Is Your Gross Leak Test Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gross leak test
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the pressing challenge of ensuring product integrity through effective testing solutions, particularly when it comes to the gross leak test. This essential method not only identifies significant leaks in various products but also safeguards against potential failures that could compromise quality and safety. As businesses expand their operations across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of gross leak testing becomes paramount for maintaining high standards in manufacturing and product delivery.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of gross leak tests, including advanced methods such as HSHLD™ and Krypton-85 testing, and explore their specific applications across industries, from electronics to medical devices. Buyers will gain insights into the critical process of supplier vetting, helping them identify reputable testing facilities that meet international standards. Furthermore, we will provide a detailed overview of associated costs, enabling informed budgeting for testing services.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the complexities of gross leak testing, this guide empowers businesses to make strategic purchasing decisions that enhance product reliability and boost customer satisfaction. Whether you’re operating in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any other region, understanding these testing processes will lead to improved operational efficiency and competitive advantage in the global market.
Understanding gross leak test Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSHLD™ Dry Gross Leak | Utilizes oxygen signature and pressure changes to detect leaks; compares to a known good sample. | Electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries. | Pros: High sensitivity; quick results. Cons: Requires specialized equipment. |
| Per-Fluorocarbon Gross Leak | Involves submersion in indicator fluid at high temperatures; detects bubble streams. | Medical device packaging and electronics. | Pros: Effective for various materials; visual detection. Cons: May need preconditioning. |
| Krypton-85 Dry Gross Leak | Uses radioactive Krypton-85 for detection; performed before fine leak testing. | Aerospace and military applications. | Pros: Eliminates false positives; reliable for small cavities. Cons: Regulatory compliance needed due to radioactivity. |
| Krypton-85 Wet Gross Leak | Employs dye to slow gas movement; visual cue for leak identification in small cavities. | Military and high-precision electronics. | Pros: Accurate for small devices; adheres to Mil-Standard. Cons: Complex setup; requires expertise. |
| Bubble Testing | Involves submerging packages to observe bubble streams; commonly used in sterile packaging. | Medical devices and pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Tests entire packaging system; straightforward procedure. Cons: Destructive testing; may not identify all leak types. |
What are the key features of the HSHLD™ Dry Gross Leak test?
The HSHLD™ Dry Gross Leak test is notable for its use of oxygen signatures and pressure changes to identify leaks. This method compares the test device with a known good sample of the same volume, providing a reliable indication of hermeticity failures. It is particularly well-suited for industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where precision and reliability are paramount. Buyers should consider the need for specialized testing equipment and training to ensure accurate results.
How does the Per-Fluorocarbon Gross Leak test work?
The Per-Fluorocarbon Gross Leak test operates by submerging the device in a high-temperature indicator fluid to observe for bubble streams, indicating a leak. This method is effective across various materials and is commonly used in medical device packaging and electronics. Key purchasing considerations include the potential requirement for preconditioning in a pressurized chamber, which may add complexity to the testing process.
What distinguishes the Krypton-85 Dry Gross Leak test?
The Krypton-85 Dry Gross Leak test utilizes radioactive Krypton-85 as a tracer gas, making it particularly useful for eliminating false positives in fine leak testing. This method is essential in aerospace and military applications, where the integrity of small cavities is critical. Buyers should be aware of the regulatory compliance associated with using radioactive materials, which may complicate the testing process.
In what scenarios is the Krypton-85 Wet Gross Leak test preferred?
The Krypton-85 Wet Gross Leak test incorporates dye to slow gas movement, providing visual cues for leak identification in devices with small cavities. This method is particularly relevant in military and high-precision electronics sectors. While it adheres to Mil-Standard testing requirements, the complexity of setup and the need for specialized expertise are important factors for buyers to consider.
Why is Bubble Testing a popular choice for medical device packaging?
Bubble Testing is a straightforward method that involves submerging packages to observe for bubble streams, indicating compromised hermeticity. It is widely used in the medical device and pharmaceutical industries to ensure sterile packaging. While its simplicity is a significant advantage, buyers should note that it is a destructive testing method that may not detect all types of leaks, necessitating a comprehensive testing strategy.
Key Industrial Applications of gross leak test
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gross leak test | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Bubble leak testing for sterile packaging | Ensures product sterility, reduces contamination risk | Compliance with ISO 11607, equipment reliability, local regulations |
| Electronics | HSHLD™ testing for hermetic seals in components | Enhances product reliability, extends lifespan | Calibration standards, testing environment, material compatibility |
| Aerospace | Krypton-85 testing for critical component integrity | Mitigates failure risks, ensures safety in operations | Certification requirements, testing facilities, international standards |
| Automotive | Gross leak testing for fuel systems | Prevents leaks, enhances safety and performance | Industry standards adherence, environmental conditions, supplier capabilities |
| Packaging | Per-Fluorocarbon testing for packaging integrity | Improves product quality, minimizes returns | Testing protocols, material compatibility, local market needs |
How is Gross Leak Testing Applied in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, gross leak testing, particularly bubble leak testing, is vital for verifying the integrity of sterile packaging. This method involves submerging packages underwater and applying pressure to identify any leaks through the emergence of bubbles. By ensuring that the sterile barrier remains intact, manufacturers can significantly reduce contamination risks, which is crucial for patient safety. International buyers must consider compliance with ISO 11607 standards and the reliability of testing equipment, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where regulatory adherence is critical.
What Role Does Gross Leak Testing Play in Electronics?
In electronics, the HSHLD™ method is commonly used to test hermetic seals in components. This test measures the oxygen signature and pressure changes to detect gross leaks, ensuring that electronic devices remain operational in challenging environments. For B2B buyers in Europe and South America, sourcing reliable testing services that adhere to stringent calibration standards is essential. Additionally, understanding the specific material compatibility and testing environments can help mitigate risks associated with product failures.
How is Aerospace Industry Safety Enhanced Through Gross Leak Testing?
The aerospace industry employs Krypton-85 testing to assess the integrity of critical components. This method helps identify gross leaks that could lead to catastrophic failures during flight. By ensuring the reliability of these components, manufacturers can enhance safety and operational effectiveness. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria should prioritize suppliers who meet international certification requirements and possess advanced testing facilities to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Why is Gross Leak Testing Important for Automotive Fuel Systems?
In the automotive sector, gross leak testing is essential for validating the integrity of fuel systems. This testing helps prevent fuel leaks, which can pose safety hazards and affect vehicle performance. For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry standards and can operate under varying environmental conditions is crucial. Additionally, evaluating supplier capabilities in delivering consistent testing results can lead to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
How Does Gross Leak Testing Improve Packaging Integrity?
The packaging industry utilizes Per-Fluorocarbon testing to assess the integrity of packaging solutions. This method ensures that packaging can withstand various conditions without compromising product quality. For businesses, this testing can significantly reduce return rates due to packaging failures. International buyers should focus on suppliers that follow established testing protocols and can address local market needs, ensuring that products meet specific regulatory requirements across different regions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gross leak test’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Achieving Accurate Leak Detection in Medical Devices
The Problem: In the highly regulated medical device industry, ensuring the integrity of packaging is paramount. B2B buyers often face challenges in detecting gross leaks that compromise sterile barriers. Inaccurate leak detection can lead to product recalls, safety risks for patients, and significant financial losses. The complexity of materials and varying environmental conditions further complicate the testing process, making it difficult to ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 11607.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, it is essential to implement a robust gross leak testing protocol that incorporates advanced methodologies like bubble testing. Buyers should invest in high-quality bubble leak testing equipment that can accurately detect leaks under controlled conditions. It’s advisable to conduct regular training for staff on proper testing techniques to enhance accuracy. Additionally, consider partnering with specialized laboratories that offer expertise in gross leak testing to gain insights into best practices and innovative testing solutions tailored for specific device types. Utilizing the ASTM F2096 standard can help ensure that the testing process is reliable and compliant.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Testing Results Across Different Environments
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience inconsistency in gross leak test results when testing the same device under different environmental conditions. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and pressure variations can influence the accuracy of leak detection methods. This inconsistency can lead to a lack of trust in testing protocols and uncertainty about product reliability, which can be detrimental in industries like aerospace and pharmaceuticals.
The Solution: To address this issue, it is crucial to standardize testing conditions as much as possible. Establish a controlled environment for conducting gross leak tests, utilizing temperature and humidity-controlled chambers to minimize external variables. Implementing a comprehensive quality management system that includes regular calibration of testing equipment can also enhance result consistency. Furthermore, consider adopting advanced technologies such as automated testing systems that can provide precise control over testing conditions and repeatability in results, ensuring that all tests are conducted under the same parameters.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Testing Method for Specific Applications
The Problem: With multiple gross leak testing methods available, B2B buyers often struggle to choose the appropriate technique for their specific application. For instance, the choice between methods such as HSHLD™ testing, bubble testing, or Krypton-85 testing can be overwhelming. This uncertainty can lead to the selection of ineffective testing methods that fail to detect critical leaks, ultimately jeopardizing product safety and compliance.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their product specifications and the environmental conditions it will face. Consulting with testing experts can provide valuable insights into the most suitable gross leak testing methods for each application. It’s beneficial to create a decision matrix that weighs factors such as product type, size, materials, and regulatory requirements against the strengths and limitations of each testing method. Additionally, pilot testing various methods on a small scale can help determine the best approach before full-scale implementation, ensuring that the selected method aligns with both operational capabilities and compliance needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gross leak test
What Are the Key Materials Used in Gross Leak Testing?
When selecting materials for gross leak testing, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compatibility with specific applications. Here are four common materials that are frequently utilized in gross leak testing processes.
1. Per-Fluorocarbon
Key Properties:
Per-fluorocarbon is known for its low boiling point and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. It is chemically inert, which allows it to resist corrosion from various substances.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of using per-fluorocarbon include its effectiveness in detecting leaks due to its ability to create a bubble stream when heated. However, it can be relatively expensive and may require specialized handling and disposal protocols, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Per-fluorocarbon is particularly effective in applications where the integrity of hermetic seals is critical, such as in the electronics and medical device industries. Its compatibility with a wide range of materials also enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, compliance with international standards (e.g., ASTM) is essential. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding the handling and disposal of per-fluorocarbons, which may vary by country.
2. Krypton-85
Key Properties:
Krypton-85 is a radioactive isotope that serves as a tracer gas for leak detection. It has a low molecular weight, which allows it to escape through small leaks, making it effective in identifying compromised seals.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of Krypton-85 is its sensitivity to minute leaks, which is crucial for high-precision applications. However, its radioactive nature poses safety concerns, requiring stringent handling protocols and regulatory compliance, which can complicate its use.
Impact on Application:
Krypton-85 is particularly suited for testing small cavity devices, such as those found in the aerospace and defense industries. Its ability to provide precise leak measurements makes it invaluable in high-stakes environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must navigate complex regulations regarding the use of radioactive materials. Compliance with safety standards and obtaining necessary permits can be a significant hurdle, especially in regions with strict nuclear regulations.
3. Helium
Key Properties:
Helium is a noble gas known for its low viscosity and high diffusivity, making it ideal for fine and gross leak testing. It has a high thermal conductivity, which allows for quick detection of leaks.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of helium include its non-toxic nature and the ability to detect extremely small leaks. However, helium can be relatively costly, and its availability may vary by region, which can affect supply chains.
Impact on Application:
Helium is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries due to its effectiveness in ensuring the integrity of critical components. Its compatibility with various materials enhances its applicability across different sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the logistics involved in sourcing helium, particularly in regions where it is less available. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding gas storage and handling is crucial for compliance.
4. Freon
Key Properties:
Freon is a chlorinated hydrocarbon known for its low density and high stability. It is effective in creating a pressure differential that aids in leak detection.
Pros & Cons:
Freon’s primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and ease of use in bubble testing methods. However, environmental concerns regarding its ozone-depleting properties have led to regulatory restrictions, which can limit its use in certain regions.
Impact on Application:
Freon is commonly used in the medical device industry for bubble leak testing. Its effectiveness in detecting gross leaks makes it a popular choice for ensuring the sterility of medical packaging.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must consider the environmental regulations surrounding the use of Freon, especially in Europe, where stringent laws are in place. Understanding local compliance requirements is essential for avoiding potential legal issues.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for gross leak test | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per-Fluorocarbon | Electronics, medical devices | Effective bubble stream detection | High cost and complex handling | High |
| Krypton-85 | Aerospace, defense | Sensitivity to minute leaks | Safety concerns due to radioactivity | High |
| Helium | Aerospace, automotive | Non-toxic and detects small leaks | Relatively costly and variable supply | Medium |
| Freon | Medical device packaging | Cost-effective and easy to use | Environmental regulations limiting use | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their gross leak testing processes while considering regional compliance and application-specific requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gross leak test
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Gross Leak Testing?
The manufacturing process for devices requiring gross leak testing typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of the final product.
How is Material Prepared for Gross Leak Testing?
Material preparation begins with selecting appropriate raw materials that meet industry specifications. These materials must exhibit the necessary properties for hermeticity, such as resistance to environmental factors and compatibility with the testing methods. For example, materials used in medical devices often require biocompatibility. Once selected, the materials undergo cleaning and surface treatment to remove contaminants that could affect the sealing process. This step is vital as any residual substances can lead to compromised seals, which may result in gross leaks.
What Techniques Are Employed in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage encompasses shaping the raw materials into the desired configuration. Techniques such as injection molding, machining, and stamping are commonly used, depending on the complexity of the components. For instance, injection molding is prevalent in producing intricate parts with high precision, while machining is suitable for creating robust components that require tight tolerances. During this stage, it’s essential to monitor dimensional accuracy to prevent defects that could lead to leaks.
How is Assembly Conducted for Leak Testing?
Assembly involves joining the formed parts to create a complete device. This process must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure that all components fit perfectly, thus maintaining hermeticity. Techniques such as welding, adhesive bonding, and mechanical fastening are typically utilized. Each method has its own set of quality assurance protocols. For example, welding might require pre-weld inspections to assess the integrity of the joining surfaces. Effective assembly also involves implementing controlled environments to minimize contamination risks.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Ensuring Quality?
Finishing processes play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall quality and durability of the device. These processes may include coating, polishing, and surface treatment. Coatings can provide additional protection against environmental factors, while polishing ensures that surfaces are smooth and free from defects that could compromise seals. Moreover, final inspections and tests are conducted to verify that the product meets specified standards before it is sent for gross leak testing.
How is Quality Control Managed During Gross Leak Testing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, particularly for devices subject to gross leak testing. Implementing a robust QC framework helps ensure compliance with international standards and minimizes the risk of defects.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for European markets and API standards for oil and gas applications are essential. These standards set the benchmarks for quality assurance, ensuring that products are safe and reliable. Understanding these requirements is crucial for buyers, especially when sourcing from diverse international markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors production processes to identify any deviations from established protocols. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) assesses the completed device, ensuring it meets all functional and regulatory requirements before shipping. These checkpoints help maintain high quality and reduce the likelihood of costly rework or recalls.
Which Common Testing Methods Are Used for Gross Leak Testing?
Common testing methods for gross leak detection include bubble testing and tracer gas methods. Bubble testing involves submerging the device in water and applying pressure to observe for bubbles, indicating leaks. Tracer gas methods, such as helium or krypton-85 testing, utilize gases to detect leaks in hermetic seals. These methods are often standardized according to military and industry specifications, ensuring reliability and consistency in results.

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control standards, B2B buyers can implement several verification strategies. Conducting audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess compliance with quality standards firsthand. Additionally, requesting detailed QC reports, including test results and certifications, can provide insights into the supplier’s testing protocols and outcomes.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in supplier quality. These independent entities assess the supplier’s adherence to agreed-upon specifications and industry standards, providing an unbiased evaluation of quality control practices. This is particularly beneficial for buyers operating in regions with varying regulatory frameworks, such as Africa and South America, where local standards may differ significantly from international norms.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing products. Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that influence the certification process. For example, buyers from Europe may prioritize CE marking, while those from the Middle East might focus on compliance with local standards. Understanding these nuances is vital for ensuring that products not only meet quality expectations but also comply with regional regulations, ultimately facilitating smoother market entry and acceptance.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices surrounding gross leak testing are essential for ensuring product reliability and safety. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality devices that meet their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gross leak test’
This practical sourcing guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a clear, actionable checklist for procuring gross leak test services or equipment. Ensuring the integrity and reliability of products through effective leak testing is crucial for maintaining quality and compliance in various industries, especially in sectors like medical devices and electronics.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider the types of products you need to test and the specific requirements for hermeticity. For instance, identify whether you require methods like HSHLD™, per-fluorocarbon, or krypton-85 tests, as each method has different applications based on the materials and product designs.
Step 2: Research and Identify Qualified Suppliers
Take the time to research potential suppliers who specialize in gross leak testing. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your industry and those that have experience with similar products. Utilize platforms such as LinkedIn, industry-specific forums, and trade shows to gather information about potential partners.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it is crucial to thoroughly vet suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry or region. Assess their technical capabilities and whether they adhere to relevant standards such as ISO 11607 or MIL-STD specifications, which are essential for ensuring quality and compliance.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that the suppliers possess the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. This step is vital for ensuring that the testing methods employed are reliable and accepted globally. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems.
Step 5: Request Sample Testing or Demonstrations
Before finalizing your decision, ask suppliers for sample testing or demonstrations of their gross leak testing methods. This hands-on experience allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of their testing processes and equipment. Ensure that the demonstration aligns with your specific product requirements and testing conditions.
Illustrative image related to gross leak test
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Terms of Service
Review the pricing structures offered by potential suppliers, ensuring that you understand what is included in the cost. Look for transparency in pricing, as hidden fees can lead to budget overruns. Additionally, evaluate the terms of service, including turnaround times, warranty provisions, and support services, to ensure they meet your operational needs.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you have selected a supplier, focus on building a long-term relationship. Open communication about your testing needs and any changes in product specifications will foster collaboration. This ongoing partnership can lead to improved testing processes and innovations that benefit both parties in the long run.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for gross leak testing, ensuring they select the right partners to maintain product integrity and compliance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gross leak test Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Gross Leak Testing?
When sourcing gross leak testing services, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The types of fluids and gases used in testing, such as helium or per-fluorocarbon, significantly affect costs. High-quality, certified materials may come at a premium, but they ensure reliable results.
-
Labor: Skilled technicians are required to conduct tests accurately. Labor costs can vary based on the region and the expertise of the personnel involved. In markets such as Africa or South America, labor costs may be lower, but ensuring quality and reliability should remain a priority.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with the testing facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can help keep these costs down.
-
Tooling: Specialized equipment and tools for conducting various gross leak tests can be a significant investment. The type of testing method (e.g., bubble testing, Krypton-85) will dictate the necessary tooling, impacting overall costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is crucial to ensure the reliability of the testing results. This may involve additional costs for certifications and compliance with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of test samples can incur extra costs, especially when dealing with international shipping. Understanding Incoterms is vital to clarify responsibilities and costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin to ensure profitability. This margin can vary significantly based on the supplier’s market position and the complexity of the services offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Gross Leak Testing Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of gross leak testing services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher volumes can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate prices for bulk orders, which is beneficial for companies with ongoing testing needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom testing protocols or specific material requirements can increase costs. Clearly defining your needs upfront can prevent unexpected expenses down the line.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Tests requiring high-grade materials or certifications (like ISO standards) may be priced higher. Ensure that the materials used align with your quality requirements to avoid future complications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is crucial. Different Incoterms can affect logistics costs and responsibilities, impacting the final price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Gross Leak Testing?
To navigate the complexities of gross leak testing sourcing effectively, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Highlighting long-term partnerships or bulk orders can leverage better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look for suppliers that offer bundled services or discounts for recurring tests. This can reduce overall costs and simplify logistics.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial pricing but also the long-term costs associated with reliability and potential product failures. Choosing a supplier with a robust QC process may be more cost-effective in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect pricing. Establishing clear communication regarding these factors with suppliers can mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers that demonstrate compliance with relevant industry standards. Investing in quality upfront can save money related to product failures and recalls later.
Disclaimer
The pricing information provided is indicative and can vary based on specific project requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always consult directly with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gross leak test With Other Solutions
In today’s competitive market, B2B buyers often seek effective methods for ensuring the integrity of their products, particularly in industries where hermeticity is crucial. While the gross leak test is a widely recognized technique, it is essential to explore alternative solutions that may offer unique advantages depending on specific operational needs and constraints. This analysis will compare the gross leak test against two viable alternatives: the fine leak test and bubble leak testing.
Illustrative image related to gross leak test
| Comparison Aspect | Gross Leak Test | Fine Leak Test | Bubble Leak Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Detects large leaks quickly; suitable for high-volume testing. | Highly sensitive; can identify very small leaks. | Effective for package integrity in sterile environments. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost; requires less specialized equipment. | Higher operational costs due to specialized equipment and longer testing times. | Moderate costs; equipment can be shared across tests. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward setup; minimal training required. | Requires specialized knowledge and calibration; more complex setup. | Simple setup; intuitive process for operators. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; less frequent calibration needed. | High maintenance; regular calibration and monitoring required. | Low maintenance; equipment is durable but requires regular checks. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-throughput applications needing quick results. | Best for high-precision applications, such as aerospace and medical devices. | Optimal for medical packaging where sterility is critical. |
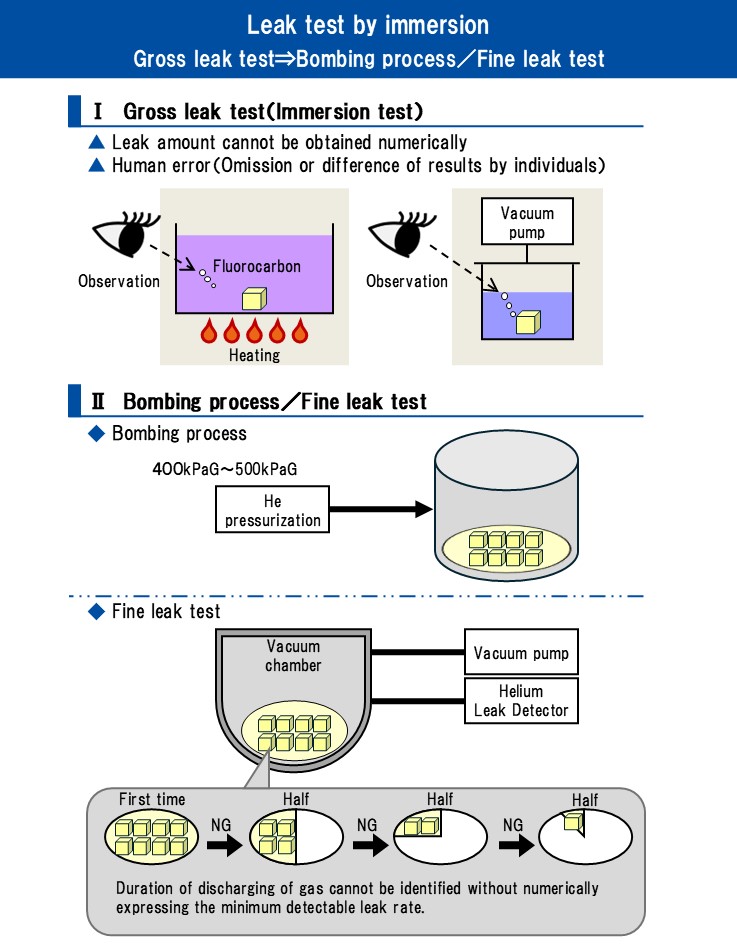
What are the Pros and Cons of the Fine Leak Test as an Alternative?
The fine leak test is renowned for its sensitivity, capable of detecting very small leaks using helium as a tracer gas. This method is particularly valuable in industries where even the slightest breach could lead to product failure or safety hazards, such as aerospace and medical devices. However, the fine leak test comes with higher operational costs due to the specialized equipment required, and its setup can be more complex, often necessitating trained personnel. Consequently, while it offers precision, its implementation can be a barrier for companies with budget constraints.
How Does Bubble Leak Testing Compare to Gross Leak Testing?
Bubble leak testing is a qualitative method primarily used in the medical packaging sector to ensure the integrity of sterile barriers. It involves submerging packages and observing for bubbles, which indicate leaks. This technique is straightforward and requires minimal training, making it accessible for many operators. However, it is not suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring quantitative data or precise measurements of leak rates. Despite its limitations, the bubble test is favored for its effectiveness in maintaining product safety and compliance in sterile environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate leak testing method, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. The gross leak test is advantageous for high-volume production environments where speed is essential, while fine leak testing is better suited for high-stakes applications demanding accuracy. Bubble leak testing serves well in the medical device industry, emphasizing sterility and contamination prevention. By aligning their choice with operational goals and industry standards, buyers can ensure they select the most effective solution for their unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gross leak test
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gross Leak Testing?
Understanding the technical properties associated with gross leak testing is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting devices for applications requiring hermeticity. Here are some essential specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
1. Material Compatibility
The materials used in the device being tested must be compatible with the testing methods. For example, some materials may not withstand high temperatures used in certain gross leak tests, such as the Per-Fluorocarbon method, which operates at temperatures up to 125°C. Buyers should ensure that their components can endure the conditions of the test without degrading, as this impacts the reliability of the results and the longevity of the product.
2. Test Pressure
The pressure at which the gross leak test is performed is vital for accurate results. Typically, the test involves submerging the device under a specific pressure to assess its hermeticity. Incorrect pressure levels can lead to false positives or negatives in leak detection. It is essential for buyers to understand the specifications of the devices being tested and ensure they meet the pressure requirements outlined in industry standards.
3. Sensitivity Level
Sensitivity refers to the smallest leak that can be detected during testing. Different testing methods have varying sensitivity levels; for instance, bubble tests may detect larger leaks but might miss smaller ones. Understanding the sensitivity required for specific applications, such as medical devices or electronics, can guide buyers in selecting appropriate testing methods and devices.
4. Calibration Standards
Calibration of testing equipment is critical for ensuring accurate results. Buyers should look for manufacturers that adhere to recognized calibration standards, such as MIL-STD or ASTM guidelines. These standards provide a framework for ensuring that testing equipment is functioning correctly, which is crucial for maintaining product quality and compliance.
5. Temperature Range
The temperature range in which the device can operate during testing is also significant. Some methods, like the Krypton-85 tests, may require specific temperature conditions to function correctly. Buyers should ensure that their products can withstand the necessary temperature fluctuations to avoid compromising the integrity of the test.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Gross Leak Testing?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some commonly used terms related to gross leak testing:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of gross leak testing, understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure that they are sourcing components that meet their quality and performance standards.

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory levels and cash flow effectively, especially when procuring specialized testing equipment or components for gross leak testing.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs that outline their specific requirements for gross leak testing, including technical specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines, to receive accurate and competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs during the import/export process, especially when dealing with international suppliers of testing equipment.
5. Calibration Certificate
A calibration certificate is a document that verifies that testing equipment has been calibrated according to specific standards. Buyers should request these certificates from suppliers to ensure that the equipment used for gross leak testing is reliable and meets industry standards.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure product integrity and compliance in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gross leak test Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Gross Leak Test Sector?
The global gross leak test market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demands for product reliability and safety across various industries, including electronics, medical devices, and automotive. Key drivers include stringent regulatory standards and the need for manufacturers to ensure the integrity of their products. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced bubble testing and new tracer gas methodologies, are revolutionizing the gross leak testing landscape. The adoption of automated testing systems is on the rise, improving efficiency and accuracy in leak detection. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence in data analysis is enabling manufacturers to predict potential failures before they occur, thus reducing costs and enhancing product longevity. These technological advancements are not only streamlining testing processes but also enabling companies to comply with international quality standards more effectively.

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
For buyers in regions with developing manufacturing sectors, such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, investing in state-of-the-art leak testing technologies can lead to enhanced product reliability and a competitive edge in the global marketplace. Furthermore, as more companies pivot towards digital transformation, the demand for remote monitoring and testing capabilities is expected to surge, aligning with the global trend of Industry 4.0.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Gross Leak Test Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become pivotal considerations in the gross leak test sector. The environmental impact of testing methods, particularly those that utilize hazardous materials, is under scrutiny from regulators and consumers alike. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and utilize eco-friendly materials in their testing processes.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially as businesses face pressure to demonstrate corporate social responsibility. By selecting partners who are committed to sustainable sourcing, companies can mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations and enhance their brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, adopting ‘green’ testing materials and methods can lead to significant cost savings in the long run, as they often result in less waste and lower disposal costs. For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, where environmental regulations are becoming more stringent, aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals will be essential for long-term viability and success in the marketplace.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Gross Leak Testing in the B2B Context?
The evolution of gross leak testing has been shaped by advancements in technology and the increasing need for product reliability. Historically, gross leak tests were primarily conducted using rudimentary methods such as water immersion and visual inspection. However, as industries evolved, so too did the testing methodologies.
The introduction of sophisticated techniques, such as HSHLD™ and Krypton-85 testing, marked a significant shift in how manufacturers approach leak detection. These methods not only improved accuracy but also allowed for the testing of smaller, more complex devices that are prevalent in today’s markets. Furthermore, the rise of digital technologies has paved the way for automated testing solutions, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis of leak test results.
As industries continue to innovate, the gross leak test sector is likely to witness further advancements, solidifying its importance in ensuring product quality and compliance across global supply chains. For B2B buyers, staying informed about these trends and technological advancements is crucial for making strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives.

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gross leak test
-
How do I choose the right gross leak test method for my product?
Choosing the right gross leak test method depends on the type of product you are testing and the specific requirements of your application. Common methods include HSHLD™, per-fluorocarbon, and krypton-85 tests. Consider factors such as the size and material of your device, the expected leak rate, and any industry standards you must comply with. Collaborate with your supplier to ensure the chosen method aligns with your product’s specifications and provides reliable results. -
What are the key benefits of gross leak testing for my products?
Gross leak testing is crucial for ensuring the hermeticity of products, especially those with internal cavities. It helps identify major leaks that could compromise product integrity and performance. By detecting leaks early, manufacturers can avoid costly recalls, enhance product reliability, and ensure compliance with industry standards. This testing also aids in improving product design and packaging, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced risk of contamination. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for gross leak testing services?
When vetting suppliers for gross leak testing, evaluate their experience, certifications, and capabilities. Look for companies that adhere to international standards like ISO and MIL-STD. Request references or case studies to assess their reliability and quality of service. Additionally, consider their technological capabilities and whether they offer customized testing solutions to meet your specific needs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gross leak testing services?
Minimum order quantities for gross leak testing can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the testing required. Some suppliers may have a low MOQ for standard tests, while specialized or custom tests could have higher MOQs. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your testing schedule and budget. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for gross leak testing services?
Payment terms for gross leak testing services can vary by supplier and may include options such as upfront payments, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon completion of testing. It’s essential to clarify these terms before engaging with a supplier. Be sure to discuss any potential discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts, which can improve your cash flow and reduce overall testing costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in gross leak testing?
To ensure quality assurance in gross leak testing, partner with suppliers that have robust QA processes in place. This includes regular calibration of testing equipment, adherence to industry standards, and comprehensive reporting of test results. Additionally, consider asking for third-party certifications or audits to verify their QA practices. Establishing clear communication regarding your expectations will also help maintain quality throughout the testing process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing gross leak testing services?
Logistics play a crucial role in the efficiency of sourcing gross leak testing services. Consider the geographical location of your supplier, as shipping times can affect project timelines. Ensure that the supplier has a reliable logistics network to handle the transportation of your products safely. Additionally, discuss customs clearance procedures, especially for international shipments, to avoid delays and unexpected costs. -
How can I customize gross leak testing to fit my specific product requirements?
Customization of gross leak testing is possible by discussing your specific product needs with potential suppliers. This may involve adjusting testing parameters, selecting the appropriate testing method, or developing tailored protocols that meet your industry standards. Collaborating closely with your supplier during the design phase can lead to more effective testing solutions that enhance product performance and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Top 8 Gross Leak Test Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Oneida Research Services – Gross Leak Testing
Domain: orslabs.fr
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Gross Leak Testing is a hermeticity testing process offered by Oneida Research Services. Key methods include: HSHLD™ Dry Gross Leak, which uses oxygen signature and pressure change to identify leaks; Per-Fluorocarbon Gross Leak, which involves submerging devices in an indicator fluid at high temperatures to observe bubble streams; Krypton-85 Dry Gross Leak, performed before Fine Leak testing to el…
2. Orslabs – Gross Leak Hermeticity Testing Solutions
Domain: orslabs.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Gross Leak Hermeticity Testing Processes include: 1. HSHLD™ Dry Gross Leak Test – uses oxygen signature and pressure change to identify leaks. 2. Per-Fluorocarbon Gross Leak Test – involves submerging the device in an indicator fluid at high temperatures to observe bubble streams. 3. Krypton-85 Dry Gross Leak Test – eliminates failures before Fine Leak testing. 4. Krypton-85 Wet Gross Leak Test – …
3. Alter Technology – Seal Test Solutions
Domain: semiconductor.altertechnology.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Seal Test: Fine and Gross Leak methods for electronic components. Purpose: Determine the effectiveness of sealing of components with internal cavities (hermeticity). Techniques: 1. Fine Leak Test – Uses pressure and vacuum chambers with a helium mass-spectrometer leak detector. Samples are placed in a helium pressurized chamber and analyzed for helium presence. Standards: MIL-STD-202 -112 and MIL-…
4. Amada Weld Tech – Hermetic Leak Testing Solutions
Domain: amadaweldtech.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Gross leak is a term used in microelectronic package hermetic leak testing. A hermetically sealed package is subjected to a bubble leak test by submerging the sealed package into a 125°C heated perfluoropolyether solution. Packages with visible bubbles exiting the package will be classified as a “gross leaker rejects.”
5. TQC – Leak Testing Solutions
Domain: tqc.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Leak Testing Methods: Observation, Chemical trace, Chemical penetration, Gas sniffing, Ultrasonic testing. Leak Testing Measurement Techniques: Pressure Measurement (Absolute measurement, Reference comparison, Differential pressure component dosing, Inter-stream testing), Continuous Flow (Controlled pressure, Free flow), Gas Trace (Helium, Hydrogen, Gas bombing).
6. Gate Energy – Leak Testing Solutions
Domain: gate.energy
Introduction: Leak testing is a method to verify the quality of facility construction, distinct from hydrostatic testing. It uses gas or service media at or near maximum working pressure to confirm that systems are leak-tight. Ideal for onshore testing, it can impact offshore project schedules due to space and personnel requirements. Initial gross-air leak tests are performed at 25% of maximum working pressure …
7. Semitracks – Leak Detection Solutions
Domain: semitracks.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Leak Detection is a method to determine the seal integrity of hermetically sealed packages, particularly integrated circuit packages used in military and high-reliability applications. The testing includes Fine Leak and Gross Leak Hermetic Seal testing, which are cost-effective methods for verifying seal breaches. Fine Leak testing uses helium-based or radioisotope tracer gas-based equipment, whil…
8. Cincinnati Test – Volumetric Fill Leak Testing
Domain: cincinnati-test.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Volumetric Fill Leak Testing for Sealed Parts is a two-step process designed for sealed devices that lack ports for pressure or vacuum testing. This method ensures there are no gross leaks before conducting a fine decay leak test. Key benefits include: providing a dry and non-destructive leak test, sensitivity to detect very small leaks, protection from over-pressurization, compliance with IP67 in…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gross leak test
In the evolving landscape of gross leak testing, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the diverse methodologies—such as the HSHLD™ and Krypton-85 tests—businesses can enhance their product reliability and compliance with stringent industry standards. Implementing effective leak testing not only safeguards product integrity but also ensures customer satisfaction by minimizing the risks associated with contamination and device failure.
Investing in advanced leak testing solutions can provide a competitive edge, allowing companies to optimize their manufacturing processes and reduce costs associated with product recalls and warranty claims. As the demand for high-quality, reliable products continues to rise, the need for robust hermeticity testing will only grow.
Looking forward, now is the time for international buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies and align with reputable testing service providers. By prioritizing quality assurance through comprehensive gross leak testing, businesses can secure their market position and drive long-term success. Engage with testing experts today to explore tailored solutions that meet your specific needs and set your products apart in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to gross leak test
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.