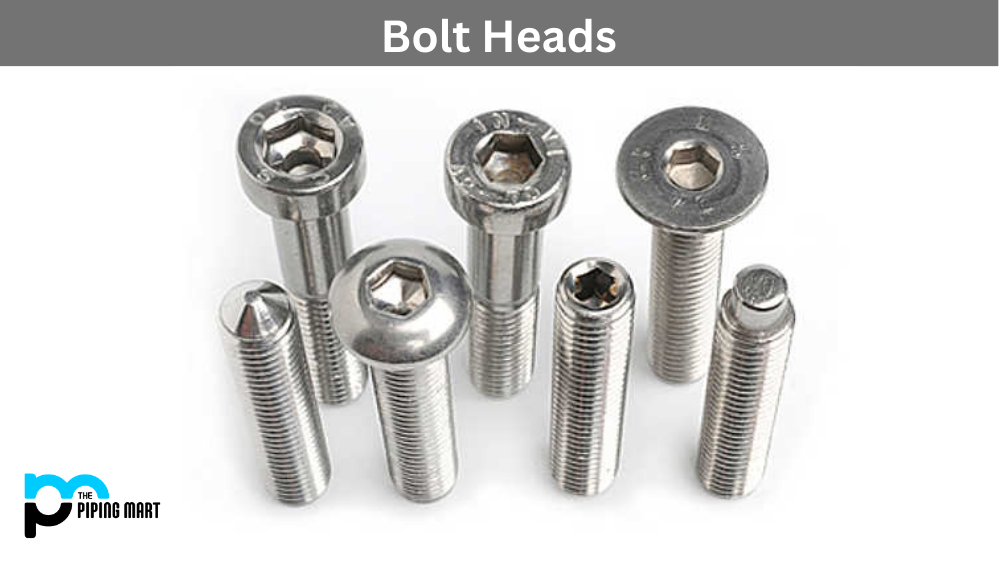
How to Source Types Of Bolt Heads Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of bolt heads
In the intricate world of international manufacturing, sourcing the right types of bolt heads can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With the diverse applications of bolt heads across various industries—from construction to automotive—understanding their specifications, load-bearing capacities, and compatibility with different materials is critical. This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad types of bolt heads available in the global market, providing insights into their unique features, applications, and advantages.
Moreover, it addresses essential aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet international standards. By examining factors such as cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal, this guide empowers buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Nigeria and Germany—to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance the structural integrity of a project or seeking specific design elements, the knowledge contained within this guide will equip you with the tools needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing bolt heads effectively. With a focus on actionable insights and practical advice, you can optimize your procurement strategy and achieve greater operational efficiency.
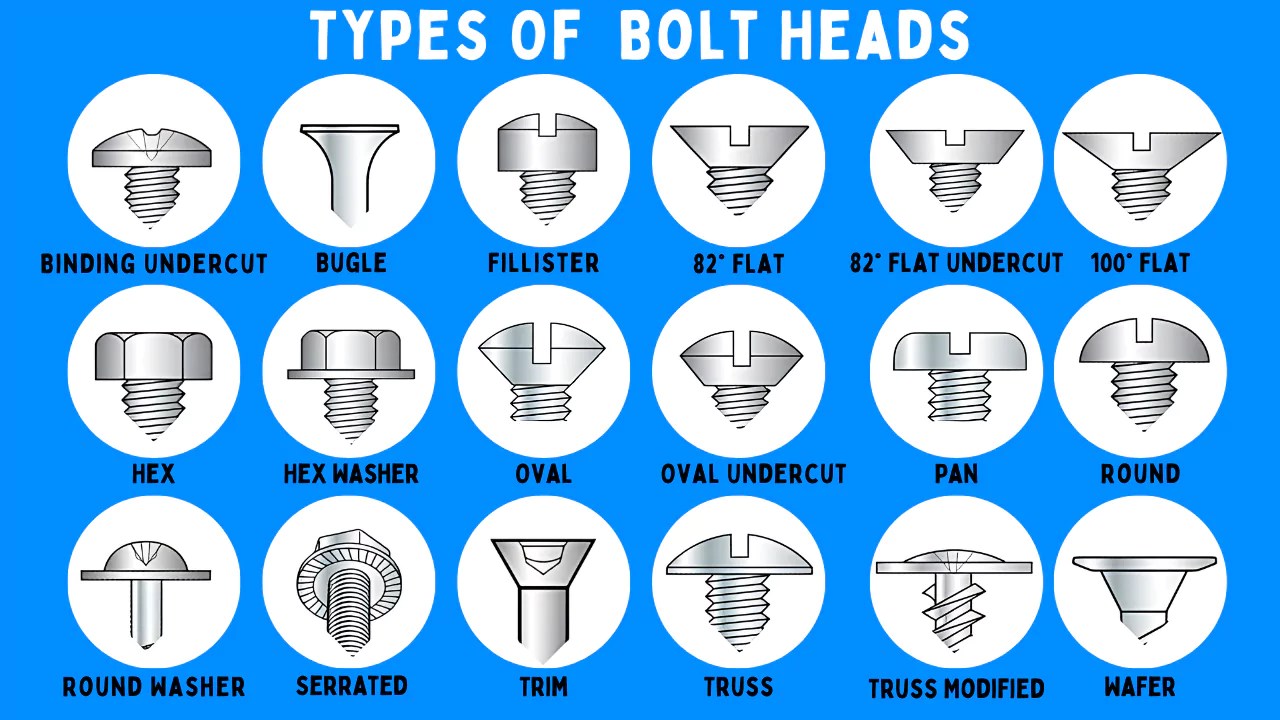
Understanding types of bolt heads Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Bolt | Hexagonal head, compatible with standard wrenches | Heavy machinery, construction, automotive | Pros: High torque capacity; Cons: Requires proper tools for installation. |
| Carriage Bolt | Rounded head with a square neck, smooth shaft | Wood structures, furniture assembly | Pros: Prevents spinning during installation; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Flange Bolt | Integrated washer at the base of the head | Structural connections, automotive applications | Pros: Distributes load effectively; Cons: More expensive than standard bolts. |
| Socket Cap Bolt | Cylindrical head designed for Allen wrench use | Precision machinery, assembly lines | Pros: Provides a clean finish; Cons: Requires specialized tools. |
| Eye Bolt | Circular ring on the head for attaching cables or ropes | Lifting, rigging, marine applications | Pros: Versatile for various applications; Cons: Limited load capacity compared to others. |
What Are the Characteristics of Hex Bolts and Their B2B Suitability?
Hex bolts are characterized by their hexagonal heads, which allow for the use of standard wrenches for installation and removal. They are highly favored in industries that require high torque applications, such as heavy machinery and construction. When purchasing hex bolts, buyers should consider the material, grade, and coating, as these factors can influence strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance in demanding environments.
How Do Carriage Bolts Function and What Are Their Key Applications?
Carriage bolts feature a rounded head and a square neck that prevents rotation during tightening. They are commonly used in wood structures and furniture assembly, providing a secure fastening solution. Buyers should evaluate the length and diameter of the carriage bolts to ensure compatibility with their specific applications. Additionally, considering the material—whether steel, stainless steel, or another alloy—can be crucial for durability and corrosion resistance.
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
What Makes Flange Bolts Unique for Structural Applications?
Flange bolts are distinguished by their integrated washer, which helps distribute the load over a larger area, reducing the risk of material deformation. This feature makes them particularly effective in structural connections and automotive applications. When sourcing flange bolts, buyers should assess the bolt’s dimensions and material properties to match their load requirements and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance.
Why Choose Socket Cap Bolts for Precision Applications?
Socket cap bolts have a cylindrical head that is designed for use with an Allen wrench, allowing for a sleek and aesthetically pleasing finish. They are ideal for precision machinery and assembly lines where space is limited. Buyers should consider the head height and diameter when selecting socket cap bolts, as well as the grade of steel, to ensure they meet the strength and durability requirements of their specific applications.
What Are the Key Benefits of Eye Bolts in Various Industries?
Eye bolts are designed with a circular ring at the head, making them suitable for attaching cables, ropes, or chains. They are widely used in lifting, rigging, and marine applications due to their versatility. When purchasing eye bolts, buyers need to consider the load capacity and material type to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, the installation method should be evaluated to ensure the eye bolts can be securely anchored in their intended environment.
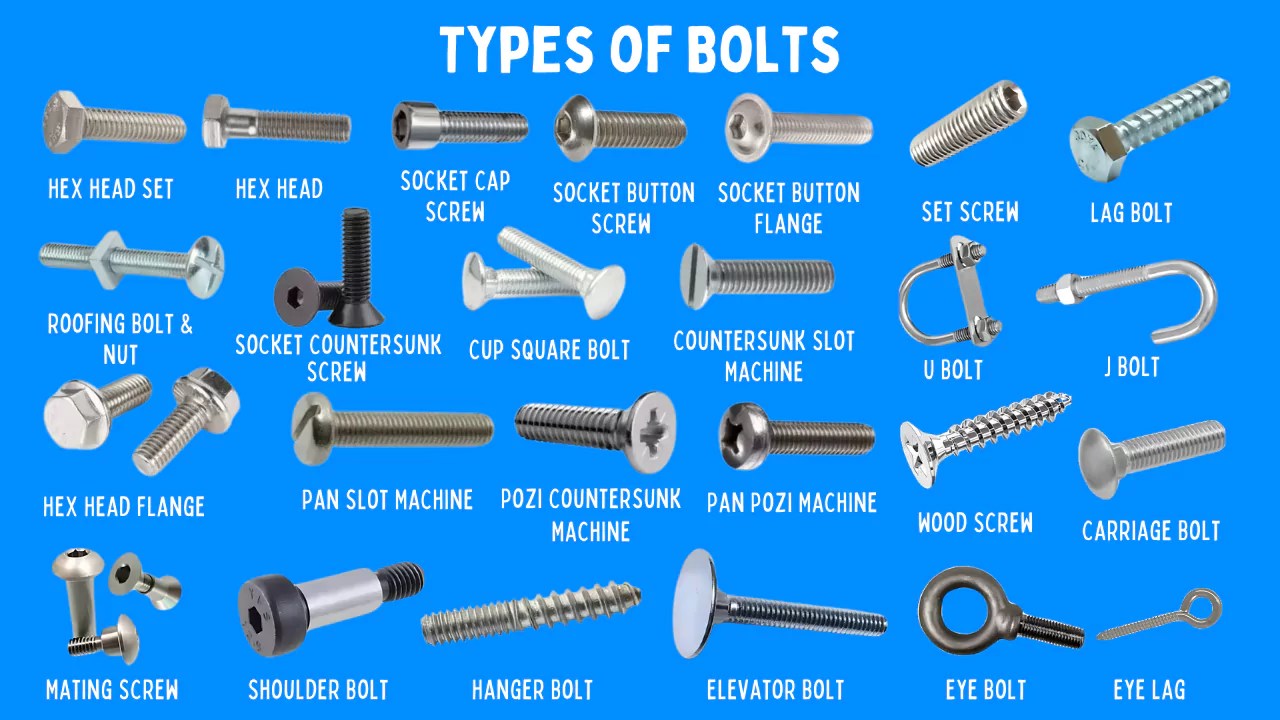
Key Industrial Applications of types of bolt heads
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of bolt heads | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Use of hex bolts for structural steel connections | Provides robust support and stability for heavy structures | Ensure compliance with local building codes and load ratings |
| Automotive | Application of socket screws in assembly of components | Enhances assembly efficiency and reduces installation time | Consider material compatibility and corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing | Use of flange bolts in machinery assembly | Distributes load evenly, reducing wear on components | Look for high tensile strength and durability under stress |
| Oil & Gas | Eye bolts for rigging and lifting operations | Ensures safety during heavy lifting and transport | Verify load ratings and environmental resistance |
| Electronics | Countersunk screws for securing circuit boards | Provides a flush finish, preventing damage to sensitive components | Focus on precision and compatibility with electronic designs |
How are different types of bolt heads utilized in the construction industry?
In the construction sector, hex bolts are essential for connecting structural steel components. Their design allows for high torque applications, providing robust support and stability for heavy structures such as bridges and high-rise buildings. This is particularly important in regions prone to seismic activity or extreme weather, where structural integrity is paramount. Buyers should ensure that the bolts meet local building codes and load ratings to guarantee safety and compliance.
What role do socket screws play in the automotive industry?
Socket screws are widely used in the assembly of automotive components due to their efficiency in installation and removal. The hexagonal drive allows for a secure grip, minimizing the risk of stripping compared to traditional screw heads. This is critical in high-volume production environments where time and precision are vital. International buyers must consider material compatibility, especially regarding corrosion resistance, to ensure longevity in various operating conditions.
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
How do flange bolts enhance manufacturing processes?
In manufacturing, flange bolts are commonly employed to assemble machinery and equipment. Their design, which includes a wider bearing surface, helps distribute load evenly, reducing stress and wear on components. This is particularly beneficial in high-load applications where durability is essential. Buyers should prioritize sourcing flange bolts with high tensile strength to maintain operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Why are eye bolts crucial in the oil and gas sector?
Eye bolts are integral to rigging and lifting operations in the oil and gas industry. They provide secure attachment points for lifting heavy equipment and materials, ensuring safety during operations. Given the hazardous environments typical in this sector, it is critical to verify the load ratings and environmental resistance of eye bolts to prevent failures that could lead to accidents or equipment loss.
How do countersunk screws improve electronics manufacturing?
Countersunk screws are used extensively in electronics manufacturing to secure circuit boards and components. Their flush finish prevents damage to sensitive electronic parts, allowing for compact designs without protruding hardware. For international buyers, focusing on precision and compatibility with specific electronic designs is essential to ensure the integrity and functionality of the final product.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of bolt heads’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment of Bolt Heads with Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter the issue of selecting the wrong type of bolt head for their specific application. This misalignment often leads to installation difficulties, structural weaknesses, or even project delays. For instance, using a countersunk head in a high-load scenario can result in inadequate load distribution, causing premature failure. Buyers may also struggle to understand the nuances between similar types, such as hex bolts versus socket screws, leading to costly mistakes.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, it’s essential to conduct a thorough application assessment before sourcing bolt heads. Buyers should engage with engineering teams to define the load requirements, environmental conditions, and aesthetic considerations. Utilizing a fastener type chart can help in comparing different bolt head types, focusing on their load-bearing capacities and installation methods. Additionally, consulting with suppliers who specialize in fasteners can provide insights into the best practices for selecting the appropriate bolt head type based on specific application needs. Involving experienced professionals in the decision-making process can ensure that the right bolt heads are specified, thereby enhancing project efficiency and reliability.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Specialized Bolt Heads
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing specialized bolt heads that meet unique project requirements. This is particularly true for industries such as construction or automotive, where specific head types are necessary for compliance with safety regulations or performance standards. Delays in sourcing can lead to halted production lines or missed deadlines, resulting in financial losses and damaged reputations.
The Solution: To address sourcing challenges, buyers should establish strong relationships with multiple suppliers, including local and international manufacturers. This strategy not only broadens the sourcing options but also ensures that buyers have access to a diverse range of bolt heads, including those with specialized designs. Implementing a vendor management system can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to track orders, manage inventory, and quickly pivot to alternative suppliers if needed. Furthermore, engaging in pre-order discussions with suppliers about anticipated project needs can lead to better stock availability and timely deliveries, ultimately safeguarding against production delays.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Knowledge of Installation Best Practices
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of knowledge regarding the correct installation practices for various bolt head types. Improper installation can lead to stripped heads, ineffective load distribution, and mechanical failures, which can be particularly damaging in high-stakes environments. Buyers may find themselves unsure about the required tools or techniques for each bolt head style, leading to inefficiencies and increased labor costs.
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their installation teams. This training should cover the specific requirements for installing different bolt head types, including the use of proper tools and techniques. Manufacturers often provide installation guidelines and technical data sheets, which can be invaluable resources. Additionally, organizing workshops or inviting experts for on-site demonstrations can enhance understanding and competence among the installation workforce. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and ensuring that teams are well-informed, companies can improve installation accuracy and efficiency, thereby minimizing the risk of costly mistakes and enhancing overall project outcomes.
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of bolt heads
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Bolt Heads?
When selecting materials for bolt heads, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Bolt Head Applications?
Carbon steel is a widely used material for bolt heads, particularly in construction and automotive applications. It offers high tensile strength and excellent load-bearing capabilities, making it suitable for heavy-duty tasks. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a significant drawback, especially in humid or saline environments. Carbon steel bolts typically require coatings or treatments, such as galvanization or black oxide, to enhance their corrosion resistance.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, it’s essential to consider local environmental conditions when selecting carbon steel bolts. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933 is critical for ensuring product reliability and safety.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Bolt Heads?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals, such as marine environments and food processing. Its durability and aesthetic appeal are additional benefits, allowing for use in visible applications without compromising performance.
However, stainless steel bolts can be more expensive than carbon steel options, which may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment. Buyers in Europe, like Germany, often prefer stainless steel due to stringent quality standards (e.g., DIN EN ISO 3506).

Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
Why Choose Brass for Bolt Heads in Specific Applications?
Brass is another material option, particularly valued for its excellent corrosion resistance and low friction properties. This makes brass bolts suitable for electrical applications and environments where non-sparking characteristics are essential. They are often used in plumbing and electrical fittings.
However, brass is softer than steel, which may limit its load-bearing capacity. Additionally, it can be more expensive, making it less suitable for large-scale projects. International buyers should be aware of the specific standards for brass fasteners, such as ASTM B16, to ensure compliance.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Aluminum Bolt Heads?
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative that offers good corrosion resistance and is often used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight savings are critical. Its ability to be anodized allows for enhanced surface protection and aesthetic appeal.
On the downside, aluminum bolts have lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit their use in high-load applications. They can also be more expensive, particularly for high-grade alloys. Buyers from South America and Africa should consider the local availability of aluminum options and their compliance with standards like ASTM B211.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Bolt Heads
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of bolt heads | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Construction, automotive | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Brass | Electrical fittings, plumbing | Good corrosion resistance, non-sparking | Softer, limited load capacity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used for bolt heads, allowing international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of bolt heads
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Bolt Heads?
The manufacturing of bolt heads is a complex process that involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Bolt Head Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Manufacturers usually select high-quality steel or other alloys based on the desired characteristics of the bolt, such as strength and corrosion resistance. The material is then cut into specific lengths and shapes, which may involve techniques like shearing or sawing.
In some cases, manufacturers will conduct an initial inspection of the raw materials to ensure they meet industry standards, such as ASTM specifications, before proceeding. This step is crucial for ensuring that the bolts will perform adequately in their intended applications.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Bolt Head Production?
The forming stage involves transforming the prepared material into the desired shape of the bolt head. This can be achieved through various techniques, including:
-
Cold Forging: This method involves shaping the material at room temperature, which enhances its strength through work hardening. Cold forging is widely used for producing hex and socket heads due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
-
Hot Forging: Used for larger or more complex bolt heads, this technique involves heating the material before shaping it. Hot forging is beneficial for achieving tighter tolerances and complex geometries.
-
Machining: In some cases, particularly for high-precision applications, bolt heads may be machined from solid stock. This technique allows for intricate designs and precise dimensions.
How Are Bolt Heads Assembled and Finished?
Once the bolt heads are formed, they may undergo assembly processes if they are part of multi-component fasteners. For example, in the case of flanged bolts, the flange may be attached to the head during this stage.
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of bolt heads. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Plating: This involves applying a thin layer of metal, such as zinc or chrome, to improve corrosion resistance.
-
Coating: Powder coating or painting may be used for additional protection and to meet specific aesthetic requirements.
-
Heat Treatment: This process can improve mechanical properties, including hardness and tensile strength, depending on the application.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Bolt Head Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of bolt heads, especially for B2B buyers who require reliability and performance in their fasteners. Several international and industry-specific standards guide the quality assurance process.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is the most widely recognized quality management standard, ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality, which is essential for B2B buyers.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications may also apply. These certifications ensure that the products comply with specific safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Bolt Head Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to verify that products meet the required specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, inspections are conducted at various stages to monitor production consistency and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After manufacturing, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance and compliance with standards. This may include dimensional checks, tensile testing, and surface quality inspections.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Bolt Heads?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of bolt heads:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile testing, hardness testing, and impact testing to assess the mechanical properties of the bolt heads.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using tools such as calipers and gauges, manufacturers verify that the dimensions of the bolt heads conform to specifications.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection can be used to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices is essential. Buyers can verify supplier QC through several methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and compliance with industry standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to standards and performance metrics.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and the products themselves.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various certification and quality control nuances, especially when sourcing from different regions.

Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
-
Regional Standards: Understanding regional certifications, such as ASME in the United States or EN standards in Europe, is vital for ensuring compliance with local regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance and manufacturing practices. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these differences to effectively communicate expectations.
-
Language Barriers: Engaging suppliers in regions where English may not be the primary language can lead to miscommunication. It’s advisable to have clear documentation and, if possible, local representatives who can facilitate discussions.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bolt heads, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of bolt heads’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring various types of bolt heads. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right products that meet your technical requirements, cost considerations, and supplier reliability, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the bolt heads you need. This includes material specifications (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel), sizes, and load-bearing capacities. Understanding these specifications will help you narrow down your options and communicate effectively with suppliers.
- Material Considerations: Assess whether you need corrosion resistance or specific strength properties.
- Load Requirements: Determine the weight and stress conditions the bolts will face in their application.
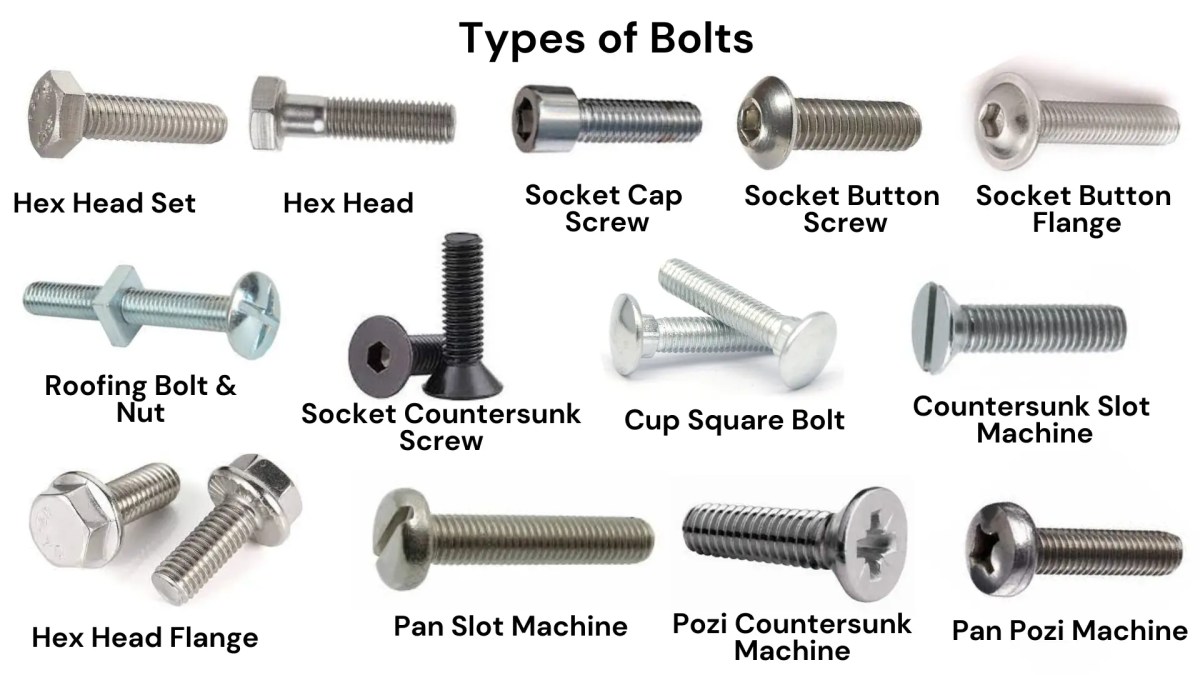
Step 2: Research Different Types of Bolt Heads
Familiarize yourself with the various types of bolt heads available and their respective applications. Different designs, such as hex, carriage, or flanged bolt heads, serve specific purposes and are suited for various environments.
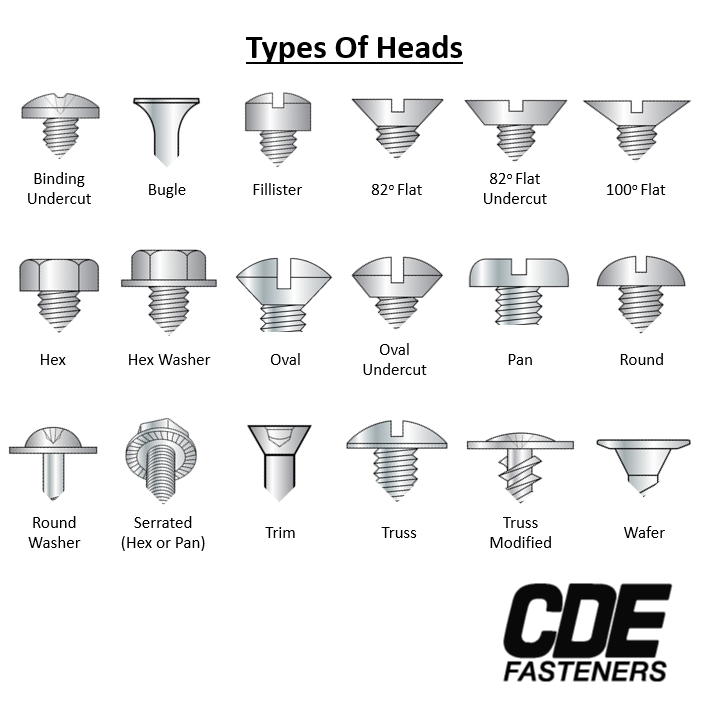
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
- Application Suitability: For example, hex bolts are ideal for high-torque applications, while carriage bolts are used for wood connections.
- Aesthetic Needs: Consider whether the appearance of the bolt head is important for your project, particularly in consumer-facing applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from buyers in similar industries. This step is essential to ensure that the supplier can meet your specific requirements and maintain quality standards.
- Certification Verification: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) that guarantee quality and compliance.
- Experience and Reputation: Assess their track record in supplying similar products and the reliability of their delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the bolt heads you are considering. Testing samples will help you verify that the product meets your quality standards and fits your technical specifications.
- Material Testing: Check for resistance to corrosion, tensile strength, and overall durability.
- Fit and Compatibility: Ensure that the bolt heads fit correctly within your assembly and meet installation requirements.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare their pricing structures. Pay attention to not only the cost per unit but also terms such as minimum order quantities, shipping costs, and payment terms.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, as this can significantly impact your total procurement costs.
- Long-Term Partnerships: Consider the potential for establishing long-term relationships with suppliers that may offer better pricing and terms over time.
Step 6: Confirm Delivery and Lead Times
Confirm the lead times for delivery before placing your order. Understanding the timeline is crucial to ensure that your project stays on schedule and that you have the necessary materials when needed.
- Contingency Planning: Have a backup supplier in mind in case of delays or issues with your primary supplier.
- Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to receive updates on order status and any potential delays.
Step 7: Review After-Sales Support and Warranty
Finally, inquire about after-sales support and warranty terms. Knowing that you have support in case of defects or issues will provide peace of mind and can protect your investment.
- Return Policies: Understand the return process for defective items or unsatisfactory products.
- Technical Support: Ensure that the supplier offers technical assistance for installation or troubleshooting as needed.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of bolt heads Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Bolt Heads?
When sourcing bolt heads, understanding the various cost components is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the cost. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each with varying price points. For instance, stainless steel is generally more expensive due to its corrosion resistance properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region of production. In countries with higher labor costs, such as Germany, the overall price of bolt heads may increase. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can provide savings but may come with trade-offs in quality and lead times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. A higher overhead can lead to increased pricing, particularly in developed nations.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, especially for unique bolt head designs. It’s essential to factor in these costs when considering custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control is crucial for maintaining product standards. Enhanced QC processes may lead to higher costs but can reduce the risk of defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on the distance from the supplier, mode of transport, and any applicable tariffs or taxes. International buyers should pay close attention to logistics costs as they can significantly impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margin for bolt head suppliers in your region can help in negotiating better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Bolt Head Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of bolt heads beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ: The Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) often dictates pricing. Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs to avoid excess inventory while maximizing savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom bolt heads or specific specifications can drive up costs. Be clear about your requirements, as customizations can lead to longer lead times and additional charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can increase costs. However, investing in certified products can provide long-term savings through improved durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products but often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect overall costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Bolt Head Sourcing?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage volume commitments or long-term contracts to negotiate better rates.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors such as longevity, maintenance, and potential failure costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect pricing. Establishing a clear understanding of these factors can help mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Understanding the local market dynamics, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, can provide insights into competitive pricing and sourcing opportunities.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Don’t settle for the first offer. Obtaining multiple quotes from different suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market rate and help secure the best deal.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for bolt heads can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Therefore, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to determine accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of bolt heads With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Bolt Heads?
In the world of fastening solutions, the diversity of bolt head types provides manufacturers and engineers with a range of options to meet specific project requirements. However, alternative fastening technologies also exist that can achieve similar objectives, such as securing components and providing structural integrity. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers who seek to optimize performance, cost, and functionality in their projects.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Types Of Bolt Heads | Alternative 1: Rivets | Alternative 2: Adhesives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load-bearing capacity, suitable for dynamic loads | Excellent for static loads, not ideal for disassembly | Varies widely, can be strong but dependent on surface preparation |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost with long-term durability | Generally lower initial cost but can require specialized tools | Can be lower cost if bulk purchased, but varies by type |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tools for installation | Simple installation with manual or pneumatic tools | Requires careful surface preparation and curing time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable and long-lasting | Generally low, but may need inspection for integrity | Can degrade over time, requiring replacement or reapplication |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, construction, automotive | Sheet metal applications, aircraft, and construction | Lightweight materials, non-load-bearing applications, or where noise reduction is important |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Rivets
Rivets are permanent mechanical fasteners that are widely used in industries like aerospace and construction. They provide a strong bond and are particularly effective in applications where the joint will not require disassembly. The installation of rivets requires specialized tools, which can add to the initial setup cost. However, once in place, they deliver excellent performance under shear loads. Rivets are ideal for applications involving thin materials, such as sheet metal, due to their ability to distribute stress evenly. The downside is that, unlike bolt heads, rivets cannot be easily removed or adjusted without drilling out the rivet, which may pose challenges in some manufacturing processes.
2. Adhesives
Adhesives represent a versatile alternative to traditional fastening methods. They can bond a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, making them suitable for lightweight applications and projects where aesthetics are a concern. While adhesive bonds can provide significant strength, their effectiveness heavily depends on surface preparation and curing conditions. Unlike bolt heads, adhesives can offer a seamless finish and can dampen vibrations, making them ideal for applications in consumer electronics and automotive interiors. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications, and their long-term durability can be a concern in harsh environments.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Fastening Solution
When considering fastening solutions, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific project requirements, including load-bearing needs, installation processes, and long-term maintenance considerations. Types of bolt heads excel in providing robust performance and durability for heavy-duty applications, while rivets offer a simpler installation method for static joints, and adhesives provide versatility for lightweight or aesthetic-focused projects. By weighing the pros and cons of each option against their operational needs, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of bolt heads
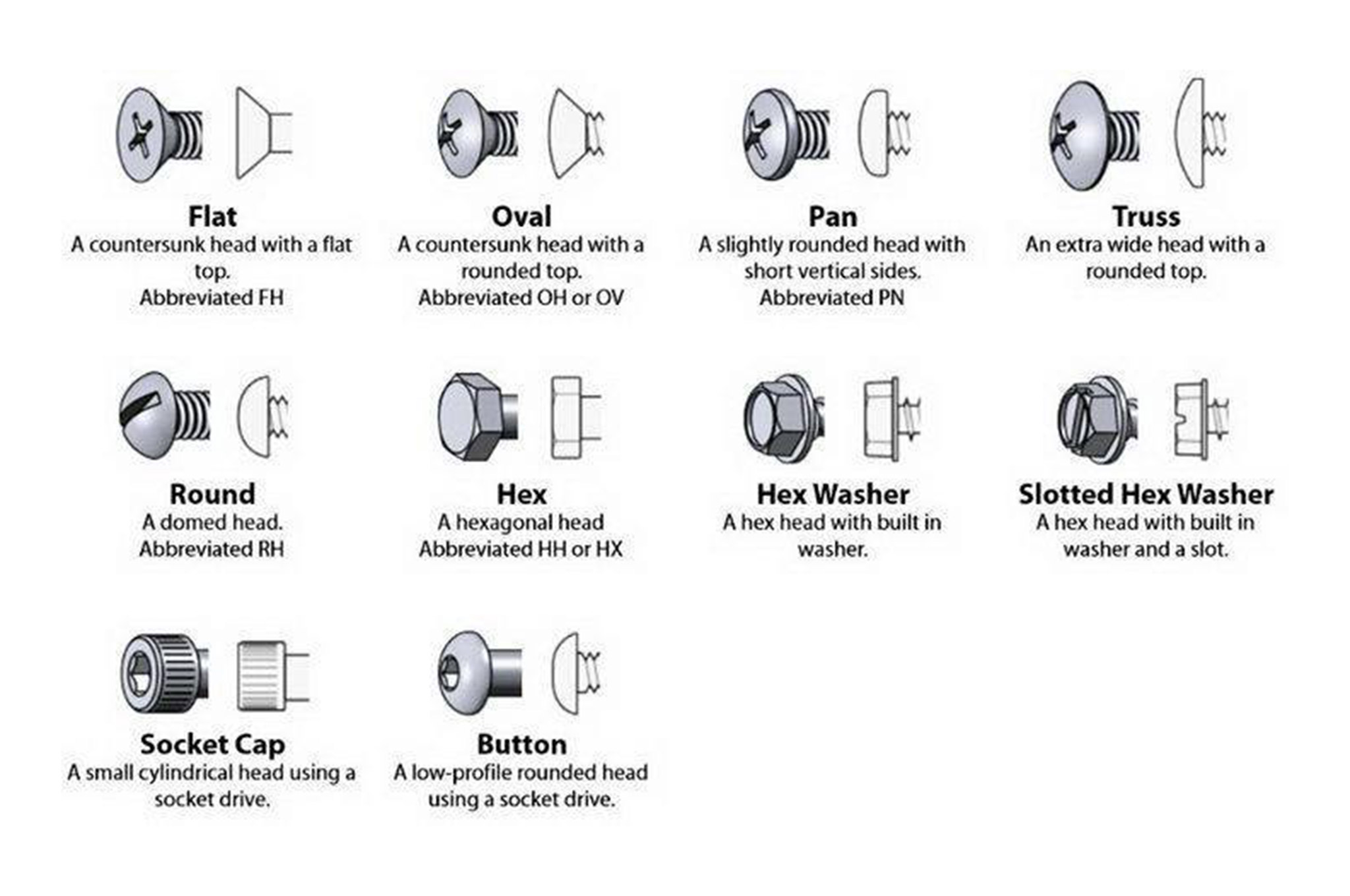
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bolt Heads?
When sourcing bolt heads for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is essential. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the quality and strength of the bolt head. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel. Each material offers different mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the assembly in specific environments, especially in industries like construction and manufacturing. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the bolt head. Tight tolerances are crucial for applications requiring precise fitting, particularly in high-stress environments. For buyers, understanding the tolerance levels can help ensure compatibility with other components, reduce wear and tear, and enhance overall assembly performance. -
Finish
The finish of a bolt head can affect its appearance and performance. Common finishes include zinc plating, powder coating, and passivation. The right finish can improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions where the bolts will be used, as this can significantly impact their durability and performance. -
Head Style
The style of the bolt head—such as hex, socket, or carriage—affects the tools required for installation and the load distribution characteristics. For instance, hex heads allow for higher torque application, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Understanding head styles helps buyers choose the right bolts for their specific assembly needs. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum load a bolt head can handle without failure. Load capacity is critical in applications involving heavy machinery or structural components, where safety and reliability are paramount. Buyers must assess the load requirements of their applications to select bolt heads that can withstand operational stresses. -
Thread Type
The thread type determines how the bolt will engage with nuts or other components. Common types include coarse and fine threads. Coarse threads are typically used for quick assembly, while fine threads provide greater tension and load distribution. Understanding thread types is essential for ensuring a secure fit and optimal performance in various applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Bolt Heads?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and procurement. Here are some common trade terms:
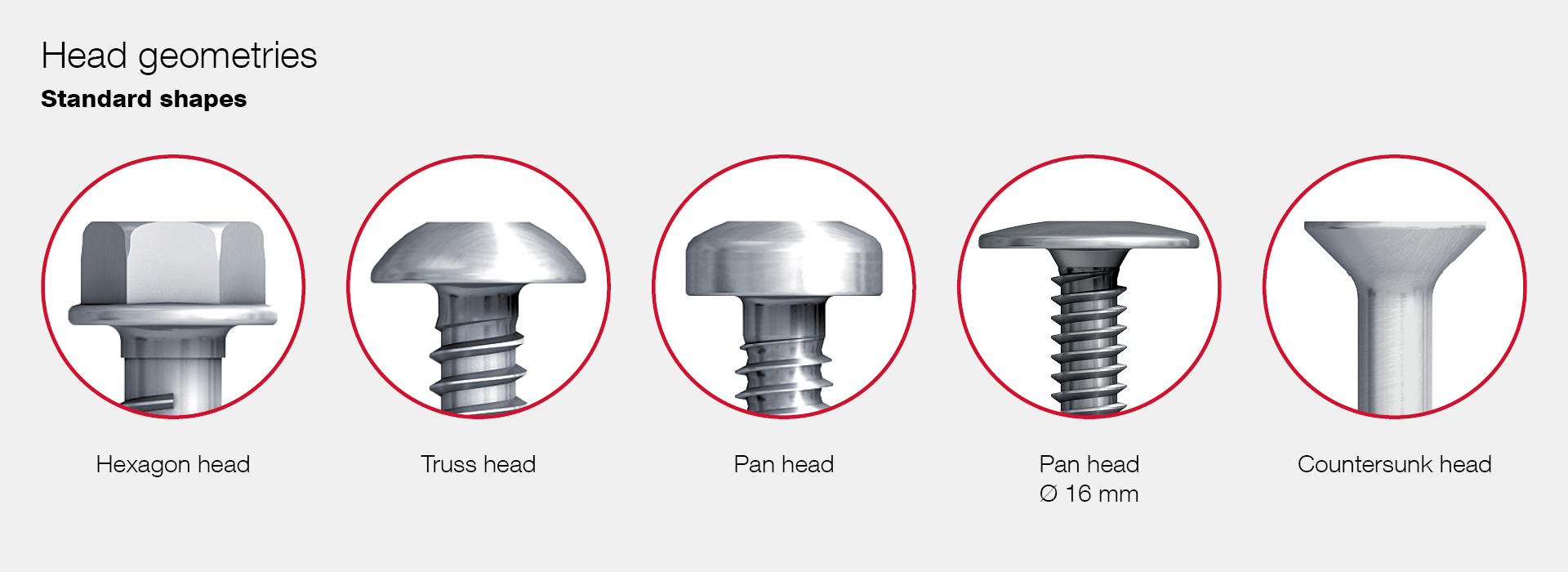
Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts that are used in another company’s product. In the context of bolt heads, OEMs often specify unique designs or materials that meet their specific performance criteria. B2B buyers should identify reputable OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is important for buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking. This term can significantly impact budgeting and procurement strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It is a critical tool for buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their bolt head procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They outline who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect overall costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international trade to avoid unexpected expenses. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Lead time can vary based on the supplier’s capacity and inventory levels. B2B buyers should consider lead times when planning projects to ensure timely delivery and avoid delays in production schedules. -
Certification
Certification indicates that a product meets specific industry standards or regulations. For bolt heads, certifications such as ISO or ASTM can provide assurance of quality and performance. Buyers should seek certified products to mitigate risk and enhance compliance with industry standards.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms is vital for making informed purchasing decisions and ensuring the success of your projects involving bolt heads.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of bolt heads Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Types of Bolt Heads Sector?
The global market for bolt heads is shaped by several key drivers, including the increasing demand for high-performance materials in construction and manufacturing sectors. As industries evolve, there is a growing emphasis on durability and load-bearing capacity, particularly in heavy machinery and infrastructure projects. In regions like Africa and South America, rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are propelling demand for robust fastening solutions. Meanwhile, European markets are witnessing a shift towards automation and advanced manufacturing techniques, which necessitate specialized bolt designs that enhance production efficiency.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and smart manufacturing, are influencing sourcing trends as buyers seek innovative solutions that reduce lead times and costs. The advent of Industry 4.0 has also prompted the integration of digital supply chain management systems, allowing B2B buyers to streamline procurement processes and enhance visibility across the supply chain. Furthermore, the trend towards customization is gaining traction, as companies look for tailored bolt solutions that meet specific project requirements.
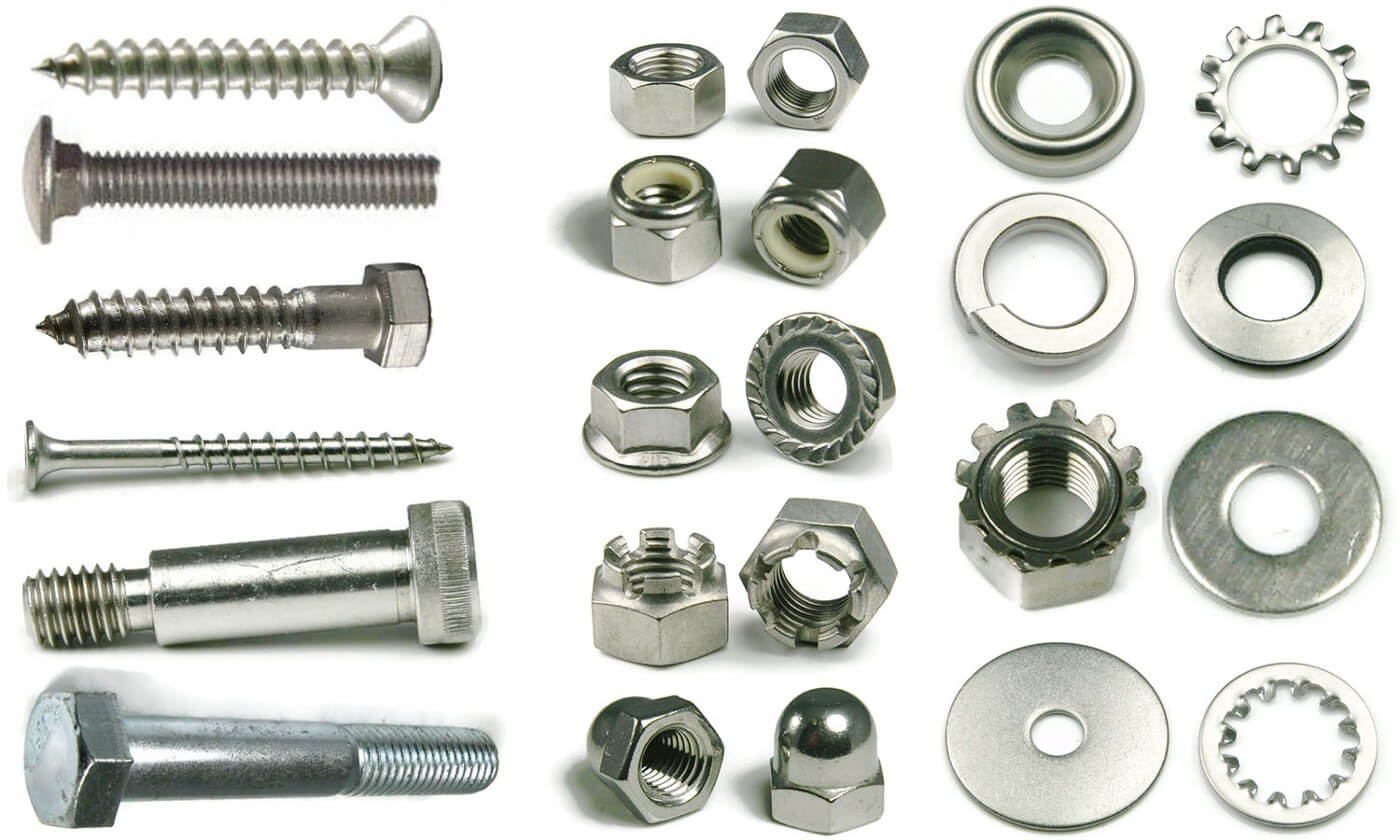

Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Types of Bolt Heads Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the bolt heads sector. Environmental concerns regarding the production and disposal of fasteners have prompted manufacturers to adopt greener practices. This includes using recycled materials and developing eco-friendly coatings that minimize environmental impact. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as obtaining certifications like ISO 14001, which indicates effective environmental management systems.
Moreover, the importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are now more vigilant about ensuring that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions such as the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory frameworks are tightening around supply chain transparency. By choosing suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, businesses not only enhance their brand reputation but also mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and supply chain disruptions.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Bolt Heads?
The evolution of bolt heads can be traced back to the early days of mechanical engineering, where basic designs were developed to fulfill simple fastening needs. Over time, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques led to the creation of diverse bolt head types, each engineered for specific applications. The introduction of standardized measurements and specifications in the 20th century further revolutionized the industry, allowing for greater interoperability and efficiency in assembly processes.

Illustrative image related to types of bolt heads
In recent years, the rise of technology has transformed the landscape, with innovations such as precision machining and automated production lines enhancing the quality and performance of bolt heads. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the manufacturing sector, where the focus has shifted towards creating high-value, customized solutions that meet the diverse needs of global industries. Today, the types of bolt heads available in the market are a testament to both historical advancements and the ongoing quest for innovation in fastener technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of bolt heads
-
How do I choose the right bolt head type for my project?
Selecting the appropriate bolt head type depends on several factors, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and assembly methods. For high-load applications, hex or flanged heads are ideal due to their larger surface area, which helps distribute stress. If aesthetics are a concern, consider countersunk heads for a flush finish. Additionally, assess the tools available for installation; for instance, socket cap bolts require specific Allen wrenches. Understanding your project specifications will guide you in making an informed choice. -
What is the best bolt head type for heavy machinery?
For heavy machinery, hexagon and flanged bolt heads are often the best options. Their designs facilitate superior load distribution and torque application, making them suitable for high-stress environments. Hex heads provide a larger grip area, allowing for better torque transmission during installation. Flanged bolts, with their integrated washer feature, help to prevent loosening under vibration, ensuring a secure fit. Always evaluate the specific mechanical requirements of your machinery before finalizing your selection. -
What should I consider when sourcing bolt heads internationally?
When sourcing bolt heads internationally, consider factors such as compliance with local standards, shipping logistics, and the reliability of suppliers. Ensure that the bolt specifications meet relevant industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Verify the supplier’s reputation through reviews or references and assess their ability to provide quality assurance documentation. Additionally, consider customs regulations and tariffs that may affect your total cost. Establish clear communication regarding lead times and delivery schedules to avoid delays. -
How can I vet suppliers for bolt heads effectively?
Vetting suppliers involves several key steps. Start by researching their industry reputation, looking for certifications that confirm their compliance with quality standards. Request samples to evaluate the material quality and manufacturing precision. It’s advisable to check for customer testimonials or case studies that illustrate their performance in similar projects. Establish direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and customer service. Finally, consider their production capacity to meet your demand, particularly if you need large quantities. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bolt heads?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bolt heads can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific type of bolt. Generally, MOQs can range from 500 to 5,000 units, depending on factors like material type, manufacturing processes, and customization requirements. It’s important to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or smaller projects, so it’s worth negotiating terms that suit your business model. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for bolt heads?
Common payment terms in international B2B transactions often include options like net 30, net 60, or payment upfront, especially for new buyers. Many suppliers may require a deposit (typically 30-50%) before production, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Letter of Credit (L/C) is a secure payment method used for larger transactions, ensuring that funds are only released upon fulfillment of contractual obligations. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing orders to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for bolt heads sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced bolt heads, establish clear quality standards and specifications upfront. Request third-party inspections or certifications that validate the manufacturing processes and material properties. Many suppliers offer quality control documentation, including test reports and compliance certificates. Consider implementing a sampling strategy where you assess a portion of the order before full acceptance. Regular communication with your supplier can help address any concerns proactively. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing bolt heads?
Logistics for importing bolt heads involve coordinating shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency and budget. Ensure that all documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations, is prepared accurately to avoid delays. Be aware of import tariffs and duties that may apply in your region. Establish a reliable logistics partner who can navigate the complexities of international shipping efficiently.
Top 3 Types Of Bolt Heads Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bolt Depot – Fasteners and Screws
Domain: boltdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fastener Categories: Wood Screws (WS), Machine Screws (MS), Thread Cutting Machine Screws, Sheet Metal Screws (SMS), Self Drilling Screws, Hex Bolts (HHMB or HXBT), Carriage Bolts, Lag Bolts, Flange Bolts, Socket Screws, Eye Bolts, Eye Lags, U-Bolts, J-Bolts, Shoulder Bolts, Elevator Bolts, Sex Bolts, Mating Screws, Hanger Bolts, Set Screws. Head Styles: Flat (FH), Oval (OH or OV), Pan (PN), Truss…
2. Tanner Bolt – Fastener Head Types
Domain: tannerbolt.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Fastener Tech: Common Head Types – This article discusses various types of fastener heads including flat, pan, round, truss, and hex heads. Each type has unique characteristics and applications, influencing their use in different projects. The article emphasizes the importance of selecting the right head type for optimal performance and fit.
3. GC Fasteners – Common Bolt and Screw Heads
Domain: gcfasteners.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Common Types of Bolt and Screw Heads: 1. Pan Heads – Large surface area for easy grip; recommended for new designs. 2. Round Heads – Previously popular, now largely replaced by pan heads; not recommended for new designs. 3. Fillister Heads – Smaller diameter for more pressure; deeper slots for assembly close to flanges. 4. Truss Heads – Low, rounded, extra wide; covers large diameter sheet metal h…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of bolt heads
In summary, understanding the diverse types of bolt heads is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in sectors where safety, load-bearing capacity, and aesthetics are paramount. By strategically sourcing the right bolt head types—such as hex, flange, or socket screws—businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability. The choice of bolt head not only affects performance but also influences manufacturability and assembly processes, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
As global markets continue to evolve, the importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. By investing time in selecting appropriate fasteners tailored to specific applications, buyers can secure a competitive edge in their respective industries. This is especially vital for companies in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse industrial needs and standards exist.
Looking ahead, we encourage international B2B buyers to leverage this knowledge in their procurement strategies. Engage with suppliers who offer a comprehensive range of bolt heads and seek partnerships that prioritize quality and innovation. Doing so will not only streamline your operations but also foster sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected global market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.