Is Your High Friction Materials Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high friction materials
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial applications, sourcing high friction materials presents a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for reliable, high-performance friction materials is paramount, especially in sectors ranging from automotive to manufacturing, where safety and efficiency hinge on material performance. This guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the global market, providing a thorough examination of various types of high friction materials, including alumina ceramics and rubberized surfaces, alongside their diverse applications.
Buyers will gain insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for ensuring compliance with international standards. Additionally, the guide addresses specific challenges faced by businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including fluctuating supply chains and regional material preferences. By empowering stakeholders with actionable information, this comprehensive resource aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing operational safety and performance across industries.
Whether you’re in Vietnam, Brazil, or beyond, understanding the nuances of high friction materials can significantly impact your procurement strategy and operational efficiency. This guide is your essential tool for mastering the intricacies of sourcing and implementing high friction solutions tailored to your business needs.
Understanding high friction materials Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramics | High hardness, long-wearing, can only be shaped by diamond grinding | Aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Excellent wear resistance; Cons: High cost and requires specialized machining. |
| Zirconia Ceramics | Exceptional strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance | Medical devices, cutting tools, dental applications | Pros: Durable and reliable; Cons: More brittle than other ceramics, may require careful handling. |
| Rubberized High-Friction Material | Flexible, non-slip surface, sound-deadening properties | Workshops, manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: Versatile and easy to use; Cons: Limited temperature resistance compared to other materials. |
| High-Friction Coatings | Sharp-edged particles enhance grip, applied to various surfaces | Safety equipment, automotive components, machinery | Pros: Improves safety and handling; Cons: Application process can be complex and costly. |
| High-Friction Fabrics | Enhanced surface friction, suitable for body armor and performance apparel | Defense, sportswear, industrial textiles | Pros: Lightweight and flexible; Cons: May have lower durability under extreme conditions. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Alumina Ceramics for B2B Buyers?
Alumina ceramics are known for their remarkable hardness and long service life, making them ideal for applications where wear resistance is critical. They are commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries, where components must withstand harsh environments. B2B buyers should consider the cost of machining these materials, as they require diamond grinding, which can increase overall production costs. However, their durability often justifies the initial investment.
Why Choose Zirconia Ceramics for Specific Applications?
Zirconia ceramics, or zirconium dioxide, exhibit exceptional toughness and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for high-stress environments like medical devices and cutting tools. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and chemical exposure makes them a preferred choice in demanding applications. B2B buyers must be cautious, as these materials are more brittle than other options, which necessitates careful handling and design considerations to avoid breakage.
How Does Rubberized High-Friction Material Benefit Workshop Environments?
Rubberized high-friction materials provide a flexible and non-slip surface that enhances safety and stability in workshops and manufacturing settings. Their sound-deadening properties further contribute to a quieter working environment, making them suitable for assembly lines and other industrial applications. Buyers should note that while these materials are versatile and easy to use, they may not perform well under extreme temperature conditions, which could limit their application in some industries.
Illustrative image related to high friction materials
What Advantages Do High-Friction Coatings Offer in Industrial Settings?
High-friction coatings utilize sharp-edged particles to create surfaces that enhance grip and prevent slips, making them essential in safety equipment and automotive components. Their ability to improve handling can significantly reduce workplace accidents. However, the application process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. It’s crucial for B2B purchasers to weigh the safety benefits against the potential application challenges.
Why are High-Friction Fabrics Important for Defense and Performance Apparel?
High-friction fabrics are designed to enhance grip and stability, making them ideal for use in body armor and performance sportswear. Their lightweight and flexible nature allows for comfort without compromising safety. However, B2B buyers should consider the durability of these fabrics, especially in extreme conditions, as they may not withstand heavy wear as effectively as traditional materials. Understanding the balance between performance and longevity is key for procurement decisions in these sectors.
Key Industrial Applications of high friction materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of High Friction Materials | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Brake Pads and Linings | Enhanced safety through improved stopping power | Compliance with safety standards and durability tests |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Increased material handling efficiency and safety | Material compatibility and load capacity |
| Construction | Non-Slip Surfaces for Equipment | Reduced accidents and enhanced worker safety | Weather resistance and ease of installation |
| Aerospace | High-Friction Coatings for Landing Gear | Improved performance and reliability in critical conditions | Weight considerations and temperature resistance |
| Textile | High-Friction Fabrics for Body Armor | Enhanced protection through improved grip and durability | Compliance with safety regulations and comfort |
How Are High Friction Materials Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, high friction materials are crucial for brake pads and linings, enhancing the vehicle’s stopping power and overall safety. These materials are engineered to withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring reliable performance under various driving conditions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international safety standards, as well as those who offer rigorous durability testing results to ensure product longevity and effectiveness.
What Role Do High Friction Materials Play in Manufacturing?
High friction materials are extensively used in conveyor systems within manufacturing settings to improve material handling efficiency and safety. These materials provide the necessary grip to prevent slippage, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing productivity. When sourcing, businesses should consider the specific load capacities and compatibility with existing equipment to ensure optimal performance and seamless integration into their operations.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
How Are High Friction Materials Beneficial in Construction?
In the construction sector, high friction materials are employed to create non-slip surfaces for various types of equipment and flooring. This application significantly reduces the risk of slips and falls, enhancing worker safety on job sites. For international buyers, it is essential to consider the weather resistance of these materials, especially in regions with extreme climates, to ensure durability and reliability throughout the project’s lifecycle.
What Advantages Do High Friction Materials Offer in Aerospace Applications?
High friction coatings are utilized on landing gear in the aerospace industry to enhance performance and reliability during critical operations. These materials provide the necessary grip to ensure safe landings and takeoffs, particularly in adverse weather conditions. Aerospace buyers must prioritize suppliers who understand the stringent weight and temperature resistance requirements of this sector, as well as those who can provide certifications for their products.
How Are High Friction Fabrics Used in Textile Applications?
In the textile industry, high friction materials are increasingly used in body armor to improve grip and durability. These specialized fabrics help absorb kinetic energy, providing enhanced protection for users. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing materials that comply with safety regulations, while also considering the comfort and flexibility of the fabrics to ensure they meet the needs of end-users, particularly in high-stakes environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high friction materials’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Consistent Grip for Machinery Components
The Problem: In industries such as manufacturing and automotive, ensuring that machinery components maintain a consistent grip is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. B2B buyers often struggle with selecting high friction materials that can withstand varying loads and environmental conditions without losing their grip. This inconsistency can lead to equipment failure, increased maintenance costs, and safety hazards, creating significant operational downtime.
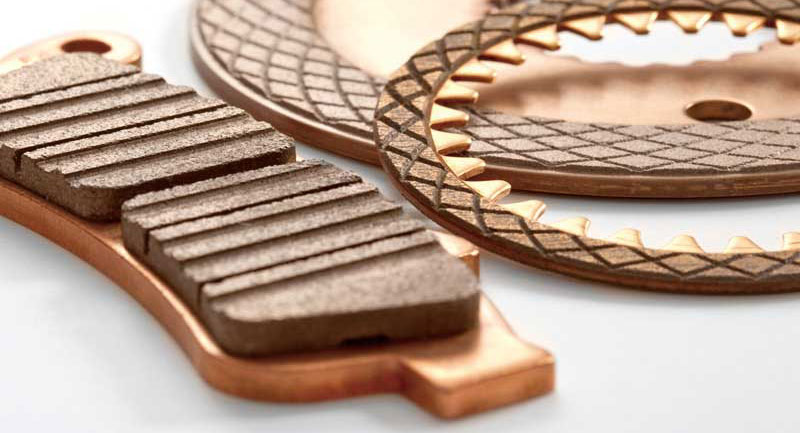

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should focus on sourcing high friction materials that are specifically designed for the intended application. Look for materials like alumina ceramics or specialized rubber composites that offer high durability and grip. It’s essential to consult with suppliers who can provide data on the material’s performance under specific conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure. Additionally, conducting thorough testing in a controlled environment before full-scale implementation will help ensure that the chosen materials can consistently deliver the required grip without degradation over time.
Scenario 2: The Challenge of Material Compatibility and Adhesion
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when integrating high friction materials with other components, leading to issues with adhesion and overall performance. This is particularly evident in applications like brake systems or conveyor belts, where mismatched materials can result in premature wear, failure to perform effectively, and safety risks. This compatibility issue often arises from inadequate surface preparation or lack of knowledge about the material properties.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize compatibility by performing a comprehensive analysis of both the high friction material and the surfaces it will interact with. For instance, using surface treatments or coatings that enhance adhesion can significantly improve performance. Engaging with suppliers who offer tailored solutions and can advise on the best practices for surface preparation is crucial. Additionally, utilizing adhesive technologies specifically designed for high friction materials can help ensure a secure bond, reducing the risk of failure and enhancing the longevity of the application.
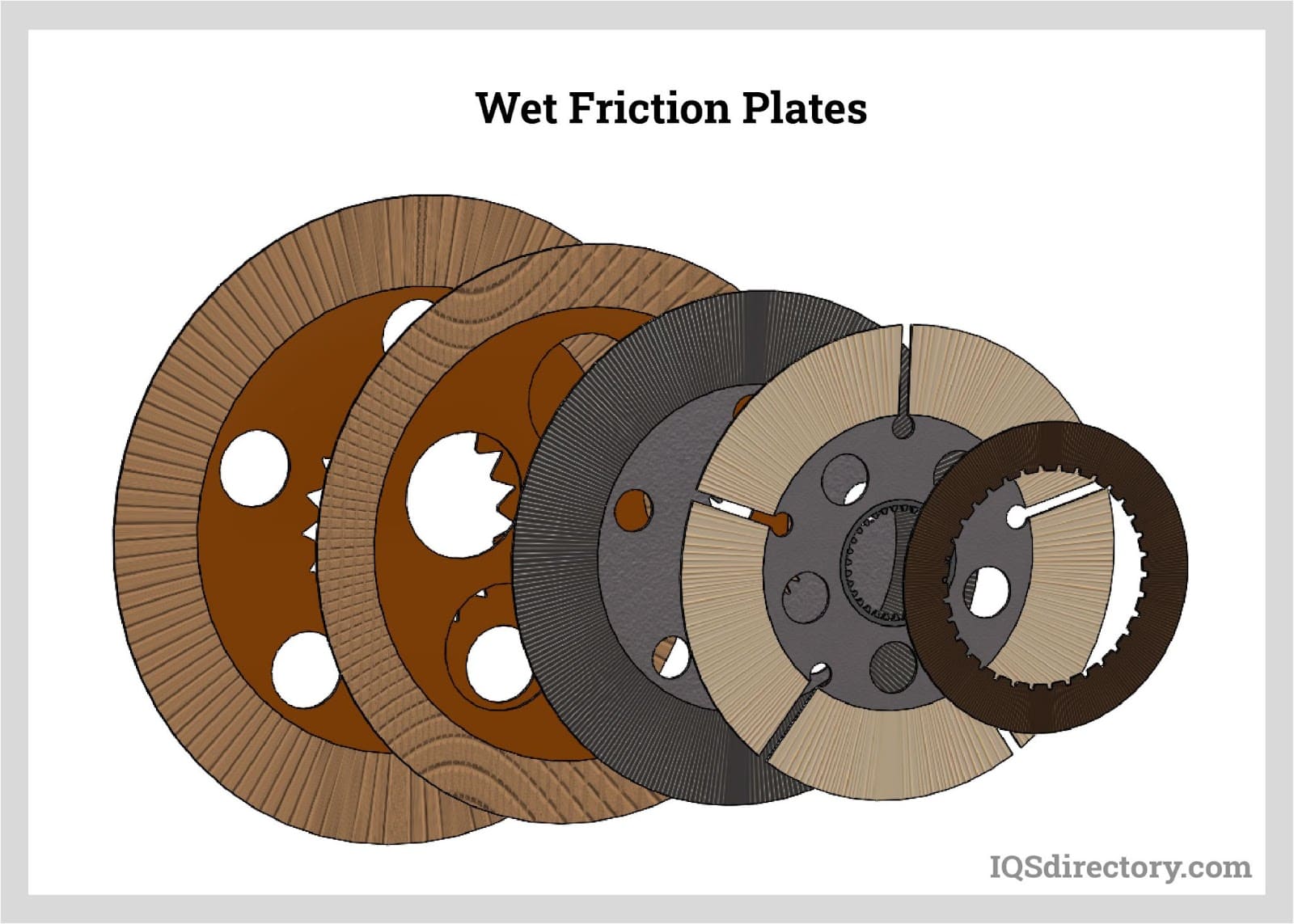
Illustrative image related to high friction materials
Scenario 3: Cost Management in High Friction Material Procurement
The Problem: Cost considerations are a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing high friction materials. Buyers often encounter high upfront costs, which can deter them from opting for superior materials that might offer better long-term value. This can lead to a reliance on cheaper alternatives that may not provide the same level of performance, ultimately resulting in higher maintenance and replacement costs.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should adopt a lifecycle cost analysis approach when evaluating high friction materials. This means looking beyond initial purchase prices to consider factors such as durability, maintenance frequency, and replacement intervals. Collaborating with suppliers who provide transparent pricing structures and offer volume discounts can also help manage costs effectively. Furthermore, investing in training for staff on the proper use and maintenance of high friction materials can extend their lifespan, leading to overall savings in the long run. By emphasizing total cost of ownership rather than upfront costs, buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high friction materials
What Are the Key Properties of Common High Friction Materials?
High friction materials are essential in various applications, from industrial machinery to consumer products. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can guide international B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
How Does Alumina Ceramic Perform as a High Friction Material?
Alumina ceramic is known for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it suitable for high-friction applications such as brake pads and wear-resistant components. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, with a thermal stability that allows it to perform in harsh environments. However, alumina ceramic is brittle, which can lead to cracking under impact. The manufacturing process is complex, often requiring diamond grinding, which can increase production costs.
For international buyers, compliance with standards like ASTM can be crucial, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations govern material properties. The high cost of alumina ceramic may be a barrier for some markets, but its longevity can offset initial expenses.
What Advantages Does Zirconia Ceramic Offer in High Friction Applications?
Zirconia ceramic, or zirconium dioxide, presents a unique combination of hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-friction applications in industries such as automotive and aerospace. It can operate effectively in extreme temperatures and is less brittle than alumina, providing better impact resistance.
The primary drawback of zirconia ceramic is its higher cost compared to other materials. Manufacturing can also be complex, requiring advanced techniques such as isostatic pressing. For B2B buyers in developing markets like Brazil and Vietnam, the investment in zirconia may be justified by its performance in demanding applications, provided they can meet international quality standards.
Why Is Rubber a Preferred Choice for High Friction Materials?
Rubber, particularly in its high-friction variants, is widely used for non-slip applications in workshops and industrial settings. Its key properties include flexibility, ease of manufacturing, and excellent grip. Rubber can be produced in various forms, including sheets and pre-cut shapes, making it versatile for different applications.
However, rubber may not withstand extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals as effectively as ceramic materials. Its durability can vary based on formulation, and while it is generally cost-effective, the performance in high-temperature environments may limit its use. Buyers from regions like Africa, where temperature fluctuations can be significant, should consider these factors when selecting rubber for high-friction applications.
What Role Do High-Friction Surfaces Play in Industrial Applications?
High-friction surfaces are engineered to enhance grip and prevent slips, often using sharp-edged particles of metals or carbides. These materials are commonly used in safety applications, such as emergency brake pads in elevators. They offer excellent performance under pressure and can be tailored for specific applications.
The downside is the potential for higher costs and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Compliance with international safety standards is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where regulatory requirements are stringent. Buyers should ensure that the materials meet relevant standards to avoid legal and operational issues.
Summary Table of High Friction Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for high friction materials | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina Ceramic | Brake pads, wear-resistant components | High hardness and thermal stability | Brittle, complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconia Ceramic | Automotive and aerospace applications | Toughness and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Rubber | Non-slip mats, workshop applications | Flexibility and ease of manufacturing | Limited temperature resistance | Medium |
| High-Friction Surface | Safety applications (e.g., brake pads) | Excellent grip and tailored performance | Higher costs, complex manufacturing | Medium to High |
This guide aims to provide actionable insights for B2B buyers, ensuring they can make informed decisions based on the properties and applications of high friction materials.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high friction materials
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Friction Materials?
The manufacturing of high friction materials involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent requirements of various industrial applications. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for High Friction Materials?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. The primary raw materials used in high friction materials often include alumina ceramics, rubber compounds, and composite materials. These materials are selected for their durability, hardness, and frictional properties.
In this stage, raw materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specified standards. For instance, alumina ceramics are sourced from bauxite and require processes like grinding and sieving to achieve the desired particle size before being used in formulations.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. Common techniques include:
- Injection Molding: This is a prevalent method for shaping rubber and composite materials. It involves injecting heated material into a mold where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
- Die Pressing: In this process, powder materials are compressed into molds under high pressure to form a solid piece, which is later sintered to enhance strength and durability.
- Isostatic Pressing: This method applies uniform pressure from all directions, ensuring a dense and uniform product, which is crucial for high-performance applications.
These forming techniques are selected based on the specific requirements of the high friction material, including its intended use and performance specifications.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for High Friction Materials?
The finishing stage is crucial as it enhances the material’s surface properties. Common finishing processes include:
- Grinding and Polishing: This technique is used to refine the surface texture and improve the friction coefficient. A finer finish can lead to better performance in applications where grip is essential.
- Coating: High-friction surfaces may undergo coating processes where materials like crushed metals or carbides are applied to enhance grip. This is particularly important for applications such as brake pads and emergency equipment.
Finishing not only contributes to the performance of high friction materials but also ensures they meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in High Friction Material Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for high friction materials. It ensures that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers aiming to compete in the global market. This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries. In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific standards such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in the oil and gas sector are also crucial.
These certifications help B2B buyers verify that the materials they procure are safe, reliable, and meet regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints during the manufacturing process typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves assessing raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor the production environment and parameters. This helps identify any deviations from quality standards early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a comprehensive inspection is performed to validate that the finished goods meet all quality criteria.
These checkpoints are vital for maintaining product integrity and ensuring consistency across batches.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Validate High Friction Materials?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that high friction materials perform as expected. Common tests include:
- Friction Testing: This evaluates the coefficient of friction under different conditions to ensure the material provides adequate grip.
- Wear Testing: This assesses the durability of the material under continuous use, which is crucial for applications such as brake pads.
- Thermal Stability Testing: This ensures that the material can withstand high temperatures without losing its frictional properties.
These tests help manufacturers and B2B buyers ascertain that high friction materials will perform reliably in their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers looking to source high friction materials should conduct due diligence to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting documentation related to quality control, such as testing results and compliance certificates, can help assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
These steps are particularly important for international buyers, who may face additional challenges related to compliance and consistency across different regions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control when sourcing high friction materials:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Each region may have different regulations and standards, impacting the quality assurance processes. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges: Variability in shipping and handling can affect product quality. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about packaging and transport conditions is essential.
- Market Expectations: Buyers should be aware of local market expectations regarding product performance and quality, which may differ from their suppliers’ standards.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers of high friction materials.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for high friction materials are complex but essential for ensuring product performance and reliability. By focusing on these critical aspects, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and achieve their operational goals.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high friction materials’
In this guide, we provide a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to source high friction materials. These materials are essential for a variety of applications, from industrial machinery to automotive components, and ensuring the right choice can significantly impact safety and performance. Here’s a practical step-by-step guide to streamline your sourcing process.
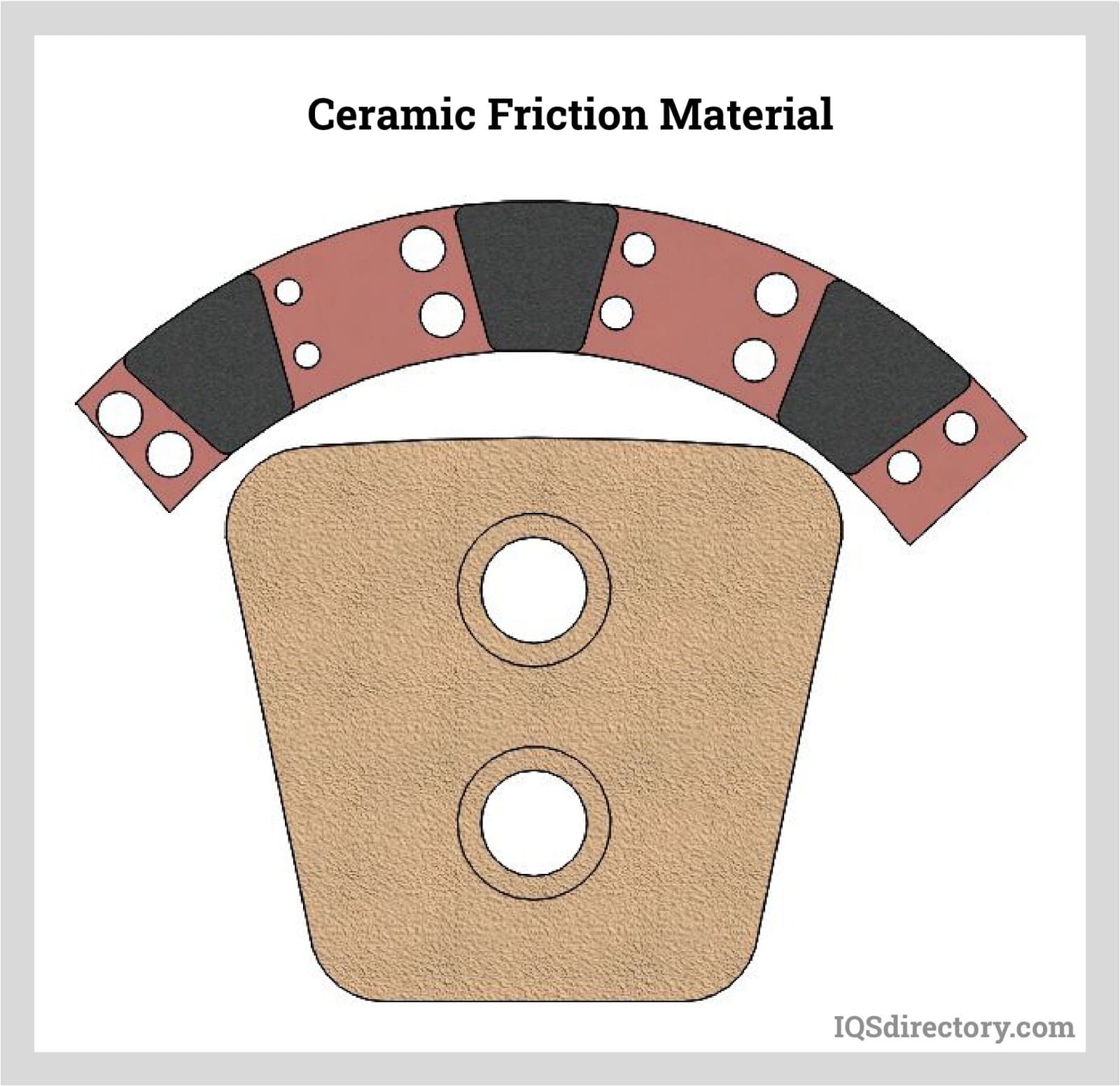
Illustrative image related to high friction materials
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the high friction materials you need. This includes understanding the application requirements, such as temperature resistance, wear characteristics, and environmental conditions. Specifics like material composition (ceramics, rubber, or composites) will also determine performance outcomes.
- Consider application needs: Different industries may have unique requirements, so tailor specifications to your operational context.
- Identify performance metrics: Assess factors like coefficient of friction, durability, and resistance to wear.
Step 2: Research Available Material Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of high friction materials available in the market. Common options include alumina ceramics, rubberized surfaces, and specialized composites that cater to various industrial needs.
- Understand their properties: Each type has distinct characteristics that affect performance in specific environments.
- Evaluate applications: Determine which materials align with your intended use cases, such as automotive brakes or industrial machinery.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing any purchases, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from existing clients in your industry or region.
- Check for industry experience: Suppliers with a proven track record are more likely to meet your quality and service expectations.
- Assess production capabilities: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume needs and quality standards consistently.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that your selected suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. This is vital for ensuring that the materials meet safety and performance benchmarks.
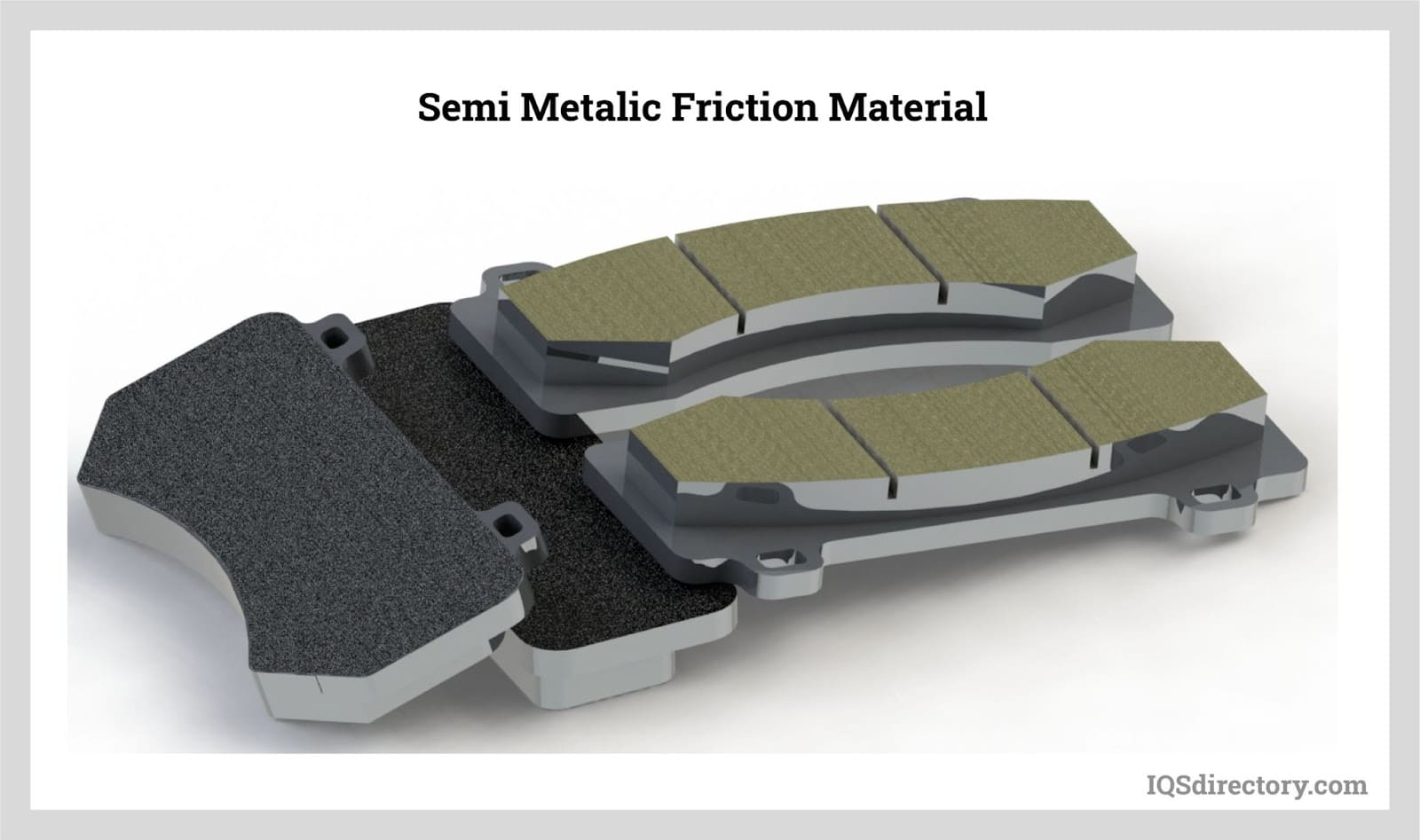

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
- Look for ISO certifications: This indicates adherence to international quality management standards.
- Review compliance with local regulations: Ensure that materials are suitable for your specific market, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples of the materials you are considering for procurement. Testing samples in your specific application can provide valuable insights into performance and compatibility.
- Conduct thorough testing: Assess friction properties, durability, and environmental resistance under real-world conditions.
- Gather feedback from your team: Engage engineers and technicians in the evaluation process to ensure the materials meet operational needs.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier and validated the materials, negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, payment terms, and warranty conditions.
- Seek favorable pricing: Use your research on competitor pricing to negotiate better deals.
- Establish clear delivery timelines: Ensure that the supplier can meet your project deadlines to avoid disruptions.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Partnership
Consider developing a long-term relationship with your selected supplier for ongoing needs. This can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaborative product development opportunities.
- Communicate regularly: Maintain open lines of communication to address any issues promptly.
- Explore joint ventures: Collaborate on innovations that can benefit both parties, particularly if you foresee future needs for specialized materials.
Following this checklist will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing high friction materials, ensuring that they meet both technical specifications and operational requirements effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high friction materials Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing High Friction Materials?
When sourcing high friction materials, buyers must understand the multifaceted cost structure involved. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can vary significantly based on the type of high friction material (e.g., alumina ceramics, rubber composites, or specialized metals). Prices are often influenced by market demand and the availability of specific materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This can vary by region, with labor-intensive operations typically more costly in developed markets compared to emerging economies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the facilities, utilities, and equipment used in production. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, which is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The creation of specialized tools or molds for manufacturing high friction materials can require significant upfront investment. This cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making it essential for buyers to consider order volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet required specifications can add to the overall cost. This includes testing, inspections, and certifications that may be necessary to comply with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must also be accounted for, especially when sourcing materials internationally. This includes shipping, tariffs, and insurance, which can vary widely based on the Incoterms agreed upon.
-
Margin: Suppliers will incorporate a profit margin into their pricing structure, which can fluctuate based on market competition and demand dynamics.
How Do Volume and Customization Impact Pricing for High Friction Materials?
Pricing is heavily influenced by order volume and customization needs.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order quantities often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to benefit from volume pricing, particularly when establishing long-term relationships with suppliers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements, such as specific dimensions or unique material compositions, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly outline their needs upfront to obtain accurate quotes and avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
What Are the Quality and Certification Considerations for High Friction Materials?
The quality of high friction materials is paramount, especially in applications where safety is a concern (e.g., automotive or industrial equipment).
- Quality and Certifications: Materials that meet specific industry standards or certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may carry a premium. Buyers should assess whether the added cost is justified based on the application and potential risks associated with inferior materials.
How Do Supplier Factors Influence the Pricing of High Friction Materials?
Supplier dynamics can significantly affect pricing strategies.
-
Supplier Reputation: Established suppliers with a track record of quality and reliability may charge higher prices. However, they often provide better guarantees and support, which can lead to lower total costs in the long run.
-
Negotiation Leverage: Buyers should leverage their purchasing power, particularly when working with multiple suppliers. Building a strong relationship can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
What Buyer Tips Should Be Considered for Cost-Efficiency in International Sourcing?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding pricing nuances is essential.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential failure rates associated with low-quality materials.
-
Incoterms: Familiarize yourself with Incoterms, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. This knowledge can help in negotiating terms that minimize hidden costs related to shipping and customs.
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of exchange rate volatility, which can impact overall costs, particularly in long-term contracts. Hedging strategies may be beneficial in mitigating these risks.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for high friction materials can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high friction materials With Other Solutions
When evaluating solutions for enhancing grip and preventing slips in various industrial applications, it’s crucial to consider alternative materials and methods alongside high friction materials. This analysis focuses on comparing high friction materials with two viable alternatives: rubberized coatings and textured surfaces. Each option offers unique benefits and limitations, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand the distinctions to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | High Friction Materials | Rubberized Coatings | Textured Surfaces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent grip and stability; ideal for dynamic applications | Good grip; often less durable under heavy stress | Variable grip based on texture; can be effective in certain conditions |
| Cost | Generally moderate to high; depends on material type | Lower initial cost but may require reapplication | Can be cost-effective, especially for large areas |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires proper installation for effectiveness | Easy to apply; can often be done in-house | Varies; some may require professional installation |
| Maintenance | Low; durable and long-lasting | Moderate; may require periodic maintenance and reapplication | Low; generally does not need frequent upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Workshops, industrial machinery, and safety applications | Non-slip surfaces in wet or slippery environments | Flooring, ramps, and surfaces requiring moderate grip |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Rubberized Coatings as an Alternative?
Rubberized coatings are a popular alternative to high friction materials, particularly due to their lower initial cost and ease of application. They can be sprayed or rolled onto surfaces, making them suitable for diverse applications, such as non-slip coatings for floors. However, while they provide good grip, their durability can be a concern, especially in high-stress environments. Over time, rubberized coatings may wear down, necessitating reapplication, which can increase long-term costs.
How Do Textured Surfaces Compare to High Friction Materials?
Textured surfaces are another alternative that can achieve a similar objective of enhanced grip. They work by creating a physical profile that increases friction. Their application can be particularly cost-effective for large areas like warehouse floors or outdoor ramps. However, the effectiveness of textured surfaces can vary significantly based on the specific design and material used. In some cases, they may not provide the same level of grip as high friction materials, particularly in wet or oily conditions, which could compromise safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between high friction materials and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. Factors such as the expected load, environmental conditions, and frequency of use play a critical role in determining the most suitable option. High friction materials excel in environments demanding exceptional grip and durability, while rubberized coatings and textured surfaces may be more appropriate for lower-stress applications or where budget constraints are a concern. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of performance requirements, cost implications, and maintenance needs will guide buyers toward the best solution for their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high friction materials
What Are the Key Technical Properties of High Friction Materials?
When dealing with high friction materials, understanding their critical specifications is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade indicates the composition and quality of the friction material. Common grades include organic, semi-metallic, and ceramic. Each grade has its unique characteristics, such as heat resistance and wear rate, which impact the performance in specific applications. For instance, ceramic materials offer higher durability and thermal stability, making them suitable for high-performance environments. Buyers should assess the material grade to ensure it meets their operational requirements.
2. Coefficient of Friction (CoF)
The coefficient of friction quantifies the frictional resistance between two surfaces. A higher CoF indicates better grip and stability, essential for applications like braking systems and conveyor belts. Understanding the CoF helps businesses select materials that enhance safety and efficiency. For instance, automotive manufacturers often require materials with a specific CoF to ensure optimal performance and safety in braking systems.
3. Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance refers to a material’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading. This property is crucial for applications exposed to heat, such as brake pads in vehicles. Materials with high-temperature resistance prevent failure during operation, ensuring longevity and reliability. Buyers should consider the operating temperatures of their applications to select appropriate materials.
4. Wear Resistance
Wear resistance defines a material’s ability to withstand abrasion and friction over time. High friction materials used in industrial settings must endure significant wear without losing effectiveness. This property directly impacts the lifespan of machinery and components, influencing maintenance costs and downtime. Companies should prioritize wear resistance to minimize operational disruptions and enhance productivity.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a material’s dimensions or properties. In high friction applications, maintaining tight tolerances ensures components fit and function correctly, reducing the risk of failure. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in assembly processes.
6. Density
Density indicates the mass per unit volume of a material, which can influence its performance in applications requiring specific weight characteristics. For instance, denser materials may provide better stability and grip. Buyers should consider density when selecting materials to meet their specific application needs.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to High Friction Materials?
Navigating the procurement process for high friction materials involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some essential terms:

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of high friction materials, OEMs often specify the materials used in their products, influencing purchasing decisions. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers align their sourcing strategies with industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and budgeting. Companies should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs to optimize purchasing efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For high friction materials, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making. This process is vital for ensuring competitive pricing and value.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in global sourcing, as they impact shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the product. For high friction materials, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing inventory. Buyers should communicate their timelines to suppliers to ensure timely deliveries.
Illustrative image related to high friction materials
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing high friction materials, enhancing operational efficiency and safety in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high friction materials Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in High Friction Materials?
The high friction materials market is experiencing significant transformation driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. Key global drivers include the rising focus on safety standards, particularly in braking systems for vehicles and machinery, where high friction materials are critical. Additionally, the shift towards automation and advanced manufacturing technologies is leading to increased utilization of high-performance friction materials that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies and data analytics into sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to gain insights into supplier capabilities and product performance. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who are seeking reliable suppliers that can meet local regulations and performance standards. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce in B2B transactions is facilitating easier access to high friction materials, allowing buyers to compare products and prices more efficiently.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
Buyers should also keep an eye on the growing importance of customization in product offerings. As industries evolve, the need for tailored solutions to meet specific operational challenges is becoming paramount. This trend underscores the necessity for buyers to engage in collaborative relationships with suppliers who can innovate and adapt their offerings to meet unique requirements.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the High Friction Materials Sector?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly vital in the sourcing of high friction materials, driven by regulatory pressures and consumer expectations for environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of traditional sourcing methods, including resource extraction and waste generation, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable alternatives. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials, such as those that use recycled components or sustainable raw materials.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction as companies recognize the importance of maintaining transparent supply chains. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where resource extraction can have significant social and environmental implications, are particularly sensitive to these issues. Engaging with suppliers that hold ‘green’ certifications or adhere to international sustainability standards can enhance a company’s brand reputation and compliance with local regulations.
Moreover, utilizing high friction materials that are manufactured with a focus on sustainability not only minimizes environmental impact but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. As such, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers committed to sustainable practices and ethical sourcing to foster long-term viability and market competitiveness.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
What Has Been the Evolution of High Friction Materials in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of high friction materials has been shaped by advancements in material science and engineering over the decades. Initially dominated by organic materials like rubber and resin-based composites, the sector has seen a significant shift towards high-performance materials such as ceramics and metal matrix composites. These innovations have improved the durability and performance of friction materials, particularly in demanding applications like aerospace and heavy-duty machinery.
Historically, the development of high friction materials was largely reactive, driven by the need to meet safety regulations and performance standards. However, as industries evolve, there is a proactive approach to material development, with a focus on enhancing performance while minimizing environmental impact. This shift reflects a broader understanding of the interconnectedness of material performance, safety, and sustainability in the global marketplace.
As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the historical context of high friction materials can provide valuable insights into future trends and innovations that will shape the market. The ongoing commitment to research and development in this field will likely yield new solutions that meet the evolving demands of various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high friction materials
-
1. How do I select the right high-friction material for my application?
When selecting high-friction materials, consider the specific requirements of your application, such as the environmental conditions, load capacity, and the type of surfaces involved. Materials like alumina ceramics and rubberized high-friction mats are suitable for different uses, from industrial machinery to workshop settings. Conduct thorough testing and consult with suppliers about customization options to ensure the material meets your performance and safety standards. -
2. What is the best high-friction material for industrial machinery?
For industrial machinery, materials like zirconia ceramics or rubberized high-friction surfaces are often preferred due to their durability and resistance to wear. Zirconia offers exceptional toughness and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding environments. Rubberized surfaces provide excellent grip and vibration dampening, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Always evaluate the specific requirements of your machinery to make the best choice. -
3. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for high-friction materials?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of high-friction material being sourced. Typically, MOQs may range from a few hundred kilograms for bulk materials to specific unit counts for pre-cut products. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to find a mutually beneficial arrangement, especially if you are a smaller business or testing new applications. -
4. How can I vet suppliers of high-friction materials effectively?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to assess the quality of their products firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality assurance measures, and compliance with international standards. Establishing clear communication and understanding their logistics capabilities can also help ensure a reliable partnership. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days post-delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and offer protection against potential disputes. -
6. How do logistics and shipping affect sourcing high-friction materials?
Logistics and shipping play a critical role in sourcing high-friction materials, particularly for international transactions. Factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations can impact overall pricing and delivery schedules. It’s essential to collaborate with suppliers who have reliable logistics partners to streamline the shipping process and avoid delays that could affect production schedules. -
7. What quality assurance practices should I look for in high-friction material suppliers?
Quality assurance practices vary among suppliers, but look for those who implement rigorous testing protocols and adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Suppliers should provide documentation of their QA processes, including material testing results, durability assessments, and compliance with safety regulations. Regular audits and feedback loops can also help maintain quality consistency over time. -
8. Can high-friction materials be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for high-friction materials to meet specific application needs. This can include variations in size, thickness, texture, and adhesive backing. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria to ensure the final product aligns with your requirements. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the development phase can lead to optimized solutions tailored to your operational demands.
Top 8 High Friction Materials Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – High Friction Materials
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – High Friction Materials, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. IQS Directory – Friction Materials
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Friction materials are engineered substances designed to generate friction between surfaces, primarily used for braking and power transfer. They are made from organic and inorganic elements such as resins, ceramics, fibers, and metals. Common products include brake pads, brake shoes, clutch plates, bonded assemblies, friction bands, liners, and rolls. Available forms include bands, blocks, pads, d…
3. Reddit – Infinite Friction Coefficients in Chemistry
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Infinite Friction Coefficients in Chemistry, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Lee Valley – Grip Disks
Domain: leevalley.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: High-friction rubber material with PSA backing, available in various forms including large sheets and pre-cut sizes. Pre-cut round 2 ¾” Grip Disks designed to fit hockey pucks for use as shop work standoffs. Smaller pre-cut disks (1″ and 2″) also available. Provides stability for routing, sanding, and other workshop tasks. Helps prevent jigs from moving during use, enhancing precision and safety. …
5. ScienceDirect – High-Friction Surfaces
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High-friction surfaces are designed to enhance grip and prevent slips, often achieved by applying sharp-edged particles of crushed metals or carbides. These surfaces improve safety in various applications, such as emergency brake pads in elevators and grippers in the paper industry. The surfaces are typically brazed with copper- or nickel-based filler metals. Additionally, self-lubricating surface…
6. Kor-Pak – Friction Materials
Domain: kor-pak.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Kor-Pak offers a range of friction materials including high and low friction options. High friction materials are characterized by their ability to generate more heat, have rougher surfaces, and can vary in lifespan, while low friction materials are designed to minimize friction. The company emphasizes the importance of selecting the right friction material for specific applications to ensure safe…
7. Eng-Tips – High Performance Friction Washers
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Material with high coefficient of friction and good structural integrity for friction washer; 20mm outer diameter; clamped against steel; functionality similar to car brake pads; needs to resist large lever moments; should not crush or disintegrate over time; sliding distance of 20-50mm once a week; positional placement must be precise to avoid judder; suggestions include G10, aluminum, oil impreg…
8. Talk Composites – Flexible High Friction Material
Domain: talkcomposites.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Plastic/silicone substance that remains flexible after curing, with very high friction ability (rubber-like feeling), durable, applicable on various surfaces, non-sticky (not glue-like), and resistant to peeling. Ideal for applications such as enhancing grip on synthetic leather football shoes.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high friction materials
In summary, high friction materials play a crucial role in enhancing safety and performance across various industries, from automotive to manufacturing. The strategic sourcing of these materials can lead to significant advantages, including improved operational efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced product reliability. By understanding the diverse applications and types of high friction materials, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional market demands.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of establishing strong supplier relationships cannot be overstated. Identifying reliable manufacturers and distributors who prioritize quality and innovation will not only ensure access to superior materials but also foster sustainable partnerships that drive growth.
As we look to the future, the demand for high friction materials is expected to rise, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing emphasis on safety standards. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, seek out innovative solutions, and position your business at the forefront of this evolving market. Embrace the potential of high friction materials to enhance your operational capabilities and achieve competitive advantages.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to high friction materials
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.