Nema Configuration Chart: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for nema configuration chart
In today’s interconnected global marketplace, sourcing the right NEMA configuration chart can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses expand operations across regions—from Africa and South America to the Middle East and Europe—understanding the intricacies of NEMA plugs and receptacles becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the various NEMA configurations, detailing their types, applications, and specifications to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
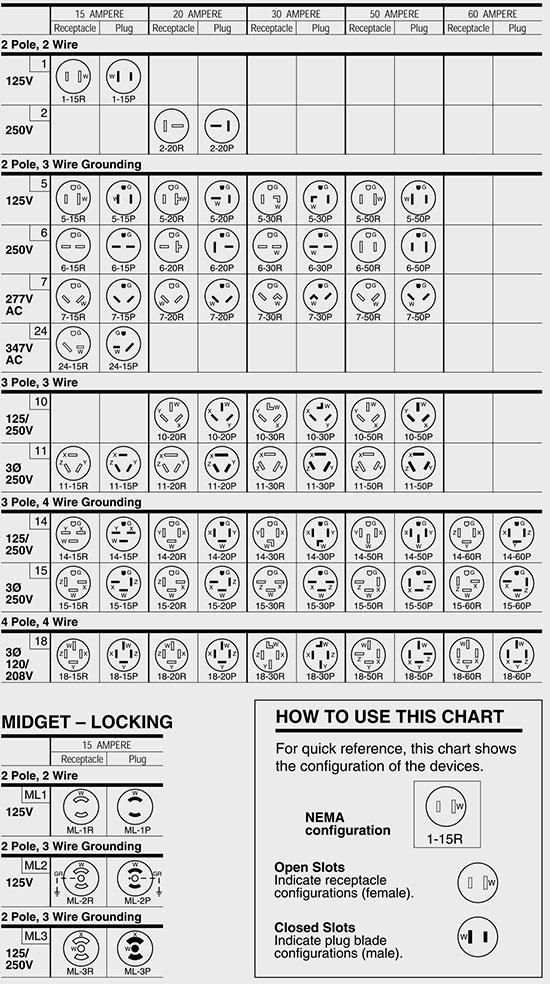
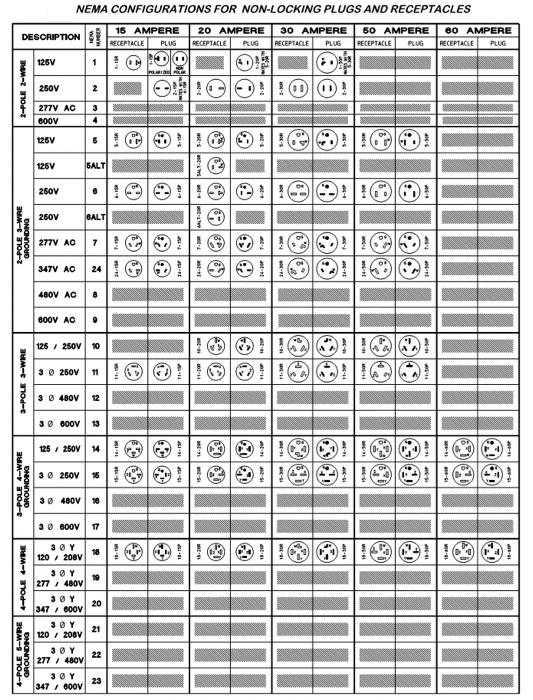
The NEMA configuration chart serves as a vital reference for ensuring compatibility and safety in electrical connections, preventing costly errors that can arise from incorrect plug and receptacle pairings. This guide will explore both non-locking and locking configurations, their voltage and current ratings, and the specific applications suited for each type. Additionally, it will provide insights into vetting suppliers, evaluating costs, and understanding regional compliance standards, thereby empowering B2B buyers to make well-informed choices tailored to their unique operational needs.
By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of NEMA configurations, this guide not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with electrical systems. Whether you are in Nigeria, Vietnam, or elsewhere, mastering the NEMA configuration landscape is essential for driving success in your business endeavors.
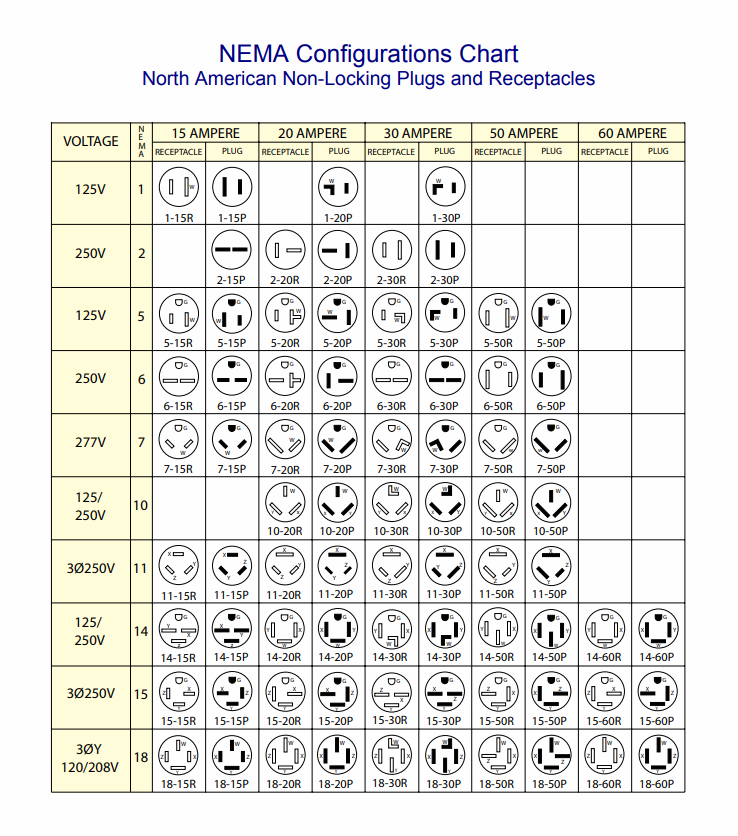
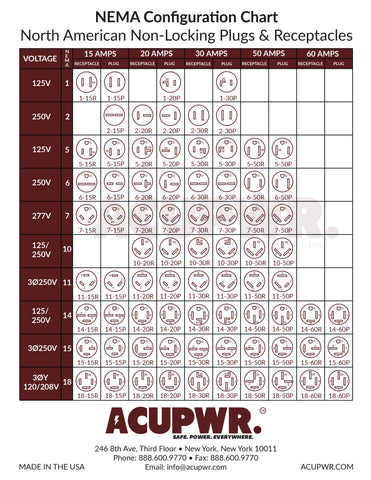
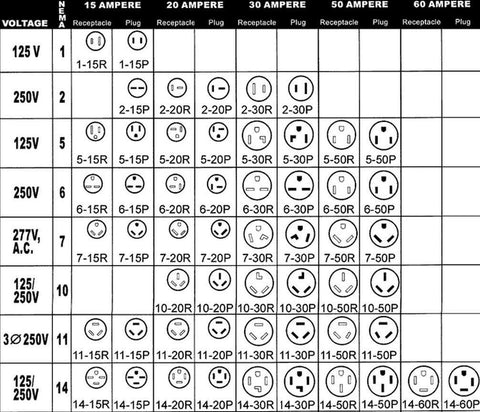
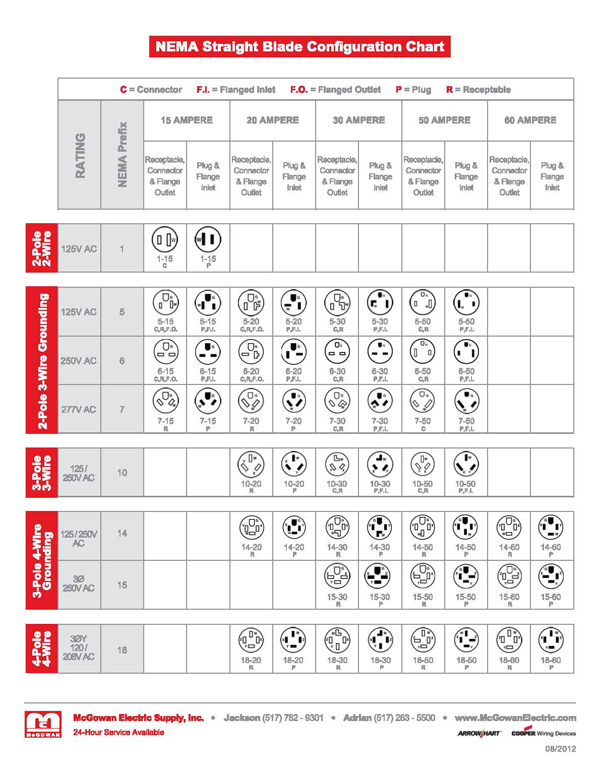
Understanding nema configuration chart Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
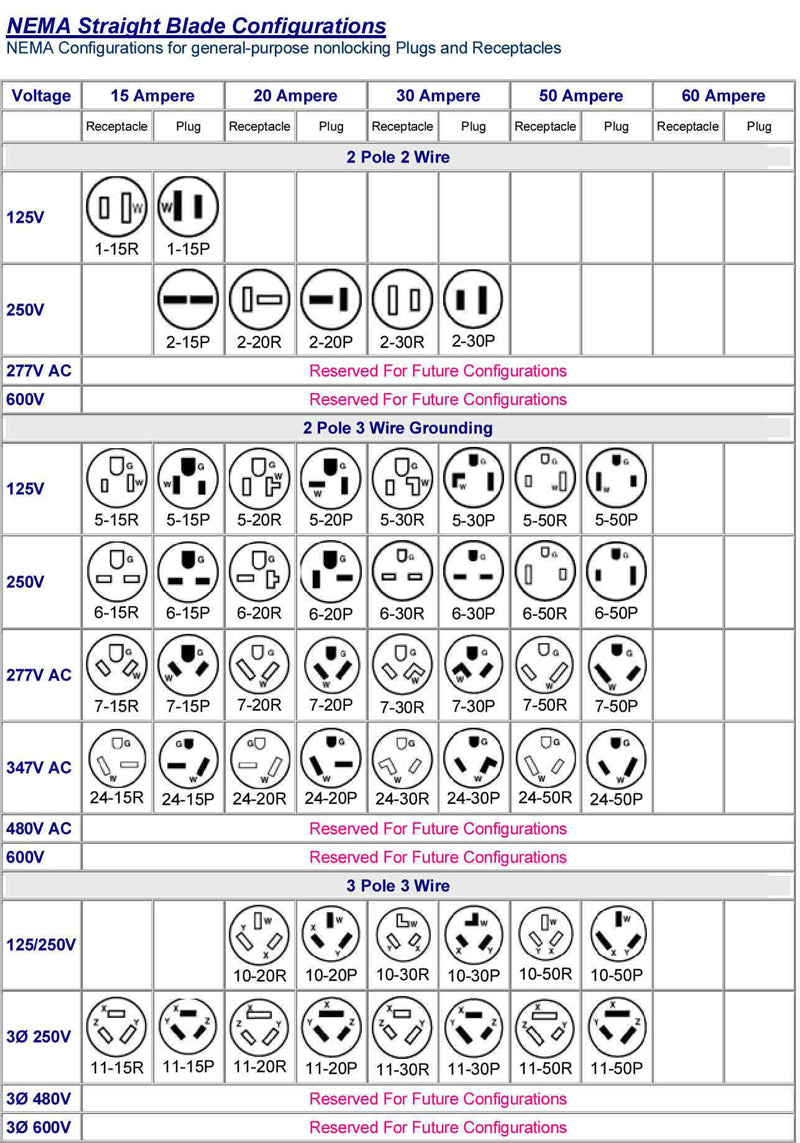
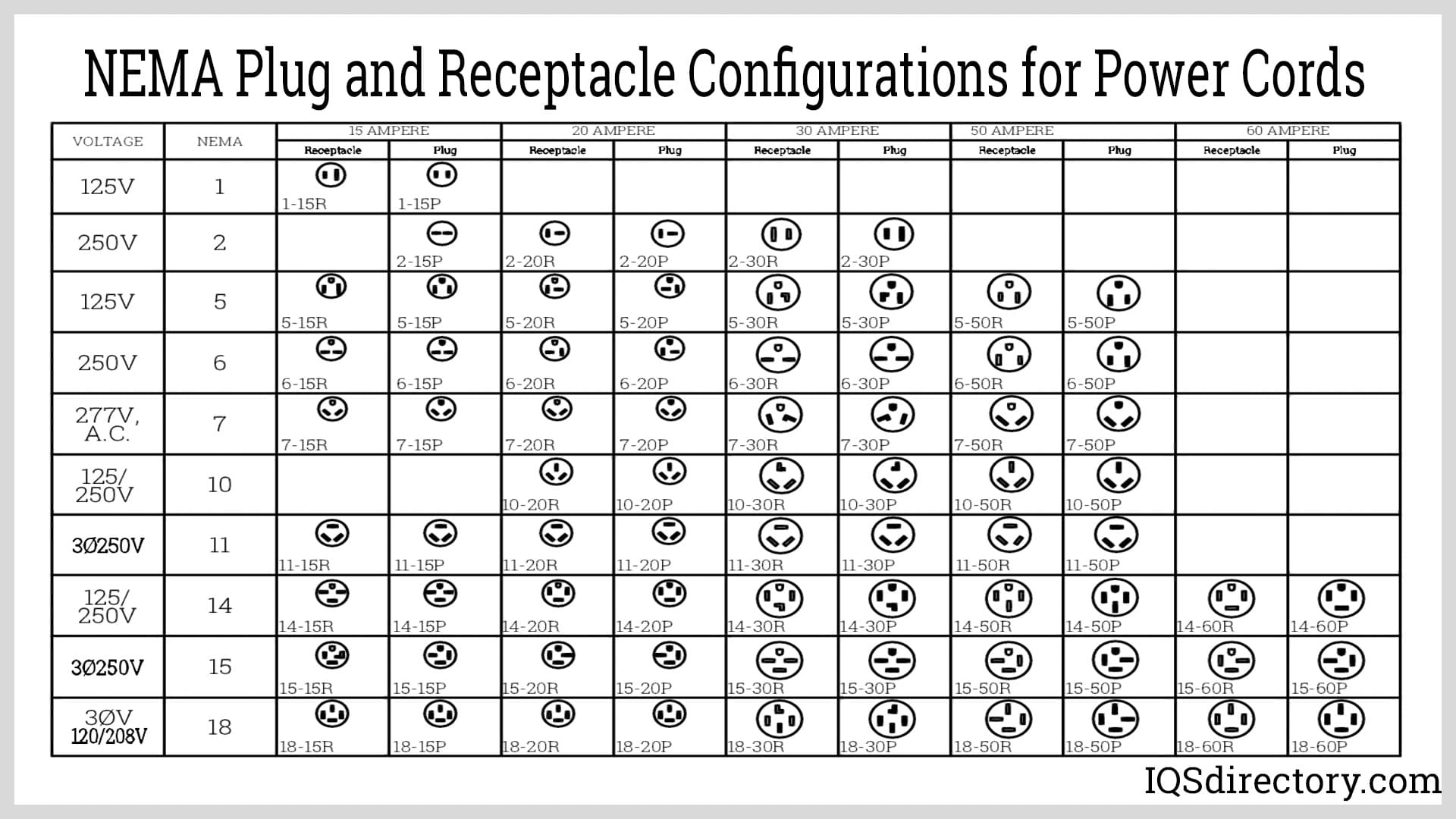
| Non-Locking Plugs & Receptacles | Simple plug-in design, available in various voltages and amperages, e.g., 5-15P, 6-20R | Residential, light commercial, small appliances | Pros: Easy to use, widely available. Cons: Less secure, potential for accidental disconnection. |
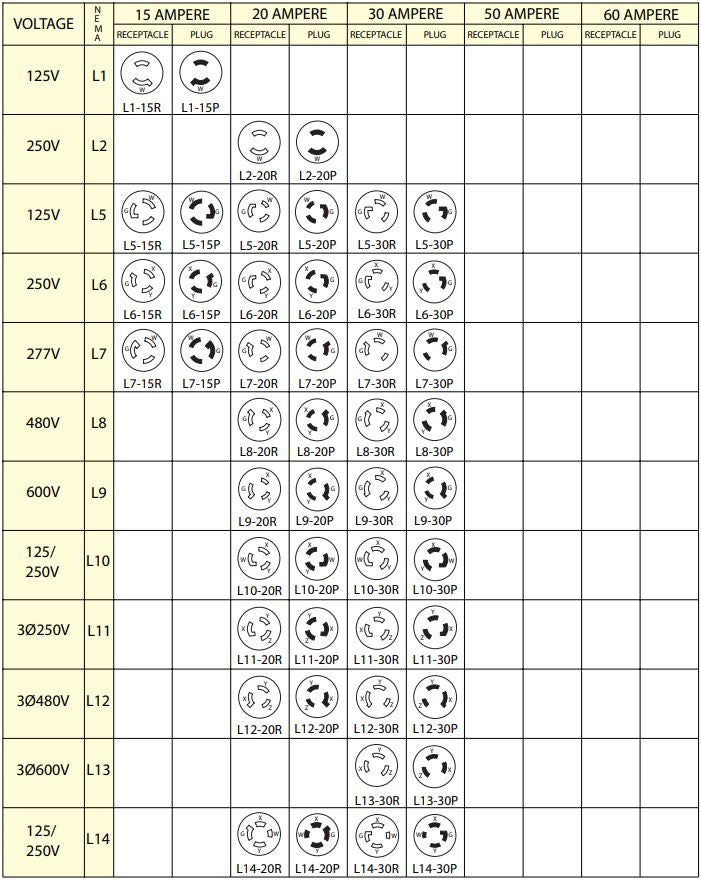
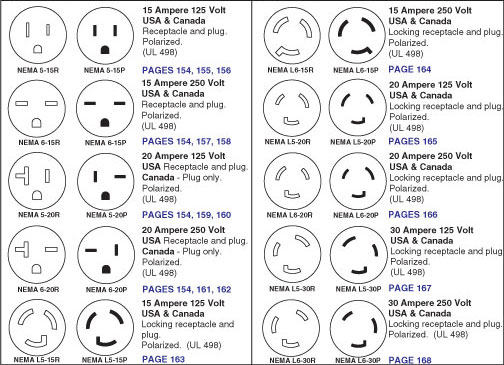
| Locking Plugs & Receptacles | Twist-and-lock mechanism, designed for higher amperage and voltage, e.g., L5-20P, L14-30R | Industrial settings, outdoor applications, sensitive machinery | Pros: Enhanced safety, prevents accidental unplugging. Cons: More complex installation, typically higher cost. |
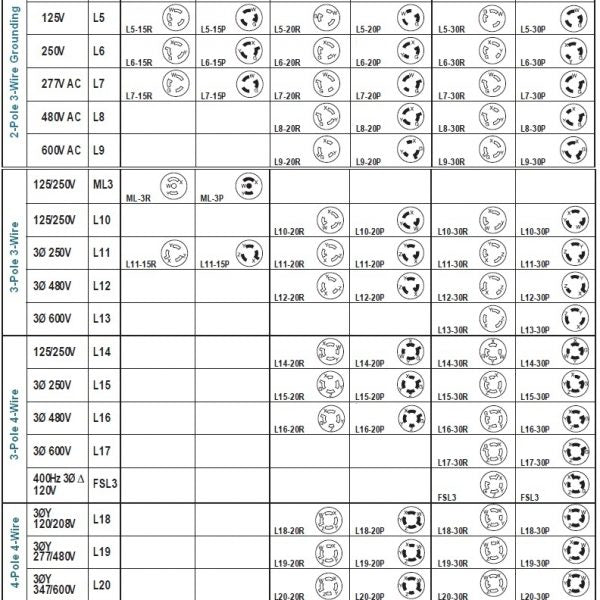
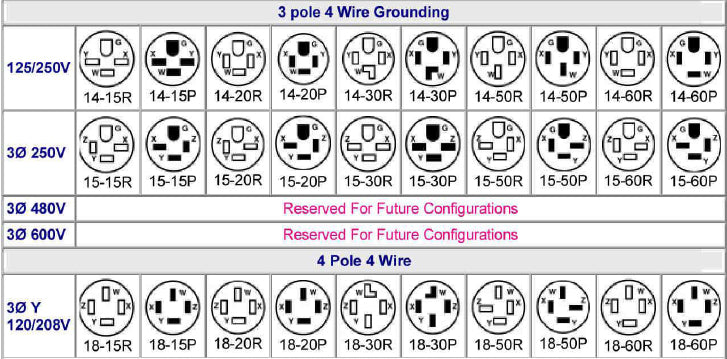
| Two-Pole, Three-Wire Configurations | Grounding capabilities, used for higher power applications, e.g., 5-15, 6-20 | HVAC systems, power tools, larger appliances | Pros: Improved safety with grounding. Cons: May require specialized receptacles and plugs. |
| Three-Pole, Four-Wire Configurations | Suitable for multi-phase systems, includes grounding, e.g., 14-30, 14-50 | Commercial kitchens, EV chargers, generators | Pros: Supports high power demands, versatile. Cons: Requires proper installation and knowledge of electrical systems. |
| Four-Pole, Four-Wire Configurations | Designed for three-phase power systems, high amperage, e.g., 18-50 | Industrial machinery, large scale electrical systems | Pros: Efficient for heavy-duty applications. Cons: Higher complexity and cost, specialized installation needed. |
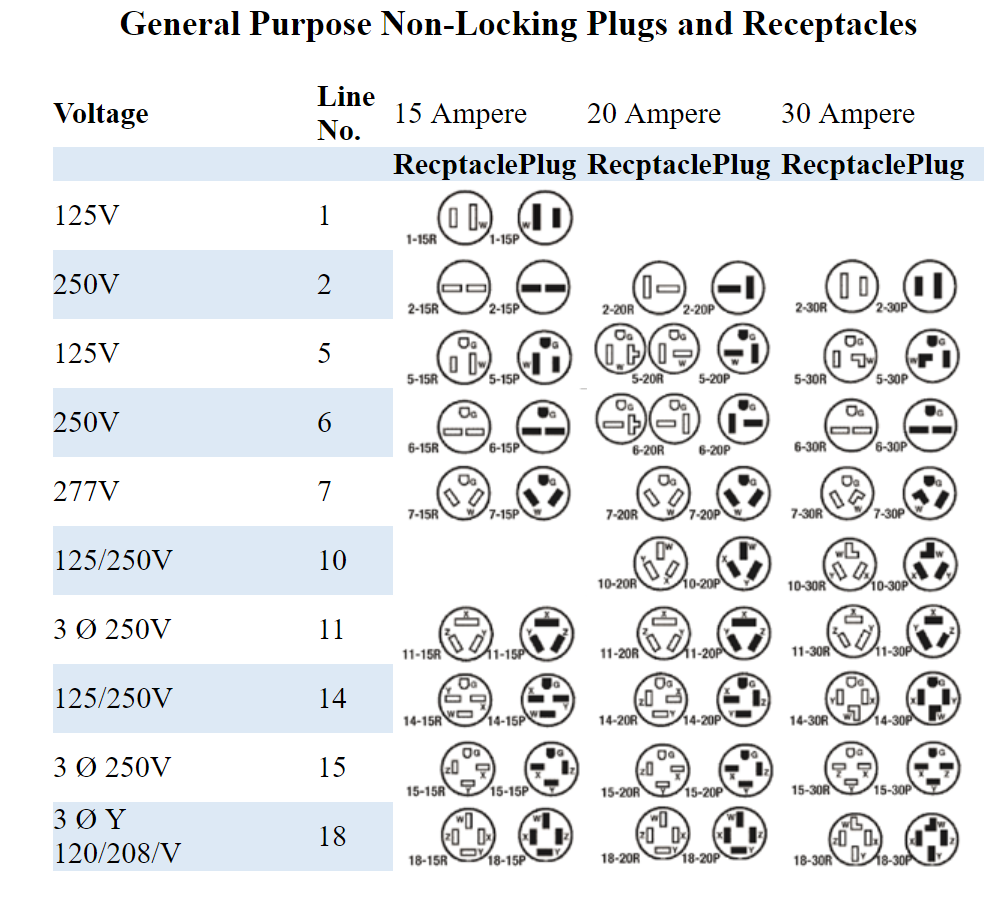
What Are the Characteristics of Non-Locking Plugs & Receptacles?
Non-locking plugs and receptacles are characterized by their straightforward plug-in design, making them user-friendly for general applications. They are available in various configurations, such as the commonly used 5-15P for 125V applications, ideal for residential and light commercial use. Buyers should consider the ease of availability and compatibility with standard household appliances, but be aware of their limitations in terms of safety, as they can be accidentally disconnected.
Why Choose Locking Plugs & Receptacles for Industrial Applications?
Locking plugs and receptacles offer a secure connection through a twist-and-lock mechanism, making them ideal for industrial and outdoor applications where disconnection due to vibration or movement is a concern. Common configurations include L5-20P and L14-30R, suitable for high-power machinery. While they provide enhanced safety and reliability, buyers should consider the additional complexity and potential higher costs associated with installation.
How Do Two-Pole, Three-Wire Configurations Enhance Safety?
Two-pole, three-wire configurations incorporate grounding capabilities, making them suitable for higher power applications such as HVAC systems and power tools. These configurations, like 5-15 and 6-20, enhance safety by reducing the risk of electrical shock. Buyers should assess their specific power requirements and ensure compatibility with existing systems, as these configurations may necessitate specialized receptacles.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
What Are the Benefits of Three-Pole, Four-Wire Configurations?
Three-pole, four-wire configurations are designed for multi-phase systems and include grounding for safety. Common in commercial kitchens and EV chargers, configurations such as 14-30 and 14-50 support high power demands. Buyers should consider the versatility and efficiency these configurations offer, but also recognize the need for proper installation and knowledge of electrical systems to avoid potential hazards.
When Should You Consider Four-Pole, Four-Wire Configurations?
Four-pole, four-wire configurations are tailored for three-phase power systems, accommodating high amperage applications in industrial settings. Examples like 18-50 are essential for powering large machinery and complex electrical systems. While they offer significant advantages for heavy-duty applications, buyers must factor in the complexity and costs associated with installation, ensuring that they have the necessary expertise for safe implementation.
Key Industrial Applications of nema configuration chart
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of NEMA Configuration Chart | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering Industrial Equipment | Ensures compatibility and safety in high-power settings | Voltage ratings, amperage capacities, and environmental ratings |
| Construction | Temporary Power Supply for Construction Sites | Provides reliable power connections for tools and machinery | Durability, weather resistance, and locking mechanisms |
| Healthcare | Medical Equipment Power Supply | Guarantees safe and consistent power for critical devices | Compliance with medical standards and grounding features |
| Agriculture | Powering Agricultural Machinery | Supports efficient operation of high-load equipment | Voltage compatibility, outdoor durability, and ease of connection |
| Telecommunications | Power Supply for Communication Equipment | Ensures uninterrupted power for essential services | Voltage and amperage ratings, environmental protection |
How is the NEMA Configuration Chart Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, the NEMA configuration chart is essential for powering industrial equipment such as CNC machines, welding machines, and assembly line robots. These machines often require specific voltage and amperage to operate efficiently, and using the correct NEMA configurations prevents equipment damage or operational failures. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the selected plugs and receptacles can handle high load demands, are compatible with existing infrastructure, and meet industry safety standards to avoid costly downtimes.
What Role Does the NEMA Configuration Chart Play in Construction?
Construction sites often require temporary power solutions to operate heavy machinery and tools. The NEMA configuration chart assists contractors in selecting appropriate plugs and receptacles that can handle the diverse power needs of equipment like excavators, concrete mixers, and cranes. The chart ensures that the connectors used are durable and resistant to harsh environmental conditions, which is critical for maintaining safety and efficiency on-site. Buyers must consider sourcing locking connectors to prevent accidental disconnection due to vibrations and movement.
Why is the NEMA Configuration Chart Important in Healthcare?
In healthcare settings, the reliability of power supply for medical equipment is crucial. The NEMA configuration chart helps facilities ensure that devices such as MRI machines, ventilators, and surgical lights are connected safely to power sources that meet their specific voltage and amperage requirements. Compliance with medical safety standards is vital, and buyers must prioritize sourcing NEMA configurations with grounding features to protect against electrical hazards, thereby ensuring patient safety and operational reliability.
How Does the NEMA Configuration Chart Benefit Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors and irrigation systems, often operates in outdoor environments where power supply connections must be robust and weather-resistant. The NEMA configuration chart provides a guide for selecting appropriate connectors that can withstand the rigors of agricultural use. Buyers in this sector need to focus on voltage compatibility and durability to ensure that equipment operates efficiently under varying weather conditions, thus maximizing productivity and minimizing equipment failure.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
What is the Significance of the NEMA Configuration Chart in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, maintaining a consistent power supply for communication equipment is critical for uninterrupted service. The NEMA configuration chart aids in identifying the correct plugs and receptacles that meet the power requirements of servers, routers, and other essential equipment. For international buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating power quality, it is essential to consider voltage and amperage ratings, as well as environmental protection features to ensure reliable operation in diverse conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘nema configuration chart’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment of Equipment and NEMA Configuration
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Nigeria has recently acquired new machinery that requires specific electrical connections. However, upon attempting to plug in the equipment, they discover that the NEMA configurations of their existing power supplies do not match the machinery’s requirements. This misalignment leads to production delays and potential safety hazards, causing frustration and increased costs for the company.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, it is essential for B2B buyers to thoroughly assess the NEMA configuration chart before making equipment purchases. Start by identifying the voltage and amperage requirements of the new machinery, which can usually be found in the equipment’s specifications. Once you have this information, consult the NEMA configuration chart to find compatible plugs and receptacles. For example, if your machinery requires a 30A, 250V connection, you would look for configurations such as NEMA L6-30P for locking plugs or NEMA 6-30P for non-locking ones. By ensuring that all new equipment aligns with existing electrical systems, companies can mitigate downtime and enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, consider investing in NEMA adapters to bridge any gaps temporarily while sourcing the correct configurations.
Scenario 2: Confusion Over Locking vs. Non-Locking NEMA Configurations
The Problem: An electrical contractor in South America is tasked with installing power connections for a new commercial building. The project specifications include both non-locking and locking NEMA configurations, but there is confusion about which type to use in specific areas, particularly in high-vibration environments. This uncertainty not only complicates the installation process but also raises concerns about safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
The Solution: To clarify the distinction between locking and non-locking NEMA configurations, contractors should refer to the NEMA configuration chart and its guidelines regarding application suitability. Non-locking configurations, like NEMA 5-15P, are generally adequate for residential and light commercial use, while locking configurations, such as NEMA L14-30, are ideal for industrial settings where secure connections are vital to prevent accidental disconnection. To streamline the decision-making process, create a checklist that categorizes areas of installation based on their specific requirements—high-vibration areas should be designated for locking connectors, while standard office spaces can utilize non-locking ones. Regular training sessions for the installation team on recognizing and implementing the correct configurations can further reduce errors and ensure compliance.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Knowledge of International NEMA Standards
The Problem: A European company that operates in multiple regions, including Africa and the Middle East, faces challenges when it comes to sourcing electrical components that meet different NEMA standards. With varying local regulations and standards, the procurement team struggles to ensure that the right NEMA configurations are used in each location, leading to compatibility issues and increased shipping costs for returns or replacements.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should invest time in understanding the international standards governing NEMA configurations in the regions they operate. This involves not only familiarizing themselves with the local electrical codes but also establishing partnerships with suppliers who have expertise in international NEMA configurations. Create a comprehensive guide that outlines the specific NEMA configurations used in each region, including any local adaptations that may apply. Additionally, consider utilizing a centralized procurement system that consolidates all electrical component orders. This system should include a database of NEMA configurations that are compliant with regional standards, enabling the procurement team to make informed decisions quickly and reduce the likelihood of errors. By proactively managing this aspect of procurement, companies can avoid costly delays and ensure seamless operations across all locations.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Strategic Material Selection Guide for nema configuration chart
What Are the Common Materials Used in NEMA Configuration Charts?
When selecting materials for NEMA configurations, it is essential to consider the performance characteristics, durability, and overall suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of NEMA plugs and receptacles, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Thermoplastic Materials in NEMA Configurations?
Thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are frequently used in NEMA configurations due to their excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to impact. They typically have a temperature rating of around 85°C to 120°C, making them suitable for most residential and light commercial applications. Additionally, thermoplastics exhibit good corrosion resistance, which is vital for outdoor or industrial environments.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to mold, allowing for complex designs. They also provide adequate safety features, including flame resistance.
Cons: However, they may not withstand extreme temperatures or harsh chemical environments, which can limit their application in heavy-duty industrial settings.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are ideal for standard residential and light commercial applications, where electrical insulation and durability are necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like IEC and ASTM is crucial, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where electrical safety regulations can vary significantly.
How Do Metal Materials Enhance the Performance of NEMA Configurations?
Metal materials, particularly brass and stainless steel, are often used for the conductive components of NEMA plugs and receptacles. These metals offer high conductivity and can handle higher amperages, with temperature ratings often exceeding 200°C. Their corrosion resistance, especially in stainless steel, makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Pros: Metals provide superior durability and electrical performance, making them ideal for industrial applications. They also have a longer lifespan compared to plastic materials.
Cons: The higher cost of metal components can be a drawback, and they may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Metals are particularly suited for high-load applications, such as industrial machinery and outdoor equipment, where reliability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that metal components meet local standards for conductivity and corrosion resistance, particularly in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
What Role Do Rubber Materials Play in NEMA Configurations?
Rubber, especially silicone and EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), is commonly used for gaskets and seals in NEMA configurations. These materials provide excellent flexibility and temperature resistance, with ratings typically between -50°C to 200°C. Rubber is also resistant to various chemicals and UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: Rubber materials enhance the sealing capabilities of NEMA configurations, preventing moisture ingress and ensuring safety.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Cons: While rubber is durable, it can degrade over time when exposed to extreme temperatures or certain chemicals, necessitating regular inspections.
Impact on Application: Rubber is essential for applications requiring moisture protection, such as outdoor electrical installations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding local climate conditions is vital, as extreme temperatures can affect rubber longevity. Compliance with international sealing standards is also important.
Why Are Composite Materials Gaining Popularity in NEMA Configurations?
Composite materials, which combine plastics with fillers or reinforcements, are increasingly used in NEMA configurations. These materials can offer enhanced mechanical properties and thermal stability, with temperature ratings often exceeding those of conventional plastics.
Pros: Composites can provide a balance between weight, strength, and cost, making them versatile for various applications.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Cons: The manufacturing complexity can lead to higher costs and longer lead times compared to standard materials.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for applications requiring lightweight yet durable components, such as portable electrical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet relevant international standards for strength and electrical performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for NEMA Configuration Chart
| Material | Typical Use Case for NEMA Configuration Chart | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Residential and light commercial applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Metal | Industrial and outdoor applications | Superior durability and conductivity | Higher cost and corrosion treatment needed | High |
| Rubber | Outdoor electrical installations | Excellent sealing and flexibility | Potential degradation over time | Medium |
| Composite | Portable electrical devices | Balanced strength and weight | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on performance requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for nema configuration chart
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for NEMA Configuration Charts?
The manufacturing of NEMA configuration charts involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets the necessary performance and safety standards. Understanding these stages will aid B2B buyers in evaluating potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is Quality Ensured Before Production?
The first stage involves sourcing high-quality materials, typically thermoplastics and metals, which are essential for manufacturing NEMA plugs and receptacles. Suppliers should adhere to international standards for material quality, such as ASTM or ISO specifications, ensuring durability and safety. Buyers should verify that suppliers conduct thorough material inspections before production begins, including tests for conductivity and insulation resistance.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create NEMA Components?
The forming process includes various techniques, such as injection molding for plastic components and stamping for metal parts. These methods ensure precision and consistency, which are crucial for electrical connections. Advanced manufacturing technologies, such as CNC machining, may also be employed to create complex geometries. B2B buyers should inquire about the machinery used and whether it is regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
Assembly: How Are NEMA Components Assembled for Maximum Reliability?
The assembly stage is where the individual components are put together to form the final product. This process often involves automated assembly lines, which enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Quality assurance during assembly includes checking for proper alignment and secure connections to ensure electrical safety. Buyers should look for suppliers that implement strict assembly protocols, including visual inspections and functional tests.
Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Enhance Product Durability?
Finishing processes, such as surface treatment and coating, are critical for improving the durability and aesthetics of NEMA configurations. Techniques like electroplating or powder coating can enhance corrosion resistance and wear resistance. B2B buyers should confirm that suppliers use high-quality finishing materials and conduct tests to ensure that finishes meet industry standards.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
How Do Quality Control Processes Ensure the Reliability of NEMA Configurations?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process of NEMA configuration charts. It ensures that products meet both international and industry-specific standards, which is particularly important for B2B buyers looking for reliability.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Apply?
Manufacturers of NEMA configurations often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for products sold in Europe or UL listing for safety compliance in North America are vital. Buyers should request documentation proving compliance with these standards to mitigate risks associated with product failures.
What Are the Critical QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are essential for maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing process help identify defects early. This can include measurements of electrical properties and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection ensures that all specifications are met, including functionality tests for electrical components.
B2B buyers should inquire about the frequency and thoroughness of these inspections, as they directly impact product reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed?
Testing methods for NEMA configurations typically include:
- Electrical Testing: To verify voltage, current capacity, and insulation resistance.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the durability of plugs and receptacles through stress tests.
- Environmental Testing: Ensuring that products can withstand various conditions, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide detailed reports of testing procedures and results, which can serve as a quality assurance benchmark.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Implement?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers is crucial for ensuring compliance with quality standards. Buyers should consider both scheduled and random audits to assess the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and adherence to safety regulations.
What Documentation Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request comprehensive documentation from suppliers, including:
- Quality Management System (QMS) certifications: Evidence of compliance with ISO 9001 or other relevant standards.
- Test Reports: Detailed testing data for each batch of products, including any deviations from specifications.
- Inspection Reports: Documentation of inspections conducted during the manufacturing process.
This information can help buyers make informed decisions about supplier reliability.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of supplier quality control practices. These services can conduct independent audits and testing, offering an additional layer of assurance for B2B buyers. It is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may face language barriers or cultural differences that could complicate direct communication with suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
What Regional Standards Should Be Considered?
Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that products must meet. For instance, products sold in the EU must comply with CE marking, while those in North America may require UL certification. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with the regulatory landscape in their target markets.
How Can Buyers Navigate Cultural and Communication Barriers?
Cultural differences can impact quality assurance practices. Buyers should establish clear communication channels with suppliers, including regular updates and feedback mechanisms. Utilizing local representatives or consultants can also help bridge any gaps in understanding.
By focusing on these aspects of the manufacturing process and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for NEMA configuration charts, ensuring that they receive reliable and compliant products tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘nema configuration chart’
The following guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing NEMA configuration charts. Understanding these specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility and safety in electrical applications, particularly in diverse international markets.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s crucial to outline your specific technical requirements. Identify the voltage, amperage, and type of NEMA configuration (locking or non-locking) needed for your applications. This step will streamline your search, allowing you to focus on suppliers that can meet your precise needs.
- Voltage Requirements: Determine whether you need configurations for 125V, 250V, or other specifications.
- Amperage Ratings: Assess the current capacities required for your equipment, such as 15A, 20A, or 50A.
Step 2: Research Market Standards and Compliance
Understanding the relevant standards, such as ANSI/NEMA WD 6-2021, is vital. These standards dictate which configurations are safe and suitable for various applications, helping you avoid unsafe interchangeability.
- Safety Considerations: Ensure that the NEMA configurations you are considering comply with international electrical safety standards.
- Market Relevance: Different regions may have unique compliance requirements; make sure to research local regulations.
Step 3: Identify Reputable Suppliers
The selection of a reliable supplier is paramount. Look for manufacturers and distributors with a strong reputation in the electrical industry.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
- Supplier Credentials: Verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards.
- Experience and Expertise: Choose suppliers who have experience in your specific market or industry to ensure they understand your unique needs.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the NEMA configurations you plan to buy. This allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the products with your existing systems.
- Quality Assurance: Inspect the materials and construction of the samples to ensure they meet your standards.
- Compatibility Testing: Test the samples with your equipment to verify that they work as intended.
Step 5: Evaluate Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. This analysis will help you find the best value for your investment.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial cost but also potential long-term savings, such as durability and maintenance.
- Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers that offer favorable payment terms that align with your cash flow requirements.
Step 6: Check Customer Support and Warranty Policies
Reliable customer support and clear warranty policies are indicators of a trustworthy supplier. Evaluate the level of support you can expect post-purchase.
- Technical Assistance: Ensure that the supplier offers technical support for troubleshooting and installation.
- Warranty Coverage: Understand the warranty terms to protect your investment against defects or failures.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Delivery
After selecting the best supplier, finalize your order and establish a delivery timeline. Monitoring the delivery process is crucial to ensure that you receive the correct products on time.
- Order Confirmation: Confirm the details of your order, including specifications and delivery dates.
- Logistics Coordination: Stay in contact with the supplier to monitor the shipping process and address any potential delays.
Following this checklist will help you navigate the complexities of procuring NEMA configuration charts effectively, ensuring that your electrical applications operate safely and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for nema configuration chart Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for NEMA Configuration Chart Sourcing?
When sourcing NEMA configuration charts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
Materials: The type and quality of materials used, such as copper for electrical connections or thermoplastics for insulation, significantly influence costs. Higher-grade materials, which ensure better performance and durability, come at a premium.
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the manufacturing and assembly of NEMA connectors. Labor costs can vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and facility expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs.
Tooling: Specialized tooling is necessary for creating NEMA configurations. The initial investment in tooling can be high, but it’s essential for maintaining quality and precision.
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure that the configurations meet safety and performance standards. The costs associated with testing and certification can impact the overall pricing.
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees, especially for international buyers, can add significant costs. Factors such as shipping distance, freight method, and customs duties must be considered.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their business costs and profit. This margin can vary based on market competition and supplier relationships.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
How Do Price Influencers Affect NEMA Configuration Chart Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of NEMA configuration charts, particularly for international buyers. Understanding these can lead to more strategic sourcing decisions.
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Suppliers may have Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) that can affect the overall cost, encouraging buyers to consolidate orders.
Specifications and Customization: Custom configurations or specific specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling or materials. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary for their applications.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials typically command higher prices. Certifications, such as UL or CE marks, can also impact costs as they require compliance with stringent safety standards.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better guarantees and support, while new entrants may have lower prices but higher risks.
Incoterms: Understanding International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international sourcing. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total landed cost.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in NEMA Configuration Chart Sourcing?
To optimize sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions to secure better terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can incentivize suppliers to offer favorable pricing.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront costs. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency, which can lead to long-term savings.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Understanding local market dynamics can also help in assessing fair pricing.
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Consider establishing partnerships with local suppliers to reduce logistics costs.
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to benchmark prices against competitors. This can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best suppliers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Please note that the pricing for NEMA configuration charts can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The prices indicated are for guidance only and should be verified with suppliers to obtain accurate quotations tailored to specific needs.
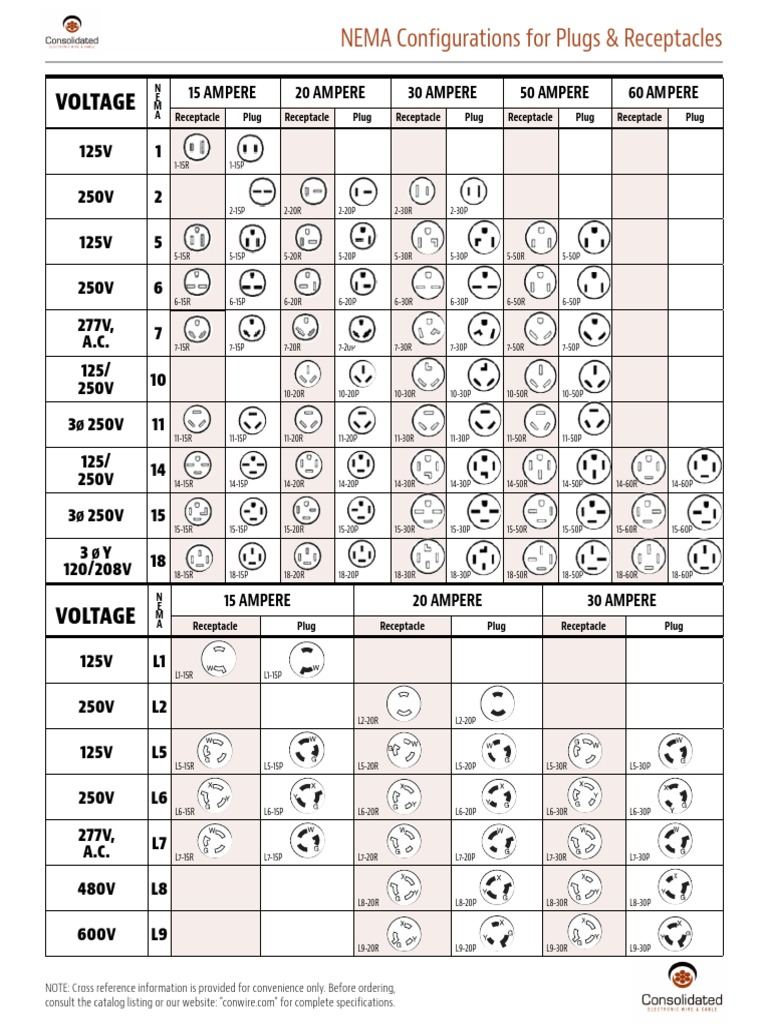
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing nema configuration chart With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the NEMA Configuration Chart
In the realm of electrical connections, the NEMA configuration chart serves as a critical resource for ensuring compatibility and safety among various plugs and receptacles. However, businesses may explore alternative solutions that offer different features or benefits. This analysis compares the NEMA configuration chart with two viable alternatives: IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) Standards and the CEE (International Commission on the Rules for the Approval of Electrical Equipment) Standards.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | NEMA Configuration Chart | IEC Standards | CEE Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High compatibility in North America; detailed voltage and amperage specifications | Global compatibility; standardized for various applications | Designed for heavy-duty industrial applications |
| Cost | Generally low; minimal investment in basic charts | Moderate; may require investment in compliant equipment | Higher cost due to robust design for industrial use |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward; widely used in North America | Requires training for international compliance | Complex; often requires specialized knowledge for installation |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal upkeep needed | Moderate; regular checks for compliance | High; requires frequent inspections in industrial settings |
| Best Use Case | Residential and light commercial applications | Global applications in commercial and industrial sectors | Heavy machinery and industrial environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
IEC Standards
IEC standards provide a global framework for electrical connections, encompassing a wide range of applications across various industries. One of the main advantages of IEC standards is their international recognition, facilitating trade and equipment compatibility across borders. This can be particularly beneficial for companies operating in multiple countries, as it reduces the risk of equipment incompatibility. However, the complexity of IEC standards may pose challenges for businesses unfamiliar with international compliance, necessitating additional training and resources for implementation.
CEE Standards
CEE standards are designed specifically for heavy-duty applications, making them suitable for industrial environments where reliability and safety are paramount. The robust design of CEE connectors ensures they can withstand harsh conditions, making them ideal for industries such as construction and manufacturing. While CEE standards offer superior durability, the higher costs associated with their implementation and maintenance can be a drawback for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets. Additionally, the complexity of installation may require specialized knowledge, increasing the demand for skilled technicians.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting an electrical connection solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including the operating environment, budget constraints, and compatibility needs. The NEMA configuration chart is an excellent choice for businesses focused on North American markets, providing ease of use and low maintenance. However, companies looking to operate internationally or in heavy-duty industrial settings might benefit more from IEC or CEE standards despite the additional complexities and costs. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance safety and efficiency in their electrical systems.
Illustrative image related to nema configuration chart
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for nema configuration chart
What Are the Key Technical Properties of NEMA Configurations?
Understanding the technical specifications of NEMA configurations is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly when making informed decisions about electrical equipment and components. Here are some critical specs to consider:
1. Voltage Ratings
Voltage ratings indicate the maximum voltage that a plug or receptacle can safely handle. Common ratings include 125V, 250V, and 480V. For B2B operations, selecting equipment that matches the voltage requirements is crucial to avoid equipment failure or electrical hazards.
2. Current Ratings
Current ratings, often expressed in amperes (e.g., 15A, 20A, 30A), denote the maximum current a plug or receptacle can carry. This specification is particularly important for ensuring that the electrical infrastructure can support the load of industrial machinery or high-power appliances, minimizing the risk of overheating and potential failures.
3. Configuration Types
NEMA configurations can be categorized into non-locking and locking types. Non-locking configurations are suitable for general use, while locking configurations are designed for high-vibration environments, offering enhanced safety. Understanding these differences helps businesses select the right connectors for specific applications, ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
4. Blade Design
The blade design of NEMA plugs varies by configuration, influencing compatibility and ease of use. For instance, straight blades are common in residential applications, while curved blades in locking configurations provide a secure connection. This aspect is vital for avoiding mismatched connections that could lead to equipment malfunction.
5. Grounding Mechanisms
Grounding is a safety feature that prevents electrical shock by ensuring that the ground pin connects first when plugging in. Many NEMA configurations include a grounding pin, which is particularly important in environments where safety is a priority, such as industrial settings.
6. Material Grade
The materials used in NEMA configurations, such as thermoplastics and metals, impact durability and performance. Selecting high-grade materials is essential for ensuring longevity and reliability, particularly in demanding environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in NEMA Configuration Sourcing?
Familiarizing yourself with trade terminology can streamline the procurement process for NEMA configurations. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source reliable and compatible components for their electrical systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQ requirements is crucial for budgeting and ensuring that you have enough inventory to meet operational needs without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and other details for specific products or services. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring that your procurement process is efficient and cost-effective.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in the transportation of goods. Familiarity with these terms is essential for managing shipping costs and liability effectively, especially when sourcing NEMA configurations from international suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving it. Understanding lead times can help businesses plan their operations and inventory effectively, preventing delays in production or project timelines.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ANSI/NEMA WD 6-2021, ensure that electrical components meet safety and performance criteria. Being aware of these standards is vital for compliance and for ensuring the reliability of electrical installations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency, safety, and compliance in electrical applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the nema configuration chart Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for NEMA Configuration Charts?
The global market for NEMA configuration charts is increasingly driven by the need for standardized electrical connections across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications. As international trade expands, the demand for reliable and safe electrical equipment becomes paramount. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing significant growth in infrastructure projects, leading to a higher demand for electrical safety standards. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the electrification of transportation systems, particularly in developing countries, is propelling the need for versatile electrical configurations that NEMA charts provide.
Current and emerging B2B tech trends also highlight the integration of smart technologies in electrical systems. Advanced monitoring and control systems require connectors that can handle varying voltages and currents efficiently. This is particularly relevant in sectors like manufacturing and construction, where high-performance electrical systems are essential. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and digital platforms facilitates easier access to NEMA products, allowing buyers from diverse regions to source components that meet their specific needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in NEMA Configuration Charts?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming crucial considerations for B2B buyers in the electrical components sector. The environmental impact of production processes and materials used in NEMA configurations cannot be overlooked. As industries shift towards greener practices, buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable manufacturing processes. This includes using recyclable materials, minimizing waste, and employing energy-efficient production techniques.
Ethical supply chains also play a significant role in sourcing decisions. Buyers should look for manufacturers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and ethically. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, opting for products made from eco-friendly materials can help businesses align their operations with global sustainability goals while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of NEMA Configuration Charts for B2B Buyers?
The NEMA configuration chart has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, driven by the need for standardized electrical connections in an increasingly complex electrical landscape. Initially designed to address safety and compatibility issues in North American electrical systems, the chart has expanded to accommodate diverse applications across various industries worldwide.
Over the years, advancements in technology and changes in regulatory standards have led to the development of new configurations, including both locking and non-locking types. This evolution reflects the growing demand for safety and reliability in electrical connections, particularly in high-stakes environments such as industrial settings. For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of NEMA configurations can provide valuable insights into current trends and help them make informed sourcing decisions that prioritize safety and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of nema configuration chart
-
How do I determine the right NEMA configuration for my equipment?
To select the appropriate NEMA configuration, consider the voltage and current requirements of your equipment. Review the specifications of your devices to identify their voltage (e.g., 125V, 250V) and amperage (e.g., 15A, 30A) needs. Refer to the NEMA configuration chart to match your equipment’s specifications with the correct plug and receptacle type. This ensures compatibility and safety, preventing potential damage or hazards from incorrect connections. -
What is the best NEMA configuration for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, locking configurations such as NEMA L14-30 or L16-20 are recommended. These connectors provide a secure connection, minimizing the risk of accidental disconnection, which is crucial in high-vibration environments. Additionally, consider the amperage and voltage requirements specific to your machinery to ensure optimal performance and safety. Always consult the NEMA chart to confirm compatibility with your equipment. -
How can I verify the quality of NEMA configurations from suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for NEMA configurations, check for certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) that ensure compliance with safety standards. Request samples to assess the physical quality and functionality of the plugs and receptacles. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes, warranty policies, and customer reviews to gauge their reliability and product performance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for NEMA configurations?
Minimum order quantities for NEMA configurations can vary significantly between suppliers. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for larger orders, while others may have strict MOQs. Understanding these terms upfront can help streamline your procurement process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing NEMA configurations?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your purchasing relationship. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or upfront payment for smaller orders. For larger contracts, suppliers might offer installment payments or letters of credit. It is essential to clarify these terms in advance to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transaction processes. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of NEMA configurations internationally?
Logistics play a critical role in international sourcing of NEMA configurations. Factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines can affect your procurement efficiency. Work closely with suppliers to understand their shipping practices and choose reliable freight forwarders familiar with electrical components to ensure timely delivery while minimizing costs and compliance issues. -
Can NEMA configurations be customized for specific applications?
Many suppliers offer customization options for NEMA configurations, allowing you to tailor products to specific applications. This can include alterations in voltage, amperage, or even unique connector shapes. Discuss your requirements with suppliers early in the procurement process to explore available customization options and ensure that your needs are met effectively. -
What should I look for in a supplier’s warranty for NEMA configurations?
When assessing a supplier’s warranty for NEMA configurations, consider the duration and coverage of the warranty. A robust warranty should cover defects in materials and workmanship for a reasonable period, typically one to two years. Additionally, review the terms regarding replacements and repairs, as well as any conditions that might void the warranty. Clear warranty policies can provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
Top 6 Nema Configuration Chart Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Americord – NEMA Plug Configurations
Domain: americord.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NEMA Plug Charts provide configurations for non-locking and locking plugs and receptacles in North America. Non-locking configurations are standard for residential, commercial, and light industrial applications, with voltage classifications of 125V, 250V, 277V, and current capacities of 15A, 20A, 30A, 50A, and 60A. Common configurations include 5-15 (standard residential), 6-20 (for appliances lik…
2. Grainger – NEMA Plug and Receptacle Configuration Chart
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: NEMA Plug and Receptacle Configuration Chart provides details on various NEMA configurations, including: 1. Two-Pole, Two-Wire configurations (NEMA 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, TT) with voltages ranging from 125V to 277V and amperages from 15A to 30A. 2. Three-Pole, Three-Wire configurations (NEMA 10, 14) with voltages of 125/250V and amperages from 20A to 50A. 3. Three-Pole, Four-Wire configurations (NEMA 14) …
3. NoOutage – NEMA Configurations
Domain: nooutage.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NEMA Configurations help prevent dangerous electrical combinations. Key terms include:
– Receptacle: Female flange mounted device, live when nothing is plugged in.
– Connector: Female cord mounted device, live when nothing is plugged in.
– Inlet: Male flange mounted device, exposed pins should not be live when unplugged.
– Plug: Male cord mounted device, exposed pins are dead until plugged in….
4. Interpower – NEMA Configurations
Domain: interpower.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: North American Non-locking NEMA Configurations include a pattern and numbering system made up of four main identifiers: 1) a blank space or the letter L (indicating straight or locking blade device), 2) a number for voltage rating, 3) a number for amperage rating, and 4) a letter indicating whether the device is a plug (P) or receptacle/outlet (R). The configurations cover various applications wit…
5. StayOnline – NEMA Receptacle Reference Chart
Domain: stayonline.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: NEMA Receptacle Chart – Twist Lock Receptacle Reference Chart. Product categories include: Power Cords, Data Center Power Cords, International Cords, Locking Power Cords, Splitter Power Cords, Hospital Grade Power Cords, IEC 60309 Pin and Sleeve Power Cords, and various plug adapters. Specific NEMA locking power cables mentioned include NEMA L5-15, L5-20, L5-30, L6-15, L6-20, L6-30, L14-20, L14-30…
6. Generator Joe – NEMA Plug and Receptacle Configurations
Domain: generatorjoe.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: NEMA Plug and Receptacle configurations: 15 AMP (2 pole 2 wire, 2 pole 3 wire grounding, 3 pole 3 wire, 3 pole 4 wire grounding), 20 AMP (2 pole 2 wire, 2 pole 3 wire grounding, 3 pole 3 wire, 3 pole 4 wire grounding), 30 AMP (2 pole 2 wire, 2 pole 3 wire grounding, 3 pole 3 wire, 3 pole 4 wire grounding), 50 AMP (2 pole 3 wire grounding, 3 pole 3 wire, 3 pole 4 wire grounding), 60 AMP (3 pole 4 w…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for nema configuration chart
As businesses increasingly rely on standardized electrical configurations, the NEMA configuration chart emerges as a pivotal resource for strategic sourcing. Understanding the differences between non-locking and locking NEMA configurations is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge enables companies to make informed decisions that enhance safety and efficiency in electrical applications.
By leveraging the NEMA charts, businesses can mitigate risks associated with electrical compatibility, ensuring that the right plugs and receptacles are utilized for their specific operational needs. This strategic sourcing approach not only safeguards equipment but also optimizes performance across various applications, from residential to industrial settings.
Looking ahead, as global markets continue to evolve, the demand for reliable and compatible electrical solutions will only increase. International buyers are encouraged to integrate NEMA configurations into their sourcing strategies, fostering safer and more efficient operations. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your electrical systems today—invest in the right NEMA configurations to future-proof your business and stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.