Mechanism Lock: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mechanism lock
In today’s dynamic global marketplace, sourcing high-quality mechanism locks poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse locking mechanisms available, from traditional mechanical options to advanced electronic systems, businesses must navigate a complex landscape to ensure optimal security solutions for their operations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the world of mechanism locks by detailing various types, applications, and key considerations for successful procurement.
Our exploration will cover essential topics such as the different categories of locking mechanisms—including keyless, electronic, and mechanical locks—along with their specific use cases in commercial and residential settings. Additionally, we will provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, enabling buyers to identify reliable manufacturers and distributors that meet their unique needs. Cost considerations, compliance with regional security standards, and trends in lock technology will also be discussed, empowering buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
This guide is tailored specifically for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Germany. By equipping you with the necessary knowledge and resources, we aim to facilitate strategic sourcing and enhance your organization’s security posture, ultimately contributing to your business’s growth and success in the global arena.
Understanding mechanism lock Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Deadbolt | Separate locking mechanism, operates with a key/turn piece | Commercial buildings, offices | Pros: High security, easy installation. Cons: Vulnerable to picking if not high-quality. |
| Mortise Lock | Integrated locking and latching mechanism in a single unit | High-traffic commercial spaces | Pros: Durable, versatile functions. Cons: Requires professional installation, can be costly. |
| Electronic Lock | Keyless entry, programmable codes, often with audit trails | Retail, warehouses, and offices | Pros: Enhanced security, remote access. Cons: Dependence on power, potential tech issues. |
| Smart Lock | Connects to smart devices, offers remote locking/unlocking | Hotels, rental properties | Pros: Convenience, integration with smart systems. Cons: Security concerns over hacking. |
| Padlock | Portable, versatile, available in various sizes and strengths | Gates, storage units, and lockers | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use. Cons: Limited security for high-risk areas. |
What are the Characteristics of Cylindrical Deadbolts and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Cylindrical deadbolts are defined by their separate locking mechanism, which operates independently from the door latch. They typically require a key or a turn piece for locking and unlocking, making them a popular choice for businesses seeking reliable security. Their straightforward installation process makes them suitable for a variety of commercial applications, from office doors to retail spaces. When purchasing, businesses should consider the lock’s quality and resistance to picking, as lower-grade options may compromise security.
How Do Mortise Locks Offer Enhanced Security in Commercial Settings?
Mortise locks are distinguished by their integrated design, combining both locking and latching functions into a single unit. This feature provides robust security, making mortise locks ideal for high-traffic commercial environments, such as shopping malls and office complexes. Their versatility allows for various functions, including entry and privacy. However, businesses must account for the need for professional installation, which can increase upfront costs. Investing in a high-quality mortise lock can significantly enhance the security profile of a facility.
What Advantages Do Electronic Locks Provide for Modern Businesses?
Electronic locks are characterized by their keyless entry systems, which can be programmed with unique codes and often include audit trails for tracking access. These locks are particularly beneficial for businesses in retail, warehouses, and offices, where managing access control is critical. The ability to grant or revoke access remotely adds a layer of convenience and security. However, potential buyers should be aware of the reliance on power sources and the possibility of technical failures, which may necessitate additional support or backup systems.
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Why Are Smart Locks Gaining Popularity in the B2B Sector?
Smart locks leverage technology to connect with smart devices, allowing for remote locking and unlocking via mobile applications. This feature is particularly appealing for hotels and rental properties, where ease of access can enhance customer experiences. While smart locks offer significant convenience and integration capabilities, buyers must consider the potential security risks associated with hacking and data breaches. A thorough assessment of the lock’s security features and vendor reputation is essential before making a purchase.
How Can Padlocks Serve as a Cost-Effective Security Solution?
Padlocks are portable locking mechanisms available in various sizes and strengths, making them versatile for use in securing gates, storage units, and lockers. Their affordability and ease of use make padlocks a popular choice for businesses looking for a quick and budget-friendly security solution. However, businesses should be cautious, as padlocks may provide limited security in high-risk areas. Selecting high-security padlocks can mitigate some risks, but they are best used in conjunction with other security measures for optimal protection.
Key Industrial Applications of mechanism lock
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mechanism lock | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Buildings | Access control for office spaces | Enhanced security and controlled access for employees | Durability, compliance with local regulations, and ease of installation |
| Manufacturing | Locking mechanisms for machinery | Protection against unauthorized access, reducing theft risk | Resistance to environmental factors and ease of maintenance |
| Transportation | Security for freight containers | Safeguarding valuable goods during transit | Weather resistance, compatibility with shipping standards |
| Healthcare | Cabinet locks for medical supplies | Ensuring safety and compliance with regulations | Compliance with health regulations and tamper-proof features |
| Education | Secure access to laboratories and storage | Protecting sensitive materials and equipment | Adaptability to various door types and ease of use for staff and students |
How Are Mechanism Locks Used in Commercial Buildings?
In commercial buildings, mechanism locks are integral for access control in office spaces. These locks help enhance security by allowing only authorized personnel to enter sensitive areas. Businesses benefit from reduced risk of theft and vandalism, which can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers should consider the durability of the locks, compliance with local regulations, and the ease of installation to ensure efficient operation and long-term reliability.
What Role Do Mechanism Locks Play in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, mechanism locks are crucial for securing machinery and production areas. They protect against unauthorized access, thus reducing the risk of theft and ensuring the safety of both equipment and personnel. Buyers should prioritize locks that are resistant to environmental factors, such as dust and moisture, and those that require minimal maintenance to ensure continuous operation in demanding settings.
How Are Mechanism Locks Essential for Transportation Security?
For the transportation industry, mechanism locks are vital for securing freight containers and vehicles. These locks safeguard valuable goods during transit, reducing the likelihood of theft or tampering. International buyers, especially those in regions like Africa and South America, should focus on the weather resistance of the locks and their compatibility with shipping standards to ensure reliable performance in diverse conditions.
Why Are Mechanism Locks Important in Healthcare Settings?
In healthcare facilities, mechanism locks are used to secure cabinets containing medical supplies and pharmaceuticals. This is essential for ensuring compliance with health regulations and protecting sensitive materials from theft or misuse. Buyers in this sector should look for locks that offer tamper-proof features and comply with safety standards to maintain a secure environment for both staff and patients.
How Do Mechanism Locks Enhance Security in Educational Institutions?
In educational settings, mechanism locks are essential for securing access to laboratories and storage areas. They protect sensitive materials and equipment, ensuring a safe learning environment. Buyers should consider the adaptability of locks to various door types and their ease of use, as the locks must be accessible for both staff and students while maintaining security.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mechanism lock’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Locking Mechanisms Leading to Security Vulnerabilities
The Problem: Many businesses face the challenge of outdated locking mechanisms that compromise security. For instance, a manufacturing facility may still be using traditional keyed locks that are easily picked or bumped. This not only puts valuable assets at risk but also affects employee confidence in the safety of their workplace. In regions with high theft rates, such vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses and increased insurance premiums, which can be especially detrimental for small to medium-sized enterprises.
The Solution: To address these security vulnerabilities, businesses should consider upgrading to high-security locking mechanisms. B2B buyers should look for locks that incorporate advanced features such as hardened steel construction, anti-drill pins, and electronic access control options. When sourcing these locks, it’s essential to engage with reputable manufacturers who offer detailed specifications and certifications, ensuring the locks meet industry standards. Additionally, conducting a thorough security assessment of the premises can help identify weak points in the current locking system, allowing for a tailored approach to upgrading locks that best fit the specific needs of the business.
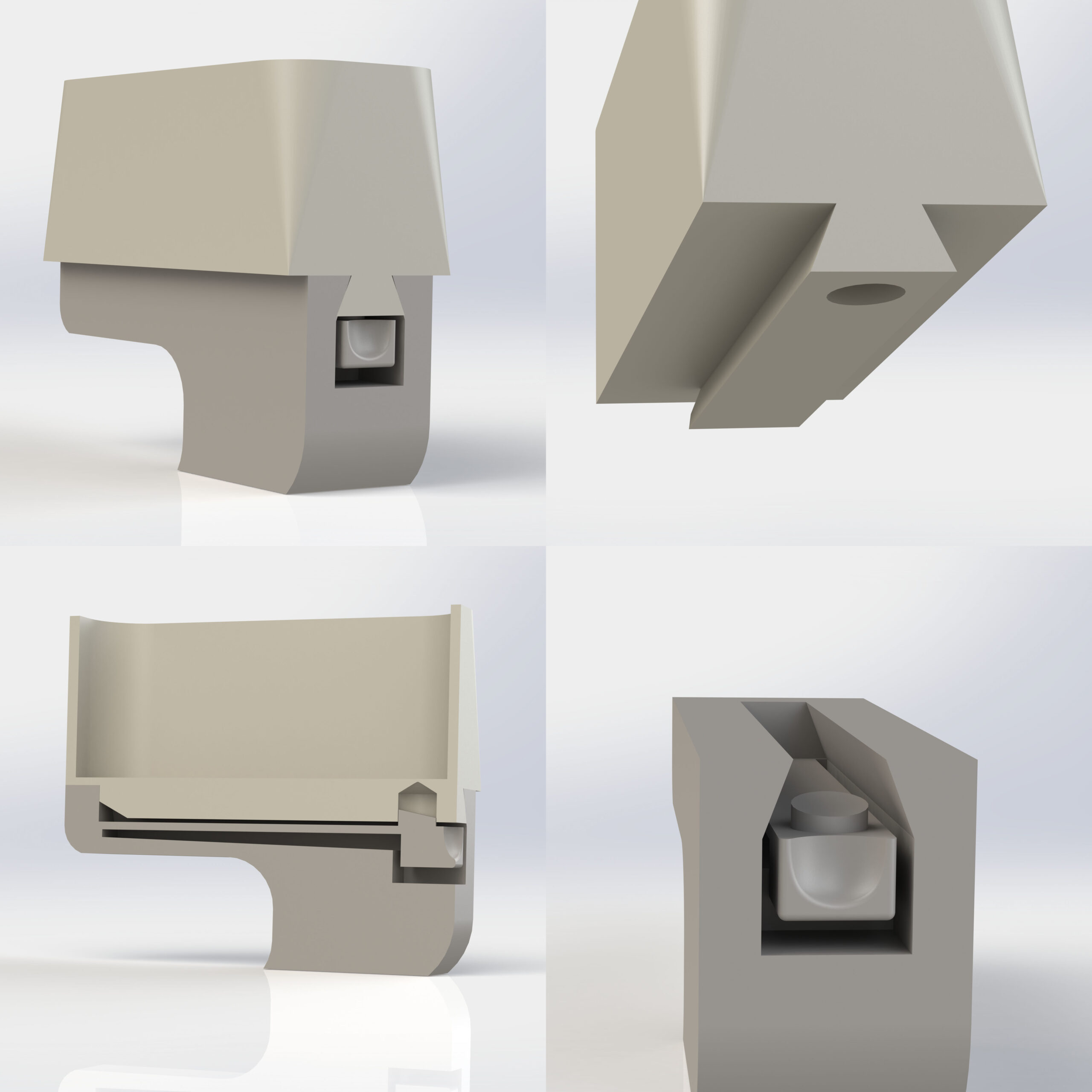

Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Existing Infrastructure
The Problem: As companies expand or relocate, they often encounter compatibility issues between new locking mechanisms and existing door hardware. A corporate office moving into a building with outdated lock systems may find that their chosen modern locking solution does not fit the existing door frames or latching systems. This can lead to costly renovations, delays in securing the premises, and operational disruptions that affect productivity.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive inventory of existing door hardware before making purchasing decisions. This includes measuring door sizes, checking frame conditions, and identifying current locking mechanisms in use. When selecting new locks, opt for those that offer adjustable backsets or are designed to fit multiple configurations. Engaging a locksmith or a door hardware consultant during the planning phase can provide invaluable insights into suitable locking solutions that will integrate seamlessly with the existing infrastructure, thus minimizing the need for extensive modifications.
Scenario 3: Lack of Key Control and Management
The Problem: Businesses often struggle with managing physical keys, especially in environments with high employee turnover or multiple access points. A hotel, for example, may find it challenging to keep track of room keys, leading to unauthorized access and potential security breaches. The lack of a streamlined key management system can create operational inefficiencies and increase the risk of theft or vandalism.
The Solution: Implementing a key control system can effectively address these challenges. B2B buyers should explore electronic locking solutions that utilize key cards or mobile access instead of traditional keys. These systems not only provide better tracking of who accesses which areas but also allow for the immediate deactivation of lost or stolen access credentials. When sourcing these solutions, buyers should inquire about additional features such as audit trails, which provide logs of access events, and remote management capabilities, enabling facility managers to oversee security from any location. Investing in a robust electronic lock system can enhance security while streamlining access management processes, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mechanism lock
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Mechanism Locks?
When selecting materials for mechanism locks, it is crucial to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: steel, brass, aluminum, and plastic.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Mechanism Locks?
Steel is a widely used material in the manufacturing of mechanism locks due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high tensile strength, making it resistant to physical attacks. Steel locks can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, which is essential for applications in harsh environments. However, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can limit its lifespan in humid or saline conditions.
Pros: High durability, excellent resistance to physical attacks, suitable for high-security applications.
Cons: Can rust if not coated, heavier than other materials, potentially higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Steel locks are ideal for industrial settings and high-security applications but may require additional coatings for corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is essential. Buyers in regions like Germany may prefer locks that meet DIN standards for quality assurance.
What Benefits Does Brass Offer for Mechanism Locks?
Brass is another popular choice for mechanism locks, known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It has good mechanical properties, including moderate strength and ductility, making it easy to machine and form into intricate designs. Brass locks are often used in residential applications due to their attractive finish and resistance to tarnishing.
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Pros: Corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing, easy to manufacture.
Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, can be more expensive than other metals.
Impact on Application: Suitable for residential and decorative applications, but may not be ideal for high-security environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B453 for brass alloys is important. Buyers from Brazil may prefer brass locks for their aesthetic value in residential settings.
Why Choose Aluminum for Mechanism Locks?
Aluminum is a lightweight material that is increasingly being used in mechanism locks. It offers good corrosion resistance and is less prone to rust compared to steel. Aluminum locks are often used in environments where weight is a concern, such as in portable security applications. However, aluminum may not provide the same level of security as steel or brass.
Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, cost-effective.
Cons: Lower strength and durability compared to steel, may not be suitable for high-security applications.
Impact on Application: Ideal for portable and low-security applications, but may not be suitable for high-risk environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards for aluminum products may be relevant, especially for buyers in the Middle East.
When Is Plastic a Suitable Material for Mechanism Locks?
Plastic is often used in low-security applications and for specialized locks, such as those found in electronic devices. It is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for environments where moisture is present. However, plastic locks generally offer lower security and durability compared to metal options.
Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, low cost.
Cons: Limited strength, not suitable for high-security applications.
Impact on Application: Best suited for low-security applications or as part of electronic locking systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant safety and quality standards, which may vary by region.
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mechanism Locks
| Material | Typical Use Case for mechanism lock | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-security industrial locks | High durability and strength | Prone to corrosion without treatment | High |
| Brass | Residential and decorative locks | Corrosion-resistant and attractive | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Aluminum | Portable security applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Plastic | Low-security electronic locks | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited strength and security | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for mechanism locks, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mechanism lock
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mechanism Locks?
The manufacturing process of mechanism locks involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required performance and safety standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting high-quality raw materials, which often include steel, brass, or zinc alloys. These materials are chosen for their durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand wear and tear. Once selected, the materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet international standards for strength and quality. This may involve chemical analysis and mechanical testing to verify their properties.
The raw materials are then cut to specific dimensions using precision machinery. Techniques such as laser cutting and water jet cutting are common, as they allow for high accuracy and minimal waste. After cutting, the materials are treated to enhance their mechanical properties, such as through heat treatment or surface hardening.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Mechanism Locks?
Forming is the next stage where the prepared materials are shaped into the components of the mechanism lock. Common techniques include stamping, forging, and machining. Stamping involves pressing flat sheets of metal into desired shapes, while forging uses compressive forces to shape the material into specific forms. Machining is employed for precision parts, where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines create intricate designs that meet tight tolerances.

Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
During this stage, the individual parts of the lock, such as the cylinder, bolt, and housing, are formed. This is a critical phase that influences the lock’s durability and functionality. Advanced technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD), are often used to optimize the design and ensure that each component fits perfectly.
How Is the Assembly of Mechanism Locks Conducted?
Once the components are formed, they are moved to the assembly line. Here, skilled workers or automated systems assemble the various parts of the lock. This process includes inserting the cylinder into the housing, fitting the bolt mechanism, and ensuring that all components operate smoothly together.
Quality control is essential during assembly. Each lock is typically tested for functionality at various stages of assembly to detect any defects early on. This can include checking the smoothness of the locking mechanism and ensuring that the key turns without resistance.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Mechanism Locks?
After assembly, locks undergo finishing processes that enhance their appearance and protect them from environmental factors. Common finishing techniques include electroplating, powder coating, and anodizing. Electroplating, for instance, applies a thin layer of metal to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
The finishing process not only affects the lock’s look but also its functionality and longevity. High-quality finishes can significantly extend the lifespan of the lock, making them more appealing to international buyers who prioritize durability.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Mechanism Lock Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of mechanism locks, ensuring that each product meets both customer expectations and regulatory standards. The QA process involves multiple international and industry-specific standards, including ISO 9001, CE marking, and API standards.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Lock Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers of mechanism locks must implement this standard to demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO 9001 involves documenting processes, conducting regular audits, and continually improving operations.
In addition to ISO standards, CE marking is crucial for companies looking to sell their products in Europe. This marking indicates that the locks comply with EU safety and health requirements. For certain applications, such as in oil and gas, manufacturers may also need to adhere to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards, particularly for locks used in hazardous environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Lock Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in mechanism lock manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
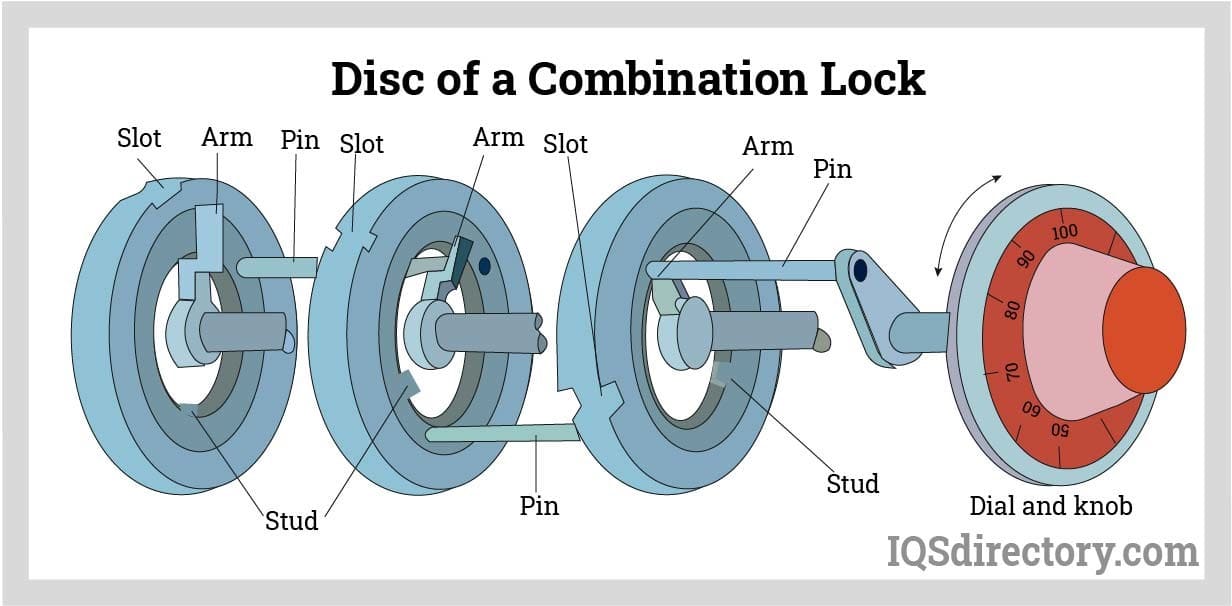
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
-
IQC: At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. Any materials that do not meet these standards are rejected.
-
IPQC: During the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor the quality of components as they are formed and assembled. This can involve visual inspections, measurement checks, and functional tests to catch defects early.
-
FQC: Finally, once the locks are fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes testing the lock’s functionality, durability, and resistance to tampering. Random sampling may be performed to ensure a statistically significant representation of the production batch.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Buyers can take several steps to ensure that suppliers maintain high QC standards.
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and interviewing staff.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality reports from suppliers provides insight into their QC practices. These reports should detail inspection results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to defects.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an impartial evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can conduct inspections at various stages of production, providing additional assurance to buyers.
-
Certifications and Compliance: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. This not only demonstrates compliance with international standards but also reflects the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control when sourcing mechanism locks. Differences in regulations, market expectations, and manufacturing practices can impact the procurement process.
For instance, while ISO 9001 is a global standard, some regions may have specific requirements that must be adhered to. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscape in their target markets to ensure compliance.
Additionally, cultural factors can influence quality perceptions. In some regions, emphasis may be placed on aesthetic qualities, while in others, functionality and durability may be prioritized. Understanding these differences can help buyers select suppliers that align with their specific needs and preferences.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of mechanism locks, B2B buyers can make educated decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers.
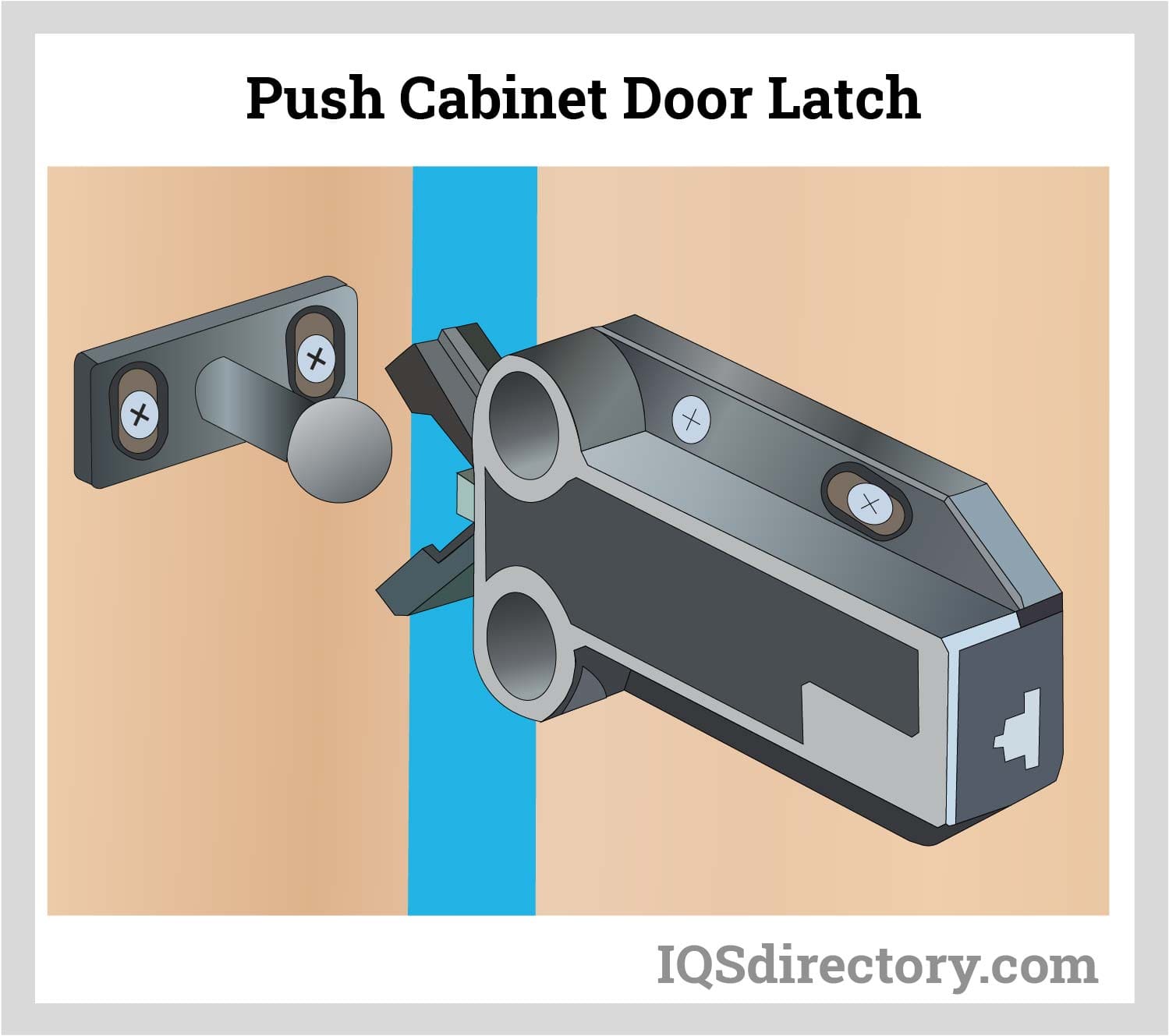
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mechanism lock’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing the right mechanism lock is essential for ensuring security and operational efficiency. This checklist serves as a practical guide for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to navigate the complexities of selecting and acquiring the appropriate locking mechanisms.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is the first step in sourcing mechanism locks. Consider factors such as the type of lock needed (e.g., deadbolt, mortise, electronic), the material (steel, brass, etc.), and the security level. Be clear about the installation environment, whether it’s for commercial buildings, residential properties, or specialized applications like gates or cabinets.
- Key Considerations:
- Door type and dimensions
- Environmental conditions (e.g., exposure to weather)
- Required security features (e.g., keyless entry, smart technology)
Step 2: Research Lock Types and Mechanisms
Familiarize yourself with the various types of locking mechanisms available. This knowledge allows you to make informed decisions and ensures compatibility with your existing systems. For example, understand the differences between mechanical and electronic locks, and the advantages of each for your specific use case.
- Types to Explore:
- Cylindrical locks
- Mortise locks
- Electronic locks with smart capabilities
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is crucial. Assess their experience, reputation, and customer service capabilities. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies from similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and product quality.
- Important Actions:
- Look for suppliers with established certifications (e.g., ISO).
- Check reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
- Inquire about after-sales support and warranty policies.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request samples of the mechanism locks you are considering. This step allows you to evaluate the quality, functionality, and ease of installation firsthand. Additionally, ask for detailed specifications and installation guides to ensure they meet your requirements.
- Sample Evaluation Criteria:
- Durability and material quality
- Ease of use and installation
- Compliance with local security standards
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare not just the prices but also the payment terms and conditions. Ensure that you factor in shipping costs, taxes, and potential customs duties, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
- Considerations:
- Bulk order discounts
- Payment flexibility (e.g., upfront payment vs. credit)
- Total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement parts
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Before finalizing any purchase, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a contract. This should include delivery timelines, warranty details, and any penalties for non-compliance. Clear agreements help mitigate risks and ensure accountability from the supplier.
- Contract Essentials:
- Delivery schedules and logistics
- Warranty coverage and service agreements
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
After procurement, consider how the installation will be handled. Depending on the complexity of the locking mechanisms, you may need professional installation services. Additionally, training for your team on the use and maintenance of the locks can enhance security and operational efficiency.
- Implementation Steps:
- Schedule installation with a qualified technician.
- Provide training sessions for staff on lock operation and security protocols.
- Establish a maintenance schedule to ensure long-term functionality.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for mechanism locks, ensuring they select the right products to meet their security needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mechanism lock Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Mechanism Lock Sourcing?
When sourcing mechanism locks, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts cost. For instance, high-grade steel or brass locks will be more expensive than those made from plastic or lower-grade metals. Buyers should consider the durability and security level when selecting materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the manufacturing location. Regions with higher labor costs may result in higher-priced locks. However, lower labor costs can sometimes mean lower quality, so it’s essential to balance cost with the desired quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These costs are typically distributed across the total production volume, influencing the unit cost of each lock.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for custom locks. Buyers should consider whether they need unique designs or features that require specialized tooling, as this will affect the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that each lock meets safety and performance standards. However, these processes add to the overall cost. Buyers should inquire about the QC measures in place and how they might impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, weight, and the chosen shipping method. Buyers should factor in logistics when calculating the total cost, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy is key to negotiating effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Mechanism Lock Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of mechanism locks, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQ) that can affect pricing. Larger orders can lead to discounts due to economies of scale, making it beneficial for businesses to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized locks that meet specific security needs or design preferences typically cost more than standard models. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary and how it aligns with their budget.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The presence of certifications (e.g., ISO, ANSI) can impact pricing. Locks with higher security ratings or certifications may command premium prices, reflecting their quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market entry.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect overall costs. For example, “FOB” (Free on Board) means the buyer assumes responsibility for shipping costs once the goods are on board, while “CIF” (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) includes shipping costs in the price. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate cost estimation.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Mechanism Lock Sourcing?
Navigating the purchasing landscape for mechanism locks requires strategic thinking. Here are some tips for B2B buyers:
-
Negotiate: Always be prepared to negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Seek Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. Sometimes, a higher upfront investment in quality locks can lead to long-term savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, currency fluctuations and tariffs can affect pricing. Additionally, logistical challenges may arise, particularly when importing to regions like Africa or South America. It’s vital to consider these factors in your budget.
-
Request Samples: Before placing a large order, request samples to assess quality and suitability. This step can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better service and pricing. Regular communication and feedback can foster a partnership that benefits both parties.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for mechanism locks can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It’s essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they secure the best deal.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mechanism lock With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Locking Solutions
In the ever-evolving landscape of security solutions, businesses must navigate various locking mechanisms to ensure safety and operational efficiency. While mechanism locks have long been a staple in securing doors and gates, several alternatives offer different features and benefits that may better suit specific needs. This section will compare mechanism locks with two viable alternatives: electronic locks and smart locks, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Mechanism Lock | Electronic Lock | Smart Lock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for physical security; good for low-traffic areas | High security with programmable options; suitable for medium to high traffic | Enhanced security with remote access and monitoring; best for high-tech environments |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Moderate cost; requires electrical installation | Higher upfront investment but offers long-term savings on key management |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; no need for power sources | Requires electrical wiring; may need professional installation | Requires Wi-Fi or Bluetooth setup; installation can be complex |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; mechanical failures are rare | Moderate maintenance; battery changes needed periodically | Higher maintenance; software updates and battery replacements are required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for traditional applications like warehouses and garages | Best for offices and commercial spaces needing controlled access | Excellent for modern homes or businesses wanting advanced features like remote access and integration with smart home systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electronic Locks
Electronic locks provide a level of security that surpasses traditional mechanism locks by allowing for programmable access codes and audit trails. They are particularly beneficial in environments where access control is crucial, such as commercial offices. However, they do come with a moderate cost and require electrical installation, which can deter some buyers. Additionally, periodic maintenance is necessary to ensure functionality, particularly with battery-operated models.
Smart Locks
Smart locks represent the cutting edge of locking technology, offering features such as remote access via smartphone apps, integration with smart home systems, and real-time monitoring. They are ideal for businesses looking to embrace digital solutions and enhance security protocols. While they provide significant advantages, such as ease of access and comprehensive security features, the initial investment is higher than both mechanism and electronic locks. Furthermore, smart locks require a stable internet connection and may involve more complicated installation and maintenance processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Locking Solution for Your Business
When selecting a locking solution, B2B buyers must assess their specific needs, operational environment, and budget constraints. Mechanism locks offer a reliable, cost-effective solution for traditional applications with low maintenance needs. Conversely, electronic and smart locks present advanced security features that can enhance access control but come with higher costs and maintenance requirements. Evaluating the trade-offs between these options will enable businesses to choose a locking mechanism that aligns with their security goals and operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mechanism lock
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Mechanism Locks?
Understanding the technical properties of mechanism locks is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
The grade of material used in mechanism locks significantly affects durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and zinc alloys. High-grade materials ensure longevity and reliability, which is essential for businesses that require high-security solutions.
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In locking mechanisms, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring that components fit together correctly, minimizing the risk of malfunction. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels helps in assessing the quality and precision of the locks being sourced.
3. Security Rating
Many countries have established standards for security ratings, such as the European standard EN 1627 or the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) grades. These ratings indicate the level of resistance against forced entry, picking, and other unauthorized access methods. Buyers must consider these ratings to ensure that the locks meet the security requirements of their applications.
4. Functionality
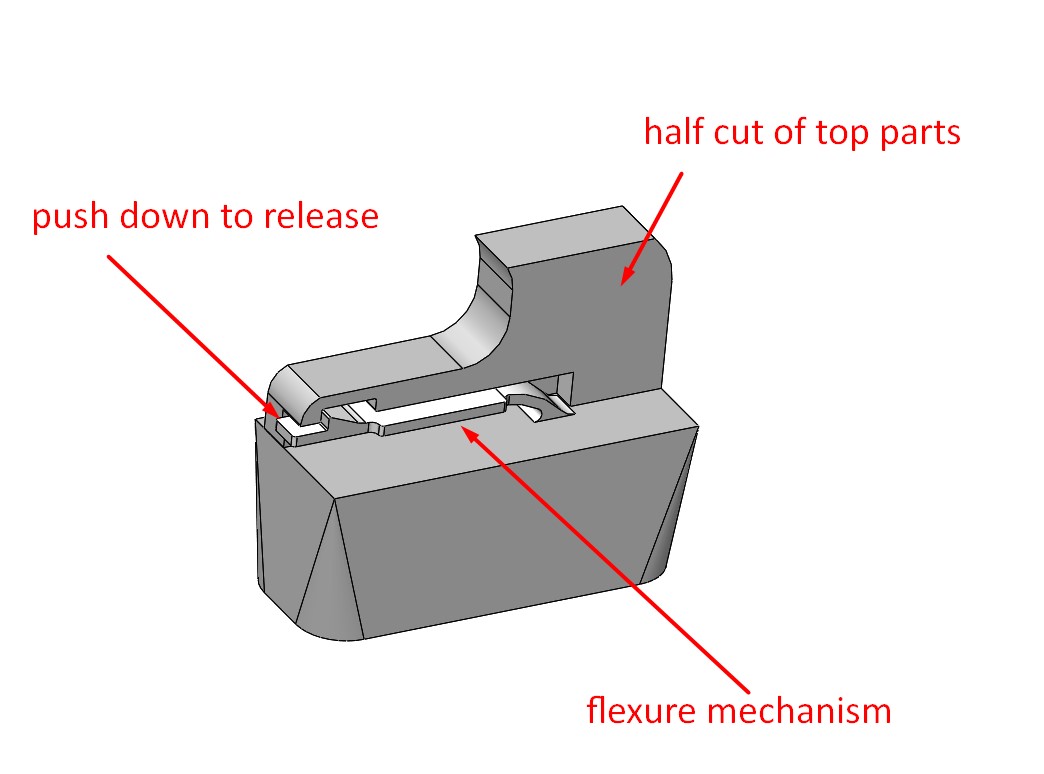
Different locking mechanisms offer varying functionalities, such as deadbolts, electronic locks, or smart locks with remote access. Understanding the specific functionality required for a given application helps buyers select locks that align with their operational needs, whether for commercial, industrial, or residential use.
5. Cycle Test Durability
This property measures how many cycles a lock can withstand before failure. A higher cycle test rating indicates that the lock can endure repeated use without compromising performance. For businesses, investing in locks with high cycle test durability reduces maintenance costs and improves overall security.
6. Finish and Aesthetics
The finish of a lock, whether it’s polished, brushed, or matte, can affect both its appearance and resistance to environmental factors. Aesthetically pleasing finishes can be essential in commercial settings where image matters. Buyers should consider the finish in conjunction with the functional requirements of the lock.

Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Mechanism Lock Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of mechanism locks, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality products that meet their specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is critical for buyers, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capabilities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the mechanism lock industry, issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping and logistics. For international B2B transactions, understanding Incoterms is crucial for clarifying shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities between parties.
5. SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
SKU is a unique identifier for each distinct product and service that can be purchased. In the context of mechanism locks, understanding SKUs helps buyers track inventory and manage stock levels efficiently.
6. Certification
Certification refers to the process of verifying that a product meets specific standards or regulations. For locks, certifications can include safety and security standards, which are critical for ensuring that products comply with legal requirements and industry best practices.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes and make more informed decisions regarding mechanism locks.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mechanism lock Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Mechanism Lock Market?
The global mechanism lock market is experiencing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. One of the primary drivers is the increasing focus on security and safety across various sectors, including commercial, residential, and industrial applications. The rise in urbanization and the need for enhanced security in both private and public spaces are propelling demand for innovative locking solutions.
Emerging technologies such as smart locks and electronic access control systems are reshaping traditional locking mechanisms. These solutions not only offer enhanced security features, such as remote access and real-time monitoring, but also cater to the growing trend of smart homes and IoT (Internet of Things) integration. B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer advanced locking solutions that align with these technological trends.
Additionally, the market is witnessing a shift toward modular and customizable locking systems that allow for tailored security solutions. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who require locks that can adapt to diverse architectural styles and security needs. Suppliers that can provide flexible options and robust customer support are likely to gain a competitive edge in these markets.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Mechanism Lock Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become pivotal in the mechanism lock sector, as businesses increasingly recognize their environmental responsibilities. The production of locks often involves materials such as metals and plastics, which can have a significant environmental impact if not sourced responsibly. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable practices, such as recycling materials and minimizing waste during production.
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Buyers are looking for locks made from sustainable materials, such as recycled metals or environmentally friendly coatings, which not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance the brand image of their organizations.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining importance, especially in regions where labor practices may vary. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing suppliers to ensure they adhere to fair labor practices and that their products are manufactured in facilities that meet ethical standards. This focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing not only aligns with global trends but also meets the growing expectations of consumers who prioritize corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of Mechanism Locks and Their Evolution?
The history of mechanism locks dates back to ancient civilizations, with the earliest known examples originating in the Near East around 4,000 years ago. These early locks used a simple pin tumbler mechanism, which secured doors by using a wooden bolt and pins that would drop into holes in the bolt. Over the centuries, locking mechanisms have evolved significantly, adapting to technological advancements and changing security needs.
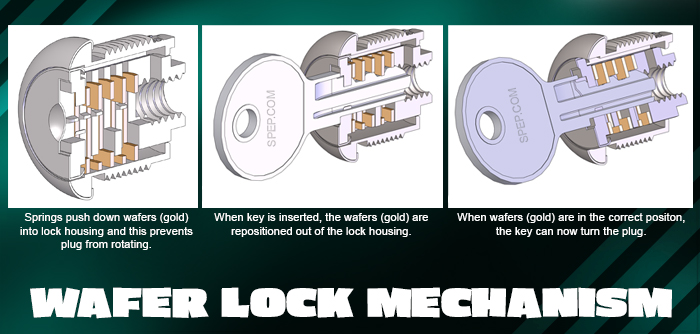
Illustrative image related to mechanism lock
During the Industrial Revolution, mass production techniques enabled the creation of more sophisticated locking systems. Innovations such as the combination lock and the modern deadbolt emerged, providing enhanced security features. The 20th century saw the introduction of electronic locks, which paved the way for the smart locking solutions we see today.
This evolution reflects not only advancements in technology but also a growing understanding of security needs across different sectors. As B2B buyers navigate this historical context, they can appreciate the trajectory of locking mechanisms and make informed decisions about sourcing modern solutions that address contemporary security challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mechanism lock
-
How do I solve security concerns for my business premises using mechanism locks?
To address security concerns effectively, evaluate your specific needs based on the type of business and the level of access control required. Consider installing high-security mechanism locks such as electronic locks or smart locks that offer advanced features like remote access and monitoring. Additionally, ensure that the locks are compatible with your existing security systems. Regular maintenance and upgrades are essential to keep your locking mechanisms functioning optimally and to deter unauthorized access. -
What is the best locking mechanism for commercial properties?
For commercial properties, the best locking mechanisms typically include electronic locks, keyless entry systems, and high-security deadbolts. These options provide enhanced security features such as programmable access codes, audit trails, and integration with access control systems. The choice largely depends on the size of your facility, the number of access points, and your budget. Consulting with a security expert can help tailor the selection to meet your specific operational needs. -
How can I vet suppliers for mechanism locks in international markets?
When vetting suppliers for mechanism locks, prioritize manufacturers with a proven track record and positive customer reviews. Request samples and certifications to assess product quality and compliance with international standards. Consider engaging in direct communication to understand their production processes, lead times, and after-sales support. Additionally, utilizing third-party verification services can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and financial stability. -
What customization options are available for mechanism locks?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for mechanism locks, including size, finish, and functionality. You may also request specific features such as key control systems, access codes, or integration with existing security systems. Communicating your requirements clearly during the initial discussions can help ensure that the final product meets your operational needs. Be sure to inquire about any additional costs or lead times associated with custom orders. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mechanism locks?
Minimum order quantities for mechanism locks can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units, particularly for customized options. It is advisable to discuss your requirements with the supplier to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a smaller business or starting a new project. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time buyers or bulk orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing mechanism locks internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your relationship and order volume. Ensure you clarify all payment terms, including currency, payment methods (like wire transfer or credit card), and any potential taxes or duties that may apply to your order. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for mechanism locks?
To ensure quality assurance for mechanism locks, request detailed specifications and certifications from your supplier, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Conducting factory audits or third-party inspections can further guarantee product quality before shipment. Additionally, consider implementing a sample testing phase where you evaluate the locks for functionality, durability, and security features before committing to larger orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mechanism locks?
When importing mechanism locks, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs specific to your country. Work with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial goods to navigate these complexities. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, are accurately prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, account for lead times and potential delays in your supply chain planning.
Top 8 Mechanism Lock Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. All From 1 Supply – Roll Up Door Locks
Domain: allfrom1supply.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, All From 1 Supply – Roll Up Door Locks, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Andersen – 3-Point Lock for Patio Doors
Domain: parts.andersenwindows.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”:”3-Point Lock for Andersen Patio Door Handles”,”Product Series”:”400 Series”,”Product Line”:”400 Series Frenchwood Hinged Patio Door, 400 Series Frenchwood Outswing Patio Door”,”Part Number”:”2579771″,”Material”:”Stainless Steel”,”Height”:”68 inches”,”Price”:”$304.13″,”Compatibility”:”Works with 400 Series Frenchwood Hinged Patio Door and 400 Series Frenchwood Outswing Patio Door”,…
3. Britannica – Lock Mechanism
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Lock is a mechanical device for securing a door or receptacle, preventing it from being opened except by a key or specific manipulations. The oldest known lock, a pin tumbler type, dates back approximately 4,000 years and was found in the Near East. Early locks used wooden bolts and pins, with keys shaped like large wooden bars. The Romans introduced metal locks and wards, enhancing security. The …
4. Pinterest – Customizable Door Locks
Domain: in.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Unique door lock that can be designed by the user. Related interests include various gate designs (modern steel gates, sliding gates), locking mechanisms (keyed security locks, adjustable door latches, anti-pry latch locking mechanisms), and metal fabrication tools. Additional related topics include DIY projects, urban furniture design, and metal art techniques.
5. CompX – C8797 Garage Door Locking Mechanism
Domain: compx.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Garage door locking mechanism – C8797 – CompX National sectional overhead garage door mechanism.
6. Instructables – Circular Vault Lock Mechanism
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Simple Vault Mechanism designed for a circular lid that locks from the inside. Key materials include 1/4″ Birch Plywood, 4 small screws, 1/4″ dowel, wood glue, and a preferred wood finish (e.g., wipe-on polyurethane). The mechanism is easy to build with access to a laser cutter and drill. The design allows for a customizable lid diameter and includes a rotating center to operate the locking arms. …
7. Talon Lock – Innovative Folding Knife Mechanism
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The product is a new locking mechanism called “talon lock” designed for folding knives. The creator has experience making fixed blades and has transitioned to designing folders due to a lack of a workshop. The design process was a personal project done for fun, with no current plans for development, production, or sale. The creator has also modeled different versions of the lock with variations in…
8. IQS Directory – Lock Mechanisms
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Locks are mechanisms designed to secure entry points using latches, solid cylinders, bolts, or similar metal plungers. Types of locks include padlocks, combination locks, door locks, deadbolts, restraining bolts, electric locks, and key-operated locks. Lock mechanisms can be warded, pin tumbler, spindle, or disk tumbler configurations. Locking systems are categorized into key-operated, combination…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mechanism lock
In navigating the complexities of strategic sourcing for mechanism locks, international B2B buyers must prioritize understanding the various types of locking mechanisms available. From mechanical to electronic solutions, the right choice hinges on specific security needs, application environments, and technological advancements. Emphasizing the importance of quality and reliability, buyers should seek partnerships with reputable suppliers who can provide comprehensive support and customization options tailored to their operational requirements.
Furthermore, as the global market evolves, the demand for innovative locking solutions is on the rise. This trend presents an opportunity for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to leverage strategic sourcing as a competitive advantage. By investing in advanced locking technologies, businesses can enhance security measures while improving operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the future of mechanism locks is promising, characterized by the integration of smart technology and enhanced security features. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements in locking mechanisms. By doing so, they can make informed decisions that not only secure their assets but also drive business growth in an increasingly interconnected world. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore the best locking solutions for your needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.