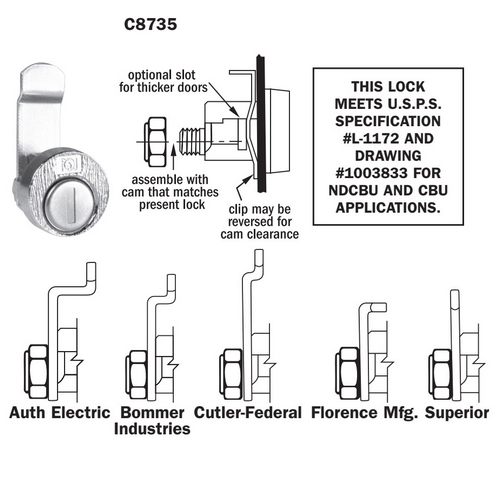
Lock Diagram Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lock diagram
In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing effective lock diagrams presents a formidable challenge for B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of various lock types—ranging from traditional pin cylinder mechanisms to advanced smart locks—is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the essential components of lock diagrams, their applications in different industries, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality and reliability.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, will find actionable insights into navigating the complexities of this market. By exploring the costs associated with various lock types, the latest innovations in security technology, and maintenance best practices, this guide empowers businesses to select the right locking solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Armed with this knowledge, B2B buyers can confidently approach their procurement strategies, ensuring they not only enhance security but also optimize their overall operational efficiency. Whether your focus is on enhancing safety protocols or investing in cutting-edge technology, understanding lock diagrams will be instrumental in driving your business success in a competitive global market.
Understanding lock diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pin Cylinder Lock | Utilizes a series of pins that align with the key | Commercial buildings, residential units | Pros: Widely available, affordable, versatile. Cons: Can be picked if not high-security. |
| Deadbolt Lock | Features a solid bolt that extends into the door frame | External doors in commercial settings | Pros: High security, resistant to forced entry. Cons: Requires a key or thumb turn for operation. |
| Smart Lock | Operates via electronic mechanisms, often smartphone-controlled | Offices, high-tech buildings | Pros: Convenient, offers remote access and monitoring. Cons: Dependent on power/battery life. |
| Mortise Lock | Built into the door, offering robust security | Hotels, commercial offices | Pros: Durable, high level of security. Cons: More complex installation, higher cost. |
| Lever Handle Lock | Features a lever mechanism for easy operation | Interior office doors, public restrooms | Pros: User-friendly, accessible. Cons: Lower security compared to deadbolts. |
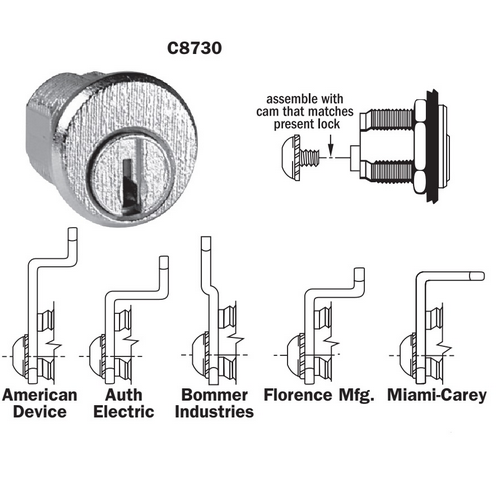
What Are the Characteristics of Pin Cylinder Locks?
Pin cylinder locks are among the most prevalent locking mechanisms used today. They consist of a cylinder that contains pins of varying lengths, which align with the key’s cuts to allow the lock to turn. These locks are commonly found in both residential and commercial properties, making them a versatile option for B2B buyers. When purchasing, consider the security features, such as anti-pick technology, and the level of protection required for your specific application.
How Do Deadbolt Locks Enhance Security for Businesses?
Deadbolt locks are designed for high security, featuring a robust bolt that extends deep into the door frame. This design makes them highly resistant to forced entry, making them ideal for external doors in commercial settings. B2B buyers should evaluate the installation requirements and ensure compatibility with existing door structures. While deadbolts provide superior security, they may require a key or thumb turn for operation, which can be a consideration for ease of access.
What Advantages Do Smart Locks Offer for Modern Businesses?
Smart locks utilize electronic mechanisms that can be controlled via smartphones or keypads, providing a modern solution for security. These locks are particularly advantageous for offices and high-tech buildings, as they allow for remote access and monitoring. B2B buyers should assess the power requirements and ensure that adequate backup systems are in place. While convenient, the reliance on technology means that potential vulnerabilities, such as hacking, should be considered.
Why Choose Mortise Locks for High-Traffic Areas?
Mortise locks are embedded within the door, providing a high level of security and durability. They are commonly used in hotels and commercial offices where robust security is paramount. When purchasing mortise locks, B2B buyers should consider the complexity of installation and the potential for higher costs compared to other lock types. However, their strength and reliability make them a wise investment for high-traffic areas.
How Do Lever Handle Locks Improve Accessibility in Workspaces?
Lever handle locks are designed for ease of use, featuring a lever mechanism that allows users to open doors with minimal effort. These locks are often found in interior office doors and public restrooms, making them suitable for spaces that require accessibility. B2B buyers should consider the balance between ease of use and security, as lever handle locks typically offer lower security compared to deadbolts. Their user-friendly design is a significant advantage in environments with high foot traffic.
Key Industrial Applications of lock diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lock diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Architectural design for secure buildings | Enhances safety, reduces liability, and increases property value | Compliance with local security regulations, durability against environmental factors |
| Manufacturing | Access control systems for production areas | Protects sensitive information and machinery, ensuring operational continuity | Integration with existing security systems, scalability for future expansion |
| Transportation | Locking mechanisms for vehicles and cargo containers | Prevents theft and unauthorized access, enhancing safety for goods in transit | Compatibility with various vehicle models, resistance to tampering or weather conditions |
| Hospitality | Security solutions for hotel room access | Improves guest experience and trust, while ensuring property security | Customization options for branding, ease of use for guests, and integration with smart technology |
| Retail | Inventory management systems with locking mechanisms | Reduces shrinkage, enhances inventory accuracy, and improves overall security | Ability to integrate with POS systems, ease of installation, and maintenance support |
How is the ‘lock diagram’ applied in the construction industry?
In the construction sector, lock diagrams are essential for designing secure building access systems. They facilitate the integration of various locking mechanisms, ensuring that buildings meet safety and regulatory standards. By employing lock diagrams, architects and builders can visualize the security layout, which helps in minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Buyers in this sector need to consider local regulations and climate impacts on lock durability, ensuring that the locking systems are both compliant and robust against environmental factors.
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
What role does the ‘lock diagram’ play in manufacturing?
Manufacturers utilize lock diagrams to design access control systems that protect sensitive areas within their facilities. These diagrams help in strategizing the placement of locks, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access critical machinery and information. This not only safeguards assets but also enhances operational efficiency by minimizing downtime due to security breaches. For international buyers, it is vital to ensure that the locking systems can seamlessly integrate with existing security frameworks and can scale with business growth.
How does the ‘lock diagram’ benefit the transportation sector?
In the transportation industry, lock diagrams are crucial for designing secure locking mechanisms for vehicles and cargo containers. They help in preventing theft and unauthorized access, thereby ensuring the safety of goods during transit. A well-implemented locking system can significantly reduce insurance costs and enhance overall supply chain security. Buyers should prioritize sourcing locks that are compatible with various vehicle models and are resistant to tampering and harsh weather conditions, especially in regions with extreme climates.
Why is the ‘lock diagram’ important for the hospitality sector?
For the hospitality industry, lock diagrams are instrumental in developing efficient and secure hotel room access systems. These diagrams assist in visualizing the layout of locks and access points, ensuring that guests can easily and safely access their rooms. Enhanced security not only improves guest satisfaction but also builds trust in the establishment. Buyers should look for customizable locking solutions that can incorporate branding elements, provide ease of use, and support integration with smart technologies for a modern guest experience.
How does the ‘lock diagram’ enhance security in retail?
In the retail sector, lock diagrams are used to create effective inventory management systems that include locking mechanisms. These diagrams help in strategizing the placement of locks to minimize shrinkage and enhance the security of merchandise. By implementing a well-designed locking system, retailers can improve inventory accuracy and reduce losses due to theft. When sourcing these systems, it is essential for buyers to consider compatibility with existing point-of-sale systems and ensure that installation and maintenance are straightforward to avoid disruptions in operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lock diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Lock Systems for Large Facilities
The Problem:
B2B buyers managing large facilities often face the daunting task of securing multiple entry points while ensuring ease of access for authorized personnel. A common challenge is the complexity of lock systems that require an understanding of intricate lock diagrams to ensure proper installation and functionality. Without clear diagrams, miscommunication among contractors or maintenance teams can lead to security vulnerabilities or operational disruptions. This is particularly critical in sectors such as hospitality, healthcare, and education, where security and access control are paramount.
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to source high-quality lock diagrams that are specific to the lock systems being implemented. Buyers should work closely with manufacturers or suppliers that provide detailed diagrams showing the installation process, key specifications, and maintenance procedures. This can include request for proposals (RFPs) that emphasize the need for comprehensive documentation. Additionally, investing in digital tools or software that visualize lock systems can streamline the communication process among teams. Training sessions for staff on interpreting these diagrams can further enhance understanding and ensure proper implementation, ultimately resulting in a secure and efficient facility management strategy.
Scenario 2: Customizing Lock Solutions to Meet Unique Security Needs
The Problem:
Many businesses, especially those in niche markets, struggle with the lack of customizable lock solutions that fit their specific security requirements. Standard lock diagrams often do not accommodate unique configurations, leading to potential security risks or operational inefficiencies. For instance, a manufacturing plant may require locks that can withstand harsh environmental conditions or specific access levels for different departments, complicating the selection process.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer customizable lock systems and corresponding lock diagrams. When engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the unique security challenges faced by the business. Request prototypes or mock-ups based on the custom diagrams to ensure functionality meets requirements before full-scale implementation. Additionally, leverage technology such as CAD software that can be used to create tailored lock diagrams that reflect specific needs, facilitating better decision-making and ensuring the right solutions are selected.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compatibility of New Locks with Existing Infrastructure
The Problem:
For businesses upgrading their security systems, a frequent pain point is ensuring that new lock installations are compatible with existing door frames and hardware. Buyers often find themselves grappling with outdated or vague lock diagrams, which can lead to mismatches in sizing and functionality, resulting in increased costs and installation delays. This issue is exacerbated when working with international suppliers, where specifications may vary widely.
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
The Solution:
To mitigate compatibility issues, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current infrastructure before engaging with suppliers. This includes taking precise measurements and documenting existing lock configurations. When sourcing new locks, insist on detailed lock diagrams that include dimensional specifications and compatibility notes. Establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers to discuss these diagrams can help in identifying potential issues early in the process. Additionally, consider utilizing local consultants or locksmiths who are familiar with regional standards and can provide insights on the best practices for integrating new locks into existing systems, ensuring a smoother transition and enhanced security overall.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lock diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Lock Diagrams?
When selecting materials for lock diagrams, it is essential to consider various factors that influence product performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This analysis focuses on four common materials: steel, brass, zinc alloy, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications in the lock industry.
How Does Steel Perform in Lock Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in the manufacturing of locks due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high temperature and pressure rating, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Steel locks are often treated with coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid or coastal environments.
Pros: Steel offers superior durability and resistance to physical attacks, making it a preferred choice for high-security locks. Its strength allows for complex locking mechanisms that can withstand significant force.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion if not properly coated or treated. Additionally, manufacturing steel locks can be more complex and costly due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly suitable for high-security applications in commercial and industrial settings, where the risk of forced entry is higher.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the steel used complies with local standards for corrosion resistance, especially in coastal areas. Compliance with ASTM or DIN standards is crucial for quality assurance.
What Are the Advantages of Brass in Lock Manufacturing?
Brass is another popular material for locks, known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically has a lower temperature rating compared to steel but is sufficient for most indoor applications.
Pros: Brass locks are resistant to tarnishing and corrosion, making them suitable for various environments. The material is also relatively easy to manufacture, allowing for intricate designs and finishes.
Cons: While brass is durable, it is not as strong as steel, making it less suitable for high-security applications. Additionally, brass can be more expensive than other materials like zinc alloy.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in residential locks and decorative applications where aesthetics are important.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific grade of brass used, as this can affect durability and performance. Compliance with JIS standards is often preferred in Asian markets like Vietnam.
How Does Zinc Alloy Compare to Other Materials?
Zinc alloy is frequently used in the production of locks due to its low cost and reasonable strength. It has good corrosion resistance, especially when coated.
Pros: Zinc alloy locks are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for mass production. They can be easily molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: However, zinc alloy is generally less durable than steel and brass, making it unsuitable for high-security applications. It may also have a lower temperature and pressure rating.
Impact on Application: Zinc alloy is often used in lower-security applications, such as padlocks and interior door locks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the quality of zinc alloy used, as inferior grades can lead to rapid wear and failure. Compliance with local manufacturing standards is essential to ensure product reliability.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Lock Design?
Plastic is increasingly being used in lock manufacturing, particularly in smart locks and electronic locking systems. It offers a lightweight alternative to metals and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros: Plastic locks can be designed to be highly resistant to environmental factors, such as moisture and UV radiation. They are also cost-effective and can be produced in various colors and styles.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic is its lower strength compared to metal options, making it less suitable for high-security applications. Over time, plastic can degrade, especially in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic is often used in residential settings and smart lock applications where aesthetics and lightweight construction are priorities.
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic used meets relevant safety and performance standards, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lock Diagrams
| Material | Typical Use Case for lock diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-security locks | Superior strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Brass | Residential and decorative locks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Less strong than steel | Medium |
| Zinc Alloy | Padlocks and interior locks | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower durability than metals | Low |
| Plastic | Smart locks and lightweight designs | Resistant to moisture and UV | Lower strength and potential degradation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations of various materials used in lock diagrams, enabling informed decisions tailored to specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lock diagram
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Lock Diagrams?
The manufacturing process for lock diagrams involves several critical stages that ensure both functionality and security. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to source quality locks.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Lock Production?
The first step in manufacturing locks is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include:
- Steel and Stainless Steel: These materials offer durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications.
- Brass: Known for its malleability and resistance to tarnishing, brass is often used in lock cylinders and keys.
- Zinc Alloy: This is frequently utilized for die-cast parts, providing an economical yet sturdy option for various lock components.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo processes such as cutting, shaping, and surface treatment to prepare them for further manufacturing stages. Proper material selection is crucial, as it directly impacts the lock’s longevity and security features.
2. Forming: How Are Lock Components Shaped and Molded?
The forming stage involves various techniques to shape the lock components. Key methods include:
- Die Casting: This technique is commonly used for creating intricate shapes, particularly for zinc alloy components. It involves pouring molten metal into a mold, allowing it to cool and solidify.
- Forging: This process uses compressive forces to shape metal into desired forms, enhancing the material’s strength and durability.
- Machining: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is often employed to achieve high precision for components such as lock cylinders and keys.
This stage is crucial for ensuring that each part fits perfectly with others, which is essential for the lock’s performance and security.
3. Assembly: What Processes Ensure Secure and Accurate Lock Assembly?
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This involves:
- Component Integration: All parts, including the cylinder, bolt, latch, and keyhole, are assembled. Skilled technicians often perform this task to ensure accuracy.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: Manufacturers implement in-process quality control (IPQC) measures. This includes verifying the alignment of components and ensuring that moving parts function smoothly.
An efficient assembly process is vital, as even minor errors can compromise the lock’s functionality.
4. Finishing: What Techniques Are Used to Enhance Lock Durability and Aesthetics?
The finishing stage enhances the lock’s durability and appearance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Electroplating: This process applies a thin layer of metal to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics.
- Powder Coating: This technique provides a durable, protective finish that can be customized in various colors.
- Polishing: This enhances the visual appeal of brass and stainless steel components, offering a high-quality look.
Finishing not only contributes to the lock’s lifespan but also plays a significant role in meeting customer expectations regarding aesthetics.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures in Lock Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is critical in the lock manufacturing process to ensure that products meet international standards and customer requirements.
1. What International Standards Are Relevant for Lock Manufacturers?
Lock manufacturers often adhere to various international standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For locks used in the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products can withstand harsh conditions.
Compliance with these standards assures buyers of the lock’s quality and reliability.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control is typically segmented into several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials for defects before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout manufacturing, processes are monitored to catch any deviations in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, locks undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specifications and function correctly.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify issues early, reducing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Lock Quality?
Testing methods vary based on the type of lock but often include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that the lock operates smoothly, including the key insertion and turning mechanisms.
- Durability Testing: Locks may be subjected to stress tests to evaluate their performance under extreme conditions.
- Security Testing: This involves testing against picking, drilling, and other forms of forced entry to ensure the lock meets security standards.
These tests help validate the lock’s performance and safety, giving B2B buyers confidence in their purchase.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is essential to ensure product reliability.
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
1. What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier Quality Control?
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits of the manufacturing facility to assess their quality control practices and adherence to international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their quality control processes, including records from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Consider engaging third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products.
These steps can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers.
2. What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing locks from different regions, international buyers should be aware of:
- Regional Standards Variations: Different countries may have specific certifications or standards, such as ANSI in the United States or SANS in South Africa. Understanding these can ensure compliance and acceptance in the target market.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding security products, as this can impact both manufacturing and marketing strategies.
Being informed about these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure that products meet local market requirements.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Manufacturing and QC Processes Is Essential for Lock Procurement
For B2B buyers, comprehending the manufacturing processes and quality control measures involved in lock production is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material selection, forming techniques, assembly methods, finishing processes, and stringent quality control practices, buyers can ensure they source reliable and secure locks that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. Additionally, understanding international standards and verification processes can help navigate the complexities of global procurement, ultimately leading to successful business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lock diagram’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring lock diagrams, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Lock diagrams are critical for understanding the mechanics of various locking systems, enhancing security, and ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selection and procurement effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of any successful procurement process. Consider the types of locks you are dealing with—be it pin cylinders, deadbolts, or smart locks. This will guide your search for diagrams that accurately represent the mechanisms involved.
- Consider dimensions: Ensure that the diagrams include accurate measurements for proper fit and function.
- Identify security features: Note any specific security requirements, such as anti-pick or anti-drill mechanisms, that should be represented in the diagrams.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability in your procurement. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry and positive reviews from other buyers.
- Check industry certifications: Suppliers should possess relevant certifications that demonstrate their adherence to safety and quality standards.
- Evaluate experience: Prioritize suppliers with extensive experience in providing lock diagrams for your specific type of lock or security system.
Step 3: Request Detailed Product Information
Once potential suppliers are identified, request comprehensive information about their lock diagrams. This should include technical drawings, specifications, and any available installation instructions.
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
- Ask for sample diagrams: Review sample diagrams to assess clarity and detail.
- Inquire about customization options: Ensure that the supplier can accommodate specific needs, such as unique lock types or configurations.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, it’s imperative to verify the certifications of your chosen suppliers. This step ensures that the supplier complies with industry standards and regulations.
- Look for ISO certifications: These are indicators of quality management and consistent performance.
- Confirm local compliance: Ensure that the supplier meets local regulations and standards pertinent to your region.
Step 5: Evaluate Pricing and Terms of Service
Understanding the pricing structure and terms of service is essential for budgeting and ensuring a smooth procurement process.
- Compare quotes: Get quotes from multiple suppliers to assess market rates and avoid overpaying.
- Review payment terms: Pay attention to payment schedules, return policies, and warranties offered for the diagrams.
Step 6: Conduct a Final Review Before Purchase
Before making a purchase, conduct a thorough review of all gathered information. This is your last chance to ensure that everything aligns with your requirements.
- Cross-check specifications: Ensure that the diagrams meet your initial technical specifications.
- Confirm delivery timelines: Understand the expected delivery timelines to avoid any disruptions in your project.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Once you have made your selection, establish clear communication channels with your supplier. This ensures that you can quickly address any questions or issues that arise during the procurement process.
- Define points of contact: Identify key contacts for both your team and the supplier for streamlined communication.
- Set up regular updates: Schedule check-ins to discuss progress and any potential adjustments needed during the procurement phase.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing of lock diagrams, ensuring they secure the best products for their needs while minimizing risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lock diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lock Diagram Sourcing?
When sourcing lock diagrams, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality metals like stainless steel or brass, commonly used for durable locks, can increase the cost compared to lower-grade materials. Additionally, the incorporation of advanced features in smart locks, such as electronics, can further elevate material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to skilled technicians and assembly workers. In regions where labor is less expensive, such as parts of South America or Southeast Asia, sourcing can be more economical. However, the quality of craftsmanship should not be compromised, as this can affect the lock’s performance and longevity.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, making it crucial to assess suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the expenses related to the creation and maintenance of molds and tools necessary for production. Custom designs may necessitate higher tooling investments, which can be amortized over larger production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that products meet specified standards, which can incur additional costs. However, investing in quality can lead to fewer returns and warranty claims, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are vital components, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and import duties can significantly influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their costs to achieve a profit margin. Understanding the standard margin within the industry can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Lock Diagram Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing lock diagrams, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in larger quantities often results in lower per-unit prices. Buyers should consider their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized locks or specific design requirements may lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-security locks made from premium materials will typically cost more than standard locks. Buyers should evaluate the balance between cost and security needs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have certifications (like ISO) may come at a premium. However, they can offer long-term savings through durability and reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and responsibility for costs (like CIF, FOB) is crucial for budgeting. These terms can significantly affect the total landed cost of products.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Lock Diagram Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially if they value long-term relationships. Be prepared to discuss volume commitments or long-term contracts to secure better rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Factors such as maintenance, durability, and potential replacement costs should be included in the overall assessment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Understanding these factors can help in budgeting accurately and negotiating effectively.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Take the time to evaluate potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for those with a proven track record of reliability, quality, and responsiveness to ensure that you are making a sound investment.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing benchmarks. This knowledge can empower negotiations and help identify the best suppliers for your needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing in the lock diagram sourcing sector can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting a competitive price tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lock diagram With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of security solutions, B2B buyers must evaluate various methods and technologies to determine which best meets their needs. The ‘lock diagram’ serves as a visual representation of lock mechanisms, helping users understand how locks function and the security features they offer. However, there are alternative solutions available that can also provide valuable insights into lock systems and security measures.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Lock Diagram | Smart Lock Technology | Traditional Key Lock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High (visual clarity for understanding mechanisms) | Very High (real-time monitoring and access control) | Moderate (basic security without advanced features) |
| Cost | Low (often free or low-cost resources) | Moderate to High (initial investment plus potential service fees) | Low to Moderate (depending on the type of lock) |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy (requires minimal training) | Moderate (requires setup and integration with smart devices) | Very Easy (simple installation process) |
| Maintenance | Low (requires minimal upkeep) | Moderate (battery changes, software updates) | Low (occasional lubrication and servicing) |
| Best Use Case | Educational and training purposes | High-security environments needing remote access | General use in residential and commercial properties |
Understanding Smart Lock Technology: Pros and Cons
Smart locks represent a significant advancement in locking mechanisms. They offer features like remote access, real-time monitoring, and integration with other smart home devices, making them ideal for businesses that require enhanced security and convenience. However, the initial investment can be higher, and ongoing maintenance may involve software updates and battery replacements. Additionally, smart locks depend on technology, which may raise concerns about cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
Evaluating Traditional Key Locks: Pros and Cons
Traditional key locks are the most commonly used security solution, favored for their simplicity and reliability. They are easy to install and maintain, making them a cost-effective choice for many businesses. However, they lack the advanced features found in smart locks and may not provide the same level of security, especially in high-risk environments. For businesses prioritizing budget over advanced security features, traditional key locks remain a viable option.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Security Solution for Your Business Needs
When considering security solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including the level of security needed, budget constraints, and the importance of convenience and technology integration. While the lock diagram provides essential insights into lock mechanisms, smart locks offer advanced features that can enhance security and operational efficiency. Traditional key locks may still be suitable for many applications, especially where simplicity and cost are paramount. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on the unique needs and priorities of each business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lock diagram
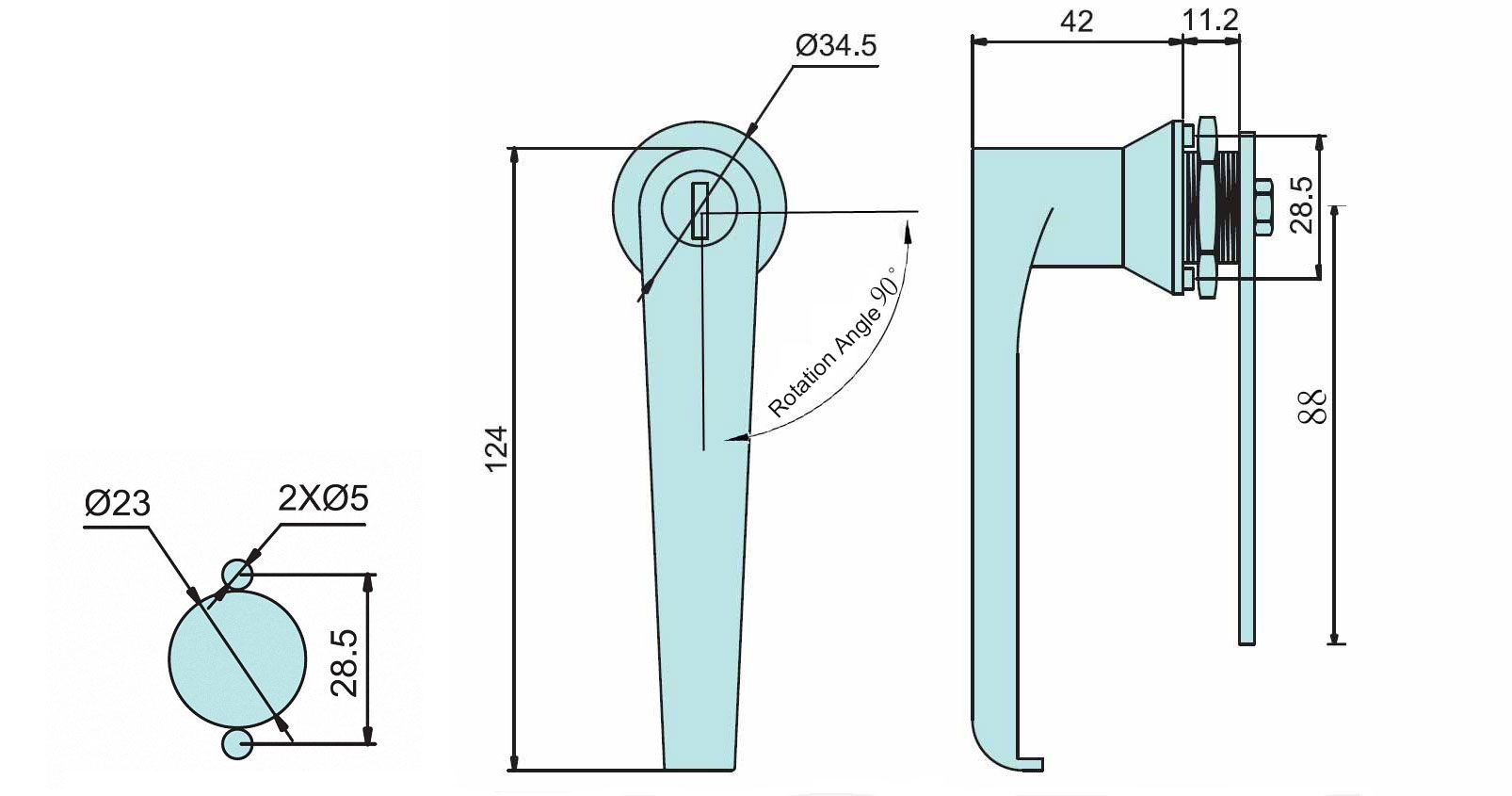
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lock Diagrams?
Understanding the technical specifications of lock diagrams is crucial for B2B buyers, as these properties impact both product performance and longevity. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
Illustrative image related to lock diagram
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of a lock component, such as stainless steel or brass, significantly affects its durability and resistance to corrosion. Higher-grade materials often result in longer-lasting products, which is especially important for security applications. Buyers should assess material grades to ensure they meet the specific environmental conditions of their installation sites. -
Tolerance Levels
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of lock parts. Precise tolerances are critical for ensuring that components fit together seamlessly, enhancing security and functionality. In B2B transactions, understanding tolerance levels can prevent costly adjustments or replacements due to compatibility issues. -
Locking Mechanism Type
– The type of locking mechanism—such as pin cylinder, deadbolt, or smart lock—determines the security level and ease of use. Each mechanism has unique strengths and weaknesses, and buyers must match these features to their specific security needs. A clear understanding of different mechanisms helps buyers make informed decisions based on risk assessments. -
Security Rating
– Many locks are rated according to industry standards, such as ANSI/BHMA (American National Standards Institute/Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association) or UL (Underwriters Laboratories). These ratings indicate the lock’s resistance to forced entry, wear, and other forms of tampering. Buyers should prioritize locks with high security ratings for critical applications to mitigate risks. -
Finish Type
– The finish of a lock, whether matte, polished, or coated, not only affects aesthetics but also plays a role in corrosion resistance and wear. Selecting the appropriate finish can enhance a product’s lifespan and ensure it maintains its appearance over time. This is particularly important for locks used in high-visibility areas.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Lock Diagrams?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are some commonly used terms in the lock industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the lock industry, buyers often seek OEMs for custom solutions or specific components that meet their unique requirements, ensuring compatibility and quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory and costs effectively. Negotiating a favorable MOQ can help businesses align their purchasing strategies with market demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Issuing an RFQ allows businesses to compare multiple suppliers efficiently and negotiate better deals, ensuring they receive competitive pricing on lock components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with lock procurement, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for a supplier to deliver goods after an order is placed. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure timely delivery of lock components, especially for projects with tight deadlines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right locks that meet their security needs and operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lock diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Lock Diagram Sector?
The lock diagram sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by global trends in security, technology, and consumer preferences. The increasing demand for enhanced security measures is a primary market driver, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The rise in urbanization and property development has led to a surge in the need for reliable locking systems. Additionally, the integration of smart technology in locking mechanisms is reshaping the landscape. Smart locks equipped with remote access, biometric features, and mobile compatibility are becoming increasingly popular, catering to both residential and commercial markets.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the adoption of cloud-based systems for managing lock security, allowing businesses to monitor and control access remotely. This trend is particularly relevant in sectors such as hospitality and commercial real estate, where security protocols are paramount. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has facilitated direct sourcing of lock components, enabling international buyers to access a wider array of products and suppliers.
International buyers must also be aware of the evolving regulatory landscape, including compliance with safety standards and certifications that vary by region. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers looking to establish partnerships and make informed purchasing decisions in the lock diagram sector.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Lock Diagram Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly vital considerations for international B2B buyers in the lock diagram sector. Environmental impact is a growing concern, with companies facing pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices throughout their supply chains. The production of locks often involves materials and processes that can be detrimental to the environment. Therefore, sourcing from suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or reducing waste in manufacturing, is becoming essential.

Illustrative image related to lock diagram
Buyers should seek out suppliers who hold ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 or LEED, which indicate a commitment to environmental management. Additionally, ethical sourcing ensures that the materials used in lock production are obtained responsibly, supporting fair labor practices and minimizing environmental degradation. By prioritizing sustainability, businesses not only enhance their brand reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Incorporating sustainability into procurement strategies can lead to cost savings over time through increased efficiency and reduced waste. Thus, B2B buyers in the lock diagram sector should actively evaluate their supply chains and consider the long-term benefits of sustainable and ethical sourcing practices.
What Is the Historical Context of the Lock Diagram Sector and Its Relevance Today?
The lock diagram sector has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where basic locking mechanisms were crafted from wood and simple materials. Over the centuries, advancements in metallurgy and engineering led to the development of more sophisticated locking systems, such as the pin cylinder lock, which remains one of the most common types used today.
The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as mass production techniques allowed for the widespread availability of locks, enhancing security in homes and businesses alike. The introduction of electronic and smart locks in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry, providing users with unprecedented control over their security systems.
Today, the evolution of locking mechanisms continues to be shaped by technological innovations, consumer preferences for convenience and security, and the need for sustainable practices. Understanding the historical context of the lock diagram sector provides B2B buyers with insights into current trends and future developments, enabling them to make informed decisions when sourcing products in this dynamic market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lock diagram
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with lock diagrams from different suppliers?
Compatibility issues can arise when integrating lock diagrams from various suppliers due to differences in design, dimensions, and locking mechanisms. To mitigate this, ensure that all suppliers provide detailed specifications and diagrams that include measurements and materials used. It’s also beneficial to conduct a compatibility assessment before finalizing orders. Collaborate closely with your suppliers to clarify any discrepancies and request sample products if necessary. Establishing a standard format for lock diagrams can streamline communication and prevent misunderstandings. -
What is the best lock type for commercial properties?
For commercial properties, deadbolt locks are often considered the best choice due to their robust security features. They are difficult to pick or break and provide a higher level of protection against forced entry compared to standard knob locks. Additionally, consider integrating smart locks that offer remote access and monitoring capabilities, which can enhance security and convenience. Always evaluate the specific security needs of your property and consult with experts to determine the best lock type suited for your environment. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing lock diagrams internationally?
To vet suppliers for lock diagrams, start by checking their reputation in the industry through online reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients and assess their experience with international shipping and compliance with local regulations. Additionally, review their certifications and quality assurance processes to ensure they meet international standards. A personal visit to the supplier’s facility can also provide insights into their operations and product quality. Establishing a clear communication channel will facilitate better collaboration and trust. -
What customization options should I look for in lock diagrams?
When sourcing lock diagrams, seek suppliers that offer customization options tailored to your specific requirements. This may include variations in size, materials, locking mechanisms, and finishes. Discuss your project needs in detail to ensure the supplier can accommodate your specifications. Additionally, inquire about the flexibility of design adjustments during the production process. A supplier that provides a range of customization options can help you achieve the desired functionality and aesthetic for your project. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lock products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lock products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of locks being ordered. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. To optimize costs, consider negotiating MOQs with suppliers, especially if you are planning to establish a long-term partnership. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time orders or if you agree to future orders. Always clarify MOQs before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by lock suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among lock suppliers, but common arrangements include net 30, net 60, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, particularly for large orders or custom products. It is essential to negotiate favorable payment terms that align with your cash flow management. Be sure to review any fees related to international transactions, such as currency conversion and bank charges. Establishing clear payment terms can prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my lock products?
To ensure quality assurance in your lock products, establish clear quality standards and specifications before placing orders. Request samples for evaluation to assess the material quality and locking mechanisms. Implementing regular quality checks during production can help identify issues early. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications such as ISO standards. Building a strong relationship with your supplier will enable better communication regarding quality expectations and any necessary adjustments. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing lock products?
When importing lock products, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping of hardware products to facilitate smooth logistics. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including import permits and customs declarations, is prepared in advance to avoid delays. Additionally, account for potential tariffs and taxes that may apply to your order. Planning for these logistics considerations will help streamline the import process and reduce the risk of unexpected complications.
Top 8 Lock Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pinterest – Understanding Door Lock Components
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Understanding the Parts Of A Door Lock: Each part is vital in keeping your family and belongings safe.
2. Sparx Systems – Lock Diagram Feature
Domain: sparxsystems.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Lock Diagram feature in Enterprise Architect allows users to protect a diagram from inadvertent changes such as moving or resizing elements. When a diagram is locked, any selected object on the diagram displays a red border or outline. Users can lock or unlock the diagram by right-clicking on the background and selecting the ‘Lock Diagram’ option. This feature is not applicable in the Corporate, U…
3. Lock Pick World – Essential Lock Pick Sets
Domain: lockpickworld.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Lock Pick Sets, Lock Picks, Beginner Lock Pick Sets, Dangerfield, Multipick, Lokko, Southord, Lockpickworld, Lishi, Goso, Peterson, Sparrows, Klom, Practice Locks, Clear Practice Locks, Metal Cutaway Locks, Lock Vices, Lock Pick Rakes, Tension Tools, Circular Tension Tools, Lock Pick Multi Tools, Tubular Lock Picks, Dimple Lock Picks, Lock Picking Accessories, Electric Lock Pick Guns, Manual Lock …
4. iStock – Lock Diagram Images
Domain: istockphoto.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 5.900+ Fotos, Bilder und lizenzfreie Bilder zu Lock Diagram – iStock Optionen und Preise Videos
5. Getty Images – Lock Diagram Stock Photos
Domain: gettyimages.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 491 Lock Diagram Stock Photos, High-Res Pictures, and Images available on Getty Images. Offers a variety of formats and styles, including exclusive visuals not found elsewhere. Access to millions of royalty-free images, videos, illustrations, and vectors. Features a user-generated content section and a digital asset management system. Provides options for custom content creation and AI-generated i…
6. Barry Bros – Security Solutions
Domain: barrybros.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Barry Bros Security offers a range of services and products related to locks and security systems, including:
– Lock Installations
– Lock Repairs & Replacements
– Key Duplication / Repairs
– Master Suited Locks & Keys
– Antique Locks & Keys
– Insurance Graded Security & Domestic Safes
– Electronic Locking Systems
– CCTV Surveillance Systems
– Access Control Systems
– Emergency Exit Compl…
7. Ford F150 – Door Lock Linkage Diagram
Domain: f150forum.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: door lock linkage diagram for 1997 – 2003 Ford F150; issues with lock cylinder and linkage; need for detailed diagram or pictures for proper reassembly; mention of bent rod causing malfunction; discussion of electric actuator not functioning properly; manual lock operation still works.
8. Ford – F250 Door Lock Wiring Solutions
Domain: ford-trucks.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 2016 Ford F250 door lock wiring issue; inside rocker switch, key fob, and keyless entry open all doors except driver’s door; replaced lock actuator; tested connections: Black, Black and yellow/purple tracer (opens all except driver’s), Yellow/purple tracer (8V), Blue/purple tracer (closes all including driver’s), Blue (8V); suspect wiring issue between rocker switch and driver’s door lock actuator…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lock diagram
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Lock Procurement Process?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing is essential for B2B buyers seeking high-quality lock solutions. Understanding the intricate components of door locks—such as cylinders, bolts, and smart technology—enables buyers to make informed decisions that prioritize security and durability. Emphasizing reliable suppliers who offer customizable products tailored to specific needs ensures that businesses not only enhance their security measures but also improve operational efficiency.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the long-term benefits of investing in robust lock systems. By prioritizing suppliers with a proven track record of innovation and quality, companies can mitigate risks associated with theft and unauthorized access, ultimately safeguarding their assets.
As the demand for advanced locking mechanisms grows, it’s crucial to stay ahead of market trends. Engage with reputable manufacturers and leverage their expertise to explore cutting-edge technologies such as smart locks that integrate seamlessly into modern infrastructures. Take the next step in securing your operations by investing in strategic sourcing for your lock solutions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to lock diagram