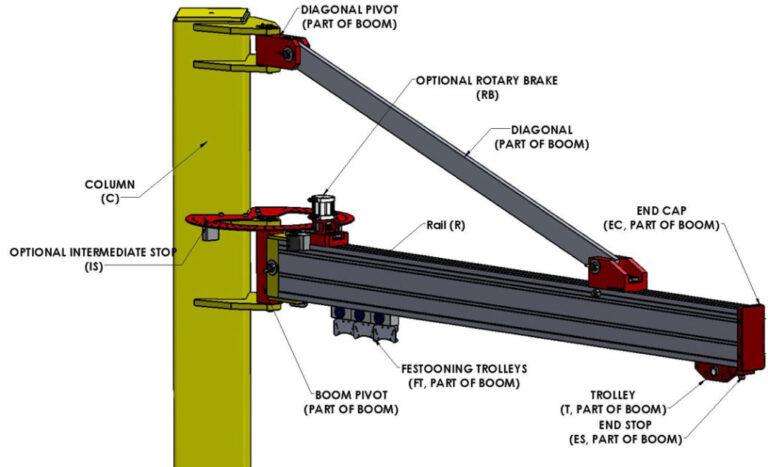
Machinery Guards: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machinery guards
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing effective machinery guards has become a critical challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. As companies strive to enhance workplace safety while optimizing productivity, understanding the diverse types and applications of machinery guards is essential. From fixed and interlocked guards to presence-sensing devices, each type serves a unique purpose in mitigating risks associated with machinery operation. This guide delves into the comprehensive spectrum of machinery guarding solutions, offering insights into selecting the right type based on specific operational needs, regulatory compliance, and risk assessment.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Germany, will find invaluable information on vetting suppliers, evaluating costs, and navigating compliance standards. By equipping themselves with this knowledge, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that not only protect their workforce but also enhance operational efficiency.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a strategic resource, empowering B2B buyers to navigate the global market for machinery guards with confidence, ensuring that safety and productivity go hand in hand in their operations. With the right machinery guards in place, companies can foster a safer working environment, reduce downtime, and drive profitability.
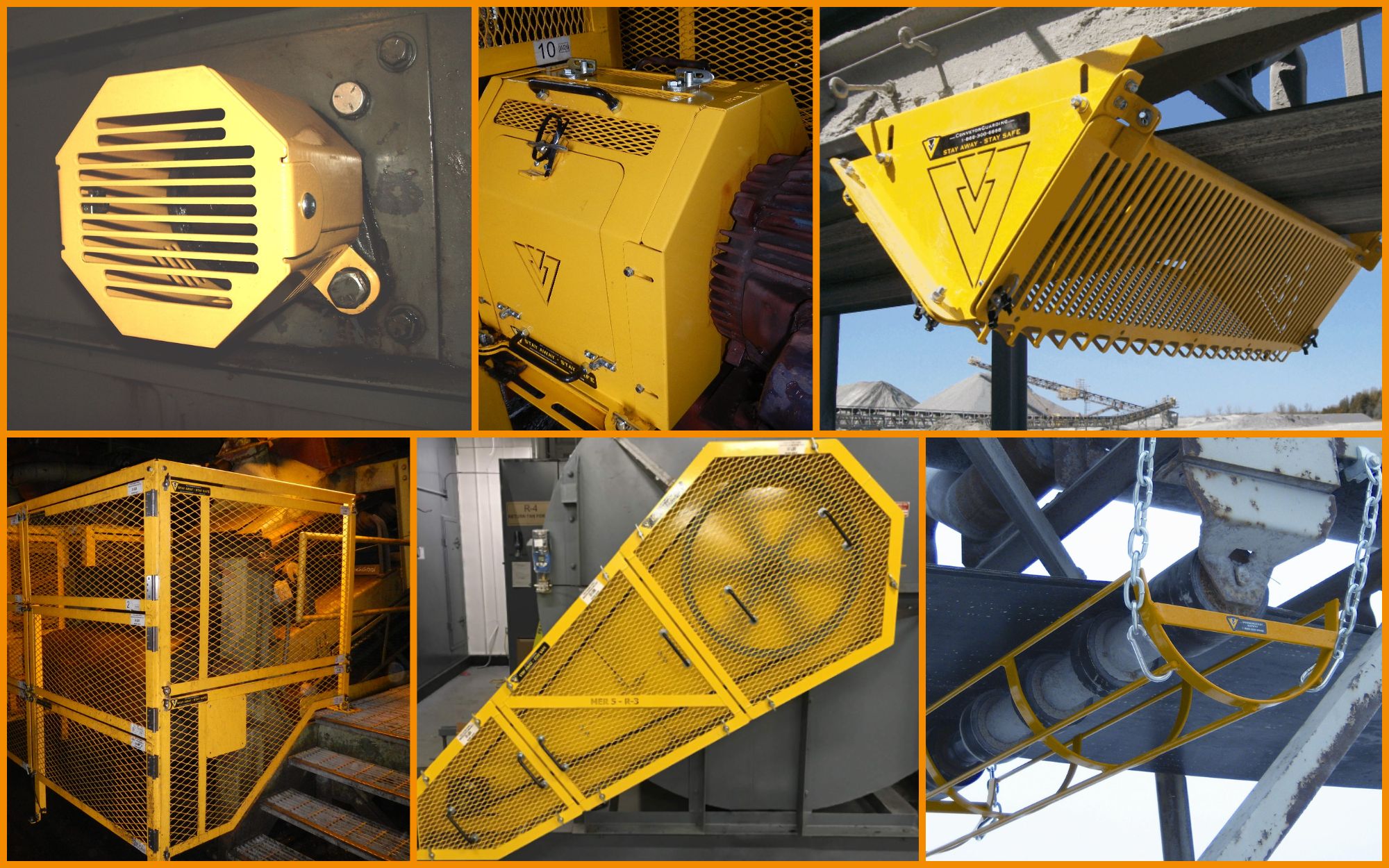
Understanding machinery guards Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Machine Guards | Permanently attached; provides constant protection | Manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: Reliable, low maintenance. Cons: Limited access for adjustments. |
| Interlocked Machine Guards | Shuts down machinery when opened; ensures safe maintenance access | Maintenance-heavy industries, robotics | Pros: Enhanced safety, prevents accidental starts. Cons: Potential delays in operation. |
| Perimeter Machine Guards | Surrounds entire machine; restricts access to hazard zones | Warehouses, robotic cells | Pros: Comprehensive protection. Cons: May require more space. |
| Presence-Sensing Guards | Uses sensors to detect presence; stops machinery automatically | Automotive assembly, packaging | Pros: Reduces human error, adaptable. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Power Transmission Guards | Encloses moving parts; prevents entanglement | Heavy machinery, mining, automotive | Pros: Critical for operator safety. Cons: Can be cumbersome for maintenance. |
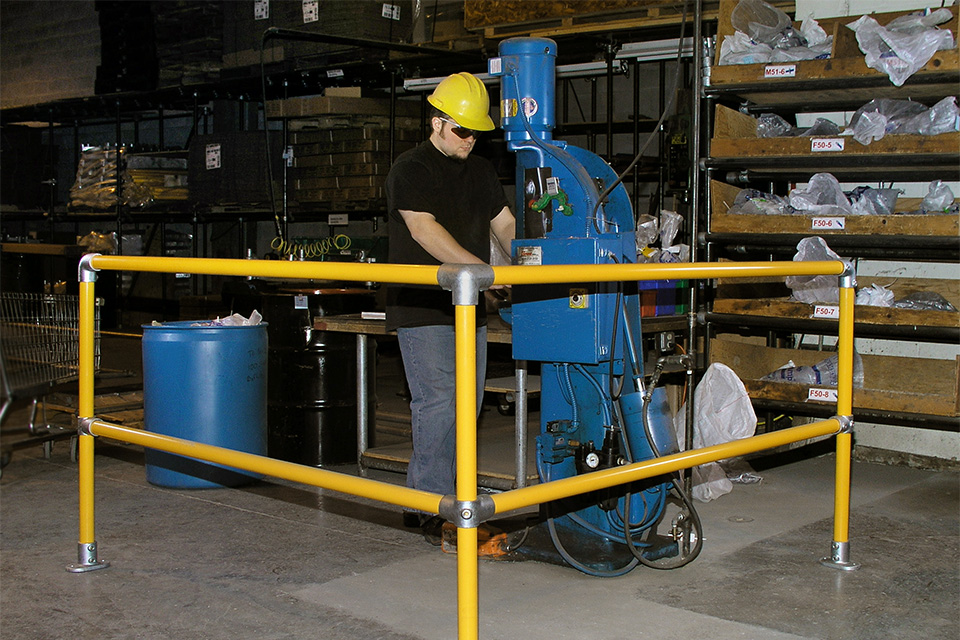
What Are Fixed Machine Guards and Their B2B Relevance?
Fixed machine guards are permanently affixed to machinery, providing continuous protection against moving parts. They are particularly suitable for machines that do not require frequent adjustments, making them ideal for manufacturing and assembly lines. When considering fixed guards, B2B buyers should evaluate the materials used for durability and the design to ensure they meet specific safety standards, as these factors directly affect the guard’s effectiveness and longevity.
How Do Interlocked Machine Guards Enhance Workplace Safety?
Interlocked machine guards are designed to automatically shut down the machinery when the guard is removed or opened, making them essential for maintenance-heavy environments like robotics and manufacturing. These guards offer significant safety benefits by preventing accidental machine startups. Buyers should consider the operational frequency and maintenance needs of their machinery when selecting interlocked guards, as they can introduce delays during routine operations if not correctly integrated.
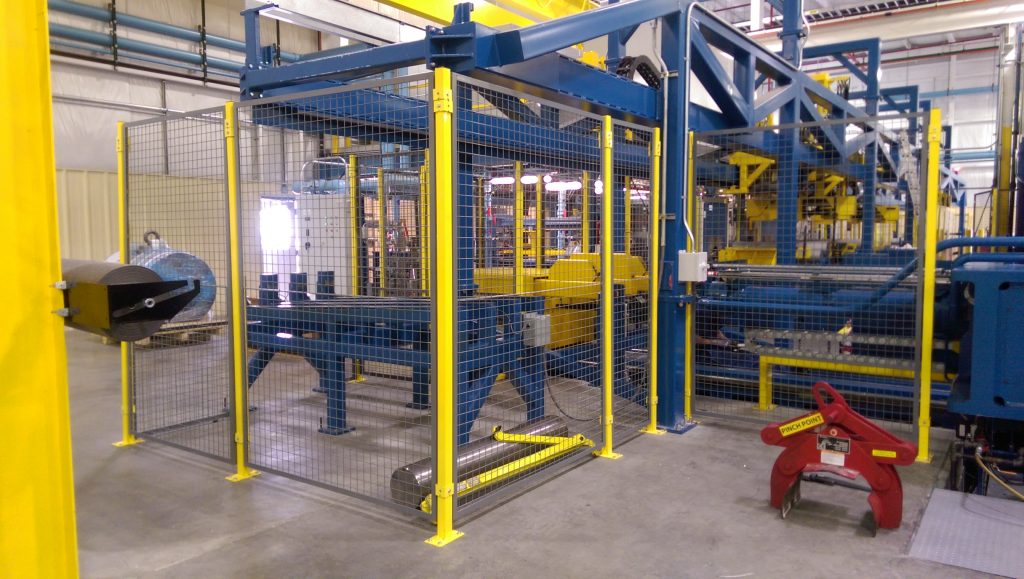
Why Choose Perimeter Machine Guards for Hazardous Areas?
Perimeter machine guards create a physical barrier around the entire machine or work area, effectively restricting access to hazardous zones. They are commonly used in warehouses and robotic work cells. When purchasing perimeter guards, B2B buyers should assess the layout of their workspace, as these guards may require more space compared to other types. Ensuring compliance with safety regulations is also crucial to mitigate liability risks.
What Are the Advantages of Presence-Sensing Machine Guards?
Presence-sensing machine guards utilize advanced sensor technology to detect the presence of individuals near hazardous areas, automatically stopping machinery to prevent accidents. These guards are particularly beneficial in high-risk environments like automotive assembly and packaging. Buyers should consider the initial investment costs and the specific technologies employed, as some sensors may offer better reliability and response times than others, impacting overall safety.
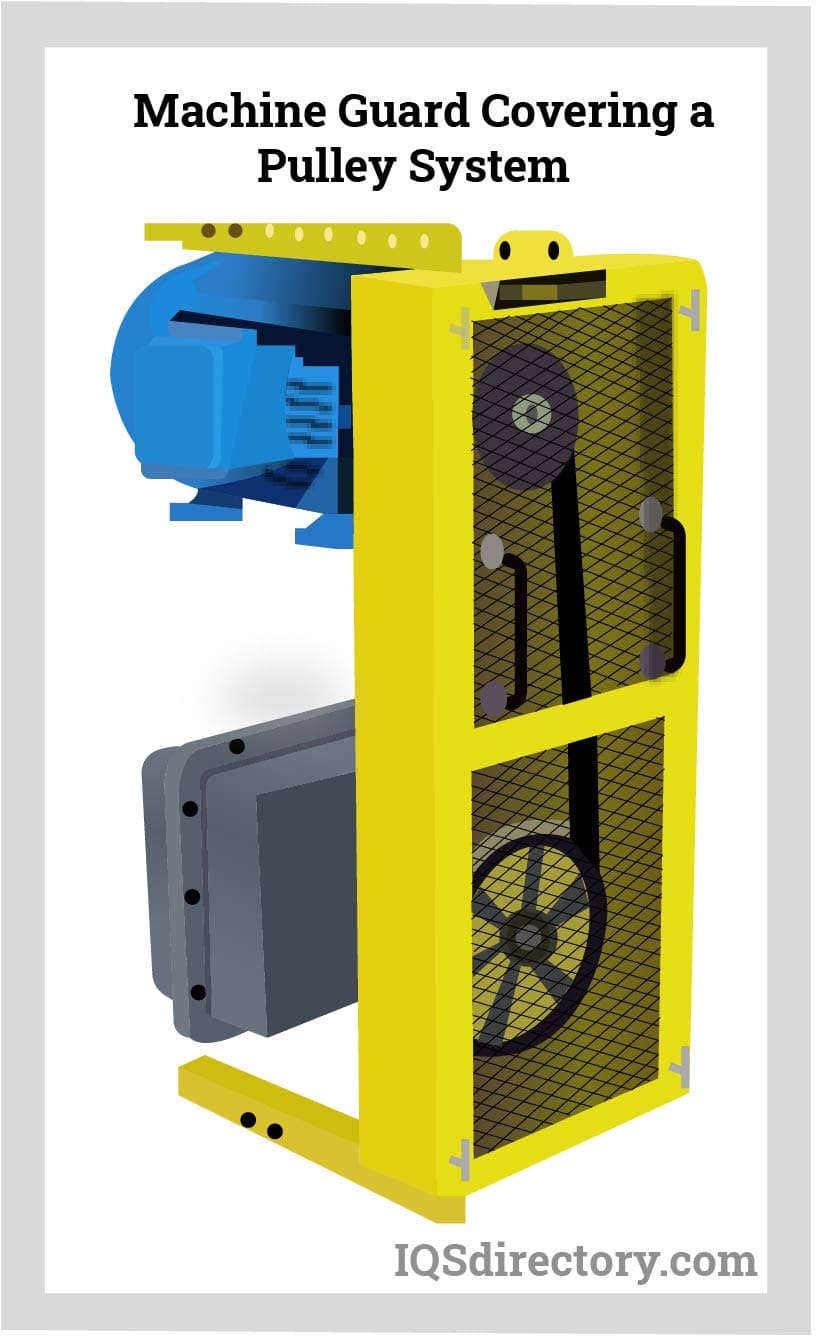
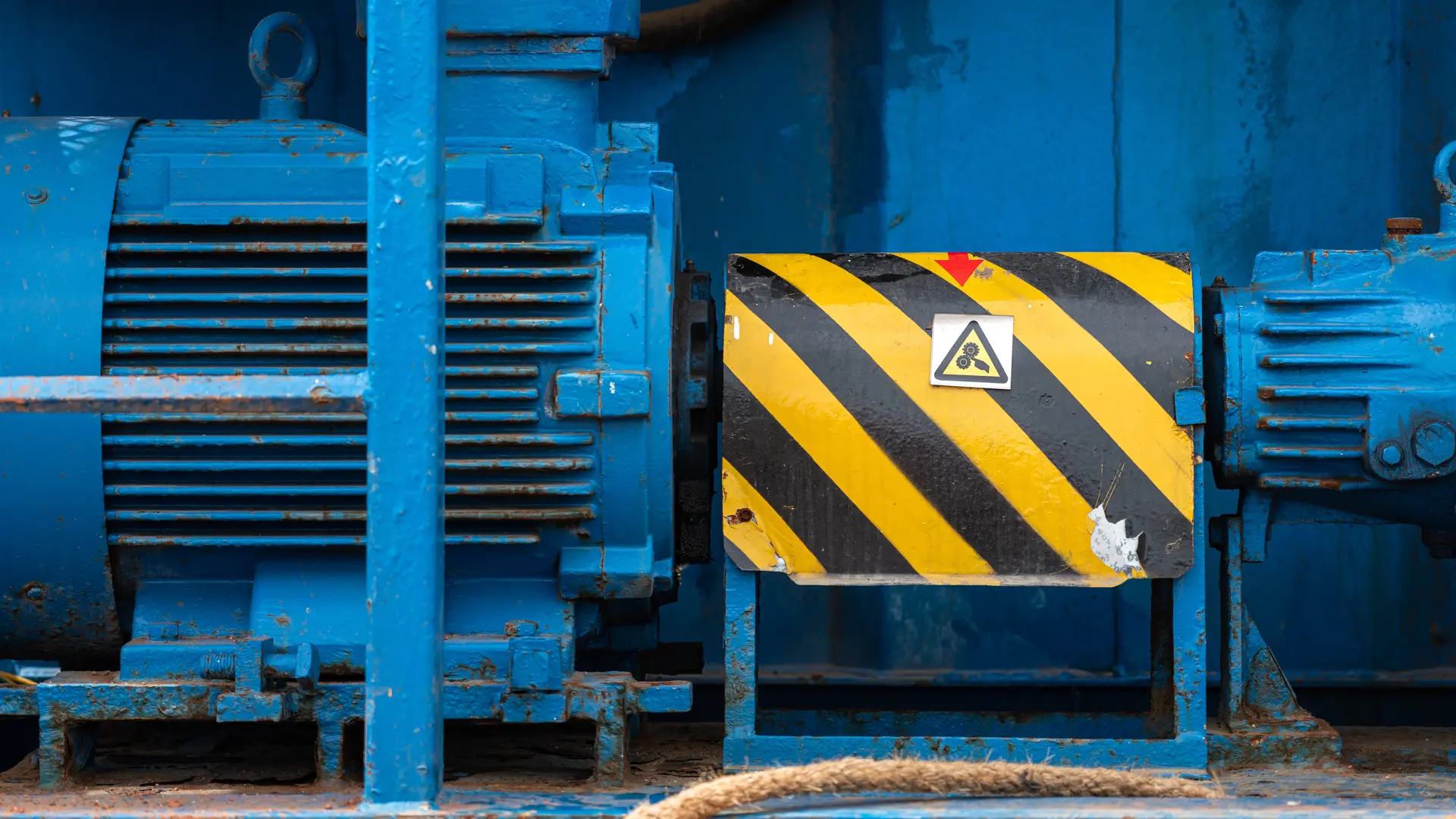
How Do Power Transmission Guards Protect Operators?
Power transmission guards are essential for safeguarding operators from hazards associated with moving components like gears, belts, and pulleys. They are widely used in industries involving heavy machinery, mining, and automotive production. When selecting power transmission guards, B2B buyers should focus on the ease of installation and maintenance, as cumbersome designs can complicate regular checks and repairs, potentially leading to safety risks.
Key Industrial Applications of machinery guards
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Machinery Guards | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Fixed Guards on CNC Machines | Enhances worker safety by preventing access to moving parts and reduces downtime from accidents. | Compliance with local safety regulations and material durability. |
| Food Processing | Interlocked Guards on Packaging Equipment | Protects workers while allowing for quick access to machinery, minimizing production interruptions. | Hygiene standards and ease of cleaning are essential. |
| Construction & Mining | Perimeter Guards around Heavy Machinery | Reduces risk of unauthorized access, protecting workers from hazardous zones and enhancing site safety. | Robust design to withstand harsh environments and compliance with safety standards. |
| Automotive Assembly | Presence-Sensing Guards on Robotic Arms | Automatically halts machinery when personnel are detected, preventing injuries and ensuring operational efficiency. | Integration capabilities with existing systems and sensor reliability in diverse conditions. |
| Woodworking | Adjustable Guards on Saws and Planers | Provides flexibility for various wood sizes while ensuring safety, thus enhancing productivity. | Customizability for different machine types and compliance with industry safety regulations. |
How are Machinery Guards Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, fixed guards are commonly installed on CNC machines to prevent workers from accessing dangerous moving parts. This application significantly enhances workplace safety, reducing the likelihood of accidents that can lead to injuries or production downtime. Buyers in this sector must consider compliance with local safety regulations and the durability of materials used, as guards must withstand frequent use and possible impacts.
What Role Do Machinery Guards Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, interlocked guards are essential for packaging equipment. These guards ensure that machines cannot operate unless securely closed, allowing operators to access machinery for maintenance without compromising safety. This application minimizes production interruptions and protects workers from potential hazards. Buyers should prioritize hygiene standards and the ease of cleaning when sourcing these guards to maintain compliance with food safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Why Are Perimeter Guards Critical in Construction & Mining?
Perimeter guards are vital in construction and mining industries, where heavy machinery operates in hazardous environments. These guards restrict unauthorized access to dangerous zones, ensuring that workers are protected from potential injuries. The robust design of perimeter guards must withstand harsh conditions, making it essential for buyers to consider the materials’ durability and compliance with safety standards when sourcing these solutions.
How Do Presence-Sensing Guards Enhance Safety in Automotive Assembly?
Presence-sensing guards are increasingly utilized in automotive assembly, particularly around robotic arms. These guards leverage advanced sensors to detect the presence of personnel and automatically halt machinery, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to ensure that these guards can integrate seamlessly with existing systems and that the sensors are reliable across diverse operational conditions.
What Benefits Do Adjustable Guards Provide in Woodworking?
In woodworking applications, adjustable guards are employed on saws and planers to accommodate various wood sizes while maintaining safety. This flexibility allows for enhanced productivity as operators can adjust guards without compromising their safety. Buyers should look for customizability options for different machine types and ensure that the guards comply with industry-specific safety regulations to safeguard their operations effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machinery guards’ & Their Solutions
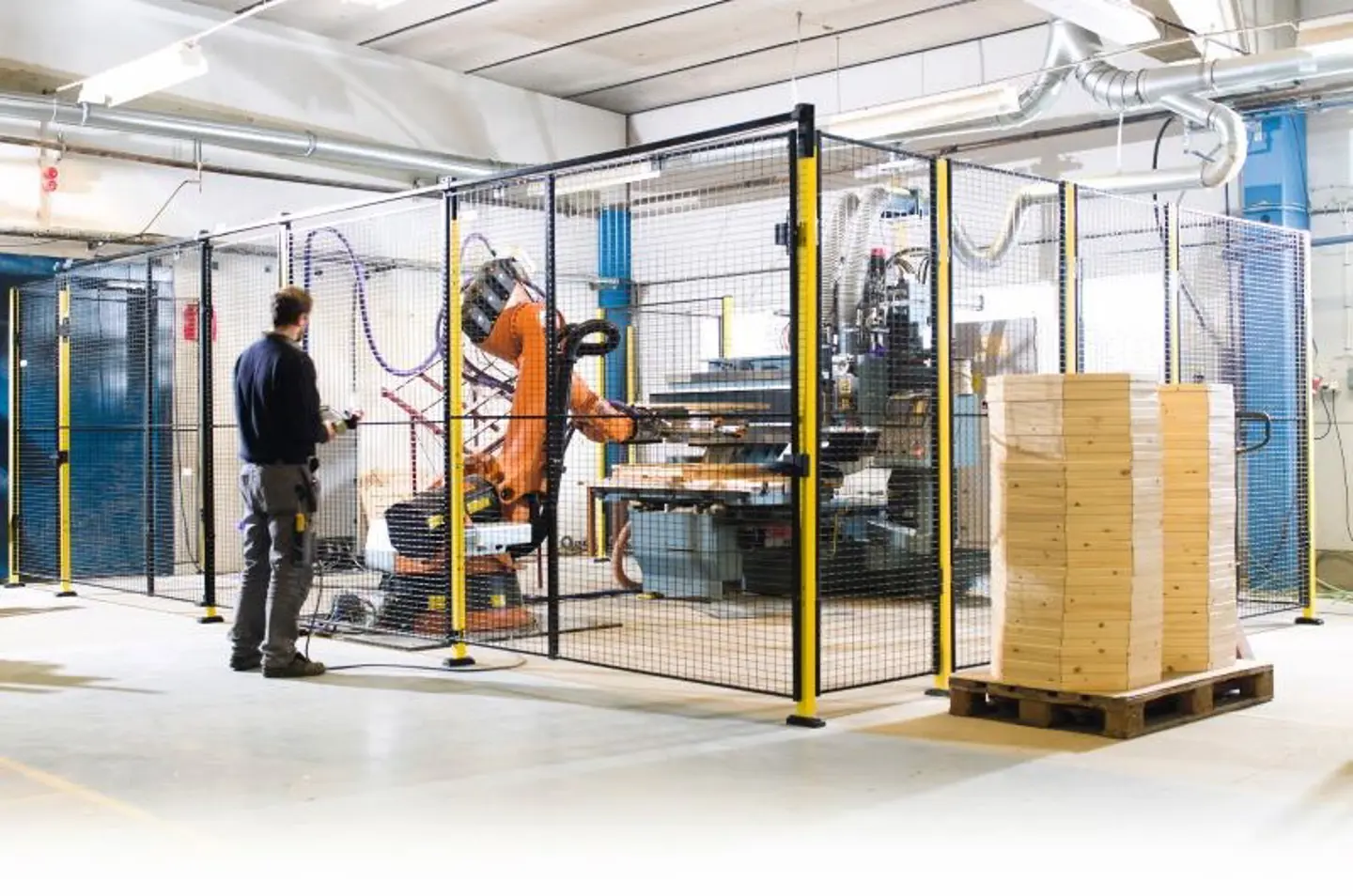
Scenario 1: Inadequate Protection Leading to Workplace Accidents
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in manufacturing and heavy industries face the challenge of inadequate machinery guards that fail to provide sufficient protection against moving parts and flying debris. This often results in workplace accidents, leading to injuries that not only harm employees but also disrupt production schedules and increase insurance costs. For buyers in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as Germany or Brazil, the repercussions of inadequate guarding can also include hefty fines and legal liabilities. The pressure to comply with safety standards while maintaining operational efficiency adds to the complexity.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is essential for buyers to conduct a thorough risk assessment of their machinery and work environment. Start by identifying all potential hazards associated with each piece of equipment, focusing on areas where employees may come into contact with moving parts or debris. Once you have a comprehensive understanding of the risks, consult with safety experts to select appropriate machinery guards tailored to your specific needs. For instance, fixed guards might be ideal for stationary machines, while interlocked guards could be necessary for equipment requiring frequent access. Ensuring that the guards meet local safety standards, such as OSHA or ANSI, will further mitigate risks. Regular training sessions for employees on the importance of using these guards can also enhance workplace safety and compliance.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Scenario 2: High Costs Due to Frequent Equipment Downtime
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the high cost associated with frequent equipment downtime caused by machinery malfunctions or accidents. In industries like mining or manufacturing, where machinery is integral to production, the inability to maintain operational continuity can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers often find themselves struggling with the dual challenges of selecting effective guards that prevent accidents and ensuring that those guards do not impede operational efficiency or accessibility.
The Solution: To minimize downtime, buyers should prioritize the selection of machinery guards that facilitate easy maintenance and access. Interlocked guards are particularly beneficial for machines that require regular checks or adjustments, as they automatically disable the machinery when removed. Additionally, investing in guards that incorporate advanced technology, such as presence-sensing features, can enhance safety without sacrificing efficiency. These systems can detect when an operator is too close to hazardous areas and can automatically halt machine operation, preventing accidents before they occur. Regular maintenance schedules for both the machinery and its guards can further reduce unexpected downtimes, ensuring smoother operations.
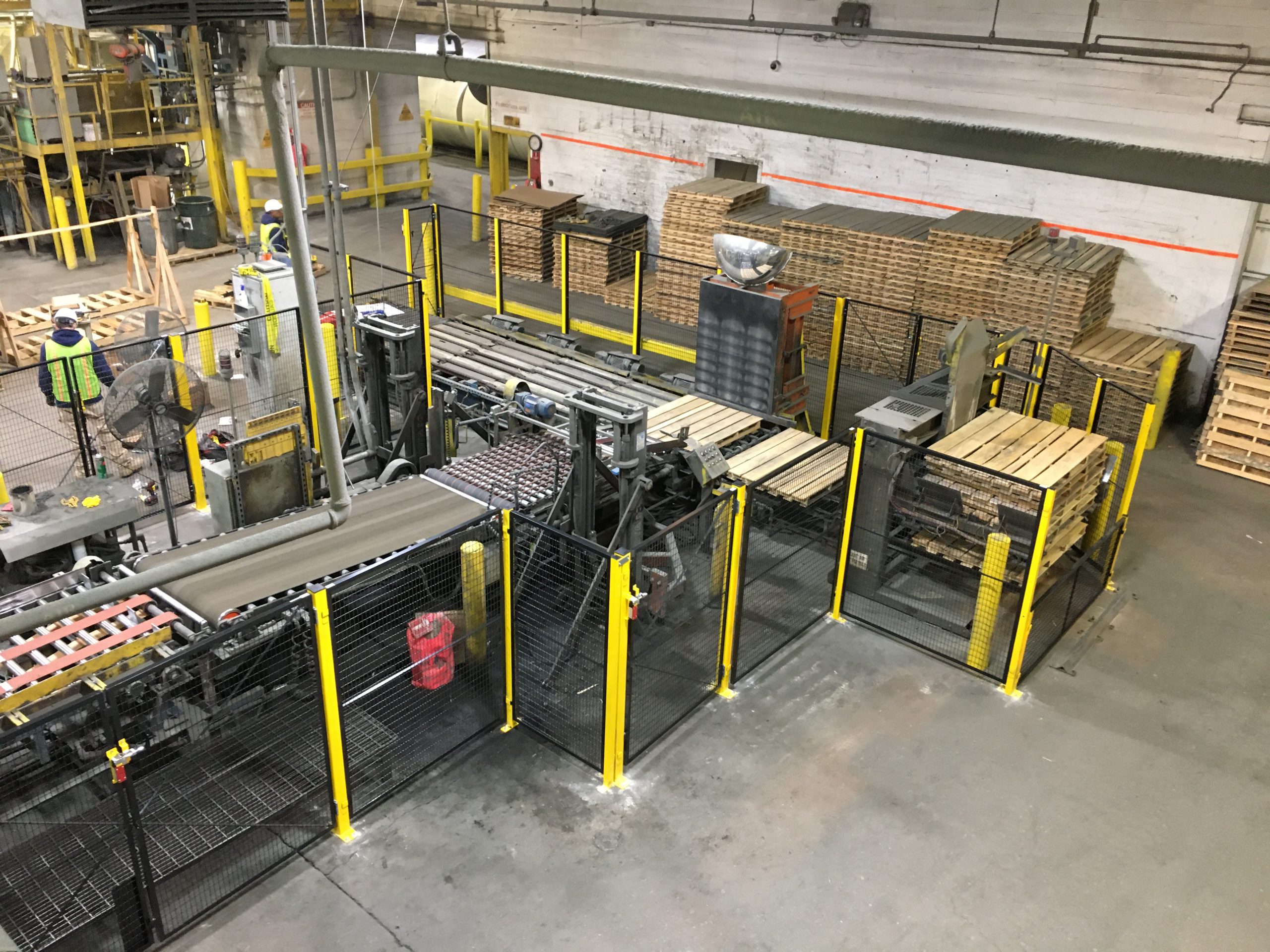
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible Machinery Guards
The Problem: Sourcing machinery guards that are compatible with existing equipment poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers. Companies may struggle to find guards that not only fit their machinery but also comply with local and international safety standards. This issue is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where access to quality safety equipment can be limited. The consequences of mismatched or inadequate guards include not only potential safety hazards but also wasted time and resources in the procurement process.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
The Solution: To effectively tackle this sourcing challenge, buyers should develop a comprehensive inventory of their machinery, including specifications, model numbers, and existing safety features. Engage with reputable suppliers who specialize in customized machinery guards, as they can provide tailored solutions that meet both compatibility and safety standards. It is also advisable to leverage technology by utilizing online platforms that compare different products and manufacturers. When exploring options, consider suppliers who offer a combination of pre-fabricated and customizable guards to ensure a perfect fit for your operations. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can also facilitate quicker sourcing and provide insights into upcoming safety innovations that could further enhance workplace safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machinery guards
What Are the Key Materials for Machinery Guards?
When selecting machinery guards, the choice of material is critical for ensuring safety, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of machinery guards, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Machinery Guards?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials for machinery guards due to its strength and durability. It typically has high tensile strength, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. Steel guards can withstand significant impacts and resist deformation, which is essential in high-traffic industrial environments.
Pros: Steel is highly durable, offers excellent protection against impacts, and is relatively cost-effective compared to other materials. It can also be easily fabricated into various shapes and sizes, making it versatile for different machinery types.
Cons: Steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can limit its lifespan in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, its weight can complicate installation and maintenance.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Impact on Application: Steel guards are ideal for environments with heavy machinery and high operational demands. However, they may require additional coatings or treatments for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety standards such as ASTM in the USA or DIN in Germany. In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity can be high, selecting corrosion-resistant steel is crucial.
What Are the Advantages of Using Polycarbonate for Machinery Guards?
Polycarbonate is a lightweight, high-impact plastic that is increasingly popular for machinery guards. It offers transparency, allowing operators to monitor machinery operations without removing the guard.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Pros: Polycarbonate is highly resistant to impact and shattering, making it a safe choice for environments where flying debris is a concern. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural load.
Cons: While polycarbonate is durable, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals. It can also be more expensive than traditional materials like steel, particularly in large applications.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate guards are suitable for applications where visibility is essential, such as in inspection areas. However, they may not be ideal for high-temperature environments.
Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that polycarbonate meets relevant safety standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN standards in Europe. Additionally, they should consider the climate; UV exposure can degrade polycarbonate over time.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Machinery Guards?
Aluminum is another common choice for machinery guards, known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It is particularly beneficial in applications where weight is a critical factor.
Pros: Aluminum is resistant to corrosion and can be anodized for additional protection. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to handle and install, reducing labor costs.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is generally less durable than steel and may not withstand heavy impacts as effectively. This can be a limitation in high-impact environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum guards are well-suited for environments where corrosion is a concern, such as food processing or chemical manufacturing. However, they may require reinforcement in high-impact applications.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards like ASTM and ensure that the aluminum used is of the appropriate grade for their specific application.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Machinery Guard Construction?
Stainless steel is favored in environments where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount, such as in food processing and pharmaceuticals. It combines the strength of steel with enhanced resistance to rust and staining.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. It also has a clean aesthetic, which is important in industries where cleanliness is critical.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to standard steel and aluminum. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to fabricate, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel guards are essential in industries with stringent hygiene standards. They are less suited for applications where cost is a primary concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with hygiene standards is crucial, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel grade used meets local regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machinery Guards
| Material | Typical Use Case for Machinery Guards | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery protection | High durability and impact resistance | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Visibility in inspection areas | Lightweight and shatter-resistant | Limited high-temperature tolerance | High |
| Aluminum | Food processing and chemical environments | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Hygiene-sensitive industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and fabrication complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed decisions when selecting machinery guards tailored to their specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machinery guards
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Machinery Guards?
The manufacturing process for machinery guards involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets safety and operational standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each step plays a vital role in the overall quality and effectiveness of the machinery guards.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
How Is Material Prepared for Machinery Guards?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process, where raw materials such as steel, aluminum, or polycarbonate are selected based on the specific requirements of the machinery guard. The materials are then cut to size using methods like laser cutting, waterjet cutting, or shearing. This process ensures that the pieces meet the exact specifications needed for the guard’s design.
Additionally, the selected materials often undergo treatments such as galvanization or powder coating to enhance their resistance to corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for machinery guards used in harsh environments, such as those found in industrial settings in Africa and South America.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Machinery Guards?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired design. Common techniques used in this stage include bending, stamping, and welding. Each technique is chosen based on the design complexity and the material properties.
- Bending: This technique is frequently used for creating the frame of the guard, allowing for the necessary contours and angles that fit around machinery.
- Stamping: For guards requiring intricate designs or perforations, stamping is employed to create precise shapes and openings.
- Welding: This is crucial for assembling different parts of the guard, ensuring structural integrity and durability.
Advanced technologies such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining may also be employed to enhance precision during the forming process.
How Are Machinery Guards Assembled?
Once the individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. Here, components are joined together using techniques such as welding, riveting, or bolting. The choice of assembly method depends on the design requirements and the expected load or stress the guard will encounter.
During assembly, it is essential to ensure that all connections are secure and that the guard aligns correctly with the machine it is intended to protect. This step often includes quality checks to verify that dimensions and tolerances meet specified standards.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Machinery Guards?
The finishing stage includes surface treatment processes that enhance the appearance and durability of the machinery guards. Common finishing techniques include painting, powder coating, or applying protective films. These processes not only improve aesthetics but also provide additional protection against environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and abrasion.
Proper finishing is crucial, especially for guards used in industries with stringent cleanliness and safety standards, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
What Are the Quality Control Measures for Machinery Guards?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for machinery guards, ensuring that each product complies with industry standards and regulations. The QC process typically encompasses several checkpoints and testing methods.
Which International Standards Apply to Machinery Guards?
Adhering to international quality standards is essential for manufacturers targeting global markets. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management system standards, applicable across various industries, including manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may be required. For example, CE marking is mandatory for machinery guards sold in the European market, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, API standards may apply for guards used in the oil and gas sector.
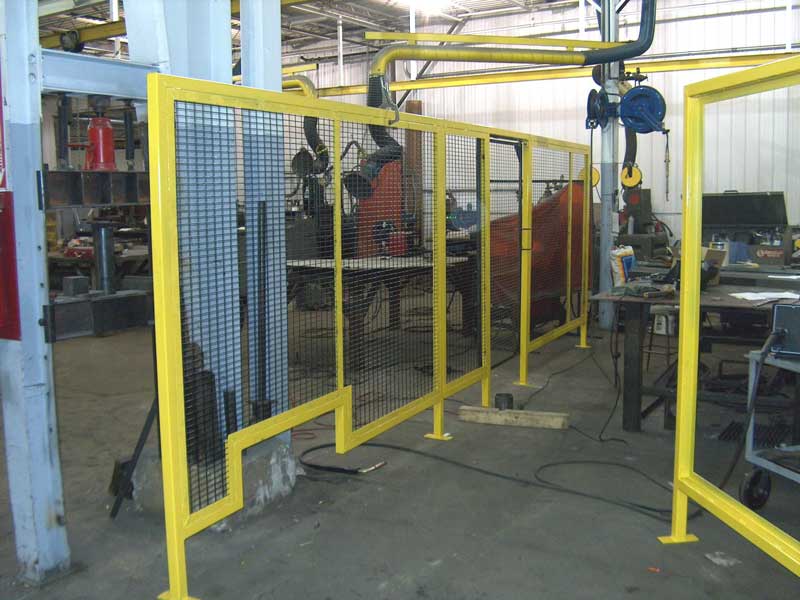

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
What Are the Common QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
The QC process typically involves three main checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival. Tests may include checking material specifications, dimensions, and quality certifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves monitoring various stages of the manufacturing process. Inspectors ensure that operations are conducted according to predefined standards and that any deviations are addressed promptly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the completed machinery guards. It includes dimensional checks, visual inspections for surface defects, and functional testing to ensure that the guards perform as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s QC practices is crucial for ensuring product quality. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and their commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and certificates of compliance, can help buyers verify that the supplier adheres to relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an independent assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is especially valuable when dealing with suppliers in different countries.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of the nuances in QC and certification requirements across different regions. For instance, while CE marking is critical for machinery guards sold in Europe, buyers in Africa may need to consider local regulations that differ from international standards.
Additionally, understanding the specific safety and quality certifications required in the buyer’s home country can help in selecting suppliers who can meet those standards. Keeping abreast of changes in regulations and standards is also essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring product safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for machinery guards is vital for B2B buyers looking to ensure safety and compliance in their operations. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with rigorous quality control practices, manufacturers can deliver high-quality machinery guards that meet international standards. Buyers should actively engage in verifying supplier QC practices to secure reliable and safe products for their industrial applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machinery guards’
Introduction
In the manufacturing and industrial sectors, ensuring worker safety is paramount, especially when dealing with machinery. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure machinery guards. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that prioritize safety, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by identifying the specific machinery that requires guarding. Understanding the type of machine and its operational hazards is crucial. Consider the following:
– Hazard Identification: Pinpoint areas where workers are at risk from moving parts, flying debris, or chemicals.
– Guard Type: Decide on the type of guard needed—fixed, interlocked, or presence-sensing—based on machine usage and access frequency.
Step 2: Conduct a Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is essential to determine the severity and likelihood of potential injuries. This step helps prioritize which machinery needs immediate attention. Focus on:
– Potential Risks: Evaluate the specific hazards associated with each machine.
– Access Requirements: Consider how often and in what manner workers will need to access the machinery for operation and maintenance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in safety solutions. Key actions include:
– Supplier Profiles: Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and safety certifications.
– References: Seek testimonials or case studies from clients within your industry or geographical region to gauge reliability.
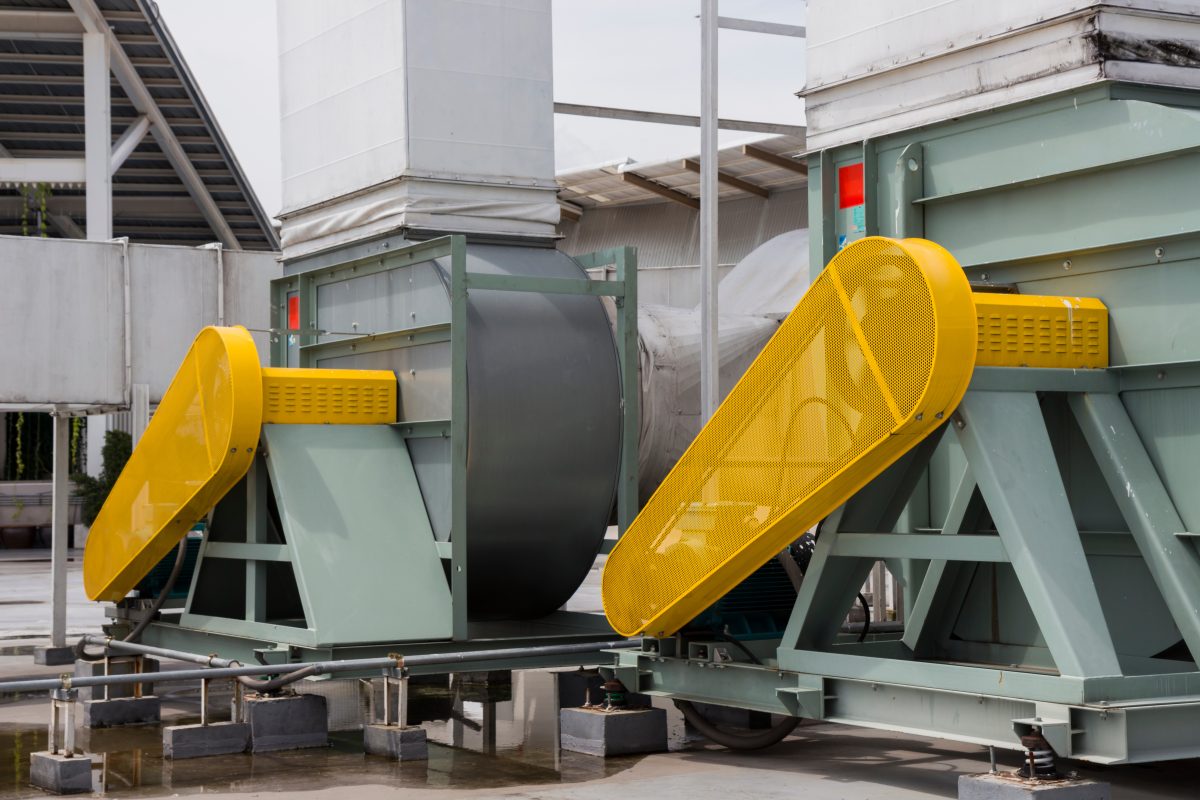

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Safety Standards
Ensure that the machinery guards meet relevant safety standards such as those set by OSHA or local regulations. Compliance is vital for legal and operational reasons. Pay attention to:
– Certification: Confirm that the guards have necessary certifications for safety and quality.
– Design Standards: Check if the design adheres to best practices in safety engineering, which can impact effectiveness.
Step 5: Assess Customization Options
In many cases, standard guards may not fit all machinery perfectly. Assess whether suppliers offer customization to suit your specific needs. Consider:
– Tailored Solutions: Look for suppliers that provide bespoke designs based on your machinery’s dimensions and operational demands.
– Adaptability: Ensure that the guard can adapt to future changes in machinery or operational processes.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Services
A strong warranty and responsive support services can save you time and money in the long run. Evaluate the following:
– Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty period and what it covers—this can indicate the supplier’s confidence in their product quality.
– Technical Support: Ensure that the supplier offers ongoing support for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Decision
After thorough evaluation, make an informed purchase decision. Ensure that all elements align with your safety requirements, budget, and operational capabilities. Consider:
– Cost vs. Value: Balance the upfront costs with the long-term benefits of enhanced safety and reduced risk.
– Supplier Reliability: Choose a supplier known for quality and customer service to ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source machinery guards that not only meet safety requirements but also enhance operational productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machinery guards Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Machinery Guards?
When sourcing machinery guards, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the price. Common materials such as metal, polycarbonate, or composite materials vary in cost and durability. High-quality materials that comply with safety standards tend to be pricier but provide better protection and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the complexity of the machinery guards. For example, custom guards that require specialized skills to design and fabricate will incur higher labor costs compared to standard, mass-produced options.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the overall production process, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers often factor these costs into the pricing of machinery guards.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom or specialized guards can be significant. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs will be amortized over large production runs, which may reduce the per-unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure that the guards meet safety standards and function as intended. The costs associated with QC, including testing and certification, can add to the overall price but are essential for compliance with industry regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international transactions. The geographical location of suppliers and the logistics involved in transporting guards can substantially affect the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their business expenses and generate profit. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and the level of competition.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Machinery Guard Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of machinery guards, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often lead to discounted pricing. Understanding the MOQ set by suppliers can help buyers negotiate better terms and reduce costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific machinery or operational needs generally incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Guards made from higher-grade materials or those that meet specific safety certifications (e.g., ISO, OSHA) tend to be more expensive. However, investing in quality can reduce maintenance costs and enhance worker safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they can also provide better assurance regarding compliance and performance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale impact shipping costs and risk. Understanding which Incoterms apply can help buyers manage their total costs effectively, especially in international transactions.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Machinery Guards?
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing machinery guards, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for large orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or better payment terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, potential downtime, and compliance costs associated with machinery guards. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower TCO if the guards are more durable and effective.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of varying import duties, taxes, and shipping costs that can affect total pricing. Researching local regulations and potential trade agreements can lead to significant savings.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market rate and help identify the best value for money.
Conclusion and Disclaimer
Pricing for machinery guards can vary widely based on several factors, including materials, customization, and supplier characteristics. Buyers should approach sourcing with a comprehensive understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers to make informed decisions. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and supplier negotiations, so it’s wise to seek up-to-date information and multiple quotes before finalizing purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machinery guards With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Machinery Guards
In industrial environments, the safety of personnel operating machinery is paramount. While machinery guards are a widely accepted solution for mitigating risks, various alternatives also aim to enhance workplace safety. This analysis compares machinery guards with two viable alternatives: safety interlocks and presence-sensing devices. By examining their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best-use cases, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
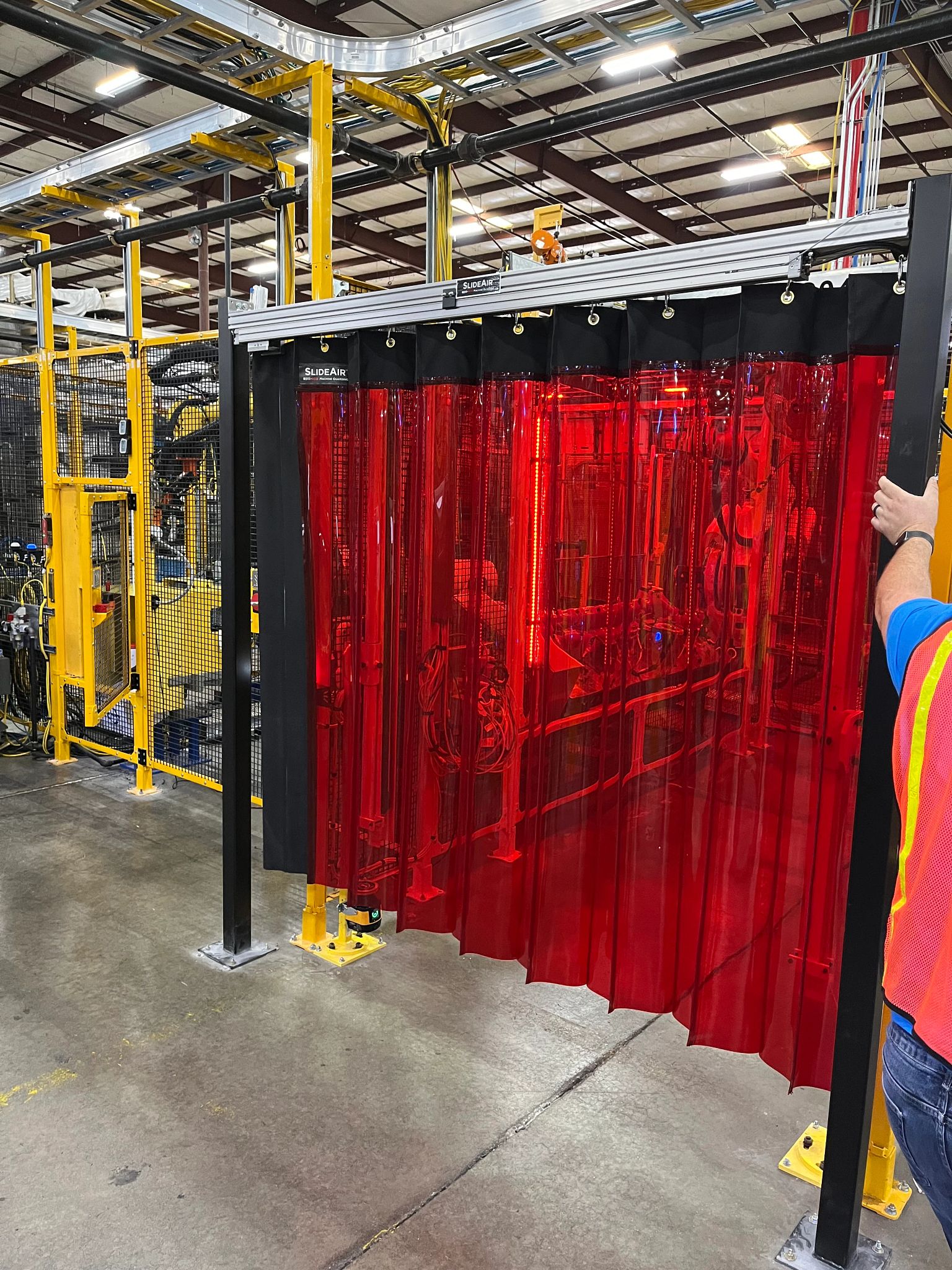

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
| Comparison Aspect | Machinery Guards | Safety Interlocks | Presence-Sensing Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High effectiveness in preventing access to dangerous parts. | Prevents operation when guards are removed, reducing risk of accidental startups. | Automatically stops machinery upon detecting a person or object in the hazard zone. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, with varying costs based on material and complexity. | Generally lower upfront costs but can be expensive if extensive modifications are needed. | Higher initial costs due to advanced technology but may save on injury-related expenses. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires installation and may need custom designs based on machinery. | Can be complex, requiring integration with existing machinery controls. | Installation can be straightforward but may require calibration and testing. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance if constructed from durable materials; regular inspections recommended. | Moderate maintenance; requires regular testing to ensure functionality. | Requires ongoing calibration and checks to ensure sensors are clean and operational. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for stationary machines with minimal access needs. | Best for machines requiring frequent operator access for maintenance or adjustments. | Suitable for dynamic environments where personnel may inadvertently enter hazardous zones. |
In-Depth Look at Alternative Solutions
What Are Safety Interlocks and Their Benefits?
Safety interlocks are devices that automatically shut down machinery when a guard is removed or opened. This solution is particularly effective for equipment that requires frequent access for maintenance or material loading. The primary advantage of safety interlocks is their ability to prevent accidental machine startups, significantly reducing the risk of injury. However, their complexity can lead to installation challenges, especially in older machinery that may require retrofitting.
How Do Presence-Sensing Devices Enhance Safety?
Presence-sensing devices utilize advanced technologies, such as light curtains or laser scanners, to detect the presence of personnel in hazardous zones. When a person or object is detected, the machine immediately halts operation, effectively preventing accidents. These devices are particularly beneficial in environments where workers may inadvertently enter danger zones. However, their higher initial costs and the need for regular calibration can be a barrier for some businesses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operational Needs
When considering safety solutions, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their operational environment. Machinery guards offer robust protection for stationary machines, while safety interlocks and presence-sensing devices provide more dynamic safety measures. Factors such as the nature of the machinery, frequency of operator access, and budget constraints will significantly influence the decision-making process. By carefully assessing these variables, businesses can implement the most effective safety measures to protect their workforce while optimizing productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machinery guards
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machinery Guards?
When selecting machinery guards, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance in industrial environments. Below are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
1. Material Grade
The material used in machinery guards significantly affects their durability and effectiveness. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and polycarbonate. Steel guards offer high strength and impact resistance, making them suitable for heavy machinery. In contrast, polycarbonate guards are lighter and provide excellent visibility while still offering adequate protection. Choosing the right material grade ensures that the guard can withstand operational wear and potential hazards.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For machinery guards, precise tolerances are essential to ensure a proper fit and function. Guards with inadequate tolerances can lead to gaps that may expose operators to moving parts, increasing the risk of accidents. Ensuring precise tolerances not only enhances safety but also improves the operational efficiency of machinery.
3. Weight Capacity
The weight capacity of a guard is critical, especially in environments where heavy machinery is used. Guards must be robust enough to handle impacts from moving parts or falling objects without compromising their integrity. Understanding weight capacity helps in selecting guards that align with the operational demands of specific machinery, ensuring long-term reliability.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
4. Compliance Standards
Machinery guards must meet specific safety standards, such as those set by OSHA or ANSI. Compliance ensures that the guards are designed and manufactured to protect workers effectively. Buyers should verify that the guards they choose are certified to meet relevant standards in their region, which is particularly important for international operations where standards may vary.
5. Customization Options
Many suppliers offer customizable guards tailored to specific machinery and operational needs. Customization may include size adjustments, additional features like interlocks, or modifications to accommodate unique machine designs. Understanding the customization options available allows businesses to select guards that provide optimal protection while integrating seamlessly with existing equipment.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know About Machinery Guards?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the purchasing process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are some common terms relevant to machinery guards:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of machinery guards, sourcing from an OEM can ensure that the guards are designed specifically for the machinery they protect, guaranteeing compatibility and effectiveness.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about MOQs when sourcing machinery guards to avoid overcommitting resources to a purchase that may exceed their immediate needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When requesting machinery guards, including detailed specifications and quantities in the RFQ can help suppliers provide accurate and competitive pricing, facilitating better purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities and costs when importing machinery guards from other countries.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This is particularly important for machinery guards, as longer lead times can impact production schedules. Understanding lead times allows buyers to plan accordingly, ensuring that safety measures are in place before machinery is put into operation.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance workplace safety and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machinery guards Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Machinery Guards Market?
The machinery guards sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing emphasis on workplace safety regulations, particularly in regions such as Europe and North America, where compliance with standards like OSHA and ISO is mandatory. This has led to a surge in demand for advanced machine guarding solutions that not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance operational efficiency.
Moreover, the rise of automation and smart manufacturing technologies is influencing sourcing trends. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking integrated safety solutions that incorporate IoT capabilities, allowing for real-time monitoring of machinery and potential hazards. This convergence of technology and safety is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and South America, where rapid industrialization necessitates robust safety measures.
Sustainability is another crucial trend impacting sourcing decisions. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who offer eco-friendly materials and practices, reflecting a broader commitment to corporate social responsibility. This includes the use of recyclable materials in the production of machine guards and the implementation of sustainable manufacturing processes.
In addition, the shift towards localized sourcing is gaining traction, especially in the Middle East and Africa. As supply chains become more complex due to geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties, buyers are looking for suppliers closer to their operations to mitigate risks associated with long-distance logistics. This trend encourages regional partnerships and the development of local manufacturing capabilities, ultimately fostering economic growth in these areas.
Illustrative image related to machinery guards
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Machinery Guards Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become integral to the machinery guards market, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental impacts among B2B buyers. The production of machinery guards often involves materials that can have a detrimental effect on the environment if not sourced responsibly. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure that materials are obtained ethically and sustainably.
The importance of certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, is rising among manufacturers of machinery guards. Buyers are more inclined to partner with suppliers who hold these certifications, as they demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental footprints. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled plastics and sustainably sourced metals, is gaining popularity. This trend not only helps reduce waste but also aligns with the corporate sustainability goals of many businesses.
Furthermore, the emphasis on ethical labor practices within the supply chain is becoming a priority. Buyers are seeking suppliers who uphold fair labor practices and provide safe working conditions, particularly in emerging markets. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, companies can enhance their brand reputation, meet consumer expectations, and contribute positively to the communities from which they source their materials.
What Is the Historical Context of Machinery Guards in B2B Operations?
The evolution of machinery guards can be traced back to the early 20th century when industrial safety regulations began to emerge in response to workplace accidents. Initially, basic protective measures were implemented, focusing primarily on preventing access to hazardous moving parts. Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have significantly improved the design and effectiveness of machine guards.

Illustrative image related to machinery guards
By the mid-20th century, the introduction of international safety standards, such as those from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), established a framework for machine guarding. This led to the development of more sophisticated guard types, including interlocked and presence-sensing guards, which enhanced safety while allowing for greater accessibility for maintenance and operation.
Today, the machinery guards sector is characterized by continuous innovation, driven by technological advancements and a heightened focus on safety and sustainability. As B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of machinery guards can provide valuable insights into current trends and future developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machinery guards
-
How do I solve safety compliance issues related to machinery guards?
To address safety compliance issues, start by familiarizing yourself with local regulations and standards, such as OSHA in the US or relevant EU directives. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify areas where machinery guards are necessary. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide guards that meet these standards. Regularly review and update your safety protocols to ensure ongoing compliance, and consider training staff on the importance of these safety measures. -
What is the best type of machinery guard for a milling machine?
The best type of machinery guard for a milling machine is typically a fixed guard, as it provides a robust barrier against moving parts. Fixed guards are securely attached and remain in place during operation, reducing the risk of accidental contact. For applications requiring frequent access, an interlocked guard may be more appropriate, as it automatically shuts down the machine when removed. Evaluate your specific operational needs and consult with a safety expert to make an informed decision. -
How can I vet suppliers of machinery guards for my business?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality. Verify that they comply with international safety standards and have certifications relevant to your region. Additionally, consider their experience in your specific industry and their ability to provide custom solutions. Engaging in direct communication can also help assess their responsiveness and willingness to support your needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machinery guards?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machinery guards can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs, while others might require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with potential suppliers and inquire about their MOQs. If your requirements are lower than their standard MOQ, consider negotiating or exploring partnerships with other businesses to consolidate orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing machinery guards internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, expect terms such as Letter of Credit (LC) or payment through escrow services for added security. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing your order to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How do I ensure the quality of machinery guards before purchase?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. It’s beneficial to ask for samples or conduct site visits to inspect the manufacturing process. Review quality assurance protocols and inquire about testing procedures for their guards. Additionally, seek feedback from other clients regarding their experiences with product durability and effectiveness in real-world applications. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing machinery guards?
When importing machinery guards, consider shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations in your region. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping methods and ensure compliance with import/export laws. It’s also wise to account for potential delays in customs clearance and have a plan for handling them. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in international shipping can streamline this process. -
Can machinery guards be customized to fit specific machinery?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for machinery guards to fit specific machines and applications. Customization can include adjustments in size, materials, and design features tailored to meet unique safety requirements. When discussing your needs with a supplier, provide detailed specifications and any relevant machine diagrams. This collaboration will ensure that the guards effectively address your safety concerns while maintaining operational efficiency.
Top 6 Machinery Guards Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Axelent – Machine Guards Solutions
Domain: axelentusa.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Axelent is a leading manufacturer of machine guards, offering a complete system that meets current directives and standards. Key product categories include: 1. Panels: Robust materials such as metal or polycarbonate for fixed guards. 2. Posts: Support structures for various types of guards. 3. Doors: Access solutions for machine guarding. 4. Locks & Switches: Safety mechanisms for secure operation…
2. Pilz – Safety Solutions for Plant and Machinery
Domain: pilz.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Selection of safeguards on plant and machinery, including sensor technology (position monitoring devices, safety switches, safety light curtains, safety laser scanners, safe radar systems, safe camera systems), relays (safety relays, monitoring relays, line monitoring devices, brake control devices), small controllers (PNOZmulti), automation systems (PSS 4000), and various applications such as saf…
3. Vestil – Machinery Guards
Domain: vestil.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Category: Machinery Guards
Vestil’s Machinery Guards provide essential protection by shielding workers from moving parts and reducing the risk of workplace accidents. Their durable and customizable design ensures safety and compliance in various industrial environments. Investing in these guards promotes a safer workspace and enhances operational efficiency.
Key Products:
– High Profile Machinery…
4. Belt Conveyor Guarding – Essential Machine Guards
Domain: conveyorguarding.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Belt Conveyor Guarding offers a variety of machine guards designed to ensure worker safety in industrial settings. Key characteristics of good machine guards include: 1. Durability: Made from high-quality materials that resist wear, tear, and corrosion. 2. Visibility: Brightly colored or marked with reflective tape for easy identification. 3. Access: Designed for easy removal or adjustment for mai…
5. SafetyVideos – Machine Guards
Domain: safetyvideos.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Machine guards, also known as safety guards, provide a physical barrier between an operator and a danger zone in machinery. They are essential for preventing workplace injuries caused by moving machine parts. There are different types of machine guards categorized by the hazards they protect against, including: 1. Point of Operation Guards – Protect against hazards where energy is applied to the s…
6. Safer.me – Machine Guarding Essentials
Domain: safer.me
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Machine Guarding Toolbox Talk: A 5-minute outline for discussing Equipment, Machine, and Tool Guards. Key points include the importance of machine guards to prevent accidents, types of guards (Fixed, Interlocking, Self-Adjusting, Adjustable), their purposes (prevent contact, ensure machine safety, protect from falling objects, aid in job efficiency), and safety tips for using machinery. Emphasizes…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machinery guards
In today’s dynamic industrial landscape, the strategic sourcing of machinery guards is essential for enhancing workplace safety and operational efficiency. By investing in high-quality machine guards, businesses not only comply with safety regulations but also protect their most valuable asset: their workforce. The various types of guards—fixed, interlocked, perimeter, and presence-sensing—offer tailored solutions that address specific hazards while accommodating operational needs.
International buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand local market demands and safety standards. A strategic sourcing approach enables companies to mitigate risks associated with machinery operation and fosters a culture of safety and productivity.
As industries evolve and automation increases, the need for advanced guarding solutions will only grow. Now is the time to assess your machinery guarding needs, seek expert guidance, and invest in solutions that not only enhance safety but also drive operational success. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure a safer and more productive tomorrow for your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.