How to Source Steel Processing For General Fabrications Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steel processing for general fabrications
In the fast-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing reliable steel processing for general fabrications presents a formidable challenge for B2B buyers. With the demand for high-quality steel products surging across industries, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—must navigate a complex supply chain to ensure they secure the best materials for their fabrication needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring various steel types, applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting, while also addressing cost considerations and logistics.
By delving into the essential elements of steel processing, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to understand the nuances of different steel grades, evaluating potential suppliers, or calculating the total cost of ownership, our detailed insights will equip you with the knowledge necessary to streamline your sourcing process. We aim to demystify the complexities of the steel market, allowing you to enhance your procurement strategies and ultimately drive your projects to success. With a focus on actionable insights, this guide is your key to navigating the global market efficiently and effectively.
Understanding steel processing for general fabrications Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Rolling | High-temperature processing; results in thinner, more uniform sheets. | Automotive, construction, and heavy machinery. | Pros: Cost-effective for large quantities. Cons: Limited dimensional accuracy. |
| Cold Rolling | Processed at room temperature; provides tighter tolerances and a smoother finish. | Precision engineering, appliances, and electronics. | Pros: Higher strength and better surface finish. Cons: More expensive than hot rolling. |
| Laser Cutting | Utilizes focused laser beams for precision cutting; ideal for complex shapes. | Custom fabrication, art installations, and signage. | Pros: High precision and minimal material waste. Cons: Slower than traditional methods for large volumes. |
| Plasma Cutting | Uses plasma to cut through thick materials; effective for heavy-duty applications. | Shipbuilding, construction, and large structural components. | Pros: Fast and efficient for thick materials. Cons: Less precise than laser cutting. |
| Waterjet Cutting | Employs high-pressure water to cut materials; suitable for various thicknesses. | Aerospace, automotive, and food industry applications. | Pros: No heat-affected zone; versatile for multiple materials. Cons: Slower than thermal cutting methods. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hot Rolling Steel Processing?
Hot rolling is a widely used steel processing method where steel is heated above its recrystallization temperature and then rolled into desired shapes. This technique produces sheets and plates that are thinner and more uniform. Due to its cost-effectiveness, hot rolling is commonly employed in industries such as automotive and construction. However, buyers should consider that while it offers significant savings for large orders, the dimensional accuracy may not meet the requirements for precision engineering applications.
How Does Cold Rolling Differ from Hot Rolling in Steel Fabrication?
Cold rolling is performed at room temperature, allowing for tighter tolerances and a superior surface finish. This method results in steel with increased strength and improved mechanical properties, making it suitable for precision engineering applications, appliances, and electronics. While cold rolling can provide a higher quality product, it often comes at a premium price. Buyers need to weigh the benefits of superior quality against the increased costs when deciding on this processing method.
What Are the Advantages of Using Laser Cutting for Steel Fabrication?
Laser cutting utilizes focused laser beams to achieve high precision in cutting steel, making it ideal for intricate designs and complex shapes. This method is particularly beneficial for custom fabrication projects, art installations, and signage. The primary advantages include high precision and minimal material waste, which can lead to significant cost savings in materials. However, the slower processing speed compared to traditional methods may be a drawback for high-volume projects, requiring buyers to assess their production timelines carefully.
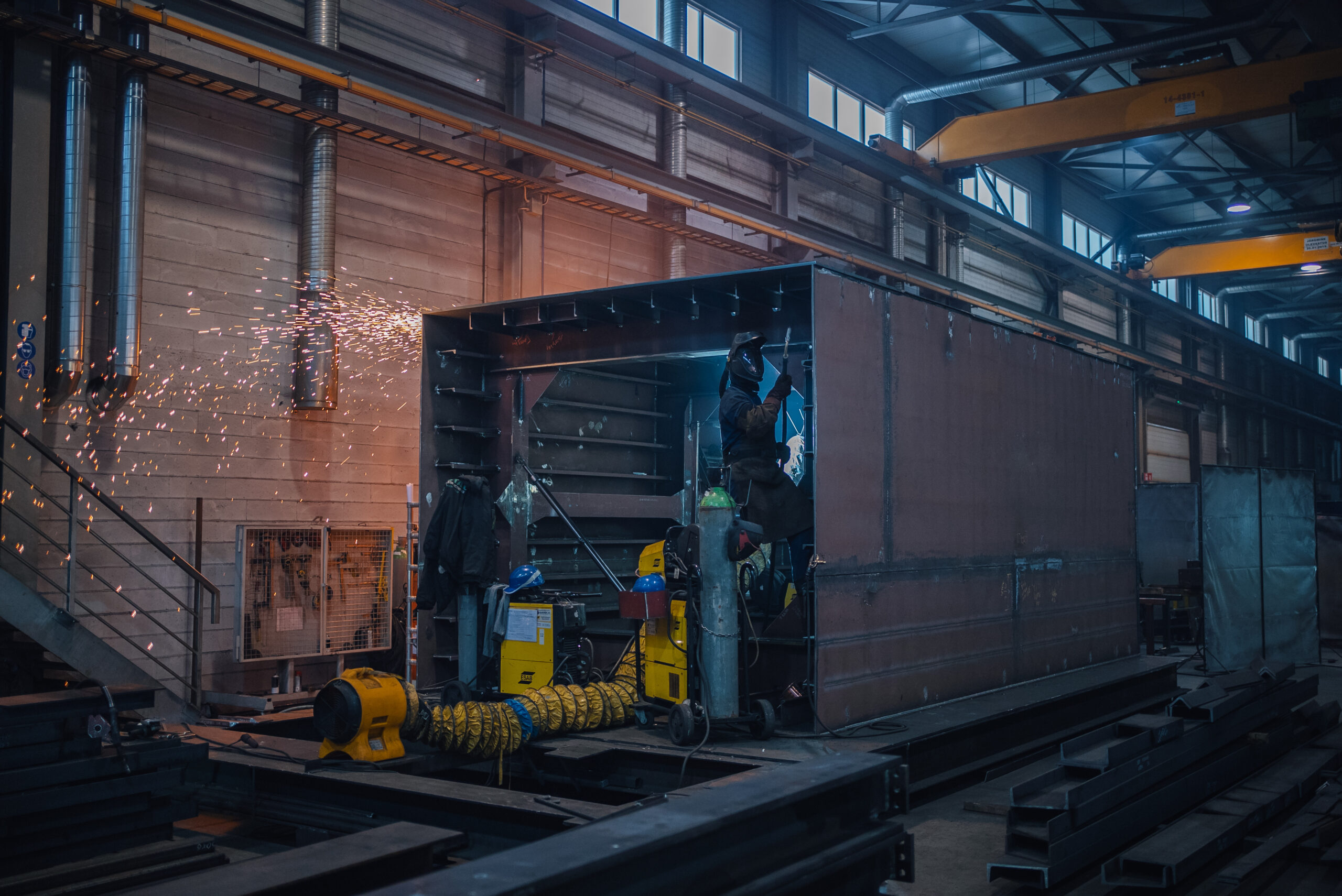

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Why Choose Plasma Cutting for Heavy-Duty Steel Applications?
Plasma cutting is a thermal cutting method that uses high-temperature plasma to slice through thick steel materials efficiently. This technique is particularly effective in industries like shipbuilding and construction, where heavy-duty applications are common. Plasma cutting offers speed and efficiency, making it suitable for larger projects. However, it may lack the precision of laser cutting, which is an important consideration for buyers who require detailed work or tighter tolerances.
In What Situations Is Waterjet Cutting the Best Option for Steel Processing?
Waterjet cutting employs high-pressure water jets to cut through various materials, including steel. It is unique because it produces no heat-affected zone, preserving the material’s integrity, making it suitable for sensitive applications in aerospace, automotive, and even food industries. The versatility of waterjet cutting allows it to handle different thicknesses and materials. However, the slower cutting speed compared to thermal methods may limit its use in mass production environments, prompting buyers to evaluate their specific needs for speed versus quality.
Key Industrial Applications of steel processing for general fabrications
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steel processing for general fabrications | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of structural components and chassis | Enhanced vehicle safety and performance | Availability of high-strength steel grades; compliance with automotive standards. |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural beams and reinforcements | Increased durability and load-bearing capacity | Sourcing from suppliers with diverse product ranges and quick delivery capabilities. |
| Oil and Gas | Manufacturing of pipelines and fittings | Ensured integrity and resistance to harsh environments | Need for corrosion-resistant materials and adherence to industry regulations. |
| Heavy Machinery | Creation of frames and components for machinery | Improved functionality and lifespan of equipment | Precision in dimensions and tolerances; sourcing from reliable fabricators. |
| Electronics | Production of casings and internal components | Enhanced product reliability and consumer safety | Demand for lightweight, durable materials; compliance with electronic safety standards. |
How is Steel Processing for General Fabrications Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, steel processing is critical for the production of structural components and chassis. These parts must meet stringent safety and performance standards, necessitating the use of high-strength steel grades. International buyers must ensure that suppliers can provide materials that not only meet their specifications but also comply with global automotive regulations. Furthermore, the availability of just-in-time delivery options can significantly reduce production downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
What Role Does Steel Processing Play in the Construction Industry?
Steel processing is fundamental in the construction sector, where it is utilized for fabricating structural beams, reinforcements, and other essential components. The durability and load-bearing capacity of steel make it an ideal choice for buildings and infrastructure projects. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who offer a wide variety of steel shapes and sizes, as well as those who can ensure timely delivery to meet project deadlines. Additionally, understanding local building codes and standards is crucial for compliance.
Why is Steel Processing Important for the Oil and Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, steel processing is essential for manufacturing pipelines, fittings, and other components that must withstand extreme environmental conditions. The integrity of these materials is vital for safety and operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing corrosion-resistant steels and ensure that suppliers adhere to industry regulations and certifications. The ability to provide custom solutions tailored to specific project requirements is also a key consideration.
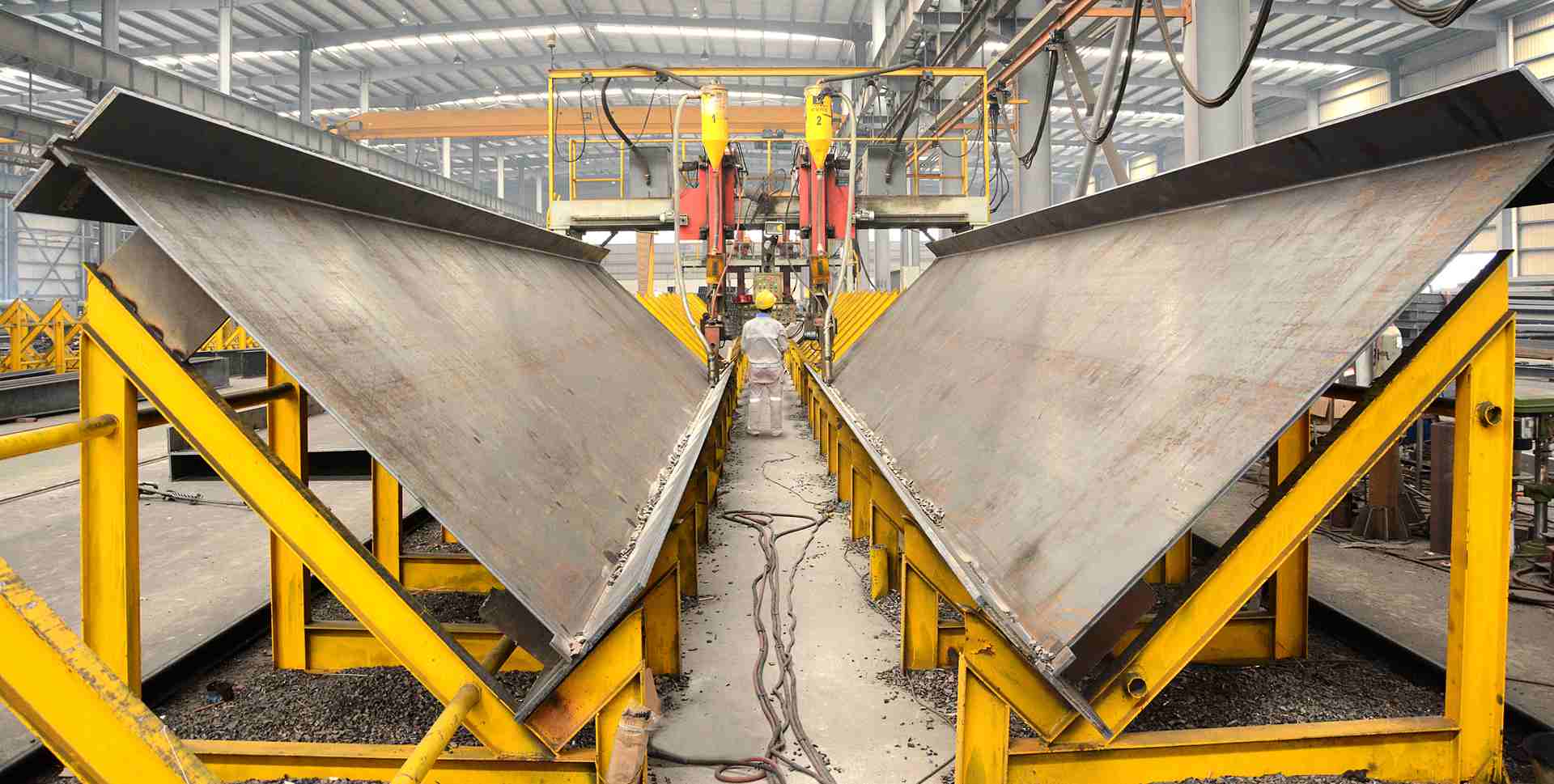

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
How is Steel Processing Beneficial for Heavy Machinery Manufacturing?
Heavy machinery relies on steel processing to create robust frames and components that enhance functionality and lifespan. The precision in dimensions and tolerances required in this sector means that sourcing from reliable fabricators with advanced processing capabilities is crucial. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide high-quality materials that can withstand heavy use, as well as their capacity for timely delivery to avoid disruptions in production.
What is the Significance of Steel Processing in the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics sector, steel processing is vital for producing casings and internal components that ensure product reliability and safety. The demand for lightweight yet durable materials drives the need for specific steel grades that can meet these requirements. International buyers must consider sourcing from suppliers that comply with electronic safety standards and can provide materials that enhance the overall performance of electronic devices. Understanding the nuances of material properties can also lead to better product designs and increased market competitiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steel processing for general fabrications’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Steel Quality and Specifications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter the issue of inconsistent steel quality and specifications, which can lead to significant project delays and increased costs. When sourcing steel for general fabrications, companies may receive materials that do not meet the required standards or grades, affecting the integrity of their final products. This inconsistency can arise from multiple suppliers providing varying quality, leading to difficulties in meeting project deadlines and specifications.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
The Solution:
To mitigate this problem, buyers should establish a robust supplier evaluation process that emphasizes quality assurance and certification. When selecting suppliers, verify that they adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Additionally, requesting material test reports (MTRs) and certifications from suppliers can help ensure that the steel meets the required specifications. Implementing a just-in-time inventory strategy can also aid in maintaining consistent quality, as it reduces the risk of stockpiling subpar materials. By fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers and consistently monitoring quality, buyers can ensure that they receive the right steel for their projects, minimizing the risk of delays and additional costs.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times and Delivery Delays
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers in the steel processing industry is experiencing long lead times and delivery delays. In many cases, fabricators operate under tight schedules and rely heavily on timely deliveries of steel materials to meet production timelines. However, unexpected delays from suppliers can disrupt the entire workflow, leading to project overruns and client dissatisfaction.
The Solution:
To address lead time challenges, B2B buyers should consider implementing a strategic sourcing plan that includes a diversified supplier base. By working with multiple suppliers across different regions, companies can reduce their dependency on a single source and enhance their chances of on-time delivery. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers regarding delivery expectations is also crucial. Buyers should negotiate service level agreements (SLAs) that outline delivery timelines and penalties for delays. Additionally, utilizing advanced supply chain management software can provide real-time visibility into order status and inventory levels, enabling buyers to proactively manage their supply chain and mitigate risks associated with delays.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Scenario 3: Complex Fabrication Requirements
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of dealing with complex fabrication requirements that necessitate precise specifications and custom processing techniques. This complexity can stem from unique project needs, varying material grades, or specific machining processes that require advanced knowledge and capabilities. Failure to accurately communicate these requirements can lead to mismatched materials, wasted resources, and ultimately, costly rework.
The Solution:
To effectively manage complex fabrication requirements, it is essential for buyers to engage in thorough project planning and specification development. This includes collaborating closely with engineers and fabricators to clearly define the project scope and requirements before sourcing materials. Investing in advanced design software and simulation tools can help visualize the final product and determine the best material choices and processing methods. Furthermore, fostering a partnership with a supplier who offers value-added services such as precision cutting, welding, and machining can streamline the process. By leveraging these capabilities, buyers can ensure that the steel processing aligns with their unique fabrication needs, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing overall project efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steel processing for general fabrications
What Are the Key Properties of Common Steel Materials for General Fabrications?
When selecting materials for steel processing in general fabrications, understanding the properties and applications of various steel types is crucial. Below are analyses of four common materials used in this industry, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its high strength and versatility. It typically has good machinability and can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a variety of applications. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and durability. It is widely available and can be easily fabricated into complex shapes. On the downside, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, requiring additional protective measures.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is ideal for structural components, automotive parts, and machinery. Its compatibility with various media is generally good, but care must be taken in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. Additionally, understanding local corrosion risks is essential for selecting the right protective coatings.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is easy to clean, making it suitable for hygienic applications.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance, which can offset its higher initial cost. However, its manufacturing complexity and the need for specialized equipment can lead to increased production costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is commonly used in food processing, medical equipment, and architectural applications. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for environments that involve moisture or harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
When sourcing stainless steel, buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Additionally, variations in alloy compositions may affect performance, so understanding local preferences is crucial.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and offers good thermal and electrical conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures but may not perform as well under high-pressure conditions compared to steel.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of aluminum is its weight-to-strength ratio, making it ideal for applications where reducing weight is critical. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. Its compatibility with various media is generally favorable, but it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications without specific alloy treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet local standards and specifications. Understanding the impact of local environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature, is also important for ensuring long-term performance.
4. Specialty Alloys
Key Properties:
Specialty alloys, which may include nickel alloys or titanium, are designed for specific applications requiring unique properties such as extreme heat resistance or enhanced corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of specialty alloys is their tailored properties that can meet demanding application requirements. However, they often come with a high price tag and may have longer lead times for procurement.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Impact on Application:
These alloys are typically used in aerospace, chemical processing, and high-performance applications where standard materials may not suffice. Their compatibility with aggressive media is often superior to standard steel.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that specialty alloys comply with relevant international standards and certifications. Due to their cost, it is essential to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to justify their use in specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steel Processing
| Material | Typical Use Case for steel processing for general fabrications | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | More expensive and complex to weld | Medium |
| Specialty Alloys | Aerospace, chemical processing | Tailored properties for specific needs | High cost and longer lead times | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions regarding steel processing for general fabrications. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will help in selecting the most suitable option for specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steel processing for general fabrications
What Are the Main Stages of Steel Processing for General Fabrications?
Steel processing for general fabrications involves a series of well-defined stages designed to transform raw materials into finished products suitable for various applications. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
How Is Material Prepared for Steel Processing?
The preparation phase is crucial as it lays the foundation for subsequent manufacturing steps. It begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, primarily iron ore, coal, and limestone. In modern steel production, electric arc furnaces (EAF) are often used, which allow for significant recycling of scrap steel—up to 100% in some cases. This not only conserves natural resources but also reduces energy consumption.
Once the raw materials are procured, they undergo processes such as melting and refining. During refining, specific alloying elements are added to achieve desired properties, resulting in a variety of steel grades tailored for different applications. This phase may also involve casting the molten steel into semi-finished products like billets or slabs, which are easier to handle in later stages.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Steel Processing?
The forming stage is where the semi-finished products are transformed into usable shapes through various techniques. Common methods include:
- Hot Rolling: This process involves rolling the steel at high temperatures, making it easier to shape while enhancing its mechanical properties.
- Cold Rolling: In contrast to hot rolling, this method is performed at room temperature, resulting in superior surface finishes and tighter tolerances.
- Machining: Techniques such as milling, turning, and drilling are employed to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances necessary for the final product.
Each of these methods can be tailored to specific requirements, allowing for a wide range of shapes and sizes to meet the diverse needs of general fabricators.
How Does the Assembly Process Work in Steel Fabrication?
Following the forming stage, the assembly process combines various components to create the final product. This may involve welding, bolting, or riveting, depending on the application and design specifications. Advanced techniques such as robotic welding are increasingly being adopted to enhance precision and efficiency in assembly.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Quality during this stage is critical. Fabricators must ensure that all joints and connections meet stringent specifications to guarantee the structural integrity of the final product. Regular inspections during assembly help identify any potential issues before they become significant problems.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used in Steel Processing?
Finishing techniques play a vital role in enhancing the aesthetics and durability of steel products. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like pickling and passivation remove impurities and enhance corrosion resistance.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve durability and aesthetic appeal. Options include galvanization, powder coating, and painting.
- Heat Treatment: This technique alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of steel, improving its strength and hardness.
These finishing touches not only enhance the product’s performance but also ensure compliance with industry standards and customer specifications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Steel Processing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the steel processing workflow, ensuring that products meet both international standards and specific customer requirements. The following are key components of a robust QA program.
Which International Standards Govern Steel Quality Assurance?
Several international standards guide quality assurance in steel processing. The most recognized among them is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. This certification is crucial for companies looking to engage in international trade, as it demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for products used in the oil and gas industry are also important. These certifications provide buyers with confidence that the materials they are sourcing meet stringent quality and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Steel Processing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with quality standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, this involves regular inspections and testing to catch any deviations from quality standards early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This step occurs after manufacturing is complete, ensuring that the final product meets all specifications and is free from defects.
These checkpoints are vital for maintaining product integrity and meeting customer expectations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Steel Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of steel products. Common methods include:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and ductility by determining how it reacts to tension.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s hardness, which correlates with its wear resistance and durability.
- Impact Testing: Evaluates the material’s toughness, particularly at different temperatures.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle testing allow for the inspection of materials without causing damage.
These methods help ensure that the steel products meet necessary performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to assess their quality management systems and manufacturing processes firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for documentation detailing their quality assurance practices, including certifications and compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product specifications.
-
Understanding Certification Nuances: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific certifications relevant to their region and industry. This knowledge can guide them in evaluating suppliers more effectively.
By implementing these strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality steel products that meet their specifications and standards.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steel processing for general fabrications’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring steel processing services tailored for general fabrications. Understanding the intricate steps involved in this sourcing process will help ensure you select the right materials and suppliers to meet your project’s specific needs, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and product quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your project requirements is the first step in the sourcing process. Specify the types of steel alloys needed, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, and detail the dimensions, grades, and finishes required. This clarity helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the delivered materials meet your quality standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in steel processing for general fabrications. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, or the Middle East. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers. Check for relevant industry certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific quality assurance standards that align with your requirements. This step is crucial to ensure that the supplier adheres to international quality and safety standards.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotes from each. Ensure that the quotes include not only pricing but also lead times, minimum order quantities, and any additional services such as cutting or finishing. Comparing these details will provide you with a clearer picture of which supplier can best meet your needs.
Step 5: Assess Value-Added Services
Consider suppliers that offer value-added services beyond basic steel processing. Services such as plasma cutting, waterjet cutting, or custom fabrication can enhance your operational efficiency by reducing the number of vendors you need to manage. A supplier that provides a comprehensive service package can streamline your supply chain significantly.
Step 6: Check References and Case Studies
Before finalizing your decision, request references and case studies from potential suppliers. Speaking to previous clients can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, quality of work, and customer service. Look for suppliers that have successfully completed projects similar to yours, particularly in your target market.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a preferred supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms and conditions. Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties to ensure mutual agreement. Clear communication at this stage helps prevent misunderstandings and sets the stage for a successful long-term partnership.
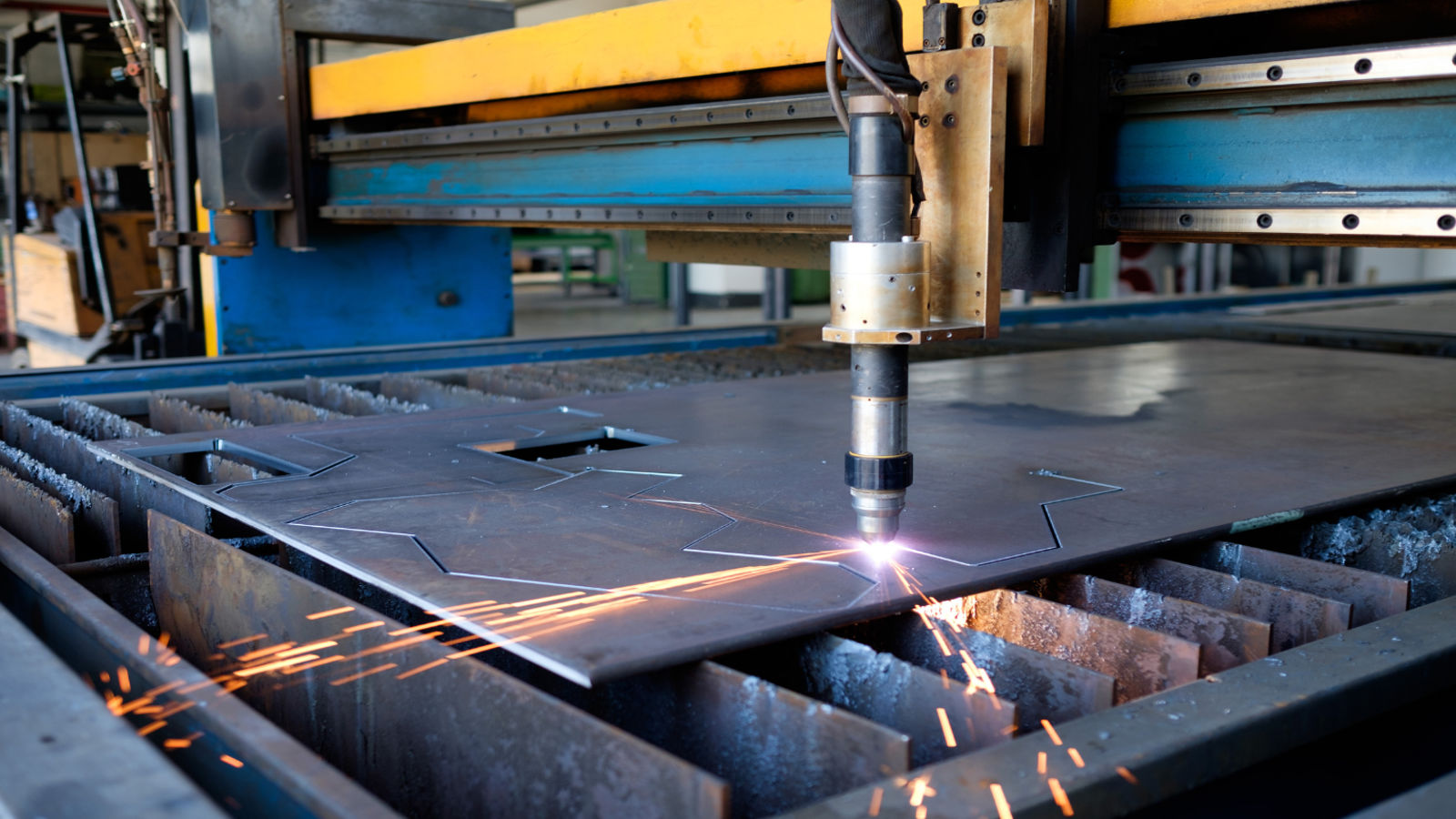

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the procurement process for steel processing services, ensuring that your fabrication projects are well-supported with high-quality materials and reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steel processing for general fabrications Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Steel Processing for General Fabrications?
Understanding the cost structure of steel processing for general fabrications is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The price of raw materials, primarily steel alloys, constitutes a significant portion of the total cost. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and geopolitical factors. For example, sourcing steel from regions with abundant natural resources may yield lower material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for processes like machining, welding, and quality control. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region. In markets like Europe and North America, higher wages may be offset by greater productivity and efficiency, while in regions such as Africa or South America, labor costs might be lower, but the skill levels may vary.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific fabrication projects. This upfront cost can be substantial but is often amortized over the production run. Buyers should consider whether the tooling can be reused for future projects to enhance cost efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the fabricated components meet required specifications involves dedicated QC processes. The costs associated with QC can influence the overall price, especially if certifications (such as ISO) are needed to ensure quality standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the distance between the supplier and buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. For international shipments, additional considerations such as tariffs, customs duties, and insurance can further affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically build a profit margin into their pricing. This margin can be influenced by market competition, supplier reputation, and the perceived value of the service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Steel Processing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of steel processing services:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications often lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and specific certifications can increase costs. Buyers should assess the importance of these factors based on their end-use applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can significantly impact pricing. Long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks, which can influence overall pricing. Buyers should carefully select terms that align with their logistics strategies.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers in Steel Processing?
Effective negotiation is vital for achieving cost efficiency. Here are some tips for buyers:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs associated with logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime. This perspective helps in evaluating the true value of suppliers.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to negotiate better pricing based on volume. Suppliers are often willing to provide discounts for larger commitments.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to better pricing, favorable payment terms, and priority service, especially during peak demand periods.
-
Be Informed About Market Conditions: Staying updated on market trends and raw material prices can empower buyers during negotiations. Knowledgeable buyers can leverage this information to secure better deals.
-
Consider Regional Differences: Be aware of the pricing nuances in different regions, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. Understanding local market conditions can help in negotiating more favorable terms.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, specific requirements, and individual supplier negotiations. Buyers should conduct thorough research and engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to determine the most accurate pricing for their specific needs.
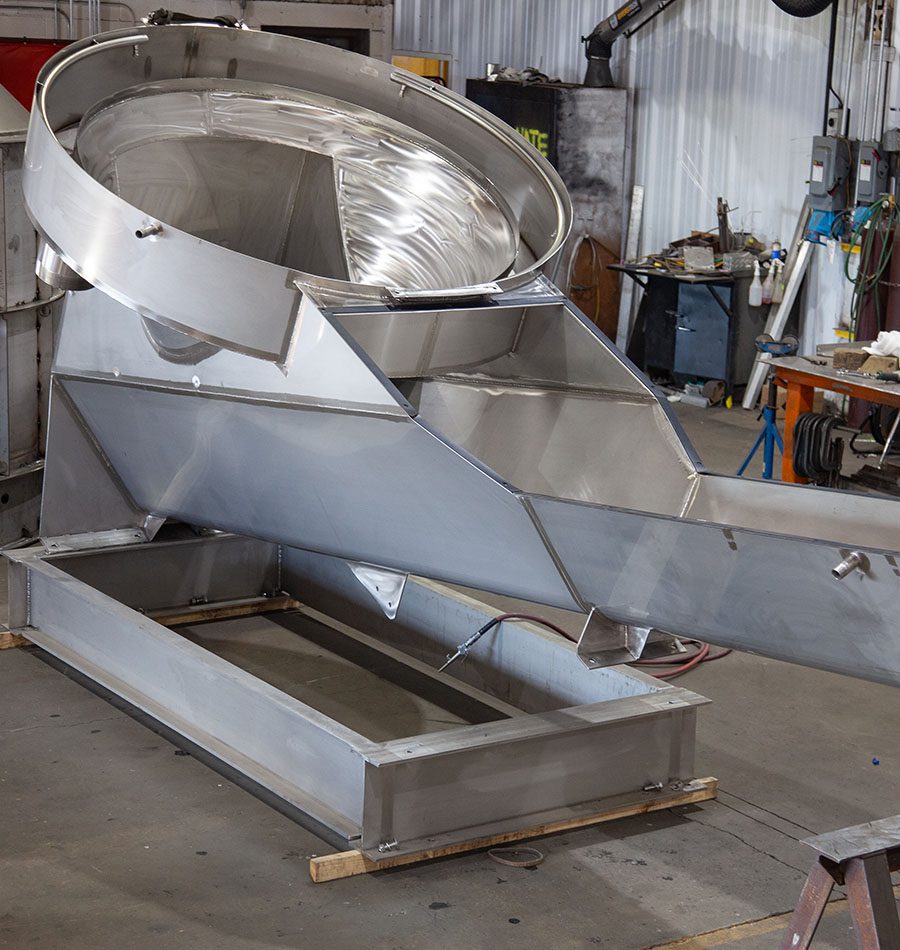

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steel processing for general fabrications With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions in Steel Processing for General Fabrications
In the realm of metal fabrication, choosing the right processing method can significantly impact both product quality and operational efficiency. While steel processing for general fabrications is a popular choice, several alternatives can also serve specific fabrication needs. Understanding these alternatives helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and operational goals.
Comparison Table of Steel Processing for General Fabrications and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Steel Processing For General Fabrications | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Aluminum Fabrication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and durability; versatile | Allows complex geometries; lower strength | Lightweight; good corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; economies of scale | Higher material costs; variable operational costs | Generally lower than steel but varies by alloy |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes; requires skilled labor | Requires specialized equipment and training | Familiar processes; less specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of machinery needed | Minimal maintenance; software updates necessary | Moderate; depends on equipment used |
| Best Use Case | Structural components, heavy machinery | Prototyping, custom parts | Automotive, aerospace, lightweight structures |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is a process that builds objects layer by layer. This technology excels in producing intricate designs and prototypes quickly. However, while it allows for significant design freedom, the materials used in 3D printing often do not match the strength of traditional steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, the initial cost of high-quality 3D printers can be substantial, and the need for specialized training can complicate implementation. Nonetheless, it is an excellent option for companies focused on rapid prototyping or those needing custom parts that traditional methods cannot easily produce.
Aluminum Fabrication
Aluminum fabrication is another viable alternative that provides a lightweight solution with excellent corrosion resistance. This method is particularly advantageous in industries where weight savings are crucial, such as automotive and aerospace. The initial costs can be lower than steel, but this varies based on the specific aluminum alloys used. Aluminum is easier to work with due to its malleability, allowing for simpler and more efficient manufacturing processes. However, it may not provide the same level of strength as steel, which can be a disadvantage for certain applications where heavy loads are involved.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a steel processing method or its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider specific project requirements, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and the desired ease of implementation. Steel processing for general fabrications remains a strong choice for durability and strength in demanding applications. However, alternatives like additive manufacturing and aluminum fabrication present unique benefits that may align better with particular projects, especially those focused on innovation or weight reduction. Assessing the pros and cons of each method will empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
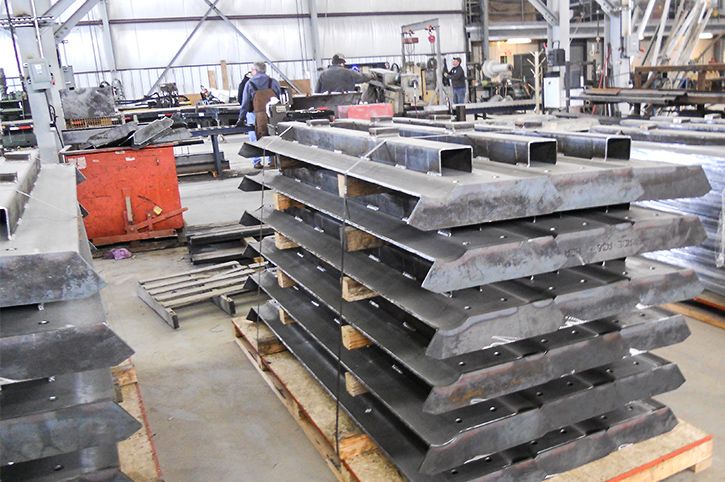

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steel processing for general fabrications
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steel for General Fabrications?
Understanding the critical specifications of steel is essential for making informed purchasing decisions in the B2B marketplace. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grades define the chemical composition and mechanical properties of steel, influencing its suitability for various applications. Common grades include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. Each grade offers unique benefits, such as enhanced corrosion resistance or improved strength, making it vital for buyers to select the appropriate grade for their specific fabrication needs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a material’s dimensions and properties. It is crucial for ensuring that fabricated parts fit together correctly and function as intended. In the B2B context, tighter tolerances may lead to higher manufacturing costs, but they are essential for high-precision applications such as aerospace or medical devices. Understanding tolerance requirements can help buyers avoid costly rework or product failures.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength indicates the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. This property is vital for determining how much load a steel component can handle before failing. Buyers should consider yield strength when assessing materials for structural applications, as inadequate yield strength could lead to safety risks and increased maintenance costs.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is the ability of steel to withstand degradation due to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, or salt. This property is particularly important for applications in harsh environments, such as coastal regions or industrial settings. Buyers should evaluate the corrosion resistance of different steel grades to ensure longevity and reduce the need for frequent replacements.
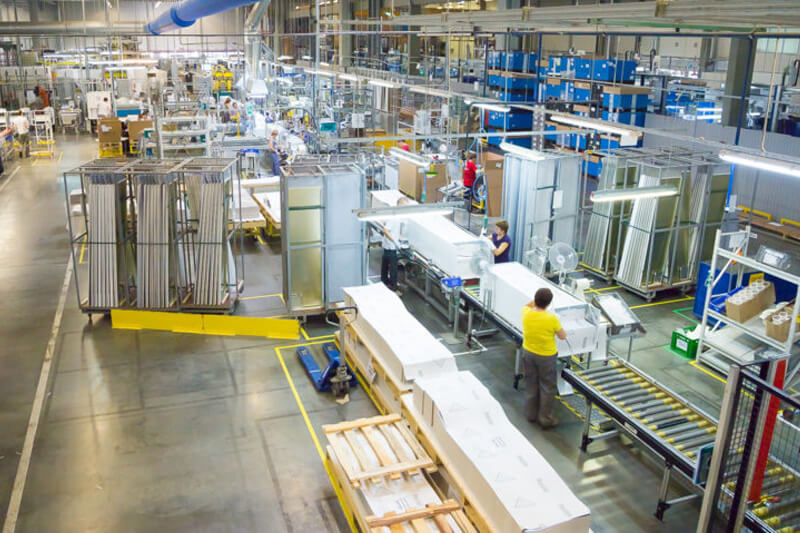

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
5. Fabricability
Fabricability refers to how easily steel can be shaped, cut, or welded into desired forms. Factors influencing fabricability include the material’s hardness, ductility, and thickness. Understanding fabricability is crucial for buyers to ensure that their chosen steel can be efficiently processed into the required components, minimizing production delays and costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Steel Processing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication between buyers and suppliers, ensuring smoother transactions. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end product. In the steel industry, buyers often source materials from OEMs who specialize in specific grades or treatments, ensuring compatibility with their manufacturing processes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and control costs. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure profitability, so buyers should negotiate based on their project needs and timelines.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific materials or services. It is a vital tool for buyers to compare offers and make informed decisions. Clear and detailed RFQs can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring that buyers get the best value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. They outline aspects such as delivery points, risk transfer, and cost allocation. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in international trade, as they help avoid misunderstandings and disputes regarding shipping and delivery.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their production schedules effectively. Long lead times can affect project timelines, so buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure timely deliveries.
In conclusion, understanding these technical properties and trade terms can significantly enhance decision-making in steel processing for general fabrications, leading to more successful projects and better supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steel processing for general fabrications Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Steel Processing for General Fabrications?
The steel processing sector for general fabrications is undergoing significant transformation, driven by global economic trends, technological advancements, and shifting buyer preferences. International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a surge in demand for high-quality steel products. Key drivers include urbanization, infrastructure development, and the rising need for durable, lightweight materials in various applications, from construction to automotive manufacturing.
Emerging technologies, such as automation and digital supply chain management, are reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers increasingly favor suppliers that leverage data analytics for inventory management and predictive sourcing, allowing for reduced lead times and enhanced cost efficiency. Additionally, the integration of advanced processing techniques like laser cutting and 3D printing is enabling fabricators to produce complex components with precision, further streamlining the fabrication process.
As global competition intensifies, international buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who can offer flexible, customized solutions. This trend is particularly relevant in regions with diverse market needs, such as the Middle East and Africa, where localized supply chains can enhance responsiveness and adaptability. Buyers must remain vigilant about geopolitical factors and trade regulations that may impact sourcing strategies, necessitating a proactive approach to supplier relationships and logistics planning.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Steel Processing Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations in the steel processing industry, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for responsible business practices. The steel industry is one of the largest industrial sources of greenhouse gas emissions, prompting a push towards greener production methods. For B2B buyers, this means sourcing steel from suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly processes, such as using recycled materials and adopting energy-efficient technologies.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices, seeking certifications that demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards. Green certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming essential criteria for selecting suppliers. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with the growing trend towards corporate social responsibility.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Moreover, the use of recycled steel is gaining traction, as it significantly reduces the energy and raw materials required for production. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that utilize electric arc furnaces, which can operate with up to 100% recycled content. This not only minimizes environmental impact but also aligns with the circular economy model, where materials are continuously reused and repurposed, providing a sustainable solution for future generations.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Steel Processing in the Context of General Fabrications?
The evolution of steel processing for general fabrications reflects a long-standing quest for innovation and efficiency. Historically, steel production began with rudimentary methods, relying on iron ore and coal. Over the centuries, advancements such as the Bessemer process and electric arc furnaces revolutionized steel manufacturing, enabling mass production and improving quality.
In recent decades, the industry has seen a shift towards high-strength, lightweight materials designed to meet the demands of modern applications. The introduction of advanced alloying techniques and processing methods, such as cold rolling and plasma cutting, has further enhanced the versatility and performance of steel products.
As the sector continues to evolve, the focus is increasingly on sustainability and ethical practices, marking a significant departure from traditional methods. This transformation not only addresses environmental concerns but also aligns with the expectations of a new generation of B2B buyers who prioritize responsible sourcing and innovation in their procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steel processing for general fabrications
-
How do I determine the right steel grade for my fabrication project?
Choosing the right steel grade is crucial for ensuring the performance and longevity of your final product. Start by assessing the specific requirements of your project, including load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and corrosion resistance. Consult with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and guidance on various grades, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys. Additionally, consider the machining and welding properties of the steel, as these factors will influence fabrication efficiency and costs. -
What is the best steel processing method for custom fabrications?
The optimal steel processing method depends on your project’s complexity and specifications. Common techniques include laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting, each offering unique benefits. For intricate designs requiring high precision, waterjet cutting is often preferred due to its ability to cut without heat distortion. Alternatively, for bulk processing, methods like shearing or sawing may be more efficient. Discuss your project needs with suppliers to identify the most suitable processing options. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing steel?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers based on their capabilities and inventory. Typically, MOQs range from a few tons to several hundred tons, depending on the type of steel and processing services required. For international buyers, it’s important to clarify MOQs early in negotiations to avoid unexpected costs or delays. Many suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for repeat customers or larger contracts, so establishing a strong relationship can be beneficial. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in steel products?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing steel for fabrications. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific material certifications (e.g., ASTM, EN) from your supplier. Additionally, consider suppliers who conduct regular inspections and testing, including tensile strength tests and corrosion resistance evaluations. Establishing clear quality standards and expectations in your purchase agreement can help mitigate risks and ensure the steel meets your project requirements. -
What are common payment terms when purchasing steel internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include advance payment, letters of credit, and net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide you with adequate security while also accommodating the supplier’s needs. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in your contract to prevent misunderstandings and protect your financial interests. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing steel?
Logistics play a vital role in the timely delivery of steel products. Consider factors such as shipping methods (e.g., sea freight, air freight), customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may impact your total cost. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to streamline the process. It’s also advisable to plan for lead times and potential delays, particularly when sourcing from regions with variable infrastructure or customs processing times. -
How do I vet suppliers for steel processing?
Vetting suppliers is essential for ensuring reliability and quality. Start by researching their industry reputation through reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Request references from previous clients to gain insights into their performance and service levels. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities, if possible, to evaluate their operational capabilities and quality control processes firsthand. Engaging in initial small orders can also help assess their reliability before committing to larger contracts. -
What are the advantages of using recycled steel in fabrications?
Using recycled steel offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and improved resource efficiency. Recycled steel often meets the same quality standards as new steel while minimizing energy consumption during production. For B2B buyers focused on sustainability, sourcing recycled materials can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Discuss recycling options with suppliers to explore how they can accommodate your sustainability goals while meeting your fabrication needs.
Top 8 Steel Processing For General Fabrications Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metals Inc – Specialty Alloys & Stainless Steel
Domain: metalsinc.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Alloys: Stainless Steel, Nickel Alloy (200, 400, 600, 625, 800/800H/800HT, 20, C-276, X-750), Specialty Alloys (Copper Nickel 90/10, Copper Nickel 70/30), Aluminum (5052, 6063, 3003, 6061), Carbon Shapes, Plate, Sheet, Slit Coil, Angle, Round Bar, Flat Bar, Tubing, Structural Tubing, Pipe Fittings, Flanges, W/F Beam, Channel. Processing Capabilities: Pancake Coil, Oscillate Wound Coil, Ribbon Woun…
2. NSSCO – General Fabrication for Steel Products
Domain: nssco.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: General Fabrication for Steel Products includes a wide range of structural steel products such as I Beams, Tee Beams, Wide Flange Beams, Square Tubing, Rectangular Tubing, Pipe (Square, Bevel, Plain End, Threaded, Coupled), Bars/Rebars (Round Bar, Square Bar, Hex Bar), Grating (Bar Grating, Expanded Metal, Walkway Grating, Stair Treads), Saddle Clips, and Sheet/Coil (Hot Rolled Sheet, Hot Rolled C…
3. Meta Fab – Metal Fabrication Solutions
Domain: metafab.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Meta Fab offers a range of metal fabrication processes including: 1. Forging – shaping metal using forced compression, often by hand with heat. 2. Casting – pouring molten metal into a mold for mass production. 3. Drawing – using tensile force to stretch metal into thinner shapes. 4. Forming – bending metal to desired angles using brake presses or hammers. 5. Machining – a subtractive process invo…
4. Signal Metal – Steel Processing Solutions
Domain: signalmetal.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Provider of Steel Processing – Irving, Texas. Specializing in heavy steel plate fabrication, machining, and flanges. Services include steel fabrication and assembly, CNC machining, flange manufacturing, flame/plasma cutting, large conventional machining, sandblasting and painting, thermal stress relieving, robotic welding, equipment repair, and engineering & design. Key equipment includes: 42″ x 4…
5. Tech Fab – Steel Processing Services
Domain: tech-fab.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Steel Processing Services in Houston, Texas. Specializes in processing and finishing commercial steel for various industrial and manufacturing purposes, including machining, drilling, rolling, cutting, manual mill and lathe, bending, shot-blasting, and more. Services include: Specialty Welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Gas Metal Arc Welding, Flux Core Arc Welding, Spiral Arc Welding, Shielded Met…
6. General Fabricator – Custom Metal Solutions
Domain: generalfabricator.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: General Fabricator specializes in custom metal solutions including tube end forming, bending, spin closing, and brazing of copper and aluminum tubing for air conditioning applications. They offer custom welding, brazing, and heat treatment services for various metals, with a CWB certified Welding Engineer available for material specification and weld design. Their capabilities include lasering, pu…
7. Delta Steel – Structural Steel Solutions
Domain: deltasteel.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Products: Wide Flange Beams, Tube, Plate, Angles, Bars, Channels, I-Beams, Pipes, Sheets, Solar Panel Mounts. Services: Plate Burning, Drilling, Saw Cutting, Forming, Robotic Processing, Cambering, T-Splitting.
8. ASGCO – Steel Fabrication Services
Domain: asgco.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: ASGCO’s Steel Fabrication Division offers a full-service steel fabrication, contract manufacturing, machining, welding, and finishing facility. Key capabilities include:
– Mild Steel Plate welding using GMAW process
– Stainless Steel Plate welding using FCAW process
– Aluminum Plate welding (GMAW and GTAW)
– Pipe Welding (GTAW, FCAW, and GMAW)
– Stud Welding capacity to 1″
– Complex We…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steel processing for general fabrications
In the rapidly evolving landscape of steel processing for general fabrications, strategic sourcing stands as a cornerstone for success. By partnering with reliable suppliers who offer a diverse range of steel alloys and value-added services, businesses can ensure a steady flow of high-quality materials tailored to their specific needs. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports timely project completion, which is critical in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
Furthermore, embracing sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled steel, can yield significant cost savings and improve your company’s environmental footprint. As the demand for advanced materials continues to rise, staying informed about the latest innovations in steel processing will position your business for growth.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic sourcing as a proactive approach to navigate market fluctuations and supply chain challenges. Engaging with suppliers who understand regional dynamics and can provide customized solutions will be essential in maintaining a competitive edge. Now is the time to explore partnerships that align with your goals and drive your business forward in the steel fabrication industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to steel processing for general fabrications
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.