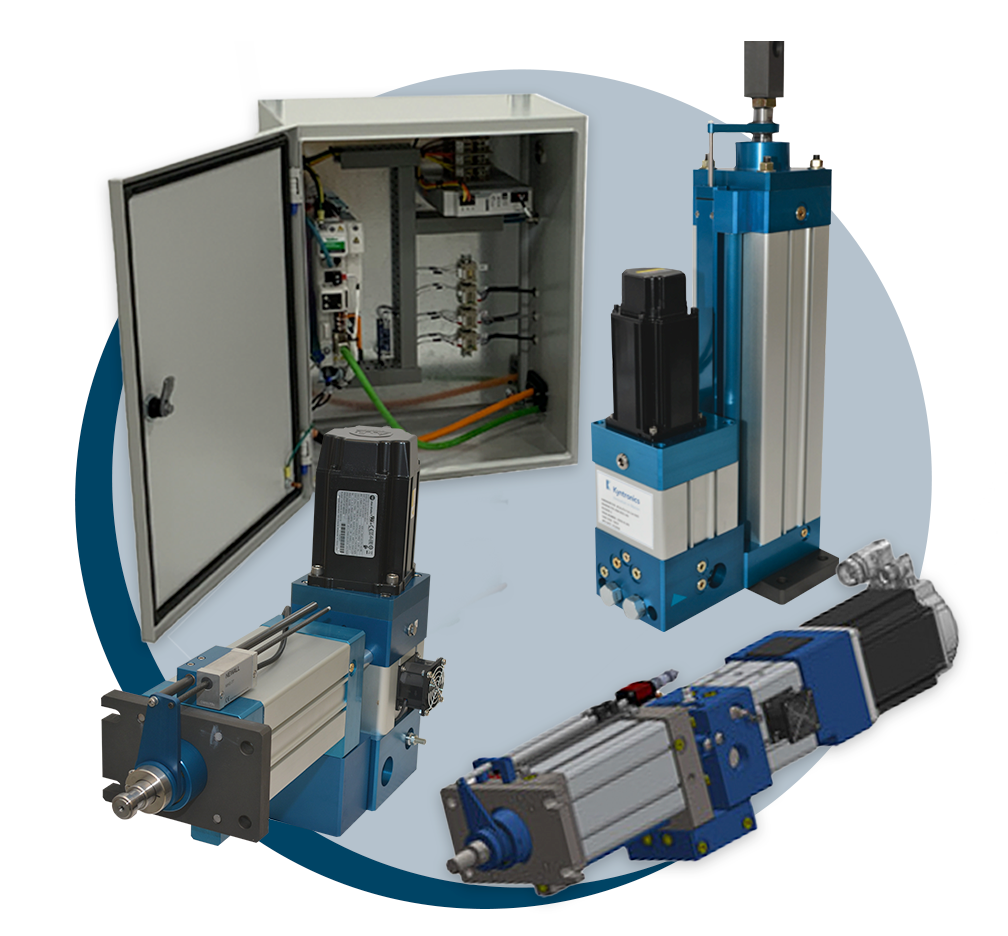
Is Your Linear Servo Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear servo
Navigating the complexities of sourcing linear servos can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a myriad of options available, from varying specifications to different control protocols, identifying the right linear servo for specific applications can feel overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify the global market for linear servos by providing a comprehensive overview that includes types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By understanding the nuances of linear servo technology—such as stroke length, thrust capabilities, and speed specifications—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Whether you are in the manufacturing sector in Germany or the automation industry in Saudi Arabia, this guide empowers you to navigate supplier options effectively and optimize your purchasing strategy. It also highlights key factors to consider when evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you choose partners who not only provide quality products but also support your business objectives.
Equipped with actionable insights and a clear framework, this guide serves as a valuable resource for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and drive innovation through the strategic use of linear servos.
Understanding linear servo Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Linear Servos | High precision, fast response, and programmable control | Robotics, automation, CNC machines | Pros: High accuracy, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Pneumatic Linear Servos | Utilizes compressed air for actuation | Manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: High speed, lightweight. Cons: Requires air supply, less precise. |
| Hydraulic Linear Servos | Operates using hydraulic fluid for high force | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | Pros: High load capacity, robust performance. Cons: Larger footprint, more maintenance. |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Servos | Designed for high thrust and rugged environments | Industrial automation, automotive | Pros: Excellent durability, capable of heavy loads. Cons: Typically more expensive. |
| Miniature Linear Servos | Compact size with moderate power | Consumer electronics, medical devices | Pros: Space-efficient, lightweight. Cons: Limited thrust and speed. |
What Are Electric Linear Servos and Their Applications?
Electric linear servos are characterized by their high precision and fast response times, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate positioning. They are commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems where programmable control is essential. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the initial investment, which may be higher than other types, but the long-term benefits of low maintenance and high accuracy can justify the cost.
How Do Pneumatic Linear Servos Function in Industry?
Pneumatic linear servos operate using compressed air, allowing for rapid movement and lightweight design. They are particularly effective in manufacturing settings and assembly lines where speed is critical. However, buyers should consider the necessity of an air supply system and the potential for less precision compared to electric options. The low upfront cost and high speed can be appealing, but operational costs may increase with air supply needs.
What Makes Hydraulic Linear Servos Suitable for Heavy Applications?
Hydraulic linear servos use hydraulic fluid to generate significant force, making them suitable for heavy machinery and construction equipment. Their ability to handle high loads and provide robust performance makes them a preferred choice in industries requiring strength. However, their larger footprint and maintenance requirements can be drawbacks for some buyers. Understanding the application environment and load requirements is crucial when considering this type.
When Should You Choose Heavy-Duty Linear Servos?
Heavy-duty linear servos are designed for demanding environments, providing high thrust and durability. They are often used in industrial automation and automotive applications where reliability under heavy loads is crucial. While these servos typically come with a higher price tag, their long lifespan and performance capabilities can offer excellent value for businesses focused on heavy-duty tasks. Buyers should evaluate their specific load and durability needs when making a decision.
How Do Miniature Linear Servos Fit into Modern Technology?
Miniature linear servos are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for applications in consumer electronics and medical devices. Their size allows for integration into tight spaces, but they come with limitations in thrust and speed. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, as these servos can provide efficient solutions where space is a constraint, despite potentially lower performance in heavy-duty scenarios.
Key Industrial Applications of linear servo
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear servo | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Reliability, stroke length, thrust capacity, and control options |
| Robotics | Robotic arms for precision tasks | Enhances precision and reduces operational downtime | Compatibility with existing systems, payload capacity, and speed |
| Aerospace | Actuation systems for control surfaces | Ensures safety and performance in critical applications | Weight, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions |
| Medical Devices | Surgical robots and prosthetics | Improves patient outcomes through precision and reliability | Compliance with health regulations, precision, and response time |
| Packaging | Automated packaging machines | Streamlines operations and reduces waste | Speed, reliability, and adaptability to various package sizes |
How Are Linear Servos Used in Manufacturing Automation?
In the manufacturing sector, linear servos are essential for automated assembly lines, where they facilitate the precise movement of components during production. These actuators enable faster cycle times and improved product quality by reducing human error. Buyers should consider factors such as reliability, stroke length, and thrust capacity when sourcing linear servos to ensure they meet the demands of high-volume production environments. Additionally, international buyers should be aware of local regulations and standards that may affect their choice of equipment.
What Role Do Linear Servos Play in Robotics?
Linear servos are integral to robotics, particularly in robotic arms that require precise movements for tasks such as welding, painting, or assembly. These servos enhance the accuracy and efficiency of robotic operations, minimizing the risk of errors and downtime. When sourcing for robotic applications, businesses should prioritize compatibility with existing systems, payload capacity, and speed. This is especially relevant for buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where advanced robotics are increasingly utilized in various industries.
How Are Linear Servos Applied in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, linear servos are crucial for actuation systems that control surfaces such as flaps and rudders. These systems must operate reliably under extreme conditions, ensuring the safety and performance of aircraft. Buyers in this sector should focus on weight, durability, and resistance to environmental factors when sourcing linear servos. International buyers, particularly from regions with stringent aerospace regulations, must ensure that their chosen products comply with industry standards.
Why Are Linear Servos Important in Medical Devices?
Linear servos are pivotal in medical devices, especially in surgical robots and prosthetics, where precision and reliability directly impact patient outcomes. These actuators allow for smooth, controlled movements that enhance surgical accuracy and the functionality of assistive devices. Buyers in the medical sector should consider compliance with health regulations, precision, and response time when sourcing linear servos. This is particularly important for international buyers in Africa and South America, where regulatory compliance can vary significantly.
How Do Linear Servos Enhance Packaging Efficiency?
In the packaging industry, linear servos are employed in automated packaging machines to ensure efficient and accurate packing of products. They help streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve overall productivity. Businesses should focus on speed, reliability, and adaptability to various package sizes when sourcing linear servos for packaging applications. For international buyers, understanding local market needs and packaging regulations is essential to make informed purchasing decisions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘linear servo’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing the Right Linear Servo for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to find linear servos that meet specific application requirements. For instance, a manufacturer in the automotive sector may need a linear servo that can operate under high temperatures and with precise control for assembly line automation. Inadequate sourcing can lead to purchasing products that either underperform or fail prematurely, resulting in costly downtime and a negative impact on production schedules.
The Solution: To effectively source the right linear servo, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before making a purchase. Start by defining the operational environment, such as temperature ranges, load capacity, and required speed. Engage with suppliers who offer customizable options to better align with unique specifications. Additionally, requesting samples or pilot products can provide insight into the performance of a linear servo in real-world conditions. Utilizing technical datasheets and consulting with engineers from the supplier can also ensure the selected product meets all operational requirements.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is the compatibility of new linear servos with existing machinery or control systems. For example, a robotics company may upgrade their actuation systems, only to discover that the new linear servos do not interface correctly with their existing control protocols, leading to integration challenges and increased costs.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize a comprehensive review of existing systems before selecting new linear servos. Understanding the control protocols (e.g., PWM, RS485, CAN) and voltage requirements is crucial. It is advisable to work closely with suppliers who can provide detailed technical support and integration guidelines. Furthermore, implementing modular designs in the system can facilitate easier updates and integration of new servos in the future. Engaging in pre-purchase consultations with the supplier can also help in identifying potential compatibility concerns early in the process.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Efficiency While Maintaining Quality
The Problem: Cost management is a persistent concern for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing linear servos. Buyers often face the dilemma of balancing cost with quality, as opting for lower-cost options may lead to subpar performance or durability issues. This is especially critical for industries like manufacturing, where operational reliability directly impacts profitability.
The Solution: Buyers should adopt a value-based approach rather than a purely cost-driven one. Begin by setting a budget that considers not only the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. Conducting a market analysis can help identify suppliers who offer high-quality servos at competitive prices. Additionally, considering long-term contracts or bulk purchasing agreements can reduce costs while ensuring a reliable supply of high-quality products. Lastly, establishing a partnership with suppliers who prioritize research and development can lead to access to innovative products that offer better efficiency and longer lifespan, ultimately providing a better return on investment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear servo
What Are the Key Materials Used in Linear Servos?
When selecting materials for linear servos, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of linear servos: aluminum, stainless steel, plastic composites, and brass.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Linear Servo Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant material often used in linear servo housings and components. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive, easy to machine, and offers excellent corrosion resistance, which is vital in humid or saline environments.
Cons: While durable, aluminum can be less resistant to wear compared to harder materials, which may affect longevity in high-friction applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and many oils, making it versatile for different environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially in markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia, where quality assurance is critical.
What Are the Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in Linear Servos?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications. Its properties include high tensile strength and resistance to oxidation, which is crucial in harsh environments.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel ensures long service life and reliability, especially in applications exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel compared to aluminum can be a drawback for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, its weight may not be suitable for applications where lightweight components are preferred.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with aggressive media, making it suitable for food processing or chemical handling applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU regulations) when using stainless steel in food-related applications.
How Do Plastic Composites Fit into Linear Servo Design?
Plastic composites are increasingly popular in linear servo applications due to their lightweight and versatility. They offer good mechanical properties and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros: Plastic composites are typically less expensive than metals and can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity.

Illustrative image related to linear servo
Cons: They may have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which can limit their use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in robotics or portable devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental impact and recycling options of plastic materials, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
What Role Does Brass Play in Linear Servo Applications?
Brass is often used in linear servo components that require good machinability and corrosion resistance, particularly in electrical connections and fittings.
Pros: Brass offers excellent conductivity and is easy to machine, making it ideal for precision components.
Cons: However, brass can be more expensive than aluminum and may not provide the same level of strength as stainless steel.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various fluids and gases, making it suitable for pneumatic or hydraulic applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the U.S. is crucial, particularly for applications in industries like aerospace or automotive.
Summary of Material Selection for Linear Servos
| Material | Typical Use Case for linear servo | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Housing and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less wear-resistant than steel | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-stress and corrosive environments | Exceptional strength and durability | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Plastic Composites | Lightweight applications in robotics | Cost-effective and easily molded | Lower temperature and pressure ratings | Medium |
| Brass | Electrical connections and fittings | Excellent machinability and conductivity | More expensive than aluminum | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions when sourcing linear servos, ensuring that the selected materials align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear servo
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Linear Servos?
The manufacturing process of linear servos involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards.
-
Material Preparation: The first stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, including metals like aluminum or steel for housing and components. Advanced materials such as composites may also be used for specific applications. Suppliers often provide certifications to confirm material quality, which is essential for B2B buyers to verify.
-
Forming: This stage includes machining processes like CNC milling, turning, and laser cutting. These techniques ensure precise dimensions and tolerances required for the servo’s functionality. The forming process may also involve the creation of gears and other mechanical components essential for the servo’s operation.
-
Assembly: In this stage, individual components are assembled into a complete linear servo unit. This process may be manual or automated, depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities. Attention to detail is crucial here, as the alignment of components directly affects performance. Automated assembly systems often incorporate real-time quality checks to ensure precision.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatments such as anodizing or painting, which enhance durability and corrosion resistance. This stage may also include the installation of electronic components and wiring for control systems. Proper finishing is vital to ensure the product’s longevity, especially in demanding environments.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Linear Servo Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in linear servo manufacturing is governed by several international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance.
-
ISO 9001: This is the most widely recognized international standard for quality management systems (QMS). It provides a framework for consistent quality assurance practices throughout the manufacturing process. Manufacturers certified to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for B2B buyers in Europe, as it ensures that products meet EU regulations.
-
API Standards: In industries like oil and gas, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are crucial. Compliance with these standards indicates that the linear servos can operate safely and effectively in harsh conditions typical of these sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Linear Servo Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process of linear servos. Several checkpoints ensure that products meet required specifications:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint occurs when raw materials arrive at the manufacturing facility. Materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various QC checks are performed. This includes monitoring machining processes, assembly accuracy, and the installation of electronic components. Regular inspections help identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each linear servo undergoes comprehensive testing. This includes functional tests to verify performance metrics such as thrust, speed, and precision. Any units that do not meet specifications are either reworked or discarded.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to robust quality control practices is critical. Here are several methods to verify supplier QC:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This is an effective way to assess compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the effectiveness of their QC processes. These reports should detail inspection results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken for any non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site audits.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Linear Servo Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure the quality and reliability of linear servos. Understanding these methods can help B2B buyers assess product quality effectively.
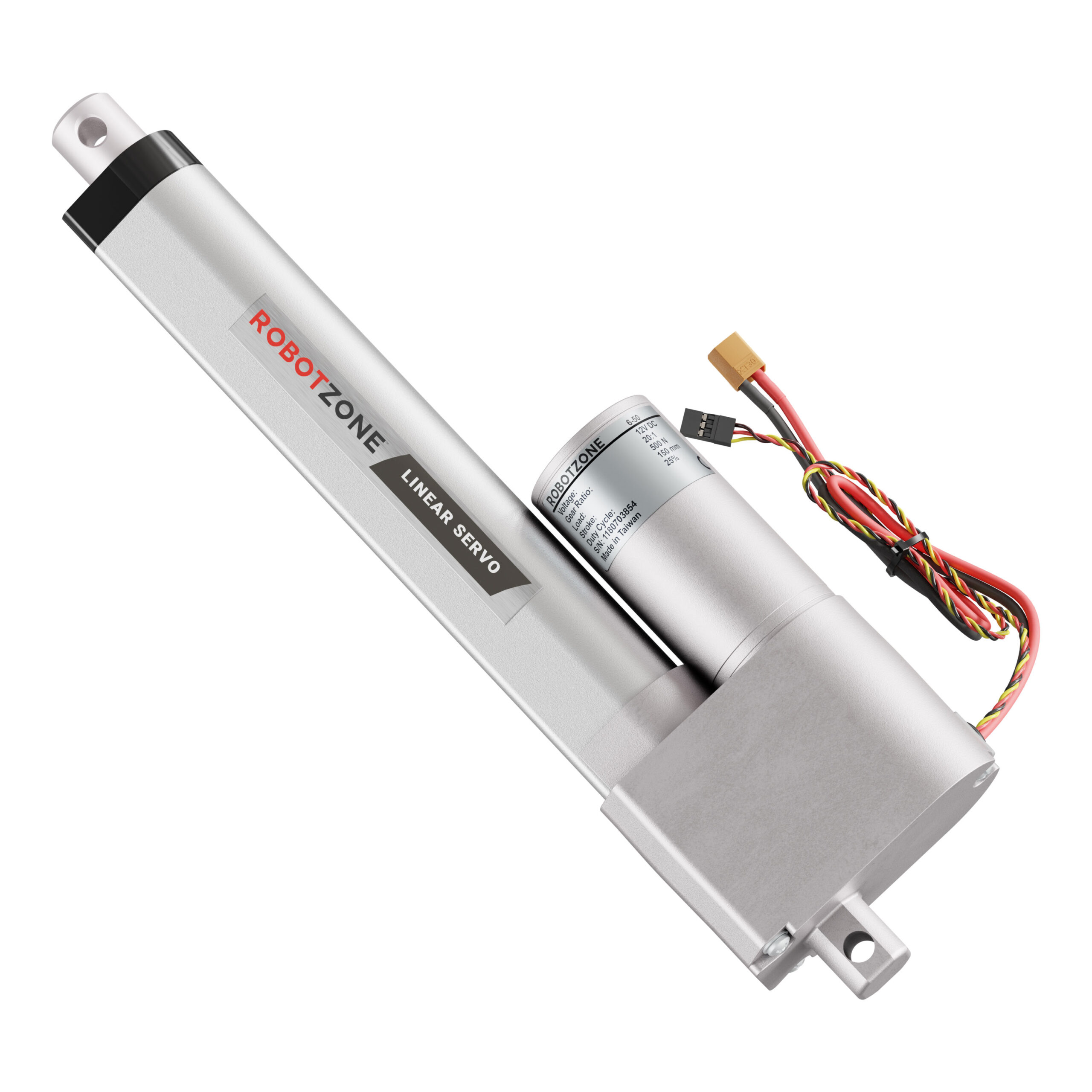

Illustrative image related to linear servo
-
Functional Testing: This involves running the servo under actual operating conditions to verify performance parameters such as speed, thrust, and response time. Functional testing helps confirm that the product meets its specified performance criteria.
-
Environmental Testing: This method assesses how well the servo performs under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, humidity, or exposure to dust and moisture. Certifications like IP67 or IP68 may be relevant for products intended for harsh environments.
-
Durability Testing: Linear servos often undergo stress testing to evaluate their longevity and reliability under continuous use. This may include cyclic loading tests that simulate real-world applications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges when navigating quality control in linear servo procurement.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in business practices can significantly impact negotiations and supplier relationships. Buyers should be aware of regional standards and expectations regarding quality assurance.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. For instance, products sold in Europe must comply with CE marking, while those in the Middle East may need to meet specific local standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are well-versed in these regulations.
-
Language Barriers: Language differences can lead to miscommunication regarding specifications and quality requirements. B2B buyers should consider employing translation services or hiring representatives fluent in the supplier’s language to facilitate clear communication.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing linear servos, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘linear servo’
The procurement of linear servos is a critical decision for businesses in various sectors, including manufacturing, robotics, and automation. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right products and suppliers for their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before starting the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the linear servo. Consider factors such as stroke length, thrust capacity, speed, and voltage. These specifications will guide your search and help you filter out unsuitable options.
- Stroke Length: Determine the distance the actuator needs to move.
- Thrust Capacity: Identify the load the servo must handle.
- Speed Requirements: Assess how quickly the servo needs to operate.
Step 2: Research Market Options
Conduct thorough research to understand the variety of linear servos available in the market. Review different manufacturers and product lines to find options that meet your specifications.
- Product Variants: Look for different models with varying features and price points.
- Technology Compatibility: Ensure the servos are compatible with your existing systems (e.g., control protocols like PWM or CAN).
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, vet potential suppliers comprehensively. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other clients in your industry or region.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews or case studies that highlight the supplier’s reliability and product quality.
- Support Services: Consider suppliers that offer technical support and after-sales service.
Step 4: Check Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the linear servos you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This is crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and reliability.
- Quality Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other industry-specific certifications that validate the quality of the products.
- Environmental Compliance: Verify that the products meet environmental regulations, especially if you are sourcing for industries with strict compliance needs.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have narrowed down your options, request samples from suppliers. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the performance of the linear servos in real-world conditions.
- Performance Evaluation: Test the servos under load conditions similar to your application.
- Durability Testing: Assess the longevity and reliability of the product through rigorous testing.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations with potential suppliers to secure favorable pricing and terms. Understand the full cost of ownership, including shipping, duties, and potential tariffs.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about discounts for large orders.
- Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that can benefit your cash flow.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Monitor Delivery
After selecting a supplier and finalizing the terms, proceed with the purchase. Maintain communication with the supplier to ensure timely delivery and address any issues that may arise.
- Delivery Tracking: Request tracking information to monitor the shipment.
- Post-Delivery Inspection: Inspect the products upon arrival to ensure they meet your specifications and quality standards.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing linear servos, ensuring they select the right products and partners to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear servo Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Linear Servo Pricing?
When sourcing linear servos, understanding the cost structure is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects the durability and performance of linear servos. High-quality metals and plastics may incur higher initial costs but contribute to longevity and reliability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Countries with higher labor costs may have higher prices for linear servos, impacting overall sourcing costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities and rent. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, translating to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can increase upfront costs but may be necessary for high-volume orders or specialized designs.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure product reliability, especially for applications in critical sectors like automotive or aerospace. The costs associated with quality assurance can influence the final price of linear servos.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on the distance and mode of transport, affecting the total cost of ownership. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers to anticipate shipping responsibilities and costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Linear Servo Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of linear servos, impacting the final cost for buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of premium materials and certifications (such as ISO or CE) can elevate costs. However, these investments often result in better performance and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge more, but they often provide better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for determining who bears the cost and risk during transportation. This knowledge can lead to better negotiation and cost management.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Linear Servos Internationally?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of linear servos requires careful consideration of various factors.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Leveraging competitive offers can lead to better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime should be factored into the overall cost analysis.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that could affect pricing. Building relationships with suppliers can also lead to better terms and pricing adjustments.
-
Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers who can provide detailed information about their QC processes and certifications. This ensures that the products meet the necessary standards, reducing the risk of defects.
-
Market Research: Familiarize yourself with local market conditions and competitor pricing. Understanding regional differences can help you make better sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, specifications, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough research and due diligence when sourcing linear servos to ensure the best outcomes for your business.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing linear servo With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Linear Servos?
In the realm of automation and motion control, linear servos are widely recognized for their precision and efficiency. However, they are not the only solution available. As B2B buyers explore options for linear motion systems, it’s essential to consider alternative technologies that may better fit their operational needs, budget constraints, or application requirements. This analysis compares linear servos with two viable alternatives: pneumatic actuators and electric linear actuators.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Linear Servo | Pneumatic Actuator | Electric Linear Actuator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and control | Moderate precision, faster speed | Good precision, slower than servos |
| Cost | Moderate ($99.99 to $299.99) | Generally lower initial costs | Varies widely ($100 to $600+) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration, requires power supply | Requires air compressor setup | Straightforward installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, reliable | Moderate, requires air quality checks | Low, but may require motor servicing |
| Best Use Case | Robotics, CNC machines | Assembly lines, packaging | Automation in various industries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to create linear motion. They are often favored in applications requiring rapid movement, such as in assembly lines and packaging. One significant advantage of pneumatic systems is their lower initial cost compared to linear servos. However, they can suffer from issues like less precision and the necessity for a compressed air supply, which adds complexity to the setup and ongoing maintenance. Furthermore, air quality and pressure can impact performance, making them less reliable in sensitive applications.

Illustrative image related to linear servo
Electric Linear Actuators
Electric linear actuators operate using electric motors to drive linear motion. They offer a good balance between performance and cost, making them a versatile option for various applications. Electric actuators can provide decent precision and are relatively easy to install, often requiring just a simple electrical connection. However, they typically do not match the speed and precision of linear servos. Additionally, they can be more expensive, particularly for high-load or high-speed applications, as the price may range from $100 to over $600 depending on specifications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate motion control solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific application, performance requirements, budget, and maintenance capabilities. Linear servos are ideal for applications demanding high precision and control, while pneumatic actuators may be suitable for high-speed tasks with lower precision needs. Electric linear actuators serve as a versatile middle ground, offering reasonable performance across various scenarios. Ultimately, the choice should align with the operational goals and constraints of the business, ensuring optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear servo
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Linear Servos?
When selecting linear servos for industrial applications, understanding their critical specifications is essential. Here are some key properties that significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications:
-
Stroke Length
The stroke length refers to the maximum distance the actuator can move. This specification is vital for determining the actuator’s capacity to handle specific tasks. For B2B buyers, understanding stroke length helps ensure the actuator will meet the requirements of their machinery or automation system, avoiding costly modifications later. -
Thrust Force
Thrust force is the maximum load the servo can push or pull. It is measured in kilograms or pounds and dictates the actuator’s ability to handle heavy loads. For manufacturers, selecting a servo with appropriate thrust ensures operational efficiency and prevents equipment failure due to overload. -
Speed
Speed indicates how quickly the actuator can extend or retract, typically measured in millimeters per second (mm/sec). This property is crucial for applications requiring rapid movements, such as assembly lines or robotic arms. Buyers must evaluate speed in conjunction with thrust to find a balance that meets their operational needs. -
Operating Voltage
The operating voltage specifies the electrical requirements for the servo to function effectively, ranging from low voltage (e.g., 6V) to high voltage (e.g., 24V). Compatibility with existing systems is essential for B2B buyers to avoid electrical issues and ensure reliable performance. -
Control Protocol
Control protocols (e.g., PWM, RS485, CAN) define how the servo is commanded and monitored. Understanding the control options available allows buyers to integrate the servo seamlessly into their existing systems, enhancing automation and control capabilities. -
IP Rating
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates the level of protection against dust and moisture. Higher ratings (e.g., IP67) are critical for applications in harsh environments, ensuring durability and longevity. Buyers must assess the environmental conditions of their operations to choose the right IP rating.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Linear Servo Industry?
Navigating the procurement of linear servos requires familiarity with industry terminology. Here are several key terms that buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking to ensure compatibility and quality in their supply chain. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and overall procurement costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production schedules and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products. This process is essential for buyers looking to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are a series of international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Understanding these terms is vital for managing logistics, costs, and risks associated with international trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it affects project timelines and inventory levels. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their production schedules. -
Warranty and Support
Warranty terms outline the manufacturer’s commitment to product quality and support. Understanding warranty policies helps buyers mitigate risk and ensures they have access to assistance if issues arise.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring linear servos, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product reliability.

Illustrative image related to linear servo
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the linear servo Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Linear Servo Sector?
The linear servo market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in automation and robotics across various industries. Key drivers include the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. The shift towards Industry 4.0, characterized by smart factories and IoT integration, is also propelling the adoption of linear servo systems, which offer enhanced control and responsiveness.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding current and emerging sourcing trends is crucial. There is a growing preference for suppliers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific applications, such as medical devices or agricultural equipment. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to a broader range of products, allowing buyers to compare specifications, prices, and delivery times more efficiently.
Moreover, the linear servo market is witnessing a shift towards more compact and lightweight designs without compromising on performance. This trend is particularly relevant for industries focused on reducing energy consumption and optimizing space. As businesses increasingly prioritize automation to enhance productivity and reduce labor costs, the demand for linear servo actuators is expected to grow significantly, presenting ample opportunities for suppliers and buyers alike.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Linear Servos?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the linear servo sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing carbon footprints in production.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies are expected to ensure that their sourcing practices comply with labor laws and environmental regulations. This has led to a growing demand for ‘green’ certifications, which can enhance a supplier’s credibility and appeal. For instance, suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials or have implemented energy-efficient manufacturing processes can differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Furthermore, buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and can provide documentation on the sustainability of their products. This not only fosters trust but also aligns with the increasing consumer demand for socially responsible products. As the linear servo market evolves, sustainability will play a pivotal role in shaping buyer preferences and influencing purchasing decisions.
What Is the Evolution of Linear Servos in B2B Applications?
The evolution of linear servos can be traced back to the early days of automation technology. Initially designed for simple applications, these actuators have undergone significant advancements in terms of precision, speed, and control capabilities. The introduction of digital control systems in the late 20th century revolutionized their functionality, enabling more complex and responsive applications.
In recent years, the integration of smart technologies and IoT has further transformed the linear servo landscape. Modern systems are equipped with advanced sensors and communication protocols, allowing for real-time monitoring and control. This evolution has expanded the applications of linear servos beyond traditional manufacturing to include robotics, medical devices, and even renewable energy systems.

Illustrative image related to linear servo
As the demand for automation continues to rise, the linear servo sector is poised for further innovation, providing exciting opportunities for B2B buyers looking to enhance their operational efficiencies and product offerings. Understanding this evolution is essential for making informed sourcing decisions in a rapidly changing market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear servo
-
How do I select the right linear servo for my application?
Selecting the appropriate linear servo involves evaluating several factors such as stroke length, thrust requirements, speed, and operating environment. Start by defining the load specifications and the application’s speed requirements. For precision tasks, consider servos with higher resolution and feedback capabilities. Additionally, assess the environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity, to ensure the servo can operate effectively. Always consult technical datasheets and, if necessary, engage with suppliers for expert recommendations tailored to your specific needs. -
What is the best thrust capacity for a linear servo in industrial applications?
The ideal thrust capacity for a linear servo largely depends on the specific application and load requirements. For light-duty applications, servos with thrust capacities ranging from 3 to 12 kg are typically sufficient. In contrast, heavy-duty applications may require thrust capacities exceeding 100 kg. Consider both static and dynamic loads, and factor in safety margins to avoid overloading. Collaborating with manufacturers can provide insights into optimal thrust specifications based on your intended use. -
What are the common customization options available for linear servos?
Most manufacturers offer various customization options for linear servos, including stroke length, thrust specifications, and control interfaces (e.g., PWM, CAN). Additionally, you can request specific materials for enhanced durability or environmental protection (like IP ratings). Custom firmware may also be available for unique operational requirements. When approaching suppliers, clearly articulate your needs to ensure they can accommodate your specifications while maintaining performance and reliability. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for linear servos?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for linear servos can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs range from a few units for standard products to larger quantities for customized solutions. It’s essential to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller orders if necessary. Many suppliers are willing to accommodate smaller initial orders, especially for new clients. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing linear servos internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of linear servos typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Suppliers may offer flexible terms based on the buyer’s creditworthiness and relationship history. It’s advisable to negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. Ensure clarity on currency exchange rates and potential additional costs, such as tariffs or taxes, that may affect the overall price. -
How can I ensure the quality of linear servos from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing linear servos internationally, start by vetting suppliers through certifications like ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Request samples for testing and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Establish clear quality assurance protocols, including defining acceptable tolerance levels and performance metrics. Regular communication with the supplier can also help address any quality concerns proactively. Consider using third-party inspection services for additional assurance, especially for large orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing linear servos?
When importing linear servos, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with your destination country’s import requirements. Understand the total landed cost, including shipping fees, duties, and taxes. Planning for potential delays in customs clearance is also crucial. Additionally, ensure that your products are packaged adequately to prevent damage during transit, and maintain open communication with your supplier throughout the shipping process. -
What are the common applications for linear servos in different industries?
Linear servos are widely used across various industries, including manufacturing, robotics, automotive, and medical devices. In manufacturing, they facilitate precise positioning in automated assembly lines. In robotics, they enable movement and actuation for robotic arms. The automotive industry utilizes linear servos for applications like seat adjustment and automated doors. In medical devices, they provide precision in surgical tools and diagnostic equipment. Understanding the specific applications can help you identify the right servo for your operational needs.
Top 8 Linear Servo Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gobilda – HLS12 Linear Actuator
Domain: gobilda.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: [{‘SKU’: ‘HLS12-100380-6V’, ‘Stroke’: ‘100mm’, ‘Retracted Length’: ‘152mm’, ‘Extended Length’: ‘252mm’, ‘Thrust’: ‘22.2kg’, ‘Speed’: ‘4.1mm/sec’, ‘Price’: ‘$99.99’}, {‘SKU’: ‘HLS12-10050-6V’, ‘Stroke’: ‘100mm’, ‘Retracted Length’: ‘152mm’, ‘Extended Length’: ‘252mm’, ‘Thrust’: ‘3.1kg’, ‘Speed’: ‘30.9mm/sec’, ‘Price’: ‘$99.99’}, {‘SKU’: ‘HLS12-100210-6V’, ‘Stroke’: ‘100mm’, ‘Retracted Length’: ‘152…
2. Hitec Commercial Solutions – Linear Servo Actuators
Domain: hiteccs.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: This company, Hitec Commercial Solutions – Linear Servo Actuators, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Servocity – 12V Heavy-Duty Linear Actuators
Domain: servocity.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Linear actuators provide a strong, reliable source of linear motion for projects. They can be operated with a battery and a switch, featuring built-in limit switches to prevent over-run. Potentiometer feedback can be utilized with an Arduino for speed control. Products include: 12V Heavy-Duty Linear Actuators with various thrusts (33lb, 112lb, 225lb) and strokes (2″, 4″, 6″, 8″, 10″, 12″) priced a…
4. Actuonix – T16-R Mini Track Actuator
Domain: actuonix.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Linear Servos for RC and Arduino by Actuonix Motion Devices include various models such as T16-R Mini Track Actuator with Servo Control available in different gear ratios (22:1, 64:1, 256:1) and a stroke length of 100mm, all operating at 12 volts and priced at $110.00 each. The servos are designed for precision, durability, and easy integration into applications, making them suitable for industrie…
5. Studica – Multi-Mode Smart Servo Motor
Domain: studica.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: { “products”: [ { “name”: “Multi-Mode Smart Servo Motor”, “sku”: “75002”, “price”: “$28.99”, “stock”: “In stock”, “features”: “All-steel gears, high torque, FTC legal” }, { “name”: “Multi-Mode Smart Servo 200 – FAST”, “sku”: “75007”, “price”: “$28.99”, “stock”: “In stock”, “features”: “200RPM, +/- 150-degree range, programmable, FTC legal” }, { “name”: “Linear Servo RC Actuator 140S-190N”, “sku”: …
6. Actuonix – L12-R Series Motors
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Actuonix L12-R series motors; servo-enabled linear actuators; extendable rod length: 2-4 inches; low power requirement; compact servo actuator systems with integrated feedback and control; mini servo actuators for lightweight tasks; built-in closed-loop control for position accuracy.
7. AndyMark – Linear Servos
Domain: andymark.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, AndyMark – Linear Servos, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. RobotShop – Compact Linear Actuator
Domain: robotshop.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, RobotShop – Compact Linear Actuator, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear servo
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Linear Servo Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of linear servo procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial differentiator for international B2B buyers. By leveraging comprehensive supplier evaluations and understanding product specifications such as thrust, speed, and stroke length, businesses can optimize their purchasing decisions. The diverse offerings from manufacturers, ranging from light-duty to heavy-duty linear servos, allow buyers to tailor solutions that meet specific operational requirements while managing costs effectively.
Furthermore, establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better negotiation terms and access to innovative technologies, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency. As markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of industry trends and technological advancements is essential.
Looking forward, organizations are encouraged to embrace a proactive approach in their sourcing strategies. Engage with suppliers that offer not just products, but also insights into emerging trends and applications. By doing so, you position your business to thrive in a rapidly changing environment, ensuring that your linear servo solutions not only meet current demands but are also poised for future growth. Take the step today to refine your sourcing strategy and unlock the full potential of your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to linear servo
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.