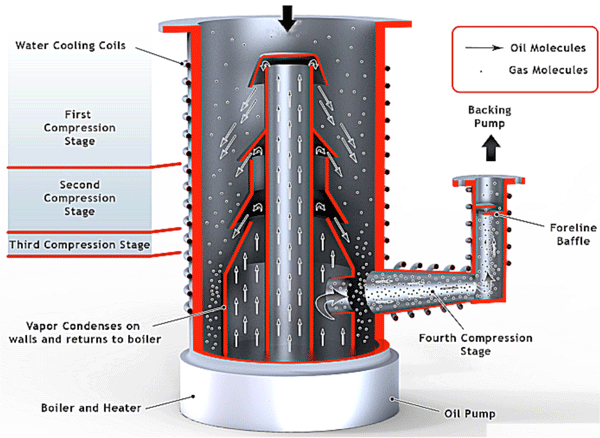
How to Source Vacuum Pump Diagram Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vacuum pump diagram
In the complex landscape of industrial equipment, understanding the intricacies of a vacuum pump diagram is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations. The challenge of sourcing reliable vacuum pumps often stems from a lack of clarity regarding their types, functionalities, and applications. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by providing a deep dive into various vacuum pump types, their respective diagrams, and the contexts in which they operate.
From oil-sealed to dry vacuum pumps, this resource covers essential information that empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It also delves into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for maintenance, ensuring that businesses can select equipment that meets their specific needs.
For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam, this guide serves as an invaluable tool. By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge to interpret vacuum pump diagrams effectively, it streamlines the sourcing process, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, this guide will provide the insights necessary to navigate the global market with confidence.
Understanding vacuum pump diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Vane Pumps | Uses rotating vanes to create a vacuum; typically oil-sealed. | Food processing, packaging, and pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Reliable, efficient for low to medium vacuum. Cons: Requires oil maintenance, potential contamination. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Employs a flexible diaphragm; oil-free operation. | Medical devices, laboratory applications. | Pros: Clean, oil-free operation; low maintenance. Cons: Limited capacity and pressure range. |
| Turbomolecular Pumps | High-speed rotor creates vacuum; suitable for ultra-high vacuum. | Semiconductor manufacturing, research labs. | Pros: Excellent for high vacuum applications; minimal contamination. Cons: High cost; requires precise control. |
| Scroll Pumps | Uses two interleaved scrolls to compress gas; oil-free. | Electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging. | Pros: Quiet, low maintenance, and energy-efficient. Cons: Limited to specific applications; higher initial cost. |
| Roots Blower Pumps | Positive displacement design; often used in combination with other pumps for high flow rates. | Steel degassing, chemical processing. | Pros: High pumping speed, effective for large volumes. Cons: Requires pre-pumping; can be bulky. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Rotary Vane Pumps for B2B Buyers?
Rotary vane pumps are characterized by their use of rotating vanes that slide in and out of a rotor to create a vacuum. They are commonly oil-sealed, which enhances performance but requires regular maintenance to prevent oil contamination. These pumps are particularly suitable for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals where consistent vacuum levels are crucial. B2B buyers should consider the balance between reliability and maintenance costs, as well as the potential impact of oil contamination on product quality.
How Do Diaphragm Pumps Stand Out in Vacuum Technology?
Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm to create a vacuum, making them an excellent choice for applications requiring an oil-free environment, such as in medical devices and laboratory settings. Their design allows for low maintenance and clean operation, making them ideal for sensitive applications. However, their capacity and pressure range are limited compared to other types. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications to determine if the benefits of cleanliness outweigh the limitations in capacity.
Why Choose Turbomolecular Pumps for Ultra-High Vacuum Applications?
Turbomolecular pumps are distinguished by their high-speed rotor, which efficiently creates a vacuum suitable for ultra-high vacuum applications. They are essential in fields such as semiconductor manufacturing and research laboratories, where precise control and minimal contamination are paramount. While they offer exceptional performance, they come at a higher cost and require sophisticated control systems. Buyers must weigh the investment against the critical vacuum requirements of their processes.
What Advantages Do Scroll Pumps Offer for B2B Applications?
Scroll pumps operate using two interleaved scrolls to compress gas, providing an oil-free vacuum solution. They are known for their quiet operation and energy efficiency, making them suitable for environments where noise is a concern, such as in pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing. While they may have a higher initial cost, their low maintenance needs can lead to cost savings over time. Companies should assess their noise and energy consumption requirements when considering scroll pumps.
How Are Roots Blower Pumps Effective for High Flow Rate Applications?
Roots blower pumps utilize a positive displacement design, making them particularly effective for high flow rate applications. They are often employed in processes such as steel degassing and chemical processing. While they can achieve high pumping speeds, they typically require a pre-pumping system to maintain efficiency and can be bulky. Buyers should consider the space requirements and the need for additional pumping systems when evaluating roots blowers for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of vacuum pump diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Vacuum Pump Diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Sterilization Processes | Ensures product safety and compliance | Regulatory standards, reliability, and maintenance support |
| Food Processing | Vacuum Packaging | Extends shelf life and preserves quality | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Vacuum Coating for Semiconductor Production | Enhances product durability and performance | Precision, scalability, and supplier expertise |
| Automotive | Brake System Testing | Increases safety and reliability | Compliance with industry standards and testing accuracy |
| Renewable Energy | Solar Panel Manufacturing | Improves efficiency and energy output | Equipment durability, sourcing sustainability, and cost |
How is the Vacuum Pump Diagram Utilized in the Pharmaceutical Industry for Sterilization Processes?
In the pharmaceutical sector, vacuum pump diagrams are crucial for visualizing and implementing sterilization processes. They help in mapping out the system components and flow, ensuring that all parts operate efficiently to eliminate contaminants. This application is vital for maintaining product safety and adhering to stringent regulatory standards. Buyers must consider the reliability of the equipment, maintenance support, and compliance with health regulations when sourcing vacuum pumps for their operations.
What Role Does Vacuum Pump Diagram Play in Food Processing for Vacuum Packaging?
In food processing, vacuum pump diagrams are used to design vacuum packaging systems that help extend the shelf life of products by removing air and sealing them tightly. This process prevents spoilage and maintains food quality. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying climate conditions, it’s essential to ensure that the vacuum pumps are compatible with the packaging materials used and that they operate efficiently to minimize energy costs while maximizing productivity.
How is the Vacuum Pump Diagram Relevant to Electronics Manufacturing in Vacuum Coating?
Vacuum pump diagrams are integral to the electronics manufacturing sector, particularly in the vacuum coating of semiconductors. These diagrams provide a clear representation of the vacuum system, ensuring optimal conditions for coating applications that enhance product durability and performance. Buyers should prioritize precision in the vacuum system design and the supplier’s expertise in handling complex processes to ensure high-quality outputs and scalability for production demands.
Why is the Vacuum Pump Diagram Important for Automotive Brake System Testing?
In the automotive industry, vacuum pump diagrams are essential for visualizing the testing processes of hydraulic brake systems. They ensure that the vacuum systems used for testing are correctly configured to guarantee safety and reliability in vehicle performance. Buyers should focus on sourcing pumps that meet industry standards, ensuring accuracy in testing procedures, and providing comprehensive technical support for maintenance and troubleshooting.
How Does the Vacuum Pump Diagram Enhance Renewable Energy in Solar Panel Manufacturing?
In renewable energy, particularly in solar panel manufacturing, vacuum pump diagrams are critical for optimizing processes such as lamination and crystal growth. These diagrams help visualize the vacuum systems that create the necessary conditions for high-efficiency solar panels. For international buyers, it is important to consider the durability of the equipment and the sustainability of sourcing practices to align with environmental goals while ensuring cost-effectiveness in production.
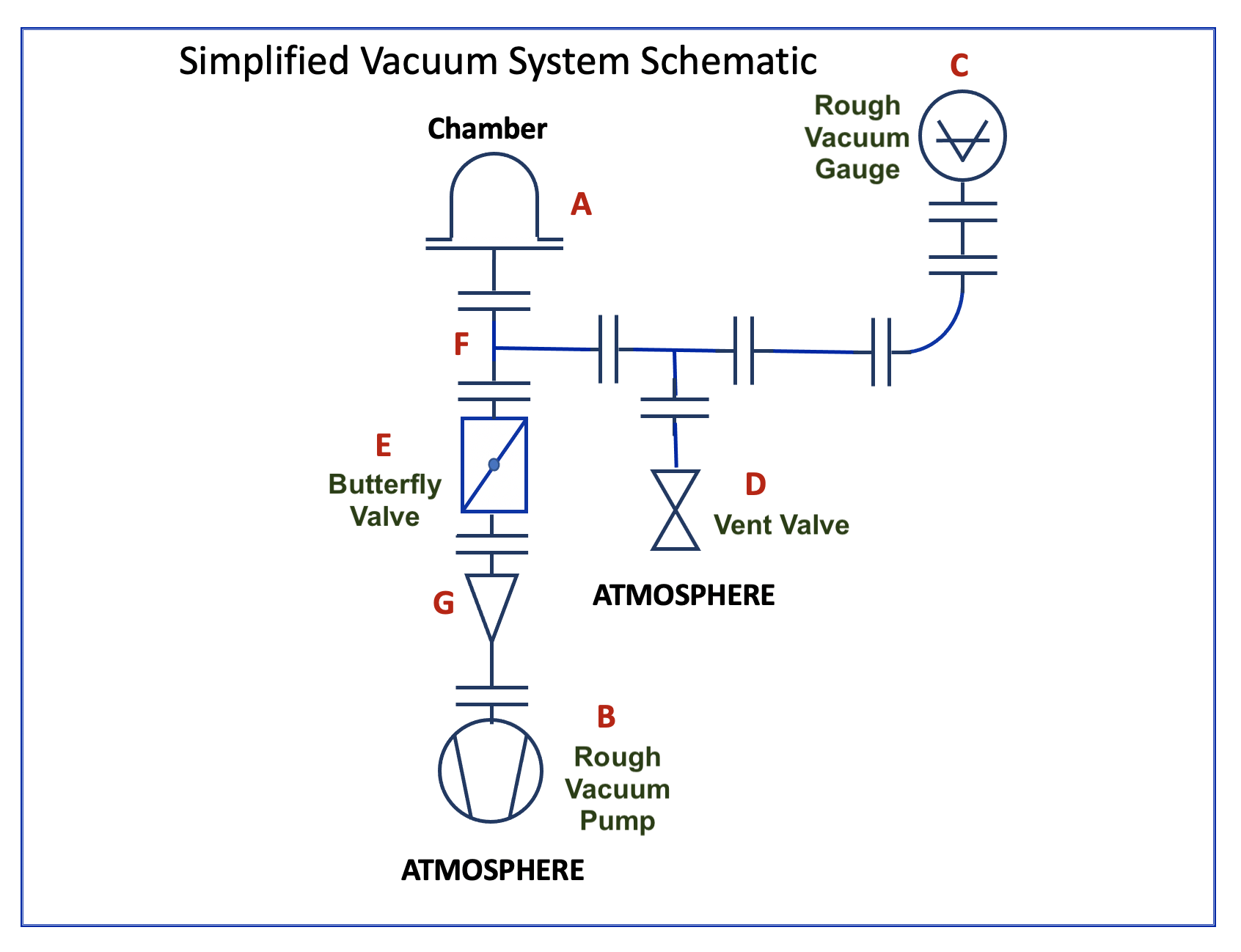
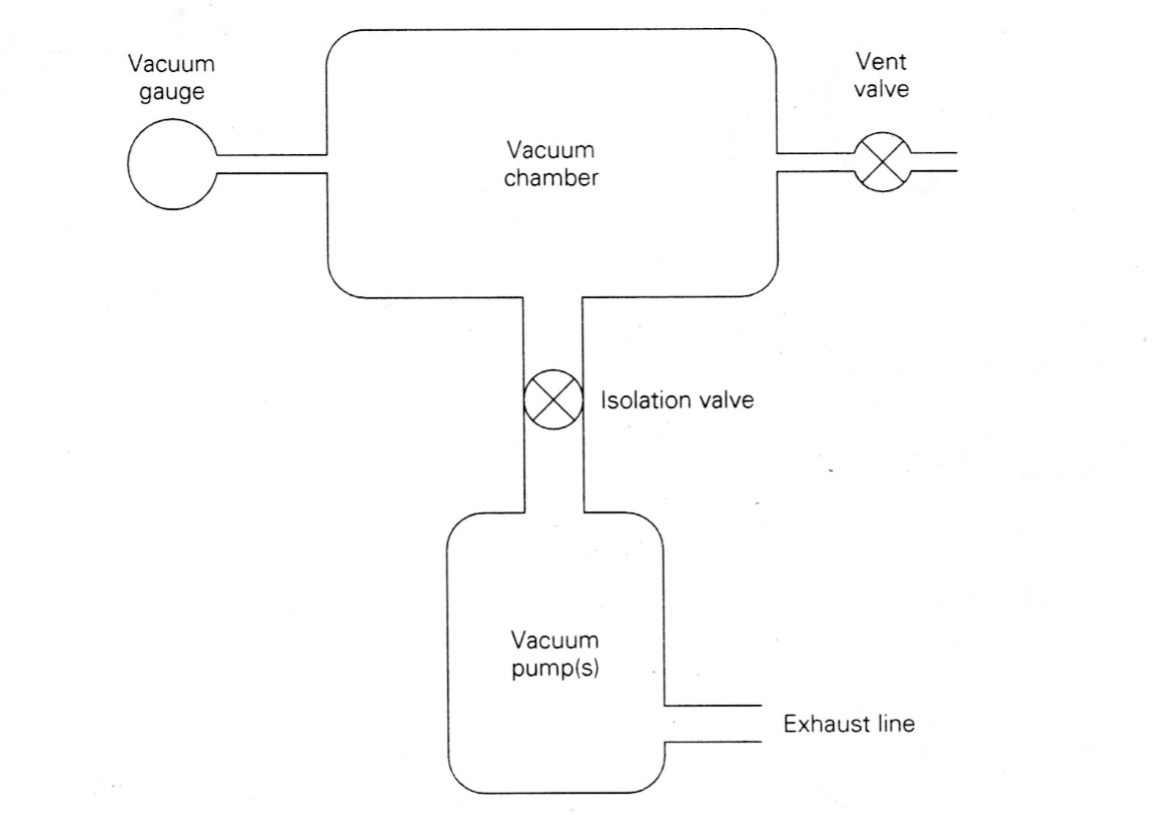
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vacuum pump diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misinterpretation of Vacuum Pump Diagrams Leads to Operational Inefficiencies
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter complex vacuum pump diagrams that can be misinterpreted due to their intricate symbols and notations. This misinterpretation can lead to incorrect installation or maintenance practices, resulting in operational inefficiencies. For example, a manufacturer in Nigeria may struggle to identify the correct vacuum pump type required for their process, leading to delays in production and increased costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, it is crucial for buyers to invest time in understanding the symbols and terminologies used in vacuum pump diagrams. Engaging in training sessions or workshops provided by suppliers can significantly enhance comprehension. Additionally, creating a comprehensive reference guide that explains each symbol and its function can serve as a valuable resource for teams. By collaborating with experienced engineers during the diagram review phase, buyers can ensure that they select the right equipment and reduce the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Lack of Standardization in Vacuum Pump Diagrams Causes Confusion
The Problem: Inconsistent representations of vacuum pump diagrams across different manufacturers can create confusion for B2B buyers. For instance, a company in Brazil may receive technical drawings from various suppliers that use different symbols or notations, complicating the decision-making process and potentially leading to mismatched equipment specifications. This lack of standardization can hinder project timelines and increase procurement costs.
The Solution: B2B buyers should advocate for standardized vacuum pump diagrams when sourcing equipment. They can establish relationships with suppliers who adhere to internationally recognized standards, such as ISO or ANSI, for technical documentation. Furthermore, developing an internal checklist that aligns with these standards can help teams evaluate the clarity and consistency of the diagrams they receive. By prioritizing standardized documentation, buyers can streamline the procurement process and enhance collaboration among teams.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Vacuum Pump Diagrams for Specific Applications
The Problem: Custom applications often require tailored vacuum pump solutions, but B2B buyers may find it challenging to adapt existing diagrams to meet their unique needs. For example, a food processing company in Vietnam may need a vacuum system that accommodates specific packaging requirements, yet the provided diagrams do not reflect these modifications. This can lead to delays in project implementation and increased costs due to the need for additional engineering work.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should collaborate closely with their suppliers during the design phase to ensure that vacuum pump diagrams are customizable. By providing detailed specifications and discussing application-specific requirements, buyers can work with engineers to create diagrams that accurately reflect their needs. Utilizing software tools that allow for diagram modifications can also enhance the customization process. Additionally, conducting regular reviews of these diagrams with the engineering team can ensure that all parties are aligned and reduce the risk of miscommunication. By fostering a collaborative environment, buyers can achieve tailored solutions that meet their operational demands effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vacuum pump diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Vacuum Pump Diagrams and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for vacuum pump diagrams, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the implications for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vacuum pump technology: stainless steel, aluminum, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), and glass.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Vacuum Pump Applications?
Stainless steel is widely regarded for its durability and strength. With excellent temperature and pressure ratings, it can withstand extreme conditions, making it suitable for high-performance vacuum pumps. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in applications where exposure to aggressive chemicals is expected.
Pros: Stainless steel offers high durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring long service life and reliability. It is also relatively easy to fabricate, which makes it suitable for complex designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than other materials. Additionally, its weight may pose challenges in applications where weight reduction is critical.
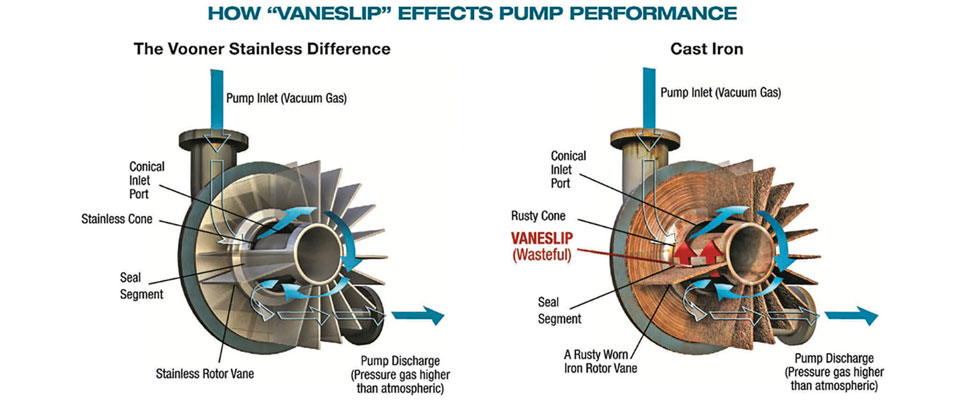
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive gases and liquids, making it versatile across various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of stainless steel grades specific to their region, as this can affect procurement and lead times.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Vacuum Pump Design?
Aluminum is another popular choice for vacuum pump components due to its lightweight and good thermal conductivity. While it has lower strength compared to stainless steel, it is often used in applications where weight savings are essential.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can lead to reduced energy consumption in transportation and operation. It is also less expensive than stainless steel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Cons: Aluminum has lower corrosion resistance and may not be suitable for all media, particularly aggressive chemicals. Its mechanical properties can also degrade at elevated temperatures.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is best suited for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as portable vacuum systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards for quality and performance. Additionally, they should be aware of the differences in aluminum alloys available in various regions.
Why is PTFE Important for Vacuum Pump Applications?
PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, is a fluoropolymer with exceptional chemical resistance and low friction properties. It is particularly useful in seals and gaskets within vacuum pumps.
Pros: PTFE’s chemical inertness makes it ideal for handling aggressive solvents and corrosive substances. It also has a low coefficient of friction, which reduces wear and tear on moving parts.
Cons: The main limitation of PTFE is its mechanical strength, which is lower than metals. It can also be more expensive than traditional materials.
Impact on Application: PTFE is critical in applications involving corrosive gases or liquids, ensuring that seals maintain integrity and prevent leaks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food and pharmaceutical-grade standards is vital for applications in sensitive industries. Buyers should verify that PTFE materials meet international certifications.
How Does Glass Contribute to Vacuum Pump Systems?
Glass is often used in vacuum pump diagrams for components that require visibility of the internal processes, such as sight glasses or pressure gauges. It is chemically inert and can handle a range of temperatures.
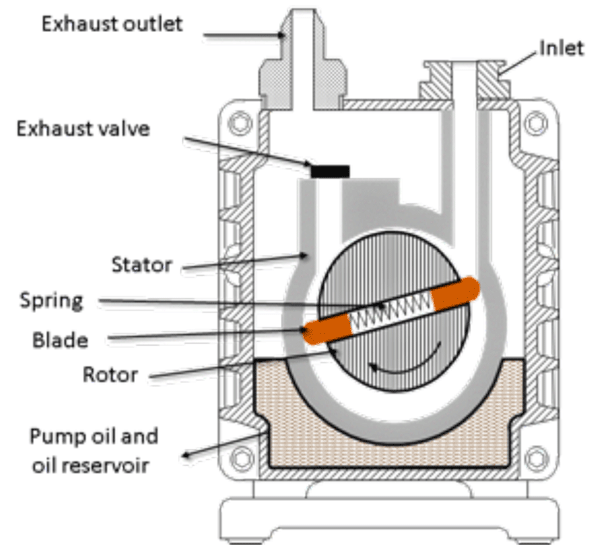
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
Pros: Glass is highly resistant to chemical corrosion and allows for easy monitoring of the vacuum process. It is also non-reactive, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: The fragility of glass can be a significant drawback, as it may break under mechanical stress. Additionally, its weight can be a concern in portable applications.
Impact on Application: Glass is particularly useful in laboratory settings where monitoring is essential, but it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that glass components meet safety standards to prevent breakage during operation. Availability may vary by region, impacting procurement.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Vacuum Pump Diagrams
| Material | Typical Use Case for vacuum pump diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-performance vacuum pumps | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Portable vacuum systems | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower corrosion resistance | Medium |
| PTFE | Seals and gaskets in vacuum pumps | Exceptional chemical resistance | Lower mechanical strength | High |
| Glass | Sight glasses and pressure gauges | Chemical inertness and visibility | Fragility and potential breakage | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in vacuum pump diagrams, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
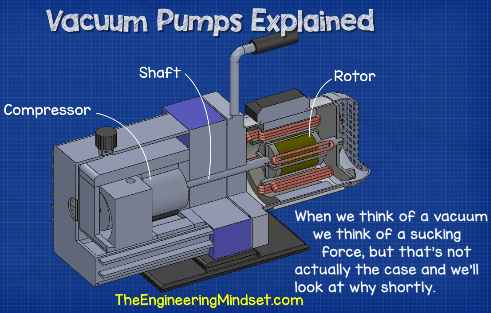
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vacuum pump diagram
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Vacuum Pumps?
The manufacturing of vacuum pumps involves several critical stages, each essential to ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials, which can include metals, plastics, and elastomers. Each material must be sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure quality. This stage often involves cutting and machining the materials to precise specifications, ensuring they are ready for the forming stage.
Forming Techniques: The forming stage employs various techniques, including casting, machining, and welding, depending on the type of vacuum pump being produced. For instance, metal components may be die-cast or machined for accuracy, while plastic parts might be injection molded. The choice of forming technique affects the pump’s efficiency and durability, making it crucial for manufacturers to select the right method based on the design requirements.
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
Assembly Process: Once the components are formed, they are brought together in the assembly stage. This process may involve manual or automated assembly, depending on the complexity of the pump design. Skilled technicians ensure that all parts fit together correctly, and seals are applied where necessary to prevent leaks. The assembly stage is critical as any errors can lead to significant performance issues in the final product.
Finishing Touches: The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes such as surface treatment, painting, or coating. These processes not only enhance the aesthetic appearance of the vacuum pumps but also improve their resistance to corrosion and wear. Quality checks are performed during this stage to ensure that the pumps meet both aesthetic and functional standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Vacuum Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of vacuum pumps, ensuring that each unit meets international and industry-specific standards. Key QA practices include adherence to relevant standards, implementation of quality checkpoints, and rigorous testing methods.
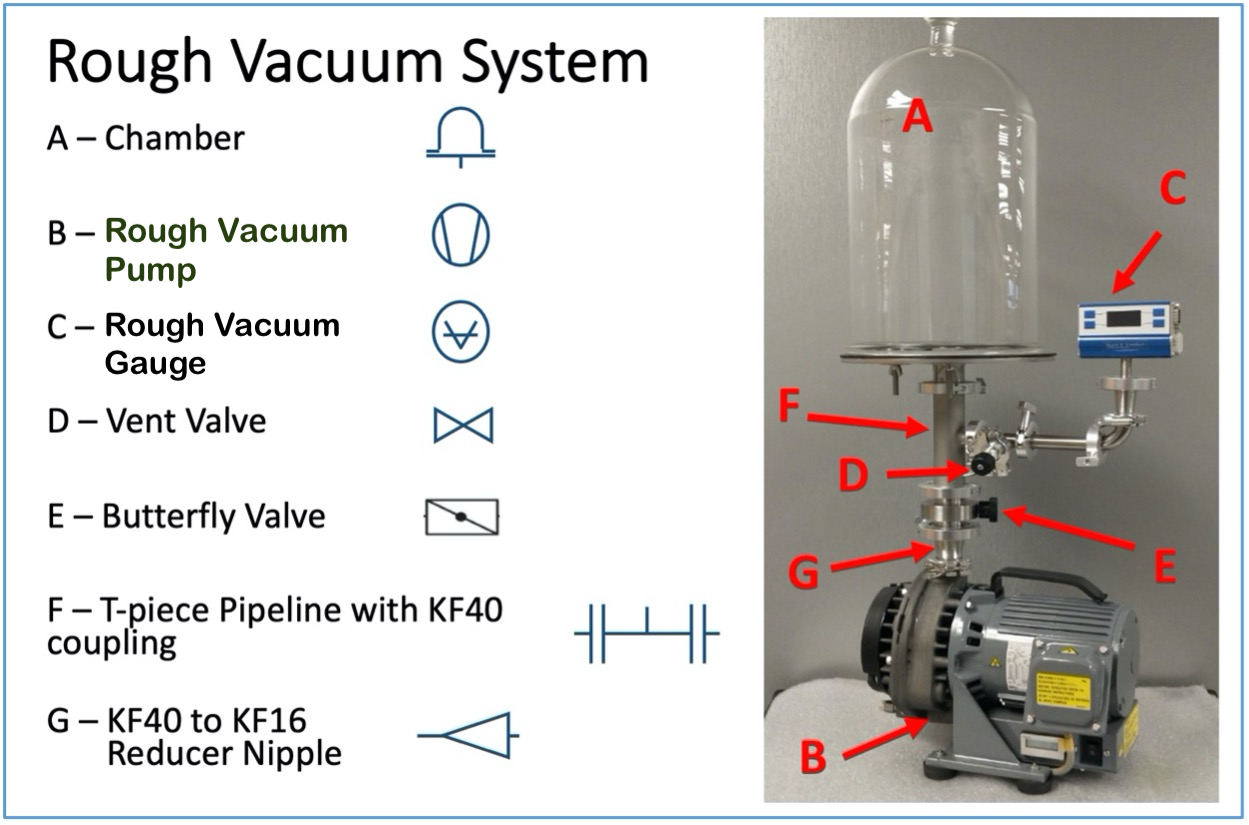
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
Adherence to International Standards: Many manufacturers seek certification to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for pumps used in the oil and gas sector are crucial for compliance.
Quality Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, various quality checkpoints are established to maintain standards. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors the manufacturing processes, ensuring that each stage adheres to the specified requirements. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) inspects the finished products before they are shipped to customers.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Vacuum Pumps?
Testing methods play a crucial role in validating the performance and reliability of vacuum pumps. Common testing techniques include leak testing, performance testing, and vibration analysis.
Leak Testing: This method verifies the integrity of vacuum pumps, ensuring that they do not leak air or gas. Techniques such as helium leak detection, which uses helium as a tracer gas, are often employed. This is particularly important in applications where vacuum integrity is critical, such as in pharmaceutical or semiconductor manufacturing.
Performance Testing: Performance tests measure the pump’s ability to achieve and maintain a specified vacuum level under various operating conditions. This testing ensures that the pump meets the operational requirements set forth by the manufacturer and the end user.
Vibration Analysis: Vibration testing is conducted to assess the mechanical condition of the pump. Excessive vibration can indicate misalignment or wear, which can lead to premature failure. By identifying these issues early, manufacturers can address them before the pumps reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can involve conducting audits, reviewing quality reports, and utilizing third-party inspections.
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality control practices. These audits can be conducted by the buyer or through independent third-party organizations. Auditors assess compliance with quality standards, review documentation, and evaluate manufacturing processes.
Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports from suppliers, which should include information on quality metrics, testing results, and any non-conformities encountered during production. Analyzing these reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s commitment to quality and identify any potential risks.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can verify that products meet specified standards and provide certification that can be crucial for international transactions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges and nuances when it comes to quality control in vacuum pump manufacturing. Understanding these nuances is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance with regional standards.
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations governing vacuum pump manufacturing. Buyers must familiarize themselves with local standards, such as CE marking in Europe or ANSI standards in the United States, to ensure compliance. This knowledge can prevent costly delays or rejections at customs.
Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences can influence communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should establish clear communication channels and expectations to mitigate misunderstandings. Regular follow-ups and updates can help maintain alignment between buyers and suppliers.
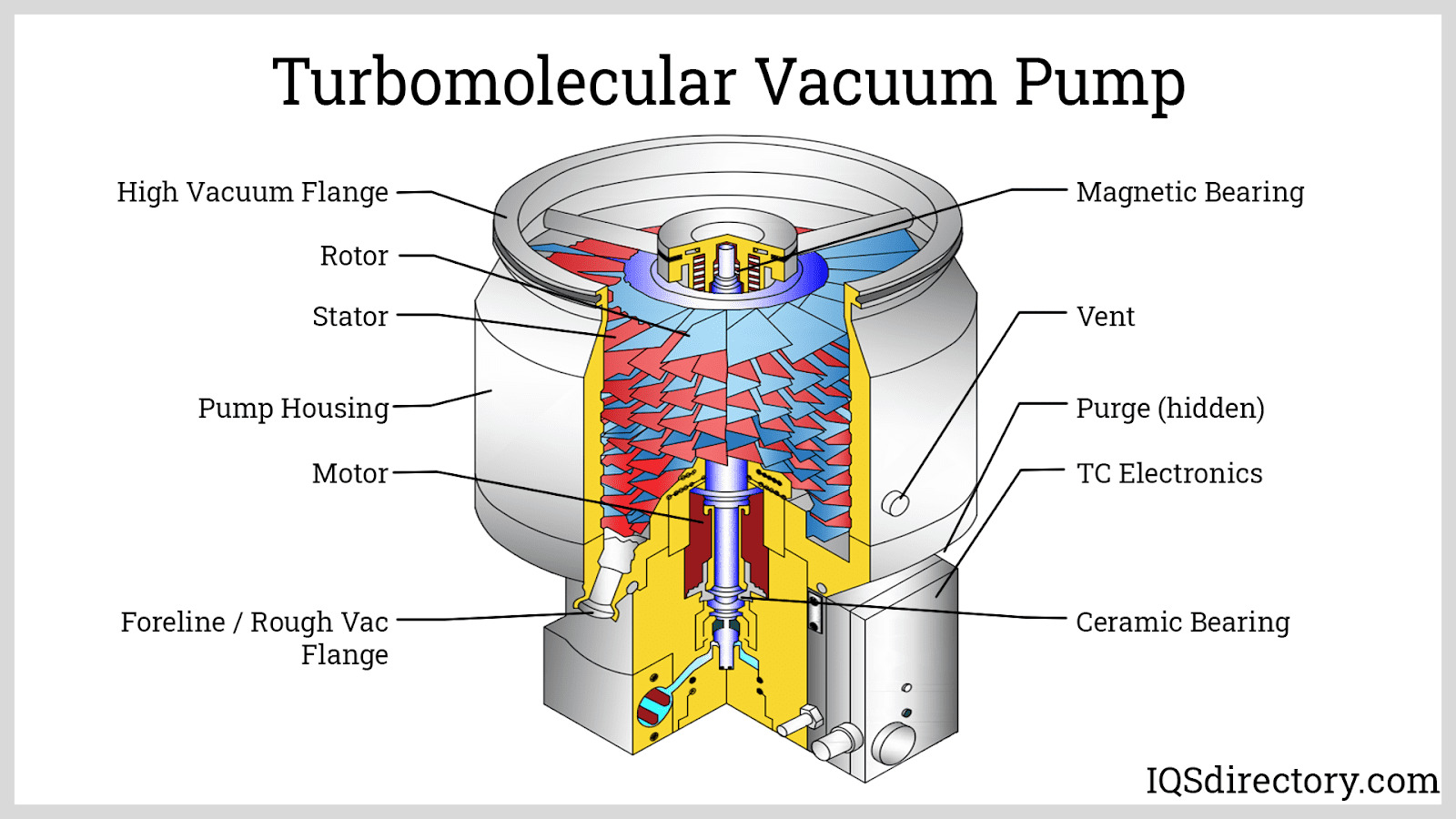
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
Logistical Challenges: Shipping vacuum pumps internationally can introduce risks related to damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers use appropriate packaging and handling procedures to minimize these risks. Additionally, understanding the logistics of importing goods, including tariffs and duties, can help buyers budget effectively.
Conclusion
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for vacuum pumps are complex and require careful attention to detail. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on supplier quality control, adherence to international standards, and the implementation of rigorous testing methods, buyers can ensure they receive reliable and high-performing vacuum pumps that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vacuum pump diagram’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure vacuum pump diagrams, essential for understanding the operational mechanics of vacuum pumps. Having a clear, detailed diagram is crucial for various applications, ranging from industrial processes to research and development. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you acquire diagrams that meet your technical requirements and enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is the first step in sourcing vacuum pump diagrams. Consider factors such as the type of vacuum pump (e.g., rotary vane, diaphragm, turbomolecular) and the application it will serve. This clarity will guide your selection process and help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
Step 2: Research Applicable Standards and Symbols
Familiarize yourself with industry standards and symbols used in vacuum technology diagrams. Knowing these can help you assess whether the diagrams you receive conform to international norms, which is critical for ensuring compatibility and safety in your operations. Look for resources that detail common symbols and their meanings, as this knowledge can help you evaluate the quality of the diagrams.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry or region. Assess their experience with vacuum technology to ensure they can provide high-quality diagrams that meet your specifications.
Step 4: Request Sample Diagrams
Ask suppliers for sample diagrams to evaluate their quality and clarity. This step is vital to ensuring that the diagrams are not only accurate but also easy to interpret. Pay attention to the detail in the diagrams, such as labels, scales, and the overall layout, which should facilitate a clear understanding of the pump’s operation.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards. Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates effective quality management systems, and any specific certifications related to vacuum technology.
Step 6: Assess Support and After-Sales Services
Evaluate the level of support offered by the supplier post-purchase. This includes technical support, updates to diagrams, and access to training materials. A reliable supplier will offer comprehensive support to help you integrate the diagrams into your operations effectively.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, discuss pricing, delivery times, and any warranties or return policies before finalizing your purchase. Clear negotiation can help ensure that you receive the best value for your investment. Make sure that all terms are documented to avoid misunderstandings later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for vacuum pump diagrams, ensuring they secure high-quality resources that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vacuum pump diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vacuum Pump Diagram Sourcing?
When sourcing vacuum pump diagrams, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the desired profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials used in manufacturing vacuum pumps significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to improved performance and longevity, thus reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the geographical location of the manufacturing facility. Skilled labor in regions such as Europe may command higher wages compared to emerging markets in Africa or South America, affecting the overall pricing structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, factory maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, making it essential to evaluate the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for custom vacuum pump diagrams. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and how they factor into the overall pricing, particularly for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control: Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the vacuum pumps meet required specifications and certifications, which can prevent costly returns and replacements. Suppliers who prioritize QC may charge a premium, but this can lead to greater long-term savings.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these logistics costs is crucial, particularly for international buyers facing customs duties and potential delays.
-
Margin: Lastly, the supplier’s profit margin will affect the final price. Buyers should seek transparency regarding how margins are calculated and consider negotiating based on volume or long-term partnership potential.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Vacuum Pump Diagram Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of vacuum pump diagrams, which buyers need to consider when sourcing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers often offer tiered pricing, where larger orders result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their needs to take advantage of bulk discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized diagrams tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. It’s essential to communicate clearly with suppliers about specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can elevate costs. Buyers must balance the need for high-quality components against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, but they can also reduce risk for buyers.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can impact the total landed cost. Understanding terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will help buyers estimate the final costs more accurately.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Pricing?
Negotiating favorable terms and pricing is crucial for achieving cost-efficiency in sourcing vacuum pump diagrams.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When placing larger orders, negotiating for volume discounts can yield significant savings. It’s beneficial to assess your procurement needs and plan orders accordingly.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also long-term operational costs. Investing in higher-quality pumps can lead to lower maintenance and operational expenses over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of potential currency fluctuations and import duties. Building relationships with suppliers that offer competitive pricing can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Engage in Transparent Communication: Clearly discussing specifications and expectations can help prevent misunderstandings that lead to additional costs. Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can also facilitate better negotiation outcomes.
-
Request Price Breakdowns: Asking for detailed cost breakdowns can provide insights into how pricing is structured, allowing buyers to identify areas for potential negotiation or cost reduction.
By understanding the cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing vacuum pump diagrams, ultimately achieving better value and operational efficiency.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vacuum pump diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Vacuum Pump Diagrams
In the realm of vacuum technology, choosing the right solution is critical for achieving desired operational outcomes. While vacuum pump diagrams serve as a valuable tool for understanding and visualizing vacuum systems, there are several alternative methods and technologies available. This section evaluates vacuum pump diagrams in comparison to other viable options to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Vacuum Pump Diagram | Alternative 1: Piping Layout Diagrams | Alternative 2: 3D CAD Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Offers clear visualization of system operation | Good for understanding flow dynamics | Provides a comprehensive view of spatial relationships |
| Cost | Generally low-cost to create and maintain | Moderate cost depending on complexity | High initial investment for software and training |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to create with basic tools | Requires knowledge of fluid dynamics | Requires advanced skills in CAD software |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; updates are infrequent | Moderate maintenance; needs updates with system changes | High maintenance; models need regular revisions |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for basic system design and troubleshooting | Best for detailed analysis of flow and pressure | Suitable for complex systems requiring spatial and mechanical detail |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Piping Layout Diagrams?
Piping layout diagrams serve as an effective alternative to vacuum pump diagrams, particularly in applications where fluid dynamics play a critical role. These diagrams illustrate the flow of materials through pipes, helping engineers understand pressure drops and potential bottlenecks.
Pros:
– They provide a detailed look at the system’s flow dynamics.
– Useful for troubleshooting complex systems where pressure changes are significant.
Cons:
– They require a solid understanding of fluid mechanics and can be complex to create.
– May not provide the same level of clarity for overall system operation as vacuum pump diagrams.
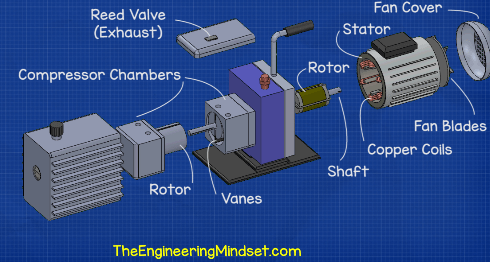
Illustrative image related to vacuum pump diagram
How Do 3D CAD Models Compare as an Alternative?
3D CAD models offer a sophisticated approach to visualizing vacuum systems. These models can accurately represent spatial relationships and mechanical components, making them invaluable for complex system designs.
Pros:
– They allow for intricate modeling of systems, facilitating better design validation and error detection.
– Enable simulation of system performance under various conditions, improving overall design accuracy.
Cons:
– They require significant investment in software and training, which may be a barrier for smaller organizations.
– Maintaining and updating CAD models can be labor-intensive and costly.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most suitable solution for vacuum system design and analysis, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the complexity of their systems. For basic designs and troubleshooting, vacuum pump diagrams offer an efficient and cost-effective solution. In contrast, if the project demands a detailed analysis of fluid dynamics or spatial relationships, investing in piping layout diagrams or 3D CAD models may be warranted. Ultimately, the choice should align with the buyer’s technical capabilities and the requirements of the application at hand, ensuring that the selected method enhances operational efficiency and reliability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vacuum pump diagram
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Vacuum Pump Diagrams?
Understanding the technical specifications of vacuum pumps is essential for B2B buyers to ensure the equipment meets operational needs. Here are several key properties:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of vacuum pumps significantly impacts their durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and various polymers. For example, stainless steel is often preferred for its resistance to corrosion, especially in chemical applications. Selecting the right material grade ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs, which is crucial for businesses operating in demanding environments. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In vacuum technology, tight tolerances are vital to maintain the efficiency and effectiveness of the pump. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm might be necessary for components that interact closely. This precision is especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals or semiconductor manufacturing, where even minor deviations can lead to significant operational issues. -
Pumping Speed
Measured in liters per second (L/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM), pumping speed indicates how quickly a vacuum pump can remove air or gas from a chamber. Higher pumping speeds are essential in applications requiring rapid evacuation, such as in research laboratories or industrial processes. Understanding the required pumping speed helps buyers select a pump that meets their production timelines and efficiency goals. -
Ultimate Pressure
This specification indicates the lowest pressure that a vacuum pump can achieve in a vacuum system. Measured in millitorr or pascals, ultimate pressure is crucial for applications in scientific research, materials processing, and semiconductor fabrication. Buyers should assess their specific pressure requirements to ensure optimal system performance. -
Power Consumption
The power rating of a vacuum pump, typically measured in watts or kilowatts, reflects its energy efficiency. Selecting a pump with lower power consumption can lead to substantial cost savings over time, especially in industries where vacuum systems operate continuously. Evaluating energy efficiency is critical for businesses looking to reduce operational costs and meet sustainability goals.
What Are Common Terms Used in Vacuum Pump Diagrams?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers to ensure they are sourcing quality components from reputable manufacturers, which can impact the overall performance of their vacuum systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers need to assess their demand and negotiate MOQ to ensure they can meet operational needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is fundamental in procurement processes, enabling buyers to compare costs and terms from different vendors, ultimately leading to informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability, reducing the risk of disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. This term is critical for B2B buyers to ensure that they can plan their production schedules effectively. Understanding lead times helps businesses manage inventory levels and avoid production delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting vacuum pumps, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vacuum pump diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the Vacuum Pump Diagram Sector?
The vacuum pump diagram market is experiencing significant evolution driven by technological advancements and global demand across various industries. Key drivers include the increasing need for efficient manufacturing processes, rising automation, and the growing importance of vacuum technology in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and electronics. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize production efficiency, they are increasingly turning to suppliers who provide comprehensive vacuum solutions, including detailed vacuum pump diagrams that illustrate system configurations and functionalities.
Emerging trends in sourcing reflect a shift toward digitalization, with many companies adopting cloud-based platforms for procurement and supply chain management. This allows for real-time collaboration and enhanced visibility into supply chain dynamics. Moreover, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT-enabled vacuum systems, is gaining traction, enabling predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency. Buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific application requirements, enhancing competitiveness in their respective markets.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Vacuum Pump Diagram Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in B2B sourcing decisions, particularly in the vacuum pump diagram sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, businesses are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and enhance the sustainability of their operations. This has led to a heightened focus on ethical sourcing practices, where buyers seek materials and components that are not only effective but also environmentally friendly.
Incorporating “green” certifications, such as ISO 14001, into sourcing criteria is essential for suppliers aiming to capture the attention of conscious buyers. Additionally, utilizing eco-friendly materials in the manufacturing of vacuum pumps and components not only reduces environmental impact but can also lead to operational cost savings in the long run. Buyers are encouraged to collaborate with manufacturers who prioritize sustainable practices, ensuring that their supply chains contribute positively to global environmental goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Vacuum Pump Technology and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of vacuum pump technology dates back to the early 17th century, when the first vacuum pumps were developed. Over the centuries, advancements in engineering and materials have transformed these devices into sophisticated systems capable of achieving ultra-high vacuum levels. The introduction of various vacuum pump types—such as rotary vane, turbomolecular, and dry pumps—has expanded the applicability of vacuum systems across diverse industries, from scientific research to industrial manufacturing.
Today, understanding the historical context of vacuum pump technology is essential for B2B buyers, as it provides insight into the reliability and advancements of existing solutions. This knowledge can guide purchasing decisions, ensuring that buyers select products that not only meet their current needs but also align with future technological trends and industry standards. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about historical developments can empower buyers to make strategic decisions that enhance their operational capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vacuum pump diagram
-
How do I interpret vacuum pump diagrams effectively?
Understanding vacuum pump diagrams requires familiarity with the symbols and components commonly used in the industry. Begin by reviewing a standardized reference for vacuum symbols, which can vary by manufacturer. Focus on key elements such as pump types, valves, gauges, and connections. It may also be beneficial to consult with suppliers for detailed explanations or training sessions. Engaging with technical documentation from manufacturers can enhance your comprehension and assist in troubleshooting or system design. -
What is the best vacuum pump type for my specific application?
The ideal vacuum pump type depends on your application’s requirements, such as the desired vacuum level, the volume of gas to be evacuated, and the process environment. For instance, rotary vane pumps are suitable for general applications, while turbomolecular pumps excel in ultra-high vacuum scenarios. Assess your operational needs and consult with manufacturers to evaluate performance metrics and compatibility with your existing systems. Consider factors like energy efficiency, maintenance needs, and cost-effectiveness when making your choice. -
How can I ensure the quality of vacuum pumps when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing vacuum pumps internationally, start by vetting suppliers thoroughly. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management systems. Request product samples or detailed specifications to compare against your requirements. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities if feasible, or rely on third-party quality assurance services to conduct inspections before shipment. Establishing clear communication and setting quality benchmarks in your contract can also safeguard your investment. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for vacuum pumps?
Minimum order quantities for vacuum pumps can vary widely depending on the supplier, pump type, and customization options. Some manufacturers may offer MOQs as low as one unit for standard products, while custom models might require larger orders. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Smaller businesses or those testing new applications should inquire about flexible options or trial purchases to minimize upfront investment and risk. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing vacuum pumps internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can differ significantly based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation power. Common terms include upfront payments, letters of credit, or installment payments upon delivery. Ensure that you understand the implications of each option, including any associated fees. It’s advisable to establish clear payment schedules in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to protect against potential fraud, especially in unfamiliar markets. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for vacuum pump purchases?
Logistics and shipping for vacuum pumps involve careful planning to ensure timely delivery and safety during transit. Coordinate with suppliers to understand their shipping options, which may include air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost savings. Verify that the pumps are packaged adequately to prevent damage. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, as customs duties and clearance procedures can impact delivery timelines and costs. -
What customization options are available for vacuum pump diagrams?
Customization options for vacuum pump diagrams often include modifications to the system layout, component selection, and integration with existing processes. Suppliers may offer tailored diagrams that reflect specific operational needs, such as specialized valves or enhanced monitoring systems. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly and collaborate with engineers or technical teams to develop diagrams that optimize performance and efficiency. Ensure that any customizations are documented thoroughly to facilitate installation and maintenance. -
How can I ensure ongoing support and maintenance for my vacuum pump systems?
To ensure ongoing support and maintenance for vacuum pump systems, establish a relationship with your supplier that includes service agreements or maintenance contracts. These agreements can provide regular inspections, repairs, and necessary parts replacements. Additionally, consider investing in training for your staff to handle basic maintenance tasks. It’s also wise to keep a list of emergency contacts for technical support, as prompt assistance can minimize downtime and enhance system reliability.
Top 9 Vacuum Pump Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leybold – Vacuum Technology Solutions
Domain: leybold.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Leybold offers a wide range of vacuum technology products including:
1. **Vacuum Pumps**:
– Oil Sealed Vacuum Pumps: TRIVAC B, TRIVAC L, SOGEVAC B, SOGEVAC BI/DI, SOGEVAC FP, NEO (S)D.
– Small Dry Pumps: VACUBE, DIVAC (Diaphragm), ECODRY plus (Dry multistage roots), SCROLLVAC plus (Oil-free scroll).
– Industrial Dry Vacuum Pumps: CLAWVAC B, DRYVAC, DRYVAC DV FP-r, DURADRY (dry screw).
…
2. Pinterest – Vacuum Pump Oil
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Vacuum Pump Oil: The “Circulatory System” of the Vacuum Furnace; critical for proper furnace operation; serves different purposes in different types of pumps; provides lubrication, seals on rotary vane and wet pumps, and propels pumped gas via kinetic action.
3. Dynamic Descaler – Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
Domain: dynamicdescaler.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Dynamic Descaler – Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Fluid Power Journal – Key Components in Vacuum Material Handling
Domain: fluidpowerjournal.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key components in vacuum material handling include: 1. Vacuum pump 2. Inlet filter 3. Control valves 4. Vacuum cups. The article discusses the importance of schematic circuits for custom-made machinery, aiding maintenance and production engineers. It highlights the use of schematic symbols to represent components functionally rather than visually. The article describes various configurations of va…
5. Facebook – Vacuum Pump Diagram
Domain: m.facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Vacuum Pump Diagram, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Inlet – Key Components of Vacuum Pumps
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Inlet: Where the gas or air is drawn into the pump. Oil Fill Port: Used for adding or checking the oil level, crucial for lubrication and sealing in many types of vacuum pumps. Rotor: The rotating part within the pump that drives the pumping action. Vanes: Typically found in rotary vane vacuum pumps, these move within the rotor to create chambers of varying volume, essential for compressing and ex…
7. Vacaero – Vacuum Pumps Overview
Domain: vacaero.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Vacuum Pumps Overview: Vacuum pumps are categorized by operating pressure into primary pumps, booster pumps, and secondary pumps. They function by removing air and gases from a vacuum chamber, operating over a pressure range from 1 to 10-6 Torr, with research applications extending to 10-9 Torr or lower. Pressure ranges include: Rough/Low Vacuum (> Atmosphere to 1 Torr), Medium Vacuum (1 Torr to 1…
8. The Engineering Mindset – Vacuum Pumps
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Vacuum pumps are mechanical devices used by air conditioning and refrigeration engineers to remove air or non-condensables like water from systems. They are essential for ensuring efficient operation and preventing corrosion of internal parts. The main components of a vacuum pump include an electrical motor, a compressor, an inlet for connecting to the system, and an exhaust for dispersing air to …
9. EvpVacuum – Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
Domain: evpvacuum.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: The liquid ring vacuum pump is composed of the following key components: pump body, impeller, end face disc, and pump body end cover.
– **Pump Body**: Requires a casting blank with no defects like sand holes or porosity; machining precision of the inner cavity is not high.
– **Impeller**: Made of ductile iron or stainless steel for corrosion resistance; can have straight blades (for small pumps)…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vacuum pump diagram
In the dynamic landscape of vacuum technology, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring businesses maximize efficiency and minimize costs. By understanding vacuum pump diagrams and the components they depict, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational performance. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right pump type for specific applications, recognizing the significance of maintenance and service plans, and leveraging local suppliers who understand regional needs and challenges.
As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evolve, the demand for reliable vacuum solutions will only increase. Buyers are encouraged to explore innovative technologies that not only meet current standards but also anticipate future requirements. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive support, from installation to ongoing maintenance, is essential for sustained success.
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced technologies such as remote monitoring and predictive maintenance will redefine the vacuum pump landscape. Now is the time for businesses to reassess their sourcing strategies, embrace collaboration with experienced partners, and position themselves for growth in an increasingly competitive market. Take the first step towards optimizing your vacuum systems today!
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.