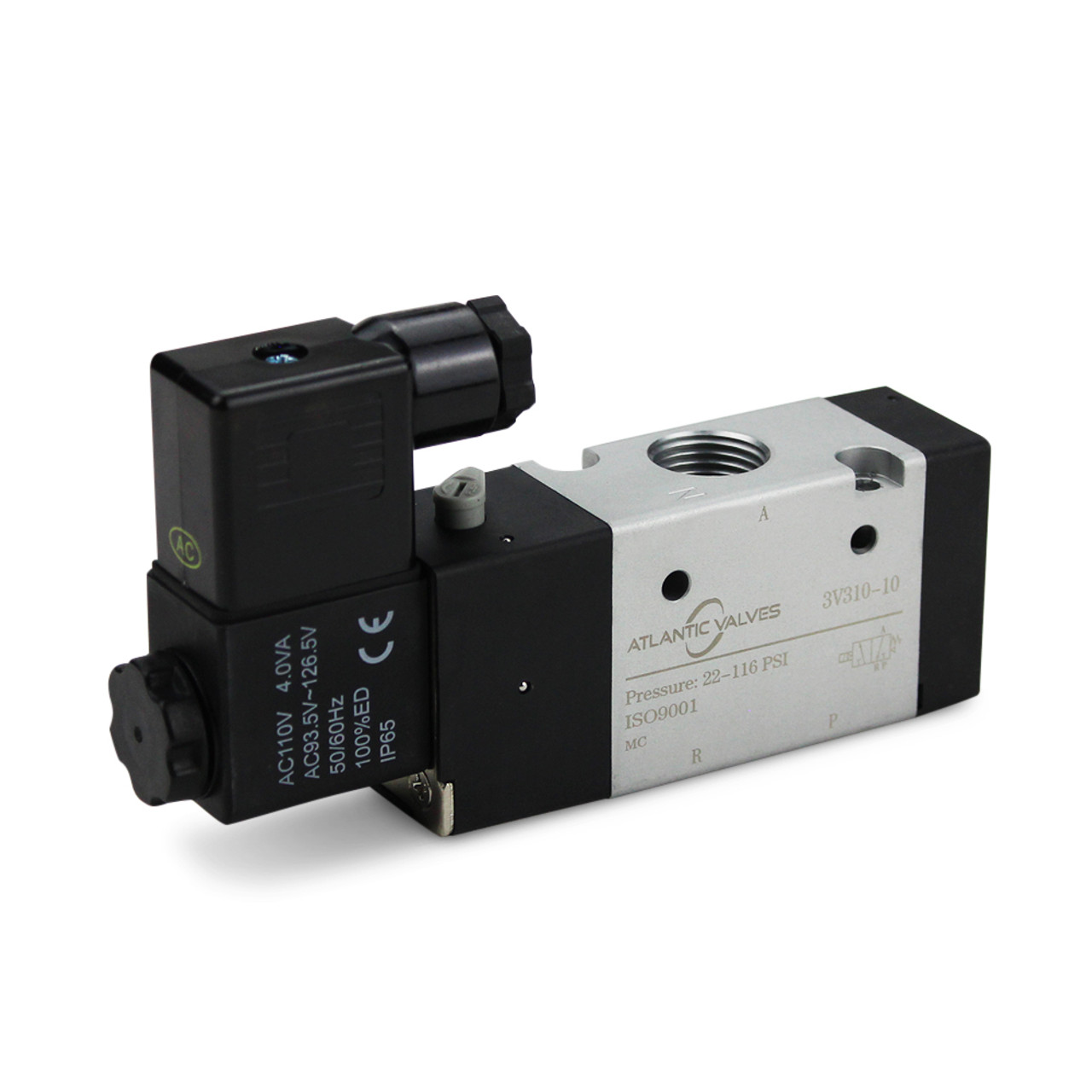
Pneumatic Solenoid Valves: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic solenoid valves
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality pneumatic solenoid valves can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in manufacturing, automotive, or aerospace industries, the need for precision and reliability in pneumatic systems cannot be overstated. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, designed to equip decision-makers with the knowledge they need to navigate the global market effectively. We delve into various types of pneumatic solenoid valves, their applications across diverse sectors, and critical factors for supplier vetting. Additionally, we address cost considerations and market trends that can impact your procurement strategy.
Understanding the intricacies of pneumatic solenoid valves is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring safety in your systems. Our guide provides actionable insights tailored to the unique needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany. By offering a detailed overview of product specifications and supplier capabilities, this resource empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions. As we explore the complexities of this vital component, you will gain the expertise necessary to enhance your procurement process and secure the best solutions for your business needs.
Understanding pneumatic solenoid valves Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Way Solenoid Valve | Simple on/off functionality; two ports (inlet/outlet) | HVAC systems, pneumatic actuators | Pros: Easy installation, cost-effective. Cons: Limited functionality for complex systems. |
| 3-Way Solenoid Valve | Three ports; can direct flow between two outputs | Air compressors, industrial automation | Pros: Versatile, can control multiple paths. Cons: More complex, higher cost than 2-way. |
| 5-Way Solenoid Valve | Five ports; often used for double-acting cylinders | Robotics, manufacturing equipment | Pros: Allows for complex control, ideal for actuators. Cons: More expensive, requires precise installation. |
| Latching Solenoid Valve | Maintains position after power is removed | Emergency shut-off systems, safety applications | Pros: Energy-efficient, retains state without power. Cons: More complex circuitry needed. |
| Miniature Solenoid Valve | Compact size; ideal for limited spaces | Medical devices, automotive applications | Pros: Space-saving, lightweight. Cons: Limited flow capacity, may not handle high pressure. |
What Are the Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves and Their Suitability?
2-way solenoid valves are the most straightforward type, featuring two ports—one for the inlet and the other for the outlet. Their primary function is to either allow or block the flow of air, making them ideal for applications requiring simple on/off control. Commonly used in HVAC systems and pneumatic actuators, they are favored for their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. However, their limited functionality makes them unsuitable for applications needing complex flow control.
How Do 3-Way Solenoid Valves Enhance Versatility in Applications?
3-way solenoid valves incorporate three ports, enabling them to direct air flow between two outputs. This versatility allows for more intricate control in systems such as air compressors and industrial automation. Buyers appreciate their ability to manage multiple flow paths, enhancing system efficiency. However, their complexity and higher cost compared to 2-way valves should be considered, particularly for budget-conscious projects.
What Advantages Do 5-Way Solenoid Valves Offer for Complex Control Needs?
5-way solenoid valves are designed with five ports, making them essential for controlling double-acting cylinders in applications like robotics and manufacturing equipment. They provide sophisticated control options, allowing for precise actuation and direction changes. While they enable complex operations, buyers must weigh their higher cost and the need for accurate installation against the benefits of enhanced functionality.
Why Choose Latching Solenoid Valves for Energy Efficiency?
Latching solenoid valves maintain their position even after power is removed, making them an excellent choice for emergency shut-off systems and safety applications. Their energy-efficient design minimizes power consumption, as they do not require constant energy to maintain their state. However, the complexity of their circuitry can be a drawback, necessitating careful consideration during the purchasing process.
What Makes Miniature Solenoid Valves Ideal for Space-Constrained Environments?
Miniature solenoid valves are compact and lightweight, making them perfect for applications where space is limited, such as in medical devices and automotive systems. Their small size does not compromise performance in low-pressure environments. However, buyers should note that their limited flow capacity may restrict usage in high-demand scenarios, necessitating a careful assessment of application requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic solenoid valves
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic solenoid valves | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | Control of actuators and cylinders in manufacturing lines | Enhanced efficiency and precision in production processes | Compatibility with existing systems and certifications |
| HVAC Systems | Regulation of air flow in heating and cooling systems | Improved energy efficiency and comfort for users | Temperature ratings and pressure specifications |
| Automotive | Operation of air braking systems in vehicles | Increased safety and reliability in braking mechanisms | Compliance with automotive industry standards |
| Chemical Processing | Control of gas flow in chemical reactors | Enhanced safety and process control | Material compatibility and safety certifications |
| Medical Equipment | Actuation of valves in respiratory devices | Critical reliability for patient care applications | Regulatory compliance and quality assurance |
How Are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Used in Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, pneumatic solenoid valves are pivotal for controlling actuators and cylinders on manufacturing lines. They enable precise regulation of air flow and pressure, ensuring that machinery operates efficiently and reliably. This technology addresses common challenges such as equipment downtime and inconsistent operation, which can lead to production delays. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing valves that are compatible with their existing systems, ensuring they meet local certifications and standards to avoid operational disruptions.
What Role Do Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Play in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, pneumatic solenoid valves are employed to regulate air flow, which is crucial for maintaining optimal heating and cooling conditions. These valves facilitate precise control over air distribution, enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort. The ability to quickly respond to changes in temperature or occupancy can significantly reduce operational costs. For international buyers, it is essential to consider temperature ratings and pressure specifications when sourcing these valves to ensure they are suitable for local climates and system requirements.
How Are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
Pneumatic solenoid valves are integral to the operation of air braking systems in vehicles, providing reliable control over braking mechanisms. Their precise actuation contributes to enhanced safety and performance, which is critical in automotive applications. Buyers in the automotive sector must ensure that the valves they source comply with stringent industry standards and regulations, particularly in markets such as Germany and Saudi Arabia, where safety and reliability are paramount.
In What Ways Are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Important for Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, pneumatic solenoid valves control the flow of gases and liquids in reactors and other equipment. Their ability to manage pressure and flow rates is vital for maintaining safety and efficiency in chemical reactions. This application is particularly sensitive, as improper flow control can lead to hazardous situations. Buyers should prioritize sourcing valves made from materials compatible with specific chemicals and ensure that they have the necessary safety certifications to comply with industry regulations.
Why Are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Crucial in Medical Equipment?
Pneumatic solenoid valves are critical in medical equipment, particularly in devices like ventilators and anesthesia machines, where precise actuation is necessary for patient safety. Their reliability can significantly impact patient care, making it essential for manufacturers to choose high-quality components. International buyers must focus on sourcing valves that meet regulatory compliance and quality assurance standards specific to the medical industry, ensuring that they can trust the performance of their equipment in critical situations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pneumatic solenoid valves’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulties in Achieving Precise Flow Control in Pneumatic Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience challenges in maintaining precise flow control within their pneumatic systems. This often occurs in complex industrial applications, such as manufacturing or chemical processing, where even slight variations in airflow can lead to inefficiencies, product defects, or equipment damage. Buyers may struggle with selecting the right pneumatic solenoid valve that meets the specific flow rate and pressure requirements of their systems, resulting in costly downtime and operational disruptions.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should conduct a comprehensive needs assessment before sourcing pneumatic solenoid valves. This includes evaluating the specific application requirements, such as flow rate, pressure settings, and the types of media being controlled. Collaborating with suppliers who offer detailed technical specifications and performance data can aid in selecting the appropriate valve. Additionally, implementing flow control devices such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) in conjunction with solenoid valves can enhance overall system precision. Regular maintenance and calibration of the valves should also be scheduled to ensure continued accuracy and performance.
Scenario 2: Frequent Valve Failures Leading to Operational Downtime
The Problem: Operational downtime due to frequent valve failures is a significant pain point for many businesses. Pneumatic solenoid valves are essential components in various systems, but they can fail due to factors like improper installation, environmental conditions, or subpar quality. This often results in halted production lines, increased maintenance costs, and a negative impact on overall productivity. Buyers may find it challenging to identify the root cause of these failures and implement effective solutions.
The Solution: To mitigate valve failures, it’s crucial for buyers to invest in high-quality pneumatic solenoid valves from reputable manufacturers that provide warranty and support services. Conducting thorough training for maintenance personnel on proper installation and troubleshooting techniques can also reduce the likelihood of failures. Additionally, implementing a predictive maintenance program that utilizes IoT sensors to monitor valve performance can help detect potential issues before they escalate, allowing for timely interventions. Regularly reviewing and adjusting operating conditions to align with the valve specifications can further enhance durability and reliability.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible Components for Global Operations
The Problem: For international B2B buyers, especially those operating across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing compatible pneumatic solenoid valves that meet varying regional standards and specifications can be a daunting task. This challenge is compounded by differences in voltage, pressure ratings, and regulatory compliance, making it difficult to ensure that the components will function correctly in different environments.
The Solution: To address sourcing challenges, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers that have a global presence and are knowledgeable about regional compliance requirements. Establishing relationships with distributors who can provide localized support can also streamline the procurement process. Furthermore, buyers should consider standardizing their pneumatic systems wherever possible, allowing for greater compatibility across different regions. Utilizing modular designs in pneumatic systems can also facilitate easier upgrades and replacements, minimizing the risk of compatibility issues. Regular audits of suppliers and their certifications can ensure adherence to international standards and enhance supply chain reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic solenoid valves
When selecting materials for pneumatic solenoid valves, it’s essential to consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and application suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of pneumatic solenoid valves, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Brass in Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Brass is a widely used material for pneumatic solenoid valves due to its excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 180°C and can withstand pressures of around 20 bar. Brass is also relatively lightweight, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Brass valves are durable and have good thermal conductivity, which aids in heat dissipation during operation. They are also cost-effective compared to other metals, making them an attractive option for mass production.
Cons: However, brass can be susceptible to dezincification, especially in aggressive environments, which can compromise valve integrity. Additionally, its performance may decline in extreme temperatures or corrosive conditions.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with air and many non-corrosive gases, making it ideal for general industrial applications. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals or high-pressure environments.
How Does Stainless Steel Enhance the Performance of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Stainless steel is favored for its superior corrosion resistance and strength, often rated for temperatures up to 300°C and pressures exceeding 30 bar. Its durability ensures a long service life, even in harsh environments.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its ability to withstand corrosive media, making it suitable for applications in chemical processing and food industries. It also has a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Cons: On the downside, stainless steel is generally more expensive than brass and can be more challenging to machine, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, or environments where corrosion is a concern. International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 for stainless steel grades.
Why is Aluminum a Popular Choice for Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for pneumatic solenoid valves, particularly in applications where weight is a critical factor. It can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures around 10 bar.
Pros: Aluminum is easy to machine and can be anodized for enhanced corrosion resistance. Its lightweight nature reduces overall system weight, which is beneficial in mobile applications.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
Cons: However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can be less durable than brass or stainless steel in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are often used in automotive and aerospace applications where weight savings are essential. Buyers in regions with strict weight regulations, such as the EU, may prefer aluminum for compliance reasons.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Design?
Plastic materials, such as polyamide or polypropylene, are increasingly used in pneumatic solenoid valves, especially for low-pressure applications. These materials can handle temperatures up to 80°C and pressures around 5 bar.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic valves is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion from various chemicals. They are also cost-effective and easy to manufacture.
Cons: However, plastic valves may lack the durability and strength of metal counterparts, making them unsuitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic valves are ideal for applications involving non-corrosive gases and low-pressure systems. Buyers should consider compliance with standards like DIN EN ISO 9001 for quality assurance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for pneumatic solenoid valves | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | General industrial applications | Good machinability and cost-effective | Susceptible to dezincification | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food industries | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace applications | Lightweight and easy to machine | Limited pressure handling | Medium |
| Plastic | Low-pressure systems, non-corrosive gases | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable than metal options | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on performance characteristics, application suitability, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic solenoid valves
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
The manufacturing process of pneumatic solenoid valves encompasses several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer requirements. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality raw materials such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic are selected based on the specific requirements of the solenoid valve, including pressure ratings and environmental conditions. Suppliers often adhere to international material standards to ensure consistency and reliability.
In this stage, materials undergo cutting, machining, and surface treatment processes to achieve the desired dimensions and properties. For instance, machining may involve turning or milling operations to create precise valve bodies and internal components. Additionally, surface treatments such as anodizing or plating can enhance corrosion resistance, extending the valve’s lifespan.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components of the pneumatic solenoid valve. Techniques such as die casting, injection molding, and CNC machining are commonly employed.
-
Die Casting: This technique is often used for metal components, where molten metal is injected into a mold to form the valve body. It allows for high precision and complex shapes, reducing the need for extensive machining later.
-
Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is favored due to its efficiency and ability to produce large quantities of uniform parts.
-
CNC Machining: This method is vital for creating intricate details and ensuring tight tolerances. CNC machines can produce components with high accuracy, which is essential for the proper functioning of solenoid valves.
How Are Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Assembled?
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This phase involves combining various parts such as the solenoid, plunger, seals, and valve body.
Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, utilizing robotic systems to improve efficiency and reduce human error. Each component is carefully inspected during assembly to ensure proper fit and function. Additionally, the assembly process may include the application of lubricants or sealants to enhance performance and prevent leaks.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Finishing processes are crucial for the aesthetic and functional quality of pneumatic solenoid valves. This stage typically includes cleaning, surface treatments, and quality inspections.
Cleaning processes remove any contaminants from the manufacturing stages, ensuring that the final product is free of debris that could affect performance. Surface treatments, such as painting or powder coating, not only improve appearance but also provide additional protection against corrosion and wear.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant to Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of pneumatic solenoid valves, ensuring that products meet specified standards for safety and performance. Several international and industry-specific standards are relevant:
-
ISO 9001: This widely recognized quality management system standard emphasizes consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers adhere to systematic processes that enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Manufacturers must ensure their products meet these regulations to gain access to these markets.
-
API Standards: For valves used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential. These standards cover various aspects of valve design, materials, and testing to ensure reliability in demanding environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications. Ensuring that materials meet quality standards prevents defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This may involve measuring dimensions, testing assembly accuracy, and monitoring machining processes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough inspection is performed. FQC checks the functionality of the valve, ensuring it operates correctly under specified conditions. Testing methods may include pressure testing, leakage testing, and electromagnetic testing for solenoid operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring product reliability. Here are several methods buyers can use:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems firsthand. This evaluation can uncover any potential issues and provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports from suppliers can provide valuable information on their processes and testing methods. These reports should outline how the supplier adheres to international standards and any certifications they hold.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can perform inspections at various stages of production, ensuring that standards are maintained throughout the manufacturing process.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of specific quality control nuances that may vary by region. For instance:

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements for pneumatic solenoid valves. Understanding these requirements is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential market entry barriers.
-
Cultural Differences: Cultural perceptions of quality and reliability can influence supplier relationships. Building trust through transparent communication and regular updates can help establish long-term partnerships.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks that affect product quality. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and handling processes can mitigate these risks and protect the integrity of the valves during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with pneumatic solenoid valves, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable supplier partnerships that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pneumatic solenoid valves’
The procurement of pneumatic solenoid valves can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of your operations. This checklist will guide you through the essential steps to ensure that you make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your pneumatic solenoid valves. Consider factors such as the valve type (e.g., 2-way, 3-way), pressure ratings, operating voltage, and the specific application within your systems. This clarity will help you communicate your needs effectively and avoid purchasing valves that do not meet your operational requirements.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in pneumatic solenoid valves. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry recommendations to compile a list of credible manufacturers and distributors. Focus on suppliers that have a strong reputation in your target markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their experience in supplying pneumatic solenoid valves and check for customer reviews to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
- Look for certifications: Ensure that suppliers comply with international standards (e.g., ISO certifications) relevant to pneumatic components.
- Assess their product range: A supplier with a diverse product range may offer better options for your specific needs.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, lead times, and terms of sale. Compare these quotes not only based on cost but also on the value offered, such as warranty periods and post-purchase support.
- Consider bulk discounts: If you plan to order in large quantities, inquire about volume pricing options.
- Understand shipping terms: Ensure clarity on shipping costs and delivery timelines, especially if sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 5: Verify Quality Assurance Processes
Before finalizing your purchase, investigate the quality assurance processes employed by the supplier. Ensure they have rigorous testing protocols in place to guarantee that their pneumatic solenoid valves meet the necessary performance and safety standards.
- Inquire about testing certifications: Ask if they provide documentation for testing results, which can assure you of the product’s reliability.
- Review return and exchange policies: Understand their policies in case the products do not meet your expectations upon delivery.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support
Strong after-sales support can be a deciding factor in your procurement process. Confirm that the supplier offers technical assistance, warranty services, and easy access to replacement parts.
- Evaluate customer service responsiveness: Reach out with questions and note how quickly and thoroughly they respond.
- Look for training resources: Some suppliers may provide training on the installation and maintenance of their products, which can be invaluable.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Document Everything
Once you are satisfied with a supplier, finalize your order and ensure that all details are documented. This includes purchase agreements, delivery schedules, and any warranties or service agreements.
- Keep clear records: Maintain organized documentation for future reference, especially for warranty claims or potential disputes.
- Communicate clearly: Confirm all order details with the supplier to avoid misunderstandings.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for pneumatic solenoid valves, ensuring that you select the right products from reliable suppliers while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic solenoid valves Sourcing
In the competitive landscape of pneumatic solenoid valves, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge enables informed decision-making, particularly for businesses operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Cost Components in Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manufacturing?
The cost of pneumatic solenoid valves can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include high-quality metals, plastics, and elastomers. The choice of materials directly impacts durability and performance, influencing overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers often include these costs in their pricing models to maintain profitability.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific valve designs can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should consider whether a supplier has the necessary tooling for their specific valve requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are essential, especially for valves used in critical applications. QC costs can vary based on the complexity of the product and the certifications required.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can be substantial, particularly for international orders. Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers add a margin to cover their operational costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Costs?
Several factors influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities often yields better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom valves with unique specifications will typically incur higher costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard models can meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Valves made from premium materials or those that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices. However, investing in higher-quality valves can reduce maintenance costs in the long term.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms can help buyers negotiate better terms regarding shipping costs and responsibilities. This knowledge is crucial for international transactions.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
-
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. Leverage volume purchases or long-term contracts to secure better pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan when assessing the value of a valve.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, currency fluctuations and import duties can significantly affect the total cost. It’s advisable to factor these elements into budgetary considerations.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and features across different suppliers. Utilize online resources and industry networks to gather insights and testimonials.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of pneumatic solenoid valves is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering key cost components, price influencers, and strategic negotiation tactics, businesses can optimize their sourcing decisions, ensuring both cost-efficiency and product quality. It is important to note that prices can vary widely based on numerous factors; thus, always seek updated quotes and engage in due diligence to avoid unforeseen expenses.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pneumatic solenoid valves With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
In the realm of industrial automation and fluid control systems, pneumatic solenoid valves are widely recognized for their efficiency and precision. However, various alternatives can also serve similar functions, each with unique benefits and limitations. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
| Comparison Aspect | Pneumatic Solenoid Valves | Electric Actuators | Mechanical Control Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in controlling airflow and pressure | Moderate precision; slower response | Variable precision based on design |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate cost | Higher initial investment | Low initial cost, but variable depending on type |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to integrate into existing systems | Moderate complexity; requires electrical setup | Simple installation but may require manual operation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks for wear and potential leaks | Low maintenance but needs electrical checks | Minimal maintenance; manual adjustments may be needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automated systems needing precise control | Suitable for applications requiring positioning and torque | Effective for simple on/off control in non-complex systems |
Understanding Electric Actuators as an Alternative
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making them a viable alternative to pneumatic solenoid valves. These devices are particularly advantageous in applications where precise positioning is required, such as robotics and CNC machinery. The primary benefits of electric actuators include a higher degree of control over motion and the ability to integrate seamlessly with digital systems. However, they tend to have a higher initial investment cost and may require more complex electrical setups, which can increase installation time and costs.
Evaluating Mechanical Control Valves as an Option
Mechanical control valves, including gate and ball valves, operate through manual or mechanical means to regulate fluid flow. They are typically less expensive than their pneumatic or electric counterparts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. These valves are straightforward to install and maintain, often requiring minimal upkeep. However, their performance can be less precise, and they lack the automation capabilities that pneumatic solenoid valves provide, making them less suitable for high-tech industrial applications where efficiency is paramount.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between pneumatic solenoid valves and their alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific application requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and installation capabilities. Pneumatic solenoid valves excel in environments requiring high precision and automation, while electric actuators may be preferable for applications necessitating detailed positioning. Mechanical control valves can provide a cost-effective solution for simpler systems. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic solenoid valves
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
When selecting pneumatic solenoid valves, understanding their technical specifications is vital for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility with your systems. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material of a pneumatic solenoid valve significantly affects its durability, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. Brass valves are cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for many industrial applications. In contrast, stainless steel valves provide superior strength and resistance to harsh environments, ideal for chemical processing or food industries.
2. Pressure Rating
Pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle without failure. It is typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. For B2B buyers, selecting a valve with an appropriate pressure rating ensures safety and functionality in high-pressure applications, such as automotive or industrial machinery. A mismatch can lead to leaks or catastrophic failures.
3. Flow Rate
Flow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM) or cubic feet per minute (CFM), determines how much air can pass through the valve. This is crucial for applications requiring precise control of airflow, such as in pneumatic actuators or cylinders. Understanding flow rate helps buyers match the valve to the specific needs of their systems, optimizing performance and efficiency.
4. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating specifies the electrical requirements for the solenoid to operate correctly. Common ratings include 12V, 24V, and 110V. Buyers must ensure compatibility with their existing electrical systems to prevent damage to the valve or operational failures. Choosing the right voltage rating also influences energy consumption and operational costs.
5. Actuation Type
Pneumatic solenoid valves can be either normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO). NC valves remain closed until activated, while NO valves are open by default. This specification is critical for ensuring that the valve operates correctly within the intended application, particularly in safety-critical systems where unintended air flow could pose risks.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
Understanding industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms you may encounter:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of pneumatic solenoid valves, it refers to suppliers that provide components used in the assembly of larger systems. Buyers often prefer OEMs for their reliability and assurance of compatibility with other components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Suppliers typically set MOQs to cover production costs, so negotiating this term can lead to cost savings for bulk purchases.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers asking for a price quote on specific products or services. This process is vital for B2B buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost of procurement. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international buyers to mitigate risks and ensure smooth transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. For pneumatic solenoid valves, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Longer lead times can impact production schedules, so buyers should inquire about this when negotiating with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure seamless integration of pneumatic solenoid valves into their systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pneumatic solenoid valves Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Sector?
The pneumatic solenoid valves market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing automation in various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and food processing. As businesses aim to enhance operational efficiency and reduce labor costs, the demand for pneumatic systems, including solenoid valves, is on the rise. Emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 are also influencing market dynamics. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of pneumatic systems, leading to improved decision-making and maintenance strategies.
Furthermore, international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are focusing on sourcing valves that offer enhanced safety and reliability. With stricter regulations on industrial safety and efficiency, companies are increasingly seeking high-quality pneumatic solenoid valves that comply with international standards. This trend is particularly evident in markets like Germany, where precision engineering is paramount, and Saudi Arabia, which is investing heavily in industrial diversification.
Emerging sourcing trends include a shift towards direct sourcing from manufacturers to reduce costs and improve supply chain transparency. Additionally, buyers are leveraging digital platforms to compare products and suppliers, which enhances their ability to make informed purchasing decisions. As e-commerce continues to grow, the accessibility of product information and supplier ratings is transforming how businesses approach procurement in the pneumatic solenoid valves sector.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the pneumatic solenoid valves market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and product lifecycle is under increased scrutiny. Many companies are prioritizing the sourcing of valves that are produced using sustainable materials and processes. This shift is not only driven by regulatory pressures but also by growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Ethical sourcing practices are essential for ensuring a responsible supply chain. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming important indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In addition to certifications, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable plastics and low-impact metals, is gaining traction. Companies that can provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices and material composition are likely to gain a competitive advantage. By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the expectations of socially conscious stakeholders.
How Has the Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of pneumatic solenoid valves can be traced back to the early 20th century when pneumatic technology began gaining traction in industrial applications. Initially, these valves were manually operated, limiting their efficiency and responsiveness. The introduction of electrical solenoids in the mid-1900s marked a significant turning point, allowing for automated control of pneumatic systems.
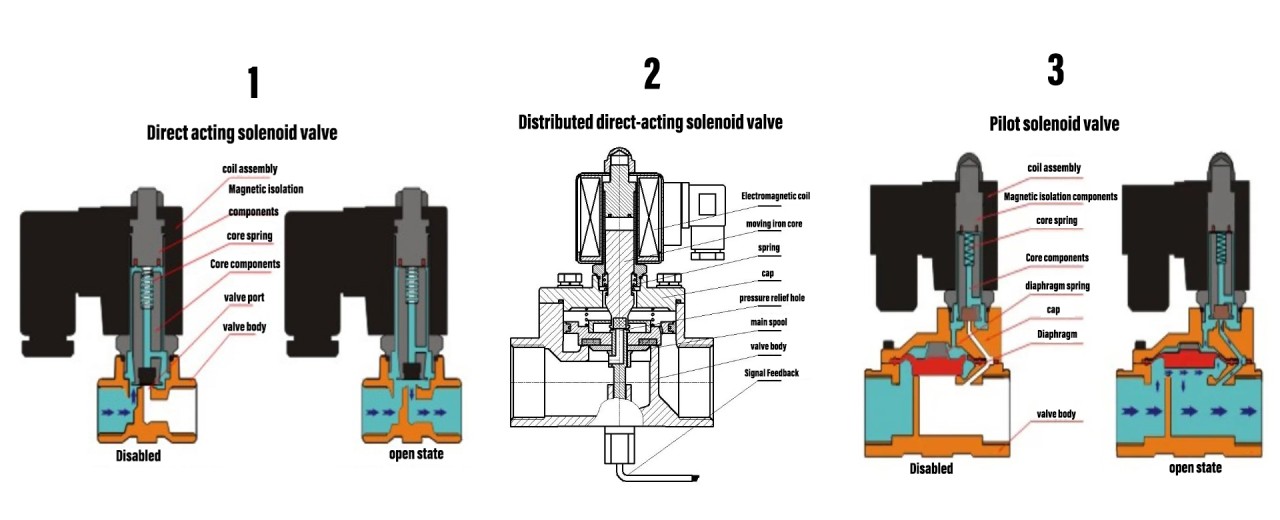
Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
As industries embraced automation, the demand for more sophisticated pneumatic solenoid valves grew. Innovations in design and materials have led to the development of valves that offer greater precision, faster response times, and enhanced durability. Today, the integration of smart technologies is paving the way for the next generation of pneumatic solenoid valves, enabling features such as remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
This historical context underscores the significance of continuous innovation in the pneumatic solenoid valves market, which is essential for meeting the evolving demands of modern industries. B2B buyers must remain vigilant about these advancements to ensure they are sourcing the most effective and reliable solutions for their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic solenoid valves
-
How do I troubleshoot pneumatic solenoid valve issues?
To troubleshoot pneumatic solenoid valve issues, first check for electrical faults such as improper voltage or connection issues. Inspect the solenoid coil for damage and ensure it is receiving power. Next, examine the valve for physical blockages, leaks, or signs of wear and tear. If the valve is not actuating, ensure the air supply is adequate and free of contaminants. Regular maintenance and periodic testing can help prevent these issues and ensure optimal performance. -
What is the best type of pneumatic solenoid valve for industrial automation?
The best type of pneumatic solenoid valve for industrial automation often depends on the specific application. Generally, 5/2 or 5/3 way valves are preferred for controlling actuators in automation processes, as they can manage the direction of airflow effectively. Additionally, consider factors like the required flow rate, pressure ratings, and the operating environment. It’s crucial to choose valves that are compatible with your existing pneumatic system to ensure efficiency and reliability. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing pneumatic solenoid valves internationally?
When sourcing pneumatic solenoid valves internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, compliance with international quality standards, and their ability to provide technical support. Evaluate their product range to ensure they offer the specific types and sizes you need. Additionally, understand their lead times, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and payment terms. It’s also wise to inquire about logistics and shipping options, especially if you require timely delivery to regions such as Africa or South America. -
How can I verify the quality of pneumatic solenoid valves from suppliers?
To verify the quality of pneumatic solenoid valves, request product certifications and compliance documents that meet international standards, such as ISO or CE markings. Conduct supplier audits or ask for references from other clients. Consider ordering samples for testing before committing to a larger purchase. Additionally, inquire about warranty policies and after-sales support, as reputable suppliers should stand behind their products and offer assistance if issues arise. -
What are the common customization options available for pneumatic solenoid valves?
Common customization options for pneumatic solenoid valves include variations in voltage, port size, and body material to suit specific applications. Suppliers may also offer tailored designs for unique operational requirements, such as modified flow rates or enhanced sealing capabilities. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to explore available options and the associated lead times. Customization can significantly enhance performance, especially in specialized industrial applications. -
What are typical payment terms when purchasing pneumatic solenoid valves?
Typical payment terms for purchasing pneumatic solenoid valves vary by supplier and region but often include options like advance payment, net 30, or 60 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer payment plans or letters of credit for larger orders. Always clarify terms before finalizing the purchase to ensure they align with your budgeting and cash flow needs. Additionally, consider the impact of currency exchange rates if purchasing from international suppliers. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing pneumatic solenoid valves?
When importing pneumatic solenoid valves, logistics considerations include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with the regulations in your country to ensure compliance and timely delivery. Additionally, consider the lead times for manufacturing and shipping, and factor in potential delays due to customs clearance. Proper documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is essential for smooth logistics processes. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of pneumatic solenoid valves?
To ensure timely delivery of pneumatic solenoid valves, establish clear communication with your supplier regarding lead times and delivery schedules. Plan your orders well in advance, especially if sourcing from international suppliers, to account for potential delays. Use reliable logistics partners and track shipments to monitor progress. Additionally, consider setting up a safety stock to mitigate risks associated with unexpected delays in supply chains.
Top 8 Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. US Solid – Pneumatic Valves
Domain: ussolid.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, US Solid – Pneumatic Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. McMaster – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Domain: mcmaster.com
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Pneumatic Plus – Solenoid Valves
Domain: pneumaticplus.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valves: G1/8 – 1/8″ NPT (18mm Body) – MSRP: $46.50; G1/8 – 1/8″ NPT (23mm Body) – MSRP: $46.88; G1/4 – 1/4″ NPT (26mm Body) – MSRP: $46.88; G3/8 – 3/8″ NPT (32mm Body) – MSRP: $67.13; M5/10-32 UNF (15mm Body) – MSRP: $46.13.
4. AutomationDirect – Directional Control Solenoid Valves
Domain: automationdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, AutomationDirect – Directional Control Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Humphrey Products – Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Domain: humphrey-products.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic Solenoid Valves by Humphrey Products include:
– Types: Direct-acting and Pilot-operated
– Categories: Miniature 2-Way & 3-Way, Small 2-Way & 3-Way, Large 2-Way & 3-Way, Small 4-Way, Large 4-Way
– Features: High-flow efficiency, accommodates compressed air, vacuum, and inert gases, compact and reliable designs, precision machined or molded valve bodies, low leak rates, bubble-tight models…
6. Baomain – 2 & 3 Space Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Domain: baomain.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Baomain 2 Space Pneumatic 1/4″PT Solenoid Valve 4V210-08 12V/24V/110V/220V Single Coil Pilot-Operated Electric 2 Position 5 Way Connection Type with Base Muffler – Regular price $20.99; Baomain 3 Space Pneumatic 1/4″PT Solenoid Valve 4V210-08 12V/24V/110V/220V Single Coil Pilot-Operated Electric 2 Position 5 Way Connection Type with Base Muffler – Regular price $29.49; Baomain 4 Space Pneumatic So…
7. SMC – Solenoid Valves & Industrial Communication
Domain: smcusa.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, SMC – Solenoid Valves & Industrial Communication, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Festo – Universal Directional Control Valves
Domain: festo.com
Introduction: Universal Directional Control Valves from Festo USA include two main models: VUVS and VUVG.
**VUVS Solenoid Valve:**
– Type: Robust solenoid-operated directional control valve
– Configurations: 3/2 normally closed, 5/2 single solenoid, 5/2 double solenoid
– Applications: Suitable for packaging, printing, machine tools, woodworking, etc.
– Mounting Options: Wide range of mounting accessories,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic solenoid valves
What are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Pneumatic Solenoid Valves?
In summary, strategic sourcing of pneumatic solenoid valves is essential for optimizing operational efficiency across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and healthcare. By understanding the specific needs of your applications, buyers can select the right valve configurations that offer precision, safety, and reliability. The diverse range of options available—such as two-way, three-way, and five-way valves—enables companies to tailor their pneumatic systems to their unique requirements.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic solenoid valves
Why is Strategic Sourcing Important for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing not only ensures compliance with regional standards but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that can yield cost savings and improved service. As global markets continue to evolve, the ability to source high-quality pneumatic solenoid valves at competitive prices will be a significant advantage.
How Can You Prepare for Future Procurement in Pneumatic Systems?
Looking ahead, consider leveraging digital platforms to enhance your sourcing strategies. By engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive support and innovative solutions, you can stay ahead of market trends and technological advancements. Equip your organization with the right tools and knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions that drive growth and efficiency in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.