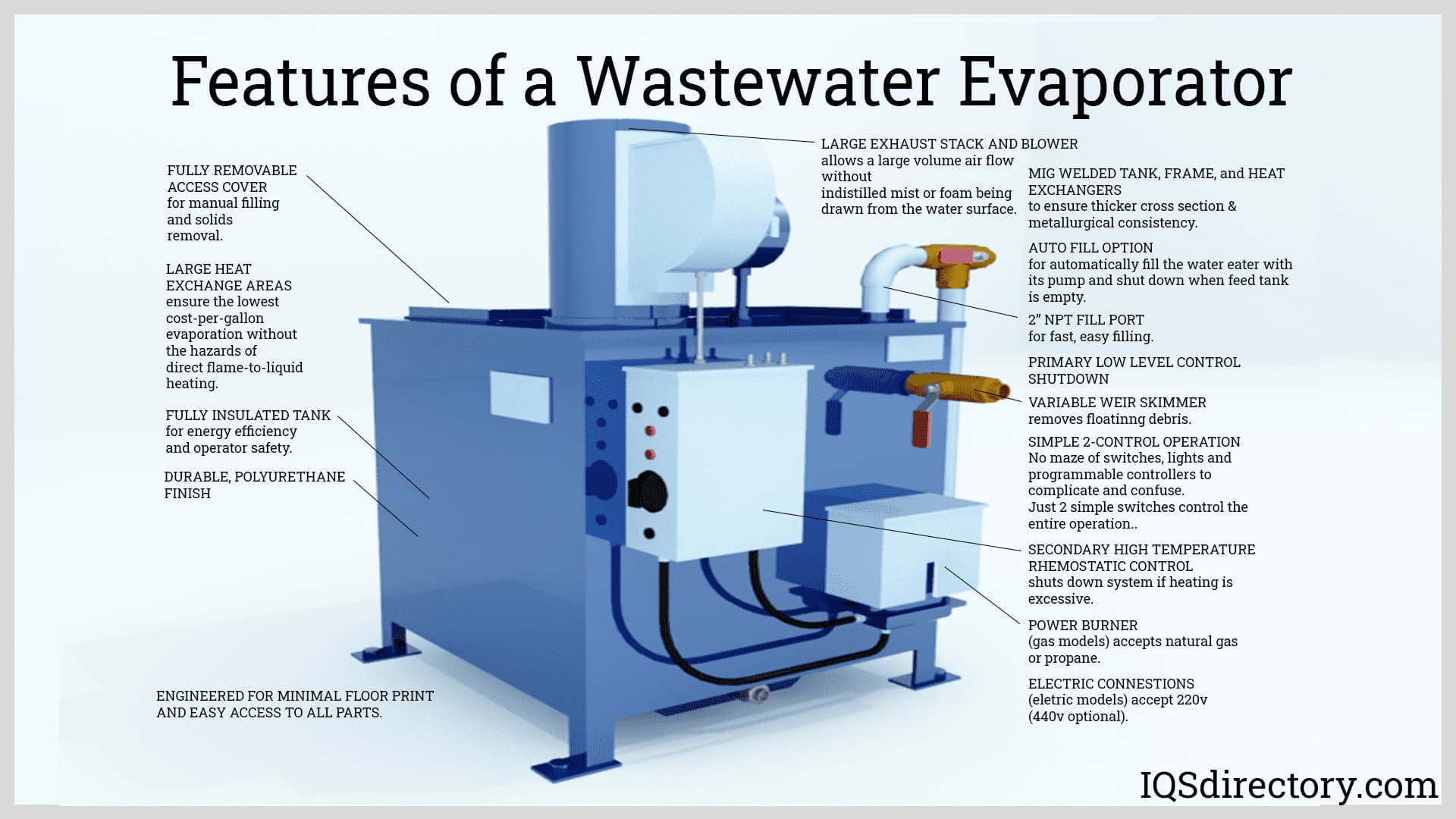
Is Your Evaporator Water Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for evaporator water
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing evaporator water solutions poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With stringent environmental regulations and the rising costs of wastewater disposal, companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking efficient methods to minimize waste and optimize resource use. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the various types of evaporator technologies available, their applications, and the critical considerations for supplier vetting, pricing, and operational efficiency.
Understanding the nuances of evaporator systems is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. From traditional thermal evaporators to cutting-edge mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) solutions, each type offers distinct advantages depending on the industry and specific waste treatment needs. Additionally, we will delve into case studies that illustrate successful implementations and provide insights into best practices for maximizing efficiency and sustainability.
By equipping B2B buyers with essential knowledge on the diverse options in the evaporator water market, this guide empowers companies to navigate the complexities of sourcing and implementing these technologies. Buyers will gain the tools necessary to assess their unique requirements, evaluate potential suppliers, and ultimately enhance their operational effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact.
Understanding evaporator water Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporator | Uses heat to evaporate water, typically operates at high temperatures. | Industrial wastewater treatment | Pros: High efficiency, suitable for large volumes. Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Vacuum Heat Pump Evaporator | Utilizes a heat pump cycle, significantly reducing energy usage. | Food processing, chemical industries | Pros: Energy-efficient, lower operational costs. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Multi-Effect Evaporator | Employs steam recycling across multiple stages for efficiency. | Pharmaceutical, chemical processing | Pros: Very efficient for large-scale operations. Cons: Complex setup and maintenance. |
| Mechanical Vapor Recompression | Compresses vapor for efficient heat transfer and low energy use. | Wastewater treatment, desalination | Pros: Very low energy consumption, high efficiency. Cons: Requires skilled maintenance. |
| Drum Evaporator | Compact design, suitable for low-volume wastewater streams. | Small-scale industries, laboratories | Pros: Space-saving, cost-effective for small volumes. Cons: Limited capacity. |
What are the Characteristics of Thermal Evaporators?
Thermal evaporators are designed to utilize heat to evaporate water, making them ideal for processing large volumes of wastewater. They typically operate at elevated temperatures, which enhances the evaporation rate. Industries such as chemical manufacturing and oil refining frequently utilize thermal evaporators to manage wastewater effectively. When considering a thermal evaporator, buyers should evaluate the energy consumption and operational costs, as these can be significant.
How Do Vacuum Heat Pump Evaporators Stand Out?
Vacuum heat pump evaporators leverage a heat pump cycle to minimize energy consumption, making them an attractive option for industries where energy efficiency is paramount. They operate under vacuum conditions, which lowers the boiling point of water, allowing for effective evaporation at lower temperatures. This technology is particularly beneficial in food processing and chemical industries. Buyers should consider the initial investment versus long-term energy savings when evaluating this option.
What Makes Multi-Effect Evaporators Efficient?
Multi-effect evaporators are known for their ability to recycle steam across multiple stages, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing energy costs. They are commonly used in pharmaceutical and chemical processing applications where large volumes of wastewater need to be treated. While they offer high efficiency, the complexity of setup and maintenance can be a drawback for some businesses. B2B buyers should assess their operational capabilities and maintenance resources before investing.
Illustrative image related to evaporator water
Why Choose Mechanical Vapor Recompression Evaporators?
Mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) evaporators are designed for high efficiency and low energy consumption. They utilize vapor compression technology to transfer heat, making them suitable for various applications, including wastewater treatment and desalination. Although MVR systems require skilled maintenance, their operational efficiency can lead to significant cost savings over time. Buyers must weigh the benefits of reduced energy costs against the need for specialized technical support.
What are the Advantages of Drum Evaporators?
Drum evaporators are compact and designed for low-volume wastewater streams, making them ideal for small-scale industries and laboratories. Their space-saving design and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive option for businesses with limited wastewater. However, buyers should keep in mind that drum evaporators have a limited capacity, which may not meet the needs of larger operations. When considering a drum evaporator, it’s crucial to assess the specific wastewater volume and treatment requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of evaporator water
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Evaporator Water | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Water management in hydraulic fracturing | Reduces water disposal costs and enhances environmental compliance | Reliability of equipment, local regulations, and energy efficiency |
| Food & Beverage | Concentration of liquid waste streams | Improves product quality and reduces waste disposal costs | Compliance with food safety standards and material compatibility |
| Pharmaceuticals | Recycling of process water | Minimizes operational costs and supports sustainability goals | Quality certifications and integration with existing systems |
| Mining | Dewatering of mineral tailings | Increases recovery rates and reduces environmental impact | Durability and efficiency under harsh conditions |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Treatment of wastewater from chemical processes | Lowers treatment costs and enhances recovery of valuable materials | Customization for specific chemical compositions and scalability |
How is Evaporator Water Utilized in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, evaporator water is crucial for managing water used in hydraulic fracturing processes. By effectively evaporating wastewater, companies can minimize disposal costs and adhere to environmental regulations. This process not only conserves water but also recycles it for reuse in operations, thus enhancing sustainability. International buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing reliable equipment that complies with local regulations and demonstrates energy efficiency to ensure cost-effectiveness.
What Role Does Evaporator Water Play in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In food and beverage production, evaporator water is utilized for concentrating liquid waste streams, such as those generated during juice extraction or brewing. This application enhances product quality by removing excess water, thereby concentrating flavors and nutrients. Additionally, it reduces waste disposal costs significantly. Buyers in South America and Europe should consider equipment that meets stringent food safety standards and is compatible with their existing production systems to ensure a seamless integration.
How is Evaporator Water Essential for the Pharmaceutical Industry?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers use evaporator water to recycle process water, which is often laden with chemicals and other contaminants. By employing advanced evaporator systems, companies can minimize operational costs associated with wastewater treatment while supporting sustainability initiatives. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and Europe, sourcing evaporators with quality certifications is critical to ensure compliance with industry regulations and to maintain product integrity.
What Benefits Does Evaporator Water Provide in Mining Operations?
In the mining sector, evaporator water is essential for the dewatering of mineral tailings, which can be highly saturated with water. This process not only increases recovery rates of valuable minerals but also significantly reduces the environmental footprint of mining operations. Buyers in regions like South America and Africa should seek durable and efficient evaporator systems that can withstand harsh operational conditions and provide scalability to adapt to varying production levels.
How is Evaporator Water Used in Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturers utilize evaporator water for treating wastewater generated during production processes. This application allows for the recovery of valuable materials while lowering overall treatment costs. As international buyers explore options, they should focus on sourcing evaporators that can be customized for specific chemical compositions and offer scalability to accommodate future growth, ensuring they remain competitive in the global market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘evaporator water’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Managing Wastewater Disposal Costs
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers face escalating costs associated with the disposal of industrial wastewater. For companies operating in sectors such as manufacturing or food processing, the volume of wastewater generated can be substantial. Traditional disposal methods often incur hefty fees, and the process can be complex, involving compliance with environmental regulations that vary by region. Buyers may find themselves caught between the need to minimize costs and the obligation to adhere to stringent environmental standards, leading to frustration and uncertainty.
The Solution:
Implementing a thermal evaporator system can significantly reduce wastewater volume—up to 99%—thereby lowering disposal costs. When sourcing evaporators, buyers should look for equipment that is energy-efficient and designed to handle their specific wastewater characteristics. For instance, a Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) evaporator offers a cost-effective solution by utilizing existing steam to generate more steam, making it ideal for high-volume operations. Buyers should also consider integrating the evaporator with a water recycling system, which can further enhance cost savings and sustainability efforts by reusing treated water within their processes. Engaging with a manufacturer that provides tailored solutions and support can help buyers navigate the complexities of installation and compliance.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of Distillate Water
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with the inconsistent quality of distillate water produced from evaporators. Variations in wastewater composition—such as fluctuating concentrations of solids or contaminants—can lead to unreliable distillate quality, impacting downstream processes and product quality. This inconsistency can create challenges for industries like pharmaceuticals or food production, where water quality is critical for compliance and product integrity.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent distillate quality, buyers should invest in evaporators equipped with advanced monitoring systems that can track key parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates in real-time. This allows for immediate adjustments to be made during the evaporation process, ensuring optimal conditions are maintained. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct regular maintenance and calibration of the evaporator systems, as well as to implement pre-treatment processes for wastewater to stabilize its composition before entering the evaporator. Buyers can also benefit from partnering with suppliers that offer robust support and training on system optimization, helping to maintain high standards of quality in the distillate produced.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
Scenario 3: High Energy Consumption of Evaporation Processes
The Problem:
Energy consumption is a significant concern for B2B buyers using evaporators, especially in regions where energy costs are high. Traditional evaporation methods can be inefficient, leading to excessive operational costs and environmental impact. Companies looking to optimize their processes often find it challenging to balance energy use with effective wastewater management.
The Solution:
To address high energy consumption, buyers should consider investing in modern evaporator technologies that utilize heat pump systems. These systems are known for their energy efficiency, using less energy by transferring heat rather than generating it from scratch. For example, a Vacuum Heat Pump Evaporator can operate with significantly lower energy inputs while achieving effective evaporation rates. Buyers should also evaluate their existing infrastructure to identify opportunities for integrating waste heat recovery systems that can harness excess heat generated during production processes. By adopting these advanced technologies and practices, businesses can significantly reduce their energy footprint while achieving effective wastewater management. Working closely with suppliers to assess specific energy needs and potential solutions will further enhance operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for evaporator water
What Are the Key Materials for Evaporator Water Systems?
When selecting materials for evaporator water systems, several factors come into play, including temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall compatibility with the specific media being processed. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in evaporator water applications, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for handling various wastewater compositions. It typically has a high-temperature rating, allowing it to withstand thermal stress in evaporator systems.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can last for many years with minimal maintenance. However, its higher cost compared to other materials can be a deterrent for budget-conscious buyers. Manufacturing complexity can also be greater due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, making it versatile in different industrial applications. Its resistance to scaling and fouling also enhances operational efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 17440. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of specific stainless steel grades may vary, impacting procurement.
2. Polypropylene
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It operates effectively at lower temperatures, typically up to 90°C, and has a lower pressure rating than metals.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication. However, it is not suitable for high-temperature applications, which limits its use in certain evaporator systems. Additionally, its lower mechanical strength compared to metals can be a drawback.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for applications involving acidic or caustic media, where corrosion resistance is crucial. However, it may not perform well in high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards like JIS K 6880 for plastic materials. In regions with extreme temperatures, such as the Middle East, the thermal limits of polypropylene may pose challenges.
3. Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for harsh environments. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, often exceeding those of stainless steel.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of titanium is its longevity and performance in aggressive media. However, it is one of the most expensive materials, and its manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is particularly beneficial in applications involving seawater or highly corrosive chemicals, where other materials would fail. Its lightweight nature also aids in reducing overall system weight.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must consider compliance with ASTM B348 and the availability of titanium in their region. The high cost may be a barrier for some industries in developing regions.
4. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is a strong material with good mechanical properties and is often used in evaporator systems that do not require high corrosion resistance. It can handle moderate temperatures and pressures effectively.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost and ease of availability. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, which can lead to increased maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for applications where the wastewater is not highly corrosive. It is often used in conjunction with protective coatings to enhance its durability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36. In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, additional protective measures may be necessary.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for evaporator water | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General industrial wastewater | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polypropylene | Chemical processing applications | Cost-effective, lightweight | Limited temperature/pressure rating | Low |
| Titanium | Seawater and aggressive chemical waste | Exceptional longevity | Very high cost, complex processing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Non-corrosive wastewater applications | Low cost, readily available | Susceptible to corrosion | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of materials suitable for evaporator water systems, aiding in informed decision-making tailored to specific operational needs and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to evaporator water
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for evaporator water
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Evaporator Water?
The manufacturing process of evaporator water involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the highest quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the reliability and efficiency of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Evaporator Water Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. High-quality water is essential, typically sourced from municipal supplies or specific groundwater reserves. The water must undergo preliminary filtration to remove large particles, sediment, and contaminants. Additionally, additives may be introduced to enhance the water’s properties, ensuring it meets specific evaporation requirements for different industrial applications.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted for Evaporator Water?
After material preparation, the forming process begins. This stage involves the controlled heating of water to initiate the evaporation process. Evaporators utilize various techniques, such as thermal, vacuum, or mechanical vapor recompression, to transform water into vapor efficiently. The choice of technique impacts energy consumption, operational costs, and the volume of water that can be processed. B2B buyers should consider the energy efficiency of the evaporator technology employed by their suppliers, as this directly affects long-term operational costs.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail in Evaporator Water Manufacturing?
In the assembly phase, the components of the evaporator system are brought together. This includes the heat exchangers, condensers, pumps, and control systems. Each component must be assembled with precision to ensure optimal performance. During this stage, manufacturers often implement standard operating procedures (SOPs) to maintain consistency and quality across production lines. B2B buyers can inquire about the assembly processes used by suppliers to ensure they adhere to rigorous quality standards.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted to Ensure Product Quality?
The finishing process involves final checks and treatments to enhance the water’s quality and ensure it meets regulatory requirements. This may include additional filtration, deionization, or the introduction of specific chemicals to balance pH levels. The final product is then stored in controlled environments to maintain its quality until it is shipped. Buyers should ask suppliers about their finishing processes and any certifications that guarantee the water meets local and international standards.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Evaporator Water Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for evaporator water. It ensures that the product meets the required specifications and industry standards, safeguarding both the supplier’s reputation and the buyer’s investment.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a crucial role in establishing quality management systems within manufacturing processes. ISO 9001 certification demonstrates that a supplier adheres to best practices in quality management, which is essential for consistency and reliability. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking (for compliance with European health and safety regulations) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may also apply, depending on the intended use of the evaporator water.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Typically, these checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive tests on the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications before shipment.
B2B buyers should inquire about these QC checkpoints and the specific methodologies used at each stage.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are commonly used in the quality assurance of evaporator water. These may include:
- Chemical Analysis: Assessing the chemical composition to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Physical Testing: Measuring parameters such as turbidity, pH levels, and conductivity.
- Microbiological Testing: Ensuring that the water is free from harmful microorganisms that could compromise safety.
Buyers should request detailed reports of testing results to verify the quality of the evaporator water.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Procedures?
Due diligence in supplier selection is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing evaporator water from international suppliers. Here are several methods to verify a supplier’s QC practices:

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request access to recent audits and quality assurance reports from potential suppliers. This includes certifications, internal audit results, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues. A reputable supplier should be transparent about their QC processes and willing to share this information.
Are Third-Party Inspections Necessary for Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an added layer of assurance. These independent entities can verify compliance with international standards and assess the supplier’s adherence to established quality protocols. Buyers should consider incorporating third-party inspections into their procurement processes, especially when dealing with suppliers from regions with varying regulatory standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of international quality control can be challenging. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances:
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Quality Control?
Different regions may have varying regulations governing water quality and safety standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply with these requirements. This is particularly important when sourcing evaporator water for industries with stringent safety and environmental regulations.
What Role Do Certifications Play in Supplier Selection?
Certifications can significantly impact supplier selection. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with internationally recognized certifications, as these demonstrate a commitment to quality and compliance. Additionally, understanding the certification process in the supplier’s region can provide insights into their operational rigor.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for evaporator water, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘evaporator water’
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial operations, sourcing evaporator water is a critical aspect for many businesses, particularly in sectors dealing with wastewater management. This guide offers a structured checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right evaporator water solutions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your technical requirements is essential before initiating the sourcing process. This includes knowing the volume of evaporator water needed, the specific contaminants present, and the desired purity level. By clearly defining these specifications, you can narrow down potential suppliers who can meet your precise needs.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Finding trustworthy suppliers is crucial for securing high-quality evaporator water. Research potential suppliers through industry directories, trade shows, and professional networks. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews from other businesses in your sector, as this can save you time and resources in the long run.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with any supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Check for ISO certifications or other relevant environmental regulations that demonstrate a commitment to quality and sustainability. Suppliers who meet these standards are more likely to provide reliable products that align with your operational requirements.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Obtaining samples of evaporator water can provide valuable insights into the quality and suitability of the product for your processes. Analyze the samples for contaminants and purity levels, ensuring they meet your established specifications. This step minimizes risks associated with purchasing subpar materials that could affect your operations.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. Look for transparency in pricing and any additional fees that may apply, such as shipping or handling charges. Evaluate whether the cost aligns with your budget while also considering the quality of the product offered.
Step 6: Review Delivery and Logistics Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s delivery and logistics capabilities is critical to ensuring timely procurement of evaporator water. Inquire about their lead times, shipping methods, and whether they can accommodate urgent orders. Reliable logistics can significantly impact your operational efficiency, especially in industries with strict timelines.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication with your chosen supplier is vital for a successful partnership. Establish clear lines of communication regarding order status, potential issues, and any changes in requirements. Regular updates can foster a cooperative relationship and help address any concerns proactively, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing evaporator water with confidence, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes and enhanced efficiency in wastewater management.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for evaporator water Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Evaporator Water Sourcing?
When sourcing evaporator water, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of water, including any necessary treatment chemicals, significantly impact the base cost. High-purity water may command a premium, while standard industrial water could be less expensive.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards and the complexity of water treatment processes. Automated systems may reduce ongoing labor costs but require higher initial investments.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Suppliers with more efficient production processes can offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Specialized equipment used in the treatment and evaporation process can add to the initial costs but may improve efficiency and reduce long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures that the water meets specific standards, which can increase upfront costs but may prevent costly issues later.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including freight and handling, are significant, especially for international buyers. Proximity to suppliers can help mitigate these expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their operational efficiencies and market conditions. Understanding these margins can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Evaporator Water Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of evaporator water that international buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often benefit from volume discounts, reducing per-unit costs. Understanding supplier MOQs can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized water treatment solutions may incur additional costs. Clearly defining your requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality water with certifications (e.g., ISO, ANSI) typically costs more. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certifications against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for perceived reliability.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and risk. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) may lead to higher upfront costs but reduce risk for the buyer.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Evaporator Water Prices?
To ensure cost-effective sourcing, consider these negotiation strategies and insights:
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to benchmark pricing and service levels. This data can enhance your bargaining position.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may yield savings over time.
-
Negotiate Terms Beyond Price: Consider negotiating payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty agreements. These factors can impact your cash flow and operational efficiency.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Prices can vary significantly between regions due to local regulations, market demand, and currency fluctuations. Familiarize yourself with these nuances to make informed decisions.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to better pricing and service flexibility. Suppliers may offer exclusive deals or priority service to long-term partners.
Disclaimer on Indicative Pricing
It is essential to note that the prices for evaporator water can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier changes, and regional variations. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and request updated quotes before finalizing any agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing evaporator water With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions to Evaporator Water
In the pursuit of effective wastewater management and reduction, businesses often explore various technologies and methods. While evaporator water technology is a leading solution for minimizing liquid waste, there are several viable alternatives that can meet similar goals. This section will compare evaporator water with two alternative solutions: multi-effect evaporators (MEE) and mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) systems. Each option has distinct advantages and limitations, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand their options thoroughly.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Evaporator Water | Multi-Effect Evaporator (MEE) | Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, reduces waste volume by up to 99% | Very high efficiency, multiple stages for steam recycling | Extremely high efficiency, low energy consumption |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, operational costs can vary | Higher upfront cost, lower operational costs due to energy savings | High initial investment, but significant savings in energy costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires moderate setup, may need site adjustments | Complex installation, requires skilled labor | Complex installation, requires skilled labor and system integration |
| Maintenance | Relatively low, routine checks needed | Moderate, requires periodic inspections and maintenance | Low, but specialized service may be required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industries with variable waste streams and lower volume | Best for continuous processes with high wastewater volumes | Optimal for industries with consistent waste streams and energy efficiency needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Multi-Effect Evaporators (MEE)?
Multi-effect evaporators utilize the steam generated in one effect to heat the next, creating a cascading effect that maximizes energy efficiency. This technology is particularly advantageous for industries generating large volumes of wastewater, such as food processing and chemical manufacturing. The main benefits include a high evaporation rate and reduced energy costs over time. However, the initial investment is considerably higher compared to evaporator water systems, and the complexity of installation and operation requires skilled labor, which may pose challenges for companies with limited technical expertise.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
How Does Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) Compare?
Mechanical vapor recompression systems offer an innovative solution by compressing and reusing vapor generated during the evaporation process. This technology is renowned for its energy efficiency, consuming significantly less energy than traditional systems. MVR is particularly suited for industries with consistent wastewater streams, such as pharmaceuticals and textiles. While the operational costs are low, the initial setup costs can be daunting, and the complexity of the system necessitates specialized maintenance. Consequently, companies must weigh the long-term energy savings against the upfront investment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
When evaluating wastewater management solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, waste characteristics, and budget constraints. Evaporator water systems are a versatile choice for those needing moderate efficiency and lower initial costs. In contrast, multi-effect evaporators and mechanical vapor recompression systems may offer higher efficiency and long-term savings, albeit with higher upfront investments and complexity. Conducting a thorough analysis of each option’s performance, cost implications, and operational requirements will empower businesses to make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for evaporator water
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Evaporator Water?
Understanding the technical properties of evaporator water is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in industries that rely on efficient wastewater management. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Purity Level
Purity refers to the concentration of contaminants in the evaporator water. High-purity water minimizes the risk of scaling and corrosion in evaporators, enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers should ensure that the evaporator systems they invest in can handle the specific purity requirements of their processes. -
Temperature Tolerance
Evaporator water often operates under varying temperature conditions, typically between 35°C to 100°C, depending on the technology used (e.g., multi-effect or mechanical vapor recompression). Understanding the temperature tolerance is vital for ensuring that the evaporator system functions optimally without risking equipment failure or reduced efficiency. -
Flow Rate
This specification denotes the volume of water that can be evaporated per hour, measured in gallons. Different applications require different flow rates, and selecting a system that meets specific operational demands is essential for maintaining productivity and minimizing downtime. -
Viscosity
Viscosity affects the fluid dynamics within the evaporator system. Higher viscosity can lead to inefficiencies in heat transfer and longer processing times. Buyers should assess the viscosity of the wastewater being treated to ensure compatibility with the chosen evaporator technology. -
pH Level
The pH level of evaporator water can significantly influence the corrosion rates of materials in contact with it. A neutral pH (around 7) is generally preferred to minimize corrosion risks. Buyers must evaluate the pH levels of their wastewater to determine the necessary treatment processes before evaporation. -
Conductivity
Conductivity measures the water’s ability to conduct electricity, which correlates with the concentration of dissolved salts. Monitoring conductivity helps in assessing the water’s quality and determining the need for pre-treatment before evaporation. High conductivity can indicate a need for advanced filtration or treatment solutions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Evaporator Water?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality in evaporator systems and components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers to know when negotiating with suppliers, as it can affect inventory management and overall project costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For evaporator water systems, issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive pricing and assess supplier capabilities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, covering aspects such as shipping costs, insurance, and risk management. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify their obligations and avoid misunderstandings in international procurement. -
TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)
TDS indicates the total concentration of dissolved substances in water, affecting evaporation efficiency. Monitoring TDS levels is essential for ensuring that the water quality meets operational standards and does not impede performance. -
WTP (Water Treatment Plant)
A WTP is a facility that treats water to make it suitable for a specific purpose, such as industrial use. Understanding the capabilities and specifications of WTPs is important for buyers looking to integrate evaporator systems with existing water treatment processes.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their wastewater management processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the evaporator water Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Evaporator Water Sector?
The global evaporator water market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing industrial wastewater management needs and stringent environmental regulations. Key factors influencing this market include the rising awareness of sustainable practices, the need for cost-effective waste disposal solutions, and advancements in technology that enhance the efficiency of evaporator systems. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing high-performance evaporators that align with local regulatory frameworks and environmental standards.
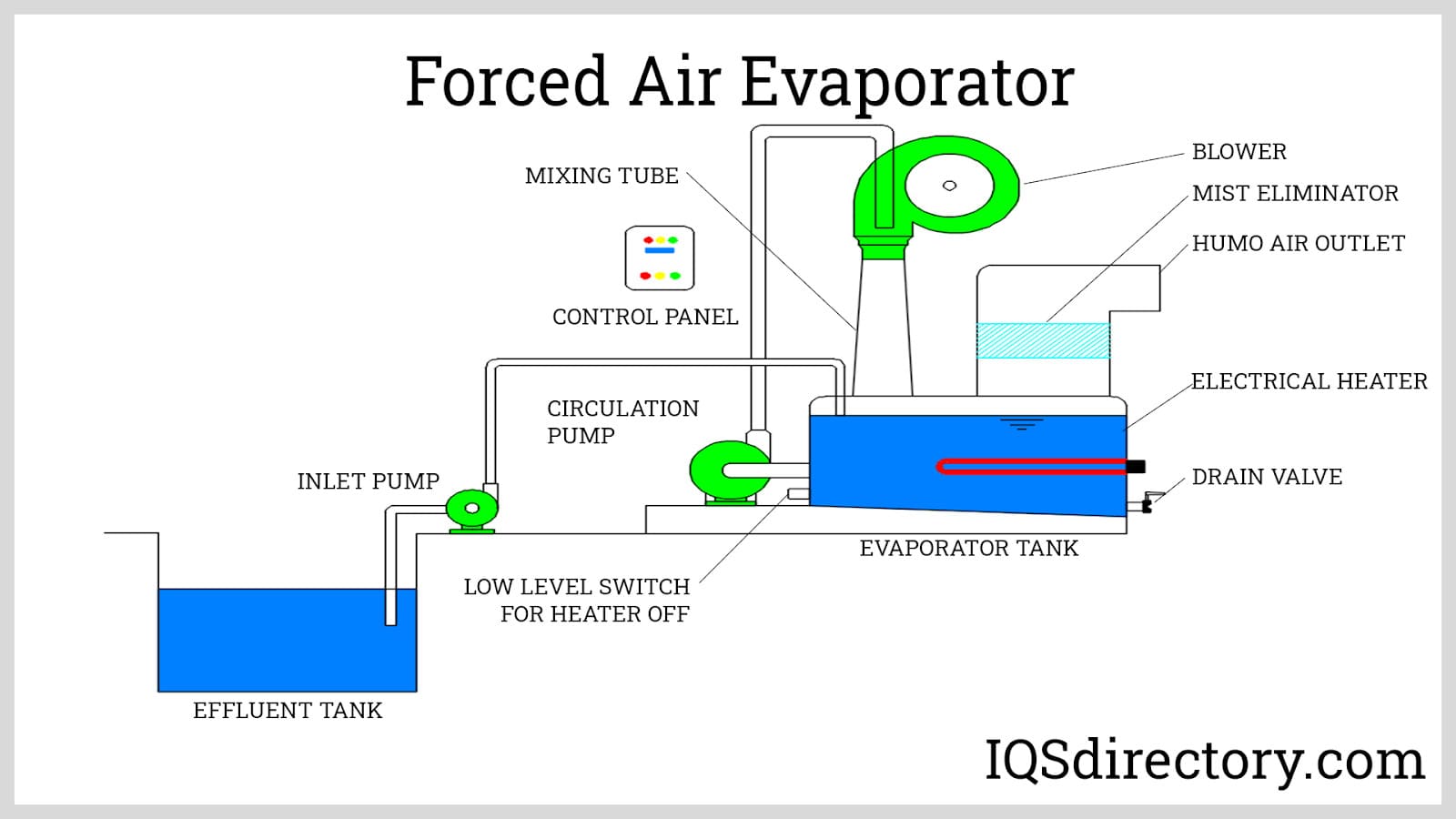
Emerging trends such as the adoption of energy-efficient solutions, including Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) and heat pump evaporators, are reshaping sourcing strategies. These technologies not only minimize energy consumption but also optimize operational costs, making them attractive for industries facing high energy prices. Additionally, the trend towards integrated water treatment systems is gaining traction, offering buyers comprehensive solutions that combine multiple treatment processes, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of wastewater management.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a shift towards rental services for evaporators, allowing companies to test and scale their operations without significant upfront investment. This flexibility is particularly appealing to businesses in emerging markets that may face budget constraints or fluctuating wastewater volumes.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Evaporator Water Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the evaporator water sector, as industries are increasingly held accountable for their environmental impact. The adoption of sustainable practices not only helps in compliance with regulations but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly technologies and ethical sourcing practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for evaporator solutions that utilize ‘green’ materials and certified technologies, such as those recognized by environmental certifications like ISO 14001. These certifications provide assurance that the products are manufactured with minimal environmental impact and are part of a responsible supply chain.
Moreover, innovative evaporator technologies that recycle steam and reduce wastewater volumes are crucial in promoting a circular economy. For instance, systems that recover and reuse heat not only conserve energy but also reduce the overall carbon footprint of industrial operations. By investing in such sustainable solutions, companies can not only improve their operational efficiency but also contribute positively to their communities and the environment.
What Is the Historical Context of the Evaporator Water Sector?
The evolution of the evaporator water sector can be traced back to the early industrial revolution, where the need for efficient wastewater management became apparent. Initially, evaporators were simple, energy-intensive systems primarily used for steam generation. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated evaporators, including multi-effect and mechanical vapor recompression systems, which significantly improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs.
As environmental awareness grew in the late 20th century, the focus shifted towards sustainable wastewater treatment solutions. This shift prompted innovations in evaporator technology, with manufacturers investing in R&D to create systems that not only meet regulatory requirements but also promote resource recovery and waste minimization. Today, the evaporator water sector stands at the forefront of industrial sustainability, providing essential solutions for companies looking to enhance their environmental performance while managing costs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of evaporator water
1. How do I solve issues with wastewater disposal in my facility?
To address wastewater disposal challenges, consider investing in an efficient evaporator system. These systems minimize wastewater volume by up to 99%, significantly reducing disposal costs and environmental impact. Evaluate your facility’s specific needs, such as the type and volume of wastewater generated, and consult with suppliers to select the right evaporator model. Additionally, ensure that your chosen solution complies with local regulations and sustainability practices to enhance your facility’s operational efficiency.
2. What is the best evaporator system for my industrial application?
The ideal evaporator system depends on your specific industrial application and wastewater characteristics. For high-volume operations, a Multi-Effect Evaporator (MEE) may be most suitable, while a Vacuum Heat Pump Evaporator is ideal for energy efficiency. Assess factors such as flow rate, temperature requirements, and the nature of the waste being treated. Engaging with suppliers for a thorough consultation can ensure you select a system that meets your operational goals and budget constraints.
3. What customization options are available for evaporator systems?
Many evaporator manufacturers offer customization options to tailor systems to your specific needs. This may include modifications in capacity, material choices, or integration with existing wastewater treatment processes. Be sure to communicate your requirements clearly to potential suppliers and inquire about their ability to meet these needs. Custom solutions can enhance efficiency and performance, ensuring optimal results for your facility.
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for evaporator systems?
Minimum order quantities for evaporator systems vary by manufacturer and product type. Generally, established suppliers may have MOQs ranging from one unit for specialized systems to multiple units for standard models. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you’re considering a pilot project or initial trial before committing to larger orders.

Illustrative image related to evaporator water
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing evaporator systems internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of evaporator systems can vary widely. Common terms include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms upfront, and consider discussing options that can help mitigate risks associated with international transactions, such as escrow services or trade financing.
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for evaporator systems?
To ensure quality assurance for evaporator systems, start by vetting suppliers based on their certifications, industry experience, and customer testimonials. Request documentation of quality control processes, including testing and inspection protocols. Engage with suppliers who offer warranties and after-sales support, as this can provide additional assurance of system reliability and performance. Conducting site visits or requesting references from previous clients can also enhance your confidence in the supplier’s quality standards.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing evaporator systems?
When sourcing evaporator systems internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Discuss with suppliers the best shipping options for your location, including freight costs and delivery schedules. Understanding import duties and taxes is crucial for budgeting. Additionally, ensure that the supplier has experience with international shipping to facilitate a smooth delivery process, including handling any potential delays or complications.
8. How do I evaluate and vet suppliers of evaporator systems?
To effectively evaluate and vet suppliers of evaporator systems, start by conducting thorough research on their reputation, experience, and product offerings. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and check for certifications that align with international standards. Request case studies or references from past clients to gauge performance and reliability. Engaging in initial discussions can also provide insights into their customer service and technical support capabilities, which are vital for long-term partnerships.
Top 5 Evaporator Water Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. ENCON – Wastewater Evaporators
Domain: evaporator.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: ENCON Evaporators designs and manufactures American-made wastewater evaporators that reduce disposal volume by up to 99%. They have over 30 years of experience and 2,000+ installations worldwide, offering reliable, energy-efficient solutions for industrial wastewater minimization. Key products include: 1. Thermal Evaporator: 8-650 Gallons Per Hour 2. Vacuum Heat Pump Evaporator: 20-70 Gallons Per …
2. IQS Directory – Wastewater Evaporators
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
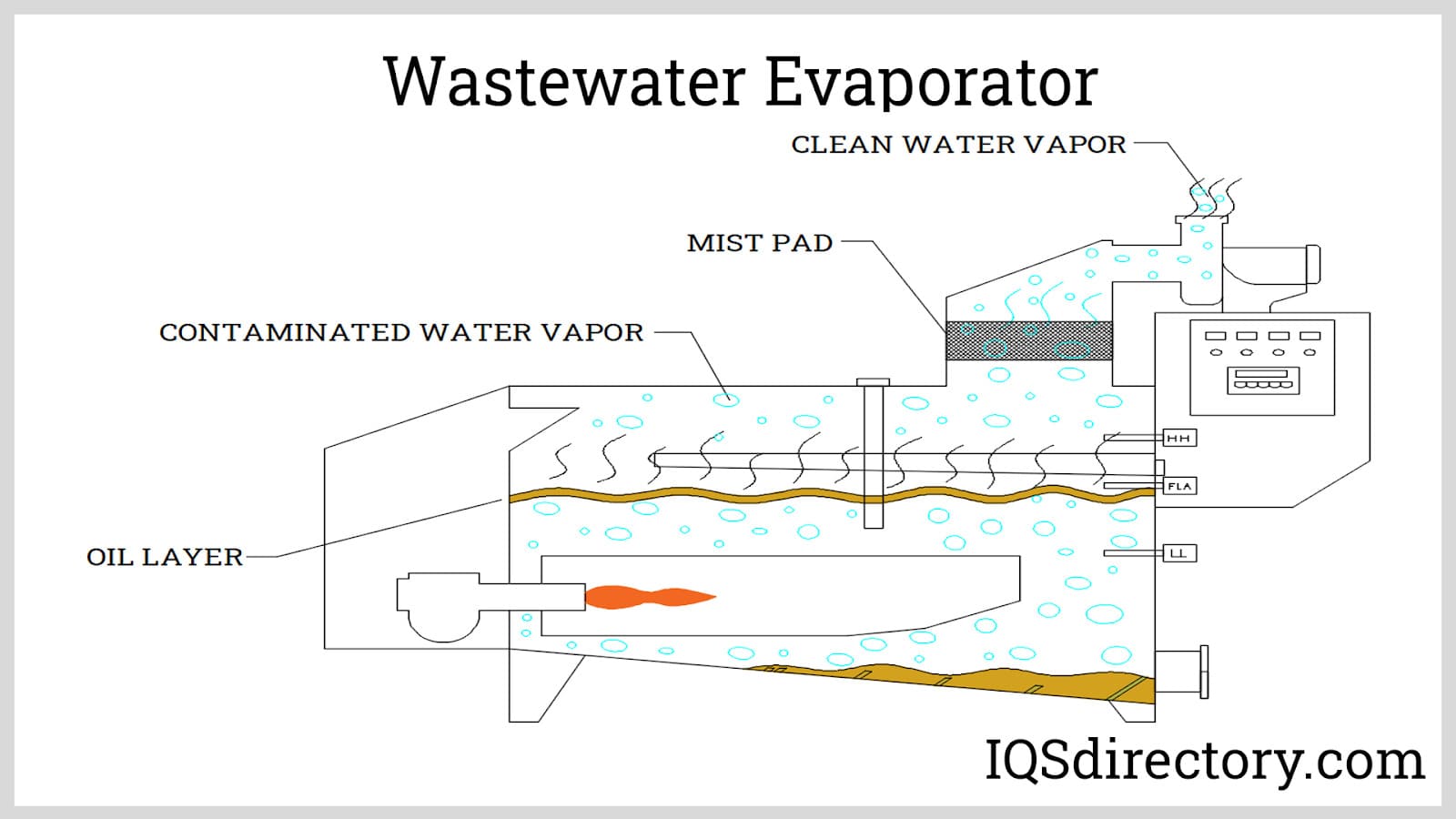
Introduction: Wastewater evaporators transform water-based waste into vapor, separating impurities and reducing waste volume. They operate using thermodynamics and mass transfer principles, applying thermal energy to liquid waste to vaporize water. Common fuel sources include natural gas, electricity, oil, or steam. Key components include a feed pump for transferring wastewater, a heat exchanger for applying he…
3. EVALED – Innovative Evaporators for Water Treatment
Domain: evaled.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: EVALED evaporators utilize three different heat exchange technologies for water treatment and energy reduction. 1. Heat Pump Evaporator: Operates with a vacuum of 6-8 kPa and a temperature of 35-45 °C, using freon gas for thermal energy transfer. 2. Hot and Cold Water Evaporator: Uses site-available hot and cold water for thermal energy, with variable vacuum conditions affecting boiling temperatur…
4. Wmaze – WB-50A Wastewater Evaporator
Domain: wmaze.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “WB-50A Wastewater Evaporator”, “model_number”: “11034740”, “type”: “Submerged combustion water evaporator”, “flow_rate_gal_per_hour”: 60, “BTU”: 571000, “container_capacity_gal”: 76, “exhaust_stack_diameter_in”: 10, “weight_without_accessories_lb”: 895, “shipping_weight_lb”: 1290, “dimensions_in”: {“length”: 75, “width”: 23, “height”: 75}, “packaged_dimensions_in”: {“length”: 84,…
5. The Engineering Mindset – Chiller Evaporators
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Chiller evaporators are located just after the expansion valve and before the suction line to the compressor. They collect unwanted heat from the building and produce chilled water, which is then circulated to air handling units (AHUs) to cool the building. The evaporator is typically insulated with vinyl nitrate polymer insulation, around 19 millimeters thick. The evaporator design is shell and t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for evaporator water
As the global demand for effective wastewater management intensifies, the strategic sourcing of evaporator water technology emerges as a vital component for businesses across various industries. By investing in advanced evaporators, companies can significantly minimize waste disposal volumes—up to 99% in some cases—while enhancing sustainability initiatives. Key considerations for B2B buyers include evaluating energy efficiency, operational costs, and the adaptability of evaporator systems to unique industrial processes.
The value of strategic sourcing lies not only in cost savings but also in the long-term operational benefits and compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. For international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers can yield customized solutions that address specific regional challenges, including resource scarcity and varying wastewater compositions.
Looking ahead, the focus should be on innovation and sustainability in evaporator technology. Companies are encouraged to explore collaborations and pilot projects to identify the best-fit solutions for their needs. By prioritizing strategic sourcing in evaporator water systems, businesses can position themselves as leaders in environmental stewardship while optimizing their operational efficiencies.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.