Is Your Conveyor Types Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for conveyor types
In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, sourcing the right conveyor types can be a complex challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a multitude of conveyor systems available—each designed for specific applications and operational needs—making an informed purchasing decision is crucial. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of the various types of conveyors, their applications across industries, and key factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
From understanding the differences between floor-mounted and overhead systems to evaluating cost implications and supplier reliability, this guide empowers international buyers to navigate the intricacies of conveyor procurement. By addressing critical questions such as “Which conveyor type best suits my operational needs?” and “How can I optimize my space utilization while enhancing productivity?” this resource aims to streamline the decision-making process.
Whether you are a manufacturer in Nigeria seeking to automate your production line or a logistics manager in Saudi Arabia looking to improve warehouse efficiency, this guide equips you with the insights needed to select the right conveyor solutions for your business. By leveraging this knowledge, you can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately drive your business forward in a competitive landscape.
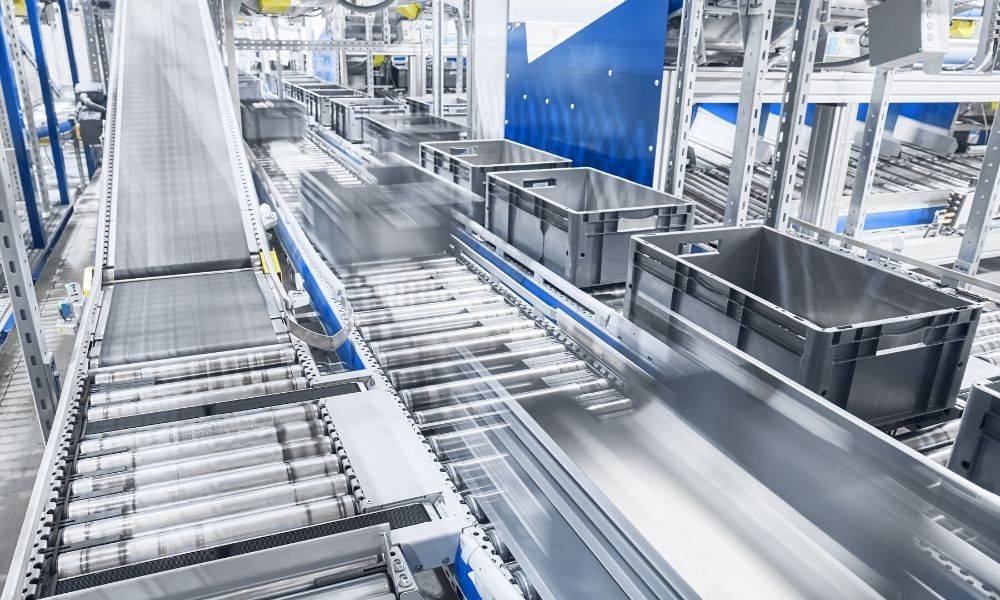
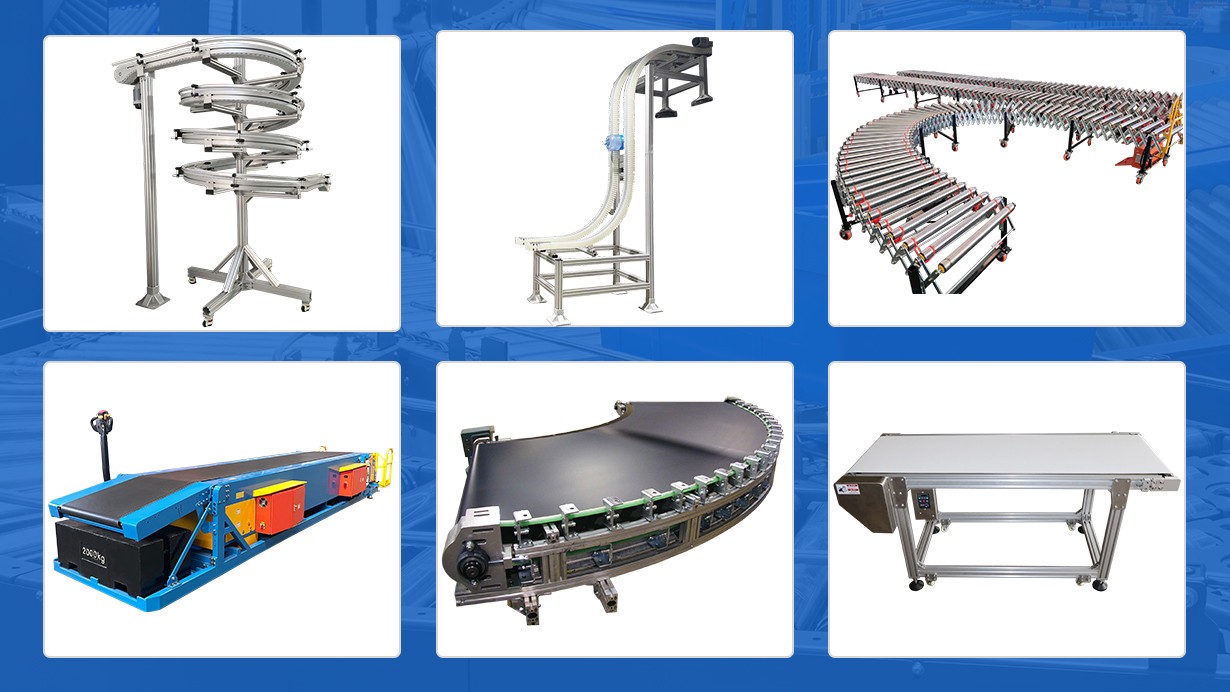
Understanding conveyor types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Conveyor | Simple design, moves products on a continuous belt | Assembly lines, packaging, material handling | Pros: Cost-effective, easy installation. Cons: Limited to straight paths, not suitable for precise positioning. |
| Gravity Roller Conveyor | Uses gravity to move items along rollers | Warehousing, shipping, and receiving | Pros: Low maintenance, simple design. Cons: Requires incline, can cause product collisions. |
| Chain Conveyor | Durable, suitable for heavy and uneven loads | Automotive, heavy manufacturing | Pros: Heavy-duty, reliable for heavy items. Cons: Slower speeds, may require more space. |
| Motorized Roller Conveyor | Integrated motors for controlled movement | Distribution centers, e-commerce fulfillment | Pros: High-speed operation, zero pressure accumulation. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex installation. |
| Overhead Conveyor | Utilizes overhead space, often hand-pushed or automated | Assembly lines, paint shops, storage | Pros: Saves floor space, versatile. Cons: Installation complexity, may require structural support. |
What Are the Characteristics of Belt Conveyors?
Belt conveyors are among the most straightforward conveyor types, featuring a continuous loop of material that transports products from one point to another. They are particularly suited for assembly lines, packaging tasks, and general material handling. Buyers should consider the belt’s material and width based on the products being transported. While cost-effective and easy to install, belt conveyors lack the ability to perform precise positioning or serve as a working surface, limiting their use in more complex applications.
How Do Gravity Roller Conveyors Operate?
Gravity roller conveyors rely on the force of gravity to move items along a series of rollers. They are particularly effective in warehousing and shipping environments where products need to flow downhill. These conveyors are low maintenance and simple in design, making them an attractive option for buyers looking to improve productivity. However, they require a slight incline for operation and can lead to product collisions if not carefully managed, which may necessitate additional control measures.
Why Choose Chain Conveyors for Heavy Loads?
Chain conveyors are designed to handle heavy items, making them ideal for industries such as automotive manufacturing. They utilize a chain system to support and transport products with uneven surfaces. Buyers should prioritize chain conveyors for applications requiring robust material handling capabilities. While they are reliable and durable, chain conveyors typically operate at slower speeds and require more space compared to other conveyor types, which can impact overall productivity.
What Are the Benefits of Motorized Roller Conveyors?
Motorized roller conveyors integrate motors within the rollers themselves, allowing for high-speed operation and precise control over product movement. They are commonly found in distribution centers and e-commerce fulfillment operations. The zero pressure accumulation feature helps prevent product damage during transport. Buyers should consider the higher initial investment and complexity of installation; however, the efficiency gains often justify the costs in high-volume environments.
How Do Overhead Conveyors Maximize Space?
Overhead conveyors are mounted above the workspace, freeing up valuable floor space for other operations. They can be hand-pushed or automated and are versatile enough for various applications, including assembly lines and storage solutions. Buyers should evaluate the installation complexity and structural requirements, as these systems can be more challenging to set up. The ability to utilize overhead space effectively can significantly enhance operational efficiency, making them a worthwhile consideration for many businesses.
Key Industrial Applications of conveyor types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Conveyor Types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Assembly line conveyors for vehicle parts | Increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs | Need for durable, heavy-duty conveyors that can handle weight and precision. |
| Food and Beverage | Automated conveyor systems for packaging and processing | Enhances hygiene and speeds up product flow | Compliance with food safety standards; materials must be easy to clean. |
| Mining and Materials | Bulk material handling conveyors for transporting ores | Reduces manual handling and increases safety | Must withstand harsh environments; consider material and design for durability. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Overhead conveyors for transporting packaged medications | Streamlines operations and minimizes contamination risk | Requires precise control and monitoring capabilities; must meet regulatory compliance. |
| Warehousing and Logistics | Motorized roller conveyors for sorting and distributing packages | Improves order fulfillment speed and accuracy | Consider layout flexibility and integration with existing systems. |
How are Conveyor Types Utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, assembly line conveyors facilitate the movement of vehicle parts through various stages of production. These conveyors are designed to handle heavy loads, ensuring that components are delivered precisely where needed without manual intervention. By automating this process, manufacturers can significantly increase production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize the risk of workplace injuries. International buyers should prioritize durable conveyor systems that can withstand the rigors of heavy manufacturing while allowing for precise positioning of parts.
What Role Do Conveyors Play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
Conveyor systems in the food and beverage industry are crucial for automating packaging and processing tasks. They help maintain hygiene standards while speeding up product flow, essential for meeting high demand. These conveyors are often designed with materials that are easy to clean and comply with food safety regulations. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing conveyors that not only enhance efficiency but also adhere to stringent health standards to avoid contamination risks.
How are Conveyors Used in Mining and Material Handling?
In mining, bulk material handling conveyors are essential for transporting ores and other materials over long distances. These systems reduce the need for manual handling, thus increasing safety for workers. They are built to withstand harsh conditions, making durability a key consideration for international buyers. When sourcing conveyors for this sector, it is important to evaluate the material and design to ensure they can handle the weight and abrasiveness of the materials being transported.
What Benefits Do Overhead Conveyors Provide in Pharmaceuticals?
Overhead conveyors are commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry for the efficient transport of packaged medications. This application helps streamline operations while minimizing the risk of contamination, as products are kept off the ground and away from potential hazards. Buyers should focus on systems that offer precise control and monitoring capabilities, ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Selecting the right conveyor can significantly enhance operational efficiency and product safety.
How Do Motorized Roller Conveyors Benefit Warehousing and Logistics?
In warehousing and logistics, motorized roller conveyors are employed for sorting and distributing packages efficiently. These systems improve order fulfillment speed and accuracy, which are critical in today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment. When sourcing these conveyors, international buyers should consider their layout flexibility and how well they can integrate with existing systems. Investing in high-quality motorized roller conveyors can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘conveyor types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Space Utilization in Production Facilities
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with optimizing their production facilities for maximum efficiency. Space is often at a premium, particularly in industries like manufacturing and warehousing. Buyers may find that traditional floor-mounted conveyors occupy valuable ground space, making it difficult to manage workflow and maintain safety standards. This inefficiency can lead to bottlenecks, increased labor costs, and even accidents if employees navigate crowded areas.
The Solution: To address space constraints, consider implementing overhead conveyor systems. These systems free up floor space by utilizing the vertical area of the facility. When specifying an overhead conveyor, assess the weight and size of the items being transported to select an appropriate system, such as a hand-pushed beam trolley or an automated overhead monorail. Ensure that the installation allows for easy loading and unloading at multiple points to facilitate smooth operations. Additionally, incorporating flexible configurations can help accommodate changes in production demands, making the system adaptable as your business evolves.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Frequent breakdowns of conveyor systems can lead to significant maintenance costs and lost productivity. Many buyers experience frustration when their conveyors, particularly those that are older or not well-suited for their specific applications, require constant repairs. These interruptions can disrupt production schedules, delay order fulfillment, and ultimately affect customer satisfaction.
Illustrative image related to conveyor types
The Solution: To minimize maintenance issues and downtime, invest in modern conveyor technologies that are designed for durability and efficiency. For example, motorized roller conveyors (MDR) with zero pressure accumulation features can enhance reliability by preventing product damage during transport, reducing wear and tear. Conduct a thorough analysis of your operational needs and choose conveyor types that align with your load requirements and processing speeds. Additionally, implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and timely upgrades to components. This approach can significantly extend the lifespan of your conveyor systems and reduce unexpected failures.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Handling Diverse Product Types
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when dealing with varied product sizes and weights on their conveyor systems. This diversity can complicate material handling, leading to inefficiencies and potential damage to products. For instance, a conveyor that works well for lightweight items may struggle to transport heavier or irregularly shaped products, causing jams or requiring manual intervention.
The Solution: To effectively manage a diverse product range, it is essential to select the right conveyor type and configuration. Consider utilizing adjustable or modular conveyor systems, such as slat conveyors or chain-driven live roller (CDLR) systems, which can accommodate various product shapes and sizes. These systems can be customized with fixtures that stabilize products, ensuring safe and efficient transport. When sourcing these conveyors, work with suppliers who offer flexible design options and can provide guidance on integrating the systems into your existing operations. Training staff on how to load and unload different products properly can also enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of damage. By proactively addressing these challenges, buyers can create a more adaptable and resilient material handling process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for conveyor types
What Are the Key Materials Used in Conveyor Types?
When selecting materials for conveyor systems, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in conveyor types: steel, aluminum, plastic, and stainless steel. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact application suitability, especially for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Conveyor Applications?
Steel is a traditional choice for conveyor systems, particularly in heavy-duty applications. Its high tensile strength allows it to support substantial loads, making it ideal for industries like mining and manufacturing. Steel conveyors can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for environments that involve heavy machinery or high operational demands.
Pros: Steel’s durability and strength make it a reliable choice for heavy loads. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: However, steel is prone to corrosion, which can be a significant drawback in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase costs if custom designs are required.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including bulk materials like gravel or ores. However, its susceptibility to rust necessitates protective coatings or regular maintenance.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in Conveyor Systems?
Aluminum is increasingly favored for its lightweight properties, making it easier to install and modify. It offers good corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in environments where moisture is present. Aluminum conveyors are often used in food processing and packaging industries due to their hygienic properties.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and installation. Its resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for diverse environments.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it may not support as heavy loads as steel, making it less suitable for heavy industrial applications. Additionally, its cost is generally higher than that of steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media but is particularly effective in applications requiring frequent cleaning or where contamination is a concern.
International Considerations: Buyers in Europe and South America should look for compliance with JIS standards to ensure quality and performance.
Why Choose Plastic for Conveyor Systems?
Plastic is a versatile material used in conveyor systems, particularly in light-duty applications. It is resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it suitable for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Plastic conveyors can be designed with modular components, allowing for easy customization.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic is its resistance to corrosion and chemicals. Its modular design allows for easy repairs and modifications.
Cons: Plastic is generally less durable than metal options and may not support heavy loads. It can also be more expensive to manufacture due to the need for specialized components.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for transporting sensitive products that require a clean environment. However, it may not be suitable for heavy bulk materials.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify compliance with food safety standards, especially in regions like South America where regulations may vary.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Conveyor Systems?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and durability, making it a preferred choice in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries. It can withstand harsh cleaning processes and is less prone to rust compared to regular steel.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for hygienic applications. It also has high strength and durability.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is significantly higher than that of other materials, and its weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances. Its robustness makes it ideal for environments requiring stringent hygiene standards.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
International Considerations: Buyers in the Middle East should ensure compliance with relevant health and safety standards to meet local regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Conveyor Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for conveyor types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Food processing and packaging | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity | High |
| Plastic | Light-duty and modular applications | Chemical resistance and modularity | Less durable than metal | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Hygienic applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost and weight | High |
This comprehensive analysis of materials for conveyor systems provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for conveyor types
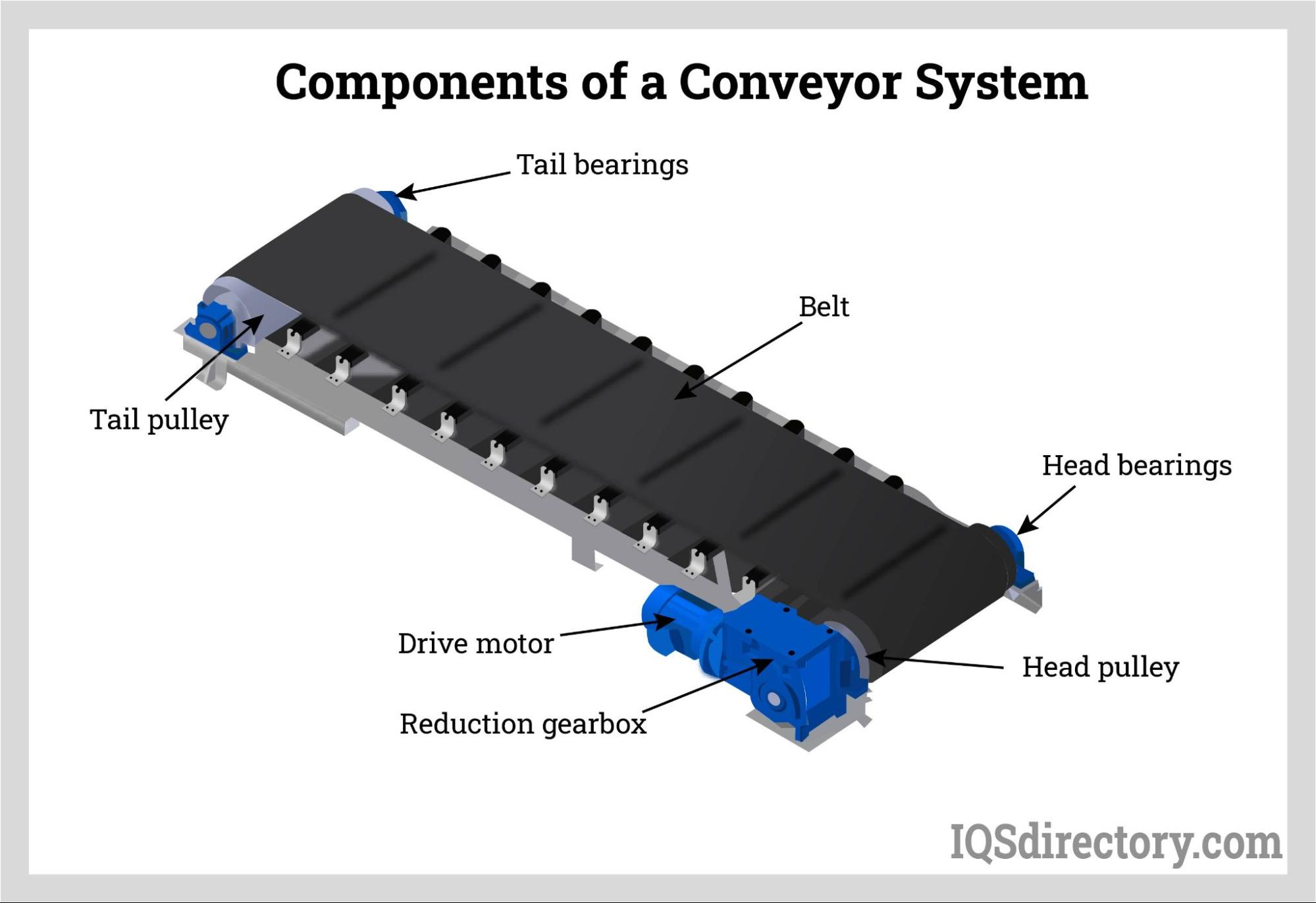
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Conveyor Types?
The manufacturing process for conveyors is multifaceted and involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring a high-quality final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step in conveyor manufacturing is material preparation, which involves selecting appropriate raw materials such as steel, aluminum, or plastics. The choice of material is often dictated by the specific requirements of the conveyor, including load capacity, environmental conditions, and the type of products being transported. Once selected, materials undergo processes such as cutting, bending, and machining to achieve the desired dimensions and specifications.
Forming Techniques Used in Conveyor Manufacturing
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared materials are shaped into the components that make up the conveyor. Common techniques include:
Illustrative image related to conveyor types
-
Welding: This is used to join metal components securely. Techniques such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are prevalent in fabricating conveyor frames and other structural elements.
-
Stamping and Pressing: These methods are employed for creating parts such as brackets and guides. Stamping can produce high volumes of identical parts quickly and accurately.
-
Injection Molding: For conveyors that include plastic components, injection molding is a vital technique. This process allows for the creation of complex shapes and is often used in manufacturing rollers or slats.
Assembly Process for Different Conveyor Types
Following forming, the assembly stage involves the integration of all components into a functional conveyor system. This may include:
-
Mechanical Assembly: Components like rollers, belts, and chains are assembled using screws, bolts, and other fasteners. Precision is crucial here to ensure the system operates smoothly.
-
Electrical Assembly: For motorized conveyors, electrical components such as motors, sensors, and control systems are integrated. Proper wiring and configuration are essential for the conveyor’s operational efficiency.
-
Testing During Assembly: As components are assembled, preliminary testing may be conducted to ensure alignment, movement, and functionality before the final assembly is completed.
Finishing Processes and Their Importance
The final stage of conveyor manufacturing is finishing, which serves both functional and aesthetic purposes. This can include:
-
Surface Treatment: Processes such as powder coating or galvanizing are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and durability, especially important for conveyors used in harsh environments.
-
Quality Inspection: Before dispatch, conveyors undergo a thorough inspection to confirm compliance with specifications. This includes checking for structural integrity, alignment, and functionality.
How Do Quality Assurance Practices Ensure Conveyor Reliability?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of conveyors, ensuring that products meet both international standards and specific customer requirements. Key aspects of QA include adherence to international standards, established checkpoints, and testing methods.
What International Standards Apply to Conveyor Manufacturing?
Several international standards guide the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for conveyors:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including conveyor manufacturing. It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, conveyors must meet specific safety, health, and environmental protection requirements to receive CE marking, which is crucial for market access.
-
API Standards: For conveyors used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that equipment meets stringent safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This ongoing inspection occurs during the manufacturing stages. It involves monitoring processes such as welding and assembly to detect any issues early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive evaluation of the finished product is performed, including functional tests and inspections for defects.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Conveyor Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of conveyors:
-
Load Testing: Conveyors are subjected to weight loads that simulate actual operating conditions to ensure structural integrity and functionality.
-
Operational Testing: This involves running the conveyor through its full range of motion to check for proper alignment, speed, and responsiveness.
-
Environmental Testing: For conveyors designed for specific environments (e.g., extreme temperatures or humidity), environmental tests ensure they can withstand these conditions without failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to mitigate risks. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. Look for certifications and compliance with ISO 9001 or similar standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certifications.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product quality.
What Are the Unique QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing conveyors internationally, buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may be complicated by language differences. Clear, concise, and standardized documentation can help alleviate misunderstandings.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Expectations regarding quality and compliance may vary by region. Buyers should establish clear communication with suppliers about their quality requirements from the outset.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices specific to conveyor types, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs. This due diligence is critical for maintaining productivity and efficiency in their own operations.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘conveyor types’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing conveyor types, this practical guide outlines essential steps for a successful procurement process. Understanding your specific requirements and the capabilities of potential suppliers can lead to improved efficiency and productivity in your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements for your conveyor system based on your operational needs. Consider factors such as the type of materials to be transported, weight capacity, speed requirements, and any space constraints. This clarity helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures they can provide suitable options.
- Material Types: Identify whether you need a conveyor for bulk materials, packaged goods, or heavy machinery.
- Space Limitations: Measure the area where the conveyor will be installed to determine if a floor or overhead system is more appropriate.
Step 2: Research Conveyor Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of conveyors available in the market, including belt, roller, chain, and overhead systems. Understanding their unique features and applications will help you make informed decisions.
- Belt Conveyors: Suitable for simple transportation needs but not ideal for precise positioning.
- Overhead Conveyors: Efficient in saving floor space and useful for assembly lines.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. This step is critical to ensure that you are working with reputable companies that can meet your technical specifications and provide quality products.
- Supplier Background: Request company profiles, years in business, and market presence.
- References: Ask for case studies or testimonials from previous clients in similar industries or regions.
Step 4: Assess Compliance and Certifications
Verify that the suppliers comply with international standards and have the necessary certifications for quality and safety. This step is crucial to minimize risks associated with equipment failure or safety hazards.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
- Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality management system certifications.
- Safety Standards: Ensure compliance with local and international safety regulations applicable to conveyor systems.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Options
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes from each. This will help you compare prices, lead times, and service agreements effectively.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in pricing, including installation and maintenance costs.
- Service Agreements: Evaluate warranty options and after-sales support offered by the suppliers.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits and Demonstrations
If possible, arrange site visits to suppliers or request demonstrations of the conveyor systems. Observing the equipment in operation can provide valuable insights into performance and reliability.
- Performance Testing: Assess how well the conveyor meets your specifications during the demonstration.
- Installation Process: Understand the complexity and time required for installation.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Negotiate Terms
After evaluating all options, make your decision based on the supplier’s ability to meet your requirements and budget. Negotiate terms to ensure you get the best deal possible.
- Contract Review: Carefully review all terms and conditions before signing.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment schedules and any financing options available.
By following these steps, you can ensure a thorough and effective procurement process, leading to a conveyor system that enhances your operational efficiency and productivity.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for conveyor types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Conveyor Types?
Understanding the cost structure of conveyor systems is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects costs. For instance, a belt conveyor may require less expensive materials compared to a heavy-duty chain conveyor. High-quality materials can increase durability but also raise initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the conveyor system. Automated systems may require skilled labor for installation, which can drive up costs. Conversely, simpler systems, like gravity roller conveyors, may require less labor for setup and maintenance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running production facilities, such as utilities and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary significantly between suppliers, influencing the final pricing.
-
Tooling: The tooling required for production can also impact costs. Custom tooling for specialized conveyor designs can increase both initial and ongoing costs.
-
Quality Control: Investing in quality control processes ensures that the conveyors meet safety and operational standards, which is particularly important for international buyers who may face stricter compliance regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be substantial, especially for large systems. Factors like distance, shipping methods, and customs duties should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risk. This margin can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Conveyor Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of conveyor systems, which international B2B buyers must consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can significantly reduce the unit price. Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for companies with high throughput requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific operational needs can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for higher expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly impacts durability and maintenance costs. Additionally, certifications (e.g., ISO) may enhance reliability but can also increase the price.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial. These terms determine who bears the costs and risks during transportation, affecting the overall expenditure.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
For B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiating effectively can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational, and logistical costs over the conveyor’s lifespan. A higher initial investment might result in lower operational costs.
-
Negotiate Specifications: Be clear about necessary specifications and explore if lower-cost alternatives can meet your needs without sacrificing quality.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International transactions may involve currency fluctuations and tariffs. Be informed about these factors when negotiating prices.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing in future negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers allows for comparison and can provide leverage during negotiations.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of the cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies can empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions regarding conveyor systems. By considering these factors, buyers can optimize their investments, ensuring efficiency and productivity in their operations. Always remember that prices can vary widely based on specifications, supplier capabilities, and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing conveyor types With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Conveyor Systems
When considering the most effective solutions for material handling and product movement in industrial settings, it is essential to evaluate not only conveyor types but also alternative methods that can achieve similar objectives. In this analysis, we will compare conveyor systems against two viable alternatives: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Manual Handling Solutions. This comparison will help international B2B buyers assess which option best aligns with their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Conveyor Types | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Manual Handling Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for continuous flow; suitable for repetitive tasks. | Flexible; effective for varied paths but slower than conveyors. | Dependent on workforce; can be inconsistent. |
| Cost | Varies widely; initial investment can be high but offers long-term savings. | Moderate to high; significant upfront costs for navigation systems. | Low initial costs; ongoing labor costs can accumulate. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space and infrastructure planning; installation can be complex. | Quick to deploy; minimal infrastructure changes needed. | Simple to implement; no equipment required. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts can be expensive. | Low maintenance; however, software updates may be necessary. | Minimal maintenance; relies on workforce training. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks in fixed pathways. | Best for dynamic environments where flexibility is crucial. | Suitable for small-scale operations with light loads. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) provide a flexible alternative to traditional conveyor systems. They can navigate autonomously through a facility, adapting to changes in layout and workflows. This adaptability allows AGVs to transport materials across various paths without being tied to fixed routes. However, their initial investment can be high due to the need for sophisticated navigation technology and ongoing costs for maintenance and software updates. AGVs are best suited for environments where flexibility is paramount, such as warehouses that require frequent reconfiguration.
How Do Manual Handling Solutions Compare to Conveyor Systems?
Manual handling solutions involve human operators transporting materials using carts, trolleys, or simply by carrying items. This method has a low initial cost and is easy to implement, making it attractive for smaller operations. However, it can lead to inconsistencies in performance due to human factors, such as fatigue or errors. Additionally, relying on manual labor can increase the risk of workplace injuries and may not be sustainable for larger operations requiring high throughput. Manual handling is best suited for low-volume tasks or environments where products are too irregular for automated systems.
Making the Right Choice: Which Solution is Best for Your Business?
Choosing the right material handling solution involves assessing your specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the nature of your products. For businesses with high-volume, repetitive tasks, conveyor systems often provide the most efficient and reliable solution. In contrast, if flexibility and adaptability are more critical due to variable workflows, AGVs might be the better choice. For smaller operations or those with limited budgets, manual handling solutions could suffice, though they may not support long-term growth. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for conveyor types
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Conveyor Types?
Understanding the technical specifications of conveyors is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Conveyors are typically constructed from various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic. The material grade affects durability, corrosion resistance, and weight capacity. For example, stainless steel conveyors are ideal for food processing due to their hygienic properties, while aluminum is lighter and suitable for less demanding environments. Choosing the right material ensures that the conveyor can withstand the specific conditions of your operation, thus minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. -
Load Capacity
– This specification indicates the maximum weight a conveyor can safely transport without failure. Load capacity is critical when selecting a conveyor for heavy items like automotive parts or bulk materials. Underestimating this requirement can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and increased operational costs. Buyers should assess their products’ weight and dimensions to select a conveyor that meets their operational demands. -
Speed
– Conveyor speed, typically measured in feet per minute (FPM), dictates how quickly products can be transported. The required speed may vary based on the production process, so it’s important to choose a conveyor that can accommodate these needs without compromising product safety or quality. For instance, high-speed conveyors are essential in packaging lines, while slower conveyors may be appropriate for assembly operations. -
Belt Width
– The width of the conveyor belt is a key factor in determining its suitability for various applications. A wider belt can handle larger or multiple products, while a narrower belt may be more efficient for smaller items. Selecting the correct belt width is essential for optimizing space and ensuring a smooth flow of materials throughout the production line. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in conveyor parts. High tolerance levels are crucial in applications requiring precise positioning, such as automated loading and unloading systems. Ensuring that components meet the necessary tolerances can enhance operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of errors during production. -
Power Requirements
– Different conveyor types have varying power needs based on their design and intended use. Understanding the power requirements will aid in assessing energy consumption and operational costs. For instance, motorized roller conveyors may require specific voltage and amperage specifications to function effectively.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Conveyor Systems?
Navigating the conveyor industry requires familiarity with specific terminology. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of conveyors, this term is relevant for buyers seeking customized solutions or replacement parts, as OEM products often ensure compatibility and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it influences procurement strategies and inventory management. For conveyors, suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs and material availability. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a vital step in the purchasing process, as it helps buyers compare options and negotiate better deals. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate and competitive responses. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is critical for B2B buyers to manage shipping costs, risk, and logistics effectively. For instance, terms like FOB (Free on Board) indicate when the risk transfers from seller to buyer. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For conveyor systems, understanding lead time is crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management. Longer lead times can impact project timelines, making it essential for buyers to factor this into their purchasing decisions. -
Integration
– This term refers to the process of incorporating a new conveyor system into existing operations or production lines. Successful integration is vital for maximizing efficiency and minimizing disruptions. Buyers should consider how well a new conveyor can work with their current systems to ensure seamless operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their conveyor systems align with operational needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the conveyor types Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Conveyor Types Sector?
The conveyor types market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the expanding manufacturing and logistics sectors globally. Key factors include the increasing demand for automation in warehouses and production lines, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. As industries strive for efficiency, technologies such as Motorized Roller Conveyors and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are gaining traction. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce in South America and Europe is propelling the need for sophisticated conveyor systems to manage high volumes of goods swiftly and safely.
Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly interested in systems that support real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with existing operations. This shift towards smart manufacturing is not only enhancing productivity but also encouraging suppliers to innovate continually. As a result, international buyers are prioritizing suppliers who can provide customized solutions that align with their unique operational requirements.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Conveyor Types Industry and What Ethical Sourcing Practices Are Emerging?
Sustainability has become a central focus for B2B buyers in the conveyor types sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in conveyor systems is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek out sustainable alternatives. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or made from renewable resources. For example, conveyor systems that utilize lightweight, durable materials can reduce energy consumption during operation, aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains is gaining recognition. International buyers are increasingly conducting due diligence to ensure their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or other green certifications are becoming crucial in supplier evaluations. Buyers are looking for partners who not only meet their operational needs but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
How Has the Conveyor Types Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of conveyor systems has been marked by significant technological advancements, reflecting broader trends in industrial automation. Initially, conveyors were simple mechanical systems designed to move materials from one point to another. Over time, innovations such as powered roller conveyors and automated guided vehicles have transformed the landscape, enabling more complex operations and increasing efficiency.
The introduction of smart technology, including sensors and IoT integration, has further enhanced conveyor systems’ functionality. These advancements not only improve operational efficiency but also allow for real-time monitoring and maintenance, which is crucial for modern manufacturing and logistics operations. As a result, today’s conveyor systems are not just tools for material handling but integral components of smart factories and automated supply chains, catering to the needs of a rapidly evolving global marketplace.
In summary, B2B buyers in the conveyor types sector should stay informed about market dynamics, prioritize sustainable sourcing practices, and consider the historical context of technological evolution to make strategic procurement decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of conveyor types
-
How do I choose the right conveyor type for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate conveyor type involves assessing your specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as the weight and dimensions of the items to be transported, the required speed, and the layout of your facility. Evaluate whether a floor-mounted or overhead system is more suitable based on your space constraints. Additionally, factor in any automation needs, as some conveyors are better suited for integration with robotics or other machinery. Consulting with a conveyor specialist can help streamline this decision-making process. -
What are the most common conveyor types used in industrial settings?
The most prevalent conveyor types include belt conveyors, roller conveyors, and motorized roller conveyors. Belt conveyors are ideal for transporting lightweight items, while roller conveyors excel in moving heavier loads. Motorized roller conveyors offer advanced features like zero pressure accumulation, making them suitable for high-speed operations. Each type serves unique functions, so understanding the specific requirements of your production line is crucial to selecting the best option. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing conveyor systems internationally?
When sourcing conveyor systems from international suppliers, it’s essential to consider factors such as compliance with local regulations, import duties, and shipping logistics. Ensure the supplier has a reliable track record and can provide appropriate documentation, including quality certifications. Communication is key; verify that the supplier can meet your specifications and timelines. It may also be beneficial to request samples or visit the manufacturing facility, if possible, to assess their capabilities firsthand. -
How can I vet potential suppliers for conveyor systems?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from previous clients. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Request references and follow up with past customers to gauge satisfaction levels. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness and willingness to customize solutions based on your specific needs, which is vital for a successful partnership. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for conveyor systems?
Minimum order quantities for conveyor systems can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of conveyor. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for standard conveyors to larger quantities for customized systems. It’s advisable to discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing conveyor systems?
Payment terms for conveyor systems can differ among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits, progress payments, and final payments upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans, especially for larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing the purchase to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure that all payment arrangements are documented in the contract. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my conveyor systems?
To guarantee quality assurance, establish clear specifications and requirements before placing an order. Request detailed documentation of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures from your supplier. Conduct inspections at various stages of production, if possible, or arrange for third-party inspections. Additionally, consider implementing a warranty clause to protect against defects or performance issues post-delivery. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing conveyor systems?
When importing conveyor systems, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Determine the most cost-effective shipping option while ensuring timely delivery. Factor in potential delays due to customs processes and prepare all necessary documentation for importation. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can help navigate these complexities and ensure a smooth delivery process to your facility.
Top 2 Conveyor Types Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ultimation – Conveyor Solutions
Domain: ultimationinc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Conveyor Types: 1. Belt Conveyors – Simple, moves parts from one end to another, variable speed, not for precise positioning or buffering. 2. Gravity Roller Conveyor – Affordable, uses rollers on a decline for self-movement, simple productivity improvement. 3. Chain Conveyors – Floor mounted, ideal for heavy items, carries pallets and large containers, slow speeds. 4. Live Roller Conveyor / Chain …
2. Exotec – Skypod System & Skypath Conveyors
Domain: exotec.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Exotec Skypod system and Skypath automated conveyors.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for conveyor types
In conclusion, the diverse range of conveyor types—each with unique functionalities—offers significant advantages for optimizing production processes. By strategically sourcing the right conveyor system, international B2B buyers can enhance operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve workplace safety. Key considerations include understanding the specific needs of your production line, evaluating available space, and determining the most suitable conveyor style, whether floor-mounted or overhead.
As businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to modernize their operations, investing in the right conveyor technology is crucial. The flexibility of conveyor systems allows for seamless integration with automated solutions, making them invaluable in today’s fast-paced industrial environment.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced conveyor solutions will continue to grow as industries evolve. Buyers are encouraged to explore innovative options and partner with reliable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet their unique requirements. Embrace the future of industrial efficiency—invest in the right conveyor system today to unlock the full potential of your production capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to conveyor types