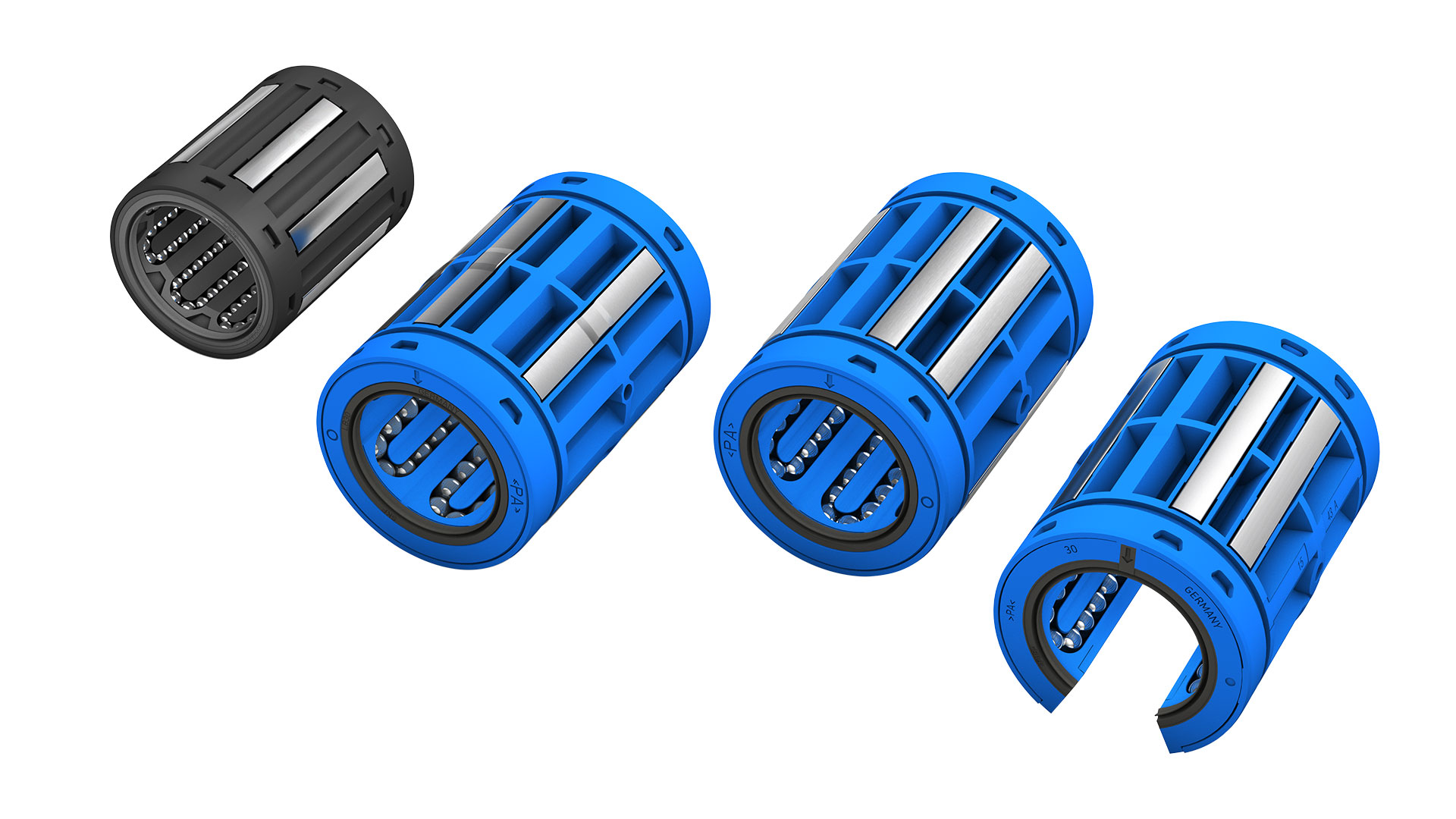
Linear Ball Bearings: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear ball bearings
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable linear ball bearings can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for precision and efficiency across various industries, understanding the nuances of linear ball bearing options is essential. This guide delves into the diverse types of linear ball bearings, their applications across sectors such as manufacturing, robotics, and automotive, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. By equipping buyers with insights on cost structures, performance characteristics, and global sourcing strategies, this comprehensive resource aims to streamline purchasing processes and enhance decision-making.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions characterized by distinct economic landscapes and manufacturing needs—this guide serves as an invaluable tool. It addresses the specific challenges faced by buyers in these markets, such as navigating import regulations and identifying quality suppliers that meet international standards. By focusing on actionable strategies and providing clarity on technical specifications, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals. Whether you are seeking to optimize production efficiency or ensure product reliability, understanding the global market for linear ball bearings is crucial to your success.
Understanding linear ball bearings Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Linear Ball Bearings | Basic design with a single row of balls; suitable for most applications. | General machinery, conveyors, robotics | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Double Linear Ball Bearings | Features two rows of balls for increased load capacity and stability. | Heavy machinery, automotive assembly | Pros: Higher load capacity, better for cantilevered loads. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Flanged Linear Ball Bearings | Includes a flange for easy mounting; ideal for constrained spaces. | Automation, packaging equipment | Pros: Simplified installation, stable alignment. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Linear Ball Bushings | Compact design with a cylindrical shape; allows for smooth linear motion. | CNC machines, 3D printers | Pros: Space-saving, precise motion. Cons: May require specific mounting conditions. |
| Closed Linear Ball Bearings | Sealed design to prevent contamination; suitable for harsh environments. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Enhanced durability, reduced maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Linear Ball Bearings?
Standard linear ball bearings consist of a single row of balls that roll between a track and a housing. They are widely used due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a range of applications, including general machinery and conveyor systems. When purchasing, businesses should consider their load requirements and operating speeds, as standard bearings may have limitations in high-load scenarios.
How Do Double Linear Ball Bearings Improve Performance?
Double linear ball bearings are designed with two rows of balls, significantly enhancing their load capacity and stability. This design is particularly beneficial in heavy machinery and automotive assembly applications where higher load support is necessary. Buyers should evaluate the specific load and speed requirements, as these bearings can handle cantilevered loads better than their single-row counterparts, albeit at a higher cost.
Why Choose Flanged Linear Ball Bearings for Tight Spaces?
Flanged linear ball bearings come equipped with a flange, allowing for easier mounting in confined spaces. This feature makes them ideal for automation and packaging equipment, where alignment and installation efficiency are crucial. Buyers should ensure that the flange design fits their application specifications, as this can limit versatility compared to non-flanged options.
What Advantages Do Linear Ball Bushings Offer in Precision Applications?
Linear ball bushings are compact, cylindrical bearings designed for smooth linear motion, making them perfect for applications like CNC machines and 3D printers. Their space-saving design allows for precise movement in tight configurations. Businesses should consider the mounting requirements and compatibility with their machinery when selecting these bearings, as they may necessitate specific installation conditions.
How Do Closed Linear Ball Bearings Enhance Durability?
Closed linear ball bearings feature a sealed design that protects internal components from contaminants, making them suitable for harsh environments such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. While they offer enhanced durability and require less maintenance, the initial investment may be higher than for open designs. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance against the upfront costs when making their selection.
Key Industrial Applications of linear ball bearings
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear ball bearings | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machining and Automation Systems | Enhanced precision and reduced friction, leading to improved operational efficiency. | Look for durable materials and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Robotics | Robotic Arm Movement and Positioning | Increased accuracy in movement, which enhances productivity and reduces errors. | Ensure bearings can handle dynamic loads and have low friction. |
| Packaging | Automated Packaging Machinery | Faster packaging speeds and reduced maintenance costs due to reliable performance. | Consider size, load capacity, and environmental resistance. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Equipment and Imaging Systems | Improved reliability and precision, critical for patient safety and operational efficiency. | Focus on sterilization compatibility and precision tolerances. |
| Textile Industry | Looms and Textile Machinery | Smooth operation and reduced wear, leading to longer equipment life and lower downtime. | Evaluate load ratings and compatibility with various textile processes. |
How Are Linear Ball Bearings Utilized in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, linear ball bearings are integral to CNC machining and automation systems. They enable smooth linear motion, which is crucial for precision tasks. By reducing friction, these bearings enhance the efficiency of machinery, allowing for faster production rates and less energy consumption. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing bearings made from durable materials, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of continuous operation and are compatible with existing equipment.
What Role Do Linear Ball Bearings Play in Robotics?
In robotics, linear ball bearings are essential for the movement and positioning of robotic arms. They facilitate accurate and controlled motion, which is vital for tasks such as assembly, welding, and material handling. The precision offered by these bearings minimizes errors, thus improving overall productivity. International buyers should focus on bearings that can handle dynamic loads and exhibit low friction, ensuring optimal performance in various robotic applications.
How Do Linear Ball Bearings Improve Packaging Operations?
Automated packaging machinery relies heavily on linear ball bearings to operate efficiently. These bearings allow for faster movement of packaging components, significantly reducing cycle times. The reliability of linear ball bearings leads to lower maintenance costs, as they require less frequent replacements. When sourcing for this application, businesses should consider the size and load capacity of the bearings, as well as their resistance to environmental factors like dust and moisture.
Why Are Linear Ball Bearings Critical in Medical Devices?
In the medical field, linear ball bearings are used in surgical equipment and imaging systems, where precision and reliability are paramount. These bearings ensure smooth movement, which is critical for the safe operation of devices that directly impact patient care. Buyers need to prioritize bearings that can withstand sterilization processes and meet strict precision tolerances to ensure patient safety and compliance with industry standards.

Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
How Do Linear Ball Bearings Benefit the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, linear ball bearings are utilized in looms and other textile machinery to ensure smooth operation and minimize wear and tear. This leads to longer equipment life and reduced downtime, which is essential for maintaining production efficiency. Buyers should evaluate the load ratings of bearings and ensure compatibility with various textile processes to optimize performance and reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘linear ball bearings’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Linear Ball Bearing Size
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate size of linear ball bearings for their specific applications. Sizing issues can lead to improper fitting, which may result in increased wear, frequent replacements, or even equipment failure. This challenge is often exacerbated when buyers are unfamiliar with the terminology or standards, leading to confusion between metric and imperial measurements. In regions like Africa or South America, where access to technical support may be limited, these sizing challenges can create significant operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To effectively address sizing issues, buyers should begin by thoroughly assessing their application requirements, including load capacity, speed, and environmental factors. It’s advisable to consult product catalogs and technical datasheets from reputable manufacturers that provide comprehensive sizing charts. Additionally, utilizing online configurators can simplify the selection process by allowing buyers to input specific parameters and receive recommendations tailored to their needs. Engaging with experienced suppliers for consultations can also help clarify any doubts regarding sizing and compatibility with existing systems, ensuring that the right linear ball bearings are sourced.
Scenario 2: High Friction and Noise Levels in Linear Motion Systems
The Problem: High friction and noise levels are common complaints among B2B buyers using linear ball bearings in their machinery. These issues can lead to decreased operational efficiency, increased energy consumption, and a less pleasant working environment. In sectors such as manufacturing and logistics, where precision and quiet operation are crucial, high friction can significantly hinder performance and result in costly downtime.

Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
The Solution: To mitigate friction and noise, buyers should look for linear ball bearings with low coefficients of friction and noise-dampening features. When sourcing these bearings, it is vital to choose products that utilize advanced materials, such as heat-treated alloy steel for durability and resin retainer polymer cages to minimize noise. Furthermore, implementing proper lubrication techniques, including the use of high-quality lubricants, can enhance performance and reduce friction. Regular maintenance checks are essential to ensure that the bearings remain well-lubricated and free from contaminants that could lead to increased wear or noise over time.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Quality and Reliability of Suppliers
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges related to inconsistent quality and reliability of suppliers when sourcing linear ball bearings. This inconsistency can manifest in product defects, variations in performance, and unreliable delivery schedules, which can disrupt production and lead to costly project delays. Buyers in regions with less robust supply chains, like parts of the Middle East and Africa, may find it particularly challenging to secure quality components consistently.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should prioritize establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who have a proven track record of quality and reliability. Conducting thorough due diligence, such as checking supplier certifications, customer reviews, and performance history, is essential. Additionally, buyers can request samples or conduct pilot tests before making large orders to verify the product quality. Engaging in open communication with suppliers about quality expectations and delivery timelines can also foster better collaboration. Finally, considering suppliers who provide warranties or guarantees on their products can serve as an additional layer of assurance for buyers, safeguarding their investments against potential quality issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear ball bearings
What Are the Common Materials Used in Linear Ball Bearings?
When selecting materials for linear ball bearings, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of linear ball bearings.
How Does Steel Impact Linear Ball Bearing Performance?
Steel is the most widely used material for linear ball bearings due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically exhibits high strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Steel bearings can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Steel bearings are robust and can handle heavy loads, which is beneficial in industrial settings. They also have a relatively low cost compared to other materials, making them an economical choice for bulk purchases.
Cons: While steel offers high strength, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated. This can be a significant drawback in humid or corrosive environments, which are common in regions like Africa and South America.
Impact on Application: Steel bearings are ideal for applications requiring high load capacity and durability, such as in manufacturing machinery. However, buyers must ensure that they are treated for corrosion resistance, especially in coastal or humid areas.
International Considerations: Buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. In regions like the Middle East, where humidity can be high, selecting stainless steel or coated variants is advisable.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Linear Ball Bearings?
Plastic bearings are becoming increasingly popular due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are often made from materials like acetal or nylon, which provide excellent chemical resistance.
Pros: Plastic bearings are lightweight, which can reduce the overall weight of machinery. They also operate quietly and are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for applications in wet or chemically aggressive environments.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic bearings is their lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel. They may also have a lower temperature tolerance, which can restrict their use in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic bearings are ideal for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and environments where moisture is prevalent. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify the compatibility of plastic materials with local regulations, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Standards such as FDA compliance may be necessary.
How Do Ceramic Bearings Enhance Performance in Linear Ball Bearings?
Ceramic materials, such as silicon nitride, are used in high-performance linear ball bearings. These materials are known for their exceptional hardness and low density.
Pros: Ceramic bearings offer excellent wear resistance and can operate at higher temperatures than steel or plastic. They are also non-corrosive, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
Cons: The primary drawback is their high cost, which can be a barrier for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, ceramic bearings can be brittle, making them susceptible to impact damage.
Impact on Application: Ceramic bearings are well-suited for applications in aerospace, automotive, and high-speed machinery where performance is critical. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them a preferred choice for specialized applications.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that ceramic bearings meet relevant international standards, particularly in high-tech industries. Compliance with standards such as JIS or ISO can enhance marketability in regions like Europe and Japan.
What Benefits Does Bronze Offer in Linear Ball Bearings?
Bronze bearings are often used in applications requiring high wear resistance and low friction. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and marine applications.
Pros: Bronze bearings provide excellent durability and are resistant to corrosion, especially in seawater environments. They also have good load-bearing capabilities.
Cons: The main limitation is the higher cost compared to steel, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, bronze bearings may require more frequent lubrication than other materials.
Impact on Application: Bronze bearings are ideal for marine applications and heavy machinery where durability and corrosion resistance are paramount. They are often used in environments where steel would corrode quickly.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider local standards for bronze materials, particularly in marine applications. Compliance with ASTM standards can ensure quality and reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Linear Ball Bearings
| Material | Typical Use Case for Linear Ball Bearings | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower load capacity | Low |
| Ceramic | Aerospace, automotive, high-speed machinery | Excellent wear resistance | High cost and brittleness | High |
| Bronze | Marine applications, heavy machinery | Corrosion-resistant and durable | Higher cost and lubrication needs | Medium |
This guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding the material selection for linear ball bearings, taking into account their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear ball bearings
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Linear Ball Bearings?
Manufacturing linear ball bearings involves several critical stages, ensuring high-quality products that meet industry specifications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Treatment
The manufacturing process begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically alloy steels known for their strength and durability. Suppliers must adhere to international material standards to ensure consistency. Once the materials are sourced, they undergo heat treatment processes to enhance their mechanical properties, such as hardness and wear resistance. This step is vital as it directly impacts the performance and lifespan of the bearings.
Forming: Precision Engineering Techniques
In the forming stage, techniques such as forging, machining, and grinding are employed. Forging shapes the steel into rough bearing components, which are then precision machined to meet exact specifications. High-precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are used to achieve tight tolerances, critical for proper functioning. After machining, components like inner and outer races are ground to ensure smooth surfaces, which reduce friction during operation.
Assembly: Ensuring Functional Integrity
The assembly process involves fitting the components together, which may include the insertion of balls, seals, and retainers. This stage often utilizes automated assembly systems to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Quality checks during assembly are essential to verify that each bearing meets design specifications before moving on to the next stage. This may include visual inspections and functional tests to ensure proper alignment and fit.
Finishing: Surface Treatments and Final Inspections
Finishing processes such as coating and polishing enhance the bearings’ surface properties, providing additional protection against corrosion and wear. Various treatments, including anodizing and plating, are applied based on the intended application. After finishing, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that each bearing meets the required specifications, including dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Linear Ball Bearings?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, especially for linear ball bearings used in various applications worldwide. Adhering to international standards is essential for ensuring product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Key International Standards: ISO and Industry-Specific Certifications
ISO 9001 is one of the most widely recognized quality management standards, applicable to manufacturing processes across industries. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant, depending on the application of the bearings. CE certification is crucial for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For applications in the oil and gas industry, API certification ensures that products meet stringent performance and safety criteria.
Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
How Do Quality Control Checkpoints Function in Linear Ball Bearing Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with multiple checkpoints established to ensure product integrity throughout production.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
The IQC phase involves inspecting raw materials and components upon receipt. This includes verifying material certificates, conducting dimensional checks, and performing hardness tests. Any non-conforming materials are rejected to prevent defects in the final product.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During manufacturing, IPQC focuses on monitoring the production process. This includes regular inspections at various stages, such as after machining and assembly. Techniques like statistical process control (SPC) may be utilized to identify trends and variations, allowing for immediate corrective actions to minimize defects.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is the last checkpoint before products are shipped. This stage involves comprehensive testing, including dimensional inspections, functional tests, and performance evaluations. Common testing methods include load testing and noise testing to ensure bearings operate smoothly under specified conditions. Certificates of compliance are often generated to document adherence to quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One effective way to verify a supplier’s quality control measures is through on-site audits. This allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and overall operational capabilities. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the effectiveness of IQC, IPQC, and FQC practices, as well as review documentation related to quality certifications.
Requesting Quality Reports and Certifications
Buyers should also request quality reports and certifications from suppliers. These documents should detail compliance with international standards, results from quality tests, and any third-party inspections conducted. Certifications like ISO 9001, CE, and API provide additional assurance of product quality.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can conduct random inspections, testing, and audits, giving buyers peace of mind regarding the quality of their purchases.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, particularly when sourcing from different regions. Understanding local regulations, quality standards, and supplier capabilities is essential.
Regional Variations in Standards
Quality standards may vary significantly across different regions. For example, while ISO standards are globally recognized, specific industries may have additional local requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional standards to ensure compliance and suitability for their markets.
Cultural Considerations in Quality Practices
Cultural differences can also influence quality practices. For instance, communication styles and approaches to problem-solving may vary. Building strong relationships with suppliers and fostering open communication can help bridge these gaps and ensure alignment on quality expectations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with linear ball bearings, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers who meet their quality standards and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘linear ball bearings’
Introduction
Sourcing linear ball bearings effectively is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of machinery and equipment in various industries. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, from defining specifications to selecting the right supplier. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Consider factors such as load capacity, inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and material composition. This clarity will help you communicate your requirements to suppliers and ensure you receive products that meet your operational demands.
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum load the bearings will support.
- Dimensions: Specify the exact ID and OD needed for compatibility with existing systems.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Understanding current market trends and industry standards is essential for making informed choices. Familiarize yourself with the latest technologies, materials, and innovations in linear ball bearings. This knowledge will help you identify high-quality products and avoid outdated or less efficient options.
- Industry Standards: Review ISO or JIS standards applicable to your region to ensure compliance.
- Emerging Technologies: Explore advancements like low-friction materials or enhanced sealing techniques.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This will not only help you gauge their reliability but also provide insight into their product quality and customer service.
- Supplier Certifications: Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance credentials.
- Customer Feedback: Look for reviews and testimonials that highlight a supplier’s performance and service reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the linear ball bearings you intend to purchase. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality, durability, and performance of the bearings in your specific application. This step can prevent costly mistakes later on.
- Performance Testing: Assess how well the samples perform under expected load and environmental conditions.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure that the samples fit seamlessly with your existing machinery.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and validated the product quality, it’s time to negotiate terms and pricing. Discuss bulk order discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules to secure a favorable deal. Effective negotiation can lead to long-term partnerships and better pricing structures.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about price breaks for larger orders.
- Payment Flexibility: Explore options for payment terms that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
After securing a supplier, ensure that they offer robust after-sales support and warranty options. This is essential for addressing any potential issues post-purchase and for maintaining operational efficiency. A reliable support system can save time and resources in the long run.
Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
- Support Availability: Confirm the accessibility of technical support and customer service.
- Warranty Terms: Review warranty policies to understand coverage and claims processes.
Step 7: Place Your Order and Monitor Delivery
With all specifications, negotiations, and support systems in place, proceed to place your order. Monitor the delivery process closely to ensure that the products arrive on time and in good condition. Effective communication with the supplier during this phase can help resolve any potential issues swiftly.
- Tracking: Use tracking systems to stay updated on the shipment status.
- Inspection Upon Arrival: Immediately inspect the bearings upon delivery to verify they meet your specifications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear ball bearings Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Linear Ball Bearings Sourcing?
When sourcing linear ball bearings, understanding the underlying cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the price. High-quality steel, polymer cages, and advanced seal technologies contribute to higher costs but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are incurred during the manufacturing process. Skilled labor may command higher wages but can lead to better quality control and precision in production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses, which are proportionally allocated to the production of bearings.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific bearing designs or sizes can add to the initial costs. Standardized tooling generally reduces expenses but may limit customization options.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and inspection processes adds to the overall cost but is crucial for maintaining performance and reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling expenses can vary based on the origin of the bearings, shipping method, and destination. International shipping may incur additional customs duties and taxes.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Linear Ball Bearings Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of linear ball bearings:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs, special materials, or specific performance characteristics can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials can significantly affect pricing. Premium materials may offer better performance but come at a higher cost.
-
Quality Certifications: Bearings that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO, JIS) may carry a premium price. Buyers should evaluate whether such certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (such as FOB, CIF) is essential. These terms affect the final cost and responsibilities for buyers, especially in international transactions.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency in Sourcing Linear Ball Bearings?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can benefit from several strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Understanding the cost structure allows buyers to challenge unreasonable prices or request discounts based on order volume.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, performance, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality bearings can result in lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of potential currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and shipping delays that may affect overall costs. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid reliance on a single supplier. Diversifying your supplier base can enhance bargaining power and provide alternatives in case of supply chain disruptions.
-
Request for Quotation (RFQ): When sourcing, send out RFQs to multiple suppliers to compare prices and terms. This practice can reveal competitive pricing and help in negotiations.
Conclusion
While indicative prices for linear ball bearings can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors, understanding the cost structure and price influencers is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging negotiation tactics and evaluating the total cost of ownership, international buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies, ensuring they obtain the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing linear ball bearings With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Linear Ball Bearings: Key Comparisons
In the realm of linear motion systems, linear ball bearings serve a crucial role in providing smooth movement and reduced friction. However, various alternative solutions also exist, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. This analysis will delve into how linear ball bearings stack up against two notable alternatives: linear roller bearings and plain bearings. Understanding these alternatives can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Linear Ball Bearings | Linear Roller Bearings | Plain Bearings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and low friction; handles cantilever loads effectively. | Higher load capacity; better suited for heavy-duty applications. | Moderate performance; suitable for light loads. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost due to advanced materials and design. | Comparable to linear ball bearings, but can vary based on size and load capacity. | Lower cost, often the most economical option. |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires precise alignment during installation. | Similar to ball bearings; some designs may require more space. | Easy installation; minimal alignment needed. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance but needs periodic lubrication to maintain performance. | Requires lubrication; maintenance intervals depend on load conditions. | Minimal maintenance; typically self-lubricating options available. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications requiring high precision and speed, such as automation. | Best for heavy machinery and industrial applications where high loads are common. | Suited for low-speed, low-load applications, such as in simple machinery. |
What Are Linear Roller Bearings and What Are Their Advantages?
Linear roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers instead of balls, enabling them to handle higher loads. This design reduces contact area, leading to lower friction and enhanced load capacity. They are particularly advantageous in applications involving heavy machinery, where durability and strength are paramount. However, their installation can be more complex due to the need for precise alignment. While they may be comparable in cost to linear ball bearings, their performance in high-load situations makes them a worthy alternative.
What Are Plain Bearings and What Are Their Key Features?
Plain bearings, also known as bushings, provide a simpler design without any rolling elements. They rely on sliding motion and can be made from various materials, including plastics and metals. The primary advantage of plain bearings is their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, making them suitable for low-speed, low-load applications. However, they tend to have higher friction compared to ball or roller bearings, which can limit their effectiveness in precision applications. Their low maintenance requirements and availability in self-lubricating materials make them an appealing option for certain scenarios.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between linear ball bearings, linear roller bearings, and plain bearings, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, including load capacity, operating speed, and environmental factors. Understanding the trade-offs in performance, cost, and maintenance can guide buyers toward the most suitable solution for their operations. For high-precision and speed applications, linear ball bearings are often preferred, while linear roller bearings excel in heavy-duty contexts. Conversely, for budget-sensitive projects with minimal performance demands, plain bearings may provide the best value. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can ensure they choose the right bearing solution to enhance efficiency and reliability in their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear ball bearings
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Linear Ball Bearings?
Understanding the technical specifications of linear ball bearings is crucial for B2B buyers as these properties directly influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential technical properties to consider:
Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
1. Material Grade
Linear ball bearings are typically made from high-grade materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum. The choice of material affects the bearing’s strength, corrosion resistance, and overall lifespan. For instance, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in humid or chemically aggressive environments. B2B buyers should assess the material grade based on their application needs and environmental conditions.
2. Inner Diameter (ID) and Outer Diameter (OD)
The inner and outer diameters are critical measurements that determine the compatibility of the bearing with shafts and housing. A precise fit minimizes play and ensures smooth operation, which is vital in high-speed applications. Buyers must ensure that the bearing dimensions align with their machinery specifications to avoid operational inefficiencies.
3. Load Capacity
The load capacity indicates the maximum load a bearing can withstand without failure. This property is essential for applications involving heavy loads or dynamic movements. Buyers should evaluate the static and dynamic load ratings to ensure the selected bearing can handle the operational demands without risk of failure, which can lead to costly downtimes.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the bearing’s dimensions. Tight tolerances lead to better performance and reduced friction, while loose tolerances can result in wear and premature failure. For B2B buyers, selecting bearings with the right tolerance levels is crucial to achieving the desired performance and longevity in their applications.
5. Coefficient of Friction
This property measures the resistance to motion between two surfaces in contact. A lower coefficient of friction means less energy loss and reduced wear, which is vital for efficient operation, especially in high-speed applications. Understanding this property helps buyers choose bearings that enhance machine efficiency and reduce operational costs.
6. Sealing Mechanism
Many linear ball bearings come with seals or shields that protect against contaminants. The type of sealing mechanism affects the bearing’s lifespan and maintenance requirements. B2B buyers should consider whether they need sealed or open bearings based on their operational environment, as sealed bearings typically require less maintenance and provide better durability.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Linear Ball Bearing Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are several common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of linear ball bearings, buyers should ensure that they are sourcing from reputable OEMs to guarantee quality and compatibility with their machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory levels and cash flow. Depending on the supplier, MOQs can vary widely, so it’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your purchasing needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for a price quote for specific products or services. B2B buyers should use RFQs to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for understanding shipping, risk, and costs associated with international purchases of linear ball bearings.
5. Tolerance Grade
This term refers to the precision of the bearing’s dimensions. Different tolerance grades can affect the performance and compatibility of bearings in various applications. Buyers should ensure that the tolerance grade meets their operational specifications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing linear ball bearings, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications and business needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the linear ball bearings Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Linear Ball Bearings Sector?
The linear ball bearings market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation and precision in various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and robotics. As global industries strive for greater efficiency, the need for reliable linear motion solutions has become paramount. Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are shaping sourcing strategies, encouraging international B2B buyers to seek advanced linear ball bearings that offer enhanced performance and compatibility with automated systems.
In regions such as Africa and South America, economic growth and industrialization are boosting the demand for linear bearings in diverse applications, from manufacturing to agricultural machinery. Meanwhile, in the Middle East and Europe, there is a strong emphasis on high-quality standards and innovative designs. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide customizable solutions to meet specific operational needs. Additionally, the trend towards digitalization in procurement processes is becoming prominent, with many businesses adopting e-commerce platforms and digital sourcing tools to streamline their operations.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Linear Ball Bearings Market?
Sustainability is no longer just a trend but a fundamental requirement in B2B sourcing, and the linear ball bearings sector is no exception. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste throughout the supply chain.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses recognize the importance of transparency in their supply chains. Buyers are increasingly seeking manufacturers that provide certifications for sustainability, such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management. Furthermore, the adoption of “green” materials in linear ball bearings, such as recyclable plastics and low-emission metals, is becoming a key differentiator for suppliers aiming to attract environmentally-conscious buyers.
How Has the Linear Ball Bearings Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of linear ball bearings dates back to the early 20th century when the need for precise motion control in machinery began to rise. Initially, these bearings were rudimentary, primarily made from basic materials. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have led to the development of high-performance linear ball bearings that offer improved load capacities, lower friction, and greater durability.
The introduction of digital technologies has further transformed the sector, enabling manufacturers to create more sophisticated bearing designs that cater to the specific needs of industries such as aerospace, automotive, and robotics. As the demand for automation continues to grow, the linear ball bearings market is poised for continuous innovation and expansion, making it crucial for international B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest trends and sourcing opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear ball bearings
-
1. How do I select the right linear ball bearing for my application?
Choosing the right linear ball bearing involves assessing several factors including load capacity, speed requirements, and environmental conditions. First, determine the type of load (static or dynamic) and its magnitude. Next, consider the operational speed and any potential contamination in the environment. Finally, consult manufacturer specifications for dimensional accuracy and compatibility with your existing systems. If necessary, seek guidance from suppliers who can offer recommendations based on your specific application needs. -
2. What are the benefits of using double linear ball bearings?
Double linear ball bearings offer enhanced load distribution and stability, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision and minimal friction. They can handle higher cantilevered loads compared to standard bearings, effectively overcoming the limitations of plain bearings. Additionally, the double-sealed design provides added protection against contaminants, which is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity in challenging environments. -
3. What are common materials used in the manufacturing of linear ball bearings?
Linear ball bearings are typically made from materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and various polymers. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and durability, while carbon steel is often chosen for its strength and affordability. Polymer components, like retainer cages, can reduce noise and friction. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the operational environment and specific application requirements, such as exposure to moisture or chemicals. -
4. How can I verify the quality of linear ball bearings from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of linear ball bearings, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to your application. Conducting supplier audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider requesting samples for testing before placing larger orders, and consult customer reviews or case studies to gauge their reliability and performance in similar applications. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for linear ball bearings?
Minimum order quantities for linear ball bearings can vary significantly between suppliers, ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on the manufacturer’s policies and the type of bearing. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to determine if they can accommodate smaller orders or offer flexibility, especially if you are testing new applications or entering a new market. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing linear ball bearings internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of linear ball bearings often include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. The terms can depend on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. It is essential to negotiate these terms upfront and ensure clarity on currency exchange rates, potential additional fees, and any payment security measures that can protect your transaction. -
7. How can I handle logistics and shipping for international orders of linear ball bearings?
When sourcing linear ball bearings internationally, consider engaging a freight forwarder who can manage logistics, customs clearance, and shipping arrangements. Ensure that you understand the shipping methods available, such as air or sea freight, and their respective costs and delivery times. Additionally, verify that the supplier provides appropriate packaging to prevent damage during transit, and discuss who will bear the shipping costs and responsibilities. -
8. What customization options are available for linear ball bearings?
Many suppliers offer customization options for linear ball bearings, including modifications to dimensions, materials, and sealing types. This can be crucial for meeting specific application requirements. When inquiring about customization, provide detailed specifications and discuss your needs with the supplier. Be prepared to discuss lead times and any implications for cost, as customized bearings may take longer to manufacture and could come with higher prices.
Top 7 Linear Ball Bearings Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bearings Direct – Linear Ball Bearings
Domain: bearingsdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Bearings Direct – Linear Ball Bearings, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. PBC Linear – Double Linear Ball Bearings
Domain: pbclinear.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Double Linear Ball Bearings are extended-length ball bearings featuring a steel outer cylinder, ball retainer, balls, and two double seals. Available in inch, metric, and JIS sizing options, they are fully interchangeable with industry standards and the Simplicity series. ID sizes range from 0.25 in to 2 in or 8 mm to 50 mm. Housed in an aluminum casing, the double size is equivalent to two standa…
3. McMaster – Mounted Linear Bearings
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Mounted Linear Bearings, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Schaeffler – Linear Ball Bearing Assemblies
Domain: schaeffler.us
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Linear ball bearing and guideway assemblies are part of the monorail guidance systems, designed for high load-carrying capacity and rigidity, enabling the movement of heavy loads with high running and positional accuracy and low friction. They are preloaded and suitable for long, unlimited stroke lengths, with acceleration values up to 150 m/s² and speeds up to 360 m/min. The system includes at le…
5. Servocity – Linear Ball Bearings
Domain: servocity.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Linear ball bearings (also known as ball bushings or shaft guiding) consist of a polymeric cage with hardened steel raceway segments to guide ball sets. They provide unlimited stroke and low friction movement, powered by a drive mechanism, inertia, or manually. Available sizes include: 6mm ID x 12mm OD, 8mm ID x 15mm OD, and 12mm ID x 21mm OD. Compatible with stainless steel shafting of the same s…
6. Thomson – Linear Bearings & Guides
Domain: thomsonlinear.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Thomson offers a wide selection of linear bearings including Ball Bushing® Bearings, RoundRail Shafting, and various types of linear guides. Key features include:
– Super Smart Ball Bushings with load capacities up to 7760 lb.
– Self-aligning design for ultra-smooth travel on wider-toleranced surfaces.
– Increased lifespan (up to 50% longer) when used with Thomson 60 Case® shafting.
– Availabl…
7. VXB – Linear Motion Systems
Domain: vxb.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Linear Motion Systems – 1 inch (1″) – Wide Selection. Free Shipping to All US States on All Non-Freight Orders! $10 Minimum Order. Address: 2165 S. Dupont Dr Ste F Anaheim CA 92806 US.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear ball bearings
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of linear ball bearings is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. By prioritizing quality and reliability, businesses can ensure that their machinery operates smoothly and effectively, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Understanding the diverse range of options available—including double linear ball bearings—allows buyers to select products that meet specific performance requirements, such as load capacity and noise reduction.
Furthermore, as global supply chains continue to evolve, international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must remain vigilant in sourcing materials that not only comply with local standards but also offer competitive pricing. Leveraging strong supplier relationships and negotiating favorable terms can significantly impact the bottom line.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-performance linear ball bearings will only grow as industries prioritize innovation and efficiency. International buyers are encouraged to engage with trusted suppliers, explore advanced materials, and invest in solutions that align with their long-term operational goals. By doing so, they can position themselves to thrive in an increasingly interconnected market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to linear ball bearings
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.