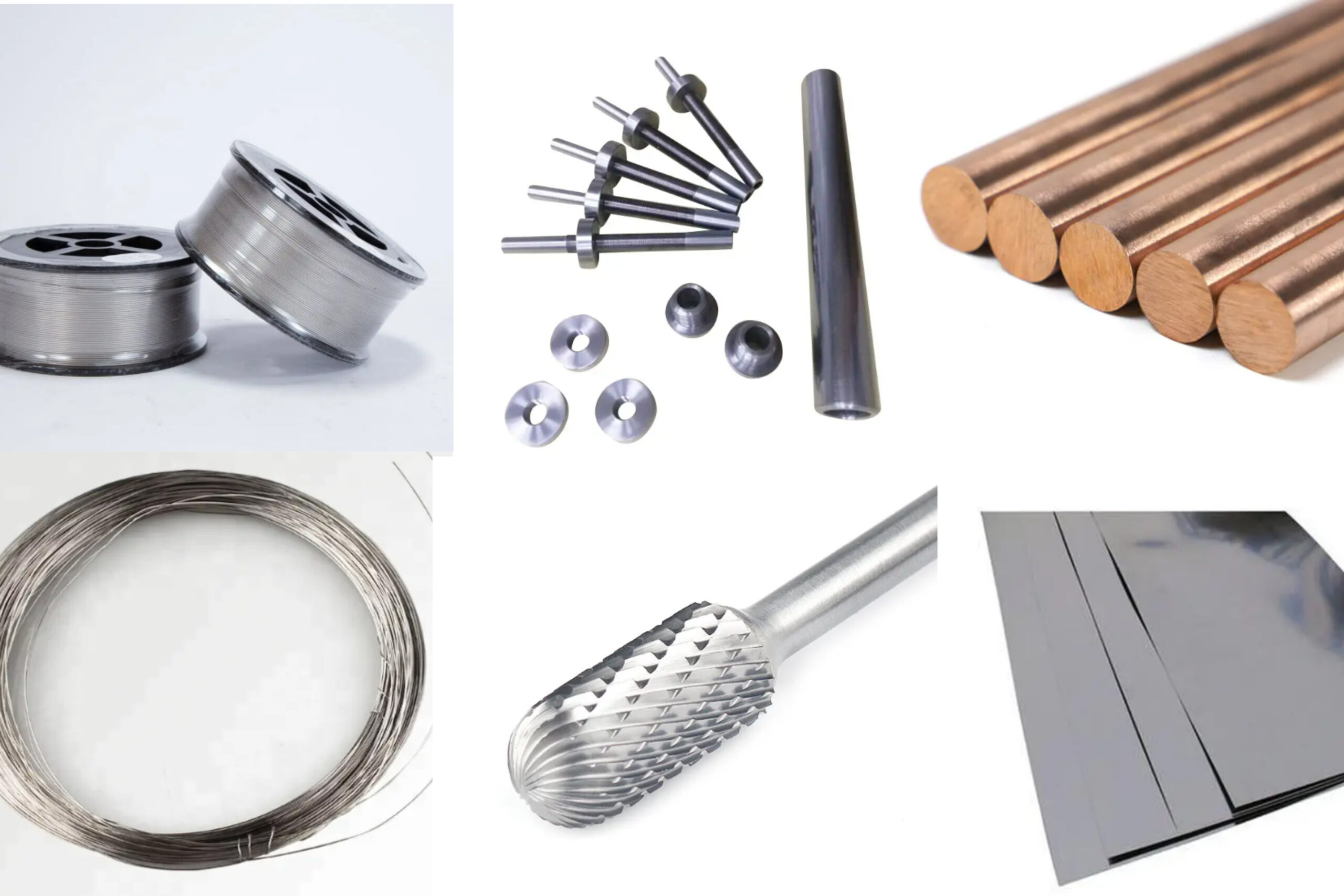
How to Source Tungsten Alloy Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tungsten alloy
Navigating the complexities of sourcing tungsten alloy can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With its unique properties—such as high density, excellent machinability, and resistance to heat and corrosion—tungsten alloy is increasingly favored across various industries, from aerospace to defense. However, understanding the nuances of different alloy types, their specific applications, and the intricacies of the global supply chain is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of tungsten alloys available, their applications in various sectors, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will address cost considerations and market trends that affect pricing, ensuring that you can navigate the sourcing landscape effectively.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil—this guide serves as a vital resource. It empowers you to make strategic decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints. By leveraging the insights provided, you can not only enhance your procurement strategy but also foster relationships with reliable suppliers, ultimately ensuring a seamless supply chain for your tungsten alloy needs.
Understanding tungsten alloy Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WHA) | Composed of 90% to 97% tungsten with nickel and copper or iron; high density and good machinability. | Aerospace, military, radiation shielding, and automotive industries. | Pros: High density, excellent radiation shielding. Cons: Higher cost compared to standard metals. |
| Tungsten Copper Alloy | Combines tungsten with copper for improved thermal and electrical conductivity. | Electrical contacts, heat sinks, and arc-welding applications. | Pros: Superior thermal and electrical properties. Cons: Lower density compared to pure tungsten. |
| Tungsten Nickel Iron Alloy | Contains tungsten, nickel, and iron; offers excellent strength and ductility. | Defense, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. | Pros: Good machinability, excellent mechanical properties. Cons: May corrode in certain environments. |
| Tungsten Molybdenum Alloy | Incorporates molybdenum for enhanced high-temperature strength. | High-temperature applications in aerospace and nuclear industries. | Pros: Exceptional heat resistance. Cons: More complex manufacturing process. |
| Tungsten Carbide | A hard, durable composite of tungsten and carbon; not a true alloy but widely used in manufacturing. | Cutting tools, mining, and drilling applications. | Pros: Extremely hard and wear-resistant. Cons: Brittle and can shatter under certain conditions. |
What Are the Characteristics and B2B Suitability of Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WHA)?
Tungsten Heavy Alloys (WHA) are known for their high density, which ranges from 17 to 19 g/cm³, and their composition typically includes 90% to 97% tungsten combined with nickel and copper or iron. This alloy is particularly suited for applications requiring significant weight in a compact form, such as in counterweights, radiation shielding, and military projectiles. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness and the specific mechanical properties required for their applications, as WHA provides excellent machinability compared to pure tungsten.
How Does Tungsten Copper Alloy Benefit Electrical Applications?
Tungsten Copper Alloys leverage the high melting point of tungsten along with the excellent electrical and thermal conductivity of copper. This combination makes them ideal for electrical contacts and heat sinks, particularly in applications involving high temperatures and electrical loads. B2B buyers should evaluate the thermal and electrical requirements of their projects, as this alloy offers a balance of performance and cost, although it does come with a lower density than pure tungsten.
What Advantages Does Tungsten Nickel Iron Alloy Offer in Manufacturing?
Tungsten Nickel Iron Alloys are characterized by their strength and ductility, making them suitable for demanding applications in the aerospace, medical, and defense sectors. With a composition that allows for good machinability, these alloys can be formed into complex shapes and components. Buyers should consider the alloy’s performance in specific environments, as it may be prone to corrosion under certain conditions. Its versatility can justify the investment for high-stakes applications.
Why Choose Tungsten Molybdenum Alloy for High-Temperature Applications?
Tungsten Molybdenum Alloys are designed for high-temperature resistance, making them suitable for aerospace and nuclear applications where durability under extreme conditions is essential. The addition of molybdenum enhances the alloy’s mechanical properties, but the manufacturing process can be more complex. B2B buyers should assess the thermal requirements and potential applications to ensure that the benefits of this alloy outweigh the increased production challenges.
What Makes Tungsten Carbide a Preferred Choice for Cutting Tools?
Tungsten Carbide, though technically a composite rather than a traditional alloy, is renowned for its hardness and wear resistance, making it a go-to material for cutting tools and drilling applications. Its durability allows for extended tool life and efficiency in manufacturing processes. However, the brittleness of tungsten carbide can pose challenges, as it may fracture under excessive stress. Buyers should weigh the performance benefits against potential limitations when selecting this material for high-impact applications.
Key Industrial Applications of tungsten alloy
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tungsten alloy | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Counterweights and ballast in aircraft | Enhances stability and fuel efficiency in flight operations | Ensure compliance with aviation standards and certifications |
| Defense and Military | Armor-piercing projectiles and penetrators | Provides superior penetration capabilities | Look for high-density alloys with proven performance metrics |
| Medical Equipment | Radiation shielding in imaging devices | Protects patients and staff from radiation exposure | Verify material certifications and compatibility with devices |
| Automotive | Crankshaft balance weights and components | Improves engine efficiency and reduces vibration | Consider custom shapes and sizes for specific engine designs |
| Manufacturing | Die casting and tooling applications | Extends tool life and reduces production downtime | Source high-quality alloys that conform to international standards |
How is Tungsten Alloy Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, tungsten alloys are utilized as counterweights and ballast in aircraft, enhancing stability during flight. Their high density allows for compact weight distribution, which is crucial for optimizing fuel efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions like the Middle East and Europe, should prioritize suppliers who comply with strict aviation standards to ensure safety and reliability in their applications.
What Role Does Tungsten Alloy Play in Defense and Military Applications?
Tungsten alloys are essential in the defense industry for manufacturing armor-piercing projectiles and penetrators. Their superior density and hardness provide significant advantages in terms of penetration capabilities against armored targets. B2B buyers in this sector, especially from Africa and South America, should seek suppliers with proven performance metrics and compliance with military specifications to ensure effectiveness in critical applications.
How Does Tungsten Alloy Contribute to Medical Equipment?
In medical applications, tungsten alloys are widely used for radiation shielding in imaging devices, such as X-ray machines and CT scanners. The high atomic number of tungsten effectively absorbs harmful radiation, protecting both patients and healthcare providers. Buyers from various regions should verify that the sourced materials meet stringent health and safety standards, ensuring compatibility with medical devices to maintain efficacy and safety.
Why is Tungsten Alloy Important in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive industry employs tungsten alloys in crankshaft balance weights and other engine components to improve overall engine efficiency and reduce vibrations. The unique properties of tungsten alloys allow for a reduction in size while maintaining weight, leading to better performance. Buyers should consider sourcing customized shapes and sizes to fit specific engine designs, ensuring optimal integration and functionality.
How is Tungsten Alloy Beneficial in Manufacturing Processes?
In manufacturing, tungsten alloys are utilized in die casting and tooling applications due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and wear. This leads to extended tool life and reduced production downtime, enhancing overall operational efficiency. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality alloys that conform to international standards, ensuring reliability and performance in demanding manufacturing environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tungsten alloy’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Complexity of Tungsten Alloy Specifications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to understanding the various specifications and properties of tungsten alloys. With numerous grades available, each offering different compositions and characteristics, selecting the right alloy for specific applications can be daunting. For instance, a buyer in the aerospace industry may require a tungsten alloy that balances high density with machinability, yet the vast array of options can lead to confusion and miscommunication with suppliers. This complexity can result in procurement delays, increased costs, and ultimately, project setbacks.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate the intricacies of tungsten alloy specifications, buyers should invest time in understanding the key properties of each alloy type, such as density, tensile strength, and thermal conductivity. Collaborating closely with suppliers is crucial; request detailed technical data sheets that outline the specific properties of each tungsten alloy, including compliance with relevant international standards. Furthermore, consider engaging with suppliers who offer sample materials for testing. This hands-on approach allows for practical evaluation, ensuring that the selected alloy meets both performance and machining requirements. Establishing a strong, communicative relationship with suppliers can streamline the sourcing process, leading to more informed decisions and successful project outcomes.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain and Lead Time Challenges
The Problem:
Supply chain issues can severely impact the availability of tungsten alloys, particularly in regions where sourcing materials is already complex. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East often encounter unpredictable lead times and limited access to quality suppliers. This can lead to production delays and increased costs, as companies may need to source alternative materials that do not meet their stringent requirements, resulting in compromised quality and performance.
The Solution:
To mitigate supply chain risks, it’s essential for buyers to diversify their sourcing strategies. Establish relationships with multiple suppliers across different geographical regions to ensure a steady flow of materials. Additionally, consider implementing a just-in-time inventory system that aligns procurement with production schedules, reducing excess inventory costs while ensuring availability when needed. Building a collaborative network with suppliers can also facilitate better forecasting of lead times and potential disruptions. Finally, leveraging technology, such as supply chain management software, can enhance visibility into inventory levels and lead times, enabling proactive decision-making.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Machining Difficulties with Tungsten Alloys
The Problem:
Despite their advantageous properties, tungsten alloys can present significant machining challenges due to their hardness and brittleness. B2B buyers in industries like automotive and defense may find that standard machining processes are insufficient, leading to increased tool wear, longer production times, and higher costs. This can be particularly frustrating for manufacturers who rely on precision components and need to adhere to tight tolerances.
The Solution:
To address machining difficulties, buyers should invest in specialized machining techniques tailored for tungsten alloys. Utilizing carbide cutting tools and optimizing machining parameters—such as slower cutting speeds and higher feed rates—can significantly improve machining efficiency and extend tool life. It’s also advisable to work with suppliers who can provide pre-machined components or custom shapes to reduce the need for extensive machining. Furthermore, training operators on the unique characteristics of tungsten alloys will enhance their ability to work with these materials effectively. By adopting these strategies, manufacturers can minimize machining challenges, reduce production costs, and maintain the high-quality standards required in their respective industries.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tungsten alloy
What are the Key Properties of Tungsten Heavy Alloys?
Tungsten heavy alloys, typically composed of 90% to 97% tungsten combined with nickel and copper or nickel and iron, exhibit exceptional density and strength. They can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications requiring thermal stability. Additionally, these alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments, which is crucial for industries such as aerospace and defense. Their machinability is significantly improved compared to pure tungsten, allowing for more complex shapes and designs.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Tungsten Alloys?
When considering tungsten heavy alloys, several advantages stand out. Their high density provides significant weight in a compact form, making them ideal for applications such as counterweights and radiation shielding. The durability of these materials ensures longevity in demanding applications, reducing the frequency of replacements. However, the primary drawback is their cost, which is generally higher than that of other metals. Manufacturing complexity can also be a concern, as specialized techniques are required to shape and finish tungsten alloys, potentially leading to increased production times.
How Do Tungsten Alloys Impact Specific Applications?
Tungsten alloys are particularly effective in applications that require high density and strength. For instance, in the aerospace sector, they are used for ballast weights and counterweights due to their ability to provide stability without adding excessive bulk. In the medical field, their radiation shielding properties make them invaluable in protecting sensitive equipment and personnel. However, it’s essential to consider the compatibility of tungsten alloys with specific media, such as corrosive chemicals or extreme temperatures, which can influence their performance.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Tungsten Alloys?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of compliance with various standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Understanding these standards ensures that the materials meet the necessary quality and safety requirements for their intended applications. Additionally, regional preferences may influence material selection; for example, buyers from Saudi Arabia may prioritize corrosion resistance due to environmental conditions. It is also advisable to consider the availability of suppliers who can provide certifications and traceability for the materials, which is increasingly important in global trade.
Summary Table of Tungsten Alloy Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for tungsten alloy | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT-17C (90% W, 6% Ni, 4% Cu) | Radiation shielding in medical devices | Excellent machinability and density | Higher cost compared to other alloys | High |
| MT-17D DieAlloy (90% W, 4% Ni) | Die casting for automotive components | Extends die life and reduces rejects | Limited to specific die applications | Medium |
| MT-18F (95% W, 3.5% Ni, 1.5% Fe) | Aerospace counterweights | High strength and thermal stability | Manufacturing complexity | High |
| MT-185 (97% W, 2.1% Ni) | Industrial applications requiring precision | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher price point | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of tungsten alloys, focusing on their properties, advantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will facilitate informed decisions in sourcing and utilizing tungsten alloys effectively across various industries.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tungsten alloy
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Alloy?
The manufacturing of tungsten alloy involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality tungsten alloy products.
Material Preparation: How is Tungsten Alloy Initially Processed?
Material preparation is the first step in the tungsten alloy manufacturing process. It begins with the selection of high-purity tungsten powder, which typically contains 90% to 97% tungsten content, depending on the desired alloy grade. This powder is often sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure quality.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
Once the tungsten powder is acquired, it undergoes a screening process to remove any impurities. The powder may then be mixed with other metals, such as nickel, copper, or molybdenum, depending on the alloy’s intended use. This mixture is crucial as it significantly influences the alloy’s properties, such as density, machinability, and strength.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Tungsten Alloys?
The forming stage is where the prepared tungsten powder is shaped into the desired form. The most common techniques include high-temperature pressing and sintering.
-
High-Temperature Pressing: The tungsten powder mixture is compacted into molds under high pressure. This process helps achieve the desired density and shape.
-
Sintering: After pressing, the shaped powder is heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace. This process causes the particles to bond at the atomic level, enhancing the material’s strength and durability. The sintering temperature and duration are carefully controlled to optimize the alloy’s properties.
-
Machining: Following sintering, the tungsten alloy may require additional machining to achieve precise dimensions. This step is essential for applications that demand high accuracy, such as aerospace and medical devices.
Assembly: How Are Tungsten Alloy Components Joined?
In applications where multiple tungsten alloy components are utilized, assembly becomes a crucial stage. Techniques such as welding, brazing, or adhesive bonding may be employed, depending on the design and application requirements.
Welding tungsten alloys can be challenging due to their high melting points, necessitating specialized equipment and skilled technicians. Brazing, on the other hand, involves melting a filler material to join components without melting the base metals, making it a preferred option for many manufacturers.
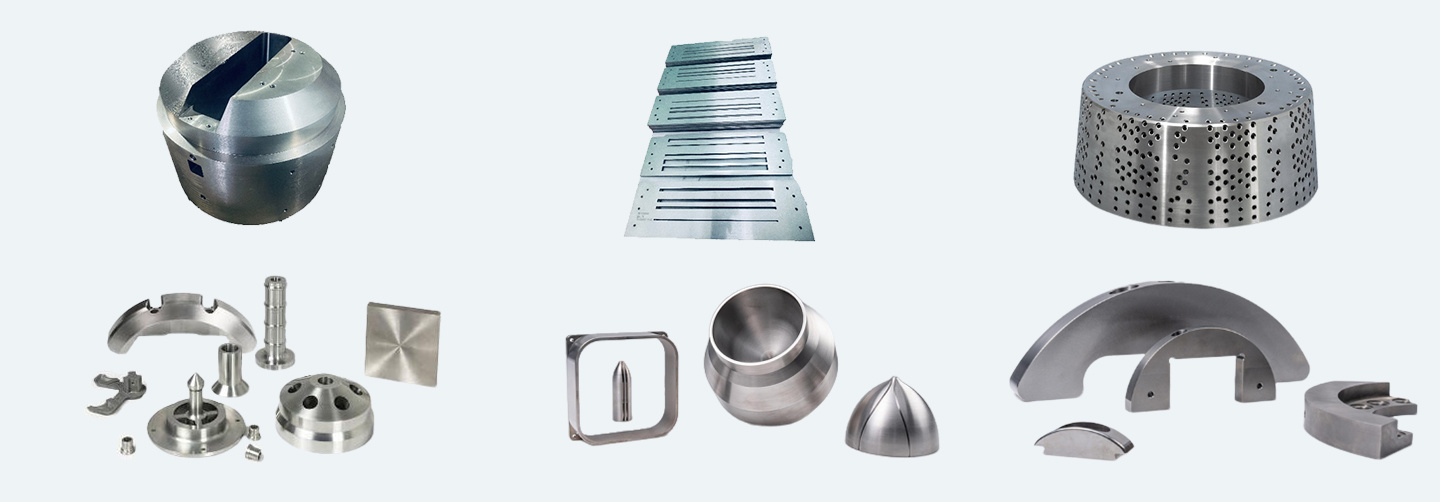

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
Finishing: What Processes Ensure the Final Quality of Tungsten Alloys?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments that improve the alloy’s performance and aesthetic qualities. Common techniques include:
-
Polishing: This enhances the surface finish, making it smoother and more resistant to wear and corrosion.
-
Coating: Applying protective coatings can significantly increase the lifespan of tungsten alloy components, particularly in harsh environments.
-
Heat Treatment: This process can further improve mechanical properties by altering the microstructure of the alloy.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Tungsten Alloy Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is pivotal in the tungsten alloy manufacturing process. It ensures that the products meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
For B2B buyers, recognizing relevant international standards is crucial. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that indicates a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications can provide further assurance of product quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Production Process?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, continuous monitoring is performed to detect any deviations from quality standards. This includes checking parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing process is complete, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that all products meet the required specifications and standards before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Several testing methods are commonly employed to verify the quality of tungsten alloys:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile strength tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to assess the material’s mechanical properties.
-
Chemical Analysis: Techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or mass spectrometry are used to confirm the chemical composition of the alloy.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing allow for the detection of internal flaws without damaging the product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request documentation that outlines the supplier’s quality control processes, including test results and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product reliability.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality certification is vital. Different regions may have varying certification requirements, which can affect product acceptance in local markets.
-
Regional Standards: Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific regional standards and regulations that may apply to tungsten alloy products. For example, CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, while compliance with ANSI and ASTM standards may be necessary for North American markets.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers can provide complete documentation and traceability for their products, including material certificates and test reports. This is particularly important for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as aerospace and defense.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tungsten alloys, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tungsten alloy’
To effectively procure tungsten alloy, international B2B buyers must navigate a series of strategic steps. This checklist serves as a comprehensive guide to ensure you make informed decisions throughout the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the desired tungsten alloy composition, dimensions, and any specific properties such as density or machinability. By having precise specifications, you can streamline communication with suppliers and ensure that the products meet your project needs.
- Consider the application: Different industries may require varying grades of tungsten alloys. For instance, high-density applications may necessitate alloys with a higher tungsten content.
- Understand international standards: Familiarize yourself with standards such as ASTM B777 to ensure compliance and quality assurance.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Invest time in researching potential suppliers and market trends for tungsten alloy. This involves identifying key players in regions relevant to your business, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Use industry directories: Leverage platforms like IQS Directory to find reputable tungsten alloy manufacturers.
- Analyze competitors: Understand how similar businesses source their materials, as this can provide insights into reliable suppliers and pricing structures.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Assess certifications: Verify if suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) to ensure quality management systems are in place.
- Request samples: Consider asking for material samples to evaluate quality and compatibility with your specifications.
Step 4: Check Production Capabilities
Understand the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your volume and timeline requirements. This step is vital to avoid delays in your supply chain.
- Inquire about customization: If you require specific sizes or shapes, confirm that the supplier can accommodate custom orders.
- Evaluate lead times: Discuss production timelines to align with your project schedules.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This step is critical in ensuring that you secure the best possible deal.
- Compare quotes: Gather quotations from multiple suppliers to understand the market pricing and negotiate effectively.
- Discuss warranties and support: Ensure that you understand the warranty terms and after-sales support the supplier offers.
Step 6: Finalize the Contract
After reaching an agreement, it’s time to finalize the contract. This document should clearly outline all terms, including specifications, prices, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Include quality control measures: Specify quality assurance processes and criteria for acceptance of the tungsten alloy.
- Establish communication protocols: Define how you will communicate throughout the order process to address any potential issues promptly.
Step 7: Review and Monitor Supply Chain Performance
After procurement, continuously monitor supplier performance to ensure adherence to quality standards and delivery timelines. This step is essential for maintaining a reliable supply chain.
- Implement feedback mechanisms: Establish a process for providing feedback to suppliers based on performance.
- Conduct regular audits: Schedule periodic reviews to assess the supplier’s compliance with contract terms and quality expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source tungsten alloy, ensuring that they meet their technical requirements while fostering productive supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tungsten alloy Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Tungsten Alloy Sourcing?
When sourcing tungsten alloys, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
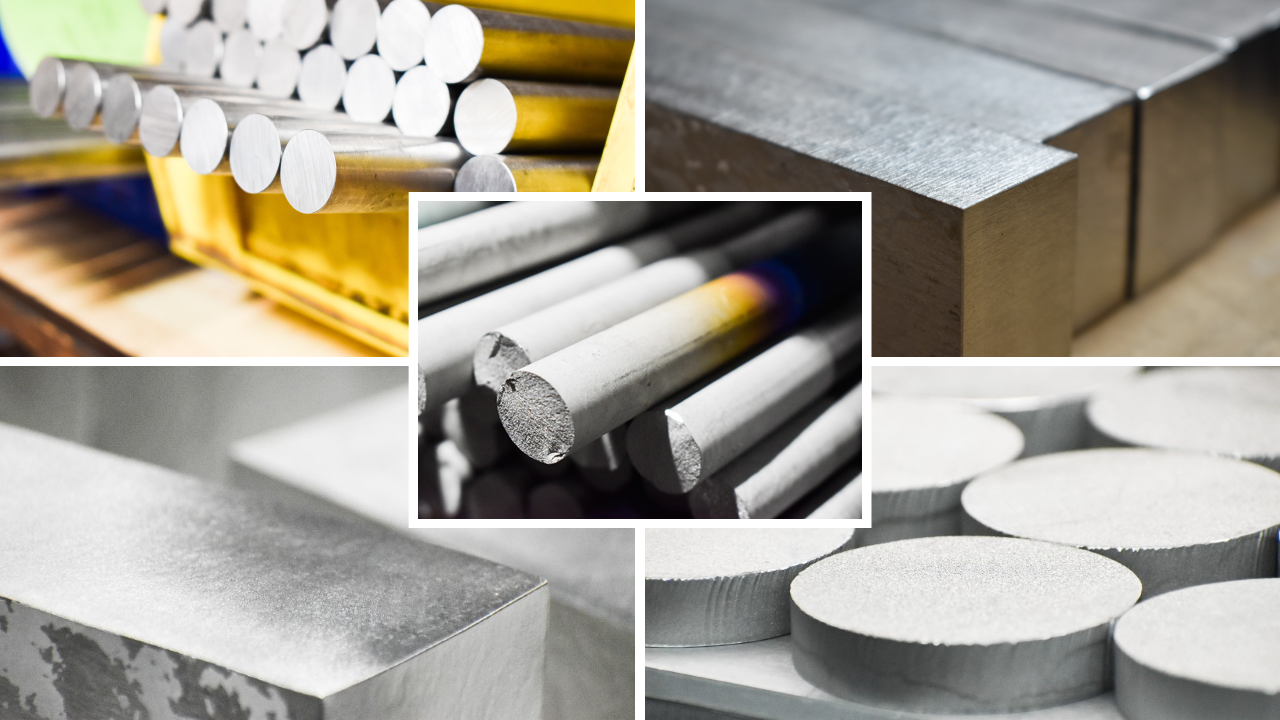

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
-
Materials: Tungsten itself is a high-cost raw material, with prices fluctuating based on global supply and demand dynamics. The alloying elements, such as nickel and copper, also contribute significantly to material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass not only the workforce engaged in production but also skilled technicians who handle machining and quality control processes. As tungsten alloys require specialized knowledge for machining, labor costs can be higher compared to more common materials.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and maintenance. Given the specific machinery needed to work with tungsten alloys, overhead can be substantial.
-
Tooling: Tungsten alloys are challenging to machine, often necessitating specialized tools that are more expensive than those required for other metals. The tooling costs must be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that tungsten alloys meet international standards requires rigorous quality control processes. This involves testing and certification, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transporting tungsten alloys, especially internationally, can be costly due to their weight and the need for secure handling. Shipping costs, import duties, and insurance should all be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and desired profit level. This margin can vary significantly based on market conditions and the supplier’s position.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Tungsten Alloy Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of tungsten alloys, making it essential for buyers to be aware of these nuances:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit prices, as suppliers can spread fixed costs over a larger quantity. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized alloys or specific grades can incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Alloys meeting higher quality standards or possessing specific certifications (e.g., ASTM) may carry a premium. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capacity can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more, but they often provide better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact the total cost. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing shipping risks and costs effectively.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should employ strategic negotiation techniques to optimize sourcing costs:
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about global tungsten market trends and price fluctuations to negotiate effectively. Being aware of supply chain issues or geopolitical factors can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but also the long-term implications of sourcing decisions. Evaluate the TCO, including maintenance and replacement costs, to justify higher upfront prices for superior quality products.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers may offer discounts for repeat business or favorable payment terms for trusted partners.
-
Explore Local Sourcing Options: Investigate local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. Regional sourcing can also mitigate risks associated with international shipping and tariffs.
What are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of tungsten alloy pricing is critical:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of currency exchange rates and how they can affect costs when sourcing from suppliers in different countries. Consider negotiating prices in a stable currency to minimize risks.
-
Tariffs and Import Duties: Different countries impose varying tariffs on imported goods. Buyers should calculate these costs into their total price to avoid surprises upon importation.
-
Shipping and Handling: International shipping can be unpredictable. Ensure that logistics costs, including potential delays and damages, are clearly defined in contracts.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost components and price influencers associated with tungsten alloy sourcing can empower buyers to make informed decisions. By leveraging effective negotiation strategies and being aware of international pricing nuances, businesses can secure better deals and optimize their procurement processes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tungsten alloy With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Tungsten Alloy
In the realm of manufacturing and industrial applications, the selection of materials is crucial for achieving optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Tungsten alloy is a popular choice due to its unique properties, such as high density and superior machinability. However, various alternatives exist that may cater to specific needs or budget constraints. This analysis will compare tungsten alloy against two notable alternatives: Beryllium Copper and Stainless Steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Tungsten Alloy | Beryllium Copper | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High density, excellent radiation shielding | High strength and electrical conductivity | Versatile, good corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost (varies by application) | Moderate cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machining | Easier to machine than tungsten | Easy to work with, widely available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance once in use | Moderate maintenance required | Low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, military, and medical devices | Electrical components, tools | General engineering and construction |
Beryllium Copper: An Alternative with High Conductivity
Beryllium copper is an alloy known for its exceptional strength and excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. It is easier to machine than tungsten alloys, making it suitable for applications in electrical connectors and precision tools. However, the key drawback is its toxicity; beryllium dust can be hazardous if inhaled during machining processes, necessitating stringent safety protocols. Additionally, while its cost is moderate, it may not provide the same high density required for certain applications as tungsten alloys do.
Stainless Steel: The Cost-Effective Workhorse
Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, is renowned for its versatility and corrosion resistance. It is significantly less expensive than tungsten alloys and is widely used in various industries, from construction to food processing. Its ease of machining makes it a preferred choice for many applications. However, it lacks the high density and specific properties that tungsten alloys offer, making it less suitable for applications requiring radiation shielding or extreme wear resistance.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between tungsten alloy and its alternatives, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application requirements, including performance criteria, budget constraints, and machining capabilities. For industries focused on high-density applications or radiation shielding, tungsten alloy remains the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for applications that prioritize electrical conductivity or corrosion resistance without the need for extreme density, beryllium copper or stainless steel may provide a more cost-effective and practical solution. Conducting a thorough needs assessment will ensure the chosen material aligns with project goals and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tungsten alloy
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with tungsten alloy is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge helps in making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring compatibility with specific applications, and optimizing supply chain processes.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Tungsten Alloy?
-
Material Grade
Material grade indicates the composition and quality of tungsten alloy. Common grades include 90% tungsten with varying percentages of nickel and copper or iron. Each grade has distinct mechanical properties, such as density and hardness, which are critical for applications like radiation shielding and high-density weights. For B2B buyers, selecting the correct grade ensures the material meets performance requirements and regulatory standards. -
Density
Density, measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cc), is a vital property that influences the alloy’s weight and strength. Tungsten alloys typically range from 17 g/cc to 18.5 g/cc. A higher density often equates to better performance in applications requiring substantial weight in a compact form, such as counterweights or ballast. Buyers must consider density to achieve the desired physical characteristics in their products. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in manufacturing. For tungsten alloys, tight tolerances (e.g., -0/+0.003 inches) ensure precision in applications like machining and die casting. Understanding tolerance levels is essential for B2B buyers to guarantee that the components fit seamlessly into their end products, minimizing the risk of costly rework or failure. -
Machinability
Machinability describes how easily a material can be shaped or cut into desired forms. Tungsten alloys are generally easier to machine than pure tungsten, making them preferable for many applications. For manufacturers, understanding machinability helps in estimating production timelines and costs, allowing for better project planning. -
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as stress relieving and sintering, enhance the mechanical properties of tungsten alloys. These processes improve strength and durability, making them suitable for high-performance environments. Buyers need to consider whether the supplier provides heat-treated options to ensure the products can withstand their intended applications.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are marketed under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for B2B buyers to identify reliable suppliers who meet industry standards and can provide quality products for integration into their own offerings. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps B2B buyers manage inventory levels and cash flow effectively. It’s crucial for negotiating terms with suppliers, especially when sourcing tungsten alloys for specific projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers use RFQs to gather competitive offers and assess supplier capabilities, facilitating better decision-making when sourcing tungsten alloys. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus avoiding potential disputes and ensuring smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is essential for B2B buyers to plan production schedules and meet customer deadlines, particularly in industries where tungsten alloys are critical for timely project execution.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies, ensuring they select the most suitable tungsten alloy products for their specific applications while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tungsten alloy Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Tungsten Alloy Sector?
The tungsten alloy market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand in various sectors such as aerospace, defense, medical, and automotive. Global trends indicate a shift towards high-density materials that offer superior performance, particularly in applications requiring high durability and resistance to extreme conditions. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are experiencing heightened interest, particularly from countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, where industrial growth is accelerating.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as advanced manufacturing techniques and digital supply chain solutions, are reshaping sourcing dynamics. Companies are increasingly adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems and leveraging data analytics to optimize procurement processes. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms tailored for industrial materials is facilitating easier access for international buyers, allowing them to compare suppliers and pricing more efficiently.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
As buyers navigate these dynamics, understanding the specifications and quality certifications of tungsten alloys, such as ASTM standards, is crucial. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions and ensure compliance with industry regulations, particularly when sourcing from diverse global suppliers.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Tungsten Alloy Procurement?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount concerns for B2B buyers in the tungsten alloy sector. The environmental impact of tungsten mining and processing can be significant, leading to habitat destruction and pollution. Consequently, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices and possess ‘green’ certifications.
Buyers should seek suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as responsible sourcing from conflict-free zones and minimizing waste through recycling initiatives. Certifications like ISO 14001 can indicate a supplier’s dedication to environmental management. Additionally, opting for tungsten alloys produced through eco-friendly processes not only aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals but can also enhance a company’s brand reputation.
As consumers and regulatory bodies demand more transparency, B2B buyers must engage with suppliers that provide detailed information about their sourcing practices. This includes the supply chain’s traceability, which is critical in ensuring that tungsten alloys are sourced responsibly and sustainably.
What Has Been the Evolution of the Tungsten Alloy Market?
The tungsten alloy market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially utilized primarily in military applications due to its density and hardness, tungsten alloys have expanded into diverse sectors, including aerospace, medical devices, and industrial manufacturing.
Technological advancements have enabled the development of various tungsten alloys with tailored properties, enhancing their machinability and performance in high-stress environments. As global industries continue to innovate, the demand for tungsten alloys is likely to grow, driven by their unique characteristics that meet the needs of modern applications.

Illustrative image related to tungsten alloy
This evolution reflects a broader trend in material science, where the focus is not only on performance but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing, shaping the future landscape of the tungsten alloy sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tungsten alloy
-
How do I choose the right tungsten alloy for my specific application?
Selecting the right tungsten alloy depends on your application requirements, such as density, strength, and machinability. For instance, if you need high density and radiation shielding, consider alloys with a higher tungsten content (up to 97%). If machinability is critical, alloys like MT-17C or MT-18F are preferable due to their easier processing capabilities. Always evaluate the alloy’s specifications against your operational needs and consult with suppliers for tailored recommendations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for tungsten alloys?
Minimum order quantities for tungsten alloys can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms to several tons, depending on the product type and supplier policies. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. For smaller projects, some suppliers might offer flexibility, especially for custom orders or samples. -
How can I ensure the quality of tungsten alloy products?
To ensure product quality, request material certifications that comply with international standards (like ASTM B777) from suppliers. Inquire about their quality control processes, including lot control, stress relief, and sintering methods. Conducting supplier audits or visiting production facilities can also provide insights into their manufacturing practices. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews from other B2B buyers. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by tungsten alloy suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include advance payments, net 30, or net 60 days. Some suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or large orders. It’s advisable to discuss payment terms early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for international transactions. -
What shipping options are available for tungsten alloy orders?
Shipping options for tungsten alloys typically include air freight, sea freight, and express courier services. The choice of shipping method often depends on the order size, budget, and urgency. For bulk orders, sea freight is usually the most economical, while air freight is faster but more expensive. Ensure your supplier can provide tracking information and that they comply with international shipping regulations to avoid delays. -
How do I vet suppliers of tungsten alloys for international trade?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their reputation, certifications, and production capabilities. Start by researching online reviews and industry references. Request documentation of their compliance with international standards and quality management systems. Engaging with third-party inspection services can also provide additional assurance of supplier credibility. Building relationships through direct communication can help gauge reliability and responsiveness. -
Can I customize tungsten alloy products to meet my specifications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for tungsten alloys, including specific sizes, shapes, and alloy compositions. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities and minimum order quantities for custom products. Customization may involve additional costs and lead times, so ensure these factors are accounted for in your planning and budgeting. -
What industries commonly use tungsten alloys, and why?
Tungsten alloys are widely used in industries such as aerospace, defense, medical, and manufacturing due to their high density, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. Applications include radiation shielding, counterweights, and precision machining tools. Understanding industry-specific requirements can help you leverage tungsten alloys effectively in your projects, making them a valuable material choice for various high-performance applications.
Top 6 Tungsten Alloy Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tungsten – Heavy Alloy Products
Domain: shop.tungsten.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Tungsten Heavy Alloy products include various shapes such as rods, bars, sheets, and plates. Key product details include:
– Material Composition:
– MT-17C: 90% Tungsten, 6% Nickel, 4% Copper, 17g/cc density
– MT-17D: 90% Tungsten, 4% Nickel, 4% Molybdenum, 2% Iron, 17g/cc density
– MT-17F: 90% Tungsten, 7% Nickel, 3% Iron, 17g/cc density
– MT-175: 92.5% Tungsten, 5.25% Nickel, 2.25% Iron,…
2. IQS Directory – Tungsten Properties and Applications
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Tungsten is a silvery-gray metal known for its impressive hardness, outstanding tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Key properties include a melting point of 6191°F (3421.7°C) and a boiling point of 10220°F (5660°C). It is found in minerals like wolframite and scheelite. Tungsten alloys include tungsten carbide, Hastelloy, and various tungsten nickel alloys. Tungsten is b…
3. ScienceDirect – Tungsten Alloys
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Tungsten alloys are composite materials primarily containing tungsten, enhanced with metals like nickel or molybdenum for improved heat resistance and strength in high-temperature applications. Common tungsten heavy alloys (WHAs) have Ni-Fe or Ni-Cu matrices, with other metals such as Co, Mo, and Mn sometimes added. WHAs are typically liquid-phase sintered, achieving green densities near 60% of th…
4. Plansee – Tungsten Alloys
Domain: plansee.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Tungsten alloys are high-density materials primarily consisting of tungsten combined with metals like nickel, iron, or copper. Key properties include exceptional physical and chemical characteristics, high purity (99.97% for tungsten), and the ability to customize properties through alloying elements and production processes. Notable alloys include WVM (tungsten-vacuum-metallizing), WVMW (WVM-tung…
5. Mi-Tech Tungsten Metals – High-Density Tungsten Alloys
Domain: mttm.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Mi-Tech Tungsten Metals offers high-density tungsten alloys suitable for various applications including radiation shielding, boring bars, crankshaft balancing, and high-temperature tooling. Key products include: Tungsten, Nickel and Iron Alloys (HD17D, HD17.5, HD18D, HD18.5), Tungsten, Nickel and Copper Alloys (HD17, HD18), and Tungsten, Nickel and Copper/Iron Blend Alloy (HD17BB). These alloys pr…
6. Reddit – Alloy Reinforcement Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Alloy Reinforcement Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tungsten alloy
In the evolving landscape of tungsten alloy sourcing, businesses must prioritize strategic partnerships to leverage the unique properties of these materials. Tungsten alloys, known for their high density and exceptional machinability, present significant advantages across various industries, including aerospace, defense, and manufacturing. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should focus on reliable suppliers who can provide certified quality materials, ensuring compliance with international standards.
The ability to customize tungsten products according to specific application needs can enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste. As demand grows, especially in high-density applications and radiation shielding, strategic sourcing becomes essential to secure competitive pricing and ensure timely delivery.
Looking ahead, businesses are encouraged to invest in strong supplier relationships and explore innovative applications of tungsten alloys to stay ahead in their respective markets. As the global demand for sustainable and efficient materials rises, the strategic sourcing of tungsten alloys will not only provide a competitive edge but also contribute to long-term growth and sustainability. Engage with trusted suppliers today to harness the full potential of tungsten alloys in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.