Is Your Chevron Belt Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for chevron belt
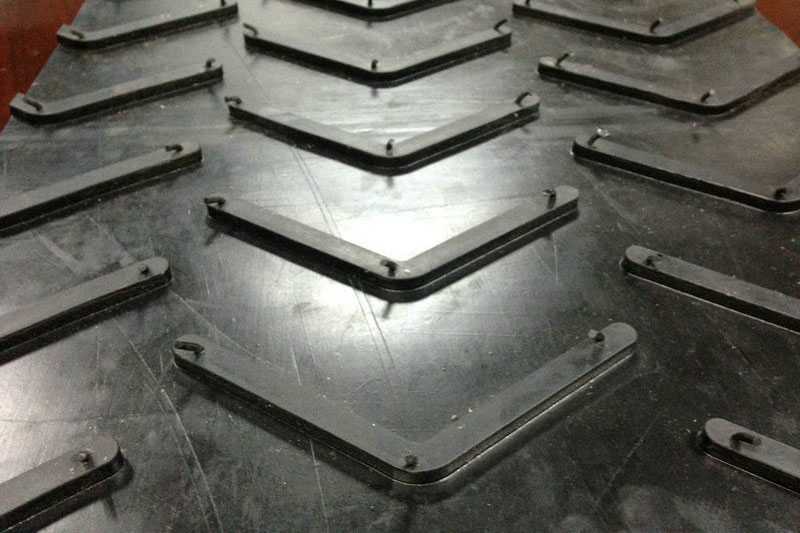
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, sourcing the right chevron belt can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers across various industries. These specialized conveyor belts, designed with cleated surfaces to transport loose and wet materials up steep inclines, are crucial for operations in sectors such as mining, agriculture, and construction. The complexity of selecting the appropriate chevron belt—from understanding different profiles and materials to assessing the specific needs of your application—can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria. It delves into various types of chevron belts, their diverse applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting. Additionally, the guide provides insights into cost factors and best practices for maintenance, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
By navigating through this guide, you will gain a deeper understanding of how to effectively evaluate and select chevron belts that not only meet your operational requirements but also enhance productivity and efficiency in your business. Whether you are looking to optimize material handling or ensure reliable performance in challenging environments, this guide empowers you with the knowledge needed to secure the best solutions for your specific needs.
Understanding chevron belt Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Profile | 16 mm height, suitable for powdery materials | Agriculture (grains), cement works | Pros: Good for fine materials; Cons: Limited incline capability (max 25°). |
| AH Profile | 25 mm height, improved grip for loose materials | Sandpits, quarries | Pros: Better performance on inclines; Cons: May not suit very heavy loads. |
| F Profile | 32 mm height, ideal for sticky and packed materials | Recycling, heavy-duty scrap metal | Pros: High inclination (up to 40°); Cons: Heavier, may increase wear on equipment. |
| AF Profile | 32 mm height, optimized for material flow | Mining, aggregate transport | Pros: Enhanced tension distribution; Cons: Requires precise installation for best performance. |
| Custom Chevron | Tailored design for specific needs | Diverse industries, including food and recycling | Pros: Flexible design; Cons: Longer lead times for customization. |
What are the Characteristics of A Profile Chevron Belts?
The A Profile chevron belt features a cleat height of 16 mm, making it suitable for conveying fine, powdery materials such as flour and lime. Its design allows for a maximum incline of 25 degrees, making it a practical choice for agricultural applications and cement works. When considering this option, buyers should assess the material characteristics and the incline of their conveyor systems, as its limited height may not be sufficient for heavier or bulkier items.
How Does the AH Profile Differ from Other Chevron Belts?
The AH Profile chevron belt has a 25 mm height and is designed to handle loose, flowing materials effectively, such as sand and gravel. This belt can accommodate inclines of up to 28 degrees, providing enhanced grip and stability compared to the A Profile. Buyers should evaluate the specific material types and operational conditions, as its improved performance on inclines can lead to increased productivity in sandpits and quarries.
What Makes F Profile Chevron Belts Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
F Profile chevron belts feature a robust 32 mm height, making them ideal for sticky and packed materials, including wet sand and heavy scrap metals. With a maximum incline capability of 40 degrees, these belts excel in demanding environments like recycling and heavy-duty transport. Buyers should consider the potential for increased wear on equipment due to the belt’s weight and the nature of the materials being conveyed, ensuring that their systems can accommodate this robust option.
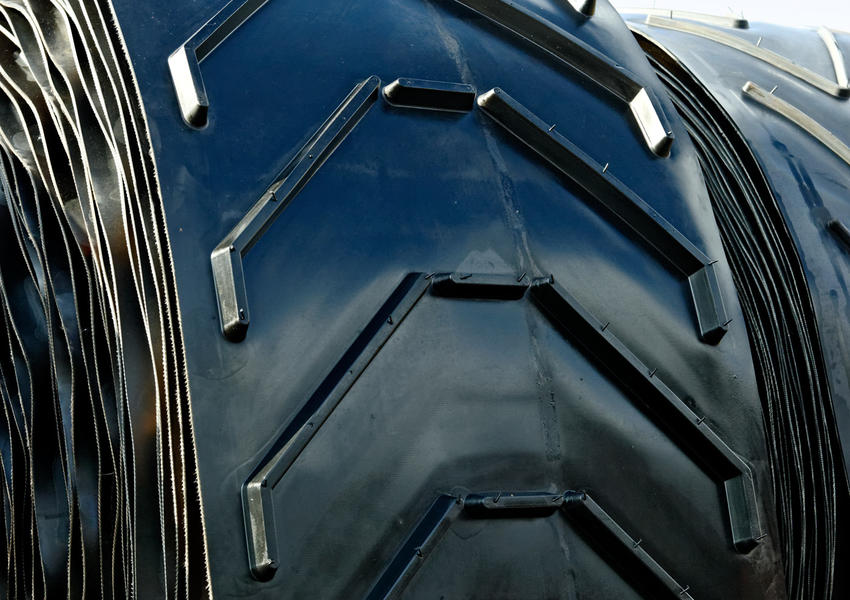

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Why Choose AF Profile Chevron Belts for Optimal Material Flow?
The AF Profile chevron belt, also with a 32 mm height, is engineered to promote optimal material flow, making it suitable for mining and aggregate transport. It features improved tension distribution and is designed to minimize vibration during operation. Buyers should focus on the specifics of their material handling needs, as this belt requires precise installation to maximize its performance benefits and reduce potential downtime.
How Can Custom Chevron Belts Enhance Operational Efficiency?
Custom chevron belts offer tailored solutions to meet unique operational requirements across various industries, including food processing and recycling. With the ability to modify cleat height, pattern, and materials, these belts can address specific challenges in material handling. While customization provides flexibility, buyers should be mindful of longer lead times and the necessity for detailed specifications to ensure that the final product meets their operational demands effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of chevron belt
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Chevron Belt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining and Quarrying | Transporting loose aggregates like gravel and sand | Efficient material handling at steep angles, reducing spillage | Durability, cleat height, and material compatibility are crucial. |
| Agriculture | Conveying grains, fertilizers, and root crops | Increased productivity and reduced material loss | Customization for specific crop types and moisture conditions. |
| Waste Management | Moving waste materials in recycling facilities | Enhanced efficiency in waste processing, reducing handling time | Resistance to wear and tear, along with drainage features. |
| Construction | Handling heavy materials like cement and asphalt | Improved safety and operational efficiency on-site | Consideration of incline angles and belt strength for heavy loads. |
| Food Processing | Transporting bulk food items like sugar and potatoes | Compliance with hygiene standards and efficient handling | Food-grade materials and customization for specific food types. |
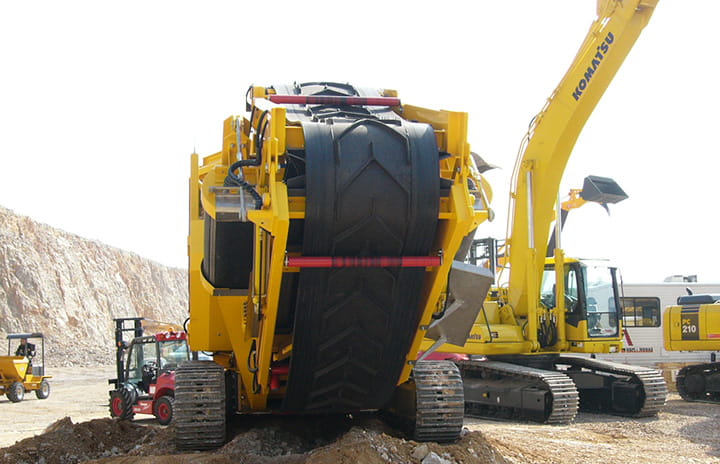
How is Chevron Belt Used in Mining and Quarrying?
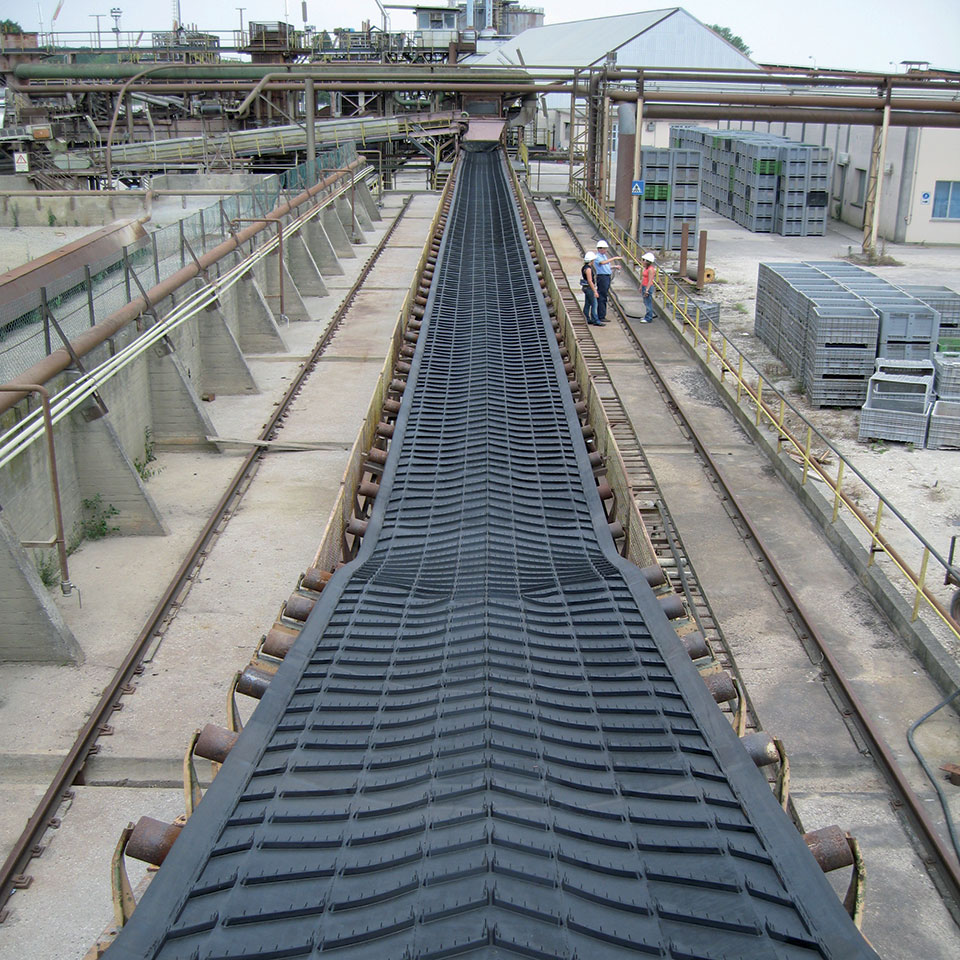
In the mining and quarrying sectors, chevron belts are essential for transporting loose aggregates such as gravel and sand up steep inclines. These belts feature raised cleats that prevent material rollback, ensuring a consistent flow of resources. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable belts that can withstand harsh conditions is critical. Buyers should consider the cleat height and the belt’s ability to handle various material sizes to optimize their operations.
What Role Does Chevron Belt Play in Agriculture?
Chevron belts are widely utilized in agriculture for transporting grains, fertilizers, and root crops. Their design allows for efficient handling of materials on inclines, reducing spillage and maximizing throughput. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must ensure that the belts are customized to cater to specific crop types and moisture levels, as these factors can significantly affect performance. The adaptability of the belt to different agricultural applications is a key consideration for sourcing.
How is Chevron Belt Beneficial in Waste Management?
In the waste management industry, chevron belts are critical for moving waste materials in recycling facilities. Their design enhances efficiency by keeping materials in place, minimizing handling time and labor costs. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, sourcing belts that are resistant to wear and tear while providing drainage features is essential. These attributes ensure that operations run smoothly, reducing downtime and maintenance needs.
Why is Chevron Belt Important in Construction?
In construction, chevron belts are employed to handle heavy materials such as cement, asphalt, and aggregates. Their ability to transport materials at steep angles improves safety and operational efficiency on-site. For buyers in Europe and Africa, it is vital to consider the incline angles and belt strength, as these factors directly influence the belt’s performance under heavy loads. Customization options can further enhance functionality, catering to specific construction needs.
How is Chevron Belt Used in Food Processing?
Chevron belts are increasingly used in food processing for the transportation of bulk food items, including sugar and potatoes. These belts meet stringent hygiene standards while facilitating efficient handling. International buyers, especially from regions like South America and Africa, should prioritize sourcing food-grade materials that can be tailored to specific food types. This customization ensures compliance with food safety regulations and enhances operational efficiency in processing facilities.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘chevron belt’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Material Rollback on Inclines
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as construction and mining often face the challenge of transporting loose materials up steep inclines. Traditional flat conveyor belts may not provide the necessary grip, resulting in material rollback and loss. This not only disrupts operations but can also lead to increased labor costs due to manual retrieval efforts and potential damage to equipment. Buyers need a solution that ensures the efficient transport of materials without the risk of spillage or downtime.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, sourcing chevron belts specifically designed for steep inclines is crucial. When selecting a chevron belt, consider the profile height and angle of inclination suited for your specific materials. For instance, profiles with a height of 25 mm or more are ideal for heavier materials like gravel and coal. Additionally, ensure that the cleats are designed to prevent rollback effectively. Opt for custom solutions if your materials or incline angles are unique, as this can significantly enhance performance. Consulting with suppliers who offer tailored chevron designs will also allow you to account for specific factors like moisture content and material shape, ensuring optimal functionality.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Material Spillage During Transport
The Problem: Material spillage is a common concern for B2B buyers, particularly in waste management and recycling sectors. When transporting loose materials, especially on inclined surfaces, even the slightest misalignment or inadequate belt design can lead to spillage. This not only creates safety hazards but also results in financial losses due to wasted materials and increased cleanup costs. Buyers need to ensure that their conveyor systems are optimized to minimize the risk of spillage during operation.
The Solution: One effective strategy to combat spillage is to choose chevron belts with proper cleat designs and spacing that allow for effective containment of materials. For example, selecting belts with open-V patterns can facilitate drainage, reducing the likelihood of accumulation and subsequent spillage. Additionally, consider integrating skirting systems that direct material towards the center of the conveyor. This not only prevents spillage but also enhances overall efficiency. Regular maintenance and alignment checks of the conveyor system can also help ensure that the belts remain properly tensioned and aligned, further reducing the risk of material loss.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Belt Performance Leading to Downtime
The Problem: Inconsistent performance of chevron belts can lead to significant operational downtime, frustrating B2B buyers who rely on continuous material flow for their operations. Factors such as improper material selection, inadequate cleat height, or poor-quality manufacturing can cause belts to wear quickly or fail unexpectedly. This unpredictability can result in costly repairs and interruptions in production, impacting overall profitability and operational efficiency.
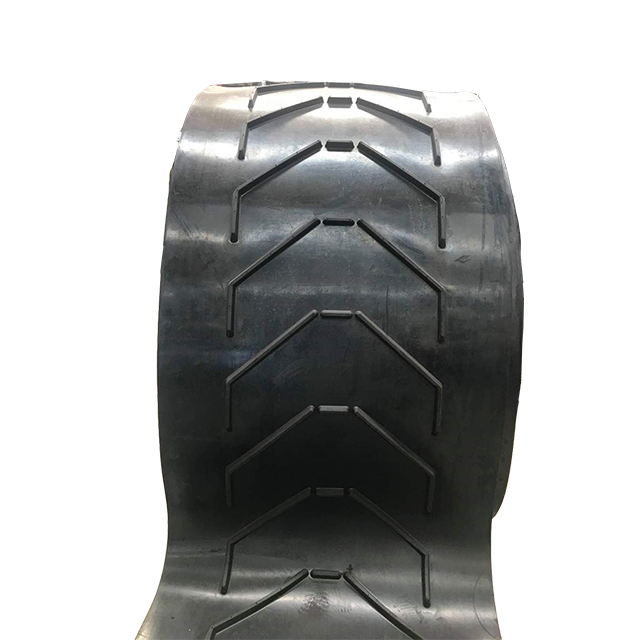

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with inconsistent belt performance, it is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of your operational requirements before purchasing chevron belts. Collaborate with manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and performance data for their products. Assess the type of materials being transported, the expected incline angles, and the environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, moisture) that may affect belt performance. Investing in high-quality, custom-designed belts made from durable materials can significantly enhance longevity and reliability. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule to inspect belts for wear and tear will help identify potential issues before they escalate, ultimately reducing downtime and maintaining smooth operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for chevron belt
When selecting materials for chevron belts, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance requirements of each material. The choice of material can significantly impact the belt’s durability, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in chevron belt manufacturing.
What are the Key Properties of Rubber in Chevron Belts?
Rubber is one of the most widely used materials for chevron belts due to its excellent elasticity and durability. High-grade rubber compounds, such as SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) and EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), provide resistance to wear, abrasion, and certain chemicals. The temperature rating for rubber belts typically ranges from -40°C to 100°C, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros: Rubber belts are highly durable and can withstand heavy loads, making them ideal for applications in construction and waste management. They are also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: While rubber has excellent flexibility, it may not perform well in extremely high-temperature environments or in the presence of certain solvents.
Impact on Application: Rubber chevron belts are commonly used in the transportation of bulk materials like sand, gravel, and coal. Their ability to conform to different shapes and surfaces enhances material handling efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider local climate conditions, as rubber can degrade faster in extreme temperatures.
How Does PVC Affect the Performance of Chevron Belts?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another popular material for chevron belts, particularly in applications requiring chemical resistance. PVC belts can withstand a range of temperatures, typically from -10°C to 60°C, and they offer good resistance to oils and greases.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Pros: PVC is lightweight and cost-effective, making it suitable for lighter applications. It also has a smooth surface that reduces friction, enhancing the efficiency of material transfer.
Cons: PVC belts may not be as durable as rubber belts and can be prone to cracking under heavy loads or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: PVC chevron belts are often used in food processing, agriculture, and packaging industries, where chemical resistance is a priority.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PVC belts meet food safety standards if used in food applications. Additionally, understanding regional regulations regarding PVC use is essential.
What Advantages Do Polyurethane Belts Offer for Chevron Applications?
Polyurethane is known for its superior abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it an excellent choice for chevron belts in demanding environments. These belts can typically handle temperatures ranging from -30°C to 80°C.
Pros: Polyurethane belts have a longer lifespan than rubber and PVC, reducing the frequency of replacements. They also offer excellent tear resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The initial cost of polyurethane belts is generally higher than that of rubber or PVC, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: These belts are ideal for industries such as recycling, mining, and heavy manufacturing, where durability and performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards and consider the specific environmental conditions of their operational areas, as polyurethane may not be suitable for extreme heat.
How Does Steel Reinforcement Enhance Chevron Belt Performance?
Steel-reinforced chevron belts combine the benefits of rubber or PVC with the strength of steel. This construction allows for higher load capacities and increased durability, making them suitable for the most demanding applications.
Pros: Steel reinforcement significantly enhances the belt’s tensile strength and resistance to elongation, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing steel-reinforced belts can lead to higher costs and longer lead times.
Impact on Application: These belts are commonly used in industries such as mining, construction, and bulk material handling, where high strength and durability are paramount.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the steel used meets relevant standards and specifications, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Chevron Belts
| Material | Typical Use Case for chevron belt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Sand, gravel, coal transportation | High durability and flexibility | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| PVC | Food processing, agriculture | Lightweight and cost-effective | Prone to cracking under heavy loads | Low |
| Polyurethane | Recycling, mining, heavy manufacturing | Superior abrasion and tear resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Steel Reinforced | Mining, construction, bulk material handling | Enhanced tensile strength and durability | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
Selecting the right material for chevron belts requires careful consideration of the application, environmental conditions, and compliance with relevant standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material type, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for chevron belt
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Chevron Belts?
The manufacturing process of chevron belts involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the durability and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing chevron belts.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Chevron Belt Production?
The foundation of a high-quality chevron belt lies in the selection of materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade rubber compounds that exhibit excellent wear resistance and flexibility. Common materials include Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which offers good tensile strength and elongation properties, and Ethylene-Propylene-Diene Monomer (EPDM) for applications requiring heat and ozone resistance.
In addition to rubber, textile reinforcements, such as polyester or nylon, are often integrated to enhance the belt’s strength and load-bearing capacity. Manufacturers may also incorporate specialized additives to improve the belt’s performance in specific environments, such as oil resistance for heavy-duty applications.
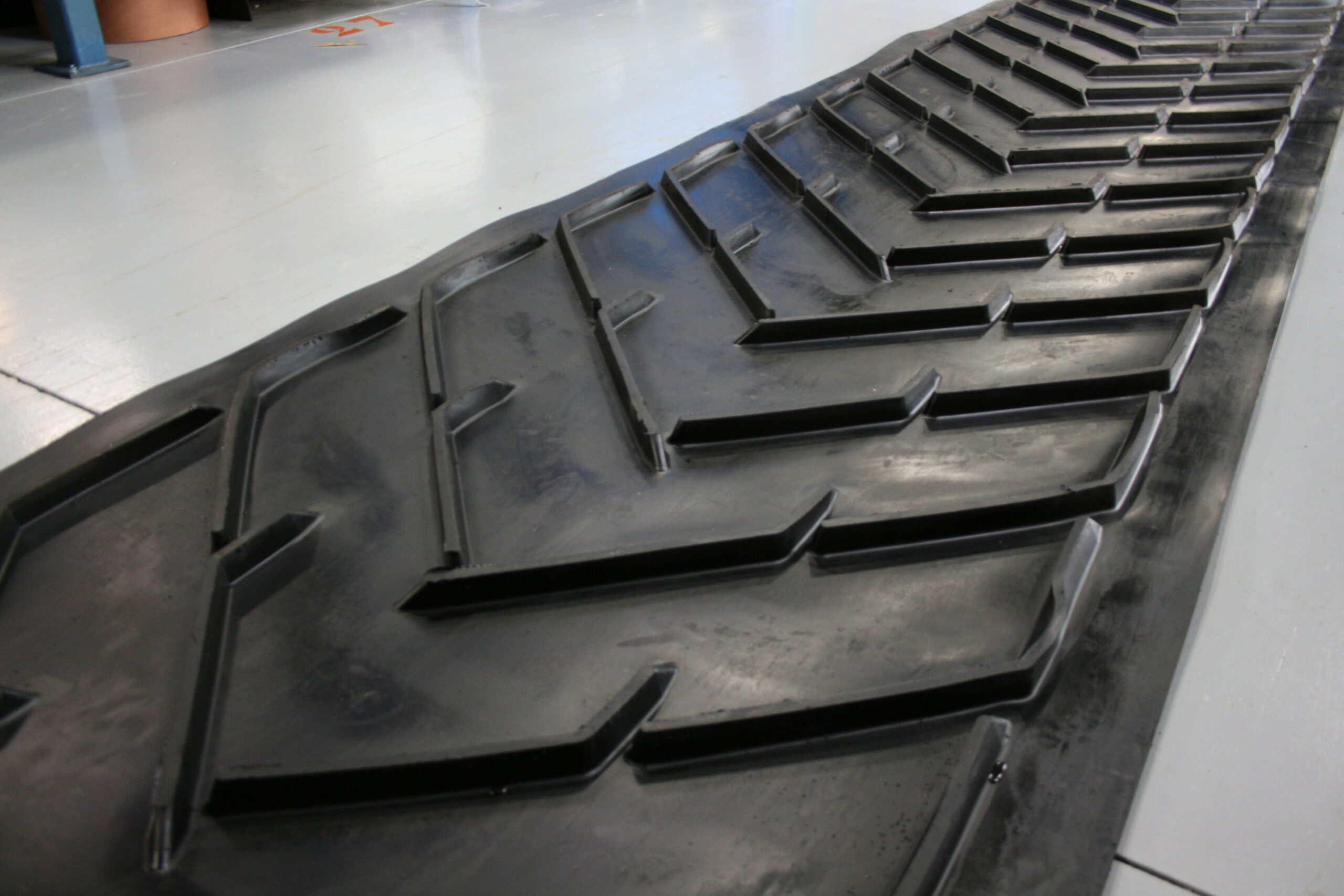
Forming: How Are Chevron Patterns Created?
The next step involves forming the chevron patterns, which are essential for the belt’s ability to transport materials at steep angles. This is achieved through a process known as vulcanization, where rubber is heated and cured to create a solid, cohesive structure.
During this phase, manufacturers utilize molds to create the specific chevron designs, which can vary in height and shape based on the intended application. Common profiles include A, AH, and F types, with varying cleat heights tailored for different materials and incline angles. The precision of this process is crucial, as any inconsistency can lead to material spillage or ineffective conveying.
Assembly: How Are Chevron Belts Assembled?
Once the cleats are formed, the assembly stage involves attaching them to the base belt. This process often employs a patented heat-cured bonding technique, ensuring that the cleats are securely affixed to the belt surface. This method not only enhances the durability of the bond but also allows for a seamless transition when materials are conveyed.
Manufacturers may also customize the belts during this stage, considering factors such as width, length, and specific cleat patterns to meet the unique requirements of their clients. This customization is particularly beneficial for B2B buyers seeking solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
Finishing: What Quality Checks Are Conducted Post-Production?
The final stage of manufacturing includes various finishing processes, such as trimming, surface treatment, and inspection. This is where manufacturers ensure that the belts meet the established specifications and performance standards. The finishing phase may also involve additional treatments, such as anti-static or flame-retardant coatings, depending on the application.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented for Chevron Belts?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process for chevron belts, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Apply to Chevron Belts?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European safety and environmental regulations, are essential for B2B buyers operating in various regions.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these certifications can provide insight into the reliability and safety of the products they are sourcing.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet the required specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the production process and to identify any deviations from standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the belts are completed, a comprehensive inspection is carried out to verify that the final products meet all quality and performance criteria.
These QC checkpoints help ensure that any potential issues are identified and rectified before the products reach the market.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to evaluate the performance and durability of chevron belts. Common tests include:
- Tensile Strength Testing: Assesses the maximum load the belt can withstand without breaking.
- Abrasion Resistance Testing: Measures how well the belt can endure wear and tear during operation.
- Flexural Testing: Evaluates the belt’s flexibility and ability to withstand bending over time.
- Cleat Adhesion Testing: Ensures that the cleats remain securely bonded to the belt during operation.
These tests provide valuable data that can help B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of the belts they are considering.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are several approaches buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess the production processes, QC measures, and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers can request documentation detailing the QC processes and testing results. This information can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and product quality, enhancing trust in the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Certifications Verification: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold the necessary certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) and ensure these are current and relevant to their industry.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various regulations and standards that may differ significantly by region. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE compliance, while those in Africa or South America may focus on local certifications that align with their regulatory environments.
Understanding these nuances is essential for ensuring compliance and mitigating risks associated with sourcing materials globally. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to establish clear communication regarding quality standards and certification requirements to facilitate a smooth procurement process.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for chevron belts are integral to ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, fostering successful partnerships with suppliers across different regions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘chevron belt’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides a systematic approach for B2B buyers looking to procure chevron belts. Chevron belts are essential for transporting materials efficiently, especially on inclines. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you select the right product and supplier for your specific needs, maximizing performance and minimizing risks.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical requirements of your application is critical. Determine the type of materials you will be transporting, the maximum incline angle, and the environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, temperature) that the belt will be exposed to. This will help in selecting the appropriate belt profile and material composition.
- Material Types: Identify if you need a belt for powdery, loose, or sticky materials as this will dictate the cleat height and profile design.
- Incline Angle: Specify the steepness of the incline where the belt will be used to ensure the selected belt can handle the load without material rollback.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers in the market. Look for companies that specialize in chevron belts and have a proven track record in your industry.
- Industry Reputation: Check online reviews, testimonials, and case studies from similar sectors to gauge supplier reliability.
- Product Range: Ensure that the supplier offers a variety of belt types and custom options to meet your specific needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a purchase, verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure that the products meet industry standards and regulations.
- Quality Assurance: Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates that the supplier follows stringent quality management practices.
- Material Safety: Ensure compliance with safety standards relevant to your region or industry, particularly for belts used in food or hazardous material transport.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Always request samples or prototypes of the chevron belts you are considering. Testing the belt in your operational environment will provide valuable insights into its performance.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate how well the sample handles the material types and incline angles specified in your requirements.
- Fit and Compatibility: Ensure that the belt fits seamlessly with your existing conveyor systems, including idler types and skirting requirements.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a potential supplier, discuss and negotiate terms such as pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty conditions. Clear communication during this phase can prevent misunderstandings later.
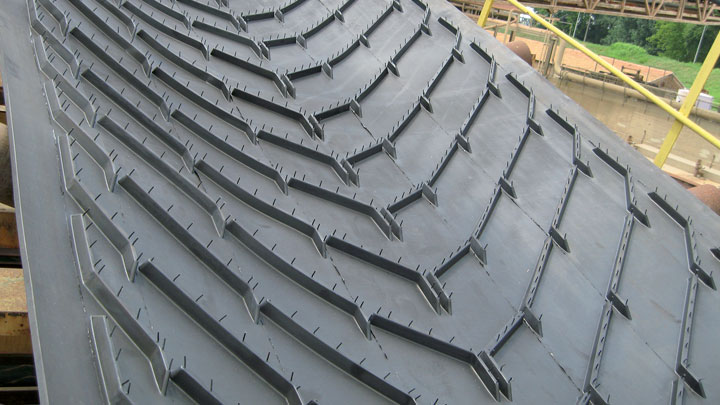

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
- Bulk Pricing: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Warranty and Support: Understand the warranty terms and the supplier’s policy on post-purchase support and maintenance.
Step 6: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After negotiating terms, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, terms, and conditions are documented.
- Clarity on Deliverables: Include detailed descriptions of the belts, delivery schedules, and payment terms to avoid potential disputes.
- Contingency Plans: Discuss what will happen in case of delays or product defects to ensure you have a plan in place.
Step 7: Monitor Installation and Performance
After receiving the chevron belts, oversee the installation process and monitor their performance closely in the initial phase. This will help identify any potential issues early on.
- Installation Checks: Ensure that the belts are installed correctly and that any necessary adjustments are made for optimal performance.
- Performance Review: Regularly evaluate the belt’s performance against your operational goals to ensure it meets your expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing chevron belts, ensuring a successful procurement process that meets their operational needs.
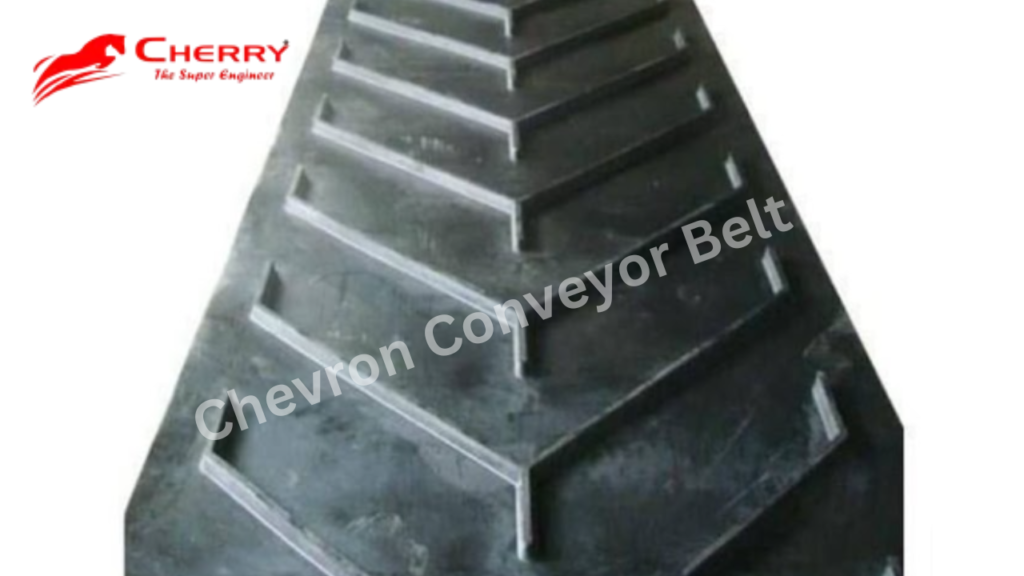

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for chevron belt Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Chevron Belt Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of chevron belts is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: High-grade rubber compounds and specialized cleat designs significantly influence material costs. The choice between standard and premium materials, such as oil-resistant or heat-resistant variants, can lead to price variations.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for the manufacturing process, especially when customizations are involved. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region, with manufacturers in countries with lower labor costs offering more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient operations can minimize overhead, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific chevron designs or sizes can add to upfront costs. This is particularly relevant for buyers requiring unique specifications or large-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each belt meets rigorous standards involves QC processes, which can contribute to overall costs. Certifications such as ISO or industry-specific standards can further influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and customs duties, are critical, especially for international buyers. The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect the final landed cost.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Chevron Belt Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable terms for MOQs can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized belts tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can enhance performance but will also raise prices. Buyers should assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) versus initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and customer service from suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and service quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) can significantly impact the total cost. Buyers should understand the implications of these terms on shipping responsibilities and costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Chevron Belts?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms with suppliers. Discussing volume discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules can lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Assess maintenance, operational costs, and the lifespan of the belts. Higher upfront costs may lead to lower long-term expenses if they result in enhanced performance and durability.
-
Regional Considerations: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions can help in finding competitive suppliers. Consideration of local sourcing versus importing can also affect logistics costs.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service. Consider long-term partnerships to negotiate more favorable terms.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
Buyers should be aware of the following nuances when sourcing chevron belts:
-
Indicative Prices: Pricing can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Always request detailed quotes that outline all potential costs.
-
Market Trends: Keep an eye on market conditions, such as fluctuations in raw material prices and changes in demand, which can affect pricing.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the suppliers comply with local regulations, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs and delays.
By understanding these elements, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing chevron belt With Other Solutions
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses are constantly seeking efficient and effective solutions for material handling and transport. Chevron belts are a popular choice for their ability to convey loose materials at steep angles, but they are not the only option available. This section explores viable alternatives, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Chevron Belt | Modular Belt System | Flat Belt Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for steep inclines, effective at preventing rollback | Versatile, can adapt to various materials and applications | Good for horizontal transport, less effective on inclines |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Higher upfront cost, but potential for lower long-term maintenance | Generally lower cost, but may require additional support structures |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires proper setup and alignment | Can be more complex to install, but modularity allows for flexibility | Straightforward installation, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed for wear and tear | Low maintenance, easy to replace individual modules | Moderate maintenance; wear can be an issue with high loads |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for mining, agriculture, and recycling operations | Suitable for diverse applications including food processing and packaging | Best for continuous, flat transport of bulk materials |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Modular Belt System?
Modular belt systems are gaining popularity due to their adaptability and ease of maintenance. These systems consist of interlocking plastic modules that can be configured to fit various layouts. The primary advantage is their flexibility; they can be designed to handle different materials and incline angles. However, the initial investment can be higher than traditional chevron belts, and installation may require more technical expertise. Despite this, their long-term durability and low maintenance needs make them a worthy consideration for many businesses.
How Does a Flat Belt Conveyor Compare?
Flat belt conveyors are the traditional choice for transporting materials over short distances, especially in horizontal applications. They are generally less expensive and easier to install, making them a common option for many industrial settings. However, they struggle with steep inclines and loose materials, which can lead to material spillage and inefficiency. While they may suit operations requiring horizontal transport, they are not ideal for applications where steep angles or bulk materials are involved.
What Should B2B Buyers Consider When Choosing a Material Handling Solution?
When selecting a material handling solution, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific operational needs, including the type of materials being transported, the layout of their facilities, and their budget constraints. While chevron belts excel in steep incline scenarios, alternatives like modular belt systems offer flexibility and adaptability, making them suitable for diverse applications. Flat belt conveyors, although more cost-effective, may not meet the needs of operations that require handling loose materials or operate on inclines.
In conclusion, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each solution will empower buyers to select the most appropriate option for their operational requirements. By carefully analyzing performance metrics, costs, and maintenance needs, businesses can optimize their material handling processes and enhance overall productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for chevron belt
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Chevron Belts?
When selecting a chevron belt for industrial applications, understanding its technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance and durability. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Chevron belts are typically made from high-grade rubber compounds, such as SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) or EP (Polyester), which provide flexibility, heat resistance, and durability. The material grade affects the belt’s longevity and its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring that the belt can handle the specific materials being conveyed without premature wear.
2. Cleat Profile and Height
The cleat design, which can vary in profile and height (commonly ranging from 16mm to 32mm), is vital for preventing material rollback on inclines. Different profiles, such as A, AH, F, and AF, are engineered for various applications and material types. Understanding the appropriate cleat profile helps buyers choose a belt that maximizes efficiency in material handling.
3. Maximum Incline Angle
Each chevron belt type has a specified maximum incline angle, typically between 20° and 40°, depending on the material being transported. This specification is critical for B2B buyers to consider, as it directly impacts the belt’s operational capacity and the design of the conveyor system. Selecting a belt with the right incline capability can enhance productivity and minimize material spillage.
4. Belt Width and Customization Options
Chevron belts come in various widths, usually ranging from 350mm to 2000mm. Customization options allow for adjustments based on the specific requirements of the application, including width and cleat design. B2B buyers should assess the available dimensions to ensure compatibility with existing equipment and operational needs.
5. Tensile Strength and Elongation
Tensile strength indicates the maximum load the belt can handle before failing, while elongation refers to how much the belt can stretch under load. High tensile strength and favorable elongation properties are essential for demanding applications, such as mining or heavy material handling. Buyers should prioritize these specifications to avoid costly downtime and maintenance issues.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Chevron Belt Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to chevron belts:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of chevron belts, understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure compatibility with their existing machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For chevron belts, this term is crucial for buyers to consider when planning inventory and procurement strategies, especially for large-scale operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products. Including detailed specifications for chevron belts in an RFQ ensures that suppliers can provide accurate quotes, helping buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers in different regions, as they dictate shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities.

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For chevron belts, shorter lead times can be critical for maintaining production schedules, making this a key factor for buyers when selecting suppliers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right chevron belt for their specific applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the chevron belt Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Chevron Belt Sector?
The global market for chevron belts is experiencing significant growth, driven by an increasing demand across various industries, including construction, agriculture, and recycling. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek efficient material handling solutions, the importance of high-performance chevron belts cannot be overstated. Key trends include the customization of belt designs to accommodate specific materials and incline angles, reflecting a shift towards tailored solutions that enhance operational efficiency.
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing technology are enabling the production of belts with improved durability and flexibility, allowing for better performance in challenging environments. For instance, new vulcanization techniques are enhancing the bonding of cleats to the base belt, thereby increasing longevity and reliability. The rise of automation in industrial settings is also pushing demand for chevron belts that can effectively transport bulk materials at steep angles, further underscoring their critical role in modern supply chains.
International buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing strategies that prioritize quality and performance, leveraging technology to analyze supplier capabilities and material specifications. This dynamic is further compounded by the need for rapid response times and adaptability in supply chains, as businesses strive to remain competitive in a fast-paced market.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Chevron Belt Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a central tenet in the sourcing of chevron belts, with growing awareness of environmental impacts prompting buyers to prioritize eco-friendly solutions. The production of chevron belts often involves materials that can be resource-intensive, such as rubber and synthetic compounds. Therefore, suppliers who incorporate recycled materials or sustainable manufacturing practices are increasingly appealing to conscientious buyers.
Ethical sourcing is crucial for maintaining a responsible supply chain. Buyers should seek manufacturers that adhere to environmental regulations and possess certifications such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to reducing environmental impact. Additionally, suppliers that utilize green materials, such as bio-based elastomers or recycled polymers, can provide significant advantages in sustainability.
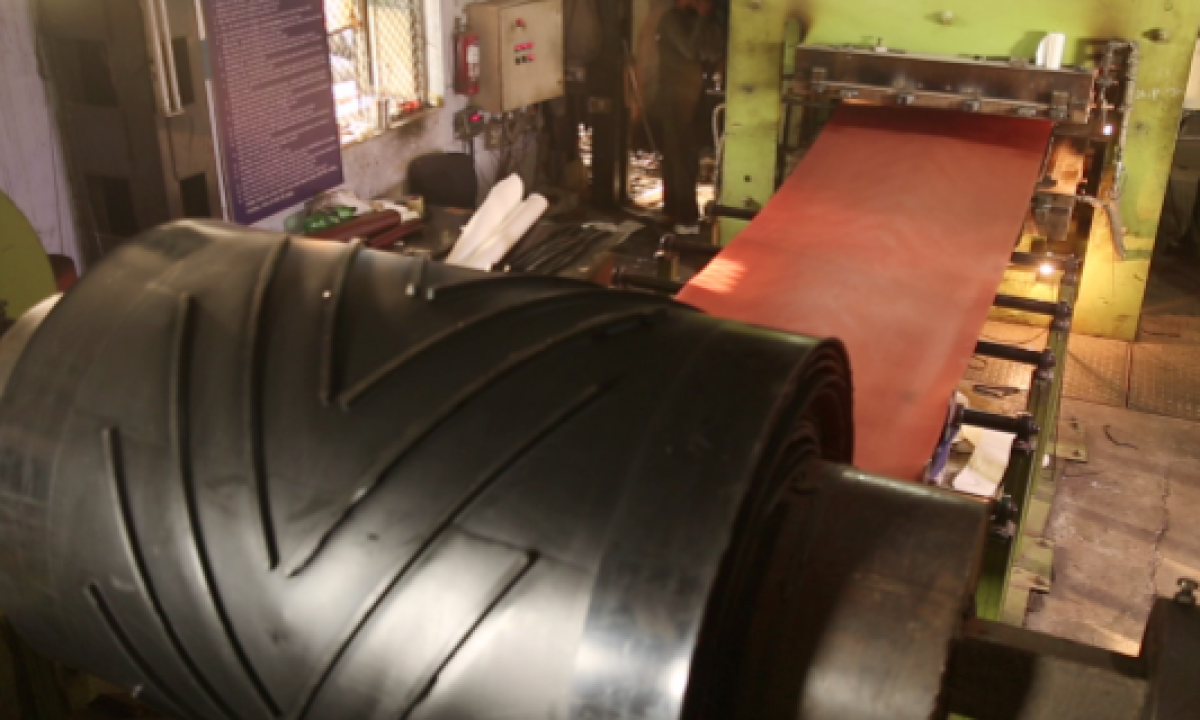

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Engaging with suppliers who prioritize ethical practices not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible sourcing. As industries move toward greener practices, B2B buyers in the chevron belt sector must consider the sustainability credentials of their suppliers as a key factor in their purchasing decisions.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Chevron Belt Sector?
The chevron belt has evolved significantly since its inception, originally designed for flat transport applications. The need for efficient handling of bulk materials at steep angles led to the development of the chevron design, featuring raised cleats that prevent material rollback. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have resulted in more robust and versatile chevron belts capable of handling a wider range of materials, from agricultural products to construction aggregates.
Today, the chevron belt sector is characterized by innovation, with manufacturers focusing on customization and enhanced performance. This evolution reflects the changing demands of industries worldwide, as businesses seek reliable and efficient solutions for their material handling needs. As the market continues to grow, the focus on sustainability and technology integration will shape the future of chevron belts, ensuring they remain a vital component in global supply chains.
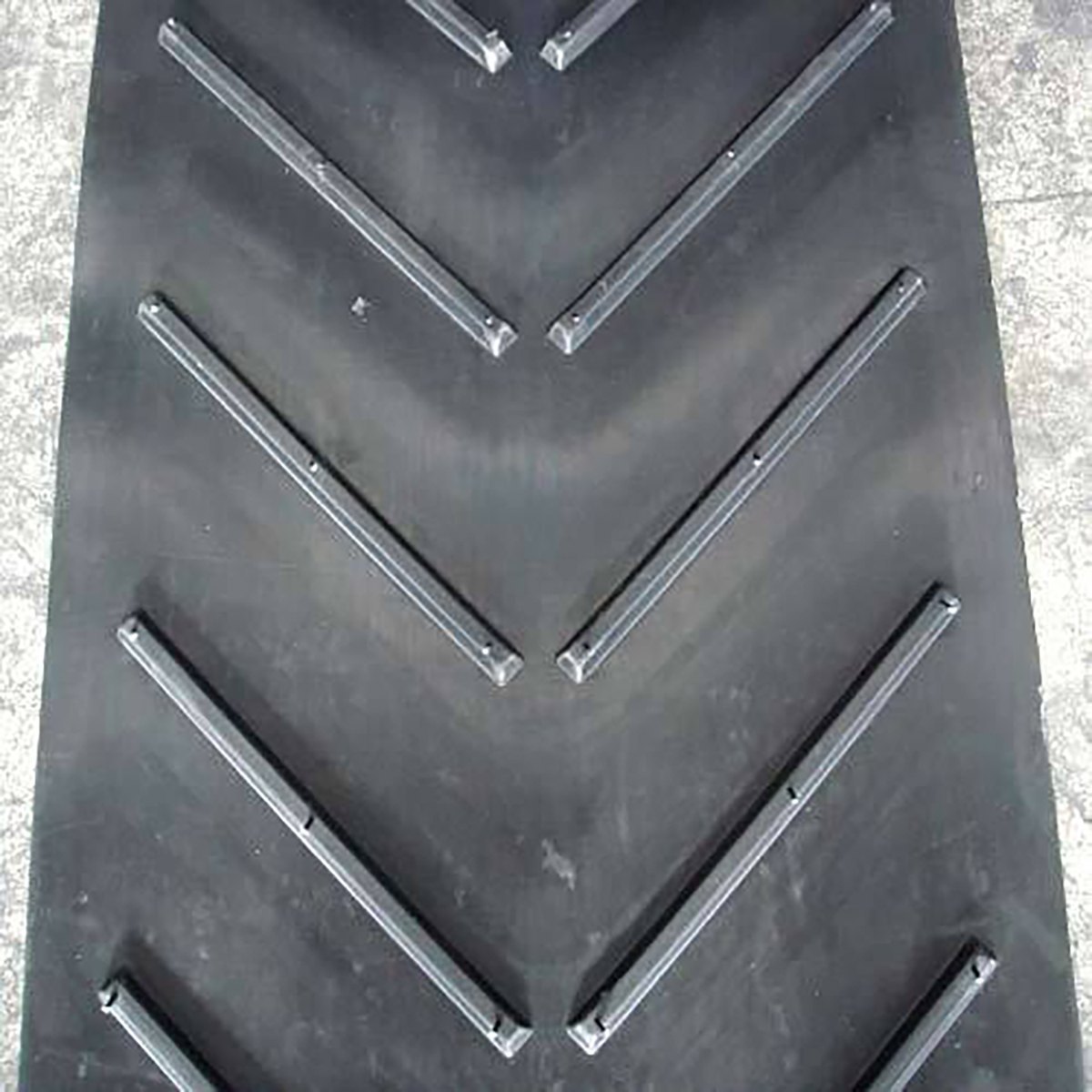

Illustrative image related to chevron belt
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of chevron belt
-
How do I select the right chevron belt for my application?
Selecting the appropriate chevron belt involves assessing factors such as the type of material to be conveyed, the incline angle, and the specific operational environment. For instance, heavier and bulk materials may require belts with taller cleats, while lighter materials may perform better with shorter cleats. It’s also essential to consider the belt’s construction material, as certain types offer better resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion. Collaborating with suppliers who provide customized solutions can help ensure you choose a belt that meets your unique requirements. -
What are the key features to look for in a chevron belt?
When sourcing a chevron belt, focus on features such as the profile height of the cleats, material durability, and the inclination angle the belt can handle. A higher cleat profile allows for steeper inclines and better material retention. Additionally, consider the bonding process used in manufacturing, as a heat-cured process typically enhances the belt’s longevity and performance. Understanding these features will help you select a belt that optimally suits your operational needs. -
What customization options are available for chevron belts?
Many manufacturers offer extensive customization options for chevron belts, including variations in cleat height, profile design, and material composition. You can tailor the belts to accommodate specific materials, operational temperatures, and incline angles. Furthermore, customizations may include the addition of features like drainage openings or specific widths to suit your machinery. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in custom solutions ensures that your chevron belts will perform effectively in your unique applications. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for chevron belts?
Minimum order quantities for chevron belts can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as the type of customization required and the materials used. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred meters to several thousand meters. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore any flexibility they may offer for smaller orders or trial runs. -
How can I ensure the quality of chevron belts from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of chevron belts, conduct thorough supplier vetting by reviewing their certifications, manufacturing processes, and customer testimonials. Request samples to assess the belt’s construction and performance under your specific conditions. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and any warranties or guarantees they provide. Establishing a relationship with reputable suppliers known for high-quality products can mitigate risks associated with sourcing. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing chevron belts internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of chevron belts can vary widely, typically ranging from upfront payments to net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow and business needs. Additionally, be aware of any currency exchange implications that might affect the final cost. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing chevron belts?
When importing chevron belts, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial materials to facilitate smooth transportation. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, are in order to avoid delays at customs. Understanding the total landed cost, including tariffs and taxes, will also help you budget accurately. -
How do I address issues with chevron belt performance?
If you encounter performance issues with your chevron belt, begin by assessing the installation and alignment to ensure proper operation. Check for material buildup or damage to the cleats that may affect functionality. If the problem persists, consult with your supplier for troubleshooting advice or potential design modifications. Regular maintenance and inspections can also prevent performance issues and prolong the lifespan of your chevron belts.
Top 6 Chevron Belt Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Beltservice – Chevron Cleated Belts
Domain: beltservice.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Chevron Cleated Belts are designed for conveying wet and/or loose materials up steep inclines. They feature fully molded chevrons of various cross sections, which can be closed in the center or open for drainage, enhancing material movement at loading points. The belts are constructed using a patented, permanent heat-cured bonding process with high-grade rubber compounds, ensuring durability and l…
2. Trelleborg – Chevron Surface Conveyor Belts
Domain: trelleborg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Chevron surface conveyor belts designed for efficient transportation of various materials. Key features include:
– Maximum inclination angle of 22 degrees.
– Homogeneous Chevron profiles vulcanized with the base belt.
– Durable and flexible with individualized design.
Applications include:
– Quarries, sandpits
– Cement works, lime works
– Farming (beets, grains, potatoes, fertilizers, wooden chip…
3. Cobra Ultimate – Conveyor Belt
Domain: americasbelting.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”:”Conveyor Belt”,”Width”:”24 inch”,”Ply”:”2 Ply”,”Top Texture”:”Chevron Top”,”Material”:”Poly/Nylon”,”Gauge”:”0.252 inch”,”Working Tension”:”150 lb/in”,”Length”:”100 feet Bulk Roll”,”Weight”:”272 lbs”,”Brand”:”Cobra Ultimate”,”Price”:”$2,323.00″,”List Price”:”$2,622.76″,”Savings”:”$299.76 (11%)”,”Part Number”:”CB-1005047-100″,”Shipping”:”Free Ground Shipping, Freight Truck Delivery”…
4. Miconveyance Solutions – Custom Rubber Chevron-Cleated Belting
Domain: miconveyancesolutions.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Custom Rubber Chevron-Cleated Belting is designed for bulk conveying applications, particularly in demanding environments like aggregate conveying and recycling. Key features include:
– Oil and heat resistance
– Available in standard SBR and Grade 1 compounds
– High-tensile strength and excellent elongation values
– Customizable based on size, shape, weight, and moisture content
– Over 150 pattern…
5. Interquip – Chevron Conveyor Belting
Domain: interquip.us
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Chevron Conveyor Belting features custom chevron cleats ranging from 1/4″ to 2″ high, designed for incline angles of 15-35 degrees to prevent product rollback. The belts can operate on traditional troughing idlers, flat idlers, and metal beds/pans. Recommended cleat indentation from belt edges allows for proper skirtboard rubber placement. Two basic chevron patterns are available: open-V (for liqu…
6. Garland Equipment – Stainless Steel Conveyor, Chevron Belt
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Stainless Steel Conveyor, Chevron Belt”, “Belt Size”: “9” x 96″”, “Condition”: “Used”, “Price”: “$4,500.00 or Best Offer”, “Seller”: “Garland Equipment”, “Seller Rating”: “99.7% positive”, “Shipping Location”: “Suwanee, Georgia, United States”, “Returns”: “Seller does not accept returns”, “Payment Options”: “PayPal Credit available”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for chevron belt
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of chevron belts is essential for optimizing material handling processes across various industries. By investing in high-quality, custom-designed chevron belts, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity. The ability to transport materials at steep angles without the risk of spillage is a critical advantage, especially in sectors like construction, agriculture, and mining.
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer durable, tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements. This proactive approach not only ensures the selection of the right product but also fosters long-term relationships that can lead to innovation and cost savings.
As global markets evolve, the demand for versatile and efficient conveyor systems will only grow. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about the latest advancements in chevron belt technology and to consider how these innovations can drive their operations forward. Engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and customization, and take the next step toward transforming your material handling processes today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.