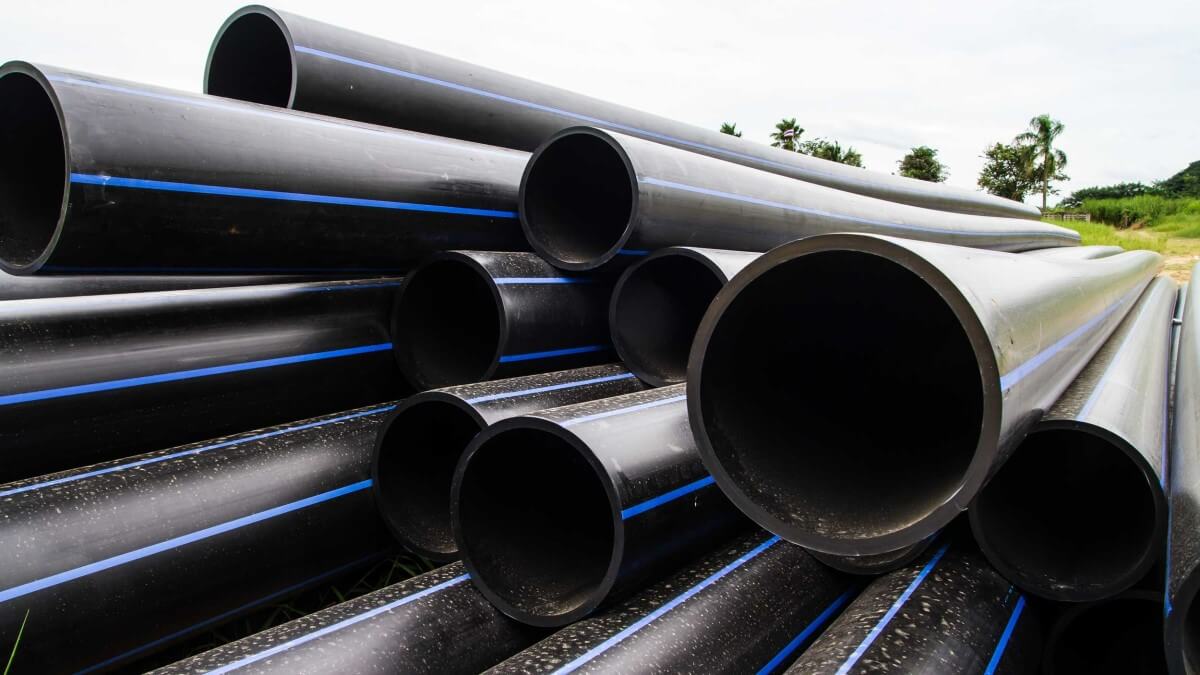
How to Source What Is Poly Pipe Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is poly pipe
As global markets expand, the quest for reliable and cost-effective materials poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially when it comes to sourcing high-quality poly pipe. Poly pipes, made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are revolutionizing infrastructure projects across various industries due to their remarkable flexibility, durability, and longevity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of poly pipes, providing valuable insights into different types, their applications, and critical considerations for sourcing and supplier vetting.
In this guide, B2B buyers will explore the diverse applications of poly pipes in sectors such as agriculture, mining, and municipal water systems, highlighting their advantages over traditional materials like PVC and concrete. Additionally, we will address key factors influencing cost, including manufacturing processes and material specifications, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Furthermore, we will provide essential tips for vetting suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet international standards. Whether you’re in Nigeria, Brazil, or the Middle East, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global poly pipe market, ultimately enhancing your project outcomes and contributing to long-term sustainability.
Understanding what is poly pipe Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE80 | Medium-density polyethylene; moderate strength | Water distribution, irrigation, drainage | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible. Cons: Lower pressure rating than PE100. |
| PE100 | High-density polyethylene; high strength and durability | Municipal water, gas distribution, sewage systems | Pros: Long lifespan, high resistance to cracking. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| MDPE | Medium-density polyethylene; good balance of strength and flexibility | Gas distribution, industrial applications | Pros: Versatile, good chemical resistance. Cons: Not as strong as PE100. |
| P100RC | Enhanced resistance to cracking; high performance | Critical infrastructure, seismic areas | Pros: Superior durability, excellent for harsh environments. Cons: Premium pricing. |
| Coextruded Pipe | Contains multiple layers for enhanced performance | Specialty applications in extreme climates | Pros: UV resistant, tailored for specific conditions. Cons: More complex manufacturing process. |
What Are the Characteristics of PE80 Poly Pipe?
PE80, or medium-density polyethylene, is known for its moderate strength and flexibility. It serves well in applications requiring a balance between durability and cost, making it popular for water distribution and irrigation systems. B2B buyers should consider its lower pressure rating compared to higher-density variants, which may limit its use in high-pressure applications. However, its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation make it an attractive option for projects with budget constraints.
Why Choose PE100 Poly Pipe for Your Projects?
PE100 is the industry standard for high-density polyethylene pipes, offering exceptional strength and longevity. It is ideal for municipal water supply, gas distribution, and sewage systems, where reliability is paramount. Buyers should note its higher initial cost, but the long lifespan and resistance to cracking often yield significant savings over time. This makes PE100 a preferred choice for infrastructure projects that demand durability and minimal maintenance.
What Are the Benefits of Using MDPE Poly Pipe?
Medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) pipes provide a good balance of strength and flexibility, making them suitable for gas distribution and various industrial applications. Their chemical resistance and ease of handling are key advantages for B2B buyers. However, while MDPE pipes are versatile, they do not possess the same strength as PE100, which may be a consideration for high-stress environments. Therefore, MDPE is best suited for projects where moderate strength is sufficient.
How Does P100RC Enhance Infrastructure Resilience?
P100RC, or rapid crack-resistant pipe, is designed for critical infrastructure, especially in seismic areas. Its enhanced durability makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring high performance under stress. B2B buyers should weigh the premium cost against the potential long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement needs. P100RC is particularly beneficial in regions prone to natural disasters, where infrastructure resilience is crucial.
What Advantages Does Coextruded Pipe Offer?
Coextruded pipes feature multiple layers that enhance their performance in extreme environments. They are particularly effective in applications exposed to harsh UV conditions, making them suitable for specialized projects. While they provide tailored benefits, buyers should consider the complexities involved in their manufacturing process, which can lead to higher costs. Coextruded pipes are ideal for businesses looking for customized solutions that meet specific environmental challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of what is poly pipe
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is poly pipe | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems | Enhanced water efficiency and reduced operational costs | Local climate conditions, pipe diameter, and pressure ratings |
| Construction | Water supply and drainage systems | Long-lasting infrastructure with minimal maintenance | Compliance with local building codes and environmental standards |
| Mining | Slurry transport and wastewater management | Improved safety and reliability in harsh environments | Resistance to chemicals and abrasion, ease of installation |
| Oil and Gas | Gas distribution and methane collection | Leak-free joints reducing environmental impact | Certifications for safety and quality, compatibility with existing systems |
| Municipal Services | Potable water distribution and sewage systems | Cost-effective and durable solutions for urban infrastructure | Availability of local suppliers and service support |
How is Poly Pipe Used in Agriculture for Irrigation Systems?
In agriculture, poly pipe is extensively used for irrigation systems, facilitating efficient water delivery to crops. Its flexibility allows for easy installation in various terrains, reducing the risk of leaks and ensuring optimal water usage. This is particularly crucial in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, where water scarcity can significantly impact agricultural yields. Buyers should consider factors such as local climate conditions, appropriate pipe diameters for their specific applications, and pressure ratings to ensure the right fit for their irrigation needs.
What Role Does Poly Pipe Play in Construction Water Supply Systems?
In the construction industry, poly pipe serves as a reliable solution for water supply and drainage systems. Its lightweight nature simplifies transportation and installation, while its durability ensures long-lasting performance even under harsh conditions. This is vital for construction projects in urban areas in Europe and the Middle East, where compliance with building codes is essential. Buyers must ensure that the poly pipe meets local regulatory standards and environmental considerations to avoid potential project delays.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
How Does Poly Pipe Improve Mining Operations?
Poly pipe is increasingly used in mining for slurry transport and wastewater management. Its chemical resistance and durability make it suitable for handling abrasive materials and harsh chemicals, ensuring safety and reliability in challenging environments. This is particularly important for mining operations in remote areas, where infrastructure is limited. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing pipes that offer high abrasion resistance and are easy to install, as well as those that comply with industry safety standards.
Why is Poly Pipe Essential for Oil and Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas sector, poly pipe is crucial for gas distribution and methane collection. Its leak-free joints and resistance to corrosion significantly reduce environmental risks, making it a preferred choice for companies focused on sustainability. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize sourcing poly pipes that come with the necessary safety certifications and quality assurance to ensure compatibility with existing systems and adherence to industry regulations.
How is Poly Pipe Beneficial for Municipal Services?
Municipal services leverage poly pipe for both potable water distribution and sewage systems due to its cost-effectiveness and durability. The long lifespan of poly pipe reduces the frequency of replacements, leading to significant savings for municipalities. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, it is essential to consider the availability of local suppliers and the capacity for ongoing service support to maintain these systems effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is poly pipe’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Variability of Poly Pipe Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the various specifications and grades of poly pipe, such as PE80 versus PE100. This can lead to misapplications in projects, resulting in costly delays and potential structural failures. For instance, a buyer in the agricultural sector may mistakenly purchase a lower-grade poly pipe, which could fail under high-pressure conditions, leading to water supply disruptions.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage with reputable suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and guidance on the appropriate grade for their specific applications. It’s essential to conduct thorough research on the environmental conditions and operational demands the poly pipe will face. Buyers should request samples and technical data sheets, which include information on pressure ratings, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals. Additionally, investing in training sessions or webinars offered by suppliers can enhance understanding of poly pipe applications, ensuring the right product is selected for each project.
Scenario 2: Installation Challenges Leading to Long-Term Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant installation challenges when working with poly pipes, particularly in remote areas or urban settings where traditional installation methods may not be feasible. For example, a contractor may struggle to lay down a long stretch of poly pipe in a densely populated area without disrupting existing infrastructure, which could lead to increased project costs and time overruns.
The Solution: To address installation challenges, buyers should consider utilizing trenchless technology, such as horizontal directional drilling (HDD). This method allows for the installation of poly pipes without the need for extensive excavation, minimizing disruption and environmental impact. Buyers should collaborate with experienced contractors who specialize in trenchless installation to ensure proper techniques are employed. Furthermore, using coiled poly pipes can facilitate easier handling and installation in tight spaces. Buyers should also ensure that installation teams are well-trained in best practices for welding and joining poly pipes to prevent leaks and ensure the integrity of the system.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Longevity and Performance in Harsh Conditions
The Problem: In regions with extreme weather conditions, such as high UV exposure in Africa or heavy rainfall in South America, B2B buyers often worry about the long-term performance and durability of poly pipes. Without the right materials, pipes may degrade quickly, leading to frequent replacements and increased maintenance costs. This scenario can be particularly daunting for municipal buyers responsible for water supply and sewage systems.
The Solution: To ensure longevity and performance, buyers should opt for UV-stabilized and impact-resistant grades of poly pipe, such as PE100 or specialized coextruded options designed for harsh climates. Conducting a thorough risk assessment of the local environmental conditions is vital. Buyers should also establish maintenance protocols that include regular inspections for signs of wear or damage, ensuring that potential issues are addressed proactively. Collaborating with local engineers who understand regional challenges can provide additional insights into selecting the right products and installation techniques that will withstand environmental stresses over time.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is poly pipe
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Poly Pipe?
When considering the selection of materials for poly pipe, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is the most prevalent choice, but other materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), and reinforced concrete are also utilized in various applications. Each material has unique properties and implications for performance, cost, and suitability in specific environments.
How Does High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Perform in Poly Pipe Applications?
HDPE is renowned for its exceptional durability, flexibility, and resistance to a wide range of chemicals. It has a high-temperature rating, typically up to 60°C (140°F), and can withstand pressures of up to 16 bar (232 psi). Its corrosion resistance is a significant advantage, particularly in environments where soil chemistry may be aggressive.
Pros: HDPE is lightweight, easy to install, and offers a long service life of over 100 years. Its weldable joints eliminate the risk of leaks associated with glued connections.
Cons: While HDPE is generally cost-effective over its lifespan, the initial investment can be higher than alternatives like PVC. Additionally, its flexibility may require specialized installation techniques in certain conditions.
Impact on Application: HDPE is suitable for transporting potable water, wastewater, and various chemicals. Its compatibility with different media makes it a versatile choice for municipal and industrial applications.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider compliance with local standards such as ASTM or ISO. The availability of HDPE in various grades (e.g., PE80, PE100) should also be assessed based on local supply chains.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in Poly Pipe?
PVC is another widely used material for poly pipe, particularly in plumbing and drainage applications. It has a lower temperature tolerance than HDPE, typically around 60°C (140°F), and is generally less flexible.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for various applications. It is resistant to corrosion and can handle a moderate range of pressures.
Cons: The rigidity of PVC can lead to cracking under extreme conditions, such as ground movement or temperature fluctuations. Additionally, PVC joints are typically glued, which can lead to potential leaks over time.
Impact on Application: PVC is often used in irrigation, drainage, and venting systems. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for transporting non-potable water and certain chemicals.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with relevant standards (e.g., DIN, EN) and consider the environmental impact of PVC, as its production involves chlorine.
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Compare for Poly Pipe Applications?
Polypropylene is less common than HDPE and PVC but offers unique advantages, particularly in high-temperature applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) and has good chemical resistance.
Pros: PP is lightweight and has excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Its resistance to fatigue makes it ideal for applications involving frequent movement.
Cons: The cost of polypropylene can be higher than HDPE and PVC, and its lower flexibility may limit its use in certain applications. Additionally, it may not be as widely available in all regions.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Impact on Application: PP is often used for hot water systems and in chemical processing applications. Its compatibility with a wide range of chemicals enhances its utility in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the availability of PP in their region and ensure compliance with local standards, particularly in the chemical industry.
What Role Does Reinforced Concrete Play in Poly Pipe Applications?
Reinforced concrete is typically used in large-scale infrastructure projects, such as sewage and stormwater systems. It offers excellent compressive strength and durability.
Pros: Reinforced concrete can handle high pressures and is resistant to environmental factors, making it suitable for underground applications.
Cons: The weight and rigidity of reinforced concrete can complicate installation and increase transportation costs. It is also more susceptible to cracking under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: This material is often used in large diameter pipes for municipal sewage and drainage systems, where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess local construction practices and standards, as reinforced concrete may require specialized installation techniques.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Poly Pipe
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is poly pipe | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Potable water, wastewater, chemicals | Long service life, flexible joints | Higher initial cost, installation complexity | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Irrigation, drainage, venting | Cost-effective, easy to manufacture | Rigid, potential for glued joint leaks | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Hot water systems, chemical processing | High-temperature resistance | Higher cost, limited flexibility | Medium |
| Reinforced Concrete | Municipal sewage, stormwater systems | Excellent compressive strength | Heavy, installation complexity | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is poly pipe
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Poly Pipe?
The manufacturing of poly pipe, specifically high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe, involves several crucial stages that ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Poly Pipe Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality polymer resin, typically in pellet form. The resin is subjected to rigorous testing to ensure it meets the required specifications for density and molecular weight, which are critical for the pipe’s performance. Once verified, the resin is fed into an extruder where it is melted down. This initial stage ensures that the raw material is free from contaminants and is uniform in consistency, which is vital for the subsequent forming processes.
Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process of Poly Pipe?
The next stage is the forming process, where the melted resin is extruded through a die to create a continuous pipe. This technique is known as extrusion, and it allows for the production of pipes in various diameters and wall thicknesses. After extrusion, the pipe is cooled, typically using a water bath or air cooling, to solidify its shape. The cooling process is critical, as it prevents warping and ensures that the pipe maintains its structural integrity.
Following this, the pipe may undergo additional shaping or coiling, depending on its intended application. For instance, longer pipes can be coiled for easier transport and installation, particularly in remote areas where traditional transport methods may be challenging.
How Is Assembly and Finishing Handled in Poly Pipe Production?
After forming, the assembly stage may involve adding fittings, joints, or additional components to the pipe. This is particularly important for applications requiring specific configurations, such as bends or junctions. The finishing process includes cutting the pipe to specified lengths and applying surface treatments as necessary. This can include the addition of a UV-resistant layer, which enhances the pipe’s durability when exposed to sunlight, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Poly Pipe?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of poly pipe production, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and client specifications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards is crucial. ISO 9001 is a prominent quality management standard that many manufacturers adhere to, ensuring consistent quality in processes and products. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications are essential indicators of compliance and quality.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Poly Pipe Manufacturing?
The quality control process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before entering the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are conducted at various stages to monitor the extrusion process, wall thickness, and dimensional accuracy of the pipes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the pipes are completed, they undergo a comprehensive inspection, including tests for pressure resistance, flexibility, and durability. This stage often includes non-destructive testing methods, such as hydrostatic testing, to ensure the pipes can withstand operational pressures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers have several methods to ensure that their suppliers adhere to quality control standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This firsthand experience can help buyers assess the capabilities and reliability of the supplier.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can provide transparency regarding the supplier’s processes and the outcomes of various quality tests. This documentation should outline compliance with relevant standards and any certifications attained.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly beneficial in regions where local compliance may vary, providing additional assurance for international buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Buyers should be aware of the varying regulatory landscapes and cultural approaches to quality assurance in different regions. This understanding can aid in navigating compliance requirements and establishing effective communication with suppliers.
-
Logistical Challenges: Transporting poly pipe across borders may introduce additional challenges, such as ensuring that products are not damaged during transit. Buyers should discuss packaging standards and shipping methods with suppliers to mitigate these risks.
-
Local Certification Requirements: Some regions may have specific local certifications that are mandatory for pipe usage in certain applications. It is vital for buyers to verify that their suppliers can provide products that comply with these local standards.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for poly pipe is essential for B2B buyers aiming to source high-quality products. By focusing on the key stages of production, international standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is poly pipe’
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing poly pipe, also known as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your procurement process is thorough, efficient, and tailored to meet your specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Consider factors such as pipe diameter, pressure ratings, and intended applications (e.g., water supply, gas distribution, or sewage management).
– Tip: Collaborate with your engineering team to ensure that all requirements align with industry standards and project needs.
Step 2: Research Material Standards and Certifications
Verify that the poly pipe you intend to procure meets relevant international standards and certifications. This ensures the quality and safety of the materials used, which is especially crucial in applications such as drinking water or gas transmission.
– Look for: ISO, ASTM, and other local certifications that indicate compliance with safety and environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Don’t just rely on their website: Conduct independent research to assess their reputation, reliability, and customer service history.
Step 4: Assess Product Range and Customization Options
Not all poly pipe products are created equal, and a reputable supplier should offer a variety of options. Assess their product range to ensure they can meet your specific needs, including different grades of HDPE and specialized fittings.
– Customization: Check if they can provide tailored solutions, such as specific lengths or coiling options, to suit your project requirements.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a large purchase, request samples of the poly pipe to evaluate quality firsthand. Testing the materials for flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance will help you determine their suitability for your applications.
– Testing methods: Consider subjecting samples to pressure tests or environmental stress tests to assess their performance under expected conditions.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines. A clear understanding of costs can prevent budget overruns and ensure timely project execution.
– Key considerations: Inquire about bulk purchase discounts, warranties, and after-sales support to maximize your investment.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, ensure that you have a logistics plan in place for the delivery of the poly pipe. Coordinate with suppliers regarding shipping methods, timelines, and any potential import/export regulations that may affect delivery.
– Documentation: Ensure that all necessary paperwork, such as customs documentation and shipping manifests, is prepared in advance to facilitate smooth transportation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing poly pipe, ensuring that they secure high-quality materials that meet their operational needs while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is poly pipe Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components Involved in Poly Pipe Sourcing?
When sourcing poly pipe, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The major material used in poly pipe manufacturing is high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Pricing can fluctuate based on global oil prices, as HDPE is derived from petroleum. Buyers should consider sourcing strategies that allow for bulk purchasing to benefit from economies of scale.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the location of manufacturing facilities. Countries with lower labor costs may provide more competitive pricing, but quality assurance and skilled labor availability should also be assessed.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, maintenance, and factory rent. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate these costs, so evaluating suppliers on their operational efficiency is beneficial.
-
Tooling: The costs associated with molds and specialized equipment for producing various sizes and specifications of poly pipes can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique applications may lead to higher initial costs but could be justified by improved long-term performance and durability.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the integrity and performance of poly pipes necessitates rigorous quality control processes. Costs associated with testing and certification can influence the overall pricing structure. Buyers should inquire about QC standards and certifications to ensure compliance with international norms.
-
Logistics: Transporting poly pipes can be costly, particularly for long-distance shipments. Factors such as shipping mode, distance, and the weight of the pipes significantly impact logistics costs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for clarifying responsibilities for shipping and handling.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. The margin can vary based on market demand, competitive landscape, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Poly Pipe Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of poly pipes beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing significantly. Larger orders often yield better unit prices, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as specific diameters, wall thickness, or co-extruded layers, can elevate costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard products.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality HDPE or additional certifications (like ISO) can result in increased costs but may enhance durability and lifespan, leading to a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability, reputation, and geographical location of suppliers can influence pricing. Local suppliers might offer better terms regarding shipping costs and lead times.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Poly Pipe Procurement?
To maximize value in poly pipe sourcing, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus not only on upfront costs but also on long-term savings from durability and reduced maintenance. This approach can justify higher initial investments.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Engage with multiple suppliers to gather quotes and assess quality. Understanding the market landscape will empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clear communication about volume requirements and project specifications can foster better relationships and potentially lead to volume discounts.
-
Consider Incoterms: Understanding and negotiating Incoterms can help clarify cost responsibilities and mitigate risks associated with shipping delays and additional fees.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can ease cash flow pressures and may incentivize suppliers to offer better pricing.
Are There Any Pricing Nuances for International Buyers from Regions Like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
International buyers should be aware of several nuances:
-
Import Duties and Taxes: These can significantly affect the final cost of poly pipes. Understanding local regulations can aid in budgeting more accurately.
-
Currency Fluctuations: For buyers purchasing from overseas, currency exchange rates can impact pricing. Locking in prices through forward contracts may mitigate risks.
-
Shipping Times and Reliability: Variability in shipping schedules can affect project timelines. Buyers should consider suppliers with a proven track record of timely delivery.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While the analysis provides a comprehensive overview of cost components and pricing influences for poly pipe sourcing, actual prices may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure the best procurement strategy.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is poly pipe With Other Solutions
In the quest for efficient piping solutions, understanding the alternatives to poly pipe (high-density polyethylene, HDPE) is essential for B2B buyers. Poly pipe has gained popularity due to its flexibility, durability, and long lifespan, but other materials and technologies also serve similar functions. This section will compare poly pipe against two viable alternatives: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes and concrete pipes.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Poly Pipe | PVC Pipes | Concrete Pipes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly flexible, resistant to corrosion, lasts over 100 years | Good chemical resistance, but brittle and prone to cracking | Strong under heavy loads but susceptible to cracking and corrosion |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost, but lower lifetime cost due to durability | Lower initial cost, but higher maintenance can increase total cost | High installation cost and labor-intensive, but very durable |
| Ease of Implementation | Lightweight, easy to install, trenchless options available | Lightweight, easier to handle than concrete, requires solvent welding | Heavy, requires specialized labor and equipment for installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to weldable joints and resistance to corrosion | Moderate maintenance, can require joint replacements | High maintenance, cracks can lead to significant repairs |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for municipal water systems, irrigation, and gas distribution | Suitable for residential plumbing and drainage | Best for heavy-duty applications like roadways and foundations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
PVC Pipes
PVC pipes are a widely used alternative, particularly in residential plumbing and drainage applications. Their lower initial cost makes them attractive, especially for smaller projects. However, PVC is more susceptible to cracking under pressure and extreme temperatures, leading to potential leaks over time. While installation is relatively straightforward, the need for solvent welding can complicate the process, especially for larger diameters. Maintenance can also become a concern, as aging PVC pipes may require frequent repairs and replacements.
Concrete Pipes
Concrete pipes are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like sewer systems and stormwater management. They can withstand significant loads and are less likely to deform under pressure. However, the installation of concrete pipes is labor-intensive and costly, often requiring heavy machinery. They are also susceptible to cracking and corrosion over time, especially in aggressive soil conditions. This can lead to high maintenance costs, undermining their initial durability advantage.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Piping Solution
When selecting the right piping solution for your project, consider the specific needs and conditions of your application. Poly pipe offers flexibility, low maintenance, and long-term durability, making it a solid choice for a variety of uses, particularly in municipal and agricultural contexts. PVC pipes may be more cost-effective initially but can incur higher maintenance costs in the long run. Concrete pipes, while robust, may not be the best option for all applications due to their installation challenges and susceptibility to cracking. Ultimately, the decision should weigh factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions to ensure the best return on investment.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is poly pipe
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Poly Pipe?
When considering poly pipe for various applications, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade: What Is PE100 and Why Is It Important?
Poly pipe is primarily made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), with PE100 being the industry standard. This grade signifies that the pipe has a minimum long-term strength of 10 MPa and is suitable for high-pressure applications. For B2B buyers, selecting PE100 ensures that the pipe can withstand rigorous operational conditions, making it a reliable choice for infrastructure projects like water distribution and sewage systems.
2. Flexibility and Bend Radius: Why Does It Matter?
Poly pipes are known for their flexibility, allowing for easy installation and maneuverability in various terrains. The bend radius refers to the minimum radius a pipe can bend without compromising its integrity. A lower bend radius means easier installation in tight spaces, which can reduce labor costs and installation time. This is particularly advantageous in urban settings where underground space is limited.
3. Pressure Rating: How Does It Affect Application Suitability?
The pressure rating of poly pipe indicates the maximum pressure the pipe can handle safely. Common ratings include PN6, PN8, and PN12.5, corresponding to 6, 8, and 12.5 bars, respectively. Understanding the pressure requirements of your project helps in selecting the appropriate pipe, ensuring safety and longevity in applications such as irrigation, gas distribution, and industrial processes.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
4. Chemical Resistance: Why Is It Essential for Durability?
One of the significant advantages of poly pipe is its excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for transporting a wide range of fluids, including corrosive substances. Buyers should assess the chemical compatibility of poly pipe with the intended media to prevent degradation over time. This property is particularly crucial in industries like mining, agriculture, and chemical processing.
5. UV Stability: How Does It Impact Outdoor Applications?
For projects exposed to sunlight, UV stability is a critical property. Poly pipes are naturally UV resistant, which minimizes the risk of degradation and ensures a longer lifespan in outdoor settings. This is particularly relevant in regions with intense sunlight, such as parts of Africa and South America. Choosing UV-stable poly pipes can significantly reduce replacement and maintenance costs.
6. Jointing Methods: What Are the Best Practices?
Poly pipe can be joined using various methods, including butt fusion, electrofusion, and mechanical fittings. Each method has its advantages and is suitable for different applications. Understanding these methods is essential for ensuring leak-free connections and maintaining the integrity of the piping system. For B2B buyers, selecting the right jointing method can lead to substantial long-term savings and increased operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Poly Pipe?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of poly pipe, an OEM may produce the pipes while another company brands and sells them. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality sources and ensure product consistency.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning. In many cases, suppliers set MOQs to ensure production efficiency, so negotiating this term can lead to better pricing and supply chain management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and select the best option based on price, quality, and delivery terms. A well-structured RFQ can streamline negotiations and lead to more favorable agreements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing of poly pipe, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping, delivery, and customs clearance.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
5. Lead Time: How Does It Affect Your Project Timeline?
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of poly pipe procurement, understanding lead times is crucial for project scheduling. Delays in delivery can impact overall timelines, making it essential for buyers to communicate their requirements clearly with suppliers.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions about poly pipe procurement, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific needs and applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is poly pipe Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Poly Pipe Sector?
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Poly Pipe Market?
The global poly pipe market is witnessing robust growth driven by increasing infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Urbanization and the need for reliable water supply and sewage systems are key factors propelling demand. In regions like Nigeria and Brazil, the implementation of large-scale irrigation and drainage projects is further stimulating the market. Additionally, the shift towards high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes due to their superior durability and flexibility is reshaping sourcing trends, favoring suppliers who can deliver high-quality, innovative solutions.
Emerging technologies, such as trenchless installation methods, are revolutionizing how poly pipes are deployed, minimizing disruption and environmental impact. Companies are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, streamlining the sourcing process, and improving supplier relationships. This trend is particularly significant in Europe, where e-procurement solutions are gaining traction among B2B buyers seeking efficiency and transparency in their supply chains.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Poly Pipe Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for international B2B buyers, with an increasing focus on environmental impact and ethical sourcing practices. The poly pipe industry is responding to these demands by promoting products made from recyclable and non-toxic materials. HDPE pipes, for instance, are recognized for their longevity and reduced environmental footprint, making them an attractive option for projects aiming for sustainability.
Ethical supply chains are paramount, as buyers seek manufacturers who adhere to responsible sourcing practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications are becoming essential for suppliers to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America are particularly sensitive to these issues, as they often operate in environments where resource scarcity and environmental degradation are pressing concerns. Therefore, selecting suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly materials and practices can enhance brand reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Poly Pipe Development?
Poly pipe technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed in Europe and the United States, the first low-density polyethylene was used during World War II, primarily for coating underwater cables. The introduction of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) in the 1950s marked a pivotal moment, as it provided a more durable and flexible alternative for various applications, including infrastructure and irrigation.
Over the decades, advancements in polymer resin technology have led to the development of different grades of poly pipes, such as PE80 and PE100, each offering enhanced performance characteristics. Today, poly pipes are widely used across multiple sectors, including civil engineering, agriculture, and mining, thanks to their remarkable resistance to corrosion, UV stability, and long service life. This historical evolution underscores the adaptability of poly pipe technology, making it a reliable choice for modern infrastructure needs.
In conclusion, navigating the poly pipe sector requires an understanding of the market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context that shape the sourcing landscape. By staying informed on these trends, international B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that align with both their operational needs and ethical commitments.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is poly pipe
1. How does poly pipe compare to traditional piping materials?
Poly pipe, made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offers several advantages over traditional materials like PVC and concrete. It is lightweight, flexible, and resistant to corrosion and chemical damage, making it suitable for various applications, from irrigation to municipal water systems. Additionally, its weldable joints eliminate the risk of leaks associated with glued connections. This durability often results in lower maintenance costs and a longer lifespan, often exceeding 100 years, which can be particularly beneficial for large-scale projects.
2. What are the key benefits of using poly pipe for international projects?
For international projects, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, poly pipe provides significant benefits. Its resistance to UV radiation and temperature fluctuations makes it ideal for diverse climates. Furthermore, the lightweight nature of poly pipe simplifies logistics and reduces shipping costs. The flexibility of poly pipe allows for easy installation in challenging terrains without the need for extensive excavation, which can save time and labor costs. Its long service life also means fewer replacements and lower overall project costs.
3. What customization options are available for poly pipe?
Poly pipe can be customized in various ways to meet specific project requirements. This includes different diameters, lengths, wall thicknesses, and pressure ratings. Some manufacturers offer coiled pipes for easier transportation and installation in tight spaces. Additionally, custom colors or markings can be applied for identification purposes. When sourcing poly pipe, it’s essential to communicate your needs clearly to ensure the supplier can meet your specifications, particularly for unique applications in different geographic regions.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe
4. What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing poly pipe?
Minimum order quantities for poly pipe can vary widely among suppliers and depend on factors such as pipe specifications, material grades, and geographic location. Typically, MOQs can range from a few hundred meters to several thousand, particularly for custom orders. It’s advisable to discuss your project scale and requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Understanding your specific needs will help you align with suppliers who can accommodate your order size without excessive costs.
5. What payment terms are typically offered for poly pipe purchases?
Payment terms for poly pipe purchases can vary by supplier and region. Common options include advance payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established businesses or large orders. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. When dealing with international transactions, consider factors like currency exchange rates and potential tariffs, which can impact the overall cost.
6. How can I ensure the quality of poly pipe from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of poly pipe, verify that suppliers comply with international standards and certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001 or ASTM standards. Request product samples for testing before making bulk purchases. Additionally, review supplier references and past project case studies to gauge their reliability and quality. Establishing a clear quality assurance process, including inspection protocols upon delivery, can help mitigate risks associated with inferior products.
7. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing poly pipe internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing poly pipe internationally. Factors to consider include shipping methods, delivery timelines, and customs regulations in your country. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with local laws and tariffs. It’s also beneficial to plan for potential delays by allowing buffer time in your project schedule. Understanding the full cost of logistics, including freight and handling fees, will help you budget more effectively.
8. How does the installation process of poly pipe differ from traditional piping systems?
The installation of poly pipe is generally more straightforward than traditional piping systems. Due to its lightweight and flexible nature, poly pipe can be easily maneuvered into place, reducing the need for heavy machinery. Its weldable joints facilitate quicker assembly, allowing for seamless connections without the need for adhesives. Additionally, trenchless installation techniques can be employed, minimizing surface disruption and environmental impact. These factors can lead to significant time and cost savings in project execution.
Top 5 What Is Poly Pipe Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Poly Tubing Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Poly Tubing is made from various polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyurethane, derived from natural gas and crude oil. The main types are High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). HDPE is rigid and strong, suitable for industrial piping and water lines, while LDPE is flexible and transparent, often used for plastic bags and protective sleeves. The manu…
2. Orbit – PVC Irrigation Piping
Domain: orbitonline.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a rigid, non-flexible piping used in irrigation systems, typically white in color. It comes in various diameters, wall thicknesses (schedule ratings), and pressure ratings, with schedule 40 being the recommended thickness for residential irrigation systems (withstanding up to 80 psi). PVC pipes are sold in straight lengths of 10 feet and require special cutting tools fo…
3. Pedredge Pipe – Poly Pipe Solutions
Domain: pedredgepipe.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Poly Pipe, also known as PE, is made from High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), a thermoplastic polymer produced from ethylene. It was first developed in the early 1930s and entered the market in 1951. Poly Pipe is manufactured in Australia since the 1950s and is used for various applications including infrastructure, civil pipelines, pressure water and sewerage, fire mains, mining, gas reticulation, …
4. RainPoint – PVC vs. Poly Irrigation Piping Comparison
Domain: rainpointonline.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: PVC vs. Poly irrigation piping comparison:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride):
– Rigid pipe made of thermoplastic material
– Strong, rigid, and lightweight
– Commonly used in high-pressure applications (water pipes, swimming pool piping, irrigation systems)
– Resistant to corrosion and chemicals
– Can withstand pressures up to 140 psi and temperatures up to 140°F
– Brittle over time, especially in c…
5. Alltex Irrigation – High Density Polyethylene Pipe (HDPE)
Domain: alltexirrigation.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: High Density Polyethylene Pipe (HDPE), also known as Poly Pipe, is a thermoplastic pipe that is rugged, flexible, and durable. It has outstanding chemical and environmental stress crack resistance, does not rust, rot, or corrode, and is resistant to biological growth. This results in an extended service life and long-term cost savings. Poly Pipe is flexible and ductile, designed to handle occasion…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is poly pipe
As the demand for efficient and sustainable piping solutions continues to rise globally, poly pipe, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), stands out as a frontrunner. Its versatility, chemical resistance, and longevity make it an ideal choice for a myriad of applications, from municipal water systems to industrial pipelines. International B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the strategic advantages of sourcing poly pipe products. These include reduced installation costs due to their lightweight nature, the potential for trenchless applications that minimize environmental disruption, and the assurance of long-term performance with a lifespan exceeding 100 years.
Investing in poly pipe not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with sustainable practices, catering to the growing emphasis on environmentally friendly solutions. As you evaluate your sourcing strategies, prioritize suppliers who offer innovative poly pipe solutions tailored to your specific needs. By doing so, you position your business to leverage the benefits of this advanced material.
Looking ahead, the poly pipe market is poised for growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing infrastructure investments. Engage with trusted manufacturers and distributors to secure high-quality poly pipe solutions that will meet your current and future project demands.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to what is poly pipe