Parts Of An Exchanger Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of an exchanger
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing the right parts of an exchanger can present significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexity of navigating regulations, quality standards, and supplier reliability can make the procurement process daunting. This guide aims to demystify the components of exchangers—specifically shell and tube heat exchangers—by providing a thorough exploration of their parts, applications, and the varying industry standards that govern them.
Our comprehensive resource covers the fundamental components, such as tubes, tube shells, nozzles, and baffles, and delves into their specific applications across various industries, including petrochemical and power generation. Additionally, we will address the critical aspects of supplier vetting to ensure that your sourcing decisions are both informed and strategic. Understanding cost implications and potential maintenance needs will also be a focus, empowering you to make choices that enhance operational efficiency and longevity.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide aims to streamline the procurement process, helping you to confidently select the right parts of an exchanger tailored to your specific needs. Whether you are based in Germany, Vietnam, or elsewhere, the information provided here will support your goal of achieving optimal performance and reliability in your operations.
Understanding parts of an exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube | Comprises a series of tubes within a cylindrical shell; suitable for high-pressure applications. | Petrochemical, power generation, HVAC | Pros: Versatile, efficient heat transfer; Cons: Space-intensive, complex maintenance. |
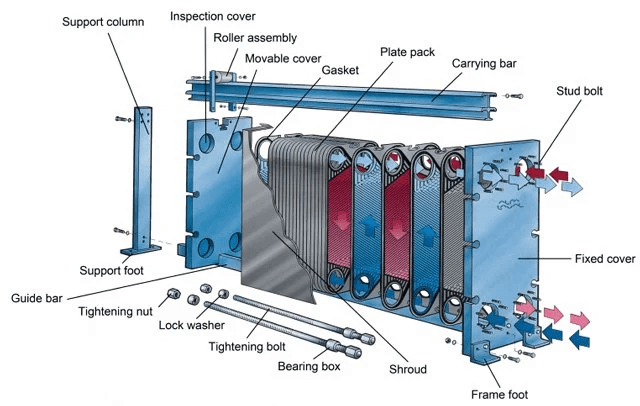
| Plate Heat Exchanger | Made up of multiple thin plates; compact design allows for high heat transfer efficiency. | Food processing, chemical industries | Pros: Smaller footprint, easy to clean; Cons: Limited pressure handling, potential for fouling. |
| Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger | Utilizes air to remove heat; no need for cooling water. | Oil refineries, gas processing | Pros: Water conservation, lower operational costs; Cons: Performance affected by ambient temperature. |
| Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger | Simple design featuring one pipe inside another; effective for small-scale applications. | Small industrial processes, laboratories | Pros: Easy to construct and maintain; Cons: Limited heat transfer efficiency compared to other types. |
| Fin Tube Heat Exchanger | Incorporates fins on tubes to increase surface area; ideal for low-flow applications. | HVAC systems, refrigeration | Pros: Enhanced efficiency, compact size; Cons: More expensive due to complex design. |
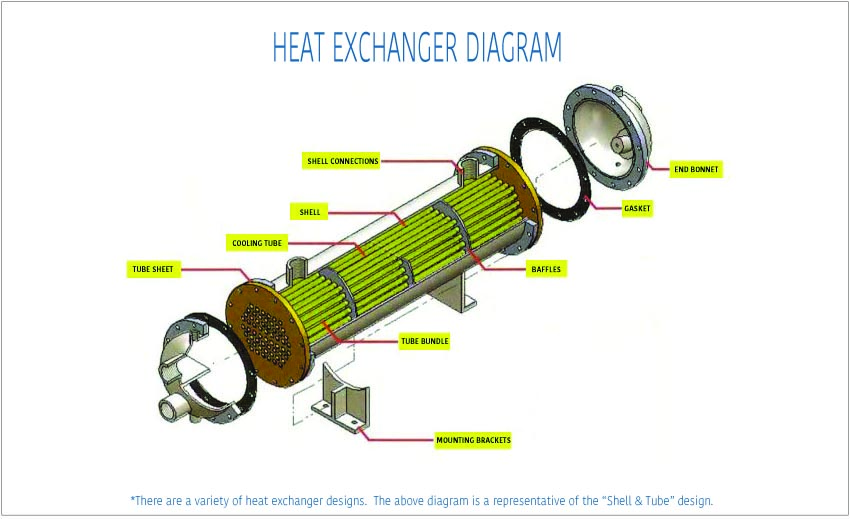
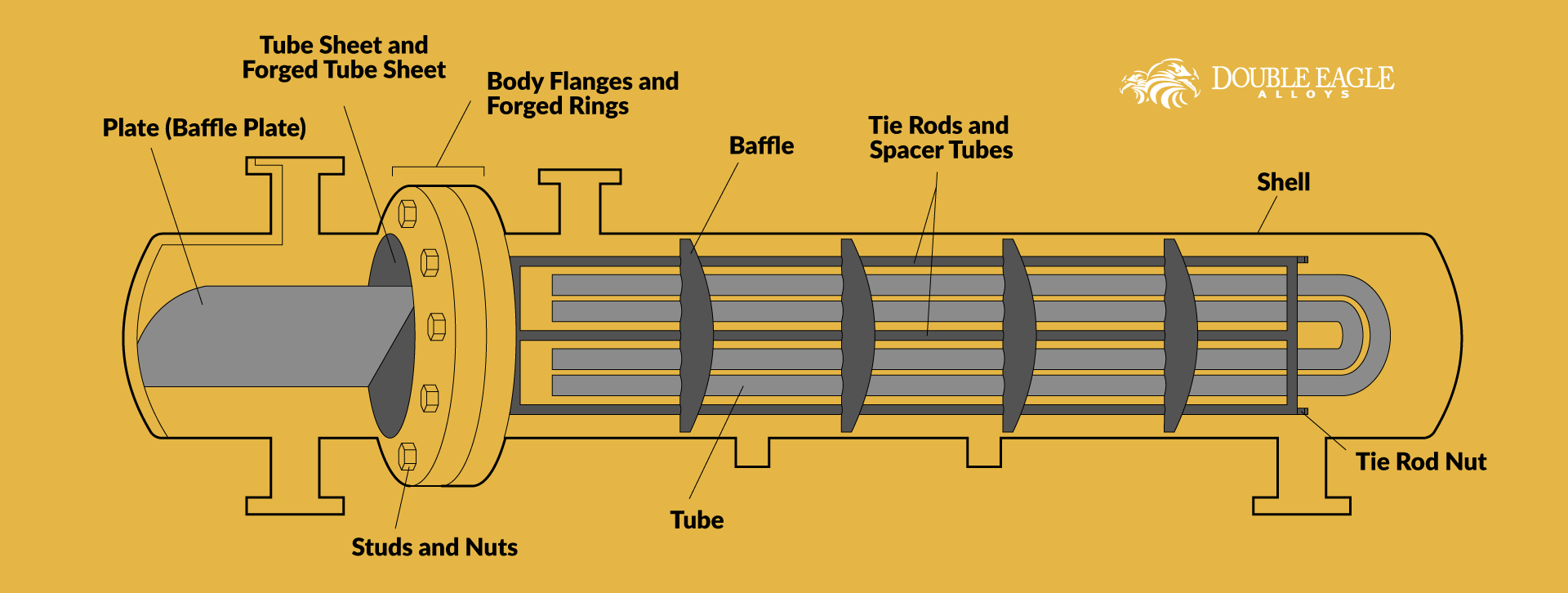
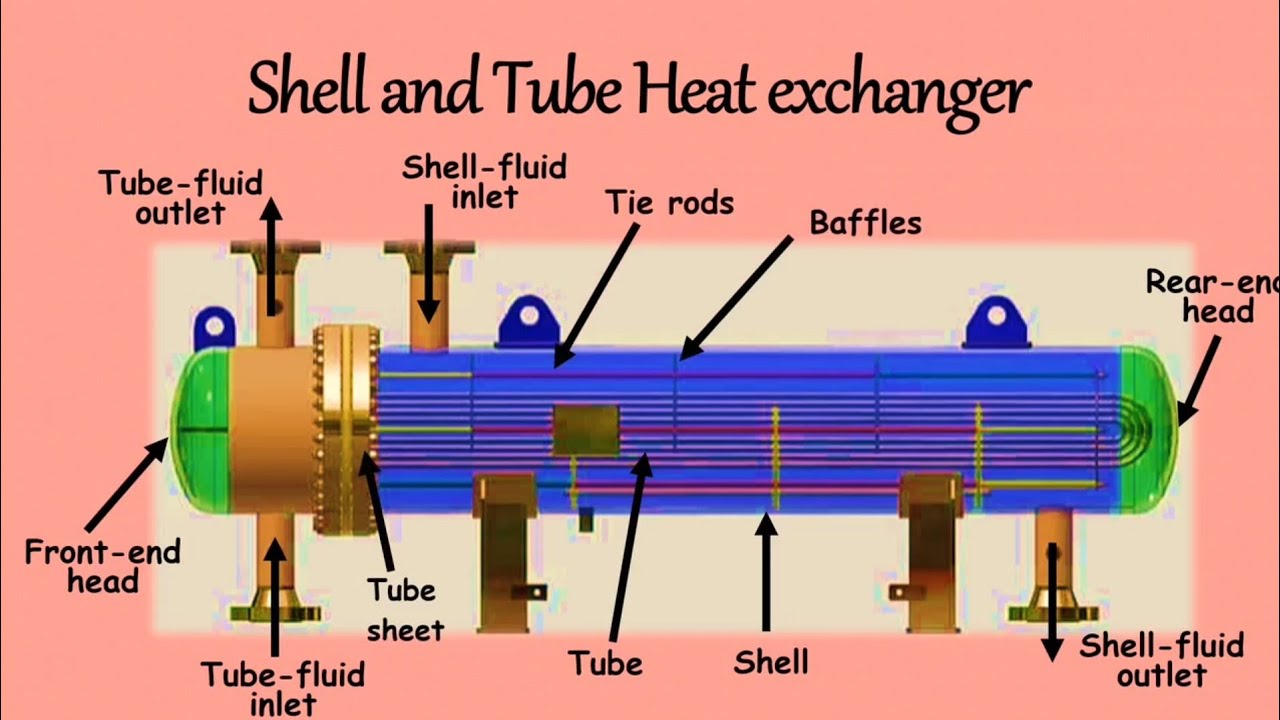
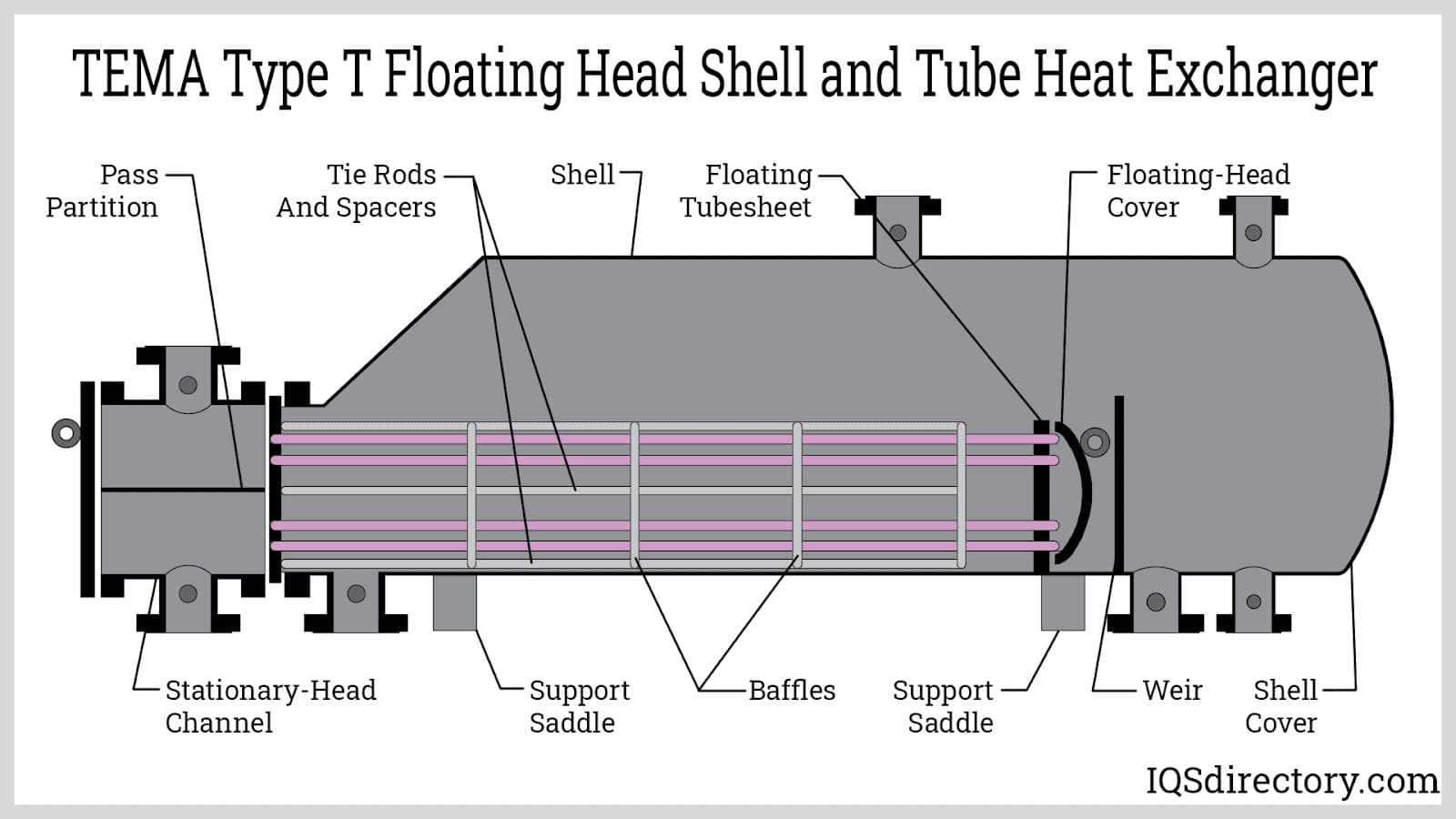
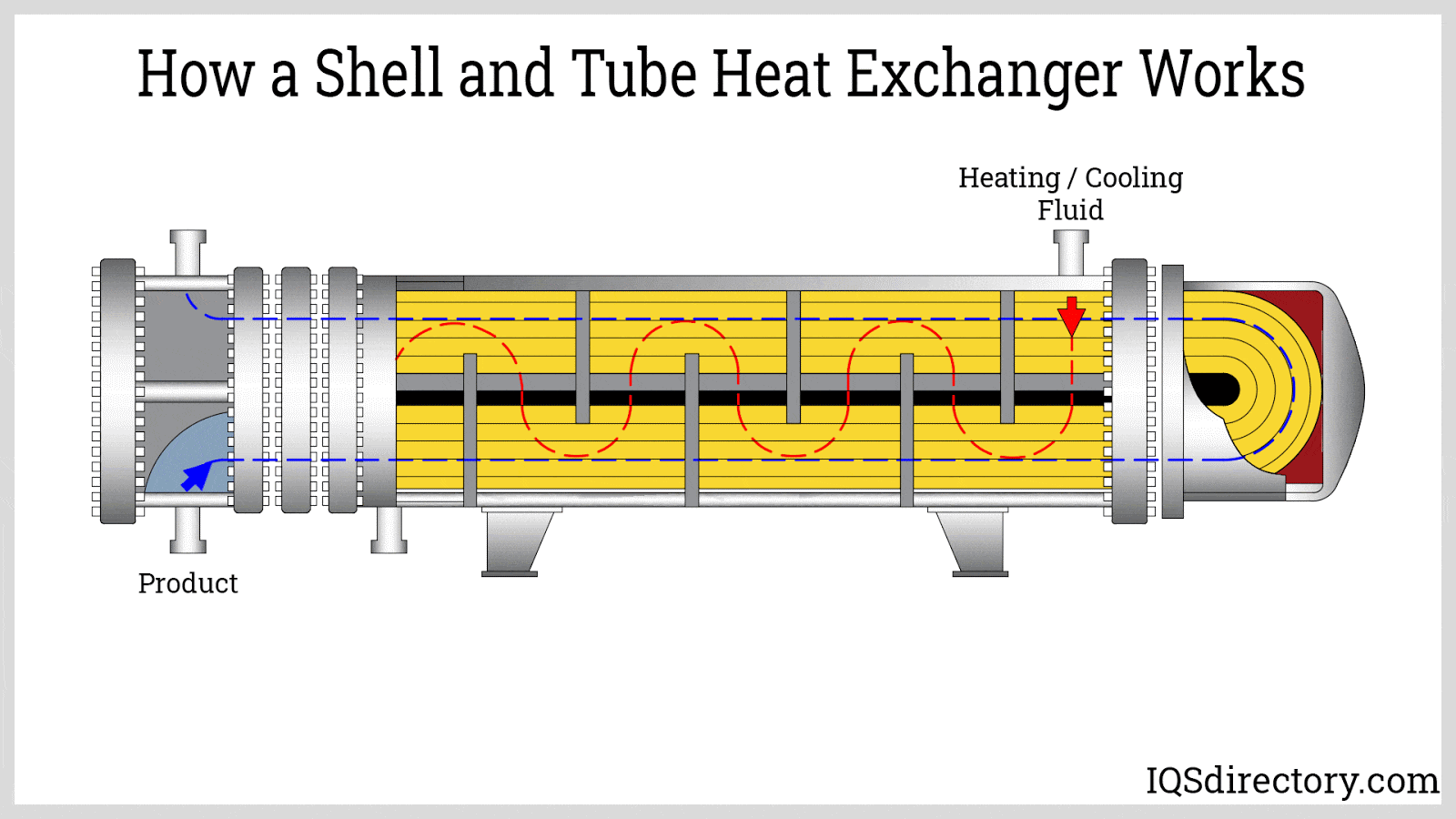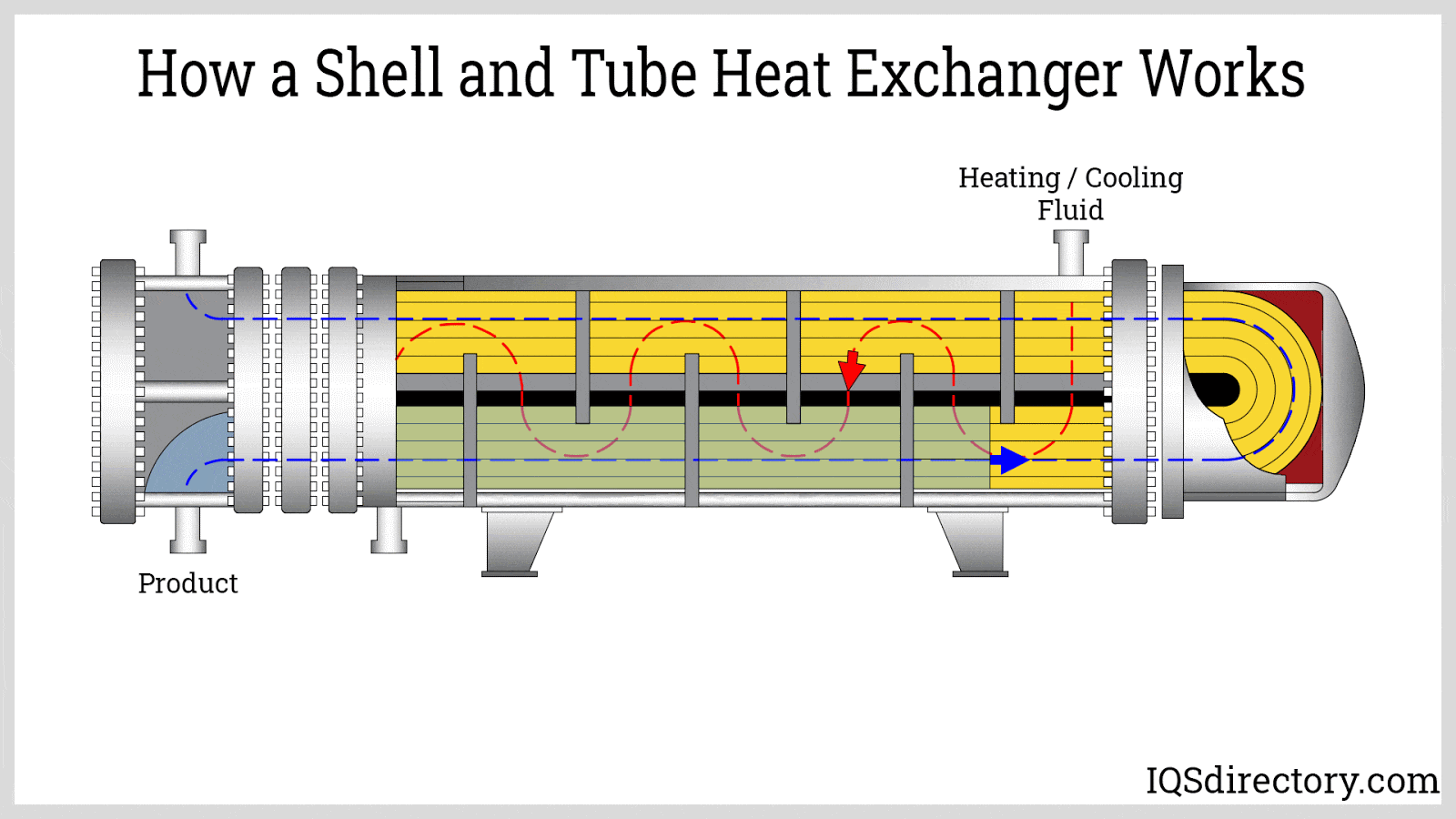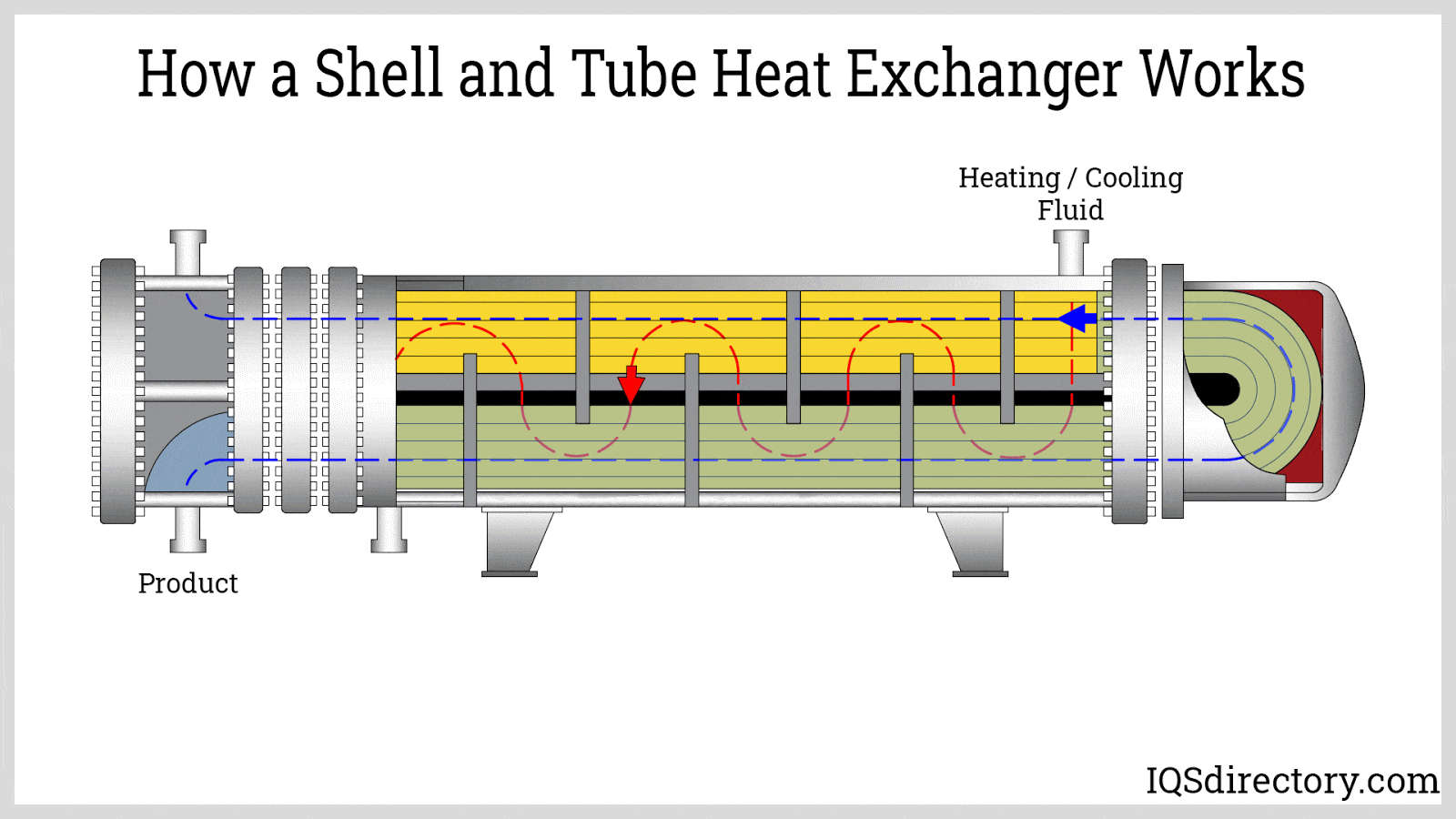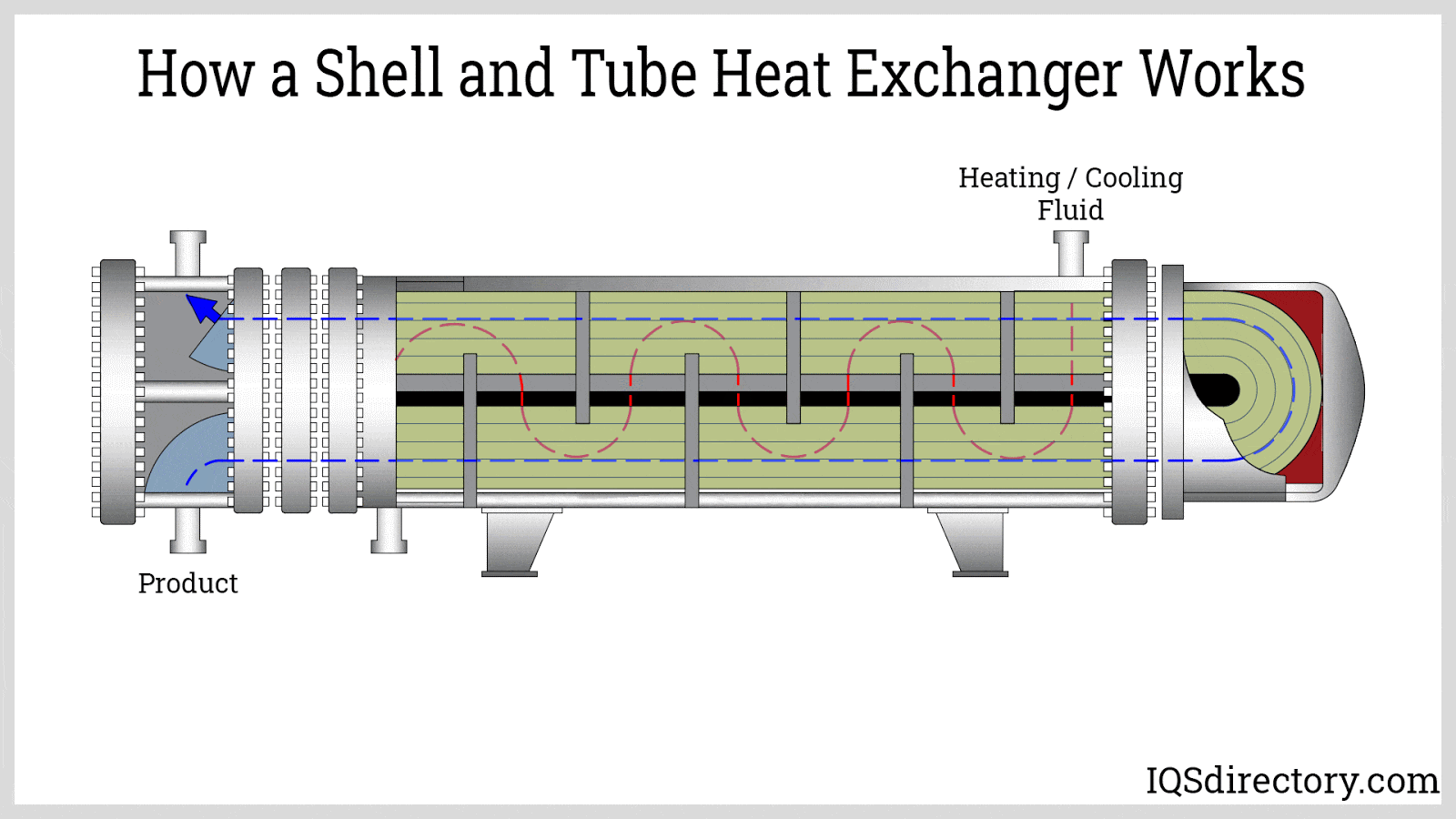
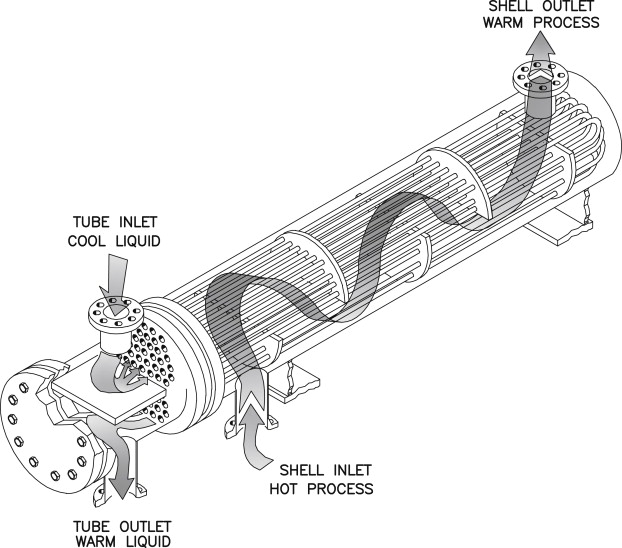
What Are the Characteristics of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
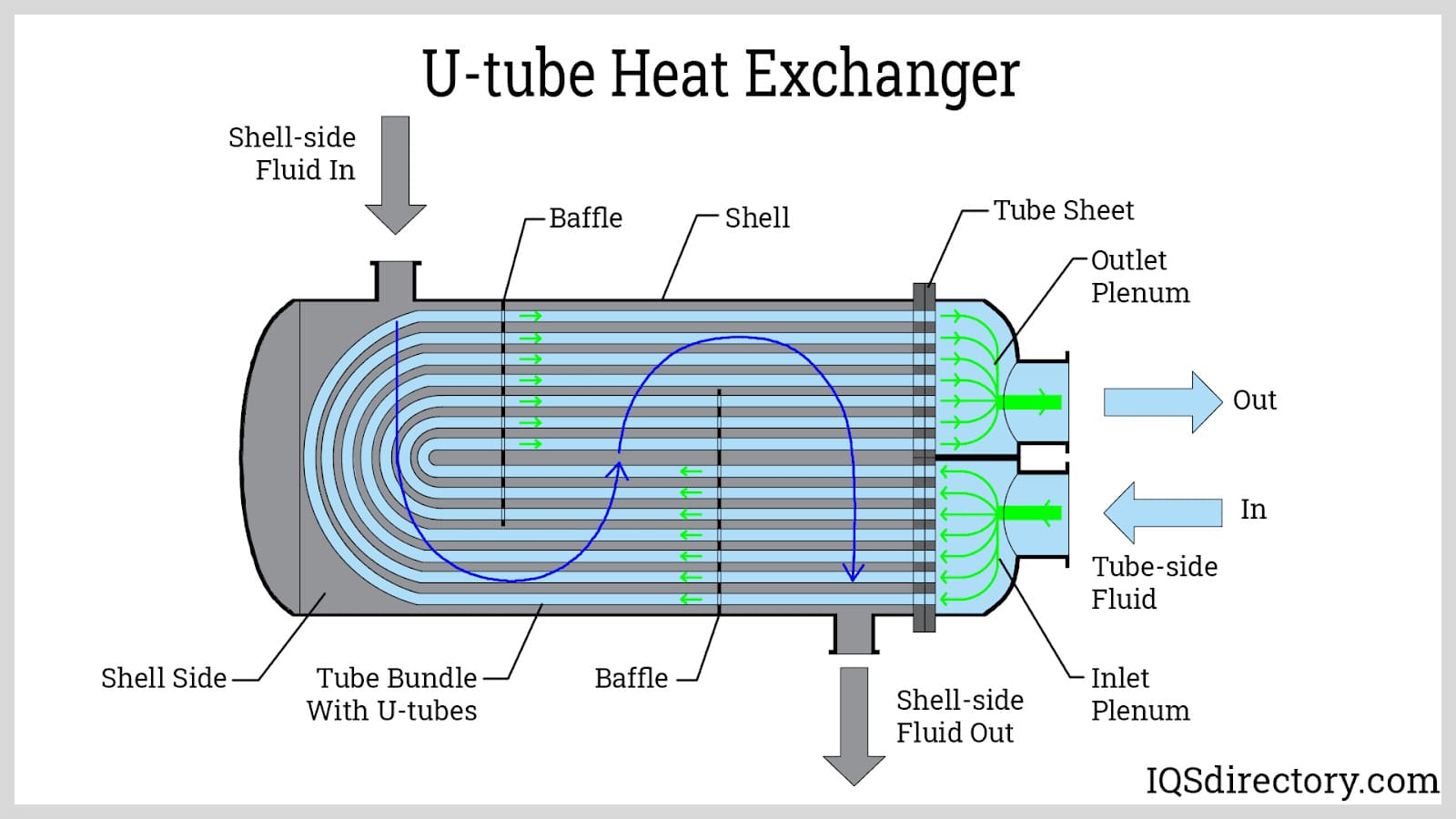
Shell and tube heat exchangers are characterized by their robust design, allowing them to handle high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for industries such as petrochemicals and power generation. The exchanger consists of a series of tubes housed within a cylindrical shell, facilitating efficient heat transfer between two fluids. B2B buyers should consider factors such as material compatibility, maintenance requirements, and space constraints when selecting this type.
How Do Plate Heat Exchangers Differ in Design and Use?
Plate heat exchangers feature a series of thin, corrugated plates that create a large surface area for heat transfer. Their compact design makes them suitable for applications in food processing and chemical industries, where space is limited. Buyers should evaluate the potential for fouling, pressure limits, and cleaning accessibility to ensure optimal performance and longevity in their specific applications.
What Are the Benefits of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers?
Air-cooled heat exchangers employ ambient air to dissipate heat, eliminating the need for cooling water. This design is advantageous in regions with limited water resources and is commonly used in oil refineries and gas processing. B2B buyers should consider the impact of environmental conditions on performance and the potential for higher operational costs in extreme temperatures when assessing suitability for their operations.
When Should You Choose a Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger?
Double-pipe heat exchangers consist of one pipe inside another, allowing for straightforward heat exchange. Their simplicity makes them ideal for small-scale applications, such as in laboratories or small industrial processes. Buyers should weigh the ease of maintenance and construction against the limited efficiency and capacity compared to more complex designs.
What Advantages Do Fin Tube Heat Exchangers Offer?
Fin tube heat exchangers are designed with fins on the tubes, increasing the surface area for heat transfer. They are particularly effective in low-flow applications, such as HVAC systems and refrigeration. While they offer enhanced efficiency and a compact size, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher costs due to the intricacies of their design.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
Key Industrial Applications of parts of an exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of an exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petrochemical | Heat exchangers in refining processes for crude oil | Enhanced efficiency in heat transfer, reducing energy consumption | Compliance with TEMA standards, material selection for corrosion resistance |
| Power Generation | Condensers in steam power plants for heat recovery | Improved energy efficiency and lower operational costs | Compatibility with existing systems, reliability under high pressure |
| Food and Beverage | Pasteurization systems utilizing shell and tube heat exchangers | Ensures food safety while optimizing energy usage | Hygiene standards, material safety certifications, ease of maintenance |
| HVAC Systems | Chillers using heat exchangers for temperature control | Increased energy efficiency and improved climate control | Size and capacity matching, energy efficiency ratings |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Process cooling in chemical reactors using tube-side heat exchangers | Enhanced reaction efficiency and safety through temperature control | Material compatibility with chemicals, adherence to safety regulations |
How Are Parts of an Exchanger Utilized in the Petrochemical Industry?
In the petrochemical sector, shell and tube heat exchangers are integral for refining crude oil. The tubes facilitate effective heat transfer between fluids, which is crucial in processes like distillation and cooling. By optimizing heat exchange, businesses can significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with TEMA standards and select materials resistant to corrosion, as the harsh chemical environments can lead to rapid degradation of components.
What Role Do Parts of an Exchanger Play in Power Generation?
In power generation, particularly in steam power plants, condensers are vital components that utilize tube-side heat exchangers. These exchangers recover waste heat, thus improving overall energy efficiency. This leads to reduced fuel costs and enhanced operational efficiency. International buyers must consider compatibility with existing systems and the reliability of materials under high-pressure conditions to ensure long-term performance and safety.
How Are Parts of an Exchanger Applied in the Food and Beverage Sector?
The food and beverage industry employs shell and tube heat exchangers primarily in pasteurization processes. These exchangers ensure that products are heated to safe temperatures without compromising quality, thus promoting food safety. The selection of materials must meet stringent hygiene standards and safety certifications, making it essential for buyers to prioritize suppliers who can guarantee compliance. Additionally, ease of maintenance is critical to minimize downtime.
What Benefits Do Parts of an Exchanger Offer in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC applications, chillers equipped with heat exchangers are essential for effective temperature control in buildings. These systems increase energy efficiency, leading to lower operational costs and improved comfort for occupants. Buyers should focus on the size and capacity of the exchangers to match specific cooling requirements and consider energy efficiency ratings to ensure optimal performance.
How Are Parts of an Exchanger Utilized in Chemical Manufacturing?
In chemical manufacturing, tube-side heat exchangers are used for process cooling within reactors. This application is crucial for maintaining optimal reaction temperatures, thereby enhancing efficiency and safety. Buyers need to ensure that the materials used can withstand the specific chemicals involved and adhere to safety regulations. This attention to detail helps prevent incidents and ensures the reliability of the manufacturing process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of an exchanger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Tubes for Exchangers
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing high-quality tubes that meet specific application requirements. The materials used in the tubes, such as copper, steel alloys, or even specialized alloys like titanium, can significantly impact the efficiency and durability of the heat exchanger. Poor-quality tubes can lead to increased corrosion, reduced heat transfer efficiency, and ultimately, system failures. In regions with variable material availability and fluctuating prices, finding reliable suppliers becomes a daunting task.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who specialize in heat exchanger components. Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers that adhere to industry standards, such as those set by ASME or TEMA. Buyers should also request samples and certifications for the materials to ensure they meet the required specifications. Additionally, leveraging local suppliers can mitigate risks related to logistics and transportation costs. Implement a rigorous quality control process, including regular inspections and testing, to ensure that the tubes maintain their integrity over time.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Inefficient Heat Transfer Due to Baffle Issues
The Problem: Inefficient heat transfer is often a consequence of improperly designed or installed baffles within the heat exchanger. Baffles play a crucial role in directing fluid flow and maintaining the spacing of tubes. If baffles are misaligned or poorly constructed, it can result in uneven flow patterns, leading to hot spots and reduced thermal performance. This issue can be particularly frustrating for B2B buyers who rely on precise temperature control for their processes.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
The Solution: To address baffle-related inefficiencies, buyers should ensure that they are sourcing high-quality baffles designed for their specific heat exchanger model. Collaborating closely with manufacturers to understand the thermal dynamics of their system can help in selecting the correct baffle design. Furthermore, implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspection and adjustment of baffles can help optimize performance. Consider using advanced simulation software to model fluid dynamics within the exchanger, allowing for more informed decisions on baffle configuration and placement.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Tube-Side Channel and Nozzle Corrosion
The Problem: Corrosion in the tube-side channel and nozzles can severely impact the operational efficiency and lifespan of heat exchangers, especially when dealing with corrosive fluids. Buyers often face challenges in identifying the right materials that can withstand the specific chemical environments encountered in their applications. This leads to costly downtime and maintenance issues, ultimately affecting productivity and profitability.
The Solution: To combat corrosion issues, it is essential for buyers to select materials that are specifically suited for the chemicals they will encounter. Collaborating with material scientists or corrosion experts can provide insights into the best alloys or coatings to use. Buyers should also consider investing in protective measures such as sacrificial anodes or protective coatings that can extend the life of the components. Regular monitoring of the condition of the tube-side channels and nozzles through non-destructive testing methods can help in identifying potential corrosion before it becomes a major problem. Establishing a proactive maintenance strategy will enable companies to replace or repair corroded parts before they lead to catastrophic failures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of an exchanger
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Exchanger Parts?
When selecting materials for parts of an exchanger, it is crucial to consider properties such as temperature and pressure ratings, as well as corrosion resistance. The most commonly used materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, copper alloys, and titanium. Each material has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications, especially in diverse environments like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Exchanger Applications?
Carbon steel is frequently used for the construction of heat exchangers due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for various industrial applications. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or acidic environments, which can lead to premature failure.
Pros: Durable, cost-effective, and easy to fabricate.
Cons: Corrosion susceptibility, requiring protective coatings or regular maintenance.
Impact on Application: Best suited for non-corrosive fluids and environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential, and buyers should consider local corrosion conditions.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Exchanger Parts?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for heat exchangers that handle aggressive fluids. It maintains its integrity at high temperatures and pressures, which is critical in many industrial processes. The manufacturing complexity can be higher due to its toughness, but the long-term benefits often outweigh these costs.
Pros: High corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, and longevity.
Cons: Higher initial costs and more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Suitable for a wide range of fluids, including corrosive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Familiarity with DIN standards in Europe and JIS in Japan can guide material selection.
How Do Copper Alloys Enhance Heat Exchanger Efficiency?
Copper alloys are often chosen for their excellent thermal conductivity, which enhances heat transfer efficiency. They are particularly effective in applications where rapid heat exchange is necessary. However, copper is less durable than steel and can be susceptible to corrosion in certain environments.
Pros: Superior thermal conductivity and good corrosion resistance in specific applications.
Cons: Higher cost and potential for corrosion in saline or acidic environments.
Impact on Application: Ideal for water and low-pressure applications but may not be suitable for high-temperature or corrosive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with local standards and consider the specific media compatibility.
What Makes Titanium a Preferred Material in Challenging Conditions?
Titanium is increasingly being used in heat exchangers due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. It performs well in highly corrosive environments, making it suitable for applications in the chemical and petrochemical industries. However, titanium is more expensive and can be challenging to machine.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
Pros: Outstanding corrosion resistance and strength, lightweight.
Cons: High cost and complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Excellent for aggressive media and high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and TEMA standards is crucial, especially for high-performance applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Exchanger Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of an exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General industrial applications | Durable and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food industry | High corrosion resistance | Higher initial costs | High |
| Copper Alloys | Water heating, low-pressure applications | Superior thermal conductivity | Corrosion in harsh environments | Medium |
| Titanium | Chemical and petrochemical industries | Outstanding corrosion resistance | High cost and machining complexity | High |
This comprehensive analysis of material options for exchanger parts provides B2B buyers with critical insights to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of an exchanger
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for Parts of an Exchanger?
Manufacturing parts for exchangers, particularly shell and tube heat exchangers, involves several critical stages that ensure high performance and reliability. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers, as it helps in evaluating suppliers and ensuring that the products meet specific requirements.
How Is Material Prepared for Manufacturing Exchanger Parts?
The first step in manufacturing exchanger parts is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate materials based on the application requirements. Common materials include various alloys of steel, copper, and, for specific applications, nickel or titanium.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes surface preparation to remove any impurities or oxidation. Techniques such as sandblasting or chemical cleaning are employed to achieve a clean surface. This step is crucial as it impacts the welding quality and overall integrity of the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Exchanger Parts Manufacturing?
Forming is a pivotal stage where the raw materials are shaped into the necessary components. Common techniques include:
-
Rolling: For creating cylindrical shells, metal plates are rolled into the required diameter and length. This method ensures uniform thickness and strength in the shell structure.
-
Machining: Components like tube sheets and nozzles are often machined from solid metal blocks to achieve precise dimensions. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is widely used for its accuracy and repeatability.
-
Welding: This technique is essential for joining various parts, such as tubes to the tube sheets. Different welding methods, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas), are selected based on the material and design specifications.
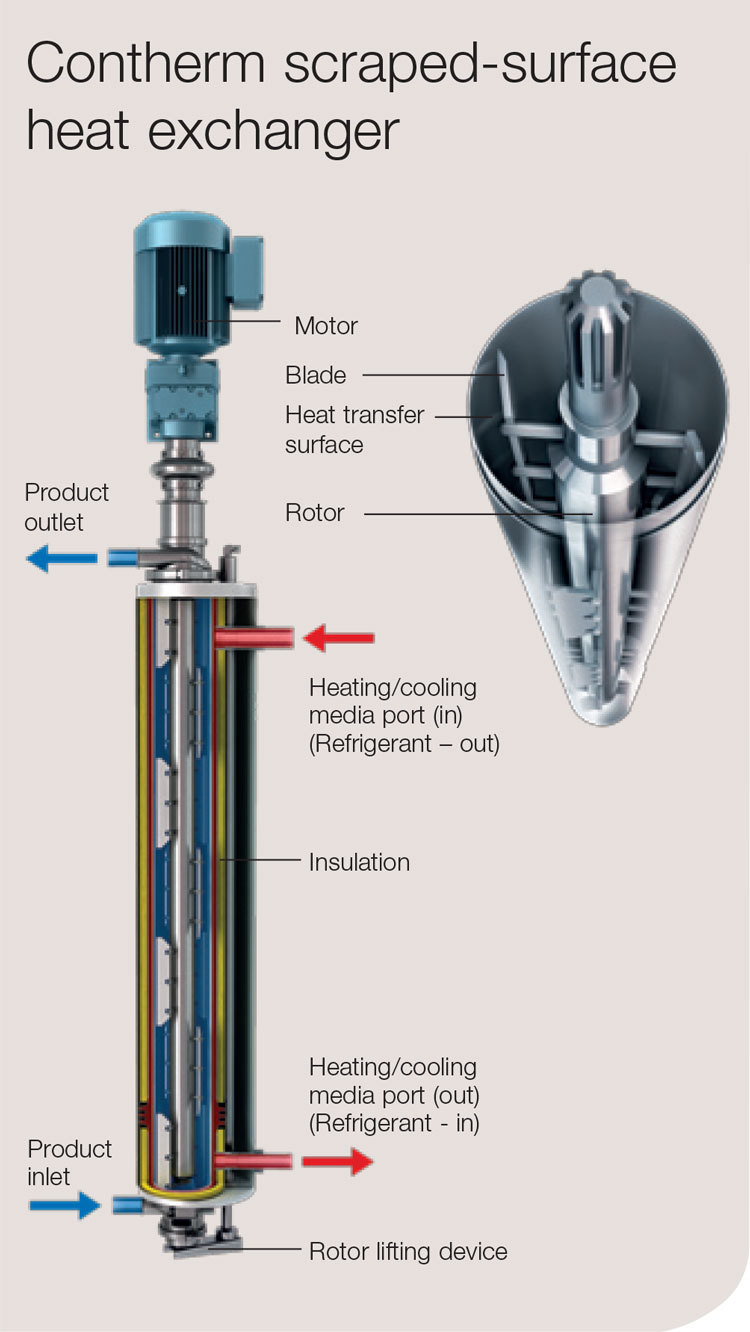
How Are Exchanger Parts Assembled?
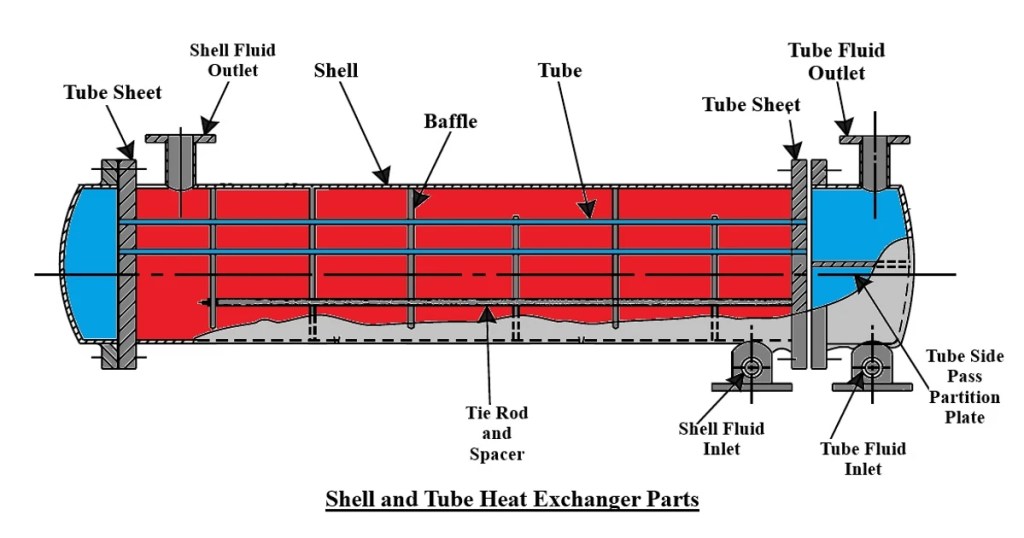
The assembly of exchanger parts requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure proper function. Key components, such as tubes, baffles, and headers, are assembled in a specific sequence.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
During assembly, baffles are positioned to stabilize the tubes and enhance fluid flow. Tie rods and spacers are also integrated to maintain the necessary spacing between baffles. This stage is critical as it directly influences the heat transfer efficiency and overall performance of the exchanger.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Exchanger Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of exchanger parts. Common techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: Processes like galvanizing or powder coating can be applied to prevent corrosion, especially for components exposed to harsh environments.
-
Inspection and Testing: After assembly, parts undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet design specifications. This includes dimensional checks and visual inspections for weld integrity.
-
Cleaning: Final cleaning is often performed to remove any contaminants resulting from the manufacturing process. This step is vital to prevent contamination during the exchanger’s operational life.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Exchanger Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of exchanger parts, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these practices is crucial for supplier selection.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance for manufacturing processes. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry standards must be adhered to, including:
-
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): Particularly relevant for pressure vessels and heat exchangers.
-
TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association): Provides guidelines for design and performance in shell and tube heat exchangers.
-
CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards within the European Economic Area.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure adherence to quality standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing stages verify compliance with specifications, focusing on critical processes like welding and machining.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection involves comprehensive testing and verification of the finished product against design specifications before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Exchanger Parts?
Testing methods are essential to verify the performance and integrity of exchanger parts. Common methods include:
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This test checks the strength and leak-tightness of the pressure-containing parts by filling them with water and applying pressure.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or radiography are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
-
Performance Testing: Evaluates the heat transfer efficiency and operational performance under simulated conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and manufacturing processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including inspection reports and testing results.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of the quality and compliance of the products being supplied.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality control, especially when sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations is crucial, as they can vary significantly between regions.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations that may apply to their products.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining comprehensive documentation of the supply chain and quality assurance processes is vital for accountability and compliance, especially in industries with stringent regulations.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they procure high-quality parts for their exchangers, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of an exchanger’
In the competitive landscape of industrial procurement, sourcing parts for an exchanger requires a systematic approach. This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with a practical checklist to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that the parts meet technical specifications, quality standards, and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is paramount to ensuring compatibility and performance. This includes determining the required materials (e.g., copper, steel alloys), dimensions, and pressure ratings. Be specific about the application environment, such as temperature ranges and fluid types, as these factors significantly influence the choice of materials and design.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Understanding relevant industry standards is essential for compliance and safety. Familiarize yourself with standards set by organizations such as the Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (TEMA) or ASME codes. Compliance with these standards not only ensures safety but can also enhance the longevity and efficiency of the exchanger.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and past projects. Look for case studies or references from clients in similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and performance.
- Check Certifications: Ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to quality management systems, such as ISO 9001.
- Assess Experience: Prioritize suppliers with proven experience in manufacturing parts for exchangers within your specific industry.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their products along with technical documentation. Samples allow you to assess the quality and craftsmanship of the parts firsthand. Technical documentation should include specifications, installation guides, and maintenance instructions, which are crucial for assessing compatibility and ease of integration.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Understand the total cost of ownership, including any hidden costs such as shipping, tariffs, or customs fees. Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational timelines while ensuring quality is not compromised.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Inspections
If possible, arrange site visits to the manufacturing facilities of potential suppliers. This allows you to inspect their operations, quality control measures, and overall working conditions. A visit can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Finally, consider the level of after-sales support and maintenance services offered by the supplier. Effective support can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the performance of your exchanger. Inquire about warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and technical support services to ensure you have reliable assistance post-purchase.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing parts for exchangers effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of an exchanger Sourcing
In the sourcing of parts for heat exchangers, a comprehensive understanding of cost structures and pricing is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will delve into the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for effective negotiation and purchasing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Parts for Heat Exchangers?
The cost structure of sourcing parts for heat exchangers typically includes several vital components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials include copper, steel alloys, and specialized alloys like titanium or aluminum for specific applications. Prices fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor involved in manufacturing and assembly. Skilled labor is often required for high-quality fabrication, especially for custom or specialized components.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary depending on the complexity of the parts being produced. Custom tooling may be necessary for unique designs, adding to initial costs but potentially lowering per-unit costs in high-volume runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet industry standards and specifications incurs additional costs. Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential, especially for components that will be subjected to high pressures and temperatures.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary significantly based on the origin of the materials and the destination. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and shipping terms (Incoterms) play a crucial role in this area.
-
Margin: Suppliers will apply a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding supplier margins can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Heat Exchanger Parts?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat exchanger parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often offer better pricing for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate more favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts may incur additional costs due to design and manufacturing complexities. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials often come with a premium price. Certifications (e.g., ASME, TEMA) may also add to costs but are crucial for ensuring compliance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices for their assurance of quality and timely delivery.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks. Understanding these terms can help buyers calculate the total cost of ownership more accurately.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing parts for heat exchangers, consider the following negotiation strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market prices and compare quotes from multiple suppliers. This information can empower you during negotiations.
-
Long-term Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Consider establishing contracts for ongoing purchases.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost, including maintenance and operational expenses, rather than just the upfront price. This perspective can help justify higher initial costs for better quality parts.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: If possible, be flexible with specifications to allow suppliers to provide alternative solutions that may be more cost-effective.
-
Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, enhancing overall cost efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and the various influencers on pricing is crucial for international B2B buyers in the heat exchanger market. By leveraging this knowledge and employing strategic negotiation tactics, buyers can secure the best possible deals while ensuring the reliability and performance of their heat exchanger parts. Always remember that prices are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, so maintaining a proactive approach is essential.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of an exchanger With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Heat Exchangers
In the quest for efficient thermal management in industrial applications, businesses are often faced with a variety of solutions for heat exchange processes. While shell and tube heat exchangers are widely recognized for their effectiveness, alternative technologies can also serve similar purposes. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize performance, cost, and operational efficiency in their systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts of an Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger | Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, suitable for high-pressure applications | Very efficient for low to moderate pressures | Suitable for low-pressure applications, relies on ambient air |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally lower initial cost | Lower initial and operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex installation requiring skilled labor | Easier to install, compact design | Simple installation, no water supply needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed, potential for fouling | Easier cleaning, fewer fouling issues | Minimal maintenance, but dependent on environmental conditions |
| Best Use Case | Chemical processing, oil refineries | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals | Power generation, HVAC applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Plate Heat Exchanger
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin plates arranged in a frame, allowing fluids to flow through alternating channels. Their compact design results in a smaller footprint and lower initial costs compared to shell and tube heat exchangers. Additionally, the ease of cleaning between plates reduces maintenance efforts, making them ideal for industries like food and beverage where hygiene is critical. However, they may not perform as well under very high-pressure conditions and can be limited in terms of the temperature range they can handle.
Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger
Air-cooled heat exchangers utilize ambient air to dissipate heat, eliminating the need for cooling water. This makes them particularly advantageous in arid regions or where water availability is limited. They tend to have lower operational costs due to reduced water usage and are simpler to install. However, their performance can be significantly affected by environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity. This limits their effectiveness in applications requiring precise temperature control and can lead to higher operational costs in less than ideal conditions.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting a heat exchanger solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. While shell and tube heat exchangers offer high efficiency and durability for demanding applications, alternatives like plate and air-cooled heat exchangers can provide significant benefits in terms of cost and ease of maintenance for less rigorous applications. By carefully assessing these factors, businesses can choose the most suitable heat exchange technology that aligns with their operational goals and environmental conditions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of an exchanger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Parts of an Exchanger?
Understanding the technical properties of exchanger parts is crucial for B2B buyers as these specifications directly impact performance, durability, and overall operational efficiency. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of alloy used in manufacturing the exchanger components, such as tubes and shells. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and nickel alloys. The selection of the right material is essential for ensuring corrosion resistance, heat transfer efficiency, and durability, particularly in harsh environments typical in industries like petrochemicals and power generation.
2. Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is a critical specification that affects the pressure rating and thermal performance of the heat exchanger. Thicker walls can withstand higher pressures and are less prone to fatigue and failure. For buyers, understanding the appropriate wall thickness for their specific application ensures safety and compliance with industry standards.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in dimensions during manufacturing. High precision in tolerances is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, which minimizes the risk of leaks and improves efficiency. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers who adhere to stringent tolerance levels can lead to better performance and reduced maintenance costs.
4. Heat Transfer Area
The heat transfer area is the total surface area available for heat exchange between the two fluids. A larger surface area generally improves heat exchange efficiency. Buyers must assess their thermal requirements and ensure that the exchanger design provides adequate heat transfer capacity for their operations.
5. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure that the exchanger can safely handle. It is vital for ensuring the safety and reliability of the system, especially in high-pressure applications. Buyers should verify that the pressure rating aligns with their operational conditions to avoid potential failures.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Exchanger Parts?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of exchangers, purchasing from OEMs ensures that buyers receive high-quality, reliable components that meet specific performance standards.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers as it affects inventory management and budgeting. Negotiating lower MOQs can be beneficial for businesses with limited storage capabilities or those looking to reduce upfront costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed price quote for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they help avoid disputes and clarify costs associated with shipping and delivery.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. For B2B buyers, knowing the lead time is crucial for planning and ensuring that projects remain on schedule. Suppliers with shorter lead times can provide a competitive edge, especially in fast-paced industries.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, leading to better procurement outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of an exchanger Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Parts of an Exchanger Sector?
The global market for heat exchanger parts is witnessing dynamic changes driven by various factors, including technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and evolving customer demands. A significant driver is the increasing need for energy efficiency across industries, leading to a surge in demand for high-performance exchangers. As industries such as petrochemicals, power generation, and HVAC continue to expand, the demand for parts that enhance operational efficiency is also rising.
Emerging technologies, such as predictive maintenance and IoT-enabled devices, are transforming how businesses source and manage their heat exchangers. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can offer integrated solutions that include smart monitoring and maintenance services. This shift towards digitalization is particularly pronounced among international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure upgrades are critical.
Furthermore, the trend towards customization is gaining traction. Buyers are seeking bespoke solutions tailored to their specific operational needs, which necessitates a closer collaboration with manufacturers. In Europe, particularly in Germany, stringent environmental regulations are pushing companies to source parts that comply with high sustainability standards. As a result, suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with these regulations are likely to gain a competitive edge.
How Does Sustainability Influence the Sourcing of Parts for Exchangers in B2B Markets?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of B2B procurement strategies, particularly in the parts of the exchanger sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of materials used in heat exchangers is under scrutiny. Companies are now more than ever focused on sourcing parts made from recyclable and low-impact materials, such as aluminum and stainless steel, which not only reduce waste but also enhance product longevity.
Ethical sourcing practices are paramount as well. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and ethically. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of green materials can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Additionally, the adoption of circular economy principles, where materials are reused and recycled, is gaining momentum in the industry. This trend is particularly strong in regions such as Europe, where consumers and businesses demand environmentally friendly practices.
Moreover, companies that actively communicate their sustainability initiatives and demonstrate commitment to ethical practices can enhance their brand reputation and foster stronger relationships with international buyers. As the market evolves, those who prioritize sustainability will not only meet regulatory requirements but also appeal to the growing segment of environmentally conscious businesses.
Illustrative image related to parts of an exchanger
What Is the Historical Context of the Parts of an Exchanger Sector That B2B Buyers Should Know?
The evolution of heat exchangers dates back to the early 19th century, primarily driven by the industrial revolution, which demanded more efficient methods for heating and cooling processes. Early designs focused on simple shell and tube configurations, which laid the groundwork for today’s advanced systems. Over the decades, significant innovations have occurred, particularly in materials science and manufacturing technologies, which have enhanced the performance and efficiency of heat exchangers.
The introduction of regulations such as the ASME code in the USA and TEMA standards globally has played a pivotal role in ensuring safety and reliability in design and production. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it provides insight into the regulatory landscape that governs sourcing decisions today. Understanding these historical developments enables buyers to appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped the current market and to make informed decisions based on industry standards and practices.
As the sector continues to evolve, staying informed about these historical trends will empower B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing parts effectively, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of an exchanger
-
1. How do I choose the right materials for exchanger parts?
Selecting the appropriate materials for exchanger parts is critical to ensure durability and efficiency. Consider the fluid types, operating temperatures, and pressures. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and specialized alloys like titanium for corrosive environments. Conduct a thorough analysis of your operational needs and consult with suppliers to understand the best material options for your specific application and budget. -
2. What is the best configuration for a shell and tube heat exchanger?
The ideal configuration often depends on the specific heat transfer requirements and space constraints. Common configurations include single-pass and multi-pass designs, which can affect efficiency and maintenance. Evaluate factors such as fluid properties, desired heat exchange rates, and available space to determine the most suitable design. Collaborating with experienced engineers can provide insights tailored to your operational needs. -
3. What are the typical lead times for sourcing parts of an exchanger?
Lead times for sourcing exchanger parts can vary widely based on the supplier, part complexity, and material availability. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks. To ensure timely procurement, communicate your project timelines with suppliers upfront and inquire about their production capabilities and stock levels. Consider establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate delays. -
4. How do I vet suppliers for exchanger parts?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and customer reviews. Request references and evaluate their responsiveness and communication. It’s beneficial to visit their facilities if possible and review their quality assurance processes. Additionally, ensure that they comply with relevant international standards and regulations applicable to your region and industry. -
5. Can I customize exchanger parts for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for exchanger parts to meet specific operational requirements. Customization can include alterations in size, material, or design features. When requesting customized parts, provide detailed specifications and discuss your needs with the supplier early in the process. This will help ensure that the final product aligns with your expectations and performance criteria. -
6. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for parts of an exchanger?
Minimum order quantities can differ significantly among suppliers and depend on the type of parts ordered. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard components to larger quantities for custom designs. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs with potential suppliers and discuss any flexibility they may have, especially if you require fewer parts for initial trials or projects. -
7. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common arrangements include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days. Be sure to discuss payment methods that suit both parties and ensure that the terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement. Consider factors like currency fluctuations and transaction fees when negotiating. -
8. How do I manage logistics and shipping for exchanger parts?
Effective logistics management involves choosing reliable shipping methods and understanding import/export regulations. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping options based on cost, urgency, and destination. Ensure all documentation is in order to prevent delays at customs. Engaging a freight forwarder with experience in handling industrial equipment can streamline the shipping process and minimize risks.
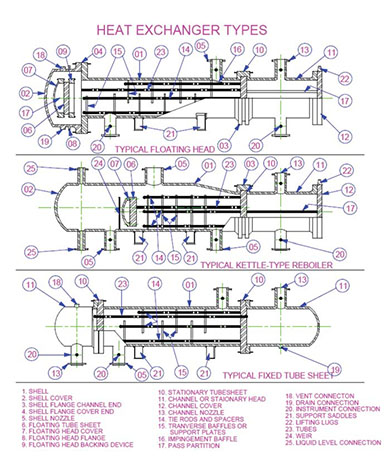
Top 6 Parts Of An Exchanger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Torq-N-Seal – High Pressure Tube Plugs
Domain: torq-n-seal.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Tube Plugs: Creates a permanent, positive seal greater than 7,000 psi for efficient maintenance.
Condenser Tube Plugs: Best for heat exchangers with pressure less than 250 psi, temperature below 300 deg F, and tube ID between 0.580″ and 1.200″.
Tapered Tube Plugs: Additional product option for tube plugging needs.
Plug Selector: Tool to find the right solution for leaking heat exc…
2. Forged Components – Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: forgedcomponents.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Components of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers include: 1. Shell – a cylindrical structure made from rolled plate metal or pipe, typically steel, designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive agents. 2. Tubes – seamless or welded tubes, usually between 5/8 inch to 1 inch in diameter, which may include fins to enhance heat transfer. 3. Tube Sheets – forged plates with drilled holes for tube i…
3. Thermopedia – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thermopedia.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are popular for their flexibility in handling a wide range of pressures and temperatures. They consist of a cylindrical shell containing tubes, allowing two fluids to exchange heat. Key components include: Front Header (fluid entry), Rear Header (fluid exit), Tube Bundle (tubes, tube sheets, baffles), and Shell (housing for the tube bundle). There are three main type…
4. Atlas Bronze – Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: atlasbronze.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Heat Exchanger Parts Diagram | Heat Exchanger Schematic. Heat exchangers are devices used to transfer heat between fluids, which may be separated by a solid wall or in direct contact. They are utilized in various industries including space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural gas processing, sewage treatment,…
5. Slideshare – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Overview
Domain: slideshare.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This document provides a comprehensive overview of various components and design considerations in shell and tube heat exchangers, detailing the functions and specifications of the shell, baffles, tube sheets, and other parts. It highlights the importance of factors such as shell diameter, baffle types, tube sizes, and flow velocities in optimizing heat transfer efficiency while managing costs. Ad…
6. SetX Industries – Heat Exchangers
Domain: setxind.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Heat exchangers are essential industrial equipment used for both heating and cooling processes, particularly in refineries and processing plants. Key components include: 1. Tubes: Crucial for transferring heat and liquids, available in welded or seamless types, with standard diameters of 5/8 inch, 3/4 inch, or 1 inch. Innovations include twisted tapes for enhanced efficiency. 2. Front and Rear Hea…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of an exchanger
In the competitive landscape of industrial heat exchangers, strategic sourcing of components such as tubes, baffles, and nozzles is paramount. Understanding the unique requirements of your application—be it in petrochemicals, power generation, or HVAC—enables buyers to select the most suitable materials and designs. Leveraging high-quality parts not only enhances efficiency and longevity but also minimizes downtime and maintenance costs.
International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize relationships with reputable suppliers who adhere to global standards like ASME and TEMA. This ensures compliance and reliability in performance, critical for maintaining operational excellence. By investing in reliable sourcing strategies, companies can achieve significant cost savings and operational efficiencies.
Looking ahead, the market for heat exchanger components is evolving, driven by innovations in materials and design. As regulations tighten and environmental concerns grow, there is a pressing need for sustainable solutions. Engage with suppliers who are at the forefront of these advancements to stay competitive. Now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies—partner with trusted manufacturers to secure the future of your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.