Is Your Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for expanded stainless steel metal
The global market for expanded stainless steel metal presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. With its unique properties, such as lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and versatile applications, expanded stainless steel is increasingly sought after across industries, from construction to manufacturing. However, the complexities involved in sourcing high-quality expanded stainless steel can be daunting, especially for buyers from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Vietnam.
This comprehensive guide addresses the critical aspects of navigating the expanded stainless steel market. It covers a wide range of topics including the various types of expanded metal, their specific applications, and effective supplier vetting strategies. Additionally, it delves into cost considerations and market trends, equipping buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable knowledge, this guide not only simplifies the sourcing process but also enhances the ability to identify reliable suppliers and negotiate favorable terms. Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or streamline your supply chain, understanding the dynamics of expanded stainless steel metal is crucial for achieving your business goals in today’s competitive landscape.
Understanding expanded stainless steel metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 304 | General-purpose stainless steel; excellent corrosion resistance | Food processing, kitchen appliances, architecture | Pros: Versatile, good weldability. Cons: Less resistant to chloride solutions. |
| Type 316 | Enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments | Chemical processing, marine applications | Pros: Superior corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher cost than Type 304. |
| Flattened Metal | Smooth, flat surface with diamond openings | Decorative applications, machine guards | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, easy to clean. Cons: Less strength than standard expanded metal. |
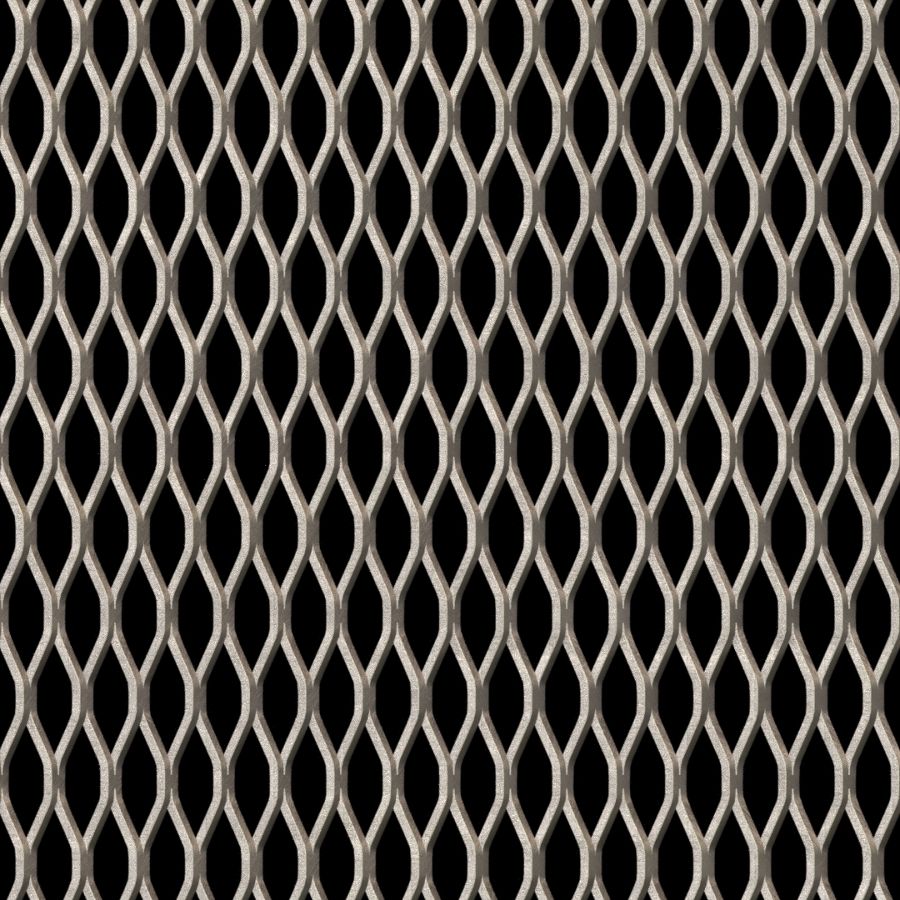
| Standard Expanded | Raised diamond pattern, strong structural integrity | Fencing, safety guards, HVAC systems | Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: More difficult to clean due to texture. |
| Designer Expanded | Unique patterns for aesthetic applications | Signage, shelving, architectural elements | Pros: Customizable designs. Cons: May have higher lead times for production. |
What are the Characteristics of Type 304 Expanded Stainless Steel?
Type 304 expanded stainless steel is the most commonly used variant, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. It is often utilized in environments where exposure to moisture or chemical substances is a concern, making it suitable for food processing equipment and kitchen applications. When purchasing, consider the specific environmental conditions as Type 304 may not be as effective against chloride solutions.
How Does Type 316 Expanded Stainless Steel Differ from Type 304?
Type 316 offers enhanced corrosion resistance compared to Type 304, particularly against saltwater and other harsh chemicals, making it ideal for marine and chemical processing industries. Buyers should weigh the increased cost against the benefits of its superior durability in corrosive environments. This type is particularly recommended for applications where longevity and reliability are paramount.
What Advantages Does Flattened Expanded Metal Provide?
Flattened expanded metal features a smooth surface that is aesthetically pleasing and easy to clean, making it ideal for decorative applications like shelving and architectural features. While it offers a refined look, buyers must consider that it may not provide the same structural strength as standard expanded metal, which could be a drawback depending on the application.
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Why Choose Standard Expanded Metal for Structural Integrity?
Standard expanded metal, with its raised diamond pattern, is celebrated for its strength and durability, making it a popular choice for safety guards and fencing. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it a cost-effective solution for many industrial applications. However, the texture can make cleaning more challenging, which is an important consideration for maintenance-heavy environments.
What are the Benefits of Using Designer Expanded Metal?
Designer expanded metal allows for unique, customizable patterns that enhance aesthetic appeal in various applications, including signage and architectural elements. While it provides creative flexibility, buyers should be mindful of potential longer lead times for production and the possibility of higher costs compared to standard options. This type is ideal for projects where visual impact is as important as functionality.
Key Industrial Applications of expanded stainless steel metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of expanded stainless steel metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Strainer baskets and filtration systems | Ensures hygiene and durability in food production | Compliance with food safety standards, corrosion resistance |
| Construction | Architectural facades and safety barriers | Enhances aesthetics while providing structural support | Custom sizes and finishes, local regulations for building materials |
| Mining & Minerals | Protective screens and equipment guards | Increases safety and equipment lifespan | Heavy-duty specifications, resistance to harsh environments |
| Chemical Processing | Tanks, piping, and equipment casings | Prevents corrosion and ensures chemical compatibility | Material certification, compatibility with specific chemicals |
| Transportation & Logistics | Loading ramps and walkways | Improves safety and efficiency in loading operations | Weight specifications, slip resistance features |
How is Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, expanded stainless steel metal is primarily utilized for strainer baskets and filtration systems. Its design allows for efficient liquid flow while preventing contaminants from entering the product stream. The corrosion-resistant properties of stainless steel ensure that it remains hygienic and durable, meeting stringent food safety standards. International buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who provide certification for compliance with food safety regulations, especially when operating in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
What Role Does Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Play in Construction?
In construction, expanded stainless steel metal finds applications in architectural facades and safety barriers. Its aesthetic appeal combined with structural integrity makes it a preferred choice for modern building designs. The ability to customize sizes and finishes allows architects and builders to create unique designs while ensuring compliance with local building codes in regions such as Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and local regulatory guidance to ensure seamless integration into their projects.
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
How Does Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Enhance Safety in Mining & Minerals?
The mining and minerals sector utilizes expanded stainless steel metal for protective screens and equipment guards. These applications enhance worker safety by preventing accidental contact with moving machinery and hazardous materials. The durability of stainless steel in harsh environments also extends the lifespan of protective equipment, reducing maintenance costs. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing heavy-duty products designed to withstand extreme conditions, ensuring compliance with safety regulations prevalent in their operational regions.
In What Ways is Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Critical for Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, expanded stainless steel metal is essential for constructing tanks, piping, and equipment casings. Its resistance to corrosion and ability to handle various chemicals make it an ideal material for this industry. Buyers must ensure that the materials sourced are certified for compatibility with the specific chemicals they will encounter, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations. Engaging with suppliers who understand these requirements can help mitigate risks associated with material failure.
How is Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Used in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sectors, expanded stainless steel metal is commonly used for loading ramps and walkways. Its lightweight yet sturdy nature improves safety and efficiency during loading operations. The design allows for good traction, reducing the risk of slips and falls. Buyers should consider sourcing options that offer slip-resistant features and comply with local safety standards, particularly in regions with varying climate conditions that could impact material performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘expanded stainless steel metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Specifications for Expanded Stainless Steel Metal
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the right type of expanded stainless steel for their specific applications. With various grades available, such as Type 304 and Type 316, the decision can be daunting. For instance, a construction firm in South Africa may require materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, while a food processing company in Germany needs to comply with stringent health regulations. Misjudging the material’s properties can lead to costly project delays and compliance issues.

Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
The Solution: To effectively source expanded stainless steel, buyers should start by clearly defining their project requirements. Understand the environmental conditions and operational needs, such as corrosion resistance or load-bearing capabilities. For example, Type 316 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine or chemical applications. When requesting quotes from suppliers, specify not only the type but also the desired thickness, opening size, and sheet dimensions. Engaging with suppliers that offer custom cuts and a variety of gauges can also ensure that the material perfectly fits your project specifications. Additionally, consider leveraging industry standards or certifications that guarantee material quality and compliance.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions in Expanded Stainless Steel Procurement
The Problem: International B2B buyers frequently encounter supply chain issues, especially in the metal industry, where demand fluctuations can lead to material shortages. For instance, a manufacturer in Brazil may find that the expanded stainless steel they require is backordered, jeopardizing production timelines and customer commitments. This unpredictability can create significant financial strain and affect long-term business relationships.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain disruptions, buyers should diversify their sourcing strategies. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can provide alternative options during shortages. Additionally, consider implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system to reduce reliance on stockpiling materials. This approach allows businesses to respond flexibly to market demands and supplier availability. Maintaining clear communication with suppliers about lead times and potential delays is essential. Regularly evaluating and updating supplier performance can help identify reliable partners who can deliver consistently, thus minimizing risks associated with procurement.

Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Scenario 3: Ensuring Proper Handling and Installation of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal
The Problem: Many B2B buyers underestimate the importance of proper handling and installation techniques for expanded stainless steel metal. A construction company in the Middle East may receive sheets that are mishandled, leading to damage or sharp edges, which can pose safety risks. Additionally, incorrect installation can compromise the structural integrity of applications such as security panels or grating.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should prioritize training for their teams on the handling and installation of expanded stainless steel. Suppliers can provide guidelines on safe handling practices, emphasizing the importance of wearing protective gear due to sharp edges. When it comes to installation, consider consulting with the supplier for detailed installation manuals or even on-site guidance if available. Utilizing professional installation services can also ensure that the materials are correctly fitted, enhancing both safety and functionality. Finally, conducting regular inspections post-installation can help identify any potential issues early, allowing for timely maintenance and avoiding costly repairs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for expanded stainless steel metal
What Are the Key Properties of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
Expanded stainless steel metal is primarily made from alloys like Type 304 and Type 316, each offering distinct properties suited for various applications.

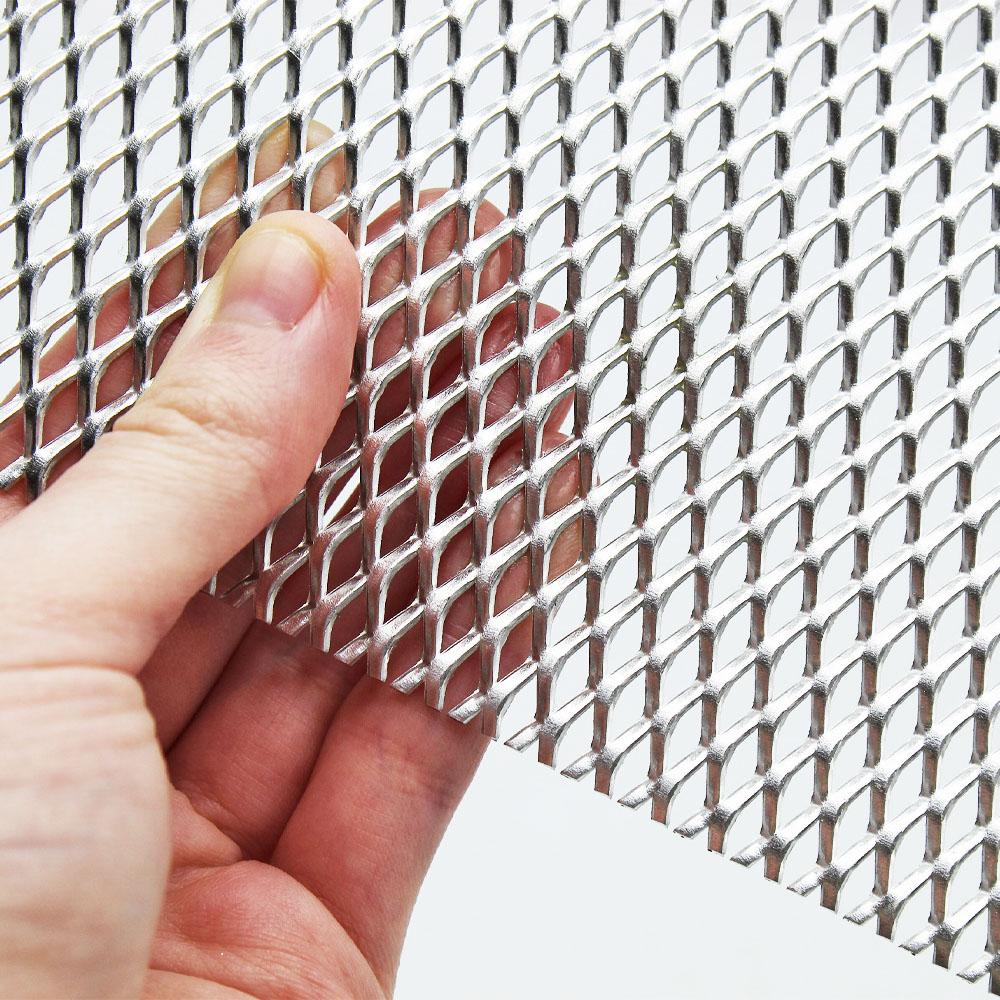
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Type 304 Stainless Steel is the most commonly used alloy in expanded metal applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. It performs well in both chemical and atmospheric conditions, making it suitable for environments with moderate exposure to corrosive elements. Its temperature rating is typically around 870°C (1600°F) for intermittent service and 925°C (1700°F) for continuous service.
Type 316 Stainless Steel, on the other hand, is known for its superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine and chloride environments. This alloy can withstand higher temperatures and is often used in applications where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern. Its temperature rating is similar to Type 304 but offers better performance in more aggressive environments.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
When considering expanded stainless steel metal, it is essential to weigh the pros and cons.
Pros:
– Durability: Both Type 304 and Type 316 provide excellent durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, which is critical for long-term applications.
– Weight Savings: Expanded metal offers a lightweight alternative to solid metal sheets, reducing overall material costs and making handling easier.
– Versatility: It can be used in a variety of applications, including architectural elements, safety guards, and filtration systems.
Cons:
– Cost: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than other materials like carbon steel or aluminum, which can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive projects.
– Manufacturing Complexity: The production process involves slitting and stretching, which can lead to increased lead times compared to simpler materials.
– Limited Aesthetic Options: While functional, expanded metal may not always meet aesthetic demands for certain architectural applications.
How Does Material Selection Impact Application?
The choice of material significantly impacts the suitability of expanded stainless steel for specific applications. For instance, Type 304 is often used in food processing and kitchen appliances due to its ease of cleaning and resistance to food-grade chemicals. Conversely, Type 316 is preferred in marine environments and chemical processing due to its enhanced corrosion resistance.
International buyers must also consider compliance with local standards and regulations. For example, in Europe, compliance with DIN standards is essential, while in the U.S., ASTM standards are often referenced. Understanding these regulations can prevent costly delays and ensure that the materials meet the necessary safety and performance criteria.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several factors should be considered:
- Compliance: Verify that the expanded stainless steel meets local and international standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN, JIS).
- Supply Chain Logistics: Assess the reliability of suppliers and their ability to deliver on time, especially for custom cuts and larger orders.
- Market Preferences: Different regions may have preferences for specific grades or finishes, which can influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Expanded Stainless Steel Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for expanded stainless steel metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 304 | Food processing equipment, architectural elements | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to carbon steel | High |
| Type 316 | Marine applications, chemical processing | Superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments | More expensive than Type 304 | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications, decorative elements | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower durability compared to stainless steel | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | General construction and safety applications | Cost-effective and widely available | Prone to rust and corrosion without treatment | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing expanded stainless steel metal, considering both performance and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for expanded stainless steel metal
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
The manufacturing process of expanded stainless steel metal involves several critical stages, each essential for producing a high-quality product that meets diverse industrial needs.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first stage involves selecting the appropriate stainless steel alloy, typically Type 304 or Type 316, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. After selecting the alloy, the steel sheets are cut to the desired dimensions. This step may also include surface treatments, such as pickling or passivation, to enhance corrosion resistance and prepare the surface for further processing.
Forming: How Is Expanded Metal Created?
The core of the manufacturing process is the forming stage, where the cut stainless steel sheets are subjected to a process called slitting and stretching. This technique involves cutting the sheets into a predetermined pattern and then stretching them to create diamond-shaped openings. Depending on the desired finish, manufacturers may use either a raised or flattened style. The result is a rigid, lightweight material that retains strength while allowing the passage of light, air, and sound.
Assembly: Are Additional Components Integrated?
In some cases, expanded metal products may require additional assembly. This could involve the integration of frames, supports, or other components to enhance functionality. For instance, expanded metal is often fabricated into machine guards or security panels, which may necessitate welding or fastening additional elements.
Finishing: What Techniques Are Used to Ensure Quality?
The final stage is finishing, which may include surface treatments to improve aesthetics and durability. Common finishing techniques include powder coating, anodizing, or applying protective films. Each technique offers different benefits, such as increased resistance to wear, enhanced appearance, or improved corrosion resistance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that expanded stainless steel metal products meet industry standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards like ISO 9001 outline the requirements for a quality management system and are critical for manufacturers targeting global markets. In addition, compliance with industry-specific standards, such as CE marking for products sold within the European Union or API specifications for oil and gas applications, is essential. These certifications indicate that the manufacturer adheres to rigorous quality and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to monitor production conditions, dimensions, and quality of the expanded metal.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished products undergo a comprehensive inspection to verify compliance with specifications and standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized?
Testing methods employed during QA can include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and mechanical property tests such as tensile strength, elongation, and hardness tests. Additionally, corrosion resistance tests, such as salt spray tests, may be performed to evaluate the material’s durability in specific environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Their Suppliers?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers.
What Should Buyers Look For in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Requesting access to supplier audits and quality reports can provide insights into a manufacturer’s compliance with international standards. Buyers should specifically inquire about:
- Certification Copies: Ensure that the supplier holds relevant ISO and industry-specific certifications.
- Quality Management System Documentation: Review how the supplier implements and maintains their quality management system.
- Testing and Inspection Reports: Request samples of testing reports that detail the results of various quality checks.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These agencies provide unbiased assessments of the manufacturer’s operations, ensuring adherence to specified quality standards. This is particularly important for international B2B buyers who may not have the capacity to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the Nuances in Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of additional considerations regarding quality control:
- Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may have varying expectations and interpretations of quality standards. It is essential for buyers to communicate clearly about their specific requirements.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Ensure that the products meet the destination country’s regulations to avoid delays or penalties upon importation.
- Logistical Considerations: Understanding the supply chain logistics can help buyers anticipate potential quality issues that may arise during transportation.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for expanded stainless steel metal, B2B buyers can make more educated purchasing decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘expanded stainless steel metal’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring expanded stainless steel metal. Whether you are involved in construction, manufacturing, or design, understanding the key steps in sourcing this material will ensure that you select the right product from reputable suppliers while meeting your specific project requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical specifications for expanded stainless steel metal. Consider factors such as the type of stainless steel (e.g., Type 304 or Type 316), thickness, dimensions, and any specific performance requirements such as corrosion resistance or load-bearing capacity. Documenting these details will streamline the sourcing process and help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of expanded stainless steel metal. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors. Pay attention to their market presence, product range, and customer reviews, as these factors can indicate reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Evaluate their production capabilities, quality control measures, and delivery timelines to ensure they can meet your needs. A supplier’s ability to provide custom cuts and sizes can also be a significant advantage.
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications and comply with international standards relevant to your industry. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and any specific material certifications that demonstrate compliance with local regulations. This step is vital to guarantee that the materials you receive meet safety and quality standards.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the expanded stainless steel metal. Assess the samples for quality, finish, and adherence to your specifications. Conduct any necessary testing, such as tensile strength or corrosion resistance tests, to validate the material’s performance in your intended application.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be clear about your budget constraints and explore volume discounts, especially if you plan to make bulk purchases. A well-negotiated agreement can lead to better pricing and favorable terms, ensuring a cost-effective procurement process.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Once you have successfully sourced your expanded stainless steel metal, consider establishing a long-term relationship with your supplier. Regular communication, feedback, and collaboration can lead to improved service, better pricing, and priority access to new products. A strong partnership can significantly enhance your supply chain efficiency and reliability.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for expanded stainless steel metal with confidence, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for expanded stainless steel metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure for expanded stainless steel metal is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of stainless steel grade, such as Type 304 or Type 316, significantly affects the material cost. Type 304 is generally more economical but offers good corrosion resistance, while Type 316 provides enhanced durability in harsh environments, resulting in a higher price point.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce needed for manufacturing and processing the expanded metal. This includes skilled labor for operating machinery and unskilled labor for handling materials. Labor rates can vary greatly depending on the region, impacting overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead, which is a crucial factor for suppliers aiming to remain competitive.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, such as dies and molds, is critical, especially for custom sizes and shapes. Initial tooling investments can be substantial but are amortized over larger production runs, making volume purchases more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that expanded stainless steel meets specified standards involves QC costs. This may include testing for durability, corrosion resistance, and dimensional accuracy, which are vital for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on the geographic location of the supplier and the buyer. Factors like shipping methods, distances, and customs duties play a pivotal role in the overall logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that reflects their operational costs, market demand, and competitive positioning. This margin can vary widely, especially in different regions.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Costs?
Several pricing influencers can affect the overall costs of expanded stainless steel metal:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer better pricing for larger orders due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can also influence pricing, as lower quantities may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, including unique dimensions, patterns, and finishes, can lead to increased costs. Standard products are typically less expensive, so buyers should weigh the need for customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can command premium prices. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, all of which can influence total costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in price negotiations can yield significant savings. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers may also lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes costs associated with shipping, handling, installation, and maintenance over the product’s life cycle.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and regional market conditions that may affect pricing. Understanding local market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Requesting Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can help buyers compare prices and services. This competitive approach often leads to more favorable terms.
-
Leveraging Technology: Utilizing online platforms for sourcing can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to quickly compare options and access a broader range of suppliers.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the multifaceted cost structure and pricing dynamics of expanded stainless steel metal is vital for international B2B buyers. By considering the key cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic sourcing tips, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and budgetary constraints. Always remember that prices can fluctuate, and it’s advisable to consult with suppliers for the most current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing expanded stainless steel metal With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Expanded Stainless Steel Metal
When considering materials for industrial applications, it’s crucial to evaluate alternatives to expanded stainless steel metal. This allows businesses to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific use cases. In this analysis, we will compare expanded stainless steel metal against two viable alternatives: Perforated Metal and Wire Mesh. Each option has unique characteristics that may align better with different project requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Expanded Stainless Steel Metal | Perforated Metal | Wire Mesh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High rigidity and strength; excellent corrosion resistance | Good load-bearing capacity; customizable hole sizes | Flexible; lightweight but lower structural integrity |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower than expanded metal | Low to moderate, depending on gauge and material |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific cutting and installation tools | Easily cut and installed; less labor-intensive | Simple installation; can be cut to size easily |
| Maintenance | Low; resistant to rust and wear | Moderate; can corrode if not treated | High; may require regular inspections and replacement |
| Best Use Case | Machine guards, window safety, architectural elements | Screens, filters, decorative applications | Fencing, security applications, filtration |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Perforated Metal?
Perforated Metal is created by punching holes into sheets of metal. This method allows for a variety of hole patterns and sizes, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros:
– Customization: The ability to tailor hole size and spacing allows for specific design requirements.
– Weight Savings: Generally lighter than expanded metal, which can reduce transportation and installation costs.
– Aesthetic Appeal: Often used in architectural designs where both functionality and appearance are important.
Cons:
– Load Limitations: While it offers good load-bearing capacity, it may not be as strong as expanded stainless steel in high-stress applications.
– Corrosion Risk: If not treated, perforated metal can be susceptible to rust, especially in humid environments.
How Does Wire Mesh Compare?
Wire Mesh consists of interwoven metal wires, creating a grid-like structure. This material is commonly used for fencing and filtration.
Pros:
– Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than both expanded metal and perforated metal.
– Lightweight and Flexible: Easy to transport and install, making it ideal for temporary or lightweight applications.
– High Air and Light Flow: Allows for excellent airflow and visibility, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
Cons:
– Lower Strength: Wire mesh may not provide the same structural integrity as expanded stainless steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
– Maintenance Requirements: Depending on the environment, wire mesh may require more frequent inspections and replacements due to wear and corrosion.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Project Needs
Choosing the right material depends largely on the specific requirements of your project. Expanded stainless steel metal is ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability, particularly in harsh environments. On the other hand, perforated metal may be more suitable for projects requiring aesthetic flexibility and weight savings, while wire mesh is a cost-effective option for fencing and filtration tasks.
Evaluate your project’s performance needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities to determine which alternative aligns best with your goals. This strategic approach will ensure that you select the most effective solution for your business’s unique requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for expanded stainless steel metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
Understanding the essential technical properties of expanded stainless steel metal is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Material Grade
The most common grades of stainless steel used in expanded metal are Type 304 and Type 316. Type 304 offers excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for a wide range of applications, while Type 316 provides superior resistance to chloride environments, making it ideal for marine and chemical processing applications. Selecting the appropriate grade is vital for ensuring longevity and performance in specific environments.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension. For expanded stainless steel, typical tolerances are around +/- 1/16 inch for custom cuts. Ensuring accurate tolerances is essential for applications requiring precise dimensions, such as architectural projects or machinery components, as it affects the fit and overall function.
3. Open Area Percentage
The open area percentage indicates the amount of space that is open compared to the total surface area. Expanded metal typically has an open area ranging from 30% to 90%. This specification is important for applications like ventilation and filtration, where air or liquid flow is necessary. A higher open area allows for greater flow, making it crucial to choose the right type based on application needs.
4. Weight and Thickness
Expanded stainless steel comes in various thicknesses, typically measured in gauges, with heavier materials offering greater strength. The weight per square foot is also a critical consideration, as it impacts shipping costs and structural requirements. Buyers must assess their needs for durability versus weight to optimize their purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of expanded stainless steel can vary from mill finish to polished options. A mill finish may have slight imperfections, while a polished finish offers aesthetic appeal and improved corrosion resistance. Understanding the desired finish is important for applications where appearance matters, such as in architectural design.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly facilitate communication and negotiations. Here are some common jargon and trade terms relevant to expanded stainless steel metal:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of expanded stainless steel, OEMs may require specific material grades and configurations tailored to their product requirements. Understanding OEM specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. For expanded stainless steel, MOQs can vary based on the supplier and the specific product. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess their needs and budget effectively, as it can influence overall procurement strategies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. When dealing with expanded stainless steel, providing detailed specifications in the RFQ can lead to more accurate pricing and faster response times. This process is crucial for budgeting and project planning.
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is vital for B2B transactions involving expanded stainless steel, as they dictate shipping costs, risk, and responsibilities.
5. Custom Cut
Custom cut refers to the process of tailoring metal sheets to specific dimensions beyond standard sizes. This option is particularly beneficial for projects that require unique specifications. Knowing about custom cut capabilities allows buyers to optimize their material usage and reduce waste.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in expanded stainless steel metal meet their operational needs and project specifications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the expanded stainless steel metal Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Market?
The expanded stainless steel metal sector is witnessing significant growth driven by diverse global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for lightweight yet strong materials across various industries, including construction, automotive, and aerospace. The versatility of expanded metal products, which offer structural integrity while allowing for airflow and light passage, makes them particularly appealing for applications such as architectural facades, security features, and industrial screens.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as advanced manufacturing techniques and digital platforms for sourcing, are reshaping how buyers and suppliers interact. Online marketplaces enable international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Vietnam) to access a broader range of products and suppliers. This transition to digital sourcing platforms is streamlining procurement processes, allowing for greater transparency in pricing and product specifications.
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Moreover, as industries become more globalized, the need for compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and ISO, is more critical than ever. Buyers must remain vigilant about the quality and specifications of expanded stainless steel products, ensuring they meet regional regulations and industry requirements. The focus on customization is also rising, as businesses seek tailored solutions to meet specific project needs, from dimensions to surface finishes.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies for B2B buyers in the expanded stainless steel metal sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has garnered increased attention, prompting companies to seek out suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprints. This shift is particularly relevant for international buyers, who are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability in their supply chains.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated; buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers that demonstrate responsible practices. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient production methods, and compliance with environmental regulations. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the trend towards green materials is gaining momentum. Expanded stainless steel products that are manufactured with minimal environmental impact not only appeal to eco-conscious buyers but also align with the growing regulatory pressures to adopt sustainable practices. By prioritizing suppliers who meet these criteria, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and contribute positively to environmental stewardship.
What Is the Historical Context of Expanded Stainless Steel Metal in B2B Markets?
The history of expanded stainless steel metal dates back to the early 19th century when the technique of expanding metal sheets was developed to create lightweight yet durable materials. Initially used in architectural and industrial applications, the material gained popularity due to its unique properties, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion.
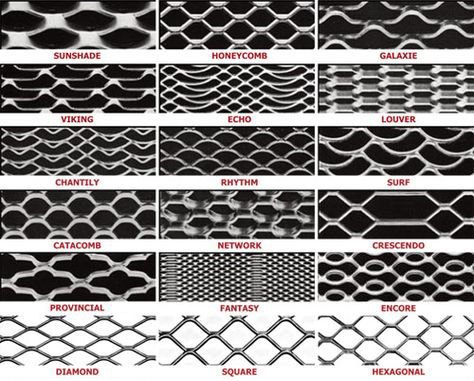
Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
As industries evolved, so did the applications for expanded stainless steel. Over the decades, it has found a place in various sectors, including construction, transportation, and manufacturing. The introduction of new alloys and production techniques has further broadened its use, allowing for innovations in design and functionality. Today, expanded stainless steel metal is recognized not only for its practical applications but also for its aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice for both functional and decorative purposes in modern architecture and design.
By understanding these market dynamics and trends, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and operational requirements in the expanded stainless steel metal sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of expanded stainless steel metal
-
How do I determine the right grade of expanded stainless steel for my application?
Choosing the appropriate grade of expanded stainless steel depends on your specific application requirements, including environmental conditions and mechanical stresses. Type 304 is commonly used for general purposes due to its corrosion resistance and formability, making it suitable for food processing and architectural applications. For harsher environments, such as chemical processing or marine applications, Type 316 offers superior corrosion resistance. Assess your project’s requirements and consult with suppliers to ensure the selected grade meets your performance criteria. -
What are the advantages of using expanded stainless steel over solid metal?
Expanded stainless steel provides several advantages, including reduced weight while maintaining structural integrity, allowing for better light, air, and fluid passage. Its unique design enhances rigidity compared to an equivalent weight of solid metal, making it ideal for various applications such as grating, security panels, and decorative features. Additionally, the open structure allows for improved drainage and airflow, which can be crucial in industrial settings. -
What customization options are available for expanded stainless steel products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including cutting to specific sizes, selecting diamond patterns, and choosing between flattened or raised styles. You can often request unique hole sizes or spacing based on your project’s needs. Before placing an order, discuss your specifications with potential suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your customization requests, which can enhance the functionality and aesthetic of your finished product. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for expanded stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities for expanded stainless steel can vary significantly by supplier. Some manufacturers may offer no minimum order for stock items, while others may require a minimum of several sheets for custom cuts. It’s advisable to communicate your needs directly with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options that fit your project scale, especially when sourcing internationally. -
How do I vet suppliers of expanded stainless steel for international trade?
Vetting suppliers involves several steps: researching their reputation in the industry, checking for certifications (like ISO or ASTM), and requesting samples to evaluate quality. Additionally, consider their experience in international trade and familiarity with your region’s regulations. Engaging with past clients or reading reviews can provide insights into their reliability and customer service. Establishing clear communication regarding lead times, payment terms, and logistics will also contribute to a successful partnership. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers?
Payment terms can significantly impact your cash flow and project timeline. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, requiring payment within that time frame after delivery. For international transactions, consider negotiating partial upfront payments to mitigate risk, followed by the balance upon delivery. Always clarify terms regarding currency, payment methods (like letters of credit or wire transfers), and any potential fees associated with international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Quality assurance measures vary by supplier, but reputable manufacturers typically implement rigorous testing and inspection protocols. Look for suppliers who provide certifications for material properties and compliance with industry standards. Ask about their quality control processes, including regular audits and testing of raw materials and finished products. A reliable supplier should be willing to share their QA procedures and documentation to ensure you receive products that meet your specifications. -
How can I manage logistics for importing expanded stainless steel?
Managing logistics for importing expanded stainless steel involves understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the best shipping options, whether by sea or air, based on your budget and timeline. Engage a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to navigate customs clearance and ensure compliance with local regulations. Proper planning, including accurate documentation and communication with your supplier, can help streamline the import process and avoid delays.
Top 6 Expanded Stainless Steel Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MetalsDepot® – Expanded Steel Sheet
Domain: metalsdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: MetalsDepot® – Buy Expanded Steel Sheet Online! Steel Expanded Metal is a sheet product that has been slit and stretched to a wide array of diamond shaped openings. Offers savings in weight and metal, free passage of light, liquid, sound and air, while providing a decorative or ornamental effect. Specifications: MIL-M-17194D, ASTM F1267-91, Type I Standard (Raised) & Type II Flattened (smooth) sur…
2. McNICHOLS – Expanded Metal & Grating
Domain: mcnichols.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Expanded Metal & Expanded Grating In-Stock | McNICHOLS®
Product Types:
– Expanded Metal
– Expanded Grating
Expanded Metal Types:
– Flattened (44)
– Standard (28)
– Grating (8)
– Catwalk Grating (2)
– Designer Expanded (4)
Materials:
– Aluminum (AL)
– Carbon Steel (CS)
– Galvanized Steel (GV)
– Stainless Steel (SS)
Alloys:
– Alloy 3003-H14 (AL)
– Alloy 5052-H32 (AL)
– Cold Rolled (CS)
– Hot Rol…
3. Competitive Metals – Expanded Metal Sheets & Grating
Domain: competitivemetals.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Expanded Metal Sheets and Grating with Diamond Openings. Available in flat or raised options. Wire thickness options range from #16 to #6. Diamond sizes range from ¼” to 1 ½” wide. Grating strands are larger than regular expanded metal. Standard sheet size is 48” x 96”; 60” x 120” sheets available in select sizes. Sold as full sheets only; most sizes can be sheared to size. Applications include ou…
4. McMaster – 316 Stainless Steel Expanded Metal
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – 316 Stainless Steel Expanded Metal, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Marco Specialty Steel – Stainless Steel Expanded Metal
Domain: marcospecialtysteel.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Expanded Metal features diamond-shaped openings that impede access without obstructing visibility. It is suitable for architectural accents and industrial safety guards. Key benefits include superior strength, corrosion resistance, lightweight, and aesthetic appeal. It is easily fabricated, resists corrosion, stands up to high and low temperatures, and is simple to clean. The mater…
6. Online Metals – Stainless Steel Expanded Metal
Domain: onlinemetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Expanded Metal – 304 stainless expanded sheet used in aerospace, food and beverage, machinery, architectural, chemical, and cryogenic applications. Made from one piece construction metal that won’t unravel. Available in full size and custom cut lengths. Custom cut sizes include: 12″ x 12″ ($36.72), 12″ x 24″ ($71.21), 12″ x 36″ ($96.91), 12″ x 48″ ($120.81), 24″ x 24″ ($120.81), 24…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for expanded stainless steel metal
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of expanded stainless steel metal presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This versatile material offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and adaptability, making it ideal for diverse applications such as architectural elements, safety guards, and filtration systems. By prioritizing suppliers who offer custom sizes and rapid shipping options, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce lead times.
Investing in expanded stainless steel not only yields cost savings through its lightweight properties but also ensures durability in demanding environments. As industries evolve and sustainability becomes a priority, sourcing materials that minimize waste and maximize performance will be crucial.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers that understand regional market dynamics and can provide tailored solutions. By fostering strong supplier relationships and exploring innovative designs, businesses can harness the full potential of expanded stainless steel metal. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy—connect with reputable suppliers today to secure the materials that will drive your projects forward.

Illustrative image related to expanded stainless steel metal
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.