Neoprene Vs Polyurethane Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for neoprene vs polyurethane
Navigating the complexities of sourcing materials like neoprene and polyurethane can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, especially when aiming to ensure quality, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific applications. Whether you are looking to procure durable components for automotive manufacturing or comfortable seating solutions for office environments, understanding the distinct properties and applications of these synthetic materials is crucial. This guide offers a comprehensive analysis of neoprene and polyurethane, covering their types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
As you delve into this resource, you will gain insights into the unique advantages each material offers, helping you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs. With a focus on the diverse markets of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key players like Germany and Brazil, this guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate the global market effectively. By understanding the nuances of neoprene and polyurethane, you will be empowered to select the right material for your business, ensuring not only quality but also optimal performance in your applications. Let this guide be your trusted resource in making strategic sourcing decisions that drive your business forward.
Understanding neoprene vs polyurethane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neoprene Closed Cell | Excellent sealing properties, good thermal insulation | Medical equipment, gaskets, seals | Pros: Water and chemical resistance; Cons: Limited high-temperature resistance. |
| Neoprene Open Cell | Soft and flexible, provides cushioning and sound absorption | Furniture, automotive seating, insulation | Pros: Comfortable and lightweight; Cons: Less durable than closed cell. |
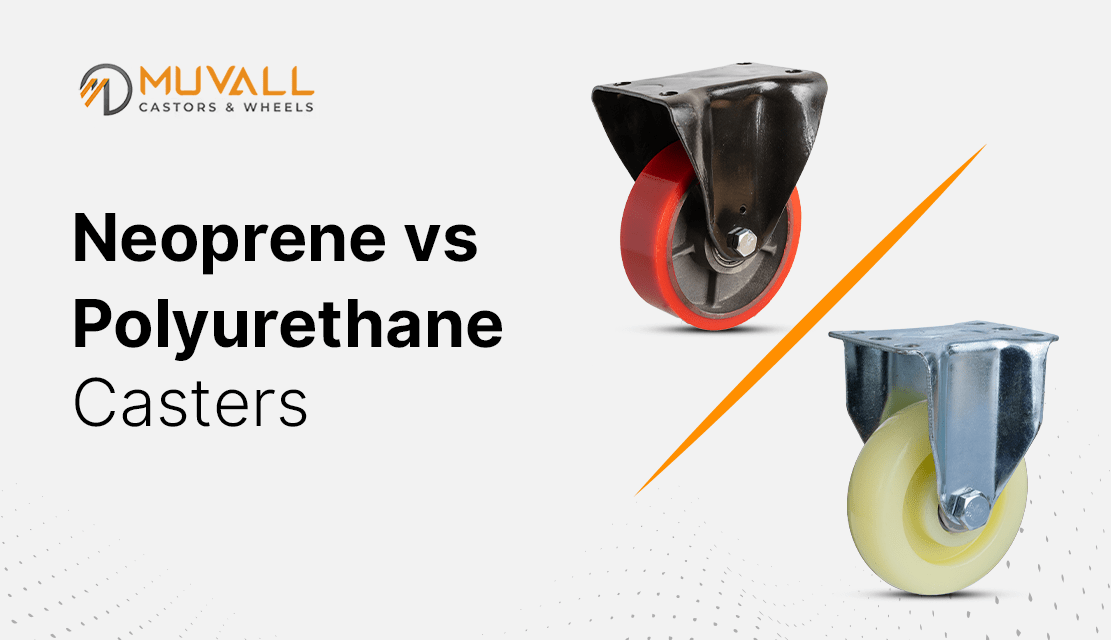
| Polyurethane Solid | High abrasion resistance, customizable hardness | Heavy-duty industrial applications, casters | Pros: Versatile and durable; Cons: Can be more expensive. |
| Polyurethane Foam | Lightweight, flexible, good thermal insulation | Packaging, automotive seating, mattresses | Pros: Excellent cushioning; Cons: Limited chemical resistance compared to solid polyurethane. |
| Blended Neoprene | Combines neoprene with other materials for enhanced properties | Specialty applications in automotive, marine | Pros: Tailored properties for specific needs; Cons: Potentially higher costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Neoprene Closed Cell Foam?
Neoprene closed cell foam is recognized for its excellent sealing capabilities, making it ideal for applications that require insulation against moisture and air. This type is often used in medical equipment, gaskets, and seals due to its ability to resist water, chemicals, and oils. When considering this material, B2B buyers should focus on its thermal insulation properties and durability, although it may not perform well in extreme high-temperature environments.
How Does Neoprene Open Cell Foam Differ?
Neoprene open cell foam is softer and more flexible than its closed cell counterpart, providing exceptional cushioning and sound absorption. This variation is commonly employed in furniture and automotive seating applications where comfort is paramount. Buyers should consider its lightweight nature and affordability, but be aware that it may not withstand heavy wear and tear as effectively as closed cell neoprene.
What Are the Advantages of Solid Polyurethane?
Solid polyurethane is known for its high abrasion resistance and customizable hardness, making it suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications, including casters and wheels. This material can withstand harsh environmental conditions and is often preferred for its durability. Buyers should weigh the higher cost against its long lifespan and low maintenance needs, as it can provide significant long-term value in demanding applications.
Why Choose Polyurethane Foam for Certain Applications?
Polyurethane foam is lightweight and flexible, offering excellent thermal insulation and cushioning properties. It is frequently utilized in packaging, automotive seating, and mattresses. While it provides great comfort, buyers should note that it has limited chemical resistance compared to solid polyurethane. Understanding the specific application requirements will help determine if this foam is a suitable choice.
What Benefits Do Blended Neoprene Materials Offer?
Blended neoprene combines traditional neoprene with other materials to enhance its properties for specialized applications, particularly in the automotive and marine sectors. This versatility allows manufacturers to tailor the material to meet specific performance needs. Buyers should consider the potential for increased costs but may find that the tailored properties justify the investment for niche applications.
Key Industrial Applications of neoprene vs polyurethane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of neoprene vs polyurethane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and gaskets made from neoprene | Enhanced durability and resistance to harsh environments | Ensure high-temperature and chemical resistance properties |
| Medical Equipment | Caster wheels for medical carts using neoprene | Quiet operation and protection of sensitive floors | Verify chemical resistance and weight capacity |
| Furniture | Cushioning foam made from polyurethane | Customizable comfort and durability | Assess the range of hardness and non-marking characteristics |
| Oil & Gas | Protective coatings and seals made from polyurethane | High resistance to oils and extreme temperatures | Evaluate compatibility with specific chemicals and temperatures |
| Construction | Insulation materials made from neoprene | Excellent thermal resistance and moisture control | Confirm compliance with local safety and environmental regulations |
How is Neoprene Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
Neoprene is extensively used in the automotive sector for manufacturing seals and gaskets. These components are crucial in preventing leaks and ensuring that vehicles maintain optimal performance in various environmental conditions. The material’s resistance to oil, grease, and temperature fluctuations makes it ideal for automotive applications. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing neoprene that meets specific automotive standards is essential to ensure reliability and longevity in harsh climates.
What Role Does Neoprene Play in Medical Equipment?
In medical settings, neoprene is favored for caster wheels on medical carts and equipment. Its smooth operation minimizes noise, which is critical in hospitals and clinics where a quiet environment is necessary. Additionally, neoprene’s chemical resistance ensures that it can withstand frequent cleaning and sanitization processes. Buyers in South America and Europe should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee high-quality neoprene that meets stringent health and safety regulations.
Why Choose Polyurethane for Furniture Applications?
Polyurethane is widely used in the furniture industry, particularly for cushioning foam. Its customizable properties allow manufacturers to create various levels of firmness, enhancing comfort for end-users. Furthermore, polyurethane is known for its durability, ensuring that furniture maintains its shape and performance over time. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers that offer a range of formulations to cater to diverse customer needs, especially in competitive markets like Germany and Brazil.
How is Polyurethane Essential in Oil & Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas sector, polyurethane is commonly employed for protective coatings and seals due to its exceptional resistance to oil and extreme temperatures. This makes it invaluable in environments where equipment is exposed to harsh chemicals and fluctuating temperatures. International buyers must ensure that the polyurethane sourced is compatible with specific operational conditions and can withstand the unique challenges posed by the oil and gas industry.
What Advantages Does Neoprene Provide in Construction Insulation?
Neoprene is also utilized in construction as an insulation material, where its excellent thermal resistance and moisture control properties are highly beneficial. This makes it suitable for various applications, including HVAC systems and piping. For B2B buyers in regions experiencing extreme weather, confirming that neoprene insulation complies with local safety and environmental standards is crucial for long-term performance and regulatory adherence.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘neoprene vs polyurethane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Material for Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in sectors such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, or food processing often face the challenge of selecting the right material for components that will be exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures. For instance, a manufacturing facility in the Middle East needs to decide between neoprene and polyurethane for seals and gaskets in equipment that will be exposed to corrosive substances. A misstep here can lead to equipment failure, increased downtime, and significant financial losses.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge effectively, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the specific environmental conditions their products will face. Polyurethane generally offers superior resistance to abrasion and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for applications involving petroleum-based products. However, neoprene is more resilient to certain oils and provides excellent sealing capabilities in closed-cell formats. B2B buyers should collaborate with material experts to specify the right formulation based on the temperature range and chemical exposure expected in their application. This ensures that the chosen material will meet performance criteria, thereby reducing the risk of premature failure and associated costs.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
Scenario 2: Balancing Cost and Performance for High-Volume Production
The Problem: Cost efficiency is a critical concern for B2B buyers engaged in high-volume production, such as those in the automotive or consumer goods sectors. A Brazilian manufacturer, for instance, might be torn between the lower costs of neoprene and the superior performance characteristics of polyurethane, especially when producing components like caster wheels or insulation materials. The pressure to maintain profit margins while ensuring product reliability can create a dilemma.
The Solution: To strike a balance between cost and performance, buyers should consider not only the initial material costs but also the long-term implications of durability and maintenance. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis is essential. Polyurethane might have a higher upfront cost but can offer longer service life and lower maintenance costs, translating to savings over time. Implementing a pilot program to test both materials under real-world conditions can provide valuable data to make informed decisions. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who offer customizable formulations can help achieve the desired performance characteristics at a competitive price point, ensuring that the final choice aligns with both budget and quality expectations.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Impact of Material Properties on Application Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to understand how the intrinsic properties of neoprene and polyurethane affect the performance of their applications. For example, a company in Europe that manufactures medical equipment needs to ensure that the materials used in their products not only comply with health regulations but also perform reliably in diverse environments. Misunderstanding these material properties can lead to product recalls or compliance issues, impacting reputation and profitability.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should invest in comprehensive material education and training for their teams. This can include workshops with material scientists or webinars that delve into the specific characteristics of neoprene and polyurethane, such as elasticity, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. Additionally, buyers should utilize prototypes to test how each material behaves in actual operating conditions. Collaborating with suppliers who can provide detailed technical data sheets and performance metrics will help in making informed choices. Furthermore, leveraging third-party testing can validate material performance claims, ensuring that the final product meets all regulatory and operational standards. By fostering a deeper understanding of material science, B2B buyers can significantly reduce risks associated with material selection and application performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for neoprene vs polyurethane
What Are the Key Properties of Neoprene and Polyurethane?
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, making it suitable for applications exposed to varying environmental conditions. Neoprene’s closed-cell structure provides insulation and buoyancy, which is advantageous in marine applications and protective gear.
Polyurethane, on the other hand, is a versatile polymer that can be formulated to achieve a wide range of hardness and flexibility. It can withstand temperatures from -45°C to 150°C, depending on the specific formulation. Polyurethane exhibits superior abrasion resistance and can endure harsh chemical environments, particularly those involving oils and solvents.
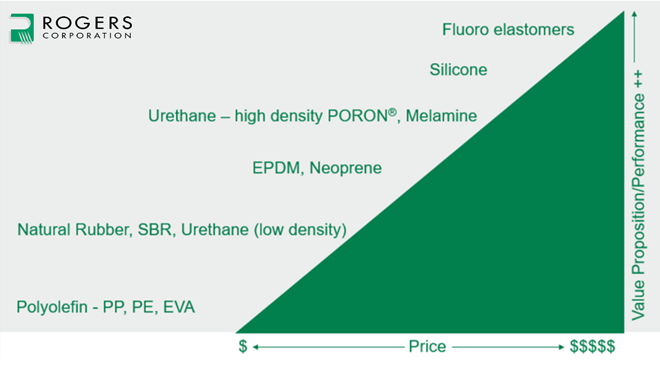
What Are the Pros and Cons of Neoprene and Polyurethane?
When evaluating neoprene, its primary advantages include high durability, flexibility, and resistance to degradation from UV light and ozone. These properties make it ideal for applications in automotive seals, gaskets, and medical devices. However, neoprene tends to be less resistant to certain solvents and has a lower tensile strength compared to polyurethane, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Polyurethane offers significant advantages in terms of mechanical properties and customization. It can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial wheels to cushioning in furniture. However, the manufacturing process can be more complex and costly, which may deter some buyers, especially in price-sensitive markets.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
How Do Neoprene and Polyurethane Impact Specific Applications?
In applications where chemical compatibility is critical, neoprene excels due to its resistance to oils and harsh chemicals, making it a preferred choice in laboratories and food processing. Conversely, polyurethane’s versatility allows it to be tailored for specific performance needs, such as load-bearing applications in heavy machinery or dynamic environments like automotive parts.
For international B2B buyers, understanding compliance with local standards is crucial. In Europe, for example, products may need to adhere to DIN standards, while in the Middle East, compliance with local regulations regarding chemical resistance may be necessary. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider the availability of materials and local manufacturing capabilities, as well as the potential for import tariffs and logistics challenges.
Summary Table of Neoprene vs Polyurethane
| Material | Typical Use Case for neoprene vs polyurethane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neoprene | Automotive seals, medical devices, gaskets | High chemical and UV resistance | Lower tensile strength than PU | Medium |
| Polyurethane | Industrial wheels, furniture cushioning | Customizable mechanical properties | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers evaluating neoprene and polyurethane. By understanding the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and regional compliance standards.
Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for neoprene vs polyurethane
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Neoprene and Polyurethane?
The manufacturing processes for neoprene and polyurethane involve several distinct stages, each critical to producing high-quality materials suited for various applications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about which material to source for their specific needs.
Material Preparation: How Are Neoprene and Polyurethane Ingredients Processed?
The first step in manufacturing both neoprene and polyurethane is material preparation. For neoprene, the primary raw material is chloroprene, which undergoes polymerization. This process involves the chemical reaction of chloroprene monomers to form long polymer chains, resulting in a durable elastomer.
In contrast, polyurethane is created through a reaction between polyols and isocyanates. The choice of polyols and isocyanates can significantly affect the final properties of the polyurethane, allowing manufacturers to customize the material for specific applications. This flexibility is essential for industries ranging from automotive to furniture manufacturing.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Neoprene and Polyurethane?
Once the raw materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. Neoprene can be processed into sheets, foams, or molded products using techniques such as compression molding, injection molding, or extrusion. Each technique allows for the production of different shapes and sizes, catering to various applications, including seals, gaskets, and protective gear.
Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
Polyurethane also utilizes similar methods, including casting, molding, and foaming. The casting process allows for intricate shapes and is often used for producing polyurethane wheels and cushioning materials. The choice of forming technique impacts the material’s hardness, flexibility, and overall performance, making it crucial for manufacturers to select the right method based on the intended application.
Assembly: How Are Components of Neoprene and Polyurethane Products Joined?
The assembly stage involves joining different components to create the final product. For neoprene, this may include bonding with other materials, such as fabric or metals, to enhance its properties. Manufacturers often use adhesives or heat sealing techniques to ensure a strong bond, which is particularly important in applications where durability is paramount.
Polyurethane products may require additional assembly steps, such as integrating metal cores for caster wheels. The assembly process can also involve layering different densities or types of polyurethane to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as increased load-bearing capacity or enhanced shock absorption.
Finishing: What Steps Are Taken to Ensure Quality in Neoprene and Polyurethane Products?
The finishing stage is critical for both neoprene and polyurethane. This stage often includes surface treatments, trimming, and final inspections. For neoprene, the surface may be treated to improve chemical resistance or enhance aesthetics. In contrast, polyurethane products may undergo polishing or coating processes to achieve desired physical properties, such as increased abrasion resistance.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Neoprene and Polyurethane Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is vital in ensuring that neoprene and polyurethane products meet international standards and customer specifications. Implementing robust QC measures can help B2B buyers avoid issues related to product performance and reliability.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For both materials, adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential. This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to manufacturers in various industries. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API specifications for oil and gas applications further ensure that products meet stringent safety and quality requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control in neoprene and polyurethane manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection assesses raw materials for compliance with specifications before production begins. For neoprene, this could involve verifying the quality of chloroprene, while for polyurethane, it may include testing polyols and isocyanates.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are performed to monitor the manufacturing process. This step helps identify any deviations from quality standards early, allowing for adjustments before final production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs once the products are completed. This step includes testing for physical properties, such as tensile strength, elasticity, and chemical resistance, ensuring that the final products meet established standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. This can include:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should request detailed reports on audit findings, including any corrective actions taken.
-
Reviewing QC Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These reports can help buyers assess the reliability and consistency of the products.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Neoprene and Polyurethane Products?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several nuances to consider:
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations regarding materials and manufacturing processes. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local standards to avoid potential legal issues.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Understanding the supply chain is crucial for maintaining quality. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of raw materials and the location of manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with international quality standards.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is vital for successful international transactions. Buyers should consider working with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in their preferred language to facilitate smoother interactions.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for neoprene and polyurethane, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements and industry standards. This knowledge is essential for ensuring the procurement of high-quality materials that will perform reliably in their intended applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘neoprene vs polyurethane’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of neoprene and polyurethane materials requires a strategic approach tailored to your specific business needs. This guide serves as a checklist to help B2B buyers make informed decisions, ensuring that the selected material aligns with their technical specifications, application requirements, and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start sourcing, clearly outline the technical requirements for your application. Consider factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and durability.
– Temperature Range: Identify the extreme temperatures the material will encounter.
– Chemical Exposure: List the chemicals the material must resist, such as oils or solvents.
Step 2: Assess Application Requirements
Understanding the intended use of neoprene or polyurethane is crucial for selecting the right material. Different applications may demand varying characteristics.
– Flexibility vs. Rigidity: Determine if flexibility (neoprene) or rigidity (polyurethane) is more beneficial for your application.
– Environmental Conditions: Consider whether the material will be exposed to harsh environments, which may favor polyurethane for its superior abrasion resistance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. A reputable supplier can ensure the quality and consistency of your chosen material.
– Request Documentation: Ask for technical data sheets and certifications that verify material properties.
– Seek References: Contact other businesses in your industry to inquire about their experiences with the supplier.
Step 4: Compare Costs and Value
While price is a significant factor, it’s essential to weigh cost against the value provided by each material.
– Initial vs. Long-Term Costs: Consider not just the upfront costs, but also the long-term durability and maintenance costs associated with each material.
– Performance Characteristics: Assess whether the higher cost of polyurethane is justified by its enhanced performance in specific applications.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the materials meet relevant industry standards for quality and safety. This is particularly important for applications in sensitive sectors such as medical or food processing.
– Check Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or compliance with local regulations in your region.
– Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures during production.
Step 6: Conduct Sample Testing
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples of both neoprene and polyurethane materials. Testing samples can help you evaluate their performance in your specific application.
– Perform Stress Tests: Assess how each material withstands the conditions it will face in real-world usage.
– Evaluate User Experience: Gather feedback from team members who will be using or handling the materials.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Partnership
Once you’ve selected a supplier, consider building a long-term relationship. Consistency in sourcing can lead to better pricing, priority service, and tailored solutions over time.
– Communicate Needs: Maintain open lines of communication to discuss future requirements or adjustments in specifications.
– Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews to ensure the supplier continues to meet your evolving business needs.
Following this checklist will help you make informed decisions when sourcing neoprene or polyurethane, ensuring that you select materials that meet your business’s specific demands while fostering successful supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for neoprene vs polyurethane Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Neoprene and Polyurethane Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing neoprene and polyurethane, several critical components should be considered. The primary cost factors include:
-
Materials: The base materials for neoprene and polyurethane differ significantly. Neoprene, derived from chloroprene, generally has a lower raw material cost compared to polyurethane, which requires a more complex chemical synthesis. Consequently, the cost of sourcing neoprene tends to be lower, making it an appealing option for budget-conscious buyers.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Polyurethane often necessitates more specialized labor due to its varied formulations and production techniques, which can drive up costs. Additionally, manufacturing overhead, including utilities and equipment maintenance, is generally higher for polyurethane due to the advanced machinery required.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized products. Both neoprene and polyurethane may require specialized molds, but polyurethane often necessitates more intricate tooling due to its customizable properties. This can further increase the initial investment for buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is essential in both cases. However, the QC processes for polyurethane products can be more rigorous due to the diverse formulations and applications. This additional scrutiny can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs vary based on the weight and volume of the materials. Neoprene is typically denser than polyurethane, which might affect shipping costs. Buyers should consider logistics costs when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers’ profit margins will vary based on the complexity of the product and market demand. Generally, polyurethane commands higher margins due to its premium characteristics and applications.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Neoprene and Polyurethane Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing for neoprene and polyurethane beyond the base costs:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often result in lower unit prices. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, which can significantly affect the overall pricing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products tailored to specific applications usually come at a premium. Buyers should balance the need for customization against cost-effectiveness.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may have higher prices due to the compliance costs associated with these certifications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a history of delivering high-quality products may charge more, but they often provide better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect the final cost by determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
When negotiating costs for neoprene and polyurethane, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs and take advantage of bulk pricing. This can lead to significant savings.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase prices, consider long-term costs related to maintenance, durability, and performance. For instance, while polyurethane may have a higher upfront cost, its longevity in harsh environments might justify the investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Regions: Pricing can vary significantly based on geographical factors. For example, buyers in Africa or South America might face higher shipping costs due to infrastructure challenges. Conversely, buyers in Europe may benefit from proximity to suppliers, reducing logistics expenses.
-
Negotiate Terms and Conditions: Don’t hesitate to discuss payment terms, lead times, and after-sales support during negotiations. These factors can greatly impact overall costs and supplier relationships.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for neoprene and polyurethane materials are subject to change based on market conditions, availability, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and informed decision-making.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing neoprene vs polyurethane With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of material selection, businesses often face the challenge of choosing the most suitable solution for their applications. Neoprene and polyurethane are two prominent synthetic materials widely used in various industries, but there are alternatives that may better meet specific needs. This section explores viable alternatives to neoprene and polyurethane, comparing them across critical performance metrics.
| Comparison Aspect | Neoprene Vs Polyurethane | Silicone Rubber | Natural Rubber | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature extremes. Polyurethane offers superior abrasion resistance. | Excellent flexibility, temperature resistance, and chemical stability. | Good elasticity and resilience but limited chemical resistance. | Moderate chemical resistance; good for low-stress applications. |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective; polyurethane is more expensive due to its specialized properties. | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity. | Lower cost, but variable quality and performance. | Inexpensive, making it appealing for budget-sensitive projects. |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally easy to implement; both materials are available in various forms. | Requires specialized handling and curing processes. | Simple to process but may require additives for enhanced performance. | Easy to mold and fabricate into various shapes and sizes. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable and long-lasting. | Requires careful handling to avoid degradation. | Moderate maintenance; prone to wear in harsh environments. | Low maintenance but may require periodic checks for brittleness. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications needing oil and chemical resistance; suitable for industrial and consumer products. | Best for high-temperature and flexible applications, such as gaskets and seals. | Suitable for general applications where elasticity is key, such as tires and footwear. | Best for construction and plumbing applications, where cost is a primary concern. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Silicone Rubber as an Alternative?
Silicone rubber is a highly versatile material known for its excellent flexibility and temperature resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. It exhibits superior chemical stability, which makes it ideal for gaskets and seals in various industries, including food and medical. However, silicone tends to be more expensive than neoprene and polyurethane, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its handling requires specialized processes to ensure optimal performance.
How Does Natural Rubber Compare in Performance and Cost?
Natural rubber is a traditional material valued for its excellent elasticity and resilience. It is typically less expensive than both neoprene and polyurethane, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive applications. However, natural rubber has limited chemical resistance, which can lead to quicker degradation in harsh environments. As such, while it is suitable for general applications, it may not be the best choice for industries requiring robust chemical or thermal stability.
Why Consider PVC as a Budget-Friendly Alternative?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a cost-effective alternative commonly used in construction and plumbing applications. It is easy to mold and fabricate, making it ideal for a range of products. However, PVC has moderate chemical resistance and is not suited for high-stress applications. While it provides a low-maintenance option, its brittleness over time may require periodic inspections to ensure integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the right material is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness. B2B buyers should first assess the specific requirements of their applications, including factors like chemical exposure, temperature extremes, and mechanical stress. Additionally, considering the total cost of ownership—including maintenance and potential replacements—can guide decision-making. By weighing the performance characteristics and cost implications of neoprene, polyurethane, and their alternatives, businesses can make informed choices that align with their operational objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for neoprene vs polyurethane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Neoprene and Polyurethane?
When considering neoprene and polyurethane for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific formulation and quality of the neoprene or polyurethane being used. Different grades exhibit varying levels of durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and temperatures. For instance, high-grade neoprene is ideal for environments exposed to oils and solvents, while premium polyurethane is often used in applications requiring high abrasion resistance. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures that the material meets the specific demands of the application, thereby enhancing product performance and longevity. -
Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance indicates the range of temperatures a material can withstand without losing its properties. Neoprene typically has a tolerance between -40°C to 100°C, while polyurethane can endure temperatures from -45°C to 150°C. This specification is critical for applications in extreme environments, such as automotive or industrial settings, where temperature fluctuations are common. A material’s ability to maintain performance under varying temperatures directly impacts operational efficiency and safety. -
Chemical Resistance
Both materials exhibit different levels of resistance to various chemicals. Neoprene is well-known for its resistance to oils, solvents, and certain acids, making it suitable for applications in medical and laboratory environments. Polyurethane, on the other hand, excels in resisting wear and tear from harsh chemicals, particularly in heavy industrial applications. Understanding chemical resistance is vital for B2B buyers to ensure that the selected material will not degrade or fail in the intended application. -
Hardness (Shore Durometer)
Hardness is measured using the Shore durometer scale, which gauges the material’s resistance to indentation. Polyurethane can be produced in a range of hardness levels, from soft to extremely hard, allowing for versatility in applications like casters and cushioning. Neoprene typically has a more uniform hardness, ideal for applications requiring a balance of flexibility and durability. Choosing the right hardness is essential to meet specific application needs, such as load-bearing capacity or shock absorption. -
Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is the ability of a material to withstand wear from friction. Polyurethane is generally superior in this regard, making it a preferred choice for applications involving heavy loads or continuous movement, such as conveyor belts. Neoprene, while also resistant, may not perform as well under extreme wear conditions. Evaluating abrasion resistance helps B2B buyers select materials that will minimize maintenance costs and extend product lifespan.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Neoprene and Polyurethane?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communications and negotiations in the B2B landscape. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of neoprene and polyurethane, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source high-quality components tailored to specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategies and ensure they meet their operational requirements without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific quantities of products. For buyers evaluating neoprene and polyurethane options, issuing an RFQ can facilitate competitive bidding and ensure they receive the best possible pricing and terms from suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, particularly in global sourcing scenarios. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. For businesses relying on neoprene and polyurethane components, understanding lead times is critical for supply chain planning and maintaining production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their supply chains, and enhance their operational efficiency in industries utilizing neoprene and polyurethane.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the neoprene vs polyurethane Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Neoprene vs Polyurethane Sector?
The global market for neoprene and polyurethane materials is influenced by several key drivers. Increased demand in industries such as automotive, construction, and medical devices is propelling growth, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. In these areas, the rising focus on durable and high-performance materials is critical. International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer tailored solutions that meet specific application requirements, from high-temperature resistance to chemical stability.
Emerging technologies such as advanced polymerization processes are leading to the development of high-performance polyurethane variants, which can be specifically engineered for unique applications. Additionally, the trend towards digital sourcing platforms is gaining traction, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and materials more efficiently. B2B buyers are now leveraging online marketplaces and data analytics to make informed decisions, ensuring they select materials that not only meet their performance needs but also align with their operational efficiency.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on cost-effectiveness is driving a comparative evaluation between neoprene and polyurethane. While polyurethane often provides superior performance, its higher cost can be a deterrent for budget-conscious businesses. As a result, B2B buyers must carefully assess their application needs against their budget constraints to make informed sourcing decisions.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Neoprene and Polyurethane Markets?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the neoprene and polyurethane sectors. Both materials are derived from petrochemical sources, raising concerns about their environmental impact. Therefore, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
The importance of ‘green’ certifications is on the rise, as buyers seek materials that are produced with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) for sustainable textiles are becoming essential in procurement processes. Additionally, companies are exploring innovative alternatives, such as bio-based polyurethanes and neoprene blends that incorporate recycled materials, to meet both performance and sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining prominence, with buyers demanding transparency regarding the sourcing of raw materials. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are becoming more stringent. Adopting sustainable practices not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings through improved resource efficiency and waste reduction.
How Has the Neoprene and Polyurethane Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of neoprene and polyurethane can be traced back to the early 20th century when synthetic materials began to emerge as alternatives to natural rubber. Neoprene was first developed in the 1930s, known for its resilience and resistance to various environmental factors, making it a preferred choice in diverse applications. Polyurethane followed suit, offering versatility and the ability to tailor properties for specific needs, which led to its widespread use in sectors ranging from automotive to consumer goods.
Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
Over the decades, advancements in polymer chemistry have significantly enhanced the performance characteristics of both materials. This evolution has resulted in specialized formulations that cater to the diverse requirements of modern industries. As global markets continue to demand high-performance, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions, the neoprene and polyurethane sectors are poised for further innovation and growth. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with current market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of neoprene vs polyurethane
-
How do I determine whether neoprene or polyurethane is suitable for my application?
To determine the best material for your application, consider the specific requirements such as temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stresses. Neoprene excels in applications needing resistance to oils and chemicals, while polyurethane offers superior durability and abrasion resistance, especially in heavy-duty scenarios. Conducting a thorough assessment of the environmental conditions and the physical demands on the material will guide your decision. Consulting with suppliers who specialize in these materials can also provide tailored recommendations based on your unique needs. -
What are the key differences in cost between neoprene and polyurethane?
Neoprene generally offers a lower cost compared to polyurethane. The price disparity is attributed to the manufacturing processes and the performance characteristics of each material. While neoprene provides good chemical resistance and flexibility, polyurethane, particularly in its solid form, boasts higher durability and abrasion resistance but at a premium price. It’s essential to evaluate the long-term value and performance of the material in your specific application rather than just the upfront costs. -
What customization options are available when sourcing neoprene or polyurethane products?
Many suppliers offer customization options such as varying thicknesses, densities, and formulations for both neoprene and polyurethane. You can also request specific shapes, sizes, or blends with other materials to suit your application needs. When discussing customization, ensure you communicate your performance requirements and environmental considerations to the supplier. This will enable them to recommend the most suitable formulations or modifications that align with your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for neoprene and polyurethane products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, MOQs for neoprene and polyurethane materials may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. If your needs are smaller, some suppliers may offer flexibility or the option to combine orders with other customers to meet MOQ requirements. -
How can I vet suppliers for neoprene and polyurethane products?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, production capabilities, and certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in producing high-quality neoprene and polyurethane products. Request samples to assess material quality and consistency. Additionally, check customer reviews and testimonials to gauge their reputation in the market. Engaging in direct communication can also help you understand their responsiveness and willingness to meet your specific needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing neoprene or polyurethane internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and regions. Common terms include payment in advance, 30% deposit with the balance upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after receipt of goods. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before placing an order and to ensure they align with your financial policies. Also, consider the implications of currency fluctuations and international transaction fees when negotiating payment terms with suppliers. -
What quality assurance (QA) processes should I look for in neoprene and polyurethane products?
Effective quality assurance processes are essential to ensure the reliability of neoprene and polyurethane products. Look for suppliers who implement rigorous testing procedures, such as tensile strength, elongation, and chemical resistance tests, to validate material performance. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with international quality standards like ISO 9001. Regular audits and certifications can also indicate a supplier’s commitment to maintaining high-quality production standards. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing neoprene or polyurethane products?
When importing these materials, consider shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in the mode of transport that best suits your timeline and budget, whether by air or sea. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and minimize potential delays.
Top 4 Neoprene Vs Polyurethane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Alanto – Neoprene and Polyurethane Solutions
Domain: alanto.co.uk
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Neoprene and Polyurethane are two materials with distinct properties. Polyurethane is composed of multiple urethane units bonded through polymerisation, resulting in a firm and rigid material. It has high abrasion resistance and performs well in harsh chemical environments, particularly with oil or petroleum-based materials, but is generally more expensive than Neoprene. Neoprene is produced from …
2. WMBerg – Neoprene & Polyurethane Timing Belts
Domain: wmberg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Neoprene Timing Belts: Characteristics include fiberglass rope core, nylon facing for wear reduction, audible noise reduction, high shock absorption, moisture resistance, resistance to twisting/flexing/stretching under load, and temperature resistance. Polyurethane Timing Belts: Characteristics include polyurethane molded over stainless steel or aramid cable spine, high chemical resistance, strong…
3. Plastics Unlimited – Urethanes & Natural Rubber Solutions
Domain: plasticsunlimited.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Urethanes: Cast polyurethanes produced by mixing polyol and isocyanate, cured in molds, available in various densities and durometers. Natural Rubber: Flexible, elastic, durable, abrasion-resistant, high tear and tensile strength, prone to degradation from sunlight and caustic chemicals. Applications include adhesives, tires, roofing, flooring, gloves, insulation. Neoprene: Synthetic rubber, corro…
4. Scribd – Neoprene & Polyurethane
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Neoprene is a family of synthetic rubbers produced by polymerization of chloroprene, known for its high resistance to chemicals and temperature extremes. Polyurethane is a polymer created from the polyaddition reaction of isocyanate and polyols, available in forms such as rubber or rigid foam, and is utilized in coatings, adhesives, insulation, and more.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for neoprene vs polyurethane
In the competitive landscape of material sourcing, understanding the distinct properties and applications of neoprene and polyurethane is crucial for informed decision-making. Neoprene offers excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature extremes, making it ideal for applications in medical and laboratory settings, as well as in office furniture. Conversely, polyurethane shines in heavy-duty applications due to its superior abrasion resistance and customizable properties, which cater to various industrial needs.
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of these materials can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced product performance. The choice between neoprene and polyurethane should align with specific application requirements, operational environments, and budget considerations.
As you evaluate your sourcing strategy, consider leveraging local suppliers and manufacturers who understand regional market dynamics. This can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce lead times. The future of material sourcing is not just about the lowest price; it’s about finding the right fit for your operational needs. Connect with trusted suppliers today to explore the best solutions tailored to your industry demands.

Illustrative image related to neoprene vs polyurethane
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.