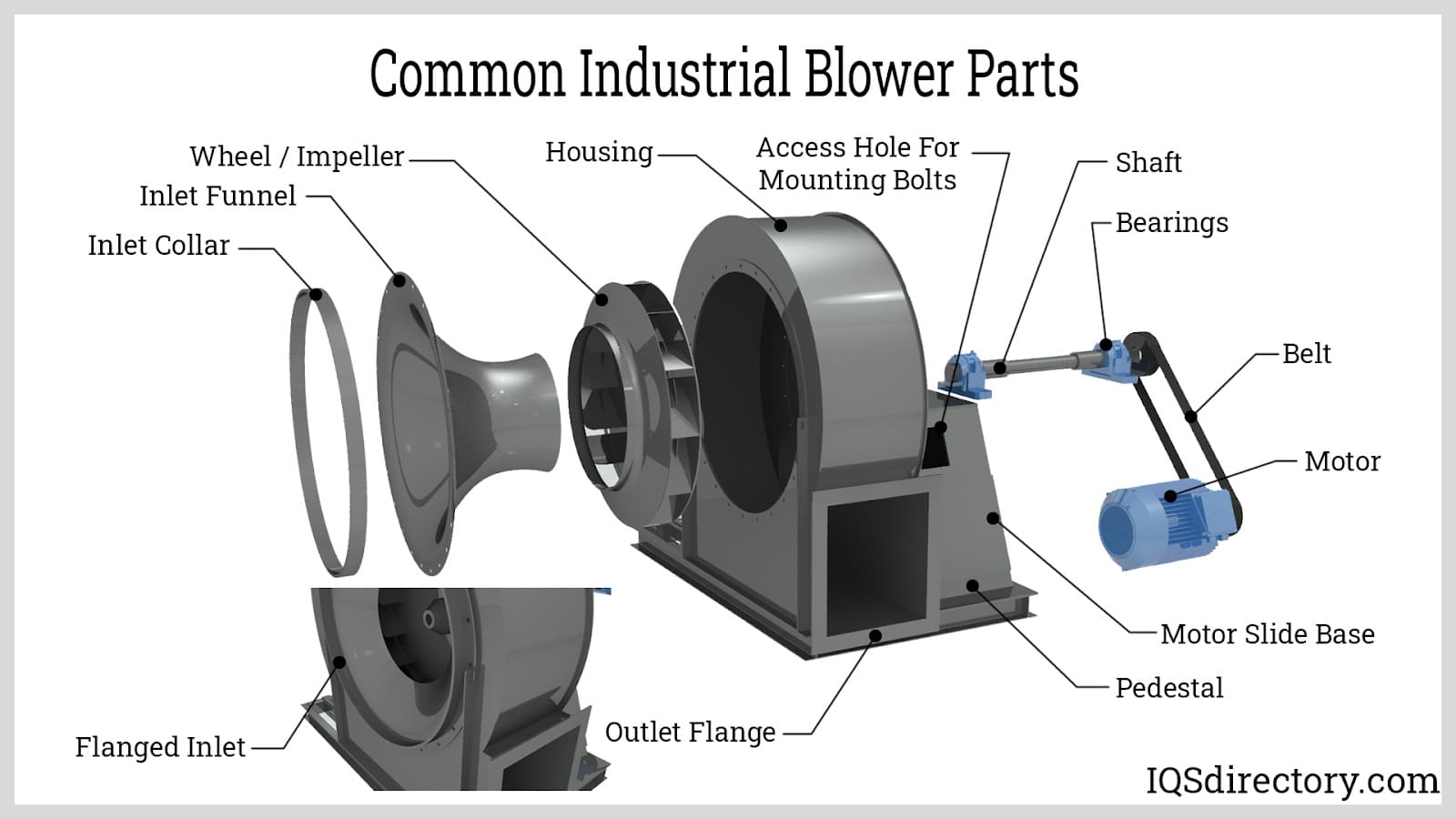
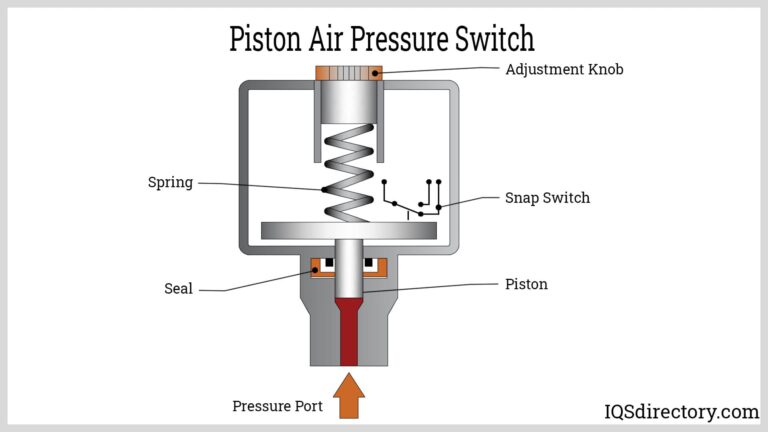
How to Source What Is A Blower Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a blower
In an increasingly competitive global market, understanding the intricacies of blowers is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking efficient solutions for their operational needs. Sourcing reliable blowers can pose significant challenges, from identifying the right type for specific applications to ensuring compliance with regional standards. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource that demystifies the world of blowers, covering essential topics such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
Blowers, which are vital for air movement and gas circulation in various industries, come in different forms—each tailored for specific functions, from pneumatic conveying systems in manufacturing to HVAC solutions in commercial buildings. By exploring the diverse types of blowers, such as centrifugal and axial blowers, alongside their applications in sectors ranging from automotive to health and wellness, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Particularly for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria—navigating supplier options and understanding cost structures are essential for maximizing investment. This guide empowers B2B buyers to confidently select the right blower solutions that align with their operational goals while ensuring quality and efficiency in their processes.
Understanding what is a blower Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Blower | Uses a rotating impeller to create centrifugal force; high pressure and flow rates. | HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, air pollution control | Pros: High efficiency, versatile; Cons: Can be noisy, requires maintenance. |
| Axial Blower | Moves air parallel to the axis of the impeller; suitable for large volumes at low pressure. | Cooling systems, ventilation in confined spaces | Pros: Compact design, low energy consumption; Cons: Limited pressure capability. |
| Positive Displacement Blower | Operates by trapping a fixed volume of air and forcing it into the discharge; provides consistent flow. | Pneumatic conveying, wastewater treatment | Pros: Stable flow, effective for high pressure; Cons: Larger size, potential for wear. |
| Regenerative Blower | Utilizes a rotating impeller and diffuser to increase pressure; efficient at low flow rates. | Vacuum systems, material handling | Pros: Low maintenance, quiet operation; Cons: Limited to lower flow applications. |
| Turbo Blower | Features a high-speed impeller for high pressure and low flow; compact design. | Chemical processing, cooling applications | Pros: High efficiency, space-saving; Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitive to operational conditions. |
What Are the Characteristics of Centrifugal Blowers for B2B Buyers?
Centrifugal blowers are designed to move air or gas through the use of a rotating impeller, which creates a centrifugal force that accelerates air outward. These blowers are suitable for applications requiring high pressure and airflow, such as HVAC systems and industrial ventilation. When considering a centrifugal blower, B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance requirements, as these can significantly impact operational costs and performance in various environments.
How Do Axial Blowers Differ in Their Applications?
Axial blowers operate by moving air parallel to the impeller’s axis, making them ideal for applications that require high airflow at low pressure, such as cooling electronic equipment and providing ventilation in tight spaces. Their compact design often translates to lower energy consumption, which is attractive for many businesses. Buyers should consider the application’s pressure requirements and space constraints when selecting an axial blower, as their efficiency diminishes at higher pressures.
Why Choose Positive Displacement Blowers for Specific Industries?
Positive displacement blowers work by trapping a fixed volume of air and forcing it into the discharge, providing a steady flow rate regardless of pressure fluctuations. This makes them particularly effective in pneumatic conveying systems and wastewater treatment facilities. Buyers looking for reliability in flow consistency and pressure should consider these blowers, but should also be aware of their larger size and potential wear on components over time.
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
What Are the Advantages of Regenerative Blowers?
Regenerative blowers use a rotating impeller and diffuser to increase air pressure and are known for their low maintenance and quiet operation. They are typically used in vacuum systems and material handling applications. For B2B buyers, the regenerative blower’s low operational costs and reliability make it a compelling choice, especially in environments where noise reduction is critical. However, they may not be suitable for high-flow applications.
When Should Turbo Blowers Be Considered?
Turbo blowers employ a high-speed impeller to achieve high pressure while maintaining a compact design, making them suitable for demanding applications in industries such as chemical processing and cooling systems. They are highly efficient, but their initial cost can be higher than other blower types. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of efficiency and space-saving design against the investment required, particularly in environments where operational efficiency is paramount.
Key Industrial Applications of what is a blower
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is a blower | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic conveying systems for bulk material transport | Enhanced efficiency in moving materials, reducing labor costs | Reliability, energy consumption, and maintenance support |
| HVAC | Air circulation and ventilation in commercial buildings | Improved indoor air quality and employee comfort | Size, noise level, and energy efficiency ratings |
| Food Processing | Vacuum packaging of perishable goods | Extended shelf life of products, reduced spoilage | Compliance with health regulations and customization options |
| Wastewater Treatment | Aeration systems for sewage treatment | Effective treatment of wastewater, meeting environmental standards | Durability in harsh conditions and energy efficiency |
| Automotive | Cooling systems in electric and hybrid vehicles | Enhanced performance and reliability of automotive systems | Compact design, weight considerations, and efficiency |
How are blowers used in pneumatic conveying systems in manufacturing?
In manufacturing, blowers are integral to pneumatic conveying systems, which transport bulk materials like powders and granules through pipelines using air or nitrogen. This method significantly enhances efficiency by automating the transport process, minimizing manual labor, and reducing the risk of contamination. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider blowers that offer high reliability and low energy consumption, as these factors directly impact operational costs and productivity.
What role do blowers play in HVAC systems for commercial buildings?
Blowers are crucial in HVAC systems for circulating air and maintaining ventilation in commercial buildings. By ensuring a consistent airflow, they help improve indoor air quality, which is vital for employee health and comfort. Businesses in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing blowers that are energy-efficient and low in noise levels, as these attributes can lead to significant cost savings and enhance the working environment.
How are blowers utilized in food processing for vacuum packaging?
In the food processing industry, blowers are used for vacuum packaging, which helps extend the shelf life of perishable goods. By removing air from packaging, they reduce spoilage and maintain product quality. B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil must prioritize blowers that comply with health regulations and offer customization options to meet specific packaging needs, ensuring both safety and efficiency in operations.
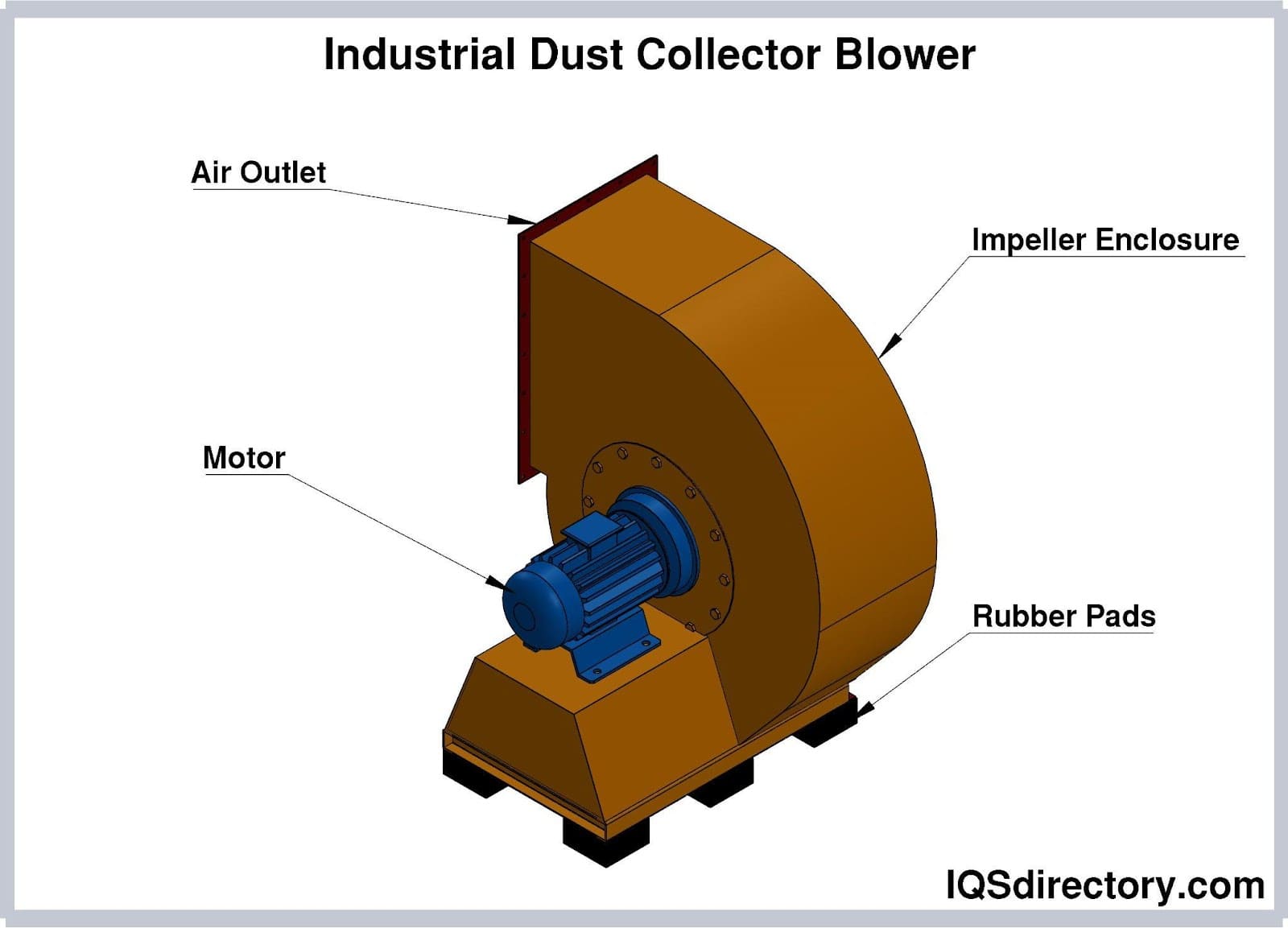
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
What is the significance of blowers in wastewater treatment processes?
Blowers are employed in aeration systems within wastewater treatment plants to introduce oxygen into sewage, facilitating the breakdown of organic matter. This process is essential for meeting environmental regulations and ensuring effective wastewater treatment. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should consider the durability of blowers in harsh environments and their energy efficiency, as these factors can significantly affect operational longevity and compliance with local regulations.
How do blowers enhance cooling systems in the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, blowers are utilized in cooling systems for electric and hybrid vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. They help manage the temperature of critical components, thus enhancing vehicle efficiency. When sourcing blowers, automotive manufacturers in Europe should look for compact designs that minimize weight while maximizing airflow efficiency, as these characteristics are crucial for modern vehicle performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a blower’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Optimal Performance in HVAC Systems
The Problem: A manufacturing facility in Nigeria is facing issues with inadequate air circulation due to outdated blower systems in their HVAC setup. The existing blowers are not delivering sufficient airflow, leading to temperature imbalances and decreased worker productivity. This situation not only affects comfort but can also impact the quality of products being manufactured. The facility manager is overwhelmed with the complexities of evaluating and replacing the blowers while also considering energy efficiency to reduce operational costs.
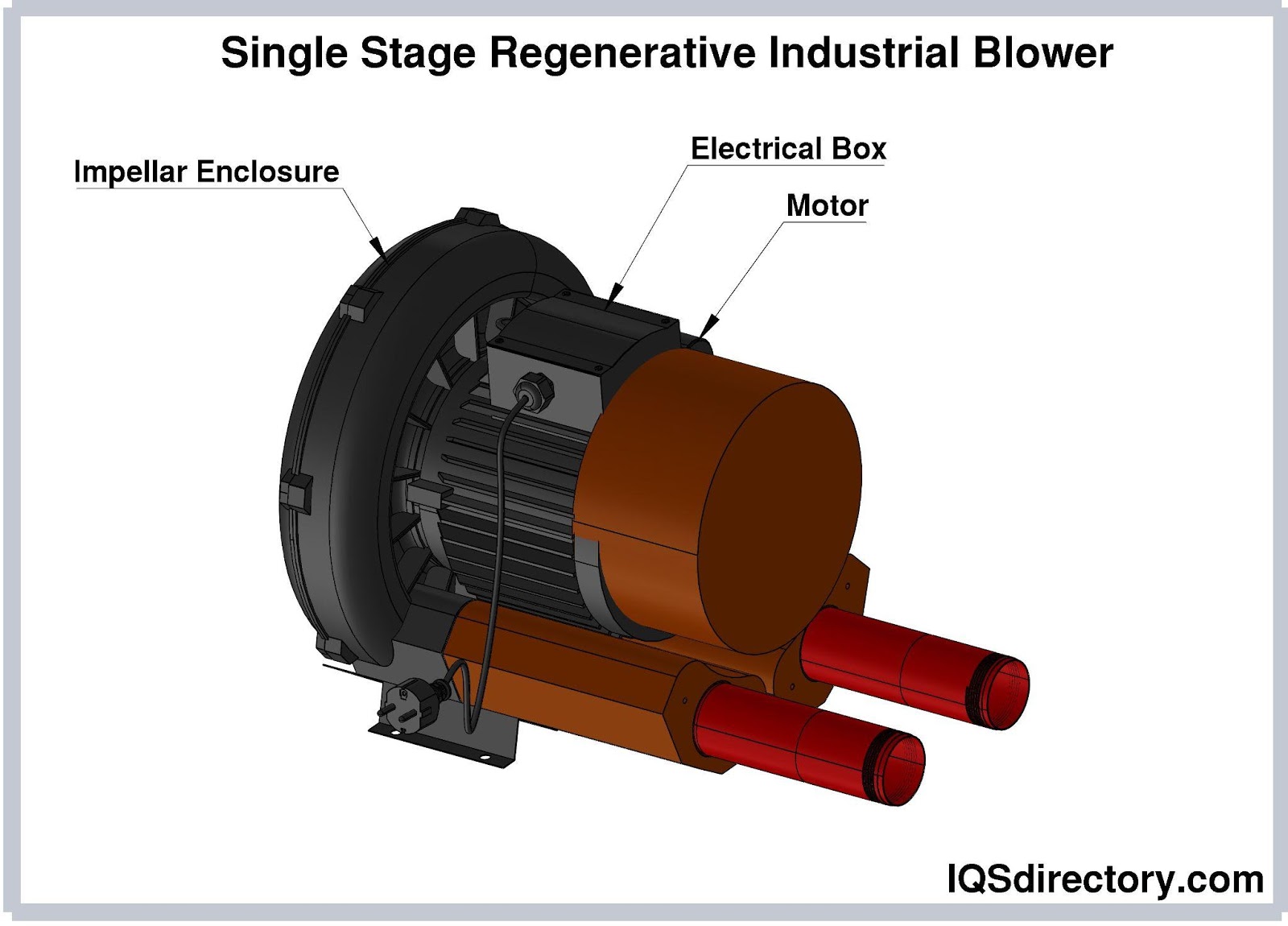
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, the facility manager should conduct a thorough assessment of the current HVAC system and the specific requirements for airflow and pressure. It is crucial to choose a blower type that aligns with the facility’s operational needs—whether that be a centrifugal blower for high-volume applications or an axial blower for directional airflow. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in energy-efficient blowers can provide insights into the latest technologies that enhance performance while lowering energy consumption. Furthermore, considering blowers with variable speed drives can allow for better control over airflow, adapting to varying operational demands and ultimately improving overall system efficiency.
Scenario 2: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions for Blower Components
The Problem: A company in Brazil that relies on blowers for pneumatic conveying systems has encountered significant delays in the supply chain for critical blower components. This disruption is affecting production schedules and leading to potential losses in revenue. The procurement manager is frustrated, facing pressure from upper management to resolve the issue quickly without compromising on quality or functionality.
The Solution: The procurement manager should diversify the supplier base by identifying multiple vendors for blower components, including local manufacturers in South America. Building relationships with these suppliers can ensure a more resilient supply chain and provide alternatives during disruptions. Additionally, it is advisable to maintain an inventory of essential components that can mitigate the impact of future supply chain issues. Engaging with suppliers to understand their manufacturing timelines and capacity can help in planning ahead and reducing lead times. This proactive approach not only secures necessary parts but also fosters collaboration for future innovations in blower technology.
Scenario 3: Customization Challenges in Blower Applications
The Problem: An engineering firm in the Middle East is developing a new product that requires a highly specialized blower system for effective cooling. However, the standard blowers available on the market do not meet the specific pressure and airflow requirements needed for their application. The design engineers are struggling to find a solution that balances performance, size, and energy consumption while still meeting project deadlines.
The Solution: To address this customization challenge, the engineering firm should collaborate closely with blower manufacturers who offer tailored solutions. By providing detailed specifications and performance parameters, the engineers can work with suppliers to create a customized blower that fits their unique application. It is beneficial to request prototypes and conduct thorough testing to ensure that the blower meets the required standards before full-scale production. Additionally, considering modular designs can provide flexibility and allow for easier adjustments in the future. This collaborative approach not only leads to effective solutions but can also result in a strong partnership with the blower manufacturer for ongoing support and innovation.
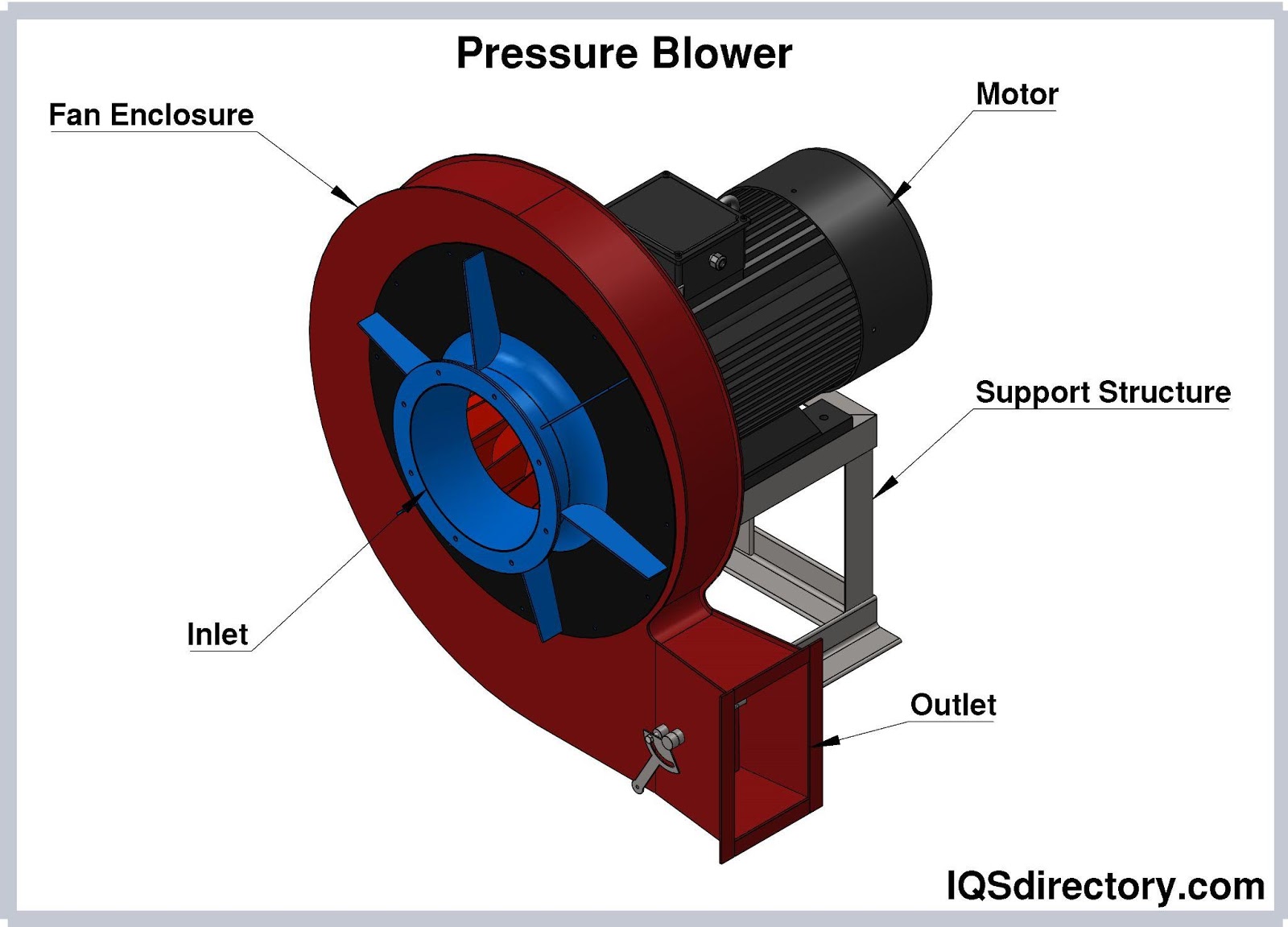
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a blower
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Blower Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for blowers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material directly impacts the blower’s performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in blower manufacturing: aluminum, stainless steel, plastic, and cast iron.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for Blowers?
Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant metal, making it a popular choice for various blower applications. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient heat dissipation.
Pros: Aluminum blowers are durable and resistant to rust, making them ideal for environments with high humidity or corrosive substances. They are also relatively easy to manufacture and can be machined into complex shapes.
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, it may not withstand extremely high temperatures or pressures as well as some other materials. Additionally, it can be prone to deformation under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications involving air and non-corrosive gases. However, it may not be the best choice for environments with abrasive materials or high-pressure requirements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards regarding aluminum alloys, which may differ from those in Europe. Common standards include ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Blower Design?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength, making it suitable for demanding applications. Its key properties include high-temperature resistance and the ability to withstand harsh chemicals.
Pros: Stainless steel blowers are highly durable and can operate effectively in extreme environments, including those involving corrosive gases or high temperatures. They also require minimal maintenance.
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
Cons: The primary drawback is the cost; stainless steel is generally more expensive than aluminum or plastic. Additionally, manufacturing processes for stainless steel can be more complex, potentially leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications in the food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. In regions with strict regulations, such as the EU, ensuring that materials meet these standards is crucial.
How Do Plastics Compare as a Material for Blowers?
Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers like polypropylene and polycarbonate, are increasingly used in blower applications. They offer excellent chemical resistance and are lightweight.
Pros: Plastic blowers are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They are also resistant to corrosion and can handle a wide range of temperatures.
Cons: However, plastics generally have lower strength and durability compared to metals. They may not be suitable for high-pressure applications or environments with extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic blowers are commonly used in HVAC systems and applications involving non-corrosive gases. They are also suitable for industries like electronics, where weight is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. In regions with varying regulations, understanding local material certifications is essential.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Blower Manufacturing?
Cast iron is a traditional material known for its durability and strength. It is often used in heavy-duty applications where robustness is required.
Pros: Cast iron blowers can withstand high pressures and are resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for industrial applications. They also provide excellent vibration dampening.
Cons: The main disadvantages are weight and cost; cast iron is heavier than other materials, which can impact installation and operational efficiency. Additionally, it may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is ideal for applications in mining and heavy manufacturing, where durability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A48 for gray iron castings. In regions with specific industrial regulations, understanding these standards is crucial for market entry.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Blowers
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is a blower | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | HVAC systems, light industrial | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature resistance | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical industries | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Electronics, HVAC systems | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength and durability | Low |
| Cast Iron | Heavy manufacturing, mining | High strength and wear resistance | Heavy and potentially costly | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a blower
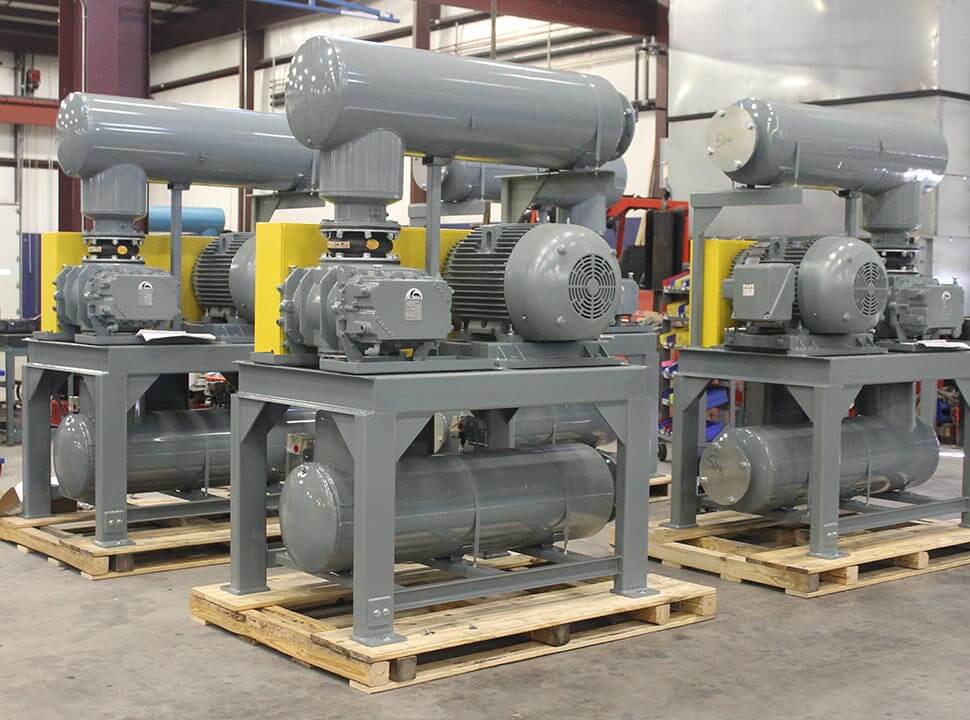
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Blowers?
The manufacturing process of blowers involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers more effectively.

Illustrative image related to what is a blower
How Is Material Prepared for Blower Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where raw materials are sourced and processed. Common materials used in blower manufacturing include metals like aluminum and stainless steel, as well as plastics and composites for specific components.
During this stage, materials undergo quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications. Buyers should look for suppliers that demonstrate stringent material selection processes and can provide material certification documentation.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Blower Components?
Forming is the next stage, where raw materials are shaped into the necessary components of the blower. This includes processes such as:
- Casting: Used for creating complex shapes, especially for blower housings and impellers.
- Machining: Involves cutting and shaping materials to achieve precise dimensions, often used for impellers and other critical components.
- Injection Molding: Typically used for plastic components, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency.
Advanced technologies like CNC machining can enhance accuracy, which is crucial for components that require high precision, such as impellers in centrifugal blowers. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques used by suppliers and their capabilities in handling custom designs.
How Are Blower Components Assembled?
The assembly stage involves putting together all the components manufactured in the previous stages. This process can vary significantly depending on the type of blower being produced. For example, centrifugal blowers may require careful alignment of the impeller and motor to ensure optimal airflow and minimize vibration.
Quality control at this stage is vital. Buyers should ensure that suppliers implement assembly checks, including torque specifications and alignment verification, to prevent operational issues later on.
What Finishing Processes Are Common in Blower Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance both the performance and aesthetics of blowers. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing or powder coating are applied to protect against corrosion and wear, especially in harsh industrial environments.
- Balancing: Ensuring that rotating components, such as impellers, are balanced to reduce vibrations and improve longevity.
- Final Inspection: A thorough examination of the assembled product to check for any defects or inconsistencies.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that utilize advanced finishing techniques and conduct rigorous final inspections to guarantee the blowers’ performance and reliability.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in blower manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Apply to Blower Manufacturing?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) sets forth various standards that many manufacturers adhere to, with ISO 9001 being the most recognized for quality management systems. This standard ensures a consistent approach to quality across all manufacturing processes.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may be required. For example, the CE mark indicates compliance with European safety standards, while API standards apply to blowers used in the oil and gas industry. Buyers should verify that their suppliers possess relevant certifications, indicating adherence to these standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Blower Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to what is a blower
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process to catch defects early, often involving visual inspections and measurements.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of finished products to confirm that they meet performance specifications and regulatory standards.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC measures implemented by suppliers and request documentation of inspection processes to ensure compliance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Blower Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for blowers can vary widely depending on their intended application. Common methods include:
- Performance Testing: Assessing airflow, pressure, and efficiency under various operating conditions to ensure the blower meets design specifications.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting blowers to prolonged use under extreme conditions to evaluate their reliability and lifespan.
- Noise Level Testing: Measuring sound output to ensure compliance with regulatory noise standards, especially for blowers used in residential or commercial environments.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers for details on their testing protocols and the results of any tests conducted, as this information is vital for assessing product quality.

Illustrative image related to what is a blower
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international markets.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier Quality Control?
Buyers can conduct audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This can include:
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes firsthand, interview staff, and review documentation.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations to perform independent inspections and assessments of supplier quality practices.
Such audits help ensure that suppliers adhere to the necessary standards and can provide the quality products that buyers require.
What Documentation Should Buyers Request from Suppliers?
Buyers should request various documents to verify a supplier’s quality control practices, including:
- Quality Management System Documentation: Evidence of ISO certifications and adherence to quality standards.
- Inspection and Test Reports: Documentation showing results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes.
- Compliance Certificates: Proof of compliance with relevant industry standards, such as CE or API certifications.
This documentation provides essential insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to deliver reliable products.
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several unique QC considerations come into play.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Control?
Different regions may have varying regulatory standards and certifications. For instance, the CE marking is crucial for products sold within the European Union, while buyers in the Middle East may require compliance with local safety regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with regional requirements and ensure that suppliers can meet these standards.
What Challenges Do International Buyers Face in Verifying Quality Control?
International buyers may encounter challenges such as language barriers, time zone differences, and varying cultural perceptions of quality. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to establish clear communication channels and possibly engage local representatives or third-party auditors who understand both the supplier’s and the buyer’s expectations.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for blowers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a blower’
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in understanding the essential steps for sourcing blowers effectively. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your procurement process is efficient and aligned with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical requirements of the blower is crucial. Consider factors such as airflow capacity, pressure requirements, and energy efficiency. Identifying these specifications helps narrow down your options and ensures that the blower will meet your operational needs.
- Airflow Capacity: Determine the volume of air required for your application.
- Pressure Requirements: Assess the pressure needed to move air or gas effectively.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for energy-efficient models to reduce operational costs.
Step 2: Identify the Type of Blower Needed
Different applications require different types of blowers, such as centrifugal, axial, or positive displacement. Each type has distinct operational principles and is suited for specific tasks. Knowing which type is appropriate for your application will streamline your sourcing process.
- Centrifugal Blowers: Ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Axial Blowers: Best for moving large volumes of air at lower pressures.
- Positive Displacement Blowers: Suitable for consistent airflow at varying pressures.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This due diligence helps ensure reliability and quality in your procurement process.
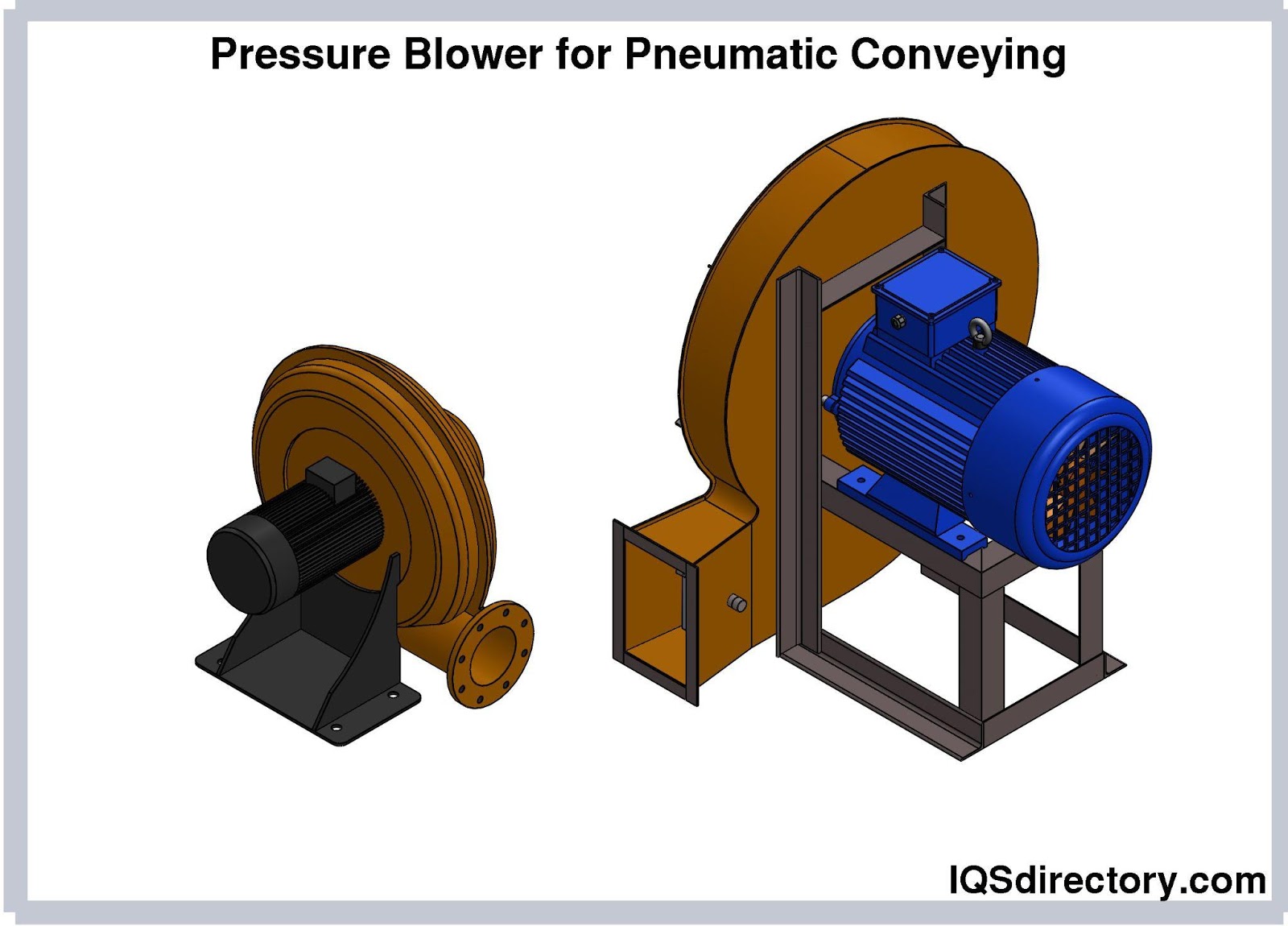
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
- Company Profiles: Review the supplier’s history and experience in the industry.
- Case Studies: Look for documented successes that illustrate the supplier’s capabilities.
- References: Speak with previous clients to gauge their satisfaction and the supplier’s performance.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the blowers and suppliers meet relevant industry standards and certifications. Compliance with international standards can affect product quality and safety, especially in regulated industries such as healthcare or food processing.
- ISO Certifications: Check if the supplier has ISO certifications relevant to manufacturing processes.
- Local Regulations: Understand any regional regulations that may impact product specifications.
- Safety Standards: Verify adherence to safety standards applicable in your industry.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information. A comprehensive quote enables you to compare offers transparently.
- Pricing Structure: Look for clarity in pricing, including any additional costs.
- Delivery Timelines: Ensure that the timelines align with your project requirements.
- Warranty Information: Understand the warranty terms to safeguard your investment.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by the supplier, as this can significantly impact your operational efficiency. Strong support can help address issues quickly and minimize downtime.
- Technical Support: Ensure the availability of technical assistance for installation and maintenance.
- Spare Parts Availability: Confirm that spare parts are readily available for future needs.
- Training Options: Look for training programs for your staff on the blower’s operation and maintenance.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly defined in the contract. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and service agreements. A well-defined contract protects both parties and ensures mutual understanding.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment schedules and methods.
- Delivery Terms: Confirm the responsibilities regarding shipping and handling.
- Service Agreements: Outline any maintenance or service commitments post-purchase.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for blowers more effectively, ensuring that they select the right products and partners for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a blower Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Blower Sourcing?
When sourcing blowers, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly influences the cost of blowers. High-quality metals, plastics, and specialized components (like impellers and casings) can drive up costs. Suppliers often provide options for both standard and premium materials, impacting durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may provide savings, but this can sometimes compromise quality. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality control, which can elevate costs in more developed regions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, but investments in automation may initially increase costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific blower designs can represent a significant upfront investment. However, this cost can be amortized over larger production runs, making it more economical for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures product reliability and performance. While this may add to the overall cost, it can reduce long-term expenses related to warranty claims and product failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and the volume of the order. International shipments may incur additional duties and tariffs, impacting total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the average margins in your specific market can aid in negotiations.
What Factors Influence Pricing in Blower Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of blowers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to significant discounts. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) set by suppliers is crucial for cost management.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized blowers that meet specific application requirements generally cost more due to additional engineering and production processes. Clearly defining your needs can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects durability but also pricing. Standard materials may be more cost-effective, but they might not meet performance requirements in demanding applications.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet industry standards or possess certifications (such as ISO) may come at a premium. However, investing in certified products can lead to lower long-term costs through enhanced reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often provide better support and warranty terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery can affect overall costs. Different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting the final price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Blowers?
-
Negotiate on Volume: Engaging in bulk purchasing can enhance your negotiating power. Suppliers are often more willing to offer discounts for larger orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may result in lower TCO if the blower is more efficient and durable.
-
Research Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Understanding regional pricing dynamics, including tariffs and local regulations, can provide leverage during negotiations, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various suppliers can provide insight into market pricing and help identify competitive offers.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing, priority service, and favorable terms over time.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices for blowers can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should conduct thorough research and engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a blower With Other Solutions
When evaluating options for air movement and gas handling in various industrial applications, understanding the alternatives to blowers is crucial for making informed decisions. Blowers are commonly used devices that generate airflow, but there are other technologies that can achieve similar results. This analysis compares blowers with two viable alternatives: fans and compressors. Each solution has unique characteristics that may suit specific operational needs better than others.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is A Blower | Alternative 1: Fan | Alternative 2: Compressor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Medium pressure (1.11 to 1.20 ratio) | Low pressure, high airflow | High pressure (1.20 and above) |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Generally lower cost | Higher upfront and operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized setup | Easy to install and use | Complex setup, often requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance requirements | Low maintenance needs | High maintenance, regular servicing needed |
| Best Use Case | Pneumatic conveying, dust extraction | Ventilation, cooling | Industrial processes requiring high pressure |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Fans as an Alternative?
Fans are typically used for low-pressure applications where high airflow is essential, such as in HVAC systems or for cooling electronic equipment. Their primary advantage lies in their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Fans are easier to install and require less maintenance compared to blowers. However, they do not provide the necessary pressure for applications like pneumatic conveying or dust extraction, which limits their usability in more demanding environments.
How Do Compressors Compare to Blowers?
Compressors are designed for high-pressure applications and are often used in industrial processes that require significant pressure differentials. Their ability to compress air makes them suitable for tasks such as powering pneumatic tools or providing high-pressure air for various applications. However, compressors typically come with a higher initial investment and operational costs. Additionally, they require more complex setups and maintenance, making them less user-friendly for some operations. Their specialized nature makes them ideal for specific high-pressure tasks but may be overkill for applications where blowers would suffice.
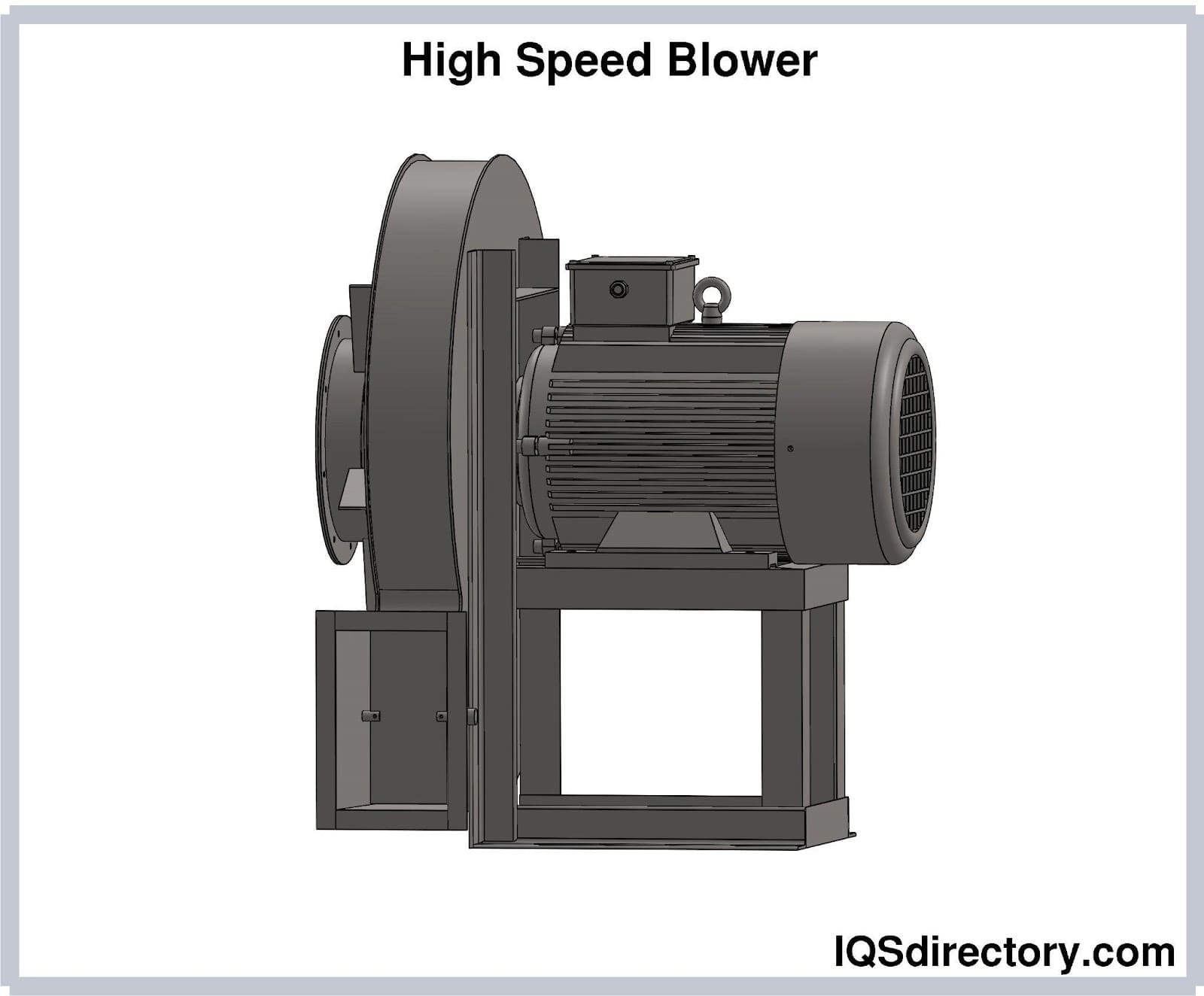
Illustrative image related to what is a blower
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate solution for air movement and gas handling, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific application needs. Blowers offer a balanced performance suitable for various industrial uses, especially where medium pressure is required. Fans are ideal for cost-sensitive applications that prioritize airflow, while compressors are best suited for high-pressure needs despite their higher costs and maintenance requirements. By assessing the performance requirements, budget constraints, and ease of implementation, buyers can make an informed choice that aligns with their operational goals. This strategic approach ensures optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a blower
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Blowers in B2B Applications?
Understanding the technical properties of blowers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating performance and compatibility with existing systems. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Pressure Rating
Pressure rating refers to the maximum pressure a blower can generate, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or pascals (Pa). This specification is vital for determining if a blower can handle the specific requirements of an application, such as pneumatic conveying or air pollution control. Buyers should ensure that the pressure rating aligns with their operational needs to avoid system failures.
2. Flow Rate
Measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or liters per second (L/s), flow rate indicates the volume of air or gas that a blower can move within a given timeframe. This property is essential for applications requiring consistent airflow, such as HVAC systems or industrial ventilation. Selecting a blower with the appropriate flow rate ensures efficiency and meets the demands of the process.
3. Power Consumption
Power consumption, usually indicated in watts (W) or horsepower (HP), reflects the energy required to operate the blower. This specification is crucial for assessing operational costs and energy efficiency. In regions where energy costs are high, selecting blowers with lower power consumption can lead to significant savings over time.
4. Material Grade
The material grade of a blower impacts its durability, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for specific environments. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and various plastics. Understanding material properties helps buyers choose blowers that can withstand harsh conditions, especially in industries like food processing or chemical manufacturing.
5. Noise Level
Noise levels are measured in decibels (dB) and indicate how loud a blower operates. This specification is particularly important in environments where noise regulations are strict or where worker comfort is a priority. Selecting low-noise blowers can enhance workplace safety and compliance with local regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Blowers?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms used in the blower industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the blower industry, this term is crucial for buyers looking to source components that fit seamlessly into existing machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It allows businesses to plan their purchases according to demand while minimizing excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. For blowers, an RFQ can help businesses obtain competitive pricing and understand delivery timelines, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities.
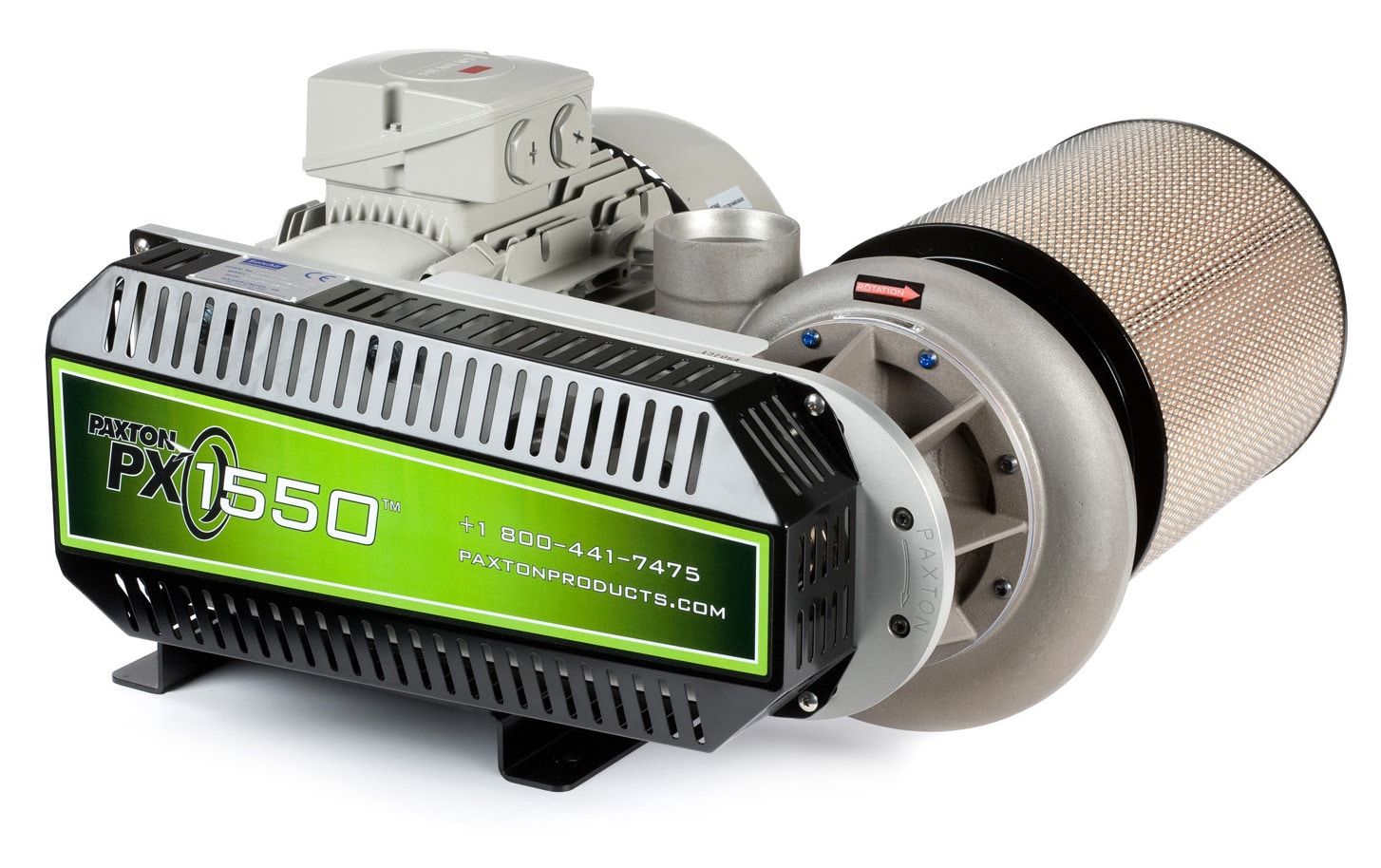
5. Centrifugal and Positive Displacement
These terms refer to the two primary types of blowers. Centrifugal blowers use a rotating impeller to increase air pressure and flow, while positive displacement blowers trap a fixed amount of air and force it into the discharge pipe. Knowing the difference helps buyers select the right blower type for their specific application needs.

Illustrative image related to what is a blower
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting blowers for their operations, ultimately leading to enhanced efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a blower Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Blower Sector?
The blower market is witnessing dynamic growth driven by several global factors, including industrialization, urbanization, and the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a burgeoning need for blowers in various sectors such as HVAC, automotive, and manufacturing. Emerging technologies, particularly in automation and smart manufacturing, are reshaping sourcing strategies. For instance, the integration of IoT-enabled blowers offers real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, significantly enhancing operational efficiency.
International buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only robust performance but also customization options that cater to specific industrial applications. Furthermore, the demand for environmentally friendly solutions is prompting manufacturers to innovate in blower design, focusing on energy efficiency and reduced noise levels. As competition intensifies, B2B buyers must stay abreast of these trends to ensure they partner with suppliers that can meet their evolving needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Blower Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the blower sector, with environmental impact assessments influencing procurement decisions. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through innovative blower designs that consume less energy and incorporate recyclable materials. The adoption of “green” certifications such as Energy Star and ISO 14001 is gaining traction, as these credentials assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are imperative in today’s market. Buyers are demanding transparency in supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly, minimizing exploitation and environmental degradation. Suppliers that adhere to ethical standards not only enhance their brand reputation but also appeal to a growing segment of socially conscious buyers. As sustainability becomes a core component of business strategy, B2B companies in the blower sector must align their sourcing practices with these values to remain competitive.
What is the Historical Context of Blower Development and Its Relevance to Current B2B Trends?
The evolution of blowers can be traced back to ancient technologies like bellows, which were initially used to supply air for iron smelting. Over time, advancements in power sources, including steam and electricity, led to the development of various pneumatic devices. Today, blowers are integral to multiple industries, from HVAC systems to pneumatic conveying systems.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the technological advancements that have shaped current market offerings. Modern blowers are not just simple air-moving devices; they are complex systems designed for efficiency and performance. Recognizing this evolution allows buyers to appreciate the innovations available today, such as energy-efficient designs and advanced control systems, which are crucial for optimizing industrial processes.
In conclusion, navigating the blower market requires a keen understanding of current trends, sustainability imperatives, and historical advancements. By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a blower
-
How do I choose the right blower for my industrial application?
Choosing the right blower depends on several factors, including the specific application, required airflow, pressure levels, and the type of materials being handled. Start by defining your operational requirements, such as airflow rate (CFM) and pressure (inches of water gauge). Assess the environment where the blower will be used, including temperature and potential exposure to corrosive materials. Consult with suppliers for recommendations based on your specifications, and consider blowers with customization options to ensure they meet your unique needs. -
What are the main types of blowers and their applications?
The main types of blowers include centrifugal, axial, positive displacement, and regenerative blowers. Centrifugal blowers are widely used in HVAC systems and industrial ventilation due to their ability to handle high volumes of air at moderate pressures. Axial blowers are ideal for cooling applications and confined space ventilation. Positive displacement blowers are often used in pneumatic conveying systems for moving bulk materials. Understanding the application will help you select the most efficient type for your needs. -
What should I consider when vetting a blower supplier?
When vetting a blower supplier, consider their industry experience, reputation, and product quality. Review their certifications and compliance with international standards, especially if you’re sourcing from regions with different regulations. Request references or case studies to gauge their reliability. Additionally, assess their ability to provide technical support, customization options, and after-sales service. A supplier’s responsiveness and willingness to engage in discussions about your specific requirements are also critical indicators of their suitability. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for blowers?
Minimum order quantities for blowers can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of blower and customization options. Generally, standard blowers may have a MOQ ranging from 10 to 100 units, while customized units may require higher quantities due to production setup costs. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs, especially if you are a smaller company or if you’re testing a new product line. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing blowers internationally?
Common payment terms for international blower purchases typically include options like T/T (telegraphic transfer), L/C (letter of credit), or D/P (documents against payment). T/T is often preferred for smaller orders due to its simplicity, while L/C may be used for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms upfront, including any deposits required, payment schedules, and the currency used. Ensure that the terms align with your cash flow capabilities and risk management strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for blowers I source?
To ensure quality assurance for sourced blowers, start by selecting suppliers who adhere to recognized quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request detailed specifications and certifications for the blowers, and consider conducting factory audits or inspections before shipment. Establish clear quality benchmarks, and ask for samples or prototypes to evaluate performance before placing a larger order. Implement a robust inspection process upon delivery to verify that the products meet your requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing blowers?
When importing blowers, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Air freight may offer faster delivery but at a higher cost, while sea freight is more economical for bulk orders but takes longer. Be aware of any import duties, taxes, and compliance requirements to avoid unexpected delays or costs. Collaborate with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to facilitate smooth customs clearance and delivery. -
Can blowers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for blowers to meet specific application requirements. Customization may include adjustments to size, airflow capacity, pressure ratings, motor types, and materials used in construction. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and operational parameters to ensure they can tailor their products to fit your application. Custom blowers can enhance efficiency and performance, making them a valuable investment for specialized tasks.
Top 3 What Is A Blower Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PDBlowers – Industrial Air Blowers
Domain: pdblowers.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Industrial air blowers are machines used for blowing or sucking air and gas, critical in various industries such as healthcare, food production, power plants, sewage treatment, plastics production, and more. They differ from fans and compressors in that blowers move large volumes of air at moderate pressure (pressure ratio 1.11 to 1.20), while fans operate at low pressure and compressors create hi…
2. Mechanics – Blower Supercharger
Domain: mechanics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: A ‘Blower’ is another name for a supercharger, particularly ‘Roots’ type superchargers that use long figure-of-8 shaped vanes to force or ‘blow’ air into the engine. Specific requirements include strong engine internals to handle extra power and a fuel system capable of providing enough fuel to match the additional air. Disadvantages include that it is belt-driven from the crank, using some power …
3. Merriam-Webster – Blower Definition
Domain: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Blower is defined as a noun with several meanings: 1) one that blows, 2) a device for producing a current of air or gas, 3) a braggart, and 4) chiefly British, a telephone. The term has been in use since before the 12th century. Examples of usage include references to devices like leaf blowers and snow blowers, as well as idiomatic expressions involving the term.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a blower
Blowers play a crucial role across various industries, from HVAC systems to pneumatic conveying and industrial processes. Understanding the different types of blowers—centrifugal, axial, and positive displacement—enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Strategic sourcing of blowers not only optimizes performance but also enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs.
In today’s competitive landscape, leveraging advanced blower technology can significantly impact productivity and sustainability. For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this presents an opportunity to explore innovative solutions that can drive growth and efficiency within their operations.
As the demand for reliable and efficient airflow solutions continues to rise, businesses should proactively seek partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize customization, performance, and cost-effectiveness. By investing in strategic sourcing of blowers, companies can ensure they are equipped to meet future challenges and capitalize on emerging market opportunities. Engage with suppliers who understand your unique requirements and can provide tailored solutions that propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.