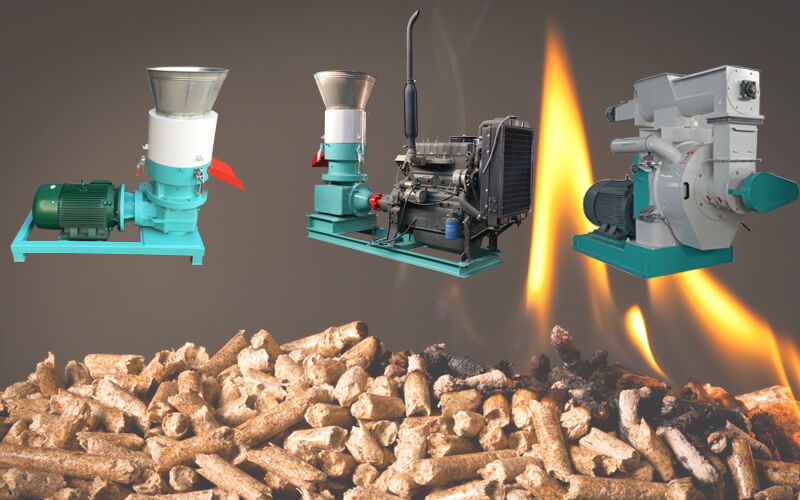
Is Your Wood Pellet Maker Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wood pellet maker
Navigating the complexities of sourcing a wood pellet maker can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a growing emphasis on sustainable energy solutions, the demand for efficient and reliable wood pellet production machinery is surging. However, the challenge lies in identifying the right equipment that meets specific operational needs while balancing cost and quality.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of wood pellet makers available in the market, including electric, diesel, and PTO-driven options. It explores their diverse applications, from biomass energy production to animal feed and fertilizer manufacturing. Additionally, the guide offers insights into supplier vetting processes, enabling buyers to make informed decisions by evaluating reliability, service capabilities, and compliance with industry standards.
Furthermore, we will address crucial factors influencing costs, such as machinery specifications and operational efficiencies, helping you to budget effectively. By equipping B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia with actionable insights and clear comparisons, this guide aims to simplify the purchasing journey and foster successful partnerships in the global market for wood pellet makers.
Understanding wood pellet maker Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Die Pellet Mills | Simple design, suitable for small-scale production | Home-based businesses, small farms | Pros: Affordable, easy to operate. Cons: Limited production capacity. |
| Ring Die Pellet Mills | High efficiency, ideal for large-scale production | Industrial pellet production, biomass fuel | Pros: High output, durable. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| PTO Driven Pellet Mills | Powered by tractor, ideal for rural settings | Agricultural applications, remote locations | Pros: Cost-effective power source. Cons: Dependent on tractor availability. |
| Diesel Powered Pellet Mills | Operates independently of electricity | Off-grid operations, remote areas | Pros: Versatile, good for areas without power. Cons: Fuel dependency. |
| Vertical Pellet Mills | Compact design, space-efficient | Urban settings, small production units | Pros: Space-saving, easy to transport. Cons: Limited output compared to horizontal models. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Flat Die Pellet Mills?
Flat die pellet mills are characterized by their straightforward design, making them an excellent choice for small-scale production. They typically feature a flat die where raw materials are compressed into pellets. These mills are particularly suitable for home-based businesses and small farms looking to produce animal feed or biofuels. When considering a flat die pellet mill, buyers should evaluate their production needs, as these mills have a lower output capacity compared to other types.
How do Ring Die Pellet Mills cater to large-scale production needs?
Ring die pellet mills are designed for high efficiency, making them ideal for large-scale production environments. They utilize a cylindrical die that allows for continuous operation, resulting in a higher output of pellets. These mills are commonly used in industrial settings for biomass fuel production or animal feed. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and operational costs, as ring die mills typically require more substantial financial resources but offer significant long-term savings through increased production rates.
What are the benefits of PTO Driven Pellet Mills for agricultural applications?
PTO driven pellet mills are powered by a tractor’s power take-off (PTO) system, making them particularly useful in rural settings where electricity may not be readily available. These mills are commonly employed in agricultural applications for producing feed pellets or biomass fuel. Buyers should assess the compatibility of the mill with their existing tractor and consider the cost-effectiveness of using a PTO-driven system, especially in areas where electricity is scarce or costly.
In what scenarios are Diesel Powered Pellet Mills advantageous?
Diesel powered pellet mills operate independently from the electrical grid, making them an excellent option for off-grid operations or remote areas. They are versatile and can be used for various applications, including biomass fuel production and animal feed processing. When purchasing a diesel powered mill, B2B buyers should evaluate fuel availability and costs, as well as the mill’s operational efficiency, to ensure it meets their production requirements effectively.
Why choose Vertical Pellet Mills for urban settings?
Vertical pellet mills are designed with a compact structure, making them ideal for urban settings or small production units where space is limited. Their space-saving design allows for easy transportation and installation in confined areas. B2B buyers considering vertical pellet mills should focus on their specific production needs and available space, as these mills may have limited output compared to larger horizontal models, but they offer practical solutions for smaller-scale operations.
Key Industrial Applications of wood pellet maker
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wood pellet maker | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Production | Manufacturing wood pellets for biomass fuel | Provides a renewable energy source, reducing fossil fuel dependency | Ensure the pellet mill can handle local raw materials and meet energy output standards |
| Animal Feed | Producing pellets for livestock and aquaculture | Enhances feed efficiency, reducing waste and costs | Consider the mill’s capacity to produce specific pellet sizes for different animal types |
| Agriculture/Fertilizer | Creating organic fertilizer pellets | Improves soil health and crop yields, appealing to eco-conscious markets | Verify compatibility with various organic materials and local regulations on fertilizer production |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Producing wood pellets for engineered wood products | Offers a sustainable raw material option, reducing environmental impact | Assess the mill’s ability to process specific wood types and comply with industry standards |
| Waste Management | Converting wood waste into pellets | Reduces landfill usage and generates additional revenue streams | Evaluate the mill’s efficiency in processing diverse waste materials and local disposal regulations |
How Can Wood Pellet Makers Transform Energy Production in Various Markets?
Wood pellet makers are pivotal in the energy sector, particularly in regions aiming to diversify their energy sources. By converting biomass into wood pellets, businesses can produce renewable energy that significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels. This transition not only lowers energy costs but also contributes to sustainability goals. Buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East must consider local raw material availability and the energy output specifications of the pellet mills to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
What Role Do Wood Pellet Makers Play in the Animal Feed Industry?
In the animal feed sector, wood pellet makers are utilized to produce high-quality pellets for livestock and aquaculture. These pellets improve feed efficiency, minimize waste, and lower overall feed costs, making them an attractive option for farmers. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, it’s crucial to select mills that can produce varying pellet sizes to meet the specific dietary needs of different animal species, ensuring optimal growth and health.
How Are Wood Pellet Makers Enhancing Agricultural Practices?
Wood pellet makers are also essential in agriculture for producing organic fertilizer pellets. These pellets enhance soil health and improve crop yields, which is increasingly important in markets focused on sustainable farming practices. B2B buyers should ensure that the pellet mills they source can handle various organic materials and comply with local agricultural regulations. This capability can significantly enhance their marketability among eco-conscious consumers.
In What Ways Can Wood Pellet Makers Support Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing industry, wood pellet makers can produce pellets for engineered wood products, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional raw materials. This not only helps manufacturers meet growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products but also reduces environmental impact. Buyers should assess the ability of the pellet mills to process specific wood types and ensure compliance with industry standards, which can vary significantly across different regions.
How Do Wood Pellet Makers Contribute to Waste Management Solutions?
Wood pellet makers play a crucial role in waste management by converting wood waste into valuable pellets. This process reduces landfill use while generating an additional revenue stream from what would otherwise be considered waste. B2B buyers in regions with stringent waste disposal regulations should evaluate the efficiency of pellet mills in processing diverse waste materials, ensuring that their operations align with local environmental policies and contribute positively to community sustainability efforts.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘wood pellet maker’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Sourcing High-Quality Raw Materials for Wood Pellet Production
The Problem: One significant pain point for B2B buyers in the wood pellet industry is sourcing high-quality raw materials. Many manufacturers struggle to find consistent, reliable suppliers of wood chips, sawdust, or other biomass materials that meet the necessary specifications for pellet production. This inconsistency can lead to variations in pellet quality, impacting end-user satisfaction and causing costly production delays. Additionally, buyers in regions like Africa and South America may face logistical challenges due to limited local suppliers or the high costs associated with importing raw materials.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate risks associated with relying on a single source. Conducting thorough market research to identify local and regional suppliers of wood by-products is essential. Participating in industry trade shows and networking events can also uncover potential partnerships. Buyers should specify quality standards for their raw materials, such as moisture content and particle size, ensuring that suppliers understand the requirements. Additionally, utilizing local resources, such as agricultural waste or wood processing residues, can enhance sustainability and reduce costs. Implementing a robust quality control process during the incoming material inspection can further ensure that only materials meeting the specified criteria are used in production.
Scenario 2: Equipment Downtime and Maintenance Issues
The Problem: Equipment reliability is another critical concern for B2B buyers investing in wood pellet makers. Downtime due to mechanical failures or maintenance issues can significantly disrupt production schedules, leading to missed deadlines and loss of revenue. This is particularly pressing for buyers in regions with limited access to technical support or replacement parts, which can exacerbate the impact of equipment failures.
The Solution: To minimize equipment downtime, buyers should prioritize investing in high-quality wood pellet mills known for their durability and reliability. It is advisable to choose manufacturers that offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support, including access to spare parts and technical assistance. Buyers should also develop a proactive maintenance schedule, which includes regular inspections and servicing of equipment to prevent unexpected breakdowns. Training operators on proper machine usage and troubleshooting techniques can empower them to address minor issues before they escalate into significant problems. Additionally, establishing a stock of critical spare parts on-site can reduce downtime and ensure that production can resume quickly after any equipment issues arise.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers in the wood pellet industry often face challenges related to compliance with local and international regulations concerning production practices and environmental impact. This is particularly true for companies operating in regions where environmental laws are stringent or rapidly evolving. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal issues, or damage to the company’s reputation.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory challenges effectively, buyers should stay informed about the legal landscape in their operational regions. Engaging with local industry associations or consulting firms specializing in regulatory compliance can provide valuable insights into current and upcoming regulations. Implementing sustainable practices, such as using certified sustainable wood sources and reducing emissions during production, can not only ensure compliance but also enhance the company’s marketability. Developing a transparent reporting process for environmental impact and compliance metrics can help in demonstrating commitment to sustainability to stakeholders and customers. Additionally, pursuing certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or ENplus can elevate credibility and assure customers of the quality and sustainability of the pellets produced.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wood pellet maker
What Are the Key Materials for Wood Pellet Makers?
When selecting materials for wood pellet makers, it’s crucial to consider the properties and performance implications of various options. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of wood pellet mills: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and cast iron. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly influence the efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Wood Pellet Makers?
Carbon steel is widely used in the manufacturing of wood pellet mills due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high tensile strength, allowing it to withstand the pressures generated during the pelletizing process. However, carbon steel can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or maintained, which could affect its longevity.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and offers good machinability, making it easier to manufacture complex components. It is also highly durable, which is essential for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The primary drawback is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can be a concern in regions like West Africa or the Middle East.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel components may require protective coatings or regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Buyers should consider the local climate and environmental factors when choosing this material.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel in Wood Pellet Mills?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for wood pellet makers, particularly for components that are in constant contact with moisture or require high corrosion resistance. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for humid or wet environments. It is also easy to clean and maintain, which is beneficial for operational efficiency.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its higher cost compared to carbon steel, which can impact the overall budget for equipment procurement.
Impact on Application: Given its durability and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel is particularly suitable for regions with high humidity, such as coastal areas in South America or the Middle East. Buyers should ensure that the grade of stainless steel meets international standards.
Why Choose Aluminum for Wood Pellet Makers?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it an attractive option for specific components of wood pellet mills. Its low density can lead to easier handling and installation.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and allows for easier assembly. It also has good thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in managing heat during the pelletizing process.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it may not be as durable as steel under high-pressure conditions, which could limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for smaller, less critical components of the pellet mill. International buyers should consider the specific performance requirements and whether aluminum can meet their operational needs.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Wood Pellet Mills?
Cast iron is often used for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for the construction of heavy-duty machinery, including wood pellet mills.
Pros: Cast iron is incredibly durable and can withstand high levels of stress without deforming. Its ability to dampen vibrations can lead to smoother operation.
Cons: The primary limitation of cast iron is its weight, which can complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, it is more brittle compared to other materials, making it susceptible to cracking under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is ideal for components that require high durability and stability. Buyers in Europe and North America may find cast iron components align well with their operational standards.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
Summary Table of Material Selection for Wood Pellet Makers
| Material | Typical Use Case for wood pellet maker | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-prone parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost than carbon steel | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components | Easy handling and good thermal conductivity | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty machinery parts | Exceptional durability and vibration absorption | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wood pellet maker
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Wood Pellet Makers?
The manufacturing process of wood pellet makers is intricate, involving several stages that ensure the final product is efficient and meets the required quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The initial stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically wood chips or sawdust. These materials are often subjected to drying processes to achieve optimal moisture content, which is critical for effective pellet production. Screening is also performed to remove impurities and ensure uniform particle size, which helps in achieving consistent pellet quality.
-
Forming: This stage is where the actual pelletization occurs. Raw materials are fed into the pellet mill, where they are compressed through a die and rollers. The application of heat and pressure converts the raw materials into pellets. The configuration of the die holes, typically ranging from 3mm to 12mm, can be adjusted based on the desired pellet size. This stage is crucial, as it directly impacts the density and durability of the pellets.
-
Assembly: After forming, the components of the pellet maker, such as the motor, gearbox, and feeding system, are assembled. This stage involves precise engineering to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly, minimizing operational issues.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves quality checks and surface treatments. Pellets may be cooled and screened again to remove any irregular shapes. This stage also includes the application of protective coatings to enhance durability, especially for machines expected to operate in harsh environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Wood Pellet Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an essential aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that wood pellet makers not only meet production standards but also comply with international regulations.
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards helps ensure consistent quality in production processes and customer satisfaction. Additionally, certifications such as CE mark and API standards may apply, especially when exporting to regions with stringent regulations.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, various quality control checkpoints are implemented:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the forming and assembly stages, continuous monitoring is conducted to identify any deviations from quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the performance and durability of wood pellet makers. These include operational tests under different conditions, stress testing of components, and performance assessments to gauge efficiency and output.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control practices. This involves visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes, check certifications, and review records of quality checks.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the supplier’s adherence to international standards. These reports can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management system and any certifications they hold.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These services can conduct thorough inspections and provide reports that can be used for decision-making.
-
Understanding Certification Nuances: International buyers should familiarize themselves with the nuances of certifications. For example, while CE marking is recognized in Europe, other regions may require different certifications. Understanding these differences can help buyers ensure compliance and avoid potential issues.
What Are the Challenges in Quality Assurance for International Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges in ensuring quality assurance when sourcing wood pellet makers. These challenges can include:
-
Language and Cultural Barriers: Differences in language and business practices can hinder effective communication about quality standards and expectations.
-
Regulatory Variations: Different countries have varying regulations regarding manufacturing and quality standards. Buyers must navigate these complexities to ensure compliance.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Issues: The global supply chain can introduce risks such as delays or damage during transportation, affecting the quality of the equipment upon arrival.
-
Cost vs. Quality: Balancing cost considerations with the need for high-quality machinery can be challenging. Buyers must carefully evaluate suppliers to ensure that lower prices do not compromise quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing wood pellet makers, ultimately leading to successful partnerships and enhanced operational efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘wood pellet maker’
Introduction
Sourcing a wood pellet maker requires a strategic approach to ensure you select the right machinery for your production needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed specifically for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Follow these actionable steps to make informed purchasing decisions that will enhance your operations and efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements for the wood pellet maker. Consider aspects like production capacity, power source (electric, diesel, or PTO), and material types you intend to process. Establishing these specifications helps streamline your search and ensures that the equipment meets your operational needs.
- Production capacity: Determine how many pellets you need to produce per hour.
- Power source: Assess the availability of electricity or other fuels in your location.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Start by compiling a list of potential suppliers specializing in wood pellet makers. Look for companies with a proven track record in manufacturing and distributing pellet mills, particularly those that cater to your regional market. An extensive search will help you identify reputable suppliers who can meet your needs.
- Online directories: Utilize B2B platforms to find manufacturers and distributors.
- Industry recommendations: Seek referrals from industry peers or trade associations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that your shortlisted suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international quality standards. This step is crucial to ensure that the machinery you purchase is reliable and safe for operation. Certifications can also indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- ISO certifications: Look for ISO 9001 for quality management.
- Safety standards: Ensure compliance with local and international safety regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed product specifications, including performance data, maintenance requirements, and warranty information. This will provide insights into the longevity and reliability of the wood pellet maker, helping you gauge its suitability for your operations.
- Product manuals: Ask for technical documentation that outlines features and capabilities.
- Maintenance guidelines: Understand the upkeep required to maintain optimal performance.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Analyze the pricing structures of the various suppliers while considering financing options available. It’s essential to understand not just the upfront costs but also the long-term financial implications, including maintenance and operational costs. This comparison will help you identify the best value for your investment.
- Total cost of ownership: Factor in installation, maintenance, and operational costs.
- Financing plans: Explore flexible payment options that suit your budget.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits and Supplier Audits
If feasible, arrange site visits to the manufacturing facilities of your top suppliers. This allows you to assess the quality of their operations, machinery, and adherence to safety and quality standards firsthand. Additionally, supplier audits can provide insights into their production processes and reliability.
- On-site evaluations: Observe the manufacturing process and quality control measures.
- Supplier reputation: Speak with existing customers about their experiences.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement. This should include delivery timelines, installation services, warranty conditions, and after-sales support. A well-defined contract protects both parties and establishes clear expectations.
- Delivery and installation: Confirm timelines and responsibilities.
- After-sales support: Ensure access to technical support and spare parts.
Following this structured checklist will enable you to make informed decisions when sourcing a wood pellet maker, ultimately enhancing your production capabilities and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wood pellet maker Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Wood Pellet Makers?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing wood pellet makers, several critical components come into play. These include raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary materials include the steel and other components used in the construction of pellet mills. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and availability, impacting the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs are often influenced by the location of the manufacturing facility. For instance, sourcing from regions with higher labor costs can increase the price of the equipment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, and indirect labor costs. Efficient manufacturing practices can reduce overhead, thereby positively influencing pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for the production of pellet mills may require significant investment, which is typically passed on to the buyer. Custom tooling for specific machine configurations will increase costs.
-
Quality Control: Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability, which can lead to higher upfront costs but ultimately reduces long-term operational risks.
-
Logistics: The cost of shipping and handling, especially for international buyers, can significantly impact the total acquisition cost. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their business costs and profit. This can vary widely depending on the supplier’s operational efficiency and market positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Wood Pellet Maker Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of wood pellet makers, which are crucial for buyers to understand:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Understanding MOQ can help buyers negotiate more favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should balance their need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect pricing. High-quality materials may offer better durability and performance but at a higher cost.
-
Quality Certifications: Equipment that meets international quality standards may command a premium price but can ensure reliability and compliance with local regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and customer service can all influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery can affect the overall cost. Buyers should clarify whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your understanding of market prices and supplier margins to negotiate better deals. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to favorable terms over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A more expensive machine may offer lower TCO due to efficiency and durability.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international pricing can be influenced by currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local economic conditions. This understanding can aid in budgeting and forecasting.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide a better understanding of the market and help identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Depending on the region, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing without the added logistics costs associated with international shipping.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While indicative prices for wood pellet makers can provide a baseline for budgeting, actual costs may vary based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain updated quotes to ensure accurate financial planning.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing wood pellet maker With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Wood Pellet Makers
In the competitive landscape of biomass production, businesses often seek efficient and cost-effective methods to convert raw materials into usable energy sources. While wood pellet makers are a popular choice, it’s essential to explore alternative solutions that may suit specific operational needs and objectives. This analysis compares wood pellet makers with two viable alternatives: briquette machines and traditional biomass boilers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Wood Pellet Maker | Briquette Machine | Traditional Biomass Boiler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in pellet production; consistent size and density | Efficient for producing high-density briquettes; less energy-intensive | Suitable for large-scale heating and energy generation; variable efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for maintenance and raw materials | Typically lower upfront costs; moderate maintenance expenses | High initial investment; potential savings on fuel costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific setup for optimal operation; user training may be necessary | Generally easier to set up; less technical knowledge required | Complex installation; may require specialized labor for setup |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance; potential wear on parts | Lower maintenance needs; occasional checks required | High maintenance demands; regular servicing essential for efficiency |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium-scale operations focusing on consistent pellet production | Best suited for users with varying raw materials; suitable for farms and small enterprises | Effective for larger facilities requiring continuous heating or energy supply |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Briquette Machines
Briquette machines offer a compelling alternative for biomass conversion, producing compressed blocks of material that can be used as fuel. Their lower initial investment makes them accessible for smaller enterprises or farms. Moreover, briquettes are easier to handle and transport compared to pellets, which can be advantageous for businesses with variable raw material supplies. However, the briquette-making process may not achieve the same energy density as pellets, potentially leading to lower efficiency in energy generation.
Traditional Biomass Boilers
Traditional biomass boilers are designed to burn wood chips, logs, or other organic materials for heating and energy generation. They are highly effective in larger industrial applications where consistent heating is needed. While they can provide significant fuel savings in the long run, the initial investment and complexity of installation can be a barrier for smaller businesses. Additionally, regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance, which may require specialized staff.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate biomass conversion method, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Wood pellet makers excel in producing uniform pellets for heating and energy, while briquette machines offer flexibility and lower costs for smaller operations. Traditional biomass boilers serve best in larger facilities but come with higher upfront costs and maintenance demands. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production capabilities and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wood pellet maker
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Wood Pellet Maker?
Understanding the essential technical properties of wood pellet makers is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their pellet production. Here are some of the most critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality of the components used in the construction of the pellet maker. High-grade materials, such as stainless steel and hardened alloys, ensure durability and longevity, reducing maintenance costs over time. For buyers, investing in machines made from superior materials translates to fewer breakdowns and greater reliability in production.
2. Production Capacity
Production capacity is measured in pounds per hour (PPH) and indicates the volume of pellets a machine can produce within a specific timeframe. Understanding this metric helps businesses estimate output against demand. A higher production capacity can lead to economies of scale, making it easier to meet large orders and reduce per-unit costs.
3. Power Source
The power source of a pellet maker—whether it is electric, diesel, or PTO (Power Take-Off)—affects its operational costs and flexibility. Electric models may be more efficient in regions with reliable power supply, while diesel and PTO options are often preferred in remote areas where electricity is scarce. Buyers should choose based on their operational environment and energy costs.
4. Die Size and Type
The die size and type directly influence the pellet diameter and quality. Typical die sizes range from 3mm to 12mm. The correct die size is crucial for ensuring that the pellets meet specific market standards. Understanding die specifications allows buyers to customize their production to various market needs, enhancing product versatility.
5. Operating Temperature and Pressure
The operating temperature and pressure are vital for the pelletizing process. Proper control of these factors ensures optimal pellet quality and reduces the likelihood of equipment malfunction. Buyers should ensure that the machine can maintain the necessary conditions for their specific raw materials, which can vary widely.
6. Moisture Content Regulation
Moisture content in raw materials affects pellet quality and machine performance. Advanced wood pellet makers often include moisture regulation features, allowing for better control over the input material. This is critical for B2B buyers looking to produce high-quality pellets that meet industry standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Wood Pellet Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for machinery and components, ensuring compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQs is important for buyers to plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, especially when dealing with large machinery or components.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers use to request pricing and terms from suppliers. It’s a critical step in the procurement process, helping buyers compare offers and negotiate better deals.

Illustrative image related to wood pellet maker
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their liability and costs involved in transporting machinery across borders, which is especially important for international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their production schedules and avoid disruptions in their operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality in the competitive wood pellet market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the wood pellet maker Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Global Wood Pellet Market?
The wood pellet market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for renewable energy sources as countries aim to meet their carbon reduction targets. Governments and organizations worldwide are increasingly investing in biomass energy, making wood pellets a preferred choice due to their efficiency and lower emissions compared to fossil fuels. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations on carbon emissions are shaping energy policies.
Additionally, technological advancements in pellet manufacturing have improved the efficiency and scalability of production processes. Innovations such as enhanced pellet mills and automated systems are becoming more prevalent, enabling manufacturers to optimize their operations and reduce costs. B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America are particularly interested in adopting these technologies to improve their production capabilities and meet local energy demands.
Emerging sourcing trends indicate a shift towards localized supply chains. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that can provide consistent quality and timely delivery, especially in light of recent global supply chain disruptions. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe are seeking partnerships with manufacturers who can ensure reliability and sustainability in their sourcing practices, thus emphasizing the importance of establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers.
How Is Sustainability Shaping B2B Sourcing in the Wood Pellet Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the wood pellet industry, influencing sourcing practices significantly. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their procurement decisions, prompting a demand for sustainable sourcing solutions. Ethical supply chains are not just a preference but a necessity for many companies aiming to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
The importance of sourcing from suppliers who adhere to sustainable forestry practices cannot be overstated. Certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) provide assurance that the wood used for pellets is sourced responsibly, minimizing deforestation and promoting biodiversity. Buyers should actively seek out these certifications when evaluating suppliers to ensure they are contributing positively to environmental sustainability.
Moreover, the use of recycled wood and by-products from other industries is gaining traction as a means to produce wood pellets. This not only reduces waste but also lowers the overall carbon footprint associated with pellet production. International buyers looking to enhance their sustainability credentials will find that collaborating with suppliers who prioritize these practices can provide a competitive advantage in the increasingly eco-conscious marketplace.
How Has the Wood Pellet Industry Evolved Over Time?
The wood pellet industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from a niche market to a mainstream energy source. Initially developed in the 1970s, wood pellets were primarily used for residential heating in Europe and North America. However, as the global focus shifted towards renewable energy in the early 21st century, the application of wood pellets expanded rapidly.
Today, wood pellets are not only a key component in residential heating but also play a crucial role in industrial energy production. With advancements in technology and increased awareness of climate change, the industry has witnessed a surge in demand, particularly from emerging markets in Africa and South America, where energy access remains a challenge. This evolution reflects a broader shift in energy consumption patterns, aligning with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable energy solutions.
In conclusion, international B2B buyers in the wood pellet sector are navigating a dynamic landscape characterized by sustainability, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing practices. By understanding these trends, buyers can make informed decisions that align with both market demands and environmental responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wood pellet maker
-
How do I choose the right wood pellet maker for my business needs?
Choosing the right wood pellet maker depends on several factors, including the scale of your operation, the type of raw materials you plan to use, and your production goals. Consider the production capacity, power source (electric, diesel, or PTO), and the available die sizes for the pellets. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s efficiency, maintenance requirements, and potential for customization. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive customer support and after-sales services can also enhance your purchasing decision. -
What is the best type of wood pellet maker for small-scale production?
For small-scale production, a single-phase electric pellet mill is often the best choice. These mills are typically more affordable, easier to operate, and require less power, making them ideal for businesses with lower production needs. Ensure that the mill you select can handle the type of wood you plan to use and offers flexibility with die sizes to produce pellets suited to your market. Additionally, consider a machine that allows for easy cleaning and maintenance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for wood pellet makers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for wood pellet makers can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, manufacturers may require a MOQ of one to five units for standard models. However, for customized machines or special orders, MOQs could be higher. It is essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and understand their production capabilities, especially if you are looking to scale operations in regions like Africa or South America. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a wood pellet maker?
Payment terms for purchasing a wood pellet maker can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiating power. Common arrangements include a deposit (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or extended payment plans. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront, including any potential fees for international transactions or currency exchange, especially when dealing with suppliers from Europe or the Middle East. -
How can I ensure the quality of the wood pellet maker I purchase?
To ensure the quality of a wood pellet maker, start by vetting suppliers through reviews, testimonials, and case studies from previous clients. Request detailed specifications and certifications regarding manufacturing standards. If possible, arrange for a factory visit or ask for samples of pellets produced by the machinery. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and the availability of spare parts to gauge the long-term reliability of the equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping?
When planning for international shipping of wood pellet makers, consider factors such as shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Work with suppliers who have experience in exporting machinery to your region to navigate these logistics smoothly. Ensure that the equipment is properly packed and insured during transit to prevent damage. Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the importation of industrial machinery to avoid any compliance issues. -
Can I customize the wood pellet maker to suit my production needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for wood pellet makers. This can include adjustments in size, power specifications, die sizes, and additional features such as automated controls or integrated hammer mills. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to see what options are available. Customization may impact the lead time and cost, so it is advisable to factor this into your planning. -
What are the common maintenance practices for wood pellet makers?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the optimal performance of wood pellet makers. Key practices include routine cleaning of the feed hopper and die, checking for wear and tear on parts such as rollers and belts, and lubricating moving components as recommended by the manufacturer. Create a maintenance schedule to minimize downtime and ensure that the machine operates efficiently. Training your staff on basic troubleshooting can also help address minor issues before they escalate.
Top 7 Wood Pellet Maker Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PelletMasters – Pellet Mills, Hammer Mills, and Grinders
Domain: pelletmasters.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: PelletMasters offers a variety of Pellet Mills, Hammer Mills, and Grinders suitable for wood, animal feed, and fertilizer production. Key product categories include:
1. **Pellet Mills for Wood**:
– Single Phase Electric Powered
– Three Phase Electric Powered
– Diesel Powered
– PTO Driven
– Die sizes available from 3mm to 12mm.
– Production rate: ~20 lbs/hp/hr for electric…
2. GEMCO – Wood Pellet Mills
Domain: biofuelmachines.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Make Your Own Wood Pellets with GEMCO Small Pellet Mill and Large Pellet Mill from Logs / Sawdust / Wood Shaving / Industry Waste. Build your pellet plant in 1 day! Small Pellet Mill: Typically for home-use, can produce heating pellets or animal feed. Production process includes raw material receiving and resizing, pelletizing, and bagging. Large Pellet Mill: Used in wood pellet plants, consists o…
3. Reddit – Basic Pellet Maker
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Basic pellet maker with a small hopper on top, capable of producing about 80kg of pellets per hour. Used for sawdust compression. Requires binding agents like potato starch or corn starch for pellet formation due to low lignin content in the sawdust.
4. USA Pellet Mill – Pellet Mill Flat Die Models
Domain: usapelletmill.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Pellet Mill Flat Die Models:
1. MKFD260C: Power Type: Electric w/Panel, Power: 15kw, Capacity: 600 – 1300 lbs/hr, Price: $6,503.00
2. MKFD120B: Power Type: Electric, Power: 2.2 kw / 3 kw, Capacity: 132 – 220 lbs/hr, Price: $2,145.00
3. MKFD150B: Power Type: Electric, Power: 4 kw / 5.5 kw, Capacity: 200 – 265 lbs/hr, Price: $2,370.00
4. MKFD200B: Power Type: Electric, Power: 7.5 kw, Capacity: 440-…
5. ELF – Industrial Pellet Mills
Domain: elfpelletmills.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: ELF Industrial Pellet Mills for sale in Canada, USA, and North America. Precision engineering with a 2-year warranty. Galvanized frame for rust prevention. Unique and innovative patented design. Available in 4 sizes. Capable of making pellets from a wide range of materials including wood, paper, cardboard, wool, alfalfa, hay, straw, hops, hemp, waste (MSW & RDF), fertilizer, digestate, and cow fee…
6. TECHTONGDA – Pellet Mill Machines
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Pellet Mill products available on eBay include various models and specifications such as: 1. TECHTONGDA Household Electric Animal Feed Food Pellet Machine 220V, suitable for 3mm and 6mm pellets, priced at ZAR 20,549.39. 2. TECHTONGDA 5mm Chicken Feed Pellet Mill Machine, 220V, 3000w, priced at ZAR 14,565.82. 3. 220V Chicken Feed Pellet Mill Machine, 2mm, priced at ZAR 20,619.54. 4. TECHTONGDA 220V…
7. Biopellet Machine – Biomass Pellet Solutions
Domain: biopelletmachine.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Biomass Pellet Machine & Wood Pellet Plants: One-Stop Service. Products include: 1T/H Sawdust Pellet Plant, 500kg/h Wood Pellet Plant, 1t/h EFB Pellet Production Line, 2t/h PKS Pellet Production Line, Giant King Grass Pellet Production Line, Straw Pellet Production Line, Coconut Shell Pellet Production Line, Alfalfa Pellet Production Line, Organic Fertilizer Pellet Production Line, Olive Pomace Pe…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wood pellet maker
In the evolving landscape of wood pellet production, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and ensure quality. By establishing robust relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can secure access to high-quality raw materials and advanced machinery, such as pellet mills and hammer mills, tailored to specific production needs. This approach not only mitigates supply chain risks but also empowers companies to remain competitive in a global market increasingly focused on sustainability.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer diverse options—ranging from electric to diesel-powered pellet mills—to meet varying energy requirements and production scales. Additionally, leveraging local resources and expertise can significantly lower costs and improve logistics.
Looking ahead, the demand for wood pellets is set to rise as industries seek renewable energy solutions. Now is the time for B2B buyers to take proactive steps in their sourcing strategies, ensuring they are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing market. Engage with trusted suppliers today to pave the way for a sustainable and profitable future in wood pellet production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.