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers proactively, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of chemical storage. By making informed sourcing decisions today, businesses can secure a competitive edge in the dynamic landscape of global trade.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.