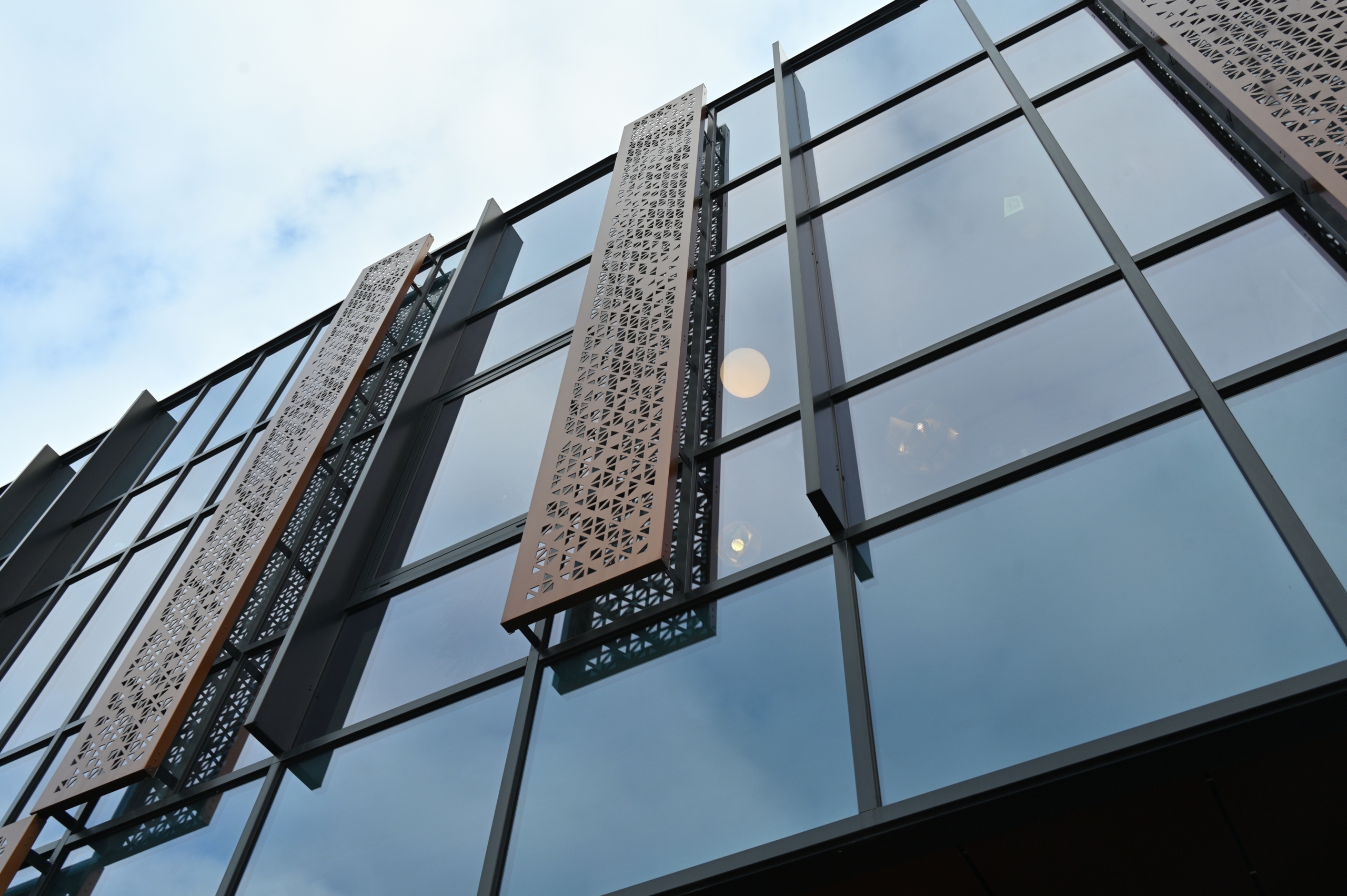
Is Your Perforated Facade Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for perforated facade
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing perforated façades that balance aesthetic appeal with functionality poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from energy-efficient shading solutions to innovative acoustic measures, the demand for tailored façade solutions has never been higher. This comprehensive guide aims to navigate the complexities of the global market for perforated façades, providing insights into various types, applications, and design options.
From understanding the nuances of material selection to evaluating supplier capabilities, we delve into the critical aspects of the procurement process. Key considerations such as cost analysis, installation techniques, and regulatory compliance are discussed, empowering buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, this guide emphasizes the unique needs of businesses operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including insights tailored for markets in Brazil and Germany.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear roadmap for sourcing perforated façades, this guide serves as an essential resource for enhancing project outcomes and fostering sustainable partnerships. Whether you’re looking to elevate the design of a new building or retrofit an existing structure, understanding the global landscape of perforated façades will ensure you achieve both aesthetic and functional excellence.
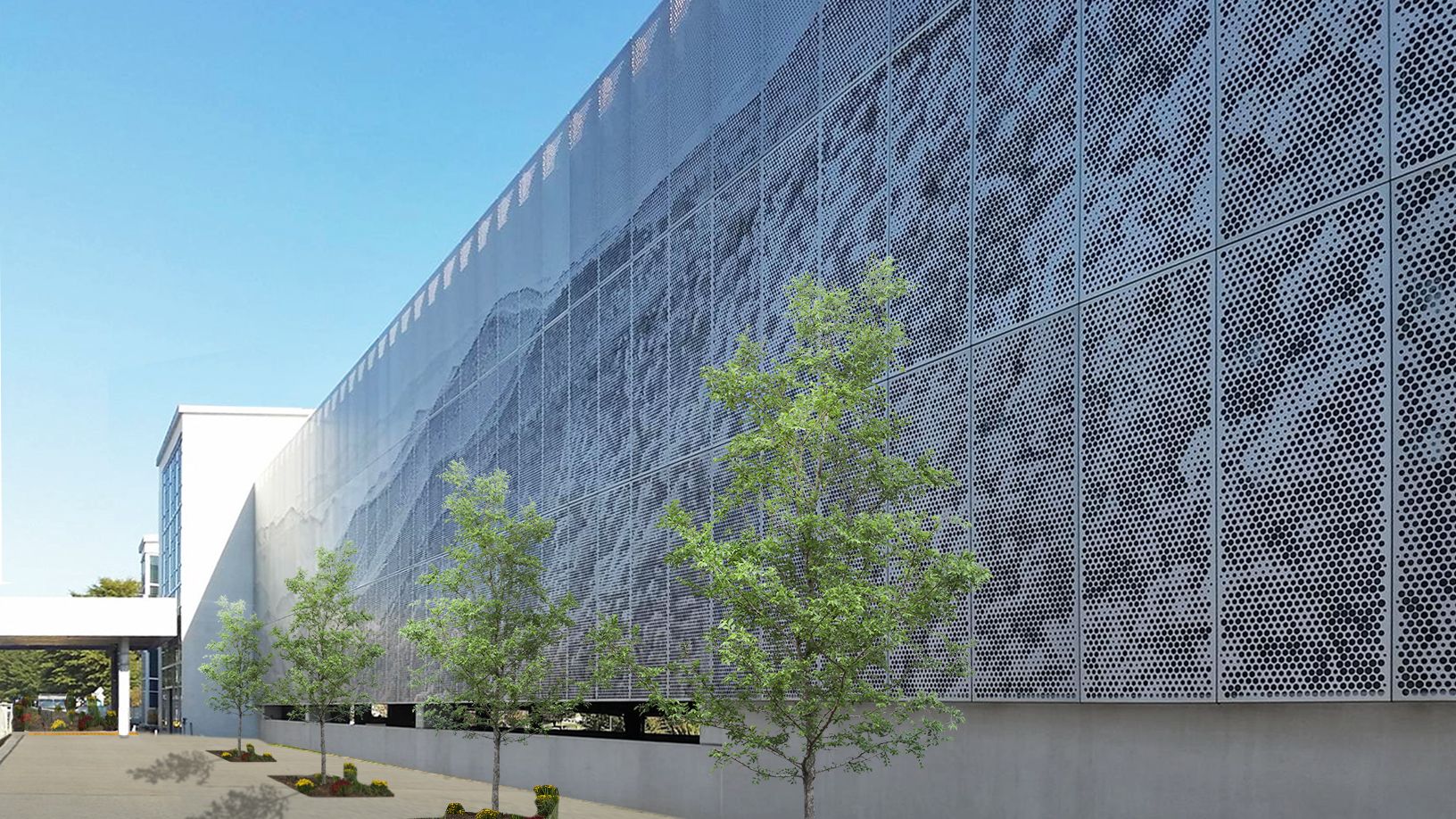
Understanding perforated facade Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standing Seam Profiles | Smooth transitions, high durability, customizable shapes | Commercial buildings, parking facades | Pros: Versatile design, excellent structural integrity. Cons: Installation may require specialized skills. |
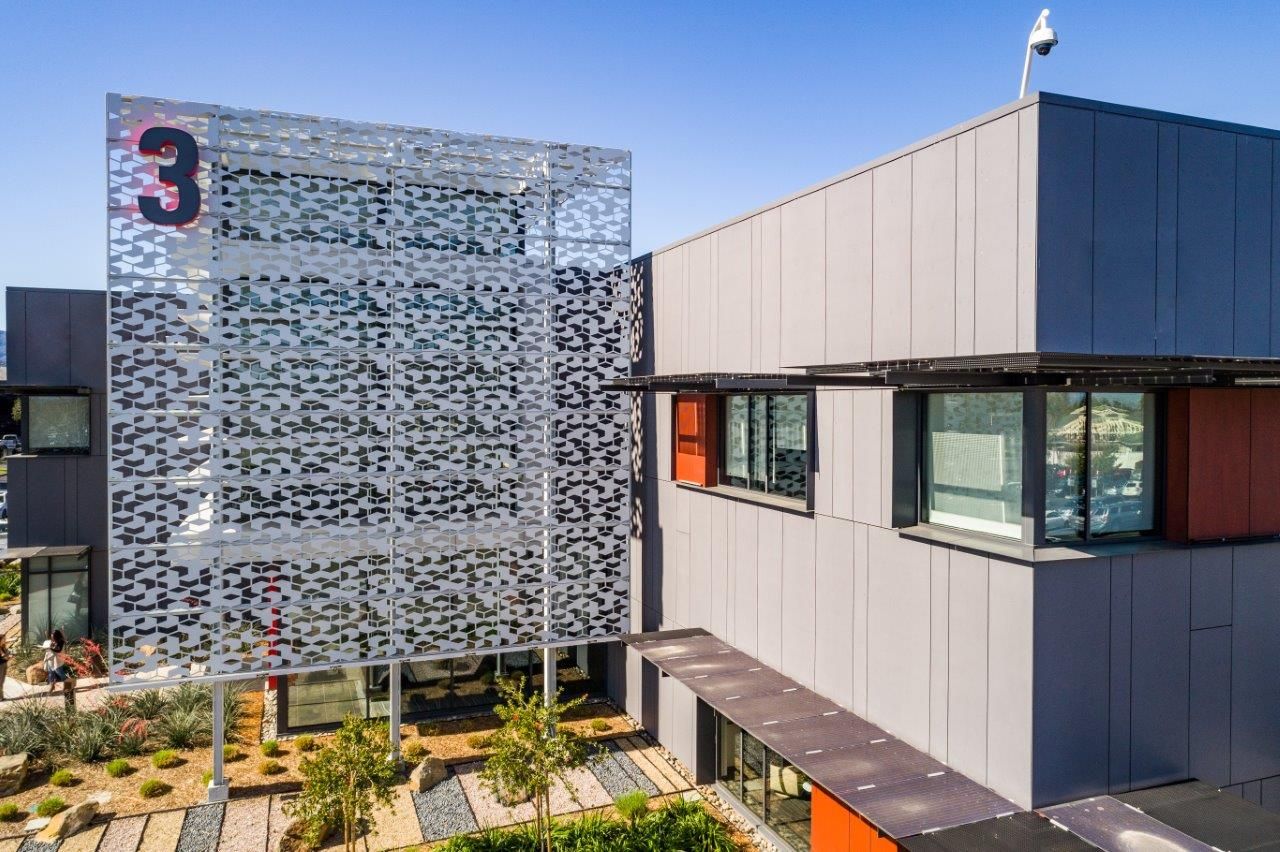
| Aluminum Composite Panels | Lightweight, high design flexibility, backlit options | Curtain walls, corporate buildings | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, easy maintenance. Cons: Higher initial costs compared to traditional materials. |
| Trapezoidal Profiles | Economical, stable, available in various geometries | Industrial buildings, warehouses | Pros: Cost-effective, quick installation. Cons: Limited design options compared to other types. |
| Corrugated Profiles | Classic design, sustainable materials | Residential and commercial projects | Pros: Attractive appearance, good weather resistance. Cons: May require more frequent maintenance. |
| Perforated Panels with Substructures | Customizable, compensates for thermal expansion | High-rise buildings, façade renovations | Pros: Reduces thermal bridging, enhances energy efficiency. Cons: Complex installation process. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standing Seam Profiles?
Standing seam profiles are characterized by their smooth transitions and robust design, allowing for a wide variety of shapes and configurations. These profiles are particularly well-suited for commercial buildings and parking facades due to their durability and ability to withstand various environmental conditions. For B2B buyers, the versatility in design and high structural integrity are significant advantages, though specialized installation may be necessary, adding to overall project costs.
How Do Aluminum Composite Panels Stand Out?
Aluminum composite panels offer remarkable design flexibility, lightweight construction, and the potential for backlit features, making them ideal for curtain walls and corporate buildings. These panels allow for a wide range of aesthetic options, which can enhance brand visibility and architectural appeal. However, B2B buyers should consider that while these panels may have a higher upfront cost, their low maintenance requirements and long-term durability can yield significant savings over time.
Why Choose Trapezoidal Profiles for Industrial Applications?
Trapezoidal profiles are known for their economical design and structural stability, making them a popular choice for industrial buildings and warehouses. Their ability to cover large spans with fewer fastening points reduces installation time and costs. While they provide a cost-effective solution, B2B buyers should note that the design options may be more limited compared to other facade types, potentially affecting aesthetic preferences.
What Benefits Do Corrugated Profiles Offer?
Corrugated profiles are a classic choice for both residential and commercial projects, providing a sustainable and visually appealing façade option. Their design is not only attractive but also offers excellent weather resistance, making them suitable for various climates. However, B2B buyers should be aware that these profiles may require more frequent maintenance compared to other façade types, which can impact long-term operational costs.
How Do Perforated Panels with Substructures Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Perforated panels with integrated substructures are designed to compensate for thermal expansion and reduce thermal bridging, making them ideal for high-rise buildings and façade renovations. This innovative approach enhances energy efficiency, contributing to lower operational costs. While they offer significant advantages, the complexity of installation may require specialized expertise, which B2B buyers should factor into their project planning and budgeting.
Key Industrial Applications of perforated facade
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of perforated facade | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture & Design | Aesthetic building cladding | Enhances visual appeal and uniqueness of structures | Customization options, material durability, and design flexibility |
| Transportation | Parking structures and transit stations | Improves ventilation and safety while maintaining aesthetics | Fire safety standards, load-bearing capacity, and weather resistance |
| Hospitality | Hotel and resort facades | Creates inviting atmospheres with energy-efficient shading | Acoustic performance, thermal insulation, and maintenance requirements |
| Retail | Storefronts and shopping malls | Attracts customers through innovative design and branding | Brand integration options, visibility, and security features |
| Industrial Facilities | Manufacturing plants and warehouses | Improves airflow and light management in large spaces | Structural integrity, compliance with local regulations, and ease of installation |
How is Perforated Facade Used in Architecture and Design?
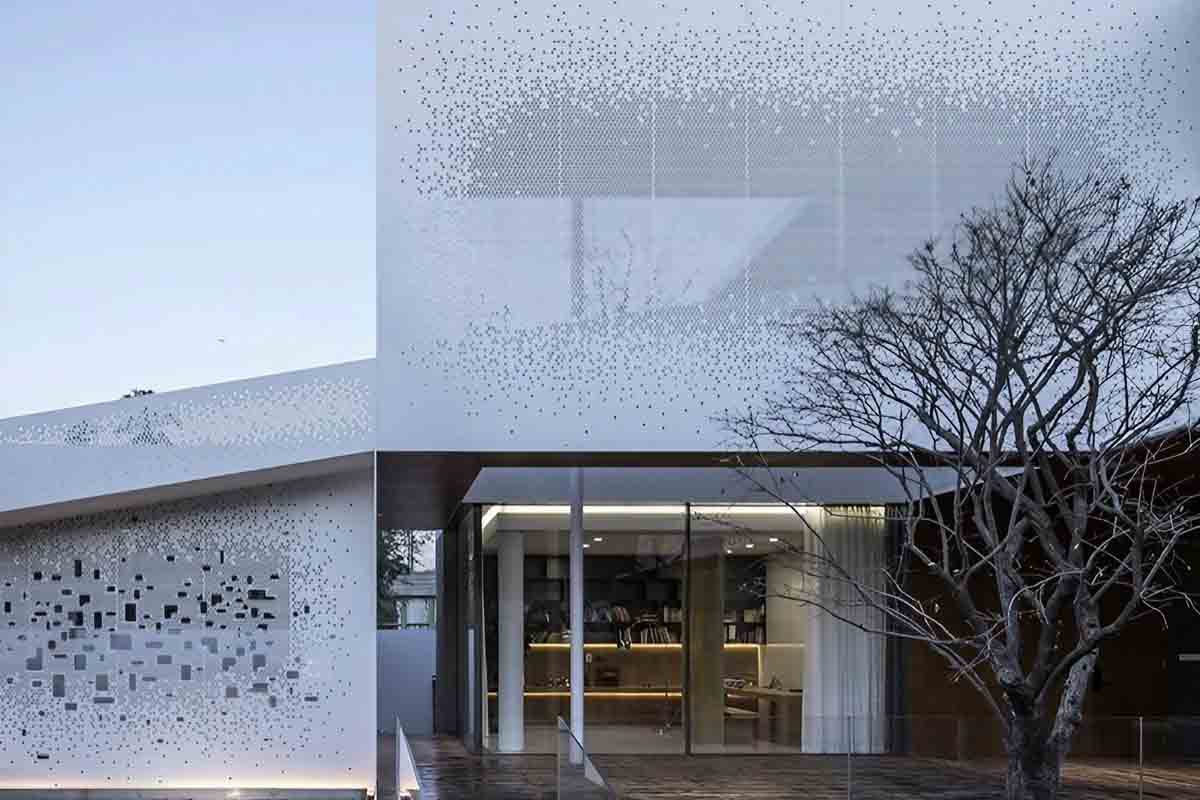
In the architecture and design sector, perforated facades serve as a sophisticated cladding solution that enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings. By allowing natural light to filter through while providing visual interest, these facades can create unique patterns and shadows that evolve throughout the day. Buyers in this sector should consider customization options for hole patterns, materials, and colors to align with their branding and design vision. Additionally, ensuring the durability and weather resistance of materials is crucial for long-term performance.
What Role Does Perforated Facade Play in Transportation Infrastructure?
Perforated facades find significant application in transportation infrastructure, particularly in parking structures and transit stations. They facilitate adequate ventilation and light penetration, crucial for safety and comfort. Moreover, the aesthetic appeal of these facades can enhance the overall experience for users. When sourcing for this application, businesses must prioritize compliance with fire safety standards, ensure adequate load-bearing capacity, and choose materials that withstand environmental conditions, particularly in regions with extreme weather.
How Can Hospitality Businesses Benefit from Perforated Facades?
In the hospitality industry, hotels and resorts utilize perforated facades to create inviting and visually appealing environments. These facades can provide effective energy-saving shading solutions, reducing cooling costs while enhancing guest comfort. The ability to integrate acoustic measures within the facade design can also improve the overall experience by minimizing noise from external sources. Buyers should focus on acoustic performance, thermal insulation capabilities, and maintenance requirements to ensure the longevity and functionality of these facades.
How Do Retailers Use Perforated Facades to Attract Customers?
Retailers often employ perforated facades in storefronts and shopping malls to create eye-catching designs that draw in customers. These facades not only enhance visibility but also allow for innovative branding opportunities through customized patterns and colors. Retail businesses should consider the integration of security features, as well as the balance between visibility and privacy. The sourcing process should also address the durability of materials to withstand high foot traffic and environmental factors.
What Advantages Do Industrial Facilities Gain from Implementing Perforated Facades?
In industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants and warehouses, perforated facades can significantly improve airflow and natural light management. This enhances the working environment and can lead to increased productivity. When sourcing perforated facades for industrial applications, businesses must ensure structural integrity and compliance with local building regulations. Ease of installation and maintenance are also critical factors, as they can impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘perforated facade’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Design Flexibility with Perforated Facades
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the limitations of traditional façade materials when it comes to achieving unique architectural designs. The challenge lies in balancing aesthetic appeal with practical functionality, particularly in diverse climates across regions like Africa and Europe. Buyers may find themselves constrained by the available options for materials, colors, and patterns, leading to a façade that fails to meet the desired visual or performance standards. This can result in missed opportunities for branding or creating an impactful first impression for clients.
The Solution: To overcome this design dilemma, B2B buyers should collaborate with manufacturers that offer a wide variety of customizable perforated façade solutions. Engaging with a supplier that provides extensive design options, including various materials such as aluminum and composite panels, can significantly enhance creative possibilities. When specifying perforated facades, consider utilizing advanced 3D modeling tools provided by manufacturers. This technology allows for precise visualization of how light interacts with different perforation patterns and materials, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that reflect both aesthetic goals and functional requirements. Additionally, buyers should leverage samples and mock-ups to assess the look and feel of different options before finalizing selections, ensuring that the chosen design resonates with the intended architectural vision.
Scenario 2: Addressing Acoustic Challenges in Urban Environments
The Problem: In bustling urban settings, noise pollution is a significant concern for building occupants and developers alike. B2B buyers often face pressure to create spaces that are not only visually appealing but also acoustically comfortable. Traditional façade materials may not adequately address sound insulation, leading to dissatisfaction among clients or tenants who expect a peaceful living or working environment.
The Solution: To effectively address acoustic challenges, buyers should prioritize perforated facades that are specifically designed with sound-absorbing properties. When sourcing these solutions, it is crucial to consult with manufacturers who can provide detailed specifications on the acoustic performance of their products. For instance, selecting perforated panels with varying hole sizes can optimize sound absorption while maintaining aesthetic integrity. Buyers should also consider integrating additional acoustic insulation behind the façade, which can further enhance soundproofing capabilities. Collaborating with architects and acoustical engineers during the design phase ensures that the chosen perforated façade meets both aesthetic and acoustic requirements, resulting in a well-rounded solution that enhances occupant satisfaction.
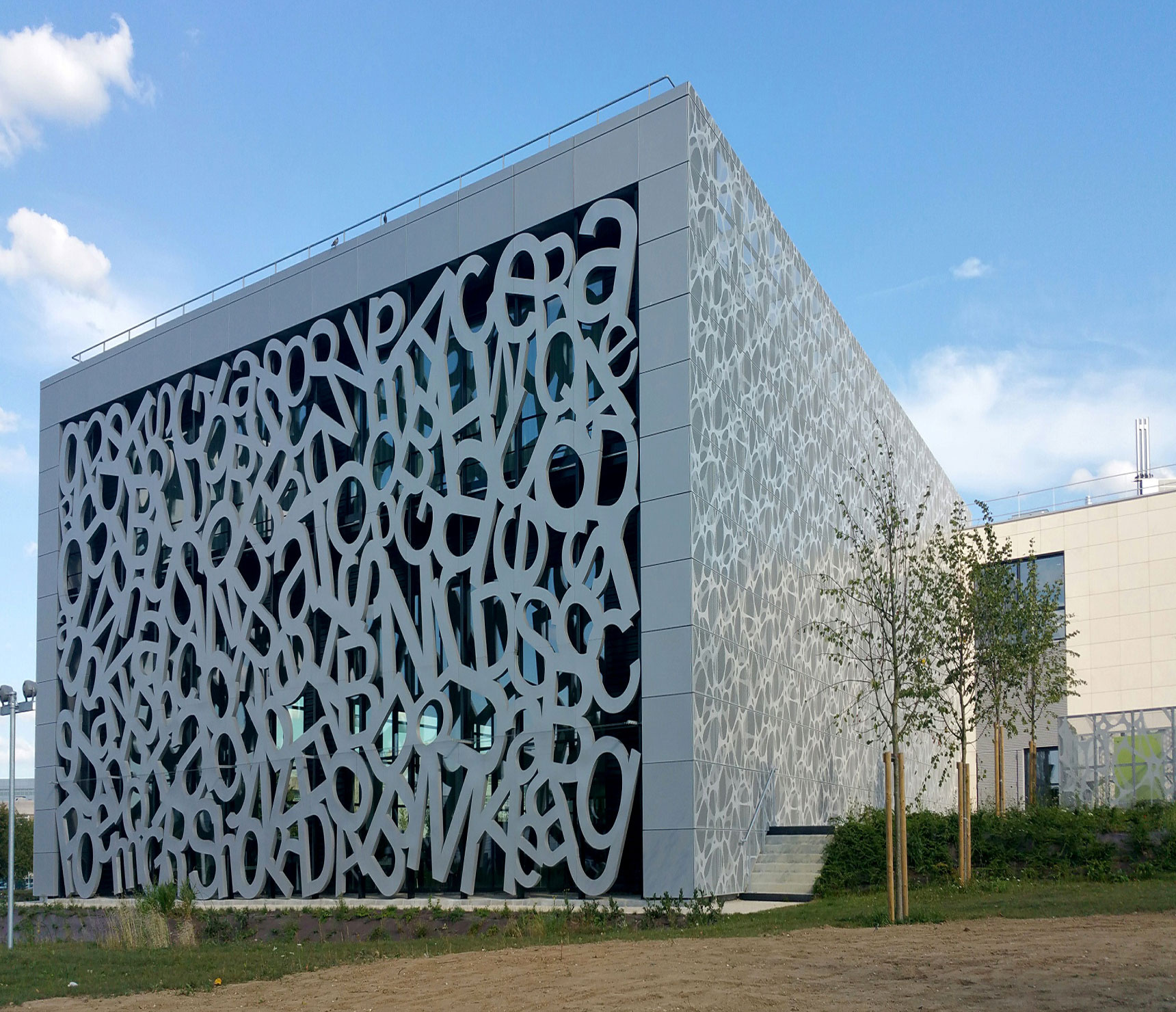

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Building Regulations and Sustainability Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers in the construction sector frequently navigate complex building regulations and sustainability standards, which can vary significantly across different regions. This can lead to confusion and delays if the selected perforated façade does not comply with local codes regarding fire safety, energy efficiency, and environmental impact. Buyers risk project setbacks, increased costs, and potential reputational damage if compliance issues arise post-installation.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance risks, B2B buyers should engage with suppliers who are well-versed in local regulations and can provide certifications for their perforated façade products. It is essential to conduct thorough research on the specific codes applicable to the project location, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. Buyers should request documentation that outlines fire ratings, energy efficiency ratings, and sustainable material sourcing for the façade systems being considered. Additionally, opting for suppliers who offer comprehensive support throughout the project lifecycle— from design and installation to post-installation inspections—can help ensure that the façades not only meet but exceed compliance requirements. By prioritizing transparency and collaboration with knowledgeable suppliers, buyers can streamline the approval process and enhance the project’s overall success.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for perforated facade
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Perforated Facades?
When selecting materials for perforated facades, it is essential to consider their properties in relation to performance, durability, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, steel, fiberglass, and composite materials.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Versatile Choice
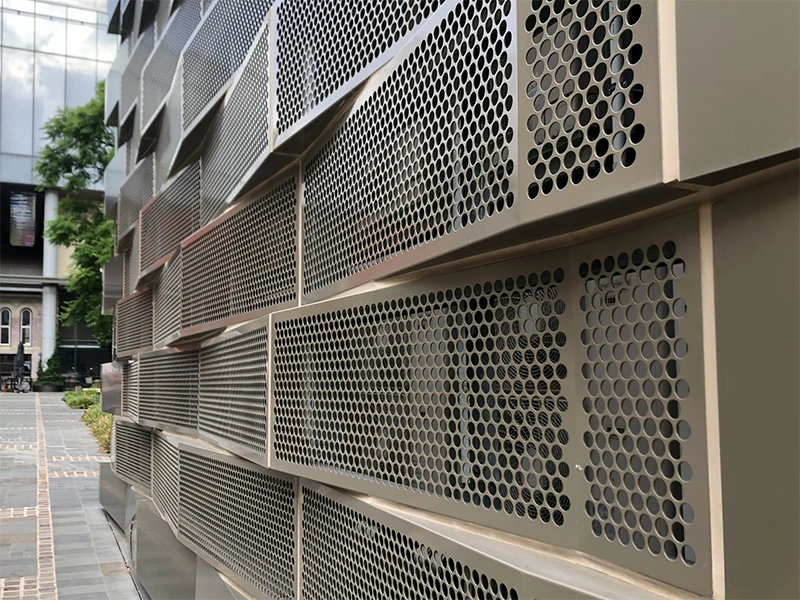
Aluminum is a popular choice for perforated facades due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 600°F (315°C) and can withstand various environmental conditions without significant degradation.
Pros: Aluminum’s durability and resistance to rust make it ideal for outdoor applications. It is also relatively easy to fabricate, allowing for custom designs and quick installation.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, it may not be as strong as steel, limiting its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, the initial cost can be higher than other materials, depending on the finish and treatment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for a variety of climates, making it a favored option in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where moisture and temperature fluctuations are common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider local preferences for finishes and coatings that enhance aesthetics and performance.
Steel: Strength and Durability
Steel is another widely used material for perforated facades, known for its strength and structural integrity. It can handle higher pressure and temperature ratings, often exceeding 1,000°F (538°C) depending on the alloy used.
Pros: Steel’s strength allows for larger spans and thinner profiles, which can reduce material usage and costs. It is also highly durable and can be treated for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which may complicate installation and require more robust substructures. Additionally, untreated steel is prone to rust, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly suitable for industrial and commercial applications, where strength is paramount. This makes it a preferred choice in South America and Africa, where robust structures are often required.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local building codes and standards like JIS and ASTM. The availability of treated steel options can also influence decisions based on local environmental conditions.
Fiberglass: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Fiberglass is a composite material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal insulation properties. It is lightweight and can withstand a variety of temperatures, typically up to 300°F (149°C).
Pros: Fiberglass is non-corrosive, making it ideal for coastal areas or regions with high humidity. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural load.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Cons: Fiberglass can be more expensive than metals, and its impact resistance is lower, making it less suitable for high-traffic areas.
Impact on Application: This material is often used in environments where moisture is a concern, making it suitable for applications in coastal regions in Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is essential, especially regarding fire ratings and structural integrity. Buyers should also consider the availability of fiberglass suppliers in their region.
Composite Materials: A Blend of Strength and Aesthetics
Composite materials, such as aluminum composite panels, combine the benefits of different materials to offer enhanced performance. They typically feature a core material sandwiched between two layers of aluminum, providing excellent durability and aesthetics.
Pros: Composite materials are lightweight, offer good thermal insulation, and can be customized in various colors and finishes. They are also resistant to weathering and UV radiation.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher costs. Additionally, they may not be as strong as solid metal options in certain applications.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for modern architectural designs, making them popular in Europe and the Middle East, where aesthetics are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with local building codes and standards, as well as the availability of custom design options to meet specific project requirements.
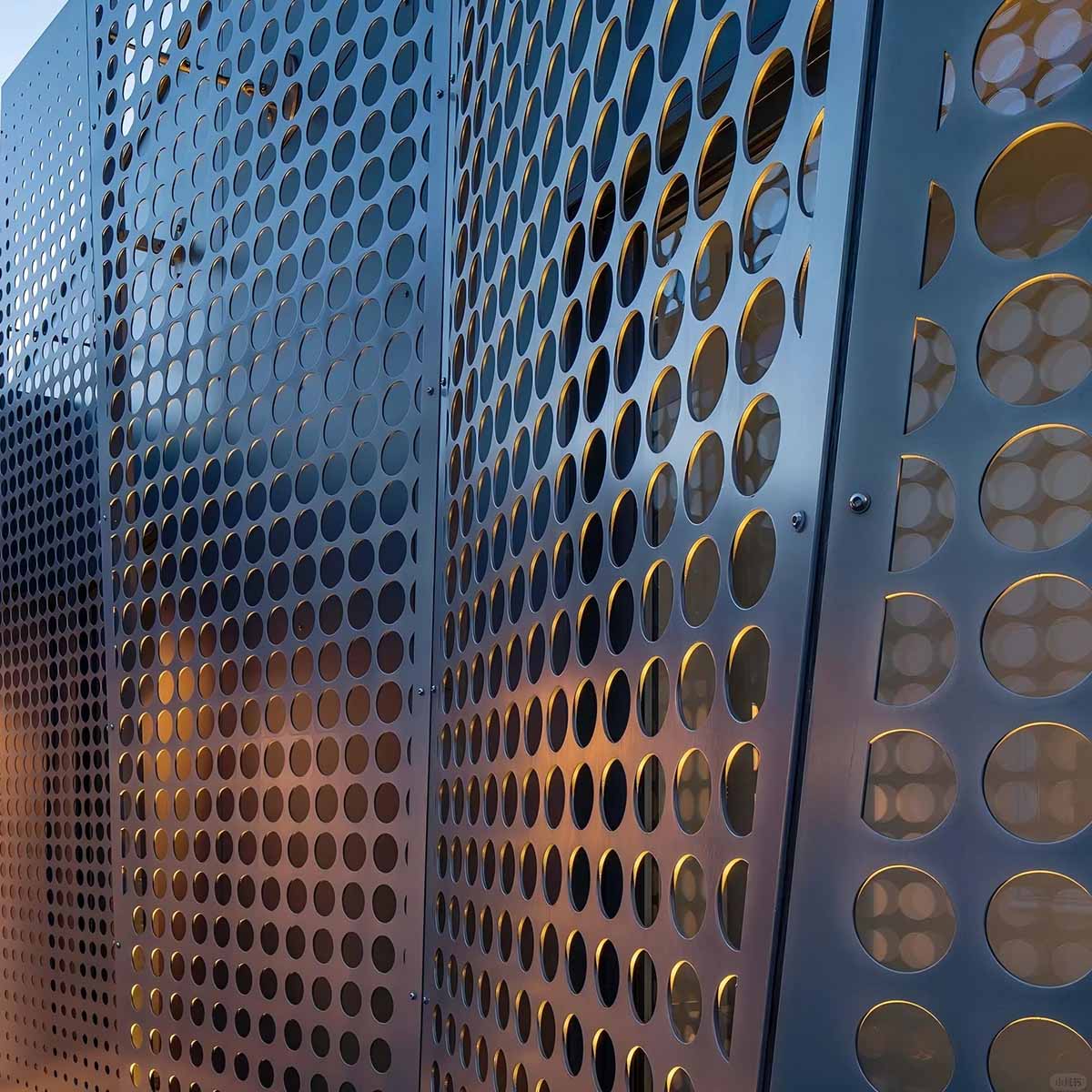

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Summary Table of Material Selection for Perforated Facades
| Material | Typical Use Case for perforated facade | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Commercial and residential buildings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher initial cost than some metals | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial and commercial applications | High strength and durability | Heavier, requires robust substructures | Medium |
| Fiberglass | Coastal and humid environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower impact resistance | High |
| Composite | Modern architectural designs | Aesthetic versatility | Complex manufacturing process | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for perforated facade
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Perforated Façades?
Manufacturing perforated façades involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the product meets the specific requirements of durability, aesthetics, and functionality. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Perforated Façades?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials for perforated façades include aluminum, steel, and composite panels. The selected material is inspected for quality and compliance with relevant standards. It is then cut into sheets of required dimensions, ensuring that the material is suitable for subsequent processes.
In addition to dimensional accuracy, surface treatment may occur at this stage. For metals, this could involve anodizing or applying a protective coating to enhance durability and corrosion resistance. For composite materials, the surface may be prepared to ensure optimal adhesion during later stages.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves creating the desired perforations and shapes in the material. This is typically achieved through advanced techniques such as laser cutting, punching, or CNC machining.
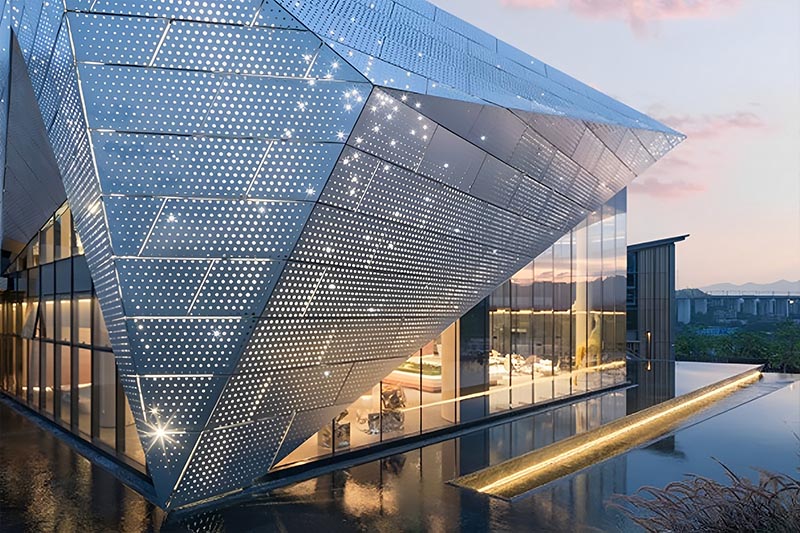

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
- Laser Cutting: This method offers precision and flexibility, allowing for intricate designs and varying hole patterns without compromising material integrity.
- Punching: A more traditional approach, punching is efficient for creating standard patterns and is often used for larger production runs.
- CNC Machining: This technique is ideal for customized shapes and designs, enabling manufacturers to achieve complex geometries with high accuracy.
After perforation, the panels may undergo bending or folding processes to achieve specific architectural forms, such as curves or angles, required by the design.
How Are Perforated Façades Assembled?
Once the panels are formed, the assembly process begins. This involves attaching the perforated panels to a substructure, which is critical for ensuring the façade’s stability and load-bearing capacity. The assembly can include the use of standing seam profiles, brackets, and other fastening systems that allow for flexibility in design.
During assembly, manufacturers must ensure that the connections between panels are secure and that any thermal expansion or contraction is accommodated. This is particularly important in regions with extreme temperature variations, as it affects the long-term performance of the façade.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed?
The finishing stage enhances both the aesthetic and functional qualities of the perforated façades. Techniques may include painting, powder coating, or applying a weather-resistant finish. These processes not only provide color and texture but also improve the façade’s resistance to environmental factors.
Quality control at this stage is vital to ensure that the finish is uniform and adheres properly to the substrate. Manufacturers often perform visual inspections and adhesion tests to verify the quality of the finish.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are In Place for Perforated Façades?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process for perforated façades. It involves adhering to international standards, implementing internal quality checkpoints, and employing various testing methods to ensure product reliability.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
Internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in the quality management of manufacturing processes. ISO 9001 sets forth requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry certifications may be relevant, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For projects in the Middle East or Africa, compliance with local regulations and standards may also be required.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet the specified standards and requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the processes and identify any deviations from quality standards. This includes verifying dimensions, checking for surface defects, and ensuring that perforations are accurately placed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a comprehensive final inspection is performed. This includes assessing the overall appearance, structural integrity, and compliance with design specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Testing methods for perforated façades can include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that the panels meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
- Load Testing: Assesses the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of the façade.
- Adhesion Tests: Verify that finishes adhere properly to the substrate.
- Weather Resistance Tests: Evaluate the façade’s performance against environmental conditions, such as rain, wind, and UV exposure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are some ways buyers can verify supplier QC:
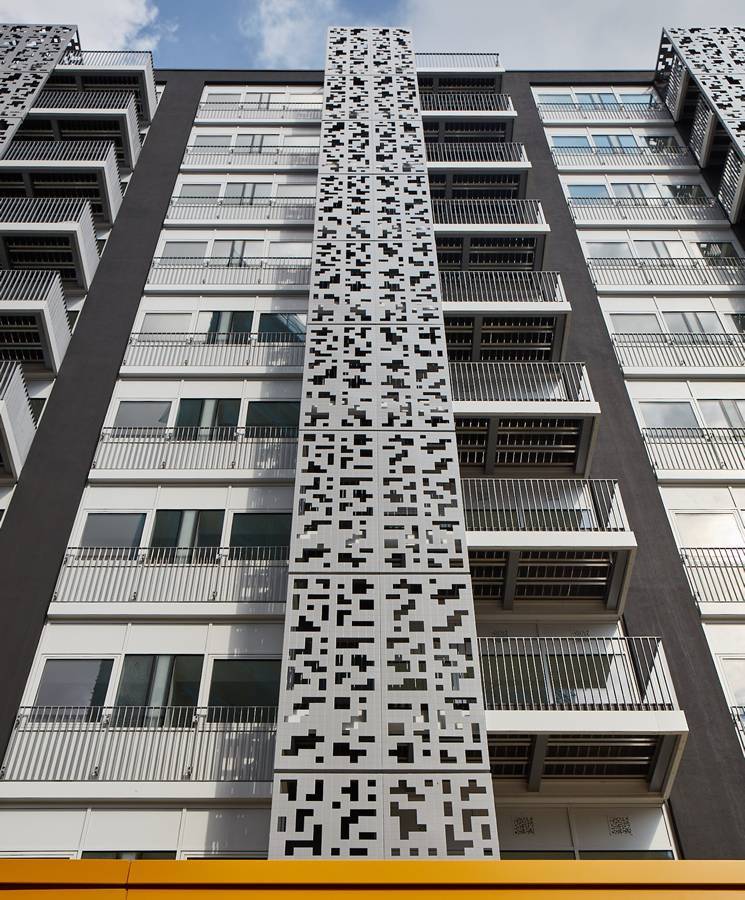

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the quality management systems in place and verify compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection and testing results, provides insight into the supplier’s QC processes and the reliability of their products.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and product quality. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the capacity to conduct audits themselves.
-
Certifications and Accreditations: Buyers should look for suppliers that hold relevant certifications, as these indicate adherence to established quality standards and best practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Different markets may have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect product specifications and compliance.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. It is advisable for buyers to establish clear quality expectations upfront and maintain open lines of communication throughout the manufacturing process.
By carefully evaluating manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select suppliers that meet their specific needs for perforated façades. This diligence ultimately contributes to the success of their projects and the long-term performance of the façades installed.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘perforated facade’
To successfully procure a perforated façade, it’s essential to follow a structured approach that ensures you make informed decisions. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the sourcing process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your perforated façade. This includes determining materials (e.g., aluminum, steel), perforation patterns, and dimensions. Understanding these specifications will guide you in selecting the right products that meet both aesthetic and functional needs, such as light management and acoustic properties.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Applications
Investigate current trends and applications of perforated façades in your target markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This step is crucial for aligning your project with regional preferences and regulatory requirements, ensuring your façade design resonates with local architectural styles and environmental considerations.
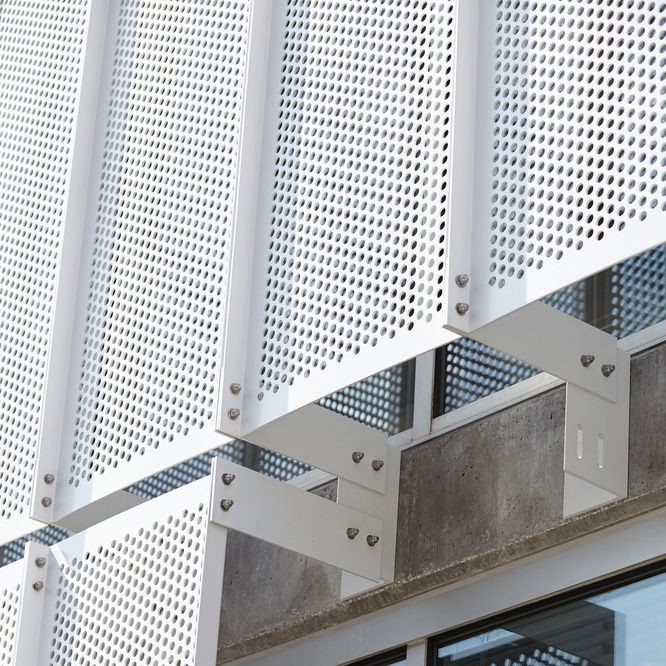

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Key factors to assess include:
– Experience: Look for suppliers with proven expertise in perforated façade systems.
– Portfolio: Review their past projects to gauge the quality and creativity of their work.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with international and local building codes and standards. Certifications related to fire safety, thermal efficiency, and environmental impact are vital. This verification protects your investment and ensures the façade will perform as expected over its lifecycle.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Ask for samples or prototypes of the perforated façade materials you’re considering. This hands-on approach allows you to evaluate the quality, finish, and performance of the materials firsthand. Pay attention to:
– Durability: Assess how well the materials withstand environmental factors.
– Aesthetics: Ensure the samples meet your design vision and color preferences.
Step 6: Discuss Customization Options
Engage with suppliers about customization possibilities. Many perforated façades offer variations in hole patterns, colors, and finishes that can enhance your building’s unique identity. Confirm that your supplier can accommodate specific design requests without compromising on quality or delivery timelines.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Delivery Schedules
Once you select a supplier, negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear agreements help to avoid misunderstandings later in the project. Make sure to outline:
– Lead Times: Confirm the expected delivery date and any potential delays.
– After-Sales Support: Inquire about the availability of technical support and warranty options.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for perforated façades, ensuring a successful project outcome that meets both design and performance expectations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for perforated facade Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Perforated Facade Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of perforated façades is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
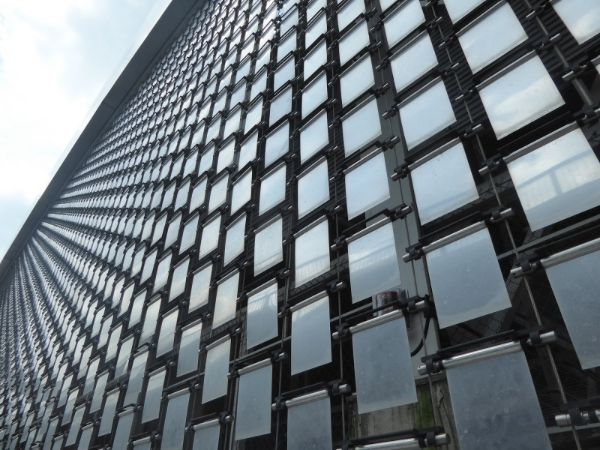

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Options typically range from aluminum and steel to composite materials, each with varying price points. Additionally, the type of perforation and surface treatment can affect material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the design and installation. Skilled labor is often required for precise installations, particularly for custom designs or when integrating acoustic and lighting solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to machinery, utilities, and other operational costs incurred during production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for unique designs or specific perforation patterns. The initial investment in tooling can be significant but is often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards involves quality control measures, which can add to overall costs. Certifications may be required for certain markets, further impacting pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and packaging requirements. Buyers should account for these expenses, especially in international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on competition, demand, and the supplier’s positioning in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Perforated Facade Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of perforated façades, impacting overall procurement costs:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide price breaks for larger orders. Understanding minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better pricing, especially for bulk projects.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to receive accurate quotations.
-
Materials: As mentioned earlier, the choice of material plays a pivotal role in pricing. Higher-quality materials or specialized coatings will typically incur higher costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet certain quality standards or certifications may come at a premium. However, investing in higher-quality products can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived value, but they often provide better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade agreed upon can affect the total cost. Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for determining who bears the costs and risks during shipping.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs for Perforated Facades?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing perforated façades, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchases and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Be open to discussing terms that can benefit both parties.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs, but also the long-term maintenance and operational costs associated with the façade. Investing in higher quality may yield savings in the long run.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand the pricing landscape. This helps in benchmarking and identifying competitive offers.
-
Evaluate Supplier Options: Diversify your supplier base to enhance competition and potentially lower costs. However, ensure that new suppliers can meet quality and delivery expectations.
-
Be Aware of International Pricing Nuances: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fluctuations in exchange rates, import duties, and local regulations can impact pricing. It is vital to factor in these elements when evaluating costs.
Disclaimer
Prices indicated in this analysis are for illustrative purposes only and can vary widely based on specific project requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always seek detailed quotes from suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to your project needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing perforated facade With Other Solutions
When evaluating façade solutions for commercial and residential buildings, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to perforated façades. Each option presents unique benefits and limitations that can significantly affect aesthetic appeal, functionality, and cost. This analysis compares perforated façades against two viable alternatives: solid metal façades and glass curtain walls, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on specific project requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Perforated Facade | Solid Metal Façade | Glass Curtain Wall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Offers light filtration, shading, and acoustic benefits. | Provides robust weather resistance and structural integrity. | Excellent natural light influx and thermal performance. |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; long-term energy savings. | Generally lower upfront costs but higher installation complexity. | Higher initial investment; energy-efficient long-term. |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick installation with pre-assembled components. | Requires precise installation and custom fabrication. | Complex installation; may need specialized labor. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; regular cleaning recommended. | Low maintenance; durable against weather elements. | Higher maintenance; glass cleaning and sealant checks needed. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for dynamic designs, energy-efficient buildings, and acoustic control. | Suitable for standard commercial buildings needing durability. | Best for high-rise buildings focused on natural light and aesthetics. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Solid Metal Façades Compared to Perforated Façades?
Solid metal façades are a popular choice due to their durability and weather resistance. They often come at a lower initial cost compared to perforated façades, making them appealing for budget-conscious projects. However, they lack the dynamic visual effects and light filtration capabilities that perforated façades offer. The installation process can be more complex, requiring precise measurements and custom fabrication, which may extend project timelines.
How Do Glass Curtain Walls Compare to Perforated Façades in Terms of Functionality?
Glass curtain walls provide a sleek, modern aesthetic while allowing abundant natural light into the building. They excel in thermal performance and energy efficiency, especially when combined with low-emissivity glass. However, the initial investment is typically higher than that of perforated façades. Maintenance can also be a challenge, as glass surfaces require regular cleaning to maintain clarity and visual appeal. Additionally, they do not offer the same shading and acoustic benefits that perforated façades provide.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Façade Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the right façade solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific project requirements, including budget constraints, aesthetic goals, and functional needs. Consideration of the local climate, building codes, and intended use of the space will also play crucial roles in the decision-making process. For projects that prioritize light control and energy efficiency, perforated façades might be the best option. In contrast, if durability and cost-effectiveness are paramount, solid metal façades could be more suitable. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will guide buyers in making a choice that aligns with their project’s objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for perforated facade
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Perforated Facades?
Understanding the technical properties of perforated facades is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed decisions. Here are several critical specifications:
Illustrative image related to perforated facade
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of material used in the fabrication of perforated facades, typically aluminum, steel, or composite materials. Higher-grade materials offer improved durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for various environmental conditions. B2B buyers should prioritize material grades that align with local climate and building regulations to ensure longevity and safety. -
Perforation Patterns
Perforation patterns determine both the aesthetic and functional aspects of a facade. They can be customized in size, shape, and arrangement, affecting light penetration, ventilation, and visual appeal. Understanding the impact of different patterns can help buyers achieve the desired architectural effect while also ensuring compliance with energy efficiency standards. -
Load-Bearing Capacity
This specification refers to the maximum weight that a perforated facade can support without compromising structural integrity. It is essential for buyers to evaluate load-bearing capacity in relation to building design and intended use, especially for high-rise constructions where wind loads and other forces are significant. -
Thermal Performance
Thermal performance measures how well the facade insulates against heat transfer. High thermal performance can lead to energy savings by reducing heating and cooling costs. Buyers should consider thermal performance ratings when selecting materials and designs, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures. -
Fire Resistance Rating
The fire resistance rating indicates how well a material can withstand fire exposure. This is critical for safety regulations and insurance considerations. B2B buyers must ensure that the selected facade materials meet local fire codes to mitigate risks associated with fire hazards. -
Acoustic Performance
Acoustic performance refers to the ability of a facade to reduce noise pollution from external sources. This property is particularly important in urban environments where noise can be disruptive. Buyers should consider acoustic ratings when designing spaces that require tranquility, such as residential or office buildings.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Perforated Facades?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of perforated facades, understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and budgeting. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and negotiating better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This process is crucial for obtaining competitive quotes and ensuring that all potential suppliers understand the requirements for perforated facades. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with the transportation of perforated facade materials. -
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. Utilizing BIM in the design phase can streamline collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors, ensuring that perforated facades are integrated efficiently into the overall building design. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and scheduling, ensuring that construction timelines are met without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes when selecting perforated facades for their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the perforated facade Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Perforated Facade Market?
The perforated facade market is experiencing significant growth, driven by various global factors. Urbanization, particularly in Africa and South America, is leading to increased demand for innovative building solutions that offer aesthetic appeal and functional benefits. Key trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 3D printing, which streamline the design and manufacturing processes, allowing for custom solutions tailored to specific architectural needs.
Additionally, the focus on energy efficiency is reshaping how perforated facades are perceived. As commercial and residential buildings increasingly incorporate sustainability into their designs, perforated facades are being utilized not only for their visual appeal but also for their ability to enhance natural ventilation and reduce energy consumption. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent building regulations are in place, these facades serve as effective solutions for compliance while providing unique design opportunities.
Emerging sourcing trends reflect a shift towards local suppliers, particularly in developing markets. This is driven by the desire for quicker turnaround times and reduced shipping costs. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers who offer comprehensive support, from design to installation, ensuring seamless project execution.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Perforated Facade Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of decision-making in the perforated facade sector. B2B buyers are more informed about the environmental impact of their sourcing choices, emphasizing the need for sustainable materials and ethical supply chains. This shift is not only about compliance with regulations but also about corporate responsibility and brand image.
The use of environmentally friendly materials, such as recycled aluminum and sustainably sourced composites, is gaining traction. Buyers are actively seeking suppliers who provide certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), which validate the sustainability of their products.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Moreover, the trend towards “green” building practices is influencing design considerations. Perforated facades can contribute to energy efficiency by optimizing natural light and reducing reliance on artificial lighting, thereby lowering carbon footprints. As international markets increasingly adopt these practices, B2B buyers must align their sourcing strategies with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability and ethical production methods.
How Has the Perforated Facade Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of perforated facades can be traced back to the early 20th century when architects began experimenting with building cladding to improve aesthetics and functionality. Initially, these facades were primarily used for decorative purposes. However, as architectural practices advanced, the focus shifted towards integrating performance features such as thermal insulation, acoustic control, and energy efficiency.
In recent decades, technological advancements have significantly transformed the sector. The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing technologies has enabled architects and builders to explore intricate designs and optimize material usage, resulting in cost-effective solutions. Furthermore, the growing awareness of environmental issues has pushed the industry towards more sustainable practices, influencing both design and sourcing trends.
Today, the perforated facade market is characterized by a diverse range of materials and innovative designs that cater to various architectural styles and functional requirements, marking a significant evolution from its early beginnings.
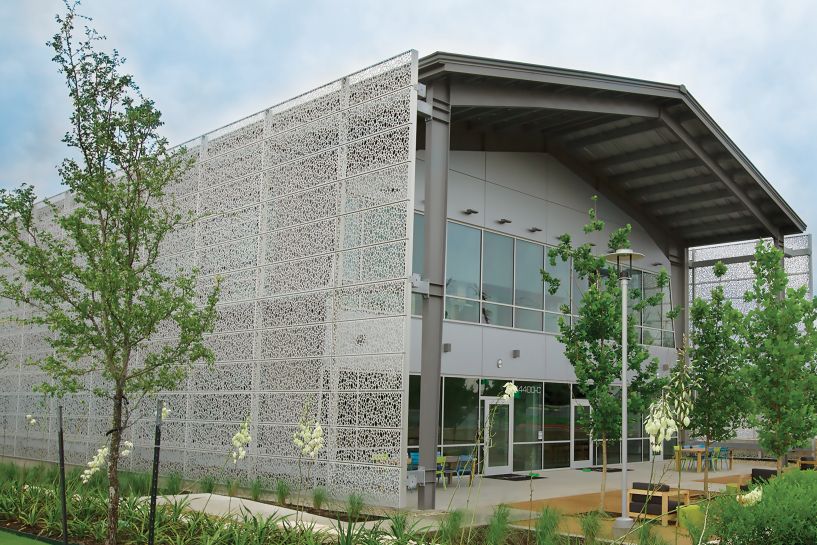

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of perforated facade
1. How do I choose the right perforated façade for my project?
Selecting the right perforated façade involves evaluating several factors, including design requirements, material preferences, and environmental considerations. First, consider the aesthetic goals of your project—what visual impact do you want to achieve? Next, assess the functional aspects, such as energy efficiency, acoustic performance, and fire safety. Collaborating with manufacturers to explore customizable options will ensure that your façade meets both aesthetic and regulatory standards. Additionally, reviewing case studies of similar projects can provide insights into effective solutions.
2. What are the benefits of using perforated façades in construction?
Perforated façades offer numerous benefits, including enhanced aesthetic appeal, energy efficiency, and functionality. They allow for unique design possibilities and play with light and shadow, creating dynamic visual effects. Functionally, they can provide shading, reduce heat gain, and improve acoustic performance. Moreover, these façades can contribute to fire safety in multi-storey buildings by facilitating smoke extraction. Overall, they are a versatile solution for modern architectural needs, adaptable to both residential and commercial applications.
3. What customization options are available for perforated façades?
Customization options for perforated façades are extensive. Buyers can choose from various materials, including aluminum and composite panels, and select hole patterns, colors, and finishes that align with their brand identity. Additionally, manufacturers often offer the ability to create bespoke designs tailored to specific architectural styles or functional requirements. Discussing your vision with suppliers can help identify the most suitable customization options that meet your project needs while adhering to industry standards.
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for perforated façades?
Minimum order quantities for perforated façades can vary significantly between manufacturers and depend on factors such as material type, design complexity, and production capabilities. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand square meters. It’s advisable to discuss your project scope with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller orders or batch production that can accommodate your budget and timeline.

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing perforated façades internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of perforated façades can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments, with the remainder due upon delivery or after installation. Many suppliers accept letters of credit or payment through secure online platforms. It is crucial to clarify payment terms in the initial negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the implications of currency fluctuations and international transaction fees when budgeting for your purchase.
6. How can I ensure quality assurance for perforated façade products?
To ensure quality assurance, work with reputable suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and certifications. Request samples to evaluate material quality and performance before making large orders. Inquire about the manufacturer’s quality control processes, including testing for durability, fire resistance, and compliance with international building codes. Establishing clear communication regarding your quality expectations and conducting regular inspections during production can help ensure that the final product meets your standards.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing perforated façades?
When sourcing perforated façades internationally, logistics play a crucial role in ensuring timely delivery. Consider factors such as shipping methods, freight costs, and potential customs duties. It’s essential to work closely with your supplier to understand the lead times for production and shipping, as well as any potential delays due to customs clearance. Additionally, ensure that your supplier has a reliable logistics partner to handle the transportation of large and often delicate façade materials.
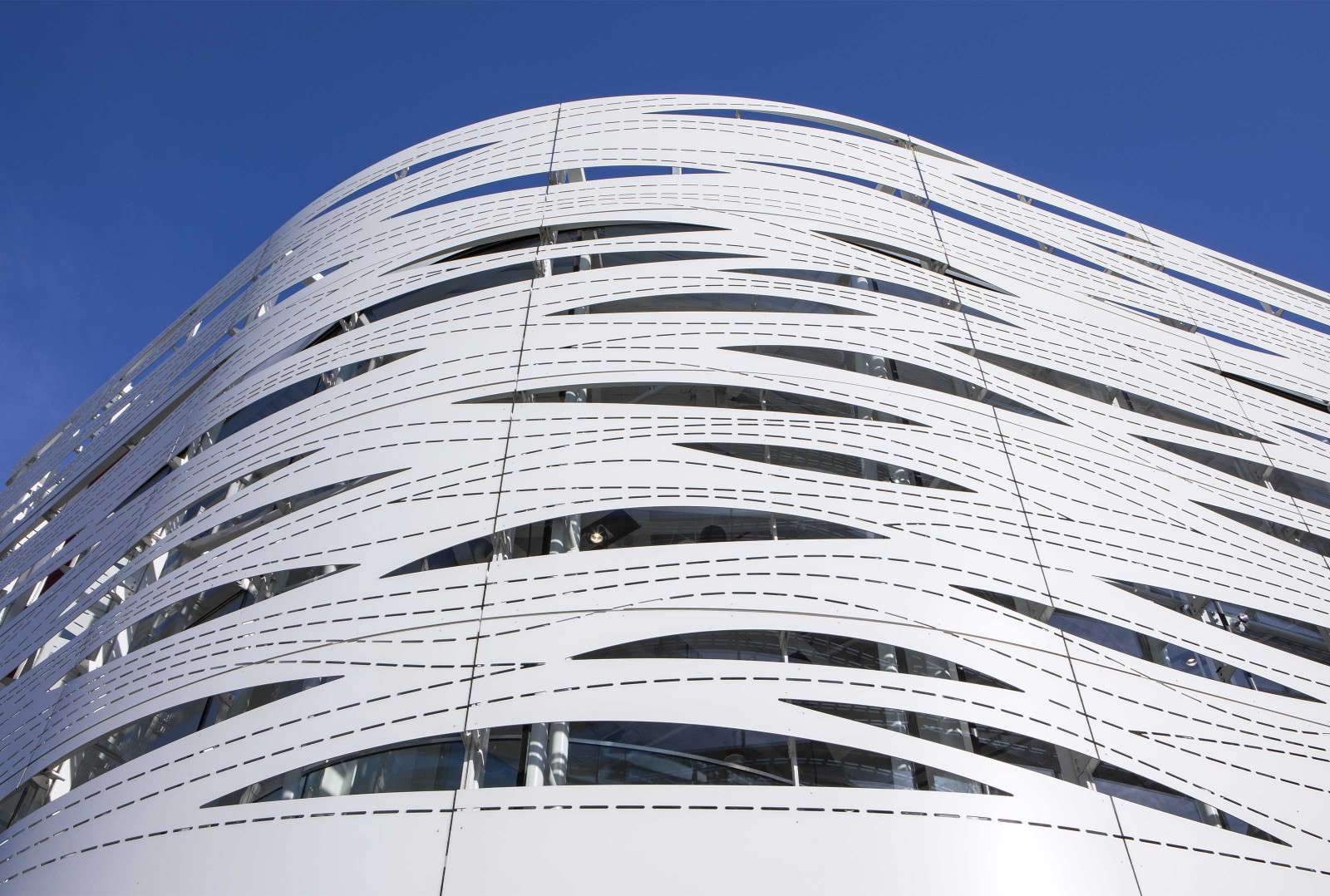

Illustrative image related to perforated facade
8. How do I vet suppliers for perforated façades?
Vetting suppliers for perforated façades involves researching their reputation, experience, and product offerings. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry, positive customer testimonials, and relevant certifications. Request references from previous clients to gauge their satisfaction with the products and services provided. Furthermore, visiting the supplier’s production facility or attending industry trade shows can offer insights into their manufacturing capabilities and quality standards. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can lead to better collaboration and project outcomes.
Top 8 Perforated Facade Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Perforated Metal Facades – Architectural Innovations
Domain: uk.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Perforated metal facades used in various architecture projects, including a skinny Taiwanese townhouse and a high-security bank in France. Featured projects include the Conservatoire of Music and Dance by PPA Architectures, RKM 740 Tower with wavy metal cladding by J Mayer H, and a Buenos Aires apartment block with aluminum façade by Juan Campanini and Josefina Sposito. Other notable designs inclu…
2. Dezeen – Perforated Metal Facades
Domain: dezeen.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, Dezeen – Perforated Metal Facades, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Bemo – Perforated Façades
Domain: bemo.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Perforated façades by Bemo offer countless design options for material, colour, profile geometry, and hole pattern. They are suitable for both interior and exterior use, serving as acoustic measures or shading elements. Key features include:
– Large selection of perforations for metal façade solutions.
– Quick and easy installation of all perforated façade solutions.
– Ability to create exciting s…
4. ArchDaily – Musharrabiya Insights
Domain: archdaily.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: The article discusses the Musharrabiya, a traditional architectural feature from the Arabic regions of the Middle East and North Africa, which is characterized by its perforated design that optimizes indoor thermal comfort and provides shade. It highlights the historical significance of Musharrabiyas in relation to environmental adaptation and their resurgence in modern architecture as a sustainab…
5. Hendrick Corp – Perforation Patterns
Domain: hendrickcorp.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“project_location”: “Dallas, TX”, “perforation_patterns”: [{“pattern”: “Pattern #1”, “hole_diameter”: “.250 inch”, “open_area”: “20%”}, {“pattern”: “Pattern #2”, “hole_diameter”: “.375 inch”, “open_area”: “44%”}]}
6. Azahner – Perforated Metal Panels
Domain: azahner.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Perforated metal panels offer architects and designers unique solutions for various applications, including lobbies, parking garage facades, and outdoor spaces. The panels are customizable to fit different budgets and timelines, available in various materials and designs. Key product features include:
1. **ImageLines®**: A graphic perforated metal panel system that combines curvilinear patterns …
7. Perforated Sheet – Kinetic Facade
Domain: perforated-sheet.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Perforated Kinetic Facade is a decorative facade made from perforated metal plates that sway like waves in the wind. It is used for large buildings such as museums and shopping malls. Key specifications include:
– Materials: aluminum, stainless steel, copper, carbon steel
– Surface treatments: mirror, brushed, anodized, powder coating, PVDF coating
– Sheet thickness: 0.6–0.8 mm
– Standard shee…
8. Accurate Perforating – Customizable Perforated Metal Facades
Domain: accurateperforating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Perforated metal facades are customizable panels used in architectural applications to improve aesthetics and functionality. They can cover unsightly areas, reduce glare, abate wind or noise, allow light in, provide privacy, and enhance overall appearance. Accurate Perforating offers a wide range of materials including aluminum, stainless steel, galvanized steel, Corten steel, brass, composites, c…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for perforated facade
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Perforated Facade Projects?
In summary, the strategic sourcing of perforated façades offers a unique opportunity for international buyers to capitalize on innovative design and functionality. The versatility of perforated façades allows for tailored solutions that enhance aesthetic appeal while addressing practical needs such as energy efficiency, acoustics, and fire safety. By leveraging a diverse range of materials, colors, and profile geometries, buyers can create distinctive façades that resonate with their brand identity and project requirements.
The importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated; it enables businesses to forge strong partnerships with suppliers, ensuring timely delivery and cost-effective solutions. Engaging with manufacturers who offer comprehensive support—from initial design consultation to final installation—can significantly streamline project execution and reduce risks associated with procurement.
As we look ahead, the demand for perforated façades is poised to grow across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This is an opportune moment for B2B buyers to invest in these innovative solutions. Embrace the potential of perforated façades to elevate your architectural projects and connect with reliable suppliers who can help you realize your vision.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.