Is Your Flat Belt Machine Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for flat belt machine
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing a reliable flat belt machine is a critical challenge that can significantly impact operational efficiency and productivity. Flat belt machines, renowned for their versatility and durability, play a crucial role in various industries, from food processing to material handling. However, navigating the myriad of options available can be overwhelming for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Brazil.
This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify the flat belt machine market, offering valuable insights into the types, applications, and specifications of these essential machines. It addresses key considerations such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and maintenance requirements, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the intricacies of flat belt technology and the factors that influence performance, businesses can enhance their production processes and reduce downtime.
Empowering B2B buyers with practical knowledge, this guide serves as a roadmap to successfully navigate the global market for flat belt machines. With actionable strategies and expert insights, companies can confidently select the right solutions that meet their operational needs while optimizing their supply chain investments.
Understanding flat belt machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt Conveyors | Continuous belt loop, low friction surface | Manufacturing, packaging, food processing | Pros: Efficient product transport; Cons: Limited incline capabilities. |
| Flat Belt Transmission | Power transmission with low wear and tear | Machinery, automotive, industrial sectors | Pros: Durable materials; Cons: Requires regular maintenance. |
| Modular Flat Belt Systems | Interchangeable segments for flexibility | Material handling, assembly lines | Pros: Customizable design; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Timing Flat Belts | Designed for precise synchronization of machinery | Robotics, automotive assembly | Pros: Accurate timing; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Heavy-Duty Flat Belts | Reinforced for heavy loads and harsh environments | Mining, construction, heavy machinery | Pros: High durability; Cons: Increased weight may impact efficiency. |
What Are the Characteristics of Flat Belt Conveyors?
Flat belt conveyors are designed to facilitate the continuous movement of materials in various industrial settings. They feature a smooth, low-friction surface that allows for easy transport of products from one point to another. Ideal for applications in manufacturing, packaging, and food processing, these conveyors can efficiently handle items of varying sizes. When considering a flat belt conveyor, buyers should evaluate the load capacity, length, and speed requirements to ensure optimal performance in their specific operational context.
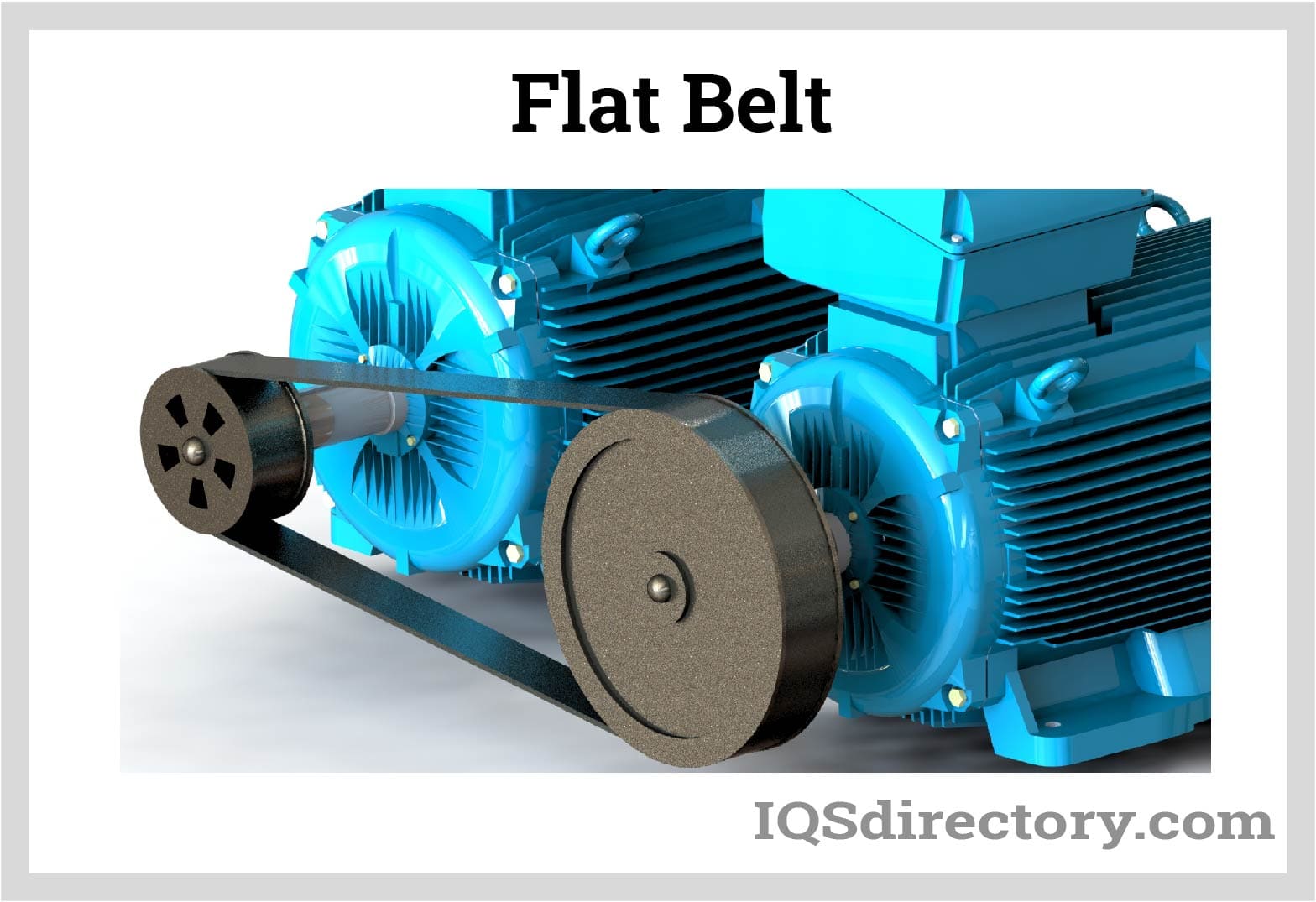
How Do Flat Belt Transmission Systems Function?
Flat belt transmission systems are primarily used to transfer power between machinery components. These belts are constructed from durable materials like nylon and rubber, which minimize wear and prolong lifespan. Industries such as automotive and manufacturing rely on these systems for effective power distribution. Buyers should consider the operational environment, as well as the required torque and speed ratios, to select the most suitable transmission system for their machinery.
What Are the Advantages of Modular Flat Belt Systems?
Modular flat belt systems consist of interchangeable segments that can be easily replaced or reconfigured, providing a high degree of flexibility in material handling. These systems are particularly beneficial in assembly lines, where adaptability to changing production needs is crucial. While they may require a higher initial investment compared to traditional belts, the long-term savings from reduced downtime and maintenance can justify the cost. Buyers should assess their specific needs for modularity and customization to maximize the benefits of these systems.
Why Choose Timing Flat Belts for Precision Applications?
Timing flat belts are engineered for precise synchronization in machinery operations, making them essential in robotics and automotive assembly lines. Their design ensures accurate timing and minimal slippage, which is critical in high-speed applications. While they offer significant advantages in precision, buyers must be aware of the more complex installation processes and potential maintenance requirements. Evaluating the specific timing needs of machinery will help buyers determine if these belts are the right fit for their operations.
What Makes Heavy-Duty Flat Belts Suitable for Tough Environments?
Heavy-duty flat belts are reinforced to withstand extreme loads and challenging conditions, making them ideal for industries such as mining and construction. These belts are designed to handle abrasive materials and rough handling, ensuring longevity and reliability. While they provide excellent durability, buyers should consider the increased weight and potential impact on system efficiency. Assessing the specific environmental conditions and load requirements will be key in selecting the appropriate heavy-duty flat belt for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of flat belt machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of flat belt machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly line automation | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Consider belt durability and compatibility with machinery |
| Food Processing | Conveyor systems for packaging | Ensures hygienic transport and compliance with safety standards | Evaluate materials for food safety certifications |
| Mining and Quarrying | Material handling and transportation | Enhances operational productivity and reduces downtime | Assess resistance to wear and environmental conditions |
| Printing Industry | Web printing and drying processes | Improves print quality and reduces waste | Look for belts that can handle high temperatures and humidity |
| Agriculture | Grain and produce handling | Streamlines operations and minimizes spoilage | Ensure belts are adaptable to various agricultural machinery |
How is Flat Belt Machinery Used in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, flat belt machines are pivotal in assembly line automation. They facilitate the efficient movement of components between workstations, significantly boosting productivity. By minimizing manual handling, businesses can reduce labor costs and enhance safety. Buyers should focus on sourcing belts that offer high durability and compatibility with existing machinery, as well as ease of installation and maintenance, to ensure seamless integration into their operations.
What Role Does Flat Belt Machinery Play in Food Processing?
In the food processing sector, flat belt machines are employed in conveyor systems to transport products through various stages of packaging. These systems ensure the hygienic handling of food items, which is crucial for compliance with health regulations. Buyers must consider sourcing belts made from food-safe materials that meet industry standards, as well as those that can withstand cleaning processes without degrading.
How Are Flat Belt Machines Beneficial in Mining and Quarrying?
Flat belt machinery plays a critical role in mining and quarrying by facilitating the transport of heavy materials across challenging terrains. Their robust design enhances operational productivity and minimizes equipment downtime, which is vital in this sector. Buyers should prioritize sourcing belts that exhibit high wear resistance and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
How Does Flat Belt Machinery Enhance the Printing Industry?
In the printing industry, flat belt machines are essential for web printing and drying processes. They help in transporting printed materials through various stages of production, ensuring high-quality output while minimizing waste. Buyers need to look for belts that can handle high temperatures and humidity levels, as these factors are common in printing environments. Selecting the right materials will help maintain print quality and operational efficiency.
What Advantages Does Flat Belt Machinery Offer in Agriculture?
In agriculture, flat belt machines are utilized for the efficient handling of grains and produce. These systems streamline operations, reducing the risk of spoilage and enhancing overall productivity. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it’s essential to source belts that are adaptable to diverse agricultural machinery and can withstand varying environmental conditions, ensuring reliability in different climates.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘flat belt machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Frequent Belt Breakage in High-Load Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as mining or heavy manufacturing face the challenge of frequent flat belt breakage when handling heavy loads. This issue not only halts production but also incurs significant replacement costs and labor expenses for downtime. Buyers often struggle to find belts that can withstand their specific load requirements, leading to frustration and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should consider sourcing flat belts specifically designed for high-load applications. It’s crucial to review the material properties and construction of the belt; options such as reinforced synthetic fibers or steel cord belts can enhance durability and load-bearing capacity. When selecting a flat belt machine, request detailed specifications from suppliers, including tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and heat tolerance. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can also help, allowing for regular inspections of the belt’s condition, which can preempt unexpected failures. Additionally, working with a manufacturer that offers customization options can ensure that the belt is tailored to your specific operational demands.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies Due to Misalignment
The Problem: Misalignment of flat belt machines can lead to inefficient operation, causing uneven wear and potential damage to both the belt and the machinery. Buyers often encounter issues where the belt drifts off its intended path, leading to increased maintenance needs and costly repairs. This misalignment can stem from several factors, including improper installation or wear of pulleys and bearings.
The Solution: To address misalignment issues, it is essential to perform a thorough alignment check during the installation of the flat belt machine. Buyers should utilize laser alignment tools or precision measuring instruments to ensure that all components are correctly aligned before operation begins. Regular training for maintenance staff on the importance of alignment can further prevent future issues. Additionally, investing in adjustable pulleys can facilitate fine-tuning during operations. Creating a culture of proactive maintenance by scheduling periodic checks can significantly reduce the risk of misalignment and its associated costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Belt Replacement and Maintenance
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, the time and complexity involved in replacing flat belts can be a significant pain point. In industries where downtime directly correlates to lost revenue, the need for quick and efficient maintenance solutions is paramount. Buyers often find themselves struggling with the logistics of sourcing compatible belts, managing stock, and executing timely replacements without disrupting operations.
The Solution: To streamline the belt replacement process, buyers should consider establishing a partnership with a reliable supplier that offers on-site service and quick delivery options. Implementing an inventory management system for spare belts can ensure that the right sizes and types are readily available when needed. Additionally, creating a standardized replacement procedure, including detailed guidelines and training for maintenance personnel, can help minimize downtime during replacements. Utilizing modular flat belt systems can also simplify maintenance by allowing for quicker belt swaps without extensive machinery disassembly. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including training and technical assistance, can further enhance operational efficiency and reduce the impact of belt maintenance on production schedules.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for flat belt machine
When selecting materials for flat belt machines, it is essential to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. The choice of material impacts not only the operational efficiency of the machine but also compliance with international standards, especially for B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we analyze four common materials used in flat belt construction: rubber, nylon, leather, and metal.
What Are the Key Properties of Rubber in Flat Belt Machines?
Rubber is a widely used material in flat belt applications due to its excellent flexibility and grip. It typically has a good temperature resistance, generally rated between -30°C to 80°C, and can withstand moderate pressure levels. Rubber belts also exhibit high abrasion resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros and Cons of Rubber
Rubber belts offer high durability and are cost-effective, making them a popular choice for many industries. However, they can be susceptible to degradation from UV exposure and certain chemicals, which may limit their use in specific environments. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can vary based on the type of rubber compound used.
Impact on Application
Rubber belts are compatible with a wide range of media, including food products, which is crucial for applications in food processing industries. Buyers should ensure that the rubber material meets relevant food safety standards.
How Does Nylon Compare as a Material for Flat Belt Machines?
Nylon is known for its high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear. It can operate effectively in temperature ranges from -40°C to 100°C, making it suitable for diverse environments. Nylon belts are often reinforced to enhance their structural integrity.
Pros and Cons of Nylon
The key advantage of nylon is its durability and lightweight nature, which can lead to energy savings in operations. However, nylon can be more expensive than rubber and may require specific conditions to prevent moisture absorption, which could affect its performance over time.
Impact on Application
Nylon belts are particularly effective in applications requiring high-speed operations and are commonly used in packaging and material handling sectors. Buyers should consider moisture levels in their operational environments to ensure compatibility.
What Are the Benefits of Leather in Flat Belt Machines?
Leather was one of the original materials used in flat belt manufacturing. It offers good flexibility and a natural ability to grip surfaces, which can be beneficial in power transmission applications.
Pros and Cons of Leather
While leather is durable and provides excellent performance in low-speed applications, it is less resistant to moisture and chemicals compared to synthetic materials. This can limit its use in harsh environments. Additionally, leather belts often come at a higher cost due to the sourcing and processing of the material.
Impact on Application
Leather belts are suitable for traditional machinery and applications where aesthetics are a consideration. Buyers must ensure that leather belts comply with environmental regulations, particularly in regions with strict animal welfare standards.
Why Consider Metal for Flat Belt Machines?
Metal belts, often made from stainless steel or aluminum, are used in specialized applications where strength and resistance to heat and chemicals are critical. They can operate in extreme temperature ranges and are impervious to moisture.
Pros and Cons of Metal
Metal belts provide unmatched durability and are ideal for high-load applications. However, they are typically more expensive and heavier than other materials, which can affect energy efficiency. The manufacturing process can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application
Metal belts are commonly used in industries such as mining and heavy manufacturing. Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards for safety and performance, such as ASTM or DIN.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Flat Belt Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for flat belt machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Conveyor systems in food processing | High durability and cost-effectiveness | Susceptible to UV degradation and chemicals | Low |
| Nylon | High-speed packaging operations | Lightweight and strong | Higher cost and moisture sensitivity | Medium |
| Leather | Traditional machinery applications | Natural grip and flexibility | Limited moisture and chemical resistance | High |
| Metal | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Exceptional durability and heat resistance | High cost and weight | High |
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate material for flat belt machines requires a thorough understanding of the specific application, environmental conditions, and compliance with international standards. B2B buyers must weigh the pros and cons of each material to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for flat belt machine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Flat Belt Machines?
The manufacturing process for flat belt machines involves several crucial stages, each designed to ensure the production of high-quality belts that meet the diverse needs of various industries. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Flat Belt Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting appropriate raw materials based on the specific requirements of the flat belt application. Common materials used include synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester, rubber composites, and reinforced materials for added durability.
During this stage, materials are evaluated for their mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Suppliers often conduct preliminary tests to ensure that the materials meet industry standards before they proceed to the next stage. This step is critical as the choice of material directly impacts the performance and longevity of the flat belt.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Flat Belt Production?
The forming stage encompasses various techniques to shape the raw materials into the desired belt configuration. Common methods include extrusion, weaving, and molding.
- Extrusion: This technique is widely used for rubber and plastic belts, where the material is heated and forced through a die to create a continuous belt of uniform thickness.
- Weaving: In cases where woven belts are required, fibers are interlaced to create a strong yet flexible structure. This method is particularly effective for high-load applications.
- Molding: For specialized belts, molding can be employed to create specific shapes or features, such as grooves or notches that enhance grip and performance.
These forming techniques are often complemented by advanced technologies like computer numerical control (CNC) machining, which ensures precision and consistency in belt dimensions.

Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Flat Belt Machines?
Once the individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process involves integrating various elements, including pulleys, rollers, and any additional components necessary for the flat belt machine’s operation.
Quality control is critical during assembly. Each component is inspected for defects and compatibility with the overall system. Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. This stage may also include the application of adhesives or stitching to ensure that all parts are securely attached and capable of withstanding operational stresses.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Flat Belts?
Finishing techniques play a vital role in enhancing the surface properties of the flat belts. This stage may involve processes such as:
- Coating: Applying protective layers to improve resistance to wear, chemicals, and environmental factors.
- Trimming: Ensuring that the edges of the belts are smooth and free from defects.
- Testing: Conducting functional tests to verify that the belts perform as intended under operational conditions.
Finishing is crucial not only for aesthetics but also for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the flat belts.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant to Flat Belt Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in the manufacturing of flat belt machines, especially for B2B buyers who require reliable and durable products. International standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system, are commonly adopted.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking in Europe and API standards for the oil and gas sector can further assure buyers of the quality and safety of the products. These standards help establish a framework for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Flat Belt Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint focuses on inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. Materials are tested for quality, and any non-compliance with specifications can lead to rejection or re-sourcing.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the forming and assembly stages, IPQC ensures that manufacturing processes adhere to predefined standards. This may include monitoring machinery settings, production speed, and environmental conditions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the belts are packaged and shipped, they undergo a final inspection to verify that they meet all specifications and performance criteria. This may include tensile strength tests, dimensional checks, and operational simulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can reveal their manufacturing capabilities, adherence to quality standards, and operational processes. This can be done either directly or through third-party audit services.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including records of inspections, tests performed, and compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly important for ensuring compliance with international standards.
-
Review Certifications: Buyers should check for relevant certifications and standards that the supplier complies with, which can serve as a testament to their commitment to quality.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider for Quality Assurance?
International buyers face unique challenges regarding quality assurance. Cultural differences in business practices can impact the reliability of communication and expectations.
Understanding regional regulations and standards is also essential. For example, EU markets may have stricter compliance requirements than those in South America or Africa. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these nuances to ensure that they are making informed decisions.
Moreover, establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can facilitate better understanding and adherence to quality expectations. Regular updates and feedback loops can help maintain quality standards throughout the production process.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for flat belt machines is critical for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure that they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs and quality expectations.

Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘flat belt machine’
In the competitive landscape of industrial machinery, sourcing the right flat belt machine is essential for optimizing operations and ensuring product quality. This guide provides a structured checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring flat belt machines, tailored to diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Identify the technical requirements such as the load capacity, belt width, and material type suitable for your application. Consider the operational environment, including temperature and humidity, as these factors can significantly affect machine performance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a strong track record in manufacturing flat belt machines. Look for companies that specialize in your industry and have experience with the specific applications you require. Utilize industry reports and trade directories to compile a list of potential vendors.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or CE marking for safety can indicate a commitment to manufacturing excellence. Ensure that the supplier adheres to the regulatory requirements specific to your region, as this can mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline their offerings. These proposals should include technical specifications, pricing, lead times, and warranty information. Analyze the proposals carefully to understand how each supplier’s machine aligns with your requirements, and don’t hesitate to ask for clarifications on any ambiguous points.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Evaluate the level of after-sales support that each supplier offers. This includes installation services, training for your staff, and availability of spare parts. Reliable after-sales support can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the longevity of your flat belt machine, making it a critical factor in your decision-making process.
Step 6: Check Customer Reviews and References
Investigate customer reviews and seek references from businesses similar to yours. Feedback from other buyers can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, product performance, and customer service. Engaging with existing customers can reveal potential issues that may not be apparent from a supplier’s marketing materials.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing your purchase, negotiate the terms and conditions, including payment terms, delivery schedules, and service agreements. Clear and mutually agreed-upon terms can prevent misunderstandings and foster a strong working relationship with your supplier. Ensure that all agreements are documented to safeguard both parties’ interests.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing flat belt machines effectively, ensuring they choose a solution that meets their operational needs and contributes to their business success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for flat belt machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Flat Belt Machines?
When sourcing flat belt machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. Common materials for flat belts include synthetic options like nylon and rubber, which offer durability and longevity. Specialty materials may incur higher costs but provide better performance and resistance to wear and tear.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In countries with higher labor costs, manufacturers may pass these expenses onto buyers. Understanding local labor market conditions can provide insights into potential pricing variations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory operations. Manufacturers often allocate these costs proportionately to each product, influencing the final price.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial investment in molds and machines necessary for production. Custom tooling for specialized flat belt designs can increase upfront costs but may reduce per-unit costs for larger orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability but also add to the overall cost. Buyers should consider the balance between quality assurance and cost, as lower QC standards can lead to higher long-term expenses due to failures or replacements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand and competition. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Flat Belt Machine Pricing?
Several factors influence pricing for flat belt machines, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs with suppliers to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses associated with last-minute changes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or industry-specific standards) can elevate costs but may be necessary for certain applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their assurance of quality and service, while newer entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for international transactions. They define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total landed cost of the machines.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Flat Belt Machine Procurement?
For B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, implementing strategic approaches can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing and payment terms. Leverage the potential for bulk purchasing to negotiate discounts or better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, replacement parts, and operational costs over the machine’s lifespan. A higher upfront cost may be justifiable if it leads to lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market trends and pricing fluctuations. Factors such as currency exchange rates, local demand, and geopolitical conditions can impact costs.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several suppliers to compare pricing and offerings. This practice can reveal market standards and help in negotiations.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to innovations in flat belt technology.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before making procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing flat belt machine With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Flat Belt Machines
In industrial applications, the choice of material handling and transport solutions can significantly influence operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Flat belt machines, commonly used for transporting goods and components, are reliable but may not always be the best fit for every operation. This section explores viable alternatives, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
Comparison of Flat Belt Machines and Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Flat Belt Machine | Roller Conveyor System | Modular Belt Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High for straight runs; limited incline capabilities | Excellent for heavy loads; adaptable to inclines | Versatile; can handle various materials and shapes |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operational costs | Higher initial cost; variable operational costs depending on load | Moderate to high cost; maintenance can increase over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward setup; requires downtime for replacement | More complex installation; may require additional structural support | Flexible design allows for easier adjustments and expansions |
| Maintenance | Simple maintenance; easy belt replacement | Moderate maintenance; requires more frequent checks | Moderate maintenance; modular components can simplify repairs |
| Best Use Case | Light to moderate loads; straight-line transport | Heavy industrial applications; bulk material handling | Diverse applications including food processing and packaging |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Roller Conveyor System
Roller conveyor systems utilize rollers to move goods, offering superior performance for heavy or bulk materials. These systems are particularly effective in environments where incline transportation is necessary, making them ideal for warehouses and distribution centers handling heavy loads. However, their initial cost can be significantly higher than flat belt machines, and installation may be more complex due to the need for structural supports. Maintenance is also a consideration, as roller systems require periodic inspections and adjustments to ensure smooth operation.
Modular Belt Conveyor
Modular belt conveyors consist of interlocking plastic or metal segments, allowing for greater flexibility in design and application. They can handle a variety of products, including those with irregular shapes, and are particularly popular in food processing and packaging industries due to their hygiene standards. While the initial investment can vary, modular systems may incur higher maintenance costs due to the complexity of the components. Their adaptability in layout and configuration makes them a strong contender for operations that require frequent changes in production lines.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating whether to invest in a flat belt machine or consider alternatives like roller conveyors or modular belt systems, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements. Factors such as the type of materials being handled, the layout of the facility, and budget constraints will heavily influence the decision. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option, buyers can select a solution that not only meets their immediate needs but also supports long-term operational efficiency and adaptability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for flat belt machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Flat Belt Machines?
When considering flat belt machines, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the key specifications that impact performance and longevity:
-
Material Grade
The material used in flat belts typically includes nylon, rubber, or synthetic composites. Each material has its advantages: nylon offers flexibility and durability, while rubber provides superior grip and resistance to wear. Choosing the right material grade is critical as it directly affects the belt’s lifespan and operational efficiency, ultimately influencing maintenance costs and productivity levels. -
Belt Width and Length
Flat belts come in various widths and lengths, with standardized sizes facilitating easy replacement and interchangeability. For industrial applications, selecting the correct dimensions ensures optimal load-bearing capacity and minimizes the risk of slippage or misalignment. This specification is essential for efficient product movement and overall operational throughput. -
Tensile Strength
Measured in pounds per inch, tensile strength indicates how much force a belt can withstand before breaking. A higher tensile strength is crucial for heavy-duty applications where the belt supports significant loads. Understanding this property helps buyers select belts that can endure their specific operational demands, reducing the likelihood of premature failures. -
Friction Coefficient
The friction coefficient determines how well a belt can grip pulleys and convey products. A higher friction coefficient means better traction and less slippage, essential for maintaining smooth operations in manufacturing and material handling. Buyers should consider this property to ensure their flat belt machine operates efficiently under varying load conditions. -
Temperature Resistance
Flat belts often encounter varying temperatures in industrial environments. The ability of a belt to withstand heat without degrading is vital for maintaining performance and safety. Buyers must assess the operating temperatures of their machinery to select belts that can endure specific thermal conditions, thereby preventing failures that could lead to costly downtime.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Flat Belt Machines?
Familiarity with industry terminology is equally important for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end products. When sourcing flat belt machines, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers ensure they are receiving high-quality, compatible parts designed for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For flat belt machines, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their budgets and inventory levels effectively, ensuring they are not over-committing to purchases that exceed their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare RFQs for flat belt machines to obtain competitive quotes, allowing for better negotiation and selection of suppliers based on price and service offerings. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers know who bears the risk and cost at each stage of shipping, which is essential for managing procurement and logistics effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. For flat belt machines, knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their production schedules and minimize delays in operations, ensuring they maintain a steady workflow.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when purchasing flat belt machines, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the flat belt machine Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Flat Belt Machine Sector?
The flat belt machine sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving market needs. Globally, the demand for efficient and reliable material handling solutions is growing, particularly in manufacturing and distribution sectors. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where industrialization efforts are ramping up. Countries like Brazil are investing in infrastructure projects that rely heavily on conveyor systems, which directly boosts the demand for flat belt machines.
Key trends influencing the market include the adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies. Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities in flat belt systems allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Additionally, customization is on the rise, with buyers seeking tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements, which emphasizes the need for manufacturers to offer flexible product lines.

Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
Moreover, as environmental concerns rise, there is a noticeable shift towards eco-friendly materials and practices within the industry. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, creating a competitive edge for companies that can align their offerings with these values.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Flat Belt Machine Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the flat belt machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, material sourcing, and product lifecycle management is under scrutiny. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East are particularly focused on reducing their carbon footprints, leading to a demand for ethically sourced materials and sustainable manufacturing practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide transparency in their sourcing practices, ensuring that raw materials are obtained responsibly and with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ labels play a crucial role in influencing purchasing decisions.
In terms of materials, the trend is moving towards the use of recycled and biodegradable components in flat belt manufacturing. Innovations in synthetic materials that offer durability while being eco-friendly are gaining traction. Buyers who prioritize sustainability not only contribute to environmental preservation but also enhance their brand reputation, making them more attractive to eco-conscious consumers.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Flat Belt Machines?
The history of flat belt machines dates back to the early industrial revolution when leather was commonly used for power transmission. As technology advanced, manufacturers began experimenting with various materials such as rubber and synthetic compounds, leading to the development of more durable and efficient belts.
The introduction of mechanized systems in the late 19th century saw flat belts being utilized extensively in factories for material handling and machinery operation. Over time, innovations in design and materials have transformed flat belts from simple power transmission tools into complex systems integrated with advanced technologies, enhancing their functionality and efficiency.
Today, flat belts are integral to numerous industries, including manufacturing, food processing, and logistics, showcasing their adaptability and critical role in modern production environments. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the technological advancements that inform current sourcing decisions and market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of flat belt machine
-
How do I solve issues with flat belt machine alignment?
Proper alignment is crucial for the efficient operation of flat belt machines. Misalignment can lead to premature wear, excessive noise, and operational inefficiencies. To solve alignment issues, regularly inspect the pulleys and the belt’s position. Utilize alignment tools or laser alignment systems for precision. Adjust the pulley positions as needed, ensuring they are parallel and properly aligned. Regular maintenance checks and timely adjustments will significantly extend the life of your flat belt system and improve productivity. -
What is the best material for flat belts in industrial applications?
The best material for flat belts largely depends on the specific application. Common materials include nylon, rubber, and reinforced synthetics, each offering unique benefits. Nylon is known for its durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Rubber belts offer excellent traction and flexibility, while reinforced synthetics can provide enhanced strength and resistance to environmental factors. Assess the operational environment, load conditions, and required lifespan to choose the most suitable material for your needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of flat belt machines from suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers thoroughly before making a purchase. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and positive customer reviews. Request samples or references from previous clients to assess product performance. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including material sourcing and testing methods. Establish clear communication regarding your quality expectations and consider conducting site visits to the manufacturing facility if possible. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks associated with product quality. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for flat belt machines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the flat belt machine. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units for standard models to larger quantities for customized solutions. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, while others may have strict requirements based on production costs. Always clarify MOQs before finalizing any agreements. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of flat belt machines?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments before shipment, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). International buyers should consider factors such as currency fluctuations and transaction fees. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that protect your cash flow and ensure that you receive the equipment as agreed. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risks. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for flat belt machine imports?
When importing flat belt machines, it’s essential to consider logistics and shipping options carefully. Work with freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial equipment to ensure compliance with international shipping regulations. Determine the best shipping method (air, sea, or land) based on cost, speed, and your specific needs. Prepare all necessary documentation, including import permits and customs declarations, to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in potential duties and taxes in your budget to ensure a smooth import process. -
What customization options should I consider for flat belt machines?
Customization options for flat belt machines can include belt width, length, material type, and surface texture. Depending on your application, you might also consider features such as integrated sensors, adjustable speed controls, and specific pulley configurations. Discuss your unique operational requirements with potential suppliers to explore available customization options. Tailoring the machine to your needs can enhance performance and efficiency, ultimately improving productivity and return on investment. -
How can I ensure timely maintenance and service for my flat belt machines?
To ensure timely maintenance and service, establish a regular maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and operational demands. Train staff on basic troubleshooting and maintenance practices to address minor issues promptly. Partner with suppliers who offer ongoing support and service agreements for more complex repairs. Consider implementing a maintenance management system to track service history and schedule inspections. Proactive maintenance can prevent unexpected downtimes and prolong the lifespan of your flat belt machines.
Top 9 Flat Belt Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Continental – Flat Belts
Domain: continental-industry.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Flat belts are part of Continental’s drive belt solutions for industrial applications. They are designed for various uses including power transmission in different sectors such as agriculture, automotive, and mechanical engineering. The product range includes heavy-duty options like CONTI® HEAVY DUTY POWER and CONTI® UNIPOWER series, which cater to specific needs in commercial and passenger vehicl…
2. Puteken – Flat Belt Solutions
Domain: puteken.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Flat Belt: A smooth surface belt made of rubber, fabric, or synthetic composites, used for power transmission and material transport between parallel axes. Types include: 1. Flat Belt for Power Transmission: Used in industrial machinery like textile machines and lathes. 2. Nylon Flat Belt: High tensile strength (400MPa), friction layer for enhanced load capacity. 3. Seamless Silicone Belt: Made fr…
3. Ammeraal Beltech – RAPPLON® High Performance Flat Belts
Domain: ammeraalbeltech.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: RAPPLON® High Performance Flat Belts are high-quality power transmission belts suitable for various industries including airports, food, metal, textile, wood, automotive, logistics, recycling, tobacco, coating & lamination, carton, paper & packaging materials, and building materials. They feature classic nylon core belting and special fabric constructions for low tensions and thermoplastic inner l…
4. Maripak – SMART Sync Motorized Flat Belt Conveyor
Domain: maripakusa.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “SMART Sync – Motorized Flat Belt Conveyor – 18″ x 79″”, “SKU”: “52593”, “Dimensions”: {“Width”: “22 inches”, “Length”: “83 inches”, “Height”: “34 inches”, “Belt Width”: “18 inches”, “Belt Length”: “79 inches”}, “Weight”: “680 lbs”, “Crated Dimensions”: {“Length”: “92 inches”, “Width”: “30 inches”, “Height”: “40 inches”}, “Power Requirements”: {“Voltage”: “220V”, “Amperage”: “10 A…
5. MISUMI – Flat Belts
Domain: us.misumi-ec.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Flat belts are a type of drive belt traditionally used to transmit power between pulleys in mechanical systems. They have a flat surface, allowing for efficient power transfer and reducing slippage. Commonly made from materials like rubber or synthetic compounds, flat belts are widely used in various applications, such as conveyor systems, industrial machinery, and automotive engines. They provide…
6. ALBG – Flat Belt FC270
Domain: albg.eu
Introduction: {“Type”:”flat belt FC270″,”Construction”:”bolted side panels made of sheet steel, incl. drum scraper (2 pieces)”,”Axle base”:”5,300 mm”,”Width of conveyor”:”800 mm”,”Construction width”:”1,066 mm”,”Cheek height”:”270 mm”,”Conveying speed”:”1.4 m/s”,”Belt quality”:”EP 400/3 3:1.5 mm Normal quality”,”Design of belt”:”Steep conveyor belt, PW 550 mm / PH 17 mm”,”Drive”:”Drum motor, Fabricate Van der G…
7. Conveyor Belting – Flat Belts
Domain: conveyorbelting.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Flat belts are linear belts used in conveyor systems, made from natural or synthetic materials like polyester and nylon. They can be embossed, homogeneous, or reinforced, with edge options including c-cure, double loop, and single loop. Common materials include natural rubber (for flexibility), synthetic rubber (for heat resistance), plastics (PVC and polyurethane for chemical resistance), and met…
8. BW Converting – Precision Engineered Flat-Belt Bottom-Seal Systems
Domain: pcmc.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: BW Converting provides precision-engineered flat-belt bottom-seal systems that deliver consistent, secure seals for a wide range of bag types. Key products include: M750-HW, an advanced seal machine designed for heavy-wall pouches; M1066/M1416, bottom seal bag machines offering versatile, high-speed solutions for the plastic converting industry; and the Flat Belt Series, featuring a flexible, modu…
9. Practical Machinist – Flat Drive Belts
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Flat drive belts are used in antique machinery, particularly for applications like wood lathes. Key details include: 1. Materials: Available in leather and synthetic options, with leather being the traditional choice until the late 1930s. Synthetic belts can be made in an endless loop without splices. 2. Joining Techniques: Leather belts can be joined using overlapping tapers and glue, or with a c…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for flat belt machine
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of flat belt machines presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the diverse applications and materials used in flat belt construction, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. The shift from traditional materials like leather to advanced synthetics demonstrates the importance of investing in quality and durability, which ultimately leads to lower maintenance costs and improved productivity.
Moreover, the ease of replacing flat belts, combined with standardized sizes for compatibility, allows for streamlined operations and minimizes disruptions. As industries evolve, leveraging technological advancements in flat belt systems will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantages.

Illustrative image related to flat belt machine
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who offer innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs. By embracing strategic sourcing practices, companies can not only optimize their supply chains but also position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected global market. Engage with leading manufacturers today to explore the best flat belt solutions for your operations and stay ahead in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.