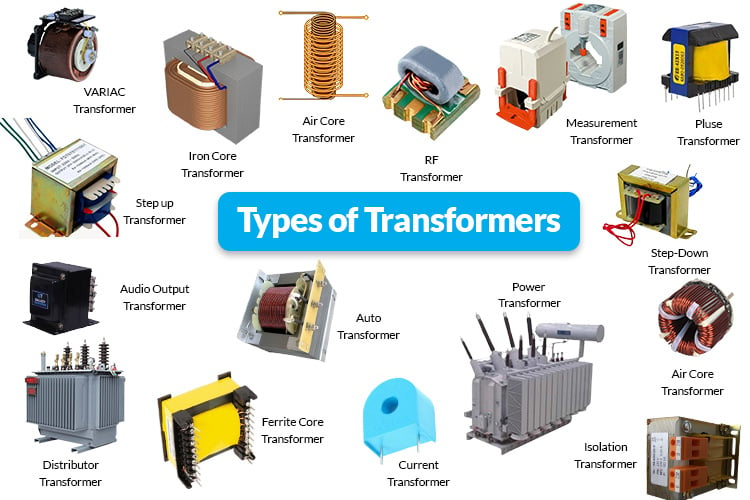
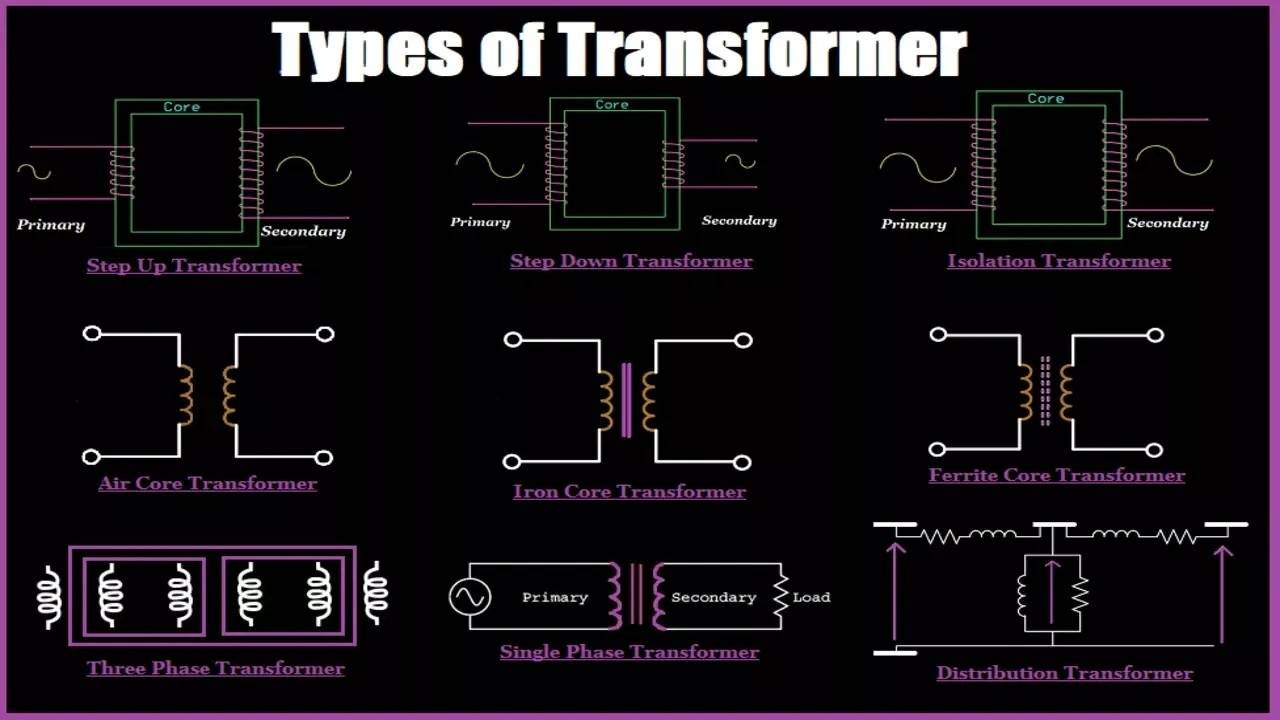
Kinds Of Transformer Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for kinds of transformer
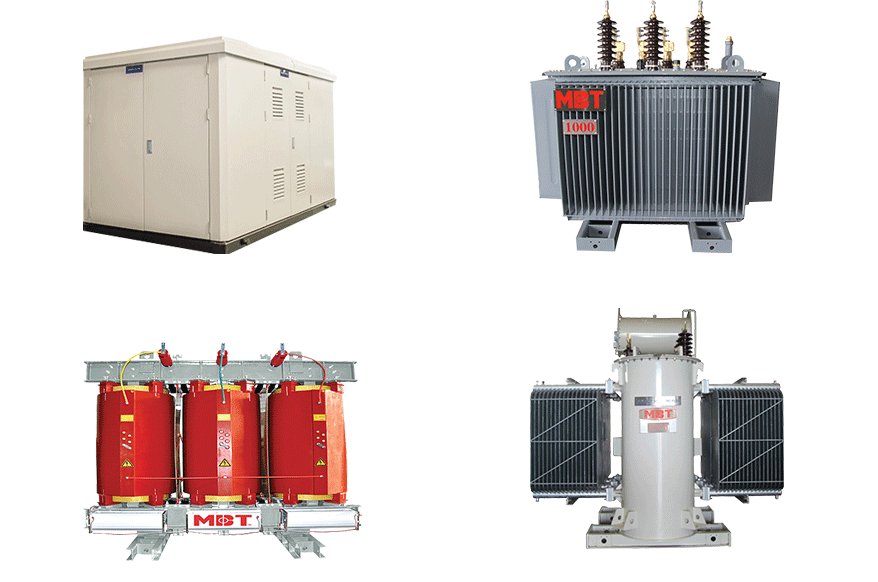
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right kinds of transformers is a pivotal challenge for B2B buyers across various industries. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the need for reliable and efficient electrical solutions has never been more critical. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the diverse types of transformers available in the global market, including liquid-filled, dry-type, padmount, and substation transformers, among others. Each type serves specific applications, and understanding these distinctions is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the complexities of transformer selection involves not only identifying the right type for your needs but also vetting suppliers, assessing costs, and ensuring compliance with international standards. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by providing insights into the applications and benefits of each transformer type, along with practical tips for evaluating suppliers and managing procurement processes. By leveraging this information, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and ultimately reduce costs, all while ensuring they meet the unique demands of their respective markets.
With a focus on actionable insights and industry best practices, this resource is designed to help you make strategic decisions that align with your operational goals and investment strategies. Whether you are based in bustling cities or remote regions, understanding the global transformer market will equip you with the knowledge needed to drive your business forward.
Understanding kinds of transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid-Filled Transformers | Use of dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation | Outdoor installations, industrial settings | Pros: Better heat dissipation, suitable for overloads. Cons: Requires containment, not ideal for indoor use. |
| Dry-Type Transformers | Air-cooled, no fluid, designed for indoor applications | Commercial buildings, data centers | Pros: No leakage concerns, easier maintenance. Cons: Less effective under overload conditions. |
| Padmount Transformers | Tamper-proof, compact design, often green for camouflage | Urban environments, public areas | Pros: Economical, easy installation. Cons: Limited to lower voltage applications. |
| Substation Transformers | Rugged design, external monitoring devices, high capacity | Heavy industrial areas, power distribution | Pros: High durability, suitable for large-scale operations. Cons: More complex installation and maintenance. |
| Autotransformers | Single coil design, cost-effective for small voltage changes | Voltage regulation in various applications | Pros: Compact, economical. Cons: Limited isolation, not suitable for all applications. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Liquid-Filled Transformers?
Liquid-filled transformers utilize a dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation, making them particularly effective in outdoor and industrial applications. Their sealed tank design allows them to handle environmental challenges, including temperature fluctuations and overload scenarios. When considering a liquid-filled transformer, buyers should assess the installation environment and determine if the benefits of enhanced cooling and overload capacity outweigh the need for additional containment measures.
How Do Dry-Type Transformers Differ and Where are They Best Used?
Dry-type transformers are designed for indoor applications, relying on air for cooling without the use of insulating fluids. This makes them a popular choice for commercial buildings and data centers, where the risk of fluid leakage is a concern. Buyers should consider the thermal management capabilities of dry-type transformers, especially in high-temperature environments, and evaluate their performance under standard loading conditions versus overload situations.
What Makes Padmount Transformers Ideal for Urban Installations?
Padmount transformers are compact, tamper-proof units designed for outdoor use, often found in urban settings. Their low-profile design allows them to blend into the environment, making them suitable for public areas like parks and campuses. When purchasing padmount transformers, buyers should consider their voltage requirements and the economic benefits of these transformers, balanced against their limitations in handling higher voltage applications.
Why Choose Substation Transformers for Heavy Industrial Applications?
Substation transformers are built with rugged designs to withstand the demands of heavy industrial applications. They often feature external monitoring devices and can handle high capacities, making them essential for power distribution networks. Buyers must weigh the complexity of installation and maintenance against the robustness and reliability offered by substation transformers, particularly in environments where other equipment may be present.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Autotransformers?
Autotransformers feature a single coil design that provides a cost-effective solution for voltage regulation, especially when only minor adjustments are needed. They are commonly used in various applications where space and budget constraints are critical. However, buyers should be aware that autotransformers lack isolation between primary and secondary circuits, which may limit their applicability in sensitive environments where electrical isolation is paramount.
Key Industrial Applications of kinds of transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of kinds of transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Utilities | Substation Transformers | Enhance grid reliability and manage high voltage distribution | Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards; consider load capacity and environmental conditions. |
| Manufacturing | Dry-Type Transformers in industrial plants | Improve energy efficiency and reduce maintenance costs | Look for durability and cooling methods suitable for the facility’s environment; assess size and weight constraints. |
| Construction | Padmount Transformers for temporary power supply | Provide reliable power in remote job sites | Evaluate ease of transport and installation; consider weather resistance and capacity for overload scenarios. |
| Telecommunications | Pole Mount Transformers for telecom networks | Support reliable communication infrastructure | Consider compatibility with existing infrastructure; focus on voltage ratings and environmental resilience. |
| Data Centers | Drive-Isolation Transformers for server operations | Protect sensitive equipment from electrical disturbances | Assess harmonic handling capabilities; ensure appropriate K-rating and thermal management features. |
How Are Substation Transformers Beneficial in the Energy Sector?
Substation transformers play a critical role in the energy and utilities sector by stepping down high voltages from transmission lines for distribution. They enhance the reliability of the power grid, ensuring that energy is delivered efficiently to residential and commercial consumers. For international buyers, especially in regions with developing infrastructure, sourcing transformers that comply with local regulatory standards and can withstand environmental challenges is crucial. These transformers must also have adequate load capacity to handle peak demands.
What Role Do Dry-Type Transformers Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing facilities, dry-type transformers are essential for stepping voltage up or down to meet specific equipment requirements. Their design allows for installation in indoor environments, minimizing the risk of leaks and enhancing safety. Businesses benefit from improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs due to their robust construction. Buyers should focus on the transformer’s cooling methods and durability, ensuring they meet the operational demands of their facilities while adhering to safety standards.

Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
How Do Padmount Transformers Support Construction Projects?
Padmount transformers provide a reliable temporary power supply at construction sites, where access to the grid may be limited. Their compact and tamper-proof design allows for easy installation in public areas without compromising safety. This is particularly valuable in remote locations. When sourcing padmount transformers, companies should consider their transportability, installation requirements, and ability to handle overload scenarios, especially in regions prone to extreme weather conditions.
Why Are Pole Mount Transformers Important for Telecommunications?
Pole mount transformers are vital for telecommunications networks, as they step down voltage for distribution to residential and commercial areas. Their design allows for efficient installation on utility poles, making them an ideal solution for urban and suburban settings. For B2B buyers, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and focusing on environmental resilience are key considerations. Proper voltage ratings are also essential to maintain the integrity of communication systems.
How Do Drive-Isolation Transformers Protect Data Centers?
Drive-isolation transformers are specifically designed for data centers that operate sensitive equipment, such as servers and storage systems. These transformers mitigate electrical disturbances by providing a stable power supply, which is crucial for preventing downtime and protecting data integrity. Buyers should evaluate the harmonic handling capabilities and ensure the transformers have a suitable K-rating for their operational environment. Thermal management features are also vital to maintain performance in high-load scenarios.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘kinds of transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Transformer for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the daunting task of selecting the appropriate transformer type for their specific applications. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Germany may require a transformer to step down voltage for heavy machinery, while a construction company in South America might need a transformer that can withstand outdoor elements. Misjudging the requirements can lead to equipment inefficiency, increased operational costs, and potential safety hazards.
Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
The Solution: To effectively source the right transformer, buyers should start by conducting a comprehensive needs assessment. This includes evaluating the voltage requirements, environmental conditions, and load capacity. Engaging with manufacturers who specialize in various transformer types—such as liquid-filled for outdoor use or dry-type for indoor environments—can provide insights into the best options available. Additionally, utilizing online resources, such as manufacturer catalogs and case studies, can help visualize how different transformers perform under specific conditions. Collaborating with engineers or technical consultants during the selection process ensures that the chosen transformer aligns with both operational needs and safety regulations.
Scenario 2: Managing Overheating Issues in Transformers
The Problem: Overheating is a prevalent issue that B2B buyers encounter, especially in regions with high ambient temperatures, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East. An overheating transformer can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear and tear, and even catastrophic failures. For example, a utility company in a hot climate might find that their substation transformers frequently trip, causing service interruptions and loss of revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate overheating risks, buyers should consider selecting transformers with higher insulation ratings or ones specifically designed for high-temperature environments. Implementing cooling solutions, such as external fans or heat exchangers, can also enhance the cooling efficiency of transformers. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring systems should be established to track temperature levels and performance metrics. Investing in smart transformers with built-in diagnostics can alert operators to potential overheating before it escalates into a serious problem, ensuring uninterrupted service and prolonged equipment life.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Local Regulations and Standards
The Problem: Navigating the complex landscape of local regulations regarding electrical equipment can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. For instance, a company in Europe may struggle to ensure that their transformers comply with stringent EU standards, while a buyer in South America might face different local codes that affect installation and operation. Non-compliance can lead to costly fines, project delays, and safety violations.

Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
The Solution: To ensure compliance, buyers should proactively engage with local regulatory bodies and familiarize themselves with applicable standards before purchasing transformers. Partnering with manufacturers who have experience in the target market can provide valuable insights into compliance requirements. Additionally, buyers should seek transformers that come with certification from recognized standards organizations, ensuring that they meet safety and efficiency criteria. Conducting a thorough review of installation and operational guidelines, as well as arranging for regular audits, can further safeguard against compliance issues. This proactive approach not only mitigates risk but also enhances the overall reputation of the business in the marketplace.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for kinds of transformer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Transformers and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for transformers, it is crucial to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in transformer construction: copper, aluminum, silicon steel, and resin. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly influence the performance and application of transformers.
How Does Copper Impact Transformer Performance?
Copper is a widely used conductor in transformer windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments. The key advantage of copper is its ability to handle higher loads with lower resistance, which translates to better efficiency and reduced energy losses.
However, copper is more expensive than aluminum, which can be a significant drawback for large-scale projects where cost efficiency is paramount. Additionally, its weight can complicate manufacturing and installation processes, particularly in regions where transportation infrastructure may be lacking.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, the high cost of copper may necessitate careful budgeting and consideration of local market conditions. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially for projects involving high-voltage applications.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Transformer Design?
Aluminum is another popular choice for transformer windings, particularly in low-voltage applications. It is lighter and less expensive than copper, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity compared to copper, which can lead to higher operating temperatures under heavy loads.
The primary disadvantage of aluminum is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in humid environments. This can affect the longevity and reliability of transformers, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions. Buyers should consider protective coatings or alloys that enhance corrosion resistance when selecting aluminum.
For buyers in regions like the Middle East, where humidity can be high, understanding the local climate’s impact on aluminum’s performance is critical. Adhering to international standards for aluminum transformers can also help ensure product quality and reliability.
How Does Silicon Steel Enhance Transformer Efficiency?
Silicon steel is commonly used in the core of transformers due to its magnetic properties. It provides low hysteresis loss and high permeability, which are crucial for efficient energy transfer. Silicon steel can operate effectively at high temperatures and is resistant to oxidation, making it suitable for various applications.
While silicon steel enhances efficiency, it is more expensive than traditional steel and can be more complex to manufacture. The weight of silicon steel can also be a consideration for transportation and installation, particularly in remote areas.
For B2B buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, where energy efficiency is a priority, the benefits of silicon steel align with regulatory standards aimed at reducing energy consumption. Buyers should ensure that silicon steel components meet the necessary compliance requirements to avoid regulatory issues.
What Are the Advantages of Using Resin in Transformer Applications?
Resin is increasingly used in dry-type transformers due to its insulating properties and resistance to environmental factors. Encapsulated transformers made with resin provide excellent protection against moisture and contaminants, making them ideal for harsh environments. Additionally, resin transformers are lightweight and easy to install.
The main drawback of resin is its higher manufacturing cost compared to traditional materials. Moreover, while resin provides good thermal insulation, it may not handle overload conditions as effectively as liquid-filled transformers.
International buyers, especially in Africa and the Middle East, should consider the local environmental conditions when selecting resin transformers. Ensuring compliance with local and international standards for resin materials will also be crucial for maintaining product quality and safety.
Summary of Material Selection for Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for kinds of transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-voltage and efficient transformers | Superior conductivity and efficiency | High cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Low-voltage transformers | Cost-effective and lightweight | Corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Silicon Steel | Transformer cores | Low hysteresis loss and high efficiency | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Resin | Dry-type transformers | Excellent environmental protection | Higher manufacturing cost | Medium |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for transformers involves balancing performance, cost, and environmental considerations. Understanding the specific needs of the application and the local market conditions will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for kinds of transformer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Transformers?
The manufacturing of transformers involves several critical stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance and safety standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first stage focuses on sourcing high-quality raw materials. The primary components include copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for cores, and various insulating materials. Rigorous material testing ensures that all components meet specific standards for electrical conductivity and thermal resistance. This stage often involves the use of specialized equipment for cutting and shaping materials to precise specifications.
-
Forming: In this stage, the core is constructed, typically using laminated silicon steel sheets. This lamination reduces energy losses due to eddy currents. The sheets are cut, stacked, and pressed into shape, ensuring tight tolerances. For windings, copper or aluminum wires are wound around the core in a specific configuration. Automated winding machines are commonly employed to enhance precision and efficiency.
-
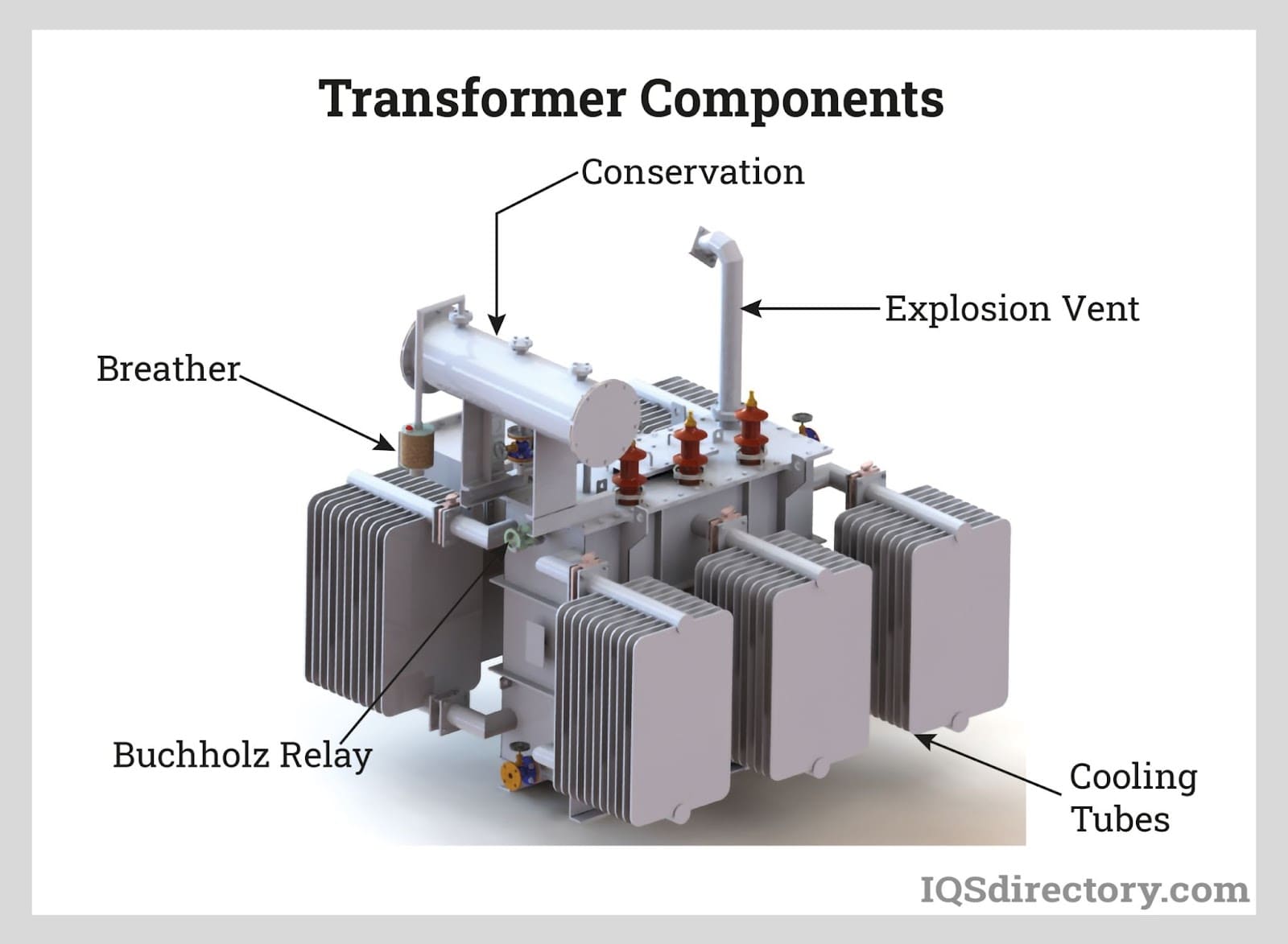
Assembly: Once the core and windings are prepared, they are assembled into the transformer tank. This tank serves as a protective enclosure and, in the case of liquid-filled transformers, a reservoir for cooling oil. During assembly, components such as tap changers, bushings, and cooling systems are integrated. The assembly process is often conducted in a clean environment to minimize contamination.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes sealing the transformer, painting, and labeling. For liquid-filled transformers, the oil is added and vacuum-sealed to prevent air ingress. Insulation and electrical tests are performed to ensure compliance with specifications. This stage may also involve the application of protective coatings for outdoor units, enhancing durability against environmental factors.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Standard in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in transformer manufacturing, as these devices are critical for safe and efficient electrical power distribution. Various international and industry-specific standards guide QA practices.

Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, ensuring consistent production processes.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: Transformers may also need to comply with CE marking requirements in Europe, API standards in the oil and gas sector, and other regional standards. These certifications often require rigorous testing and documentation.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. Suppliers must provide certifications and test results for materials.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to ensure that processes align with predefined standards. This may include dimensional checks and functional tests of components.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a thorough inspection is performed. This stage often includes high-voltage testing, thermal imaging, and sound level testing to ensure the transformer operates within acceptable parameters.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Transformer Quality Assurance?
Testing methods are essential for verifying the quality and reliability of transformers. Common testing approaches include:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes insulation resistance tests, power factor tests, and winding resistance tests. These tests ensure that the transformer can handle operational stress without failure.
-
Thermal Imaging: Thermal imaging cameras detect hotspots and other anomalies during operation, helping to prevent potential failures before they occur.
-
High-Voltage Testing: A high-voltage test is performed to verify the insulation strength of the transformer. This test checks for dielectric strength and ensures that the transformer can withstand surges and spikes in voltage.
-
Load Testing: Transformers are subjected to load tests to simulate real-world conditions. This helps verify that the transformer can handle the specified load without overheating or exhibiting performance issues.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify supplier quality control processes. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing facilities, processes, and QA practices firsthand. This provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request comprehensive quality reports that detail testing results, compliance with international standards, and any certifications held by the supplier. These documents provide transparency into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an independent assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These organizations can conduct tests and audits to ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Understanding Certifications: Familiarizing oneself with relevant certifications (like ISO 9001 or CE marking) can help buyers assess the credibility of suppliers. A supplier’s ability to maintain these certifications indicates a serious commitment to quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing transformers. These nuances can affect procurement decisions:
-
Regulatory Variations: Different regions have unique standards and regulations governing transformer manufacturing. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local standards to avoid issues with importation and use.
-
Cultural Differences: Cultural attitudes toward quality assurance and manufacturing can vary significantly. Buyers should consider these differences when establishing relationships with suppliers, ensuring clear communication about quality expectations.
-
Logistical Considerations: The distance between the buyer and supplier can complicate quality assurance. Buyers should factor in logistics when planning for inspections, audits, and communication to ensure that quality is maintained throughout the supply chain.
-
Currency Fluctuations: Economic factors, such as currency fluctuations, can impact the cost of quality assurance measures. Buyers should account for these variations when negotiating contracts and pricing with suppliers.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of transformers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure their electrical needs are met with reliability and safety.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘kinds of transformer’
Introduction
Procurement of transformers is a critical aspect for businesses seeking reliable electrical distribution solutions. This guide offers a step-by-step checklist to assist B2B buyers in identifying, evaluating, and securing the right transformer types for their specific needs. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to articulate your technical requirements clearly. Identify the type of transformer needed—whether liquid-filled or dry-type—and consider factors such as voltage ratings, power capacity, and installation environment. This clarity will guide your supplier discussions and help you avoid unsuitable options.
- Voltage Requirements: Specify the input and output voltage levels necessary for your application.
- Load Capacity: Determine the transformer size based on the expected load to ensure it can handle peak demands.
Step 2: Research Different Transformer Types
Understanding the various transformer types available is vital for making an informed choice. Familiarize yourself with options such as padmount, pole mount, substation, and submersible transformers, along with their respective applications. This knowledge will enable you to select a transformer that best fits your operational context.
- Application Suitability: Assess where and how the transformer will be used—outdoor vs. indoor, heavy industrial vs. residential settings.
- Cooling Methods: Consider the cooling requirements (liquid vs. dry) based on your installation environment.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thorough supplier evaluation is crucial to ensure reliability and quality. Review company profiles, request case studies, and seek references from other businesses in your region or sector. A reputable supplier will provide transparency about their products and previous projects.
- Certifications and Standards: Verify that suppliers meet international standards and possess necessary certifications.
- Experience and Reputation: Assess the supplier’s track record in the transformer market to gauge reliability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. This will allow you to compare offers comprehensively and ensure all your requirements are met.
- Cost Breakdown: Analyze the total cost, including installation, maintenance, and any additional components.
- Delivery and Lead Times: Confirm how quickly the supplier can deliver the transformer to align with your project timeline.
Step 5: Conduct Site Assessments
If possible, conduct site assessments with your shortlisted suppliers to discuss installation specifics. This step is crucial for understanding logistical challenges and ensuring that the transformer selected will fit within your operational framework.
- Space Constraints: Evaluate the physical space available for installation and any potential challenges.
- Environmental Considerations: Discuss how environmental factors may affect transformer performance and longevity.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of the contract carefully. Pay attention to warranty provisions, maintenance agreements, and support services. A well-negotiated contract protects your investment and ensures long-term reliability.
Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
- Warranty Length: Ensure the warranty covers essential components and offers adequate protection.
- Support Services: Inquire about post-installation support and maintenance services.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Plan Installation
After agreeing on terms, finalize your purchase and develop a clear installation plan. Coordinate with your supplier to ensure all necessary resources are available for a smooth installation process.
- Installation Timeline: Establish a timeline that aligns with your operational schedule.
- Training and Documentation: Ensure that documentation and training for your team are part of the installation package to maximize operational efficiency.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for transformers, ensuring they make informed, strategic decisions that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for kinds of transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Transformer Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of transformers is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. For instance, transformers made with copper windings are generally more expensive than those with aluminum due to copper’s higher conductivity and durability. Additionally, specialized materials for insulation and cooling, such as dielectric fluids for liquid-filled transformers, can further impact costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America often facing different wage structures compared to Europe or the Middle East. Skilled labor is particularly essential in manufacturing transformers, where precise assembly and testing are crucial for performance and safety.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Overhead can vary significantly based on the geographic location of the manufacturer and the technological sophistication of their production processes.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be high, especially for custom transformers. The complexity of the design will influence tooling costs, impacting the final price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that transformers meet specific international standards and certifications adds to the cost. Buyers should consider the implications of QC on pricing, as thorough testing can prevent future failures and associated costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the destination and the chosen Incoterms. Additional considerations include shipping methods (air vs. sea) and potential tariffs or duties for international transactions.
-
Margin: The profit margin for manufacturers can vary based on competition, brand reputation, and market demand. Understanding typical margins in the transformer market can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Transformer Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of transformers, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk typically leads to lower per-unit costs. Manufacturers often provide better pricing for larger orders, which can significantly reduce overall procurement expenses.
-
Specifications and Customization: Transformers designed for specific applications or custom configurations will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials affects both the initial cost and the long-term performance of the transformer. Selecting high-quality materials can lead to lower maintenance costs and a longer lifespan.
-
Quality and Certifications: Transformers that meet stringent quality standards and certifications (like ISO or IEC) may be priced higher but offer enhanced reliability and safety, thereby justifying the investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge premium prices but offer peace of mind through quality assurance and better customer service.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can affect the final cost of acquisition. For example, choosing Ex Works (EXW) may require buyers to manage all logistics, potentially increasing costs, while Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) includes shipping and duties, simplifying the process.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Transformer Sourcing?
When sourcing transformers, especially in international markets, consider the following tips to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Be prepared to discuss specifications and potential customizations that may affect costs.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While upfront costs are crucial, evaluating the TCO—accounting for maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan—can lead to better investment decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Regions: Be aware that pricing structures can vary significantly between regions. For example, manufacturers in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Vietnam or certain African nations.
-
Research Supplier Backgrounds: Conduct due diligence on potential suppliers, focusing on their quality assurance processes and customer service reputation. This research can provide insights into the value they offer relative to their pricing.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends, including shifts in material costs and technological advancements, can help buyers anticipate price fluctuations and make timely purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
The landscape of transformer sourcing is complex, with numerous factors influencing costs and pricing. By understanding the components of the cost structure and the various price influencers, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to more effective procurement strategies. It’s crucial to approach sourcing with a comprehensive view, balancing immediate costs against long-term value and reliability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing kinds of transformer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Kinds of Transformers
When considering power distribution solutions, it’s essential to evaluate various technologies that can achieve similar objectives as transformers. While transformers are widely used for voltage regulation and distribution, alternatives may offer advantages depending on specific use cases, budget constraints, or operational requirements. This analysis compares transformers with two viable alternatives: Voltage Regulators and Static Frequency Converters (SFCs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Kinds of Transformer | Voltage Regulators | Static Frequency Converters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in stepping voltage up or down; reliable for stable power supply. | Effective for maintaining output voltage; limited to specific voltage ranges. | Converts AC to DC and back to AC at a different frequency; ideal for specific applications. |
| Cost | Varies significantly based on type and application; generally high initial investment. | Lower initial cost but may require additional equipment for integration. | Higher initial investment; cost-effective in applications requiring frequency adjustment. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful planning and installation; often needs specialist knowledge. | Easier to install, especially in existing systems; may need minimal adjustments. | Complex setup due to the need for synchronization with existing systems. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; periodic inspections required to ensure optimal performance. | Low maintenance; infrequent checks needed unless under heavy load. | Higher maintenance due to potential wear on electronic components. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industrial and commercial applications with variable load demands. | Best suited for applications with fluctuating voltage levels, such as in residential areas. | Optimal for industries requiring variable frequency drives, like manufacturing or renewable energy systems. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators are devices designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. They are particularly beneficial in environments where voltage fluctuations can affect equipment performance. The primary advantage of voltage regulators is their ability to provide a more straightforward, cost-effective solution for voltage management without the need for complex installations. However, they are limited to specific voltage ranges and may not be suitable for high-power applications where transformers excel.
Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
Static Frequency Converters (SFCs)
SFCs are specialized devices that convert electrical power from one frequency to another, making them invaluable in applications where the frequency of the electrical supply does not match the requirements of the load. The key benefits of SFCs include their versatility in frequency adjustment and the ability to optimize the performance of certain equipment. However, they come with a higher initial investment and require careful integration into existing systems, making them less appealing for some businesses.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers evaluating power distribution solutions, the choice between transformers, voltage regulators, and static frequency converters depends on several factors, including the specific application, budget, and maintenance capabilities. Transformers remain the go-to solution for high-efficiency voltage regulation in industrial settings, while voltage regulators and SFCs offer valuable alternatives for specific scenarios. Conducting a thorough needs assessment and consulting with industry experts can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for kinds of transformer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Transformers That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When evaluating transformers for industrial or commercial applications, understanding their critical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in transformer construction directly affect performance and longevity. Common materials include copper and aluminum for windings, with copper being favored for its superior conductivity and durability. The choice of insulation materials, such as kraft paper or resin, also impacts the transformer’s thermal management and operational lifespan. Selecting the right material grade can lead to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
2. Voltage Rating
Transformers are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges, which are categorized as low, medium, or high voltage. Understanding the voltage requirements of your application is critical, as selecting a transformer with an inadequate rating can lead to overheating and equipment failure. B2B buyers should ensure that the transformer matches the voltage of their electrical system to maintain operational integrity.
3. Power Rating (kVA)
The power rating, measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), indicates the maximum load a transformer can handle. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the transformer can support the electrical demands of connected equipment without risk of overloading. When assessing potential transformers, B2B buyers should calculate their load requirements to select an appropriately rated unit.
4. Temperature Rise
Temperature rise refers to the increase in temperature of the transformer windings under full load conditions. This specification is vital for determining the cooling requirements and the overall efficiency of the transformer. A lower temperature rise generally indicates better cooling capabilities, which can enhance the reliability and lifespan of the transformer. Buyers should consult the temperature rise rating to ensure compatibility with their operational environment.
5. Impedance
Impedance in a transformer affects voltage regulation and short-circuit performance. It is typically expressed as a percentage and represents the voltage drop under full load conditions. A higher impedance can protect against overloads but may also lead to greater voltage drops. Understanding impedance helps B2B buyers balance the need for protection with the operational efficiency of their electrical systems.

Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
Which Trade Terminology Is Crucial for B2B Buyers in the Transformer Market?
Navigating the technical jargon of the transformer industry can be daunting for non-technical decision-makers. Familiarity with the following terms can greatly enhance the purchasing process:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding who the OEM is can help B2B buyers assess quality and compatibility, especially when sourcing transformers that need to integrate with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand, as it can affect budgetary constraints and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and aligning them with project timelines.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to submit price proposals for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to gather competitive pricing and detailed specifications from multiple suppliers, ensuring informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and logistical responsibilities, which can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
5. K-Rating
K-Rating is a designation for transformers that indicates their ability to handle non-linear loads and harmonic distortion. This specification is particularly relevant in environments with variable frequency drives or other electronic devices. B2B buyers should consider K-Rating to ensure that their transformers can efficiently manage the specific electrical characteristics of their applications.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed, strategic purchasing decisions in the transformer market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the kinds of transformer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Transformer Sourcing?
The transformer market is currently experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. A surge in renewable energy projects, particularly in Africa and South America, is creating a demand for efficient and reliable transformers to facilitate energy distribution. Additionally, urbanization and industrialization in regions such as the Middle East and Vietnam are necessitating upgrades to aging electrical infrastructure, resulting in increased investments in both distribution and substation transformers. The emphasis on smart grids and digitalization is also reshaping the transformer landscape, with advanced monitoring and control technologies becoming essential for optimizing performance and reliability.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing highlight the increasing importance of digital platforms for procurement. Buyers are leveraging online marketplaces and e-procurement solutions to streamline their purchasing processes, gain access to a wider range of suppliers, and make informed decisions based on real-time data. The rise of modular and customizable transformer designs is another key trend, allowing buyers to tailor solutions to meet specific application requirements while also reducing installation time and costs. Furthermore, the integration of IoT technology is revolutionizing maintenance practices, enabling predictive maintenance and enhancing the overall lifecycle management of transformers.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Transformer Sourcing Decisions?
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the transformer sector. The environmental impact of transformer manufacturing and operation is significant, particularly concerning energy efficiency and material sourcing. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of environmentally friendly materials, such as non-toxic insulation fluids and recyclable components, which minimize the ecological footprint of transformers.
Ethical sourcing has also gained traction, with buyers seeking to ensure that their supply chains are free from practices such as child labor and exploitation. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) certification, are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection. By choosing suppliers with these certifications, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and align with global sustainability goals. Additionally, as regulatory pressures increase, companies that invest in sustainable sourcing practices will be better positioned to navigate compliance challenges and capitalize on emerging market opportunities.

Illustrative image related to kinds of transformer
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Transformer Sector?
The transformer sector has evolved significantly since the late 19th century when the first practical transformers were developed. Initially, transformers were primarily used for long-distance power transmission, enabling the distribution of electricity from centralized power plants to urban areas. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering led to the development of various transformer types, including liquid-filled and dry-type transformers, each designed for specific applications.
The 20th century saw the rise of electrification, which accelerated the demand for transformers in industrial and residential settings. With the advent of digital technology in the late 20th century, transformers began to incorporate smart features, enhancing their functionality and efficiency. Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and resilience, with innovations aimed at reducing energy losses and improving operational reliability in the face of climate change and urbanization challenges. These historical developments have laid the groundwork for the current transformer market, shaping sourcing strategies for international buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of kinds of transformer
-
How do I determine the right type of transformer for my application?
Choosing the right transformer involves assessing your specific needs, including voltage requirements, load capacity, and environmental conditions. For outdoor applications, liquid-filled transformers are often preferred due to their superior cooling and weather resistance. Conversely, dry-type transformers are ideal for indoor use where space is limited and moisture is a concern. Consider consulting with a transformer supplier to evaluate your requirements and receive tailored recommendations based on your operational context. -
What is the best transformer for renewable energy projects?
For renewable energy projects, such as solar or wind farms, step-up transformers are typically the best choice. These transformers increase the voltage generated by the renewable source to match the grid requirements. Additionally, consider using dry-type transformers for indoor installations or liquid-filled transformers for outdoor applications to enhance safety and efficiency. It’s advisable to work with suppliers familiar with renewable energy systems to ensure compatibility and compliance with local regulations. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing transformers internationally?
When sourcing transformers internationally, consider factors such as compliance with local standards and regulations, supplier reputation, and product certifications. Additionally, assess the supplier’s ability to provide technical support and after-sales service. Understanding the logistics of shipping, including customs duties and delivery timelines, is also crucial. Engaging in thorough due diligence, including references and reviews, can help mitigate risks associated with international procurement. -
How can I customize a transformer to meet my specific needs?
Customization options for transformers may include altering voltage ratings, insulation types, and enclosure designs to fit unique application requirements. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions, allowing you to specify features such as temperature ratings and cooling methods. When approaching a supplier, provide detailed specifications regarding your application needs and operational environment to receive accurate customization options and quotes. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for transformers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers based on the type of transformer, production capabilities, and market demand. Generally, larger suppliers may offer lower MOQs, while specialized or custom transformers may have higher MOQs due to their unique manufacturing processes. Always clarify the MOQ with potential suppliers during the initial discussions to ensure alignment with your purchasing needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing transformers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but typically include options such as upfront payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Be sure to discuss and negotiate terms that suit your cash flow and risk management strategies. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction process. It’s also wise to inquire about any financing options or discounts for larger orders. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for transformers purchased overseas?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing transformers internationally, request certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO or IEC. Additionally, consider asking for product samples or visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility if feasible. Establishing a clear quality control process, including inspections at various production stages, can further mitigate risks and ensure the transformers meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for transformer shipments?
When planning logistics for transformer shipments, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and handling requirements due to the size and weight of transformers. It’s essential to work with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy industrial equipment to ensure safe transportation. Additionally, be aware of import/export regulations in your country, and ensure that all necessary documentation is in order to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process.
Top 7 Kinds Of Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Maddox – Types of Transformers
Domain: maddox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: 1. Padmount Transformers: a. 3-Ph Padmount Transformer b. 1-Ph Padmount Transformer c. Polemount Transformers 2. Substation Transformers 3. Dry-Type Transformers: a. Low Voltage Dry-Type Transformers b. Medium Voltage Dry-Type Transformers c. Cast Coil Transformers 4. Mini Power Centers 5. Switchgear: a. Metal-Enclosed Switchgear b. Pad-Mounted Switchgear
2. Meta Power Solutions – Pad Mount Transformers
Domain: metapowersolutions.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Single Phase Pad Mount Transformers: 25 kVA, 50 kVA, 75 kVA, 100 kVA, 125 kVA, Clam-Shell 150 kVA; Three Phase Pad Mount Transformers: 50 kVA, 80 kVA, 100 kVA, 160 kVA, 200 kVA, 250 kVA, 315 kVA, 500 kVA, 630 kVA, 800 kVA, 1000 kVA, 1500 kVA, 2000 kVA, 2500 kVA, 3000 kVA, 3750 kVA, 5000 kVA; Substation Transformers: 76 MVA, 1000 kVA, 1500 kVA, 2000 kVA, 2500 kVA, 3000 kVA, 3750 kVA, 5000 kVA, 1000…
3. Vietnam Transformer – Types of Transformers
Domain: vietnamtransformer.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: 1. Based on Core Design: a. Core Type Transformer – Two cylinders and two horizontal bars, square magnetic core. b. Shell Type Transformer – Center cylinder with two outer cylinders, dual magnetic circuit. c. Berry Type Transformer – Magnetic circuit resembling a wheel, filled with oil. 2. Based on Voltage Conversion: a. Step-Up Transformer – Increases output voltage, used i…
4. Monolithic Power – Distribution Transformers
Domain: monolithicpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Distribution transformers play a crucial role in electrical power distribution, carrying out the final voltage transformation stage before delivering electrical energy to the end user. They reduce high voltage electrical power transferred over long distances to lower voltage levels suitable for commercial, industrial, and residential settings. Distribution transformers are designed for continuous …
5. Byju’s – Transformers
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The transformer is a device that steps up or steps down voltage, widely used in the distribution and transmission of alternating current (AC) power. It operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction and mutual induction. Key types include: 1. Step-up Transformer: Increases output voltage; used between power generators and power grids. 2. Step-down Transformer: Decreases output voltage; co…
6. Elprocus – Types of Transformers
Domain: elprocus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers include: 1. Step-Up Transformer: Increases secondary voltage compared to primary voltage, used in power plants to connect generators to the grid. 2. Step-Down Transformer: Decreases voltage from primary to secondary, commonly used in distribution networks to convert high grid voltage to low voltage for home appliances. 3. Air-Core Transformer: Wound on a non-magnetic strip, w…
7. IQS Directory – Electric Transformers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electric transformers are devices that change electrical currents into necessary voltage levels, utilizing electromagnetic coupling to transmit electrical energy between circuits. They come in various sizes for different applications, from small units for electronics to large systems for power stations. Key types include low voltage transformers for small electronics and high voltage transformers …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for kinds of transformer
In the dynamic landscape of electrical infrastructure, understanding the diverse types of transformers is crucial for strategic sourcing. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the importance of selecting the right transformer based on application—be it liquid-filled for outdoor settings or dry-type for indoor use. Additionally, factors such as voltage requirements, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs play a pivotal role in decision-making.
Strategic sourcing not only optimizes operational efficiency but also enhances cost-effectiveness and reliability in electrical systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s vital to align procurement strategies with local market conditions and technological advancements. Engaging with reputable suppliers who understand regional specifications can yield significant long-term benefits.
As the demand for efficient energy solutions continues to rise, staying informed about innovations in transformer technology will be essential. We encourage you to assess your current and future needs, explore partnerships with trusted manufacturers, and make informed sourcing decisions that will empower your business to thrive in a competitive marketplace. Let’s connect and discuss how we can support your transformer sourcing journey today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.