Is Your Holes In Burn Barrel Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for holes in burn barrel
As global markets increasingly focus on sustainable waste management solutions, understanding the intricacies of burn barrels, particularly the strategic placement and design of holes, becomes paramount for B2B buyers. Sourcing effective burn barrels that incorporate optimal ventilation holes can significantly enhance combustion efficiency and reduce harmful emissions, addressing both environmental concerns and regulatory compliance. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of the various types of burn barrels available, their applications across different industries, and the critical role that hole design plays in maximizing performance.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany—will benefit from a thorough examination of supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for implementation. By offering actionable insights into the factors that influence burn barrel efficacy, including material quality and design specifications, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you’re looking to enhance operational efficiency, comply with local regulations, or invest in environmentally-friendly solutions, understanding the nuances of burn barrel design will be instrumental in navigating the complexities of the global market. Dive into the guide to discover how to strategically select the right burn barrel that meets your specific business needs while promoting sustainable practices.
Understanding holes in burn barrel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilation Holes | Located near the bottom, evenly spaced for airflow | Waste disposal, landscaping, agriculture | Pros: Enhances combustion efficiency; reduces smoke. Cons: May require regular maintenance to prevent clogging. |
| Drainage Holes | Positioned at the bottom to allow water runoff | Industrial waste management | Pros: Prevents rusting; extends barrel lifespan. Cons: Potential for debris accumulation if not monitored. |
| Airflow Slots | Diagonal cuts or larger openings on sides for improved airflow | Fire control, outdoor heating | Pros: Facilitates better burning; reduces smoke and emissions. Cons: May compromise structural integrity if not designed properly. |
| Ash Collection Holes | Smaller holes or compartments for ash removal | Recycling, eco-friendly operations | Pros: Simplifies ash management; enhances safety. Cons: Requires additional design considerations for effective function. |
| Safety Vent Holes | Positioned to release pressure during burning | Hazardous material disposal | Pros: Reduces risk of explosion; enhances safety during burning. Cons: May require regulatory compliance checks. |
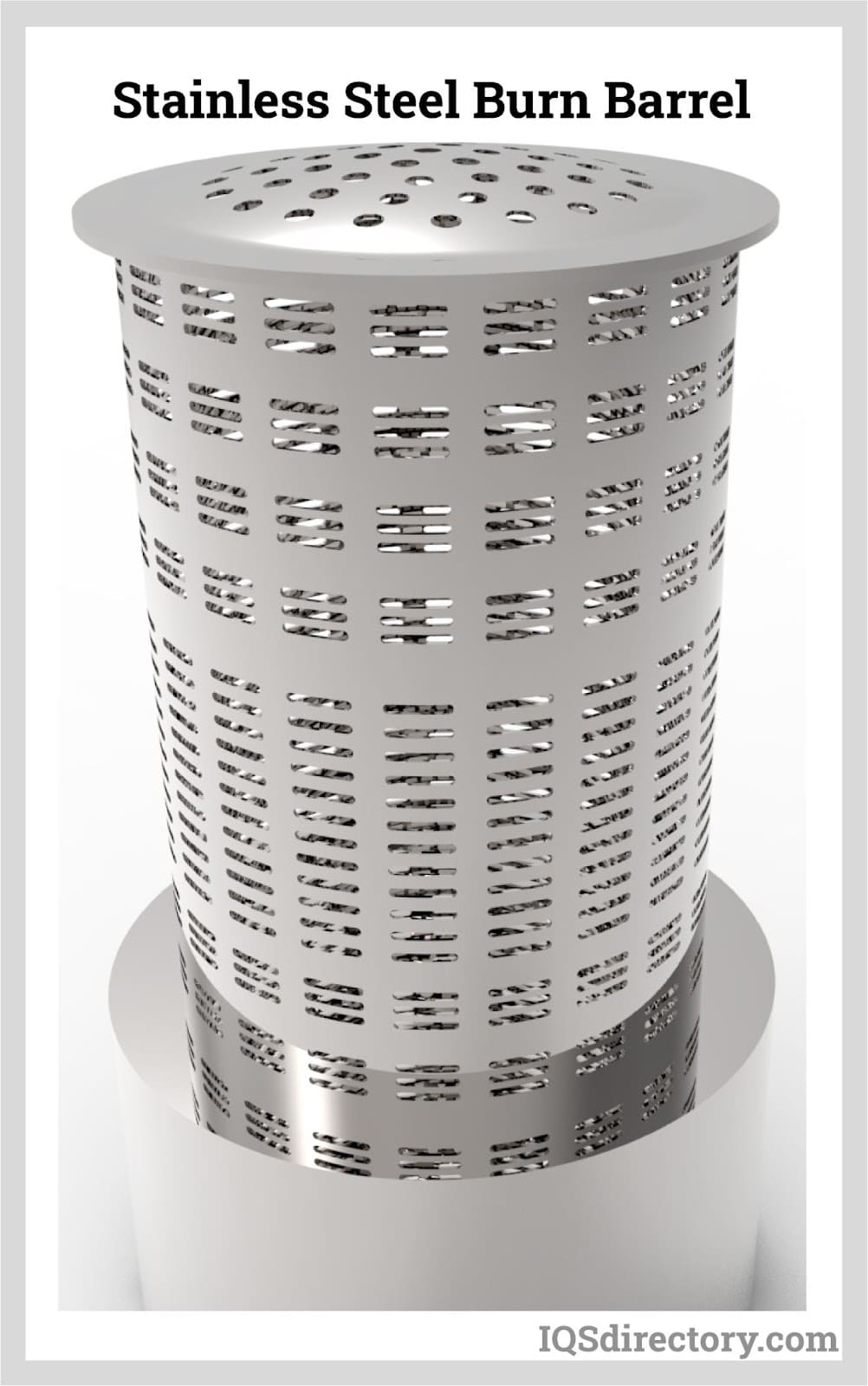
What Are Ventilation Holes in Burn Barrels and Their Importance?
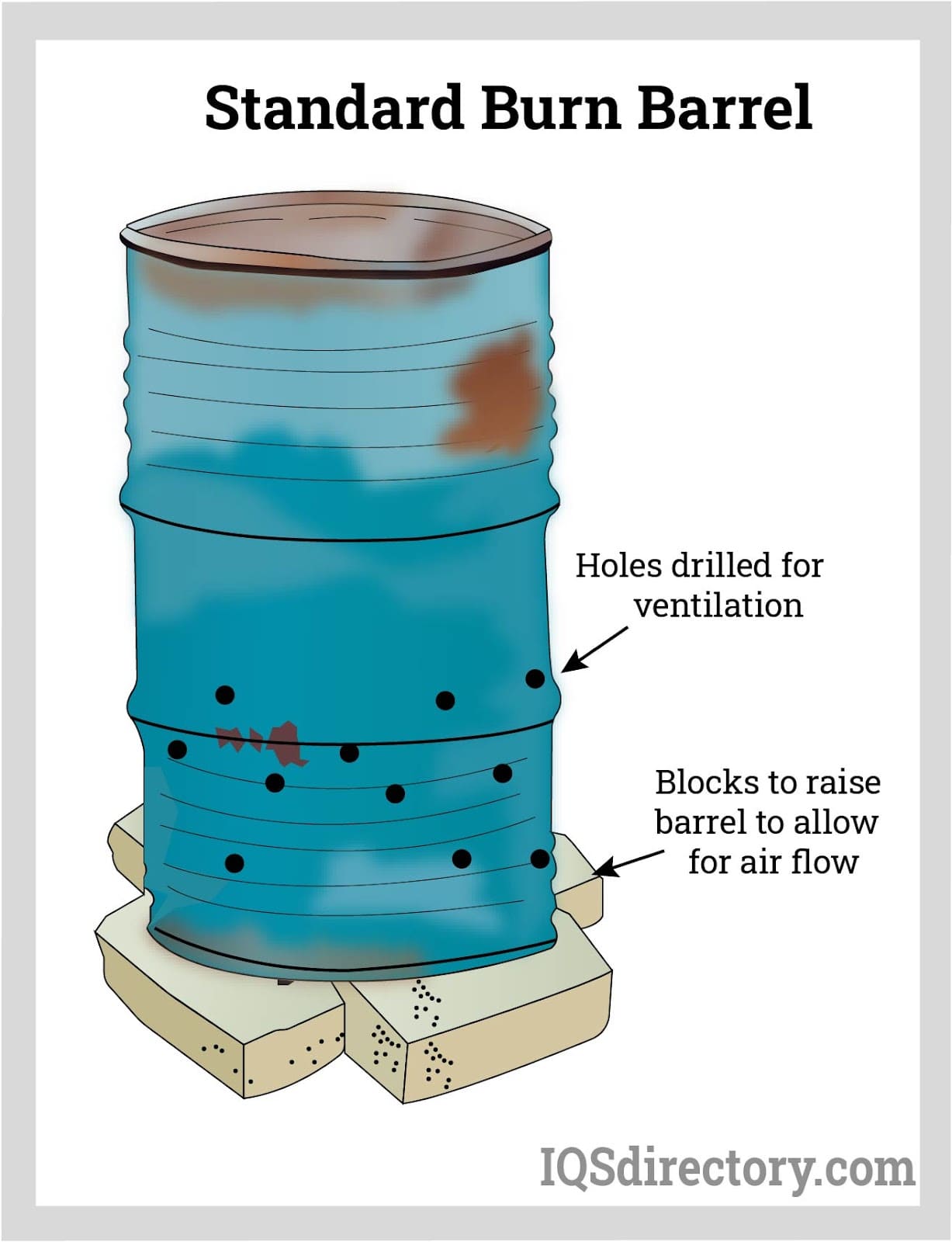
Ventilation holes are critical for ensuring adequate airflow in burn barrels. Typically drilled near the bottom, these holes allow oxygen to fuel the fire, leading to more efficient combustion. For B2B buyers, especially those in waste management or landscaping, understanding the placement and size of these holes can significantly impact the efficiency of waste disposal operations. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent clogging, which can affect performance.
How Do Drainage Holes Contribute to Burn Barrel Durability?
Drainage holes are strategically placed at the bottom of burn barrels to facilitate the escape of water. This feature is essential for preventing rust and prolonging the life of the barrel, making it a valuable consideration for buyers in industrial waste management. While they enhance durability, buyers should be aware that debris can accumulate in these holes, necessitating routine inspections to maintain functionality.
What Are the Benefits of Airflow Slots in Burn Barrels?
Airflow slots, often created through diagonal cuts on the sides of the barrel, serve to improve air circulation and combustion efficiency. This design feature is particularly advantageous for businesses that rely on burn barrels for fire control or outdoor heating. Enhanced airflow reduces smoke emissions and increases burning efficiency. However, buyers must ensure that the structural integrity of the barrel is not compromised during the cutting process.
How Do Ash Collection Holes Facilitate Waste Management?
Ash collection holes are designed to simplify the removal of ash, making burn barrels easier to manage for businesses focused on recycling and eco-friendly operations. These holes can improve safety by reducing the risk of ash buildup, which can lead to fire hazards. Buyers should consider the design of these holes to ensure they effectively serve their intended purpose while also being easy to access for maintenance.
Why Are Safety Vent Holes Essential for Hazardous Material Disposal?
Safety vent holes are crucial for releasing pressure during the burning process, particularly when dealing with hazardous materials. For B2B buyers in industries that require strict safety protocols, such as hazardous waste disposal, incorporating these holes can significantly reduce the risk of explosions. While beneficial, compliance with local regulations regarding safety features is essential, making it a critical consideration for any purchase.
Key Industrial Applications of holes in burn barrel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of holes in burn barrel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management | Efficient disposal of organic waste | Reduces landfill waste and promotes sustainable practices | Regulatory compliance, material durability, size options |
| Agriculture | Burning agricultural byproducts (e.g., crop residues) | Enhances soil quality through ash and reduces pest habitats | Heat resistance, portability, safety features |
| Construction | Disposal of construction debris (wood, paper) | Streamlines waste management on-site, reducing transportation costs | Compliance with local regulations, ease of assembly |
| Environmental Services | Controlled burning for land clearing and waste reduction | Minimizes environmental impact while managing land effectively | Airflow design, structural integrity, size adaptability |
| Outdoor Recreation | Portable campfire solution for outdoor events | Provides a safe and contained environment for burning materials | Lightweight design, ease of transport, safety features |
How is the ‘holes in burn barrel’ used in Waste Management?
In the waste management sector, burn barrels with strategically placed holes facilitate the efficient burning of organic waste, such as yard debris and food scraps. The holes allow for adequate airflow, promoting complete combustion and reducing smoke emissions. This application is particularly valuable for municipalities aiming to minimize landfill waste. International buyers must consider local regulations regarding burning practices, as compliance is crucial for operational legality. Additionally, the material used for the barrel must withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion.
What role do holes in burn barrels play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, burn barrels serve to dispose of crop residues and other organic materials. The holes in the barrel enhance airflow, enabling a hotter and more efficient burn that produces ash beneficial for soil enrichment. This practice not only helps in pest control but also contributes to soil health by returning nutrients to the earth. Buyers from regions with strict environmental regulations must ensure that their burn barrels comply with local agricultural guidelines and are constructed from durable materials that can withstand repeated use.
How do construction companies utilize burn barrels?
Construction sites often generate considerable amounts of waste, including wood and paper. Burn barrels equipped with holes allow for the efficient disposal of this debris on-site, reducing the need for transportation to landfills. This not only cuts costs but also streamlines waste management processes. For B2B buyers in the construction industry, it is essential to source burn barrels that meet safety regulations and are easy to assemble and transport, especially for projects in remote locations.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
In what ways do environmental services benefit from burn barrels?
Environmental services utilize burn barrels for controlled burning of waste and land clearing operations. The holes in the barrels are designed to optimize airflow, ensuring that burning is efficient and minimizes harmful emissions. This application is critical for maintaining ecological balance while managing waste effectively. International buyers should prioritize sourcing barrels that meet environmental standards and offer structural integrity, as these factors directly impact the sustainability of their operations.
How can burn barrels be adapted for outdoor recreation?
In the outdoor recreation industry, burn barrels with holes can serve as portable campfire solutions, providing a safe space for burning materials during camping trips or outdoor events. The design allows for proper ventilation, reducing smoke and enhancing the overall experience for users. Buyers in this sector should focus on lightweight and easy-to-transport designs, ensuring that safety features are included to prevent accidents in natural settings. Compliance with local fire regulations is also a key consideration for international buyers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘holes in burn barrel’ & Their Solutions
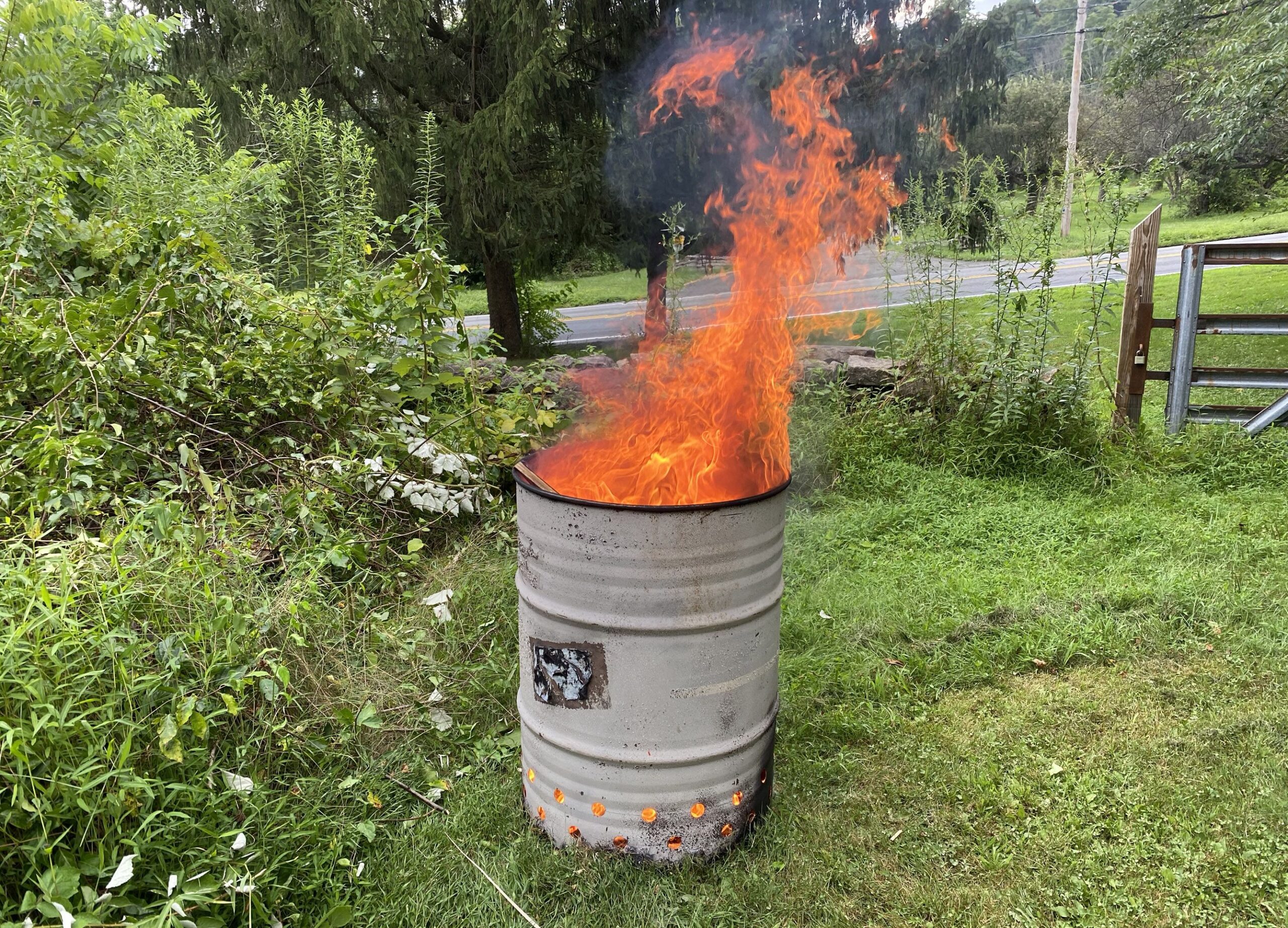
Scenario 1: Inefficient Burning Due to Insufficient Airflow
The Problem: One common issue B2B buyers face when using burn barrels is inefficient burning caused by insufficient airflow. Many users drill holes in the barrel, but they often neglect the optimal placement and size of these holes. This can lead to incomplete combustion, excessive smoke, and higher emissions, which can affect compliance with environmental regulations and disturb nearby communities. Buyers may find that their waste is not being disposed of effectively, resulting in a buildup of unburned materials and a potential fire hazard.
The Solution: To enhance airflow, buyers should consider both the placement and size of the holes in the burn barrel. A proven method involves drilling a series of holes about 4-6 inches from the bottom, spaced approximately ten inches apart. Additionally, creating diagonal cuts between holes can further improve air circulation. For an even more efficient setup, incorporating a metal grate at the bottom allows ash to fall away from the burning materials, maintaining airflow. Buyers can source high-quality burn barrels from reputable suppliers who offer guidance on optimal designs and modifications to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Scenario 2: Risk of Rusting and Structural Integrity
The Problem: Another significant pain point is the risk of rusting and loss of structural integrity in burn barrels due to moisture accumulation. Water can collect in the barrel, leading to premature degradation and potential safety hazards. This is particularly concerning in regions with high humidity or frequent rainfall, where the lifespan of a burn barrel can be drastically reduced, resulting in the need for more frequent replacements and increased costs.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
The Solution: To combat rusting, buyers should ensure that proper drainage holes are drilled in the bottom of the burn barrel. This allows any accumulated water to escape, significantly extending the barrel’s lifespan. In addition, buyers can opt for galvanized steel barrels, which offer better resistance to corrosion compared to standard steel. Regular maintenance checks should also be part of the operational protocol. By investing in quality materials and performing routine inspections, businesses can minimize long-term costs and ensure safe, effective burning operations.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges with regulatory compliance concerning the use of burn barrels. Different regions have specific laws governing what can be burned and under what conditions. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in fines or even legal action, creating an unnecessary burden for businesses that rely on burn barrels for waste disposal. Additionally, environmental concerns about air quality and emissions can put pressure on companies to find more sustainable waste management solutions.
The Solution: To address regulatory compliance, buyers should proactively research local laws and regulations regarding burn barrels. This includes understanding permissible materials for burning and obtaining any necessary permits. Collaborating with local environmental agencies can provide insights into best practices and emerging regulations. Furthermore, buyers can consider integrating alternative waste management strategies, such as composting or recycling, into their operations to reduce reliance on burn barrels. By diversifying waste disposal methods and staying informed about regulations, businesses can enhance their compliance and contribute positively to environmental sustainability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for holes in burn barrel
What Materials Are Best for Creating Holes in Burn Barrels?
When selecting materials for the holes in burn barrels, several factors must be considered, including durability, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of burn barrels, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
1. Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and excellent heat resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 1,500°F (815°C) and can withstand significant pressure.
Pros & Cons: Steel is highly durable and can last for many years if properly maintained. However, it is prone to rusting if not coated or treated, which can be a concern in humid or wet climates. The cost of steel can vary, but it is generally considered a medium-cost material.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various burning materials makes it a versatile choice for burn barrels. However, buyers must consider the local environment and the potential for corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial, especially in regions like Europe and North America. Buyers in Africa and South America should ensure that the steel used meets local regulations regarding emissions and fire safety.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,800°F or 982°C) without degrading.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than regular steel, which can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is less likely to leach harmful substances into the environment, making it a safer option for burning waste materials. Its durability ensures that the burn barrel maintains its integrity over time.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Germany, may prefer stainless steel for its lower environmental impact. Compliance with DIN standards is essential for ensuring quality and safety.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, making it an effective material for heat dissipation. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°F (649°C) but is less durable than steel.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its resistance to corrosion and lightweight nature, which facilitates easier handling and transportation. However, its lower strength compared to steel may limit its use in high-stress applications.
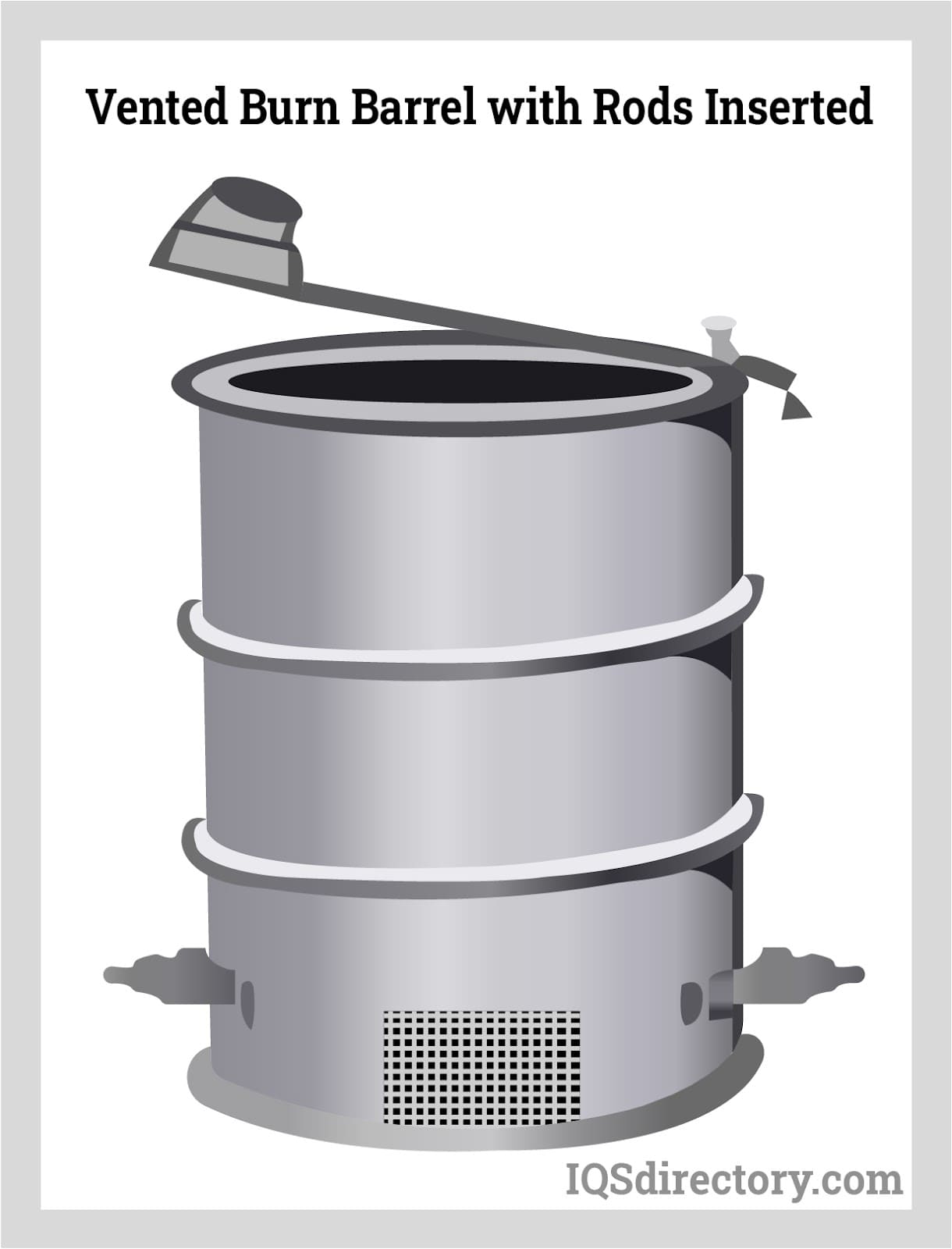

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for smaller burn barrels or those used for lighter materials. However, its limited temperature resistance may not be ideal for all burning scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East, where temperatures can be extreme, should consider aluminum’s limitations. Compliance with local standards regarding material safety and emissions is also crucial.
4. High-Temperature Resistant Coatings
Key Properties: These coatings are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and provide a barrier against corrosion. They can be applied to various substrates, including steel and aluminum.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage is that they enhance the lifespan of the underlying material while providing excellent heat resistance. However, the application process can be complex and may increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Coatings can significantly improve the performance of burn barrels, allowing them to handle higher temperatures and resist corrosion more effectively.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the coatings used comply with international safety and environmental standards. In regions like Europe, adherence to REACH regulations is important for chemical safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Burn Barrel Holes
| Material | Typical Use Case for holes in burn barrel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | General-purpose burn barrels | High durability and heat resistance | Prone to rust without treatment | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Long-lasting outdoor burn barrels | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to regular steel | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight burn barrels for lighter waste | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength and temperature resistance | Medium |
| High-Temperature Coatings | Enhancing existing burn barrels | Extends lifespan and improves heat resistance | Complex application process and higher costs | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials suitable for creating holes in burn barrels, offering international B2B buyers critical insights for informed decision-making.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for holes in burn barrel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Holes in Burn Barrels?
Manufacturing holes in burn barrels involves several critical stages that ensure the final product is efficient, safe, and compliant with international standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-quality steel drums, typically 55-gallon in capacity. These drums must meet specific standards for thickness and corrosion resistance to withstand high temperatures and prolonged exposure to combustion byproducts. Once sourced, the drums undergo cleaning to remove any contaminants, ensuring a safe working environment and preventing impurities from affecting the burn quality.
Forming: After preparation, the manufacturing process moves to forming the holes. This is typically achieved through drilling and cutting techniques. Using precision equipment, manufacturers will drill holes at specified intervals and dimensions, typically around 4-6 inches from the bottom of the barrel and spaced approximately ten inches apart. Additional holes may be cut into the bottom of the barrel to facilitate drainage and prevent rusting.
Assembly: While the assembly phase for burn barrels is relatively straightforward, it is crucial to ensure that all parts fit together correctly. For example, the integration of a metal grill at the bottom of the barrel can enhance air circulation, improving combustion efficiency. This grill must be securely attached to support the weight of the ashes and materials burned.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Finishing: The finishing stage includes surface treatment to enhance durability and resistance to rust and corrosion. Common techniques involve powder coating or galvanization, which provides an additional layer of protection. This stage is vital for extending the barrel’s lifespan, especially in humid environments prevalent in many regions, including parts of Africa and South America.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Burn Barrel Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process to ensure that burn barrels meet international standards and provide safety and efficiency for end-users.
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. This standard focuses on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, compliance with CE marking regulations and API standards may be necessary, especially when dealing with international markets.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Quality Control Checkpoints: Effective QA involves multiple checkpoints throughout the production process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet predetermined specifications. Any non-compliant materials are rejected.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to ensure adherence to quality standards. This includes checking dimensions and the integrity of drilled holes.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the barrels are fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes testing for structural integrity, verifying hole dimensions, and assessing the overall finish.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Burn Barrels?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and safety of burn barrels. Common methods include:
- Dimensional Testing: This involves verifying that the holes are drilled to the correct specifications and that the overall dimensions of the barrel are consistent with design requirements.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Samples may undergo salt spray testing to assess their resistance to corrosion, especially for barrels intended for use in humid climates.
- Functional Testing: This involves conducting a burn test to evaluate the efficiency of airflow and combustion within the barrel. It helps identify any design flaws that could affect performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability. Here are actionable steps to consider:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify adherence to quality standards. During these audits, buyers can assess manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes and results from any relevant testing. These reports can offer insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing standards.
What Are the QC/CERT Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the quality control landscape can be complex for international buyers due to varying standards and regulations. Here are some nuances to consider:

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
- Regional Regulations: Buyers should be aware of specific regulations in their region that may affect the manufacturing and use of burn barrels. For instance, certain countries may have stricter environmental regulations regarding emissions from burning materials.
- Documentation Requirements: Different regions may require various documentation for imports, including certificates of conformity, safety data sheets, and compliance with local fire safety standards. Buyers should clarify these requirements with their suppliers to avoid delays or non-compliance issues.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and negotiation styles is critical for successful supplier relationships. Building strong, trust-based relationships can enhance collaboration and ensure better quality outcomes.
By paying close attention to these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers for burn barrels that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘holes in burn barrel’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure burn barrels, particularly those with specific hole configurations that optimize airflow and burning efficiency. Understanding the intricacies of sourcing burn barrels with the right specifications is crucial for ensuring compliance with local regulations, maximizing safety, and enhancing operational efficiency in waste disposal.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly define the technical specifications for the burn barrels you need. Consider factors such as barrel size (typically 55 gallons), material type (preferably steel for durability), and the specific hole dimensions and placements to ensure optimal airflow.
- Airflow Requirements: Adequate ventilation is essential for efficient burning. Specify the number and size of holes based on your intended use.
- Durability Needs: Determine the expected lifespan and weather resistance based on your operational environment.
Step 2: Research Local Regulations and Compliance
Different regions have specific regulations regarding the use of burn barrels. Investigating these laws is vital to avoid legal complications.
- Permit Requirements: Some areas may require permits for burning activities. Ensure that your use of burn barrels complies with local laws to mitigate risks.
- Environmental Guidelines: Confirm that your specifications align with environmental protection standards to prevent harmful emissions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Vetting suppliers is a critical step in the procurement process. A thorough evaluation ensures that you partner with reliable manufacturers who can meet your specific needs.
- Request Documentation: Ask for company profiles, product specifications, and compliance certificates to verify their capabilities.
- Seek References: Contact other businesses that have previously purchased from the supplier to gauge satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: Assess Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount when sourcing burn barrels. Investigate the supplier’s quality assurance processes to ensure the products meet your specifications.
- Material Inspection: Confirm that the steel used for the barrels is of high quality and suitable for prolonged exposure to fire and weather.
- Testing Procedures: Inquire about any testing protocols they follow to ensure the barrels perform effectively and safely.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms. Understanding the market value of burn barrels can help you make informed decisions.
- Volume Discounts: If you plan to purchase in bulk, inquire about discounts or pricing tiers.
- Warranty and Support: Clarify warranty periods and post-purchase support options, ensuring you have assistance if issues arise.
Step 6: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Terms
Logistics plays a vital role in the procurement process. Ensure that you discuss delivery timelines, shipping costs, and any special handling requirements.
- Delivery Schedule: Confirm the expected delivery timeframe to align with your operational needs.
- Transportation Safety: Discuss how the barrels will be transported to avoid any damage during transit.
Step 7: Implement a Trial Period
After receiving the burn barrels, consider implementing a trial period to assess their performance in real-world conditions. This step allows you to identify any potential issues before committing to larger orders.
- Performance Monitoring: Track the efficiency of the burn barrels in actual use, paying attention to airflow and burning effectiveness.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from users to identify any areas for improvement or adjustments needed in future orders.
This structured approach will enhance your sourcing process, ensuring you procure burn barrels that meet your operational needs effectively and safely.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for holes in burn barrel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Holes in Burn Barrels?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing holes in burn barrels, several key components need to be considered. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of steel used in burn barrels is crucial. High-quality, corrosion-resistant steel will typically incur a higher cost but will offer better longevity and performance. Additionally, the cost of drilling bits and any custom grates for airflow will also impact material expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs will vary significantly based on geographic location. In regions with higher wages, such as Germany, labor costs for drilling and modifying barrels could be substantial compared to lower-wage regions like parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Manufacturers must account for these overheads in their pricing structure, which can vary greatly depending on the operational efficiency of the production facility.
-
Tooling: If specialized tools are required for creating holes in burn barrels, this will add to the initial investment. Tooling costs can be amortized over a production run, making it crucial to consider volume when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the holes are drilled to the correct specifications is vital for safety and functionality. QC processes add to the overall manufacturing cost but are essential for maintaining product standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs to move the finished barrels to buyers can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and local regulations. Incoterms will play a significant role in determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Holes in Burn Barrels?
Several factors influence the pricing of holes in burn barrels:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order quantities can significantly reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better pricing for bulk orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications, such as the size, number, and placement of holes, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the initial cost but also impacts the long-term value. Opting for higher-quality materials may lead to lower total ownership costs due to durability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international standards may increase initial costs but can enhance the product’s marketability and safety, especially in regions with strict regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is critical. They define the responsibilities of both the buyer and seller, affecting overall costs and risk management.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
International B2B buyers should consider the following tips to enhance their negotiation strategies:
-
Know the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may result in higher long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When possible, consolidate orders to reach minimum order quantities that unlock better pricing. This strategy is particularly effective for businesses with consistent needs.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first quote. Evaluate multiple suppliers to understand market pricing and leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Explore Alternative Materials: Investigate if there are alternative materials that can reduce costs while still meeting safety and functional requirements.
-
Understand Local Regulations: Compliance with local laws can impact the feasibility and cost of burn barrel usage. Familiarize yourself with regulations in your target regions to avoid costly fines or product modifications.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing good relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and favorable terms over time.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for holes in burn barrels can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. The information provided here is indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and changes in manufacturing practices. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing holes in burn barrel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Holes in Burn Barrel Solutions
When considering waste disposal methods, particularly for combustible materials, it’s essential to evaluate various alternatives. While holes in burn barrels enhance airflow and burning efficiency, several other solutions exist that may better suit the needs of businesses, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis compares the efficacy of holes in burn barrels against alternative waste disposal methods, providing actionable insights for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Holes In Burn Barrel | Composting Facilities | Industrial Incinerators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient burning with airflow | Reduces waste volume significantly | High-temperature combustion |
| Cost | Low initial setup costs | Often free or low-cost | High capital and operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple DIY modifications | Requires transport of waste | Complex installation and operation |
| Maintenance | Minimal, check for rust | Low, periodic checks | High, requires trained personnel |
| Best Use Case | Small-scale, localized burning | Organic waste disposal | Large-scale waste management |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Composting Facilities
Composting is an eco-friendly alternative that converts organic waste into nutrient-rich compost. This method is highly efficient for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainability. The primary advantage is cost-effectiveness, as many communities offer free composting services. However, the need for transportation can be a downside, particularly for businesses located far from these facilities. Additionally, composting is limited to organic materials, which may not address all waste types.
Industrial Incinerators
Industrial incinerators represent a more advanced waste disposal technology designed for high-volume waste management. These systems operate at extremely high temperatures, ensuring complete combustion of waste materials, including hazardous ones. The benefit of incinerators is their ability to handle large quantities of waste while significantly reducing its volume. However, the initial investment and operational costs are substantial, making this solution less accessible for smaller businesses. Moreover, incinerators require skilled personnel for operation and maintenance, adding to the overall complexity.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Waste Disposal Solution
For B2B buyers, the choice between holes in burn barrels, composting facilities, and industrial incinerators hinges on specific operational needs and waste profiles. Companies with smaller-scale waste disposal needs might find holes in burn barrels to be a cost-effective and efficient solution. In contrast, businesses focused on sustainability may prefer composting as a viable alternative for organic waste. For those managing larger volumes or hazardous waste, investing in industrial incinerators could be justified despite the higher costs. Understanding the unique requirements of your business and the characteristics of each solution will enable informed decision-making in waste management strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for holes in burn barrel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Holes in a Burn Barrel?
When constructing or evaluating burn barrels, understanding the technical specifications of the holes is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Diameter of Holes
The diameter of the holes typically ranges from 0.5 inches to 1 inch. A diameter of 0.5 inches is common for air intake, while larger holes can facilitate better airflow and combustion efficiency. Correct sizing is vital; too small may restrict airflow, resulting in incomplete combustion, while too large can allow debris to enter. -
Placement of Holes
Holes should be strategically placed, generally 4-6 inches from the bottom and spaced approximately 10 inches apart. This arrangement ensures even airflow throughout the barrel, promoting efficient burning of materials. Proper placement is critical to reduce smoke production and enhance fire efficiency. -
Material Thickness
The burn barrel is typically made from steel, with a thickness of at least 14 gauge (0.0747 inches). Thicker materials provide better durability and resistance to rust, especially important in humid environments. This property directly impacts the longevity of the burn barrel, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers. -
Corrosion Resistance
Holes should ideally be treated with anti-corrosive coatings or materials that resist rusting. Given that moisture can accumulate in the barrel, ensuring that holes do not compromise the structure’s integrity is vital for safety and longevity. Corrosion resistance is particularly important in regions with high humidity or frequent rainfall. -
Ventilation Efficiency
The overall design should allow for optimal ventilation, which can be tested through airflow measurements. A well-ventilated burn barrel helps to maintain a consistent flame and minimizes the risk of smoke buildup. This property is crucial for compliance with local regulations regarding air quality and burning practices.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Burn Barrels?
Understanding industry terminology is essential for effective communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms relevant to burn barrels:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that may be marketed by another company under its brand name. In the context of burn barrels, an OEM may produce the barrels or components, ensuring that buyers receive high-quality products that meet specific standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For burn barrels, understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses looking to stock inventory or launch a new product line without overcommitting financially. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for burn barrels allows for comparison of quotes and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms related to shipping burn barrels, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), can help manage logistics and cost expectations. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. Knowing the lead time for burn barrels is vital for inventory management and planning, especially for businesses with tight project deadlines. -
Compliance Standards
These are regulations that burn barrels must meet to ensure safety and environmental protection. Familiarity with compliance standards can help B2B buyers avoid legal issues and ensure that their products meet local and international safety requirements.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing burn barrels, ensuring that they meet operational needs while adhering to safety and environmental standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the holes in burn barrel Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Holes in Burn Barrels?
The market for holes in burn barrels is witnessing a notable shift driven by increasing demand for efficient waste management solutions across various global regions. In Africa and South America, where traditional waste disposal methods are often limited, burn barrels offer a practical option for disposing of organic waste, particularly in rural areas. The Middle East and Europe are focusing on enhanced outdoor living spaces, thereby increasing the popularity of burn barrels for recreational purposes, such as outdoor cooking and ambiance creation.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the integration of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as laser cutting, which allows for more precise hole placements and enhanced airflow in burn barrels. Additionally, suppliers are leveraging e-commerce platforms to reach international buyers, enabling streamlined procurement processes. Sustainability trends are also influencing the market, with buyers increasingly favoring barrels made from recycled materials or those that adhere to environmental regulations.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Burn Barrel Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the sourcing of burn barrels, with buyers placing greater emphasis on the environmental impact of their purchases. The production of burn barrels involves various materials, primarily steel, and suppliers are increasingly adopting practices that minimize waste and energy consumption. Ethical sourcing is critical, as it ensures that materials are procured responsibly, without contributing to environmental degradation or social injustice.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Buyers should look for suppliers who provide ‘green’ certifications, indicating that their products meet specific environmental standards. This could include certifications from organizations that track sustainable practices in manufacturing or supply chains. Additionally, using materials that are recyclable or made from post-consumer waste not only enhances the product’s eco-friendliness but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. As international buyers become more aware of their environmental footprint, selecting ethically sourced burn barrels will be essential for maintaining compliance with local regulations and satisfying consumer demand.
What Is the Historical Context of Burn Barrels in B2B Markets?
Historically, burn barrels have been a popular solution for waste disposal, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. Initially, these barrels were often homemade, crafted from repurposed metal drums. Over time, as environmental awareness increased, the focus shifted towards creating burn barrels that are both efficient and compliant with safety regulations.
In the B2B context, manufacturers began recognizing the potential for burn barrels as a product line, leading to the development of standardized designs that include features such as ventilation holes for improved airflow and ash management systems. This evolution has enabled businesses to cater to a growing market that values not just functionality but also environmental responsibility. As the market continues to evolve, the integration of innovative technologies and sustainable practices will likely shape the future of burn barrel sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of holes in burn barrel
-
How do I ensure compliance with local regulations for burn barrels?
To ensure compliance with local regulations regarding burn barrels, it’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area. Regulations can vary significantly between countries and even within regions. Contact local environmental agencies or fire departments to obtain necessary permits and guidelines on what materials are permissible to burn. Additionally, staying informed about burn bans or restrictions during certain weather conditions will help you avoid fines and ensure safe usage. -
What is the best material for constructing holes in a burn barrel?
The ideal material for constructing holes in a burn barrel is a high-quality steel drum, typically 55 gallons in size. Steel is durable and withstands high temperatures. When creating holes, a half-inch drill bit is recommended, spaced appropriately to promote airflow and efficient burning. Ensure that the holes are placed about 4-6 inches from the bottom and spaced ten inches apart to optimize combustion while maintaining structural integrity. -
What are the common customization options for burn barrels?
Customization options for burn barrels can include hole size and spacing, additional ventilation features, and the incorporation of a metal grate at the bottom for better ash management and airflow. Buyers may also request specific coatings for corrosion resistance or designs that fit their branding. Discussing your requirements with manufacturers can lead to tailored solutions that enhance the functionality and longevity of the burn barrel. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for burn barrels?
Minimum order quantities for burn barrels can vary by supplier and region. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 100 units for bulk orders, especially for custom designs. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your purchasing needs. Smaller businesses may seek partnerships with suppliers who offer flexible MOQs to accommodate varying demands. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing burn barrels internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of burn barrels often depend on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common terms include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or a letter of credit. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, currency, and potential additional fees for international transactions to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I vet suppliers for burn barrels?
Vetting suppliers for burn barrels involves a thorough assessment of their credentials and track record. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO standards, and seeking reviews or testimonials from previous clients. Request samples to evaluate product quality and inquire about their production capacity and lead times. Engaging with suppliers through platforms that specialize in B2B trading can also enhance trust and transparency. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing burn barrels?
Logistics considerations for importing burn barrels include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with logistics partners experienced in international shipping to ensure compliance with import regulations in your destination country. It’s also vital to factor in lead times for production and delivery, as well as insurance for goods in transit to mitigate risks. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers of burn barrels?
Quality assurance measures can vary by supplier, but reputable manufacturers typically conduct regular inspections throughout the production process. Look for suppliers who provide certifications for their materials and have established quality control protocols. Request documentation of testing results, especially concerning heat resistance and structural integrity, to ensure the burn barrels meet safety standards and performance expectations.
Top 7 Holes In Burn Barrel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Good Morning Gloucester – Vortex Burn Barrel
Domain: goodmorninggloucester.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Vortex Burn Barrel made from a 55-gallon steel drum. Modifications include drilling holes (4-6 inches from the bottom, 10 inches apart, and additional holes for drainage) and cutting a diagonal opening for air flow. The barrel should be propped up on bricks, kept away from structures, and operated with safety precautions such as having a hose nearby and wetting the surrounding area.
2. Milwaukee – Titanium Step Bits
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 85 gallon steel salvage drum, 3/4″ holes, cordless drill, titanium step bits, thread cutting oil, Milwaukee step bit, knockout set, corded drill, Annular Cutter, Rotabroach, plasma cutter.
3. DIY Chatroom – Burn Barrel Solutions
Domain: diychatroom.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Burn barrel, 55-gallon drum, cutting tools (torch, drill, chisel, jigsaw, hatchet, grinder), ventilation holes, screen for ashes, bricks for elevation, Budd wheel for ash drainage, lid for weather protection.
4. My Tractor Forum – 55-Gallon Burn Barrel
Domain: mytractorforum.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Standard 55-gallon burn barrel available for $10-30; recommended modifications include removing the top, drilling 5 holes in the base and 12-20 holes around the body for airflow; set on bricks or concrete blocks to allow air circulation; best to empty ashes after use; avoid rainwater saturation to prevent rust; suggested materials include old oil barrels, water heater tanks, or air compressor tank…
5. TractorByNet – Burn Barrel Setup
Domain: tractorbynet.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Burn barrel setup involves cutting six vertical slots between each ridge, totaling eighteen slots, to improve airflow. The user starts with wood, paper, and kerosene, resulting in flames that can reach higher than head height. The setup is effective for burning various materials, including old rugs.
6. WikiHow – Burn Barrel Guide
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: To make a burn barrel, you need a 55 gallon (208.2 L) steel drum, which can be acquired from manufacturing plants, scrap yards, or recycling facilities, sometimes for free or for $80-120 if purchased new. The drum must be made of thick, heat-resistant steel. Steps include opening one end of the drum, creating drainage holes (3-4 holes of 1/2 inch (1.3 cm) at the bottom), and ventilation holes (12-…
7. Facebook – Metal Barrel Safety Guidelines
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Use a metal barrel in good condition. Cover the barrel with a metal screen with holes not larger than 5/8 inch. Cut 3 evenly spaced 3-inch vents around the bottom of the barrel, backed by metal screen. Clear away all flammable debris and vegetation for 10’ around the barrel. Always have a water source close by, and never leave your fire.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for holes in burn barrel
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for burn barrels, particularly those designed with optimal ventilation through strategically placed holes, is essential for enhancing efficiency and safety in waste disposal. Buyers should prioritize sourcing barrels that meet local regulations and environmental standards, ensuring compliance with fire safety measures and community guidelines. The emphasis on proper airflow not only promotes efficient burning but also minimizes harmful emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider their sourcing strategies, it is crucial to engage with suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and expertise. This ensures that the burn barrels not only perform well but also contribute positively to waste management practices.

Illustrative image related to holes in burn barrel
Looking ahead, the demand for environmentally friendly waste disposal solutions is set to grow. By investing in innovative burn barrel designs, businesses can lead the way in sustainable practices while meeting the needs of their communities. We encourage buyers to explore partnerships that prioritize quality, compliance, and sustainability in their sourcing decisions. Embrace this opportunity to enhance operational efficiency and contribute to a greener future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.