How to Source Tire Shredder For Sale Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tire shredder for sale
In the dynamic landscape of industrial recycling, sourcing a tire shredder for sale presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The increasing volume of waste tires necessitates efficient processing solutions, yet navigating the myriad options can be overwhelming. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the diverse types of tire shredders available, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when evaluating suppliers.
By delving into aspects such as operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and technological advancements, this guide empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Nigeria seeking robust machinery for local recycling efforts or in Saudi Arabia looking to enhance your waste management capabilities, understanding the nuances of tire shredding technology is crucial.
From identifying the right specifications to vetting suppliers based on reliability and support, this guide will equip you with actionable insights. By leveraging this knowledge, businesses can optimize their investments in tire shredding solutions, ensuring they meet both environmental standards and operational goals effectively. As you embark on your journey in the tire recycling industry, let this guide be your trusted companion in navigating the global market for tire shredders.
Understanding tire shredder for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Tire Shredders | Towable, diesel-powered, fast processing (25 tires in 6 min) | Small to medium recycling operations, remote sites | Pros: Mobility, quick setup; Cons: Limited capacity compared to stationary units. |
| Primary Tire Shredders | High-volume processing, shearing design, robust construction | Initial tire processing, high-throughput facilities | Pros: Efficient size reduction; Cons: Higher upfront cost. |
| Secondary Tire Shredders | Further size reduction, top-feed design | Fine shredding for crumb rubber production | Pros: Enhanced material quality; Cons: Requires integration with primary shredders. |
| Stationary Tire Shredders | Fixed installation, electric or hydraulic options, high capacity | Large-scale recycling plants | Pros: High throughput, lower operational costs; Cons: Less flexible than portable options. |
| Custom Tire Shredders | Tailored solutions based on specific needs | Specialized recycling applications | Pros: Meets unique operational requirements; Cons: Potentially longer lead times and costs. |
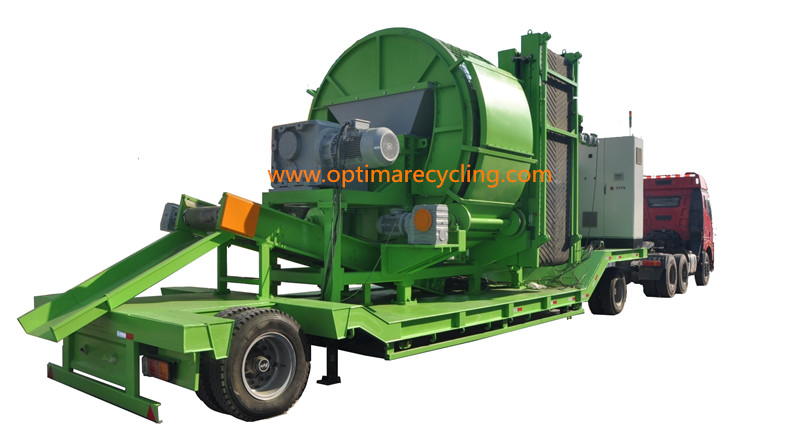
What Are the Key Characteristics of Portable Tire Shredders?
Portable tire shredders are designed for versatility and mobility, making them ideal for businesses that operate in remote locations or require frequent relocation of equipment. These machines can be towed by standard vehicles, enabling quick deployment. They are particularly suited for small to medium-sized recycling operations where space and budget constraints exist. Buyers should consider their operational needs, as while these shredders offer quick setup and mobility, they typically have a lower processing capacity compared to stationary models.
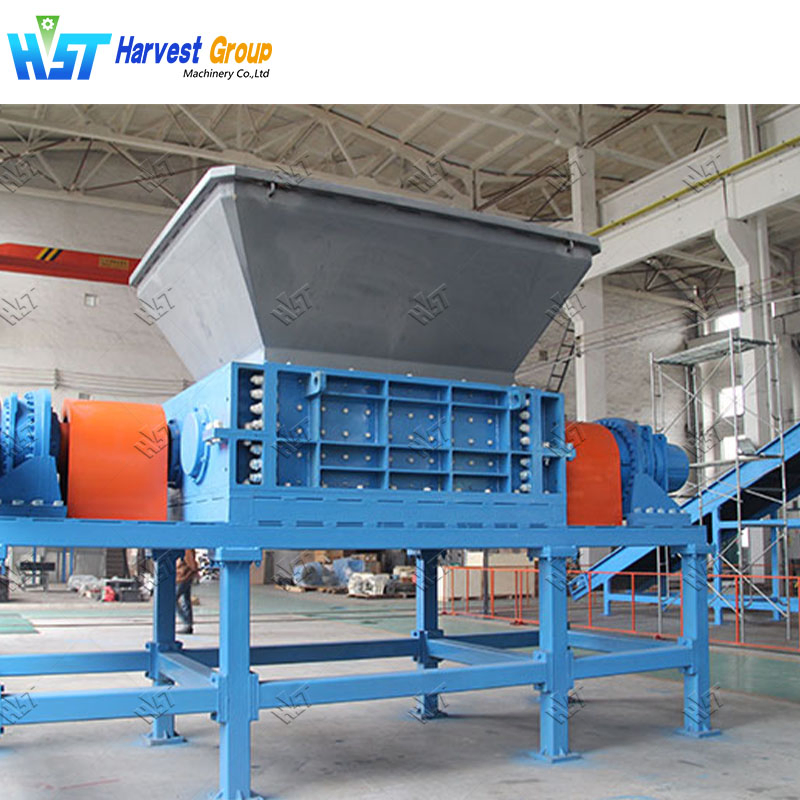
How Do Primary Tire Shredders Function in Recycling Operations?
Primary tire shredders are engineered for high-volume processing, utilizing a shearing mechanism that efficiently reduces tires into manageable strips. Their robust construction allows them to handle a variety of tire types, making them essential for large-scale recycling facilities. When purchasing a primary shredder, businesses should evaluate throughput capacity and maintenance requirements, as the initial investment can be significant. However, their efficiency and durability can lead to lower costs per ton over time.
What Role Do Secondary Tire Shredders Play in Material Processing?
Secondary tire shredders are designed to further reduce the size of tire material processed by primary shredders, typically producing finer rubber granules suitable for crumb rubber applications. Their top-feed design enhances operational efficiency, allowing for continuous processing. Businesses looking to enhance the quality of their end product should consider integrating secondary shredders into their systems. While they improve material quality, buyers must account for the additional need for primary shredders, which increases overall operational complexity.
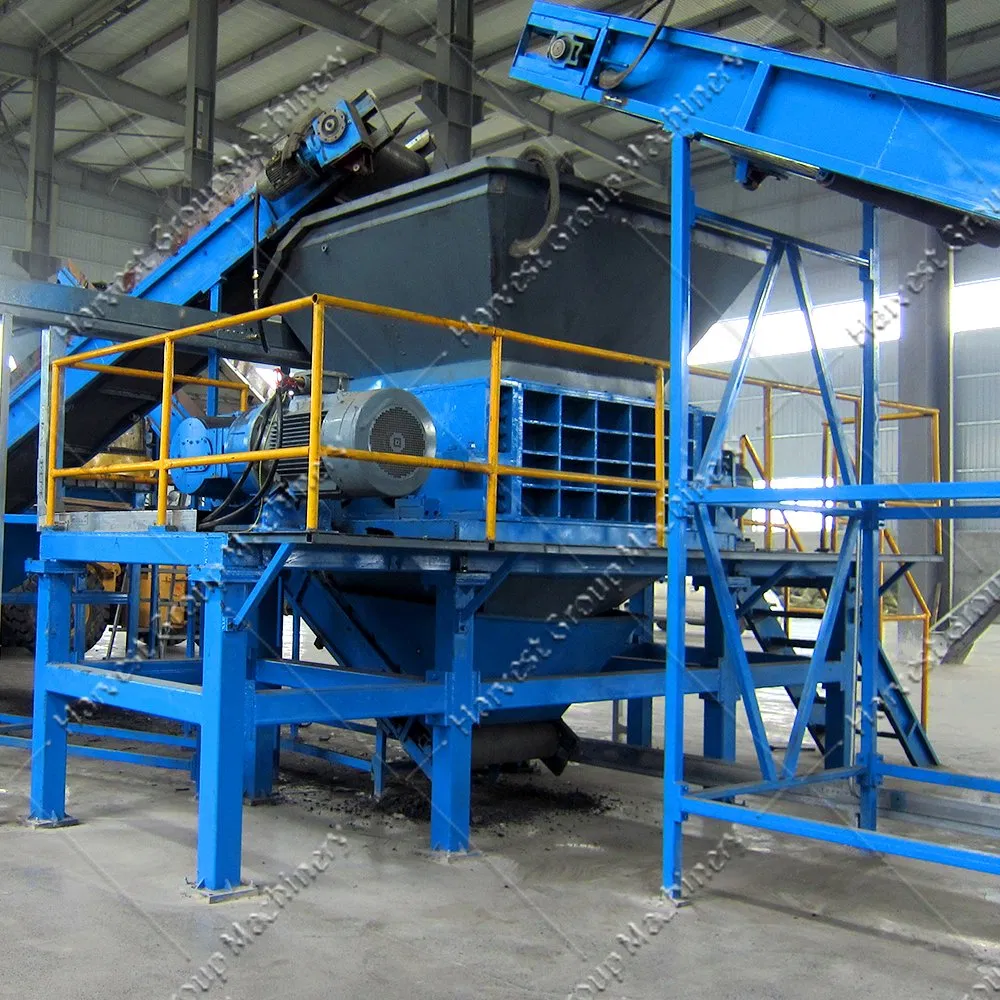
Why Choose Stationary Tire Shredders for Large-Scale Operations?
Stationary tire shredders are fixed installations that often provide the highest processing capacities, making them ideal for large recycling plants. Available in electric or hydraulic options, they are designed for continuous operation with minimal downtime. When considering a stationary shredder, businesses should assess the total cost of ownership, including energy consumption and maintenance. Although these machines offer the lowest operational costs per ton, their lack of flexibility compared to portable units may limit their use in varied operational scenarios.
What Advantages Do Custom Tire Shredders Offer to Specific Industries?
Custom tire shredders are tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses, allowing for unique configurations based on operational requirements. This adaptability makes them suitable for specialized applications within the tire recycling industry. Buyers should weigh the benefits of a custom solution against potential longer lead times and higher costs. However, the ability to precisely match equipment to operational demands can lead to significant efficiency gains and improved product quality, making them a worthwhile investment for niche markets.
Key Industrial Applications of tire shredder for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tire shredder for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire Recycling | Processing scrap tires into reusable materials | Reduces waste and generates revenue from recycled rubber | Equipment durability, maintenance ease, and throughput rates |
| Construction and Roadworks | Production of tire-derived aggregate (TDA) for asphalt | Enhances road durability and sustainability | Compatibility with existing systems, size reduction capabilities |
| Energy Production | Creation of tire-derived fuel (TDF) for energy generation | Provides a cost-effective alternative energy source | Fuel efficiency, processing speed, and compliance with regulations |
| Automotive Industry | Shredding end-of-life tires for component recovery | Maximizes material recovery and minimizes landfill use | Precision cutting capabilities and operational efficiency |
| Environmental Management | Shredding tires for environmentally safe disposal | Ensures compliance with environmental regulations | Proven track record, certifications, and support services |
How is a Tire Shredder for Sale Used in Tire Recycling?
In the tire recycling sector, tire shredders convert scrap tires into reusable materials, such as shreds or chips, which can be further processed. This application helps businesses minimize waste while generating revenue from recycled rubber products. International buyers should consider the durability and maintenance requirements of the shredders to ensure they can withstand the rigors of processing high volumes of tires efficiently.
What Role Do Tire Shredders Play in Construction and Roadworks?
Tire shredders are crucial in the construction industry for producing tire-derived aggregate (TDA), which is used as a lightweight fill material in road construction. This application not only enhances the durability of roads but also promotes sustainability by repurposing waste materials. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should assess the compatibility of shredders with existing construction processes and their ability to reduce tire size effectively to meet project specifications.
How Are Tire Shredders Used in Energy Production?
In energy production, tire shredders facilitate the creation of tire-derived fuel (TDF), which serves as an alternative energy source for cement kilns and power plants. This application allows companies to reduce energy costs and reliance on fossil fuels. Buyers should prioritize shredders that offer high fuel efficiency and fast processing speeds to maximize their energy output, while also ensuring compliance with local environmental regulations.
What is the Importance of Tire Shredders in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive sector utilizes tire shredders to process end-of-life tires for component recovery, allowing manufacturers to reclaim valuable materials like steel and rubber. This application helps in maximizing resource recovery and significantly reducing landfill waste. Buyers in the automotive industry should focus on shredders with precision cutting capabilities to ensure high-quality material recovery, while also considering operational efficiency to lower costs.
How Do Tire Shredders Contribute to Environmental Management?
In environmental management, tire shredders are essential for shredding tires for safe disposal or recycling, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This application supports initiatives aimed at reducing landfill waste and promoting sustainable practices. International buyers must look for shredders with a proven track record and necessary certifications that guarantee their reliability and support services, ensuring they meet local regulatory standards effectively.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tire shredder for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating High Operational Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the tire recycling industry face escalating operational costs associated with tire shredders. These costs can stem from high energy consumption, frequent maintenance, and expensive replacement parts. Companies in regions like Africa and South America, where budget constraints are common, often struggle to find a shredder that balances performance with affordability. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, reduced profitability, and even potential financial strain.
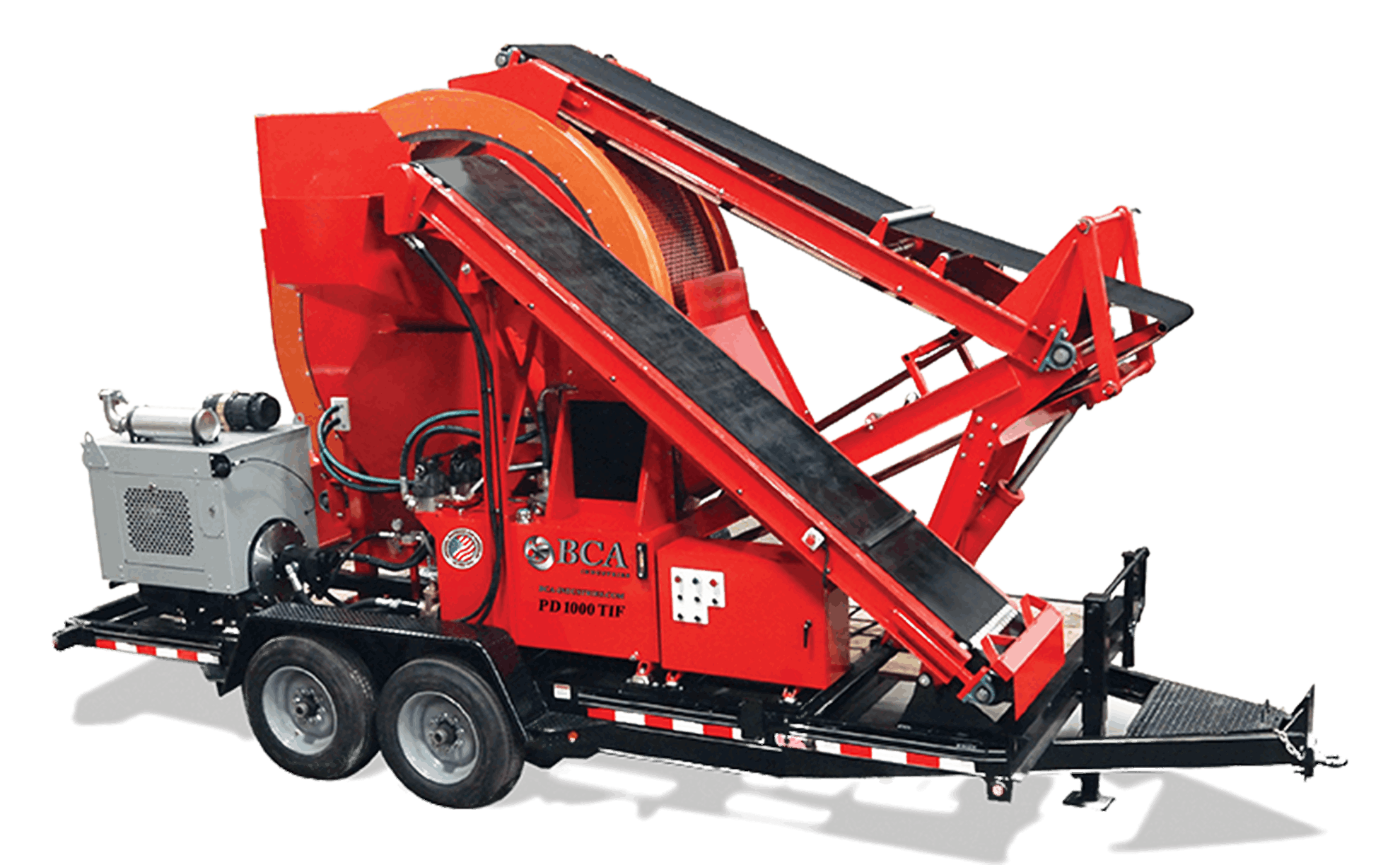
The Solution: To mitigate high operational costs, buyers should consider investing in tire shredders that are specifically designed for efficiency. Look for models that feature high-torque capabilities, as these often require less horsepower and energy to operate effectively. For example, the BCA PD1000 series boasts a modular head design that can be easily serviced, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, buyers should request detailed operating cost analyses from manufacturers to ensure they understand the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and parts replacement. By carefully selecting equipment based on these factors, businesses can achieve significant long-term savings while maintaining high throughput.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Reliable Performance Under Varying Conditions
The Problem: Buyers often worry about the reliability of tire shredders when operating under diverse environmental conditions, particularly in regions with extreme weather or challenging terrain. Shredders that frequently break down due to harsh conditions can lead to significant operational delays and lost revenue. This is particularly concerning for companies in the Middle East or rural areas in Europe, where access to service and parts can be limited.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
The Solution: To enhance reliability, it is crucial to invest in tire shredders designed with robust construction and advanced features. Buyers should prioritize models with features such as computer-controlled operations, which can adjust performance based on the conditions of the materials being processed. Additionally, consider portable shredders like the BCA PD1000TIF, which are engineered for easy transport and setup, allowing for flexibility in various operational environments. Buyers should also inquire about warranty options and after-sales support, ensuring they have access to timely repairs and maintenance when needed. Choosing a shredder that is built to withstand local conditions can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected downtime.
Scenario 3: Customization and Scalability Challenges
The Problem: As businesses grow, their tire processing needs can change, requiring a shredder that can adapt to increased volume or different types of tires. Many B2B buyers encounter challenges with equipment that lacks the necessary scalability or customization options. This can lead to over-investment in machinery that is either underutilized or inadequate for future demands, creating further financial strain.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should seek out tire shredders that offer modular designs and customization options. This allows companies to tailor their shredding systems to meet current and anticipated needs without incurring unnecessary costs. For instance, the Barclay Roto-Shredder allows for customization based on specific tire types and desired output sizes, ensuring that businesses can scale their operations effectively. Buyers should also engage with manufacturers to understand the potential for future upgrades or expansions. By investing in flexible equipment, companies can adapt to changing market demands and avoid the pitfalls of equipment obsolescence, positioning themselves for sustained growth in the tire recycling industry.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tire shredder for sale
What are the Key Materials Used in Tire Shredders for Sale?
When selecting a tire shredder, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and overall cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of tire shredders, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. High-Strength Steel
Key Properties: High-strength steel offers excellent tensile strength and resistance to wear and deformation under heavy loads. It typically has a high temperature rating and can withstand significant mechanical stress, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of high-strength steel is its durability and longevity, which translates to lower replacement costs over time. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing initial costs.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly suited for components like shredding blades and frames, where high wear resistance is crucial. It ensures that the shredder can handle various tire types without frequent maintenance.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards for steel quality and performance, such as ASTM or DIN. High-strength steel is widely accepted and preferred for its reliability.
2. Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel is a blend of carbon steel and other elements, such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, enhancing its hardness and corrosion resistance. This material can handle elevated temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steel is its superior strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for lighter designs without sacrificing performance. However, it can be more complex to manufacture and may require heat treatment processes, raising costs.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is ideal for components exposed to high wear and tear, such as shredding knives and gears. Its corrosion resistance also contributes to longer service life, especially in humid or corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe and South America should be aware of specific alloy compositions that comply with local regulations. Understanding the alloy grades and their properties can help in selecting the right equipment for regional conditions.
3. Hardfacing Materials
Key Properties: Hardfacing involves applying a layer of hard material (often tungsten carbide or chrome) to enhance surface hardness and wear resistance. This process significantly increases the lifespan of critical components subjected to extreme abrasion.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of hardfacing is its ability to extend the life of shredding components, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. However, the application process can be labor-intensive and may increase the overall cost of the component.
Impact on Application: Hardfaced components are particularly effective in shredders processing abrasive materials, ensuring consistent performance and reducing the frequency of blade replacements.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in regions with high abrasive materials, such as certain parts of Africa and South America, investing in hardfaced components can lead to significant long-term savings. Compliance with local welding and hardfacing standards is essential.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or fiber-reinforced polymers, offer a lightweight alternative with good resistance to corrosion and wear. They can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, including flexibility and impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is their lightweight nature, which can reduce operational costs related to energy consumption. However, composites may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals, limiting their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for non-critical components, such as covers and casings, where weight savings are beneficial. They can also be used in areas where corrosion is a concern, extending the life of the shredder.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the environmental impact of composites and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material disposal and recycling.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Tire Shredders
| Material | Typical Use Case for tire shredder for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Strength Steel | Shredding blades and frames | Exceptional durability | Higher initial cost | High |
| Alloy Steel | Gears and high-wear components | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | Complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Hardfacing Materials | Critical wear parts like knives | Extended lifespan | Labor-intensive application | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Non-critical components like casings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited load-bearing capacity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions when investing in tire shredders, ensuring they choose the right materials that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tire shredder for sale
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Tire Shredders?
The manufacturing of tire shredders involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets rigorous performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-quality materials, typically high-strength steel and other alloys that can withstand the stresses of tire shredding. Suppliers may undergo stringent vetting processes to ensure compliance with international quality standards. Materials are inspected for defects and tested for mechanical properties before being approved for production.
-
Forming: This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the components of the tire shredder. Techniques such as laser cutting, CNC machining, and forging are commonly used to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. Advanced forming techniques ensure that parts like the cutting chamber and knives have the necessary durability and performance characteristics.
-
Assembly: After forming, components are assembled into the complete shredder system. This step includes integrating the cutting head, motor, hydraulic systems, and control panels. Automated assembly lines may be utilized to enhance precision and efficiency. Each component is carefully aligned and secured to ensure optimal operation.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatments such as powder coating or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear. This step not only enhances durability but also improves the aesthetic appeal of the machine. Final inspections are conducted to ensure all components fit correctly and function as intended.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented During Tire Shredder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical to the manufacturing process of tire shredders, ensuring that each unit meets specified performance and safety standards. Implementing robust QA practices involves adhering to international standards and conducting multiple checkpoints throughout the production process.
-
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers seek certification to ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with CE marking standards is also essential for products sold within the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For specific applications, adherence to API standards may be necessary, particularly in sectors requiring high reliability.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: The QA process typically incorporates several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor production quality, ensuring that components are being manufactured correctly.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the final product undergoes rigorous testing to verify that it meets all performance criteria before shipping. -
Testing Methods: Common testing methods include tensile strength tests, hardness testing, and operational testing of the shredding system. Some manufacturers may also conduct dynamic tests to assess the machine’s performance under simulated operational conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers looking to purchase tire shredders should conduct thorough due diligence to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through several methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers can assess the facility’s cleanliness, equipment condition, and adherence to safety protocols.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s quality management system and performance metrics. This includes documentation of past inspections, test results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be scheduled at various stages of production to ensure compliance with agreed standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may affect their purchasing decisions:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements for machinery. Buyers must ensure that the equipment meets local standards, which may differ from those in the supplier’s country. Familiarity with local regulations can help prevent delays in customs and ensure compliance.
-
Logistics and Shipping: The transportation of tire shredders across international borders can introduce additional risks. Buyers should verify that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping protocols to protect the equipment from damage during transit.
-
Post-Purchase Support: Understanding the level of support offered post-purchase is crucial. Buyers should inquire about warranty terms, maintenance programs, and availability of spare parts, as these factors significantly influence the long-term operational efficiency of the tire shredder.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is essential in international transactions. Buyers should ensure that they can communicate clearly with suppliers regarding specifications, expectations, and quality assurance practices to avoid misunderstandings.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for tire shredders is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable and efficient machinery. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tire shredder for sale’
When sourcing a tire shredder for sale, B2B buyers must navigate various technical, operational, and supplier-related considerations. This guide provides a structured approach to help you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your operational requirements is essential. Consider factors such as the types of tires you will shred (e.g., passenger, truck, or off-road tires) and the desired output size. Specific features like horsepower, cutting chamber dimensions, and the shredding capacity (tires per hour) should also be defined to ensure the machine meets your processing needs.
Step 2: Research Available Shredder Types
Not all tire shredders are created equal; they can be stationary or mobile, electric or diesel-powered. Research the types that best suit your operations. For instance, portable shredders may offer flexibility if you have multiple processing locations, while stationary models could provide higher throughput for dedicated facilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries or regions. It’s important to assess their reputation and customer service track record; this can often be a deciding factor in your long-term satisfaction with the equipment.
Step 4: Inspect Machine Specifications and Features
Review the specifications of the machines you are considering. Look for features that enhance efficiency, such as high-torque capabilities, ease of maintenance, and quick knife change-out times. Also, consider whether the machine includes infeed/outfeed conveyors and classifiers, as these can improve your overall operational workflow.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
After narrowing down potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Ensure that the quotes include all necessary components and potential additional costs such as shipping, installation, and maintenance. Comparing total cost of ownership over the machine’s lifespan will provide a clearer financial picture.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications and Support
Check if the suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Additionally, inquire about their support services, including warranty, spare parts availability, and after-sales support, to ensure you receive ongoing assistance post-purchase.
Step 7: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Demonstration
If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to see the machine in action or request a virtual demonstration. Observing the shredder’s performance can provide valuable insights into its operation and help validate your purchase decision. This step can also facilitate discussions about customization options specific to your business needs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they select the most suitable tire shredder, minimizing risks and optimizing their investment in tire recycling operations.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tire shredder for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Tire Shredder?
When considering the purchase of a tire shredder, it is crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the total expenditure. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing the shredder significantly influence the price. High-strength steel and advanced alloys are often employed to enhance durability and performance, which can increase initial costs but reduce long-term maintenance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring high-quality assembly and adherence to design specifications, thus impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these expenses, which can be reflected in more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tools and dies used for production can be significant, especially for customized or high-precision machines. Investing in efficient tooling can reduce the cost per unit over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC measures are vital for ensuring the shredder meets performance and safety standards. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent costly failures and repairs down the line.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the location of the buyer and the supplier. International shipments may incur additional fees related to customs and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Purchase of Tire Shredders?
Several factors can influence the pricing of tire shredders, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounted pricing. Suppliers may offer better terms for bulk orders, which can be advantageous for businesses with significant processing needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or higher specifications can raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses on features that may not be required.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Machines made from higher-quality materials or those that meet specific industry certifications may command a premium price. However, these investments often translate to lower maintenance costs and higher efficiency.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established brands may charge more due to their proven track record, while lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices but could come with increased risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks during transit. This can significantly impact the total landed cost of the equipment.
What Tips Can Buyers Utilize for Cost-Efficient Tire Shredder Sourcing?
To maximize value when sourcing tire shredders, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you are considering bulk purchases or long-term contracts. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate terms to secure a deal.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but also the ongoing operational and maintenance expenses. A lower-priced shredder may incur higher costs in repairs or inefficiencies over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may affect pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various suppliers allows for effective comparison and can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Consider Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with a supplier can lead to better pricing and support, especially for maintenance and spare parts in the future.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that the prices for tire shredders can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. Always seek updated quotes and detailed breakdowns to ensure an informed purchasing decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tire shredder for sale With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Tire Shredders
When considering tire recycling solutions, businesses often evaluate various methods to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance output. While tire shredders for sale provide a robust solution for processing scrap tires, alternative technologies exist that may suit different operational needs. This analysis compares tire shredders with alternative methods, highlighting their respective advantages and drawbacks.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Tire Shredder For Sale | Alternative 1: Tire Granulator | Alternative 2: Tire Pulverizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 250 tires per hour | Processes up to 4 tons per hour | Processes up to 2 tons per hour |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operating costs | Higher initial investment; moderate costs | High initial investment; high operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space and logistics planning | Requires skilled operators; complex setup | Requires significant space and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; parts easily replaceable | Moderate maintenance; specialized parts | High maintenance; complex components |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale tire recycling operations | Producing rubber granules for resale | Creating fine rubber powder for industrial applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
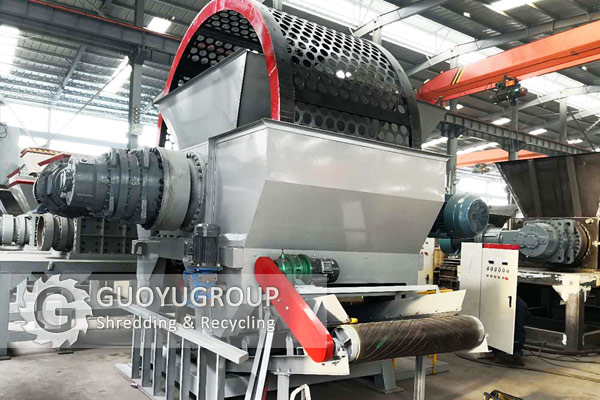
Tire Granulator
A tire granulator is designed to reduce shredded tires into smaller granules, typically used for producing rubber granules that can be sold or repurposed. Granulators often yield a higher quality product suitable for applications in playground surfaces, sports fields, and as a material for asphalt. However, they require a higher initial investment compared to traditional shredders and may necessitate skilled operators for optimal performance. The maintenance can also be moderate due to the need for specialized parts.
Tire Pulverizer
Tire pulverizers take the recycling process a step further by producing fine rubber powder from shredded tires. This equipment is ideal for applications requiring a finer product, such as in the manufacturing of new rubber products or for use as an additive in asphalt. However, the operational costs can be high, not only due to the initial investment but also in terms of maintenance. The complexity of the machinery can lead to increased downtime if not managed properly, making it less suitable for businesses that prioritize quick turnaround times.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Tire Recycling Needs
Selecting the appropriate tire recycling solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your operation. Tire shredders for sale are well-suited for large-scale operations that demand high throughput and low maintenance costs. In contrast, tire granulators and pulverizers may offer more specialized outputs but come with higher costs and maintenance considerations. B2B buyers should evaluate their production goals, budget constraints, and operational capabilities to determine which solution aligns best with their tire recycling objectives. By carefully analyzing these factors, businesses can invest in technology that maximizes efficiency and profitability in their tire recycling endeavors.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tire shredder for sale
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Tire Shredders for Sale?
When evaluating tire shredders, several technical specifications are critical to ensuring that the equipment meets operational requirements and provides value for investment. Here are some essential properties to consider:
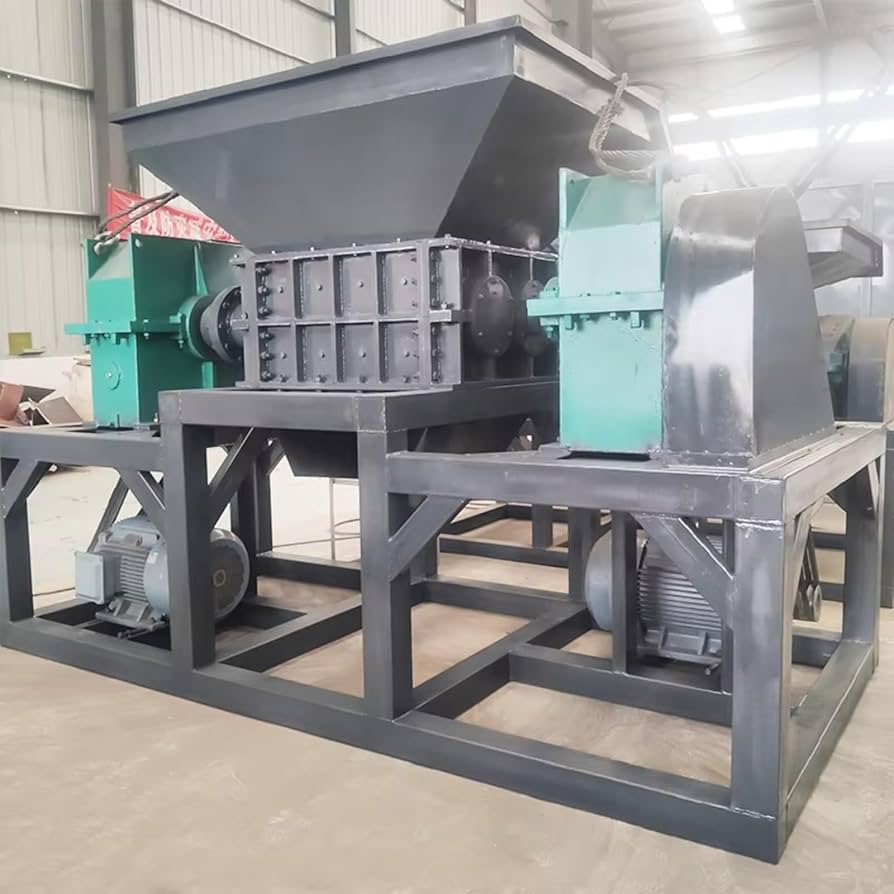

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
1. Throughput Capacity
Throughput capacity refers to the volume of tires a shredder can process within a specified timeframe, often measured in tons per hour (TPH). This metric is vital for businesses that need to handle large volumes of waste tires efficiently. For example, a shredder with a capacity of 30 TPH can significantly reduce processing time and labor costs, making it suitable for high-demand operations.
2. Cutting Chamber Size
The cutting chamber size determines the maximum tire size that can be processed. A larger cutting chamber allows for the shredding of different tire types, including truck and off-road tires. This versatility can be crucial for operations that manage diverse tire inventories, as it eliminates the need for multiple shredders, thus optimizing space and investment.
3. Knife Material and Design
The knives used in tire shredders play a critical role in their efficiency and longevity. High-quality, hardened steel knives are designed to withstand the rigors of shredding tough materials. Features such as re-sharpenable blades and modular knife systems can reduce maintenance costs and downtime. Understanding the knife design can help buyers assess the long-term operational efficiency of the shredder.

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
4. Power Source and Motor Specifications
Tire shredders can be powered by electric or diesel engines, each with distinct advantages. Electric motors typically offer lower operational costs and reduced emissions, while diesel engines may provide greater mobility and power for heavy-duty applications. The horsepower rating of the motor is directly related to the shredder’s performance, influencing both efficiency and maintenance needs.
5. Control Systems
Modern tire shredders often include advanced control systems that enable automated operation, monitoring, and diagnostics. Features such as auto-reverse functions and overload protection enhance safety and reduce the risk of mechanical failure. Buyers should consider how these systems can improve operational efficiency and reduce labor costs by minimizing manual intervention.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Navigating the purchase of a tire shredder involves understanding industry-specific terminology that can impact negotiations and contracts. Here are key terms to be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the tire shredding industry, understanding whether you are dealing with an OEM can influence decisions regarding warranties, support, and compatibility of replacement parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For tire shredders, knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their budgets and inventory. This is particularly relevant for businesses looking to scale operations or invest in additional units.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. This process is essential for obtaining competitive quotes and ensuring that you understand the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational expenses.
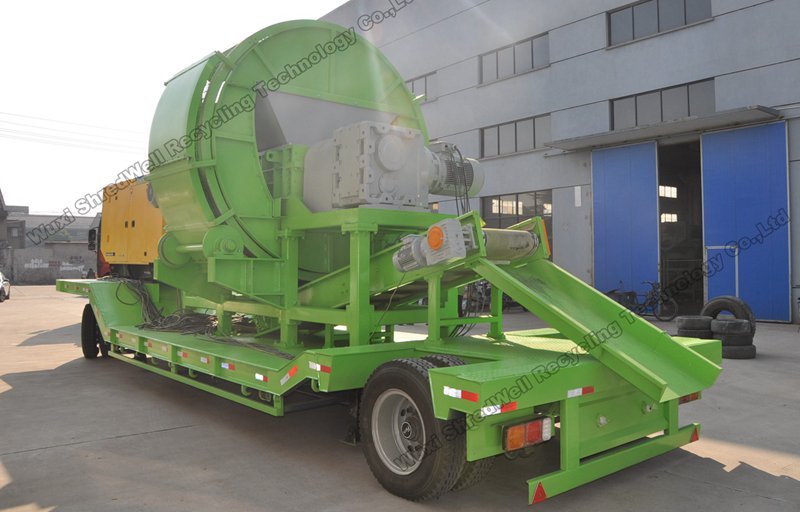

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers as they outline who bears the costs and risks at various stages of shipping, including delivery, insurance, and customs duties.
5. TDF (Tire Derived Fuel) and TDA (Tire Derived Aggregate)
These terms refer to the end products of tire shredding. TDF is often used as a fuel source in energy production, while TDA is utilized in construction and civil engineering. Understanding these applications can help buyers align their shredding operations with market demands.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market opportunities.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tire shredder for sale Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends for Tire Shredders?
The tire shredder market is experiencing significant growth driven by increased awareness of environmental sustainability and the need for efficient waste management solutions. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to meet stringent regulations on waste disposal, the demand for tire recycling is on the rise. This has led to innovations in tire shredding technology, including mobile and portable systems that provide flexibility and efficiency for businesses operating in diverse geographical conditions.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the integration of smart features such as IoT connectivity, which allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This capability enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, thus appealing to buyers looking to optimize their investment. Additionally, advancements in blade technology and materials are contributing to longer-lasting and more efficient shredders, lowering the overall cost per ton of processed tires.
Moreover, the global push towards circular economy practices is reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer sustainable solutions and innovative designs, which can lead to increased throughput and reduced operational costs. As a result, partnerships with manufacturers that provide customizable shredding solutions are becoming a strategic advantage for businesses looking to stay competitive.
How Does Sustainability Influence the Sourcing of Tire Shredders?
Sustainability is now a cornerstone of the tire shredder market, influencing purchasing decisions and supply chain dynamics. The environmental impact of tire disposal is significant, with millions of tires ending up in landfills, posing serious ecological risks. Consequently, businesses are focusing on ethical sourcing and sustainable practices in their supply chains.
Buyers are seeking equipment that not only meets performance standards but also aligns with their corporate social responsibility goals. Many manufacturers are now offering ‘green’ certifications for their products, ensuring that the shredders are made from sustainable materials and designed to minimize environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 can provide assurance to buyers that their suppliers are committed to reducing their carbon footprint.
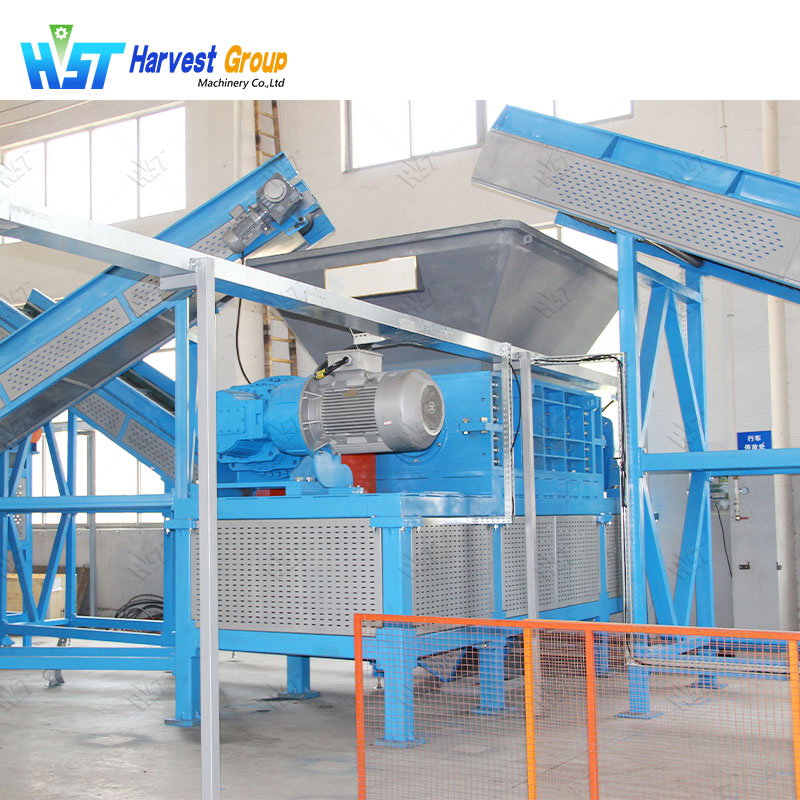

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
Furthermore, the growing trend of recycling tire-derived products—such as rubber mulch, fuel, and aggregates—highlights the importance of investing in high-efficiency shredding systems. Buyers can benefit from selecting suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, as this can enhance their own brand reputation while contributing positively to the environment.
How Has the Tire Shredder Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the tire shredder market reflects broader changes in waste management and recycling practices. Initially, tire shredding technology was basic and primarily focused on reducing tire volume for disposal. However, as environmental regulations tightened and the recycling industry matured, the focus shifted towards more efficient and effective processing systems.
In recent decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have led to the development of high-torque shredders capable of processing a wide variety of tire types at much higher rates. This transition has been marked by a growing emphasis on operational efficiency, with modern machines designed to require less maintenance and provide longer service life.
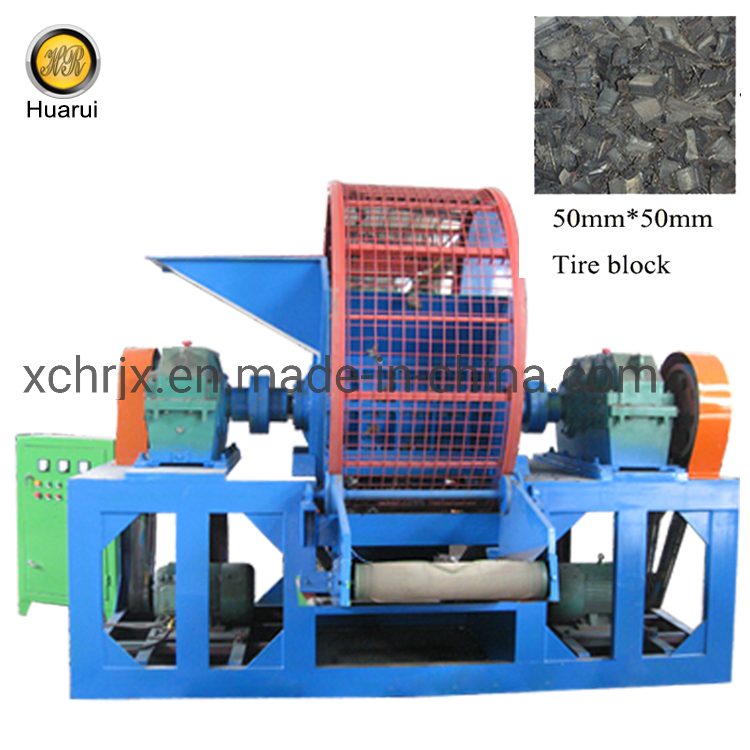

Illustrative image related to tire shredder for sale
As a result, tire shredders have become integral to the recycling ecosystem, facilitating the conversion of waste into valuable resources. This ongoing evolution positions tire shredding technology as a crucial component in achieving sustainability goals across various industries, making it an essential consideration for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tire shredder for sale
-
How do I choose the right tire shredder for my business needs?
Selecting the right tire shredder involves assessing your operational requirements, including the volume of tires to be processed, the desired output size, and the types of tires you will shred (e.g., passenger, truck, or off-road). Consider the machine’s capacity, efficiency, and maintenance needs. It’s also essential to evaluate whether you need a stationary or portable unit, as this impacts installation and mobility. Consulting with manufacturers can help you customize a solution tailored to your business model and operational goals. -
What are the key features to look for in a tire shredder?
When evaluating tire shredders, prioritize features such as cutting efficiency, motor power, and durability of the blades. Look for machines that offer easy maintenance, such as quick knife change-outs and accessible service points. Automated features like overload protection and computer-controlled operations enhance safety and efficiency. Additionally, check if the shredder can handle various tire sizes and if it includes infeed and outfeed conveyors for streamlined operations. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing a tire shredder?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. For large purchases, some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted, including bank transfers, letters of credit, or trade financing, especially when dealing with international transactions to ensure smooth processing. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing tire shredders internationally?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and willingness to provide information. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if feasible or requesting references from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing tire shredders?
Logistics for importing tire shredders include understanding shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Confirm whether the supplier handles shipping or if you need to arrange transportation. Be aware of customs regulations in your country, including import duties and taxes. It’s also crucial to plan for installation and commissioning, which may require skilled personnel. Partnering with a logistics expert can facilitate smoother importation and compliance with local laws. -
Can I customize the tire shredder to meet my specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor tire shredders to your business needs. This can include modifications to the cutting chamber size, blade configuration, and additional features such as shredding speed and output size. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to explore available customizations. Custom solutions can enhance operational efficiency and ensure the shredder aligns with your production goals. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for tire shredders?
The minimum order quantity for tire shredders varies by manufacturer. Some suppliers may allow the purchase of a single unit, while others may require bulk orders to justify production costs. When sourcing internationally, inquire about MOQs and whether discounts apply for larger orders. Understanding MOQ can help you plan your budget and inventory management, especially if you’re just starting in tire recycling. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for tire shredders I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from the supplier, including compliance with international safety and performance standards. Many manufacturers provide warranties and after-sales support, which can be indicative of their commitment to quality. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or inspections before shipment, if possible. Establishing a clear communication line with the supplier can also facilitate ongoing quality checks and support.
Top 2 Tire Shredder For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Shred-Tech – Tire Shredders
Domain: shred-tech.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Tire shredders play a pivotal role in the tire recycling ecosystem, capable of processing automobile, truck, and off-road tires at rates in excess of 30 tons per hour. Key product details include: 1. Primary Shredders: Break down whole tires into roughly sized shreds for various applications. 2. Chipping Shredders: Transform tires into specifically sized pieces. 3. Wire Liberator Systems: Separate…
2. CM Shredders – Pre-Owned Equipment
Domain: cmshredders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pre-Owned Equipment – CM Shredders includes the following products: CM Primary Shredder (Remanufactured), CM Dual Speed Tire Shredder (Remanufactured), CM Solo 40 XL Shredder (Demo), CM H-10 Shredder (Demo), CM H-50 Shredder (Demo).
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tire shredder for sale
In navigating the tire shredder market, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international buyers. Understanding the unique features and operational efficiencies of various tire shredders is essential to making informed investment decisions. Machines like the PD1000TIF and models from Barclay and CM Shredders provide diverse options tailored to specific processing needs, allowing buyers to select solutions that optimize performance and minimize costs.
Moreover, the focus on low maintenance and high throughput can significantly enhance operational efficiency and profitability. For regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in reliable tire shredding technology not only supports local recycling initiatives but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
As you consider your next purchase, prioritize suppliers who offer robust support and customization capabilities. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operational framework with state-of-the-art tire shredding solutions that meet your business requirements. The future of tire recycling is bright, and with the right equipment, you can position your company for success in this evolving market. Take the next step towards sustainable operations by exploring the diverse tire shredder options available today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.