How to Source Smallest Diesel Engine Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for smallest diesel engine
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the smallest diesel engine for specialized applications presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are operating in the agricultural sector in Brazil or managing marine operations in Germany, finding a compact, efficient, and reliable diesel engine can significantly impact your productivity and operational costs. This guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the global market for the smallest diesel engines, providing you with essential insights into various engine types, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting processes.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we delve into critical factors such as engine specifications, performance metrics, and compliance with regional emissions standards, which are paramount for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. You will learn how to evaluate suppliers based on quality assurance, after-sales support, and customization options that align with your specific needs. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations and financing options that can facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
By arming you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers you to make strategic choices that not only meet your operational requirements but also enhance your competitive edge in the marketplace.
Understanding smallest diesel engine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Cylinder Diesel Engine | Compact size, air-cooled, direct injection, 4-stroke design | Agricultural machinery, small generators, pumps | Pros: High efficiency, low maintenance; Cons: Limited power output |
| Common Rail Diesel Engine | Electronically-managed fuel injection, low emissions | Marine propulsion, small commercial vessels | Pros: Improved fuel economy, quieter operation; Cons: Higher initial cost |
| Multi-Cylinder Diesel Engine | Enhanced power output, water-cooled, complex design | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Pros: Greater power and torque; Cons: Larger footprint, more maintenance |
| Mini Diesel Generator | Portable, compact, integrated generator unit | Backup power, remote site operations | Pros: Mobility, ease of use; Cons: Limited run time, lower power capacity |
| Marine Inboard Diesel Engine | Designed for marine applications, compact and efficient | Leisure boats, small commercial vessels | Pros: High efficiency, low noise; Cons: Requires specialized installation |
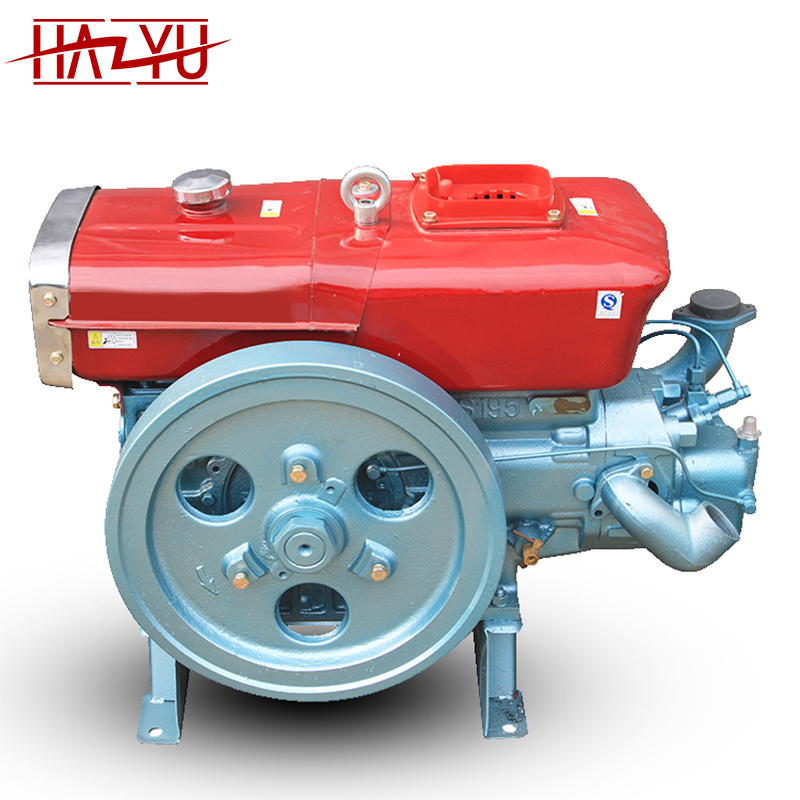
What are the Characteristics of Single Cylinder Diesel Engines?
Single cylinder diesel engines are known for their compact design and simplicity. Typically featuring a direct injection system, these engines are air-cooled and operate on a four-stroke cycle. Their size makes them particularly suited for applications in agricultural machinery, such as micro-tillers and small water pumps. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should weigh their need for efficiency and low maintenance against the engine’s limited power output, which may not meet the demands of heavier applications.
How Do Common Rail Diesel Engines Stand Out?
Common rail diesel engines utilize electronically-managed fuel injection technology, allowing for precise control over fuel delivery. This results in lower emissions and enhanced fuel efficiency, making them ideal for marine propulsion and small commercial vessels. B2B buyers should consider the benefits of improved performance and lower operational costs, although the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional engines. This technology is increasingly becoming a standard in the marine industry, appealing to environmentally-conscious operators.
What Advantages Do Multi-Cylinder Diesel Engines Offer?
Multi-cylinder diesel engines provide greater power output and torque, making them suitable for heavy machinery and industrial applications. These engines are typically water-cooled and have a more complex design, which can lead to higher maintenance requirements. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs carefully; while these engines can handle demanding tasks, the larger footprint and maintenance complexity may be drawbacks for smaller operations or those with limited space.
Why Choose Mini Diesel Generators for Your Business?
Mini diesel generators are compact, portable units designed to provide reliable backup power or support operations in remote locations. Their ease of use and mobility make them a popular choice for various industries. However, buyers should keep in mind the limited run time and lower power capacity compared to larger generators. These units are particularly effective for businesses needing flexibility and quick deployment, especially in sectors like construction or emergency services.
What Makes Marine Inboard Diesel Engines Ideal for Nautical Use?
Marine inboard diesel engines are specifically engineered for boat propulsion, combining compactness with efficiency. They are often designed to operate quietly and with minimal emissions, making them suitable for leisure and commercial vessels alike. B2B buyers in the marine sector should consider the advantages of high efficiency and low noise levels, while also being aware of the specialized installation requirements that can affect overall costs. This type of engine is particularly valuable for operators seeking reliable performance in marine environments.
Key Industrial Applications of smallest diesel engine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of smallest diesel engine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Powering small agricultural machinery like tillers and pumps | High fuel efficiency and reliability for continuous operation | Engine durability, fuel type compatibility, and maintenance support |
| Marine | Inboard propulsion for small leisure boats and commercial crafts | Enhanced performance with low emissions and noise levels | Compliance with environmental regulations and ease of installation |
| Construction | Generating power for portable tools and small equipment | Compact size allows for versatility on job sites | Sourcing for ruggedness and adaptability to various environments |
| Energy Generation | Fuel-efficient generators for remote locations | Reliable power supply in off-grid situations | Fuel consumption rates and generator compatibility |
| Transportation | Small transport vehicles for urban logistics | Cost-effective operation and maneuverability in tight spaces | Weight considerations and engine power output |
How is the smallest diesel engine used in agriculture, and what problems does it solve?
In the agricultural sector, the smallest diesel engine is integral to powering small machinery such as micro-tillers, water pumps, and irrigation systems. These engines provide a high power-to-weight ratio, ensuring that farmers can efficiently manage their land with minimal fuel consumption. Additionally, their robust construction allows them to operate under tough conditions, addressing challenges like fuel availability and maintenance frequency. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing engines that can handle local fuel types and environmental conditions is crucial for operational success.
What are the applications of the smallest diesel engine in marine environments?
In marine applications, the smallest diesel engine serves as a compact and efficient propulsion system for smaller leisure boats and light commercial vessels. The latest models, such as YANMAR’s 3JH40, offer advanced common rail technology that significantly reduces fuel consumption while meeting stringent emission regulations. This is particularly beneficial for operators in Europe and the Middle East, where environmental compliance is critical. Buyers should consider factors like engine weight, compatibility with existing boat systems, and ease of installation to optimize performance and adherence to local regulations.
How does the smallest diesel engine enhance construction operations?
The construction industry utilizes the smallest diesel engines to power portable tools and equipment, which are essential for various on-site tasks. Their compact design allows for easy transport and setup, making them ideal for urban construction sites where space is limited. These engines help solve the problem of providing reliable power in remote or off-grid locations, ensuring that work can continue uninterrupted. Buyers should look for engines that offer durability and can withstand harsh job site conditions, as well as those that have a solid support network for maintenance and parts availability.
In what ways does the smallest diesel engine contribute to energy generation?
The smallest diesel engine is commonly used in generators for energy production, especially in remote areas lacking stable electricity supply. These engines are valued for their reliability and efficiency, providing a steady power source for homes, businesses, and agricultural operations. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, the ability to source engines that are fuel-efficient and designed for low maintenance can significantly impact operational costs and energy availability. Sourcing considerations should include fuel consumption rates and compatibility with various generator types to ensure optimal performance.
How does the smallest diesel engine support transportation needs?
In the transportation sector, the smallest diesel engine is used in small vehicles designed for urban logistics and last-mile delivery. These engines offer cost-effective operation with lower fuel consumption, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance their logistics efficiency. Their compact size allows for maneuverability in congested urban environments, addressing the challenge of navigating tight spaces. Buyers should prioritize sourcing engines that deliver adequate power output while considering weight and vehicle compatibility to ensure smooth operations and compliance with local regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘smallest diesel engine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Reliability Concerns in Diesel Engines
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with concerns about the reliability and durability of the smallest diesel engines. In industries such as agriculture or construction, where these engines are frequently used, any downtime can lead to significant financial losses. Buyers may worry about the engine’s ability to withstand harsh operating conditions, such as extreme temperatures or heavy loads. Additionally, they may be uncertain about the quality of materials used in manufacturing, which directly impacts engine longevity.
The Solution: To ensure reliability, buyers should prioritize sourcing engines from reputable manufacturers known for their stringent quality control processes. Look for engines that utilize high-quality materials, such as cast iron cylinder liners and forged steel components, which enhance durability. It’s also beneficial to request detailed specifications and performance data, including fuel consumption rates and maintenance requirements. Furthermore, consider partnering with suppliers who offer robust after-sales support, including warranties and readily available replacement parts. By selecting a reliable engine and a supportive supplier, buyers can mitigate downtime and maintain operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Addressing Environmental Regulations and Compliance
The Problem: In today’s regulatory landscape, businesses must navigate complex environmental standards, especially when it comes to emissions from diesel engines. Buyers of the smallest diesel engines may struggle to find options that comply with local and international emissions regulations, such as EPA Tier 3 or EU RCD Tier 2 standards. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and damage to a company’s reputation, making it crucial to choose engines that not only meet but exceed these requirements.
The Solution: When sourcing diesel engines, buyers should conduct thorough research on the latest emissions regulations in their target markets. Opt for engines equipped with advanced technologies, such as common rail fuel injection systems, which improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Engage with manufacturers that transparently provide emissions data and certification documents to verify compliance. Additionally, consider exploring engines designed for specific applications—like marine or agricultural uses—that are engineered to meet stricter environmental standards. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also aligns the business with sustainability goals, enhancing its market position.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Sizing and Space Constraints
The Problem: Buyers in sectors such as construction or marine applications often face challenges related to space constraints when integrating the smallest diesel engines into their equipment. Limited space can restrict engine options, leading to compromises in power output or efficiency. Buyers may feel overwhelmed trying to balance the need for a compact engine with performance requirements, potentially impacting overall productivity.
The Solution: To address sizing challenges, buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of the available space and determine the specific power requirements for their applications. Collaborate with manufacturers who specialize in compact engine designs, as they often have tailored solutions that maximize power output without compromising on size. Additionally, consider engines with versatile mounting options and configurations that can be adapted to fit various applications. Engaging in direct discussions with suppliers about customization options can also yield solutions that enhance compatibility with existing machinery, ultimately optimizing space utilization without sacrificing performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for smallest diesel engine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Small Diesel Engines?
Selecting the right materials for the smallest diesel engines is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these engines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Diesel Engine Applications?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It has a high thermal conductivity, which helps in dissipating heat effectively.
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron makes it ideal for engine blocks and cylinder heads. However, it is relatively heavy, which can impact the overall weight of the engine. Additionally, manufacturing complexities arise in machining cast iron, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with various fuels and lubricants, making it versatile for different engine applications. However, it may be prone to corrosion if not properly coated or maintained.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for emissions and material safety. Cast iron’s heavy weight may also affect shipping costs and logistics.
Why Is Aluminum a Popular Choice for Diesel Engine Components?
Key Properties: Aluminum offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various engine components.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to overall engine efficiency and performance. However, it may not withstand the same high temperatures as cast iron, which could limit its use in high-performance applications. Additionally, the cost of aluminum is generally higher than that of cast iron.
Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in components like cylinder heads and pistons, where weight savings are critical. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for marine applications, especially in regions with high humidity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential for quality assurance. In Europe, where lightweight and fuel-efficient solutions are prioritized, aluminum is often favored.
What Role Does Steel Play in Diesel Engine Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and toughness. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for critical components like crankshafts and connecting rods.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability and strength make it ideal for high-stress applications. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can affect overall engine weight. The manufacturing process can also be complex, leading to higher production costs.
Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Impact on Application: Steel components are essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of diesel engines. Its compatibility with various fuels and lubricants makes it versatile for different applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of steel that comply with local regulations. In regions like the Middle East, where extreme temperatures are common, selecting the right steel grade is crucial for performance.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Diesel Engine Performance?
Key Properties: Composite materials, often made from a combination of plastics and fibers, offer lightweight properties and excellent corrosion resistance. They can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can improve fuel efficiency. However, they may not have the same strength as metals, which can limit their application in high-stress areas. Additionally, the cost of composites can be higher due to advanced manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in non-structural components, such as engine covers and insulation. Their corrosion resistance makes them suitable for applications in humid or corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America may find composites appealing due to their lightweight nature, which aligns with current trends in fuel efficiency. However, compliance with material safety standards is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Small Diesel Engines
| Material | Typical Use Case for smallest diesel engine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, cylinder heads | High durability and wear resistance | Heavy weight, complex machining | Medium |
| Aluminum | Cylinder heads, pistons | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | High |
| Steel | Crankshafts, connecting rods | High strength and toughness | Heavier than aluminum, complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Composite | Engine covers, insulation | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to metals | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their diesel engine applications, ensuring compliance with local standards while balancing performance and cost.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for smallest diesel engine
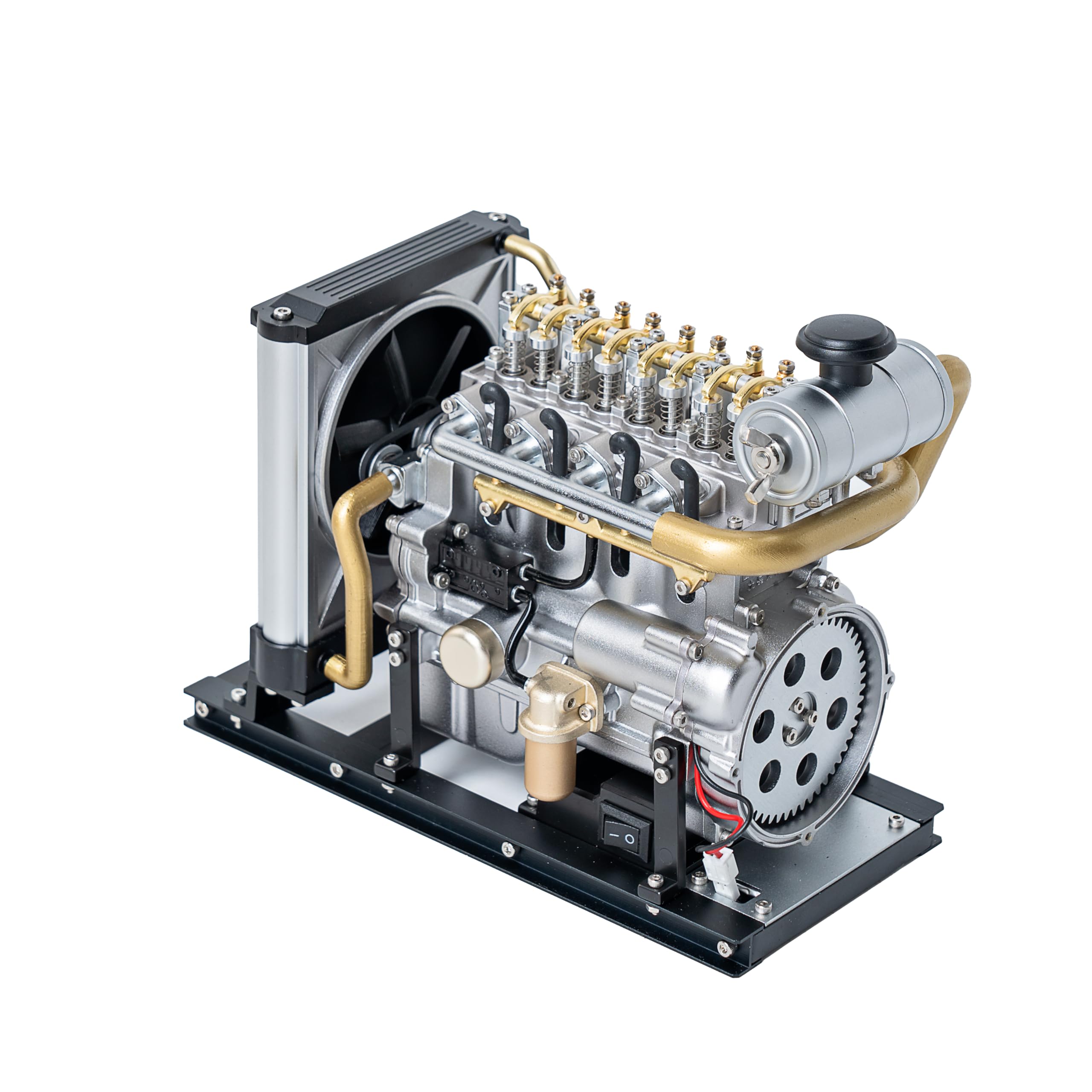
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing the Smallest Diesel Engine?
The manufacturing process of the smallest diesel engine, such as the single-cylinder 170F model, involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensure the engine meets stringent performance and durability standards.
Material Preparation: How Are Components Selected?
The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, which are crucial for the engine’s performance and longevity. Common materials include cast iron for the cylinder, forged steel for crankshafts, and aluminum alloys for various engine components. These materials are chosen for their strength, heat resistance, and ability to withstand the rigors of diesel combustion.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet industry specifications. This preparation phase sets the foundation for the subsequent manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the required components using advanced manufacturing techniques. Machining processes, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling and turning, are commonly employed to achieve precise dimensions for parts like the cylinder head and crankcase.
Casting techniques, particularly sand casting for the engine block, are also prevalent. This method allows for complex shapes and ensures the structural integrity of the engine components. After forming, components are cleaned and inspected for defects, ensuring only quality parts proceed to assembly.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
The assembly process is a critical phase where individual components come together to form a complete engine. Skilled technicians follow detailed assembly instructions to ensure accuracy. During this stage, key components such as pistons, crankshafts, and fuel injectors are meticulously installed.
Additionally, assembly lines often incorporate automation to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Quality checks are conducted at various points during assembly to ensure that each engine is built to specification. This can include torque checks on bolts and alignments of moving parts.
How Are Finishing Touches Applied to the Engine?
The finishing stage involves several processes to ensure the engine is ready for market. This includes surface treatments such as painting or powder coating for corrosion resistance, as well as the installation of external components like exhaust systems and fuel tanks.
Final inspections are conducted to verify that the engine meets all performance standards. This includes running the engine under controlled conditions to monitor performance metrics such as power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Essential for Small Diesel Engines?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of diesel engines, particularly given the rigorous demands of international markets. Compliance with international standards and industry-specific regulations is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product reliability and safety.
Which International Standards Are Relevant?
Manufacturers of small diesel engines typically adhere to several international quality standards, including ISO 9001 for quality management systems. This certification ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes and products.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Additionally, engines may need to comply with emissions standards such as EPA Tier 3 in the U.S. and EU regulations in Europe. Compliance with these standards is crucial for products intended for export, as it assures buyers of their environmental responsibility and performance efficiency.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before they enter the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages helps identify defects early. This may include monitoring dimensions during machining or verifying assembly processes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the completed engines is conducted to ensure they meet all performance and safety standards. This often includes running the engine and testing for emissions, noise levels, and power output.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure they receive reliable products. There are several strategies buyers can employ:
What Are Effective Audit Strategies?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers is one of the most effective ways to assess their quality control processes. Buyers can request to visit manufacturing facilities to observe their practices firsthand. During the audit, buyers should look for evidence of adherence to international standards, such as ISO certifications, as well as the presence of systematic QC checkpoints.
How Can Buyers Use Reports and 3rd-Party Inspections?
Buyers should also request quality assurance reports that detail testing results and compliance with industry standards. These reports can provide insights into the reliability and safety of the engines.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate a supplier’s claims. These services can conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures, providing an unbiased evaluation.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
Navigating quality control and certification can be complex for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Purchases?
Buyers must be aware of local regulations and standards that may affect the import and use of diesel engines. Different regions may have specific certifications required for compliance, impacting the marketability of the engines. For example, engines sold in the EU must meet CE marking requirements, while those in the U.S. must comply with EPA regulations.
Why Is Communication Key in International Transactions?
Clear communication with suppliers about these regional requirements is vital. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are well-versed in the necessary certifications and can provide the required documentation. This includes understanding the implications of non-compliance, which can lead to costly delays and fines.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Small Diesel Engine Procurement
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for small diesel engines are critical factors that B2B buyers must consider. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and the nuances of international certification, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they procure reliable and efficient engines. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right supplier but also safeguards against potential compliance issues in diverse markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘smallest diesel engine’
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in successfully sourcing the smallest diesel engines for various applications, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you select the most suitable engine and supplier for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for the smallest diesel engine you need. Consider factors such as engine type (e.g., single-cylinder, four-stroke), displacement, power output, and fuel efficiency. This step is critical to ensure that the engine meets the specific operational demands of your application, whether for agricultural machinery, generators, or marine use.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in small diesel engines. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates. Assess their market presence and reputation to ensure reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international standards, such as ISO or CE marking. This step is essential for ensuring product quality and safety. Additionally, check if they meet local regulations in your target market, especially for emissions and performance standards.
Step 4: Request Product Samples and Specifications
Once you narrow down your list of suppliers, request product samples and detailed technical specifications. Examine the engine design, materials used, and any unique features that enhance performance or durability. Samples allow you to assess the quality firsthand and ensure that the product aligns with your requirements.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales service offered by suppliers, including warranty terms, customer support, and availability of spare parts. Reliable after-sales support is crucial for minimizing downtime and addressing any operational issues that may arise. Ensure that the warranty period is satisfactory and covers major components.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing. Consider not only the upfront cost but also the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and fuel consumption. Additionally, review payment terms, delivery schedules, and any potential hidden costs. This comprehensive analysis will help you make an informed financial decision.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After selecting a supplier, draft a clear purchase agreement that outlines all terms, including delivery timelines, payment schedules, and product specifications. Ensure that both parties agree to the terms to avoid any misunderstandings. This step is vital for establishing a professional relationship and ensuring smooth transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing the smallest diesel engines, leading to informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for smallest diesel engine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing the Smallest Diesel Engine?
When considering the sourcing of the smallest diesel engine, understanding the various cost components is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: High-quality materials such as cast iron for cylinder liners and forged steel for crankshafts significantly impact cost. The selection of durable components can enhance engine longevity, thus affecting the total cost of ownership.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this should be weighed against potential quality variations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lead to lower overhead, influencing the final product price.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized tools and molds can be substantial, especially for customized engines. Buyers should be aware that these costs may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that engines meet specific performance and safety standards is essential. Robust QC processes may increase upfront costs but can prevent expensive recalls or failures later.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the destination, weight, and size of the engine. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital to manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, brand reputation, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Small Diesel Engines?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure of the smallest diesel engines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for favorable terms based on their anticipated needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized engines tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Engines built with premium materials or those that meet specific industry certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should assess the long-term benefits of investing in quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established brands may charge a premium, but their proven track record can justify the cost.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the total landed cost. Buyers should understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency in Diesel Engine Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing the smallest diesel engines, consider these actionable strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power to negotiate better terms, especially when placing bulk orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment in a more reliable engine can lead to significant savings over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may experience price fluctuations due to local demand, currency exchange rates, and trade regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should stay informed about these dynamics.
-
Request Samples or Prototypes: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate quality. This can help prevent costly mistakes and ensure the product meets your expectations.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor the market for changes in material costs, labor rates, and technological advancements. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain quotes tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing smallest diesel engine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Smallest Diesel Engine
When evaluating the smallest diesel engine for industrial applications, it is essential to consider alternative solutions that may fulfill similar operational requirements. This analysis focuses on comparing the smallest diesel engine with electric motors and gasoline engines, two viable alternatives that cater to various business needs in sectors such as agriculture, construction, and marine operations.
| Comparison Aspect | Smallest Diesel Engine | Electric Motor | Gasoline Engine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, continuous operation; suitable for heavy loads. | Moderate torque; efficiency varies with load. | High RPM, good for lighter loads; less torque than diesel. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; competitive long-term fuel costs. | Lower initial cost; potential high electricity costs depending on local rates. | Generally lower initial cost; fluctuating fuel prices can impact long-term expenses. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires diesel fuel infrastructure; installation may be complex. | Easier installation; often requires less specialized infrastructure. | Simple installation; widely available fuel sources. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance; potential for higher wear in harsh conditions. | Generally low maintenance; fewer moving parts result in less wear. | Requires regular maintenance; can be less reliable in extreme conditions. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for heavy-duty applications and remote areas without electricity. | Best suited for urban applications with reliable power sources. | Effective for light to moderate applications where fuel availability is not an issue. |
Understanding the Alternatives in Detail
Electric Motors
Electric motors are gaining traction as an alternative to diesel engines, especially in urban settings. They offer the advantage of lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts, resulting in reduced operational costs over time. However, electric motors may lack the high torque required for heavy-duty tasks, making them less ideal for applications demanding continuous operation under heavy loads. Additionally, the reliance on a stable electricity supply can be a limitation in remote locations, where infrastructure may not support consistent power delivery.
Gasoline Engines
Gasoline engines present a cost-effective solution for light to moderate applications. Their initial purchase price is often lower than that of diesel engines, making them attractive for businesses with budget constraints. However, gasoline engines typically do not provide the same torque levels as diesel engines, which can hinder performance in heavy-duty tasks. Additionally, fuel price volatility can significantly impact operational costs, particularly in regions with fluctuating gasoline prices. Their installation is generally straightforward, and they are widely compatible with existing fuel infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When selecting the appropriate engine type for your operations, it is crucial to assess the specific needs of your business. The smallest diesel engine excels in heavy-duty applications and environments lacking reliable electricity, making it a preferred choice for agricultural machinery or construction equipment in remote areas. Conversely, electric motors may be the best fit for urban environments where low maintenance and efficiency are prioritized, while gasoline engines serve well in applications requiring lower initial costs and straightforward installation.
Ultimately, understanding the performance characteristics, costs, and operational environments of each option will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational requirements.
Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for smallest diesel engine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the Smallest Diesel Engine?
When evaluating the smallest diesel engines, several technical specifications are crucial for B2B buyers to consider. Understanding these properties can help ensure that the engine meets specific operational requirements and is suitable for various applications, particularly in regions with unique operational demands.
1. Displacement (cc or L)
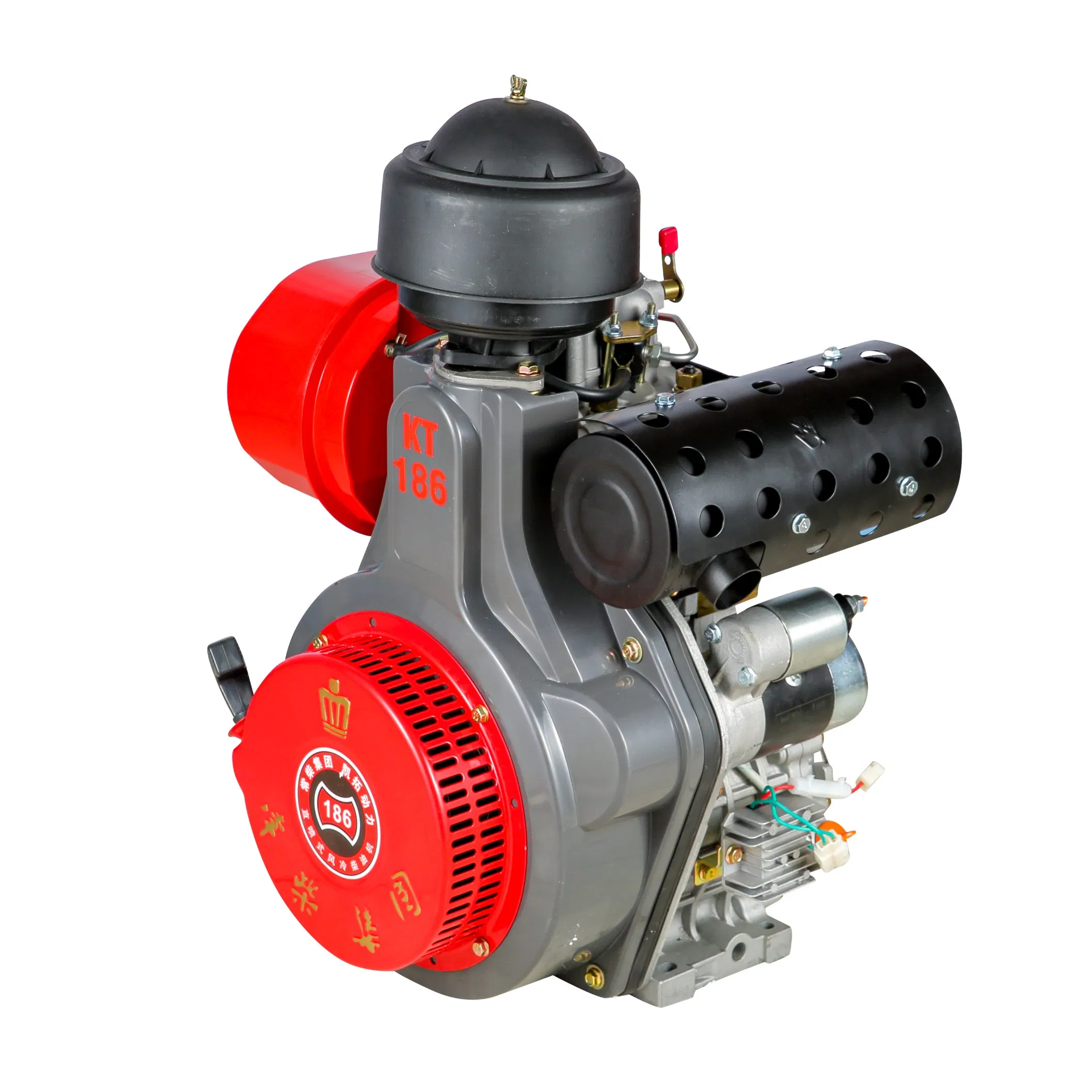
Displacement measures the volume of the engine’s cylinders and is typically expressed in cubic centimeters (cc) or liters (L). For instance, the BISON BS170F has a displacement of 211cc. Higher displacement often correlates with increased power output, which is vital for applications requiring robust performance, such as agricultural machinery or small generators.
2. Power Output (kW/hp)
The power output indicates the engine’s capability to perform work, measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (hp). The BS170F engine has a rated output of 2.5 kW (3.5 hp) at 3000 rpm. Selecting an engine with the appropriate power output is essential to ensure it can handle the intended load without overexertion, which could lead to failures or inefficiencies.
3. Fuel Consumption Rate (g/kW·h)
This specification indicates the efficiency of the engine in terms of fuel usage relative to power produced. The BISON BS170F engine has a fuel consumption rate of 280 g/kW·h. Understanding fuel efficiency is particularly important for cost-conscious buyers, as it directly impacts operational costs and environmental considerations.
4. Cooling System Type
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperatures and preventing overheating. The BS170F employs forced air cooling, which is effective for smaller engines. Buyers should consider the cooling system type based on the operating environment, as some regions may require more robust cooling solutions due to higher ambient temperatures.
5. Starting System
The starting system, whether recoil or electric, affects the ease of use and reliability of the engine. The BS170F offers both options, catering to different user preferences and operational contexts. An efficient starting system can significantly reduce downtime, especially in agricultural or remote applications where reliability is paramount.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
6. Weight and Dimensions (L x W x H)
The physical dimensions and weight of the engine influence installation and portability. The BS170F measures 420 x 380 x 470 mm and weighs approximately 28 kg. Smaller and lighter engines are often preferred for applications where space is limited or mobility is required, making them suitable for various industries.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Small Diesel Engines?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms related to the procurement of small diesel engines:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of diesel engines, an OEM may provide engines that are integrated into larger machinery. Establishing relationships with reputable OEMs can ensure quality and reliability in engine performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Understanding the MOQ helps buyers negotiate better purchasing terms, especially when sourcing engines in bulk.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for small diesel engines can facilitate competitive bidding and help in selecting the best supplier based on price and terms.

Illustrative image related to smallest diesel engine
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time between placing an order and receiving the product. For businesses that rely on small diesel engines for operations, understanding lead times is essential for planning and ensuring timely project execution.
In summary, both technical properties and industry terminology are crucial for B2B buyers seeking the smallest diesel engines. A firm grasp of these elements will empower decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the smallest diesel engine Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Driving the Smallest Diesel Engine Sector?
The smallest diesel engine sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for efficient and compact power solutions is primarily fueled by the agricultural, construction, and marine sectors. In regions like Africa and South America, where agriculture is a primary economic driver, there is a surge in the adoption of small diesel engines for machinery such as tillers and pumps, which enhance productivity while minimizing operational costs. Similarly, in Europe and the Middle East, the push for more efficient marine engines is evident, with innovations in common rail technology enabling enhanced performance and reduced emissions.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of digital monitoring systems and IoT capabilities into diesel engines. These advancements allow operators to monitor engine performance in real-time, leading to improved maintenance schedules and operational efficiency. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on modular designs that facilitate easier upgrades and repairs, catering to the diverse needs of international buyers.
Market dynamics are also influenced by the regulatory landscape, particularly concerning emissions standards. Buyers from regions like Europe are particularly sensitive to compliance with stringent environmental regulations, pushing manufacturers to innovate in fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. This creates opportunities for B2B buyers to source engines that not only meet local requirements but also provide long-term operational savings.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Smallest Diesel Engine Market?
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration for B2B buyers in the smallest diesel engine market. The environmental impact of diesel engines, particularly concerning emissions and fuel consumption, has prompted manufacturers to adopt greener practices. The development of engines that meet or exceed EPA and EU emissions standards is not just a regulatory requirement but also a market expectation.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital, as buyers increasingly demand transparency in supply chains. This includes ensuring that materials used in engine production are sourced responsibly, and that manufacturers adhere to labor and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can provide assurance to buyers that they are sourcing products that align with their corporate sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the demand for alternative fuels and hybrid solutions is on the rise, encouraging manufacturers to innovate in fuel technology. By investing in engines designed for biofuels or those that are compatible with hybrid systems, B2B buyers can reduce their carbon footprint while enhancing operational efficiency.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of the Smallest Diesel Engine Sector?
The evolution of the smallest diesel engine sector dates back to the early 20th century when the first diesel engines were introduced as more efficient alternatives to steam engines. Over the decades, advancements in engineering led to the development of smaller, more powerful diesel engines that became integral to various applications, particularly in agriculture and transportation.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, driven by regulatory pressures and environmental concerns. Manufacturers have invested in research and development to innovate technologies such as direct fuel injection and turbocharging, which have significantly improved engine performance while maintaining compact sizes.
As we look to the future, the integration of smart technologies and the ongoing pursuit of sustainability will continue to shape the smallest diesel engine market, making it an exciting space for B2B buyers seeking reliable and efficient power solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of smallest diesel engine
-
How do I determine the right smallest diesel engine for my application?
When selecting the right smallest diesel engine, consider the specific power requirements of your application, such as horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency. Evaluate the engine’s dimensions to ensure it fits within your equipment. Additionally, assess the engine’s cooling type, maintenance needs, and compatibility with existing machinery. Consulting with suppliers about the intended use can also provide insights into the most suitable engine models. -
What are the key features of the smallest diesel engines available in the market?
The smallest diesel engines typically feature compact designs, high fuel efficiency, and robust construction for durability. Look for engines with low emissions and noise levels, which are increasingly important in compliance with environmental regulations. Features such as direct injection technology and overhead valve (OHV) designs enhance performance and fuel combustion efficiency, making them suitable for applications in agriculture, construction, and small machinery. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for smallest diesel engines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and engine model. Typically, MOQs may range from a single unit for customized orders to several dozen for standard models. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a small or medium-sized enterprise. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to flexibility in order quantities. -
What payment terms can I expect when sourcing smallest diesel engines internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions often include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders or customized engines. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing any agreements, as they can vary based on your location and the supplier’s policies. Additionally, consider the implications of currency exchange rates on your total costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing smallest diesel engines?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation such as product specifications, certifications, and quality control processes from potential suppliers. Conducting factory visits or audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing practices. Look for suppliers who offer warranties and after-sales support, as these indicate a commitment to product quality and customer satisfaction. Reading reviews and seeking references from other buyers can further validate a supplier’s reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing smallest diesel engines?
Logistics for importing engines involve understanding shipping methods, potential customs duties, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who can navigate international shipping regulations and documentation requirements. Additionally, factor in the costs of insurance and storage, as these can impact your overall budget. Timely communication with suppliers about shipping schedules is crucial to ensure that your operations are not disrupted. -
Are customization options available for smallest diesel engines?
Many manufacturers offer customization options, such as branding, packaging, or modifications to meet specific operational needs. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore available options, including engine specifications and accessories. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly. Ensure that any modifications comply with local regulations and standards. -
What are the advantages of using a single-cylinder diesel engine compared to multi-cylinder options?
Single-cylinder diesel engines, such as the smallest models, are often more compact, lighter, and less expensive than multi-cylinder alternatives. They typically have fewer moving parts, which can lead to lower maintenance costs and increased reliability. These engines are ideal for applications requiring less power and are favored in rural or developing regions for agricultural machinery and small generators due to their efficiency and ease of operation.
Top 6 Smallest Diesel Engine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Suzuki – 0.8L Turbo-Diesel Engine
Domain: carbuzz.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Engine: 0.8L turbo-diesel I2, Power: 32-47 hp, Torque: 55-95 lb-ft, Bore x Stroke: 3.03 x 3.35 Inches, Compression Ratio: 15-16:1, Production Years: 2016-2020, Primary Market: India, Additional Market: Philippines, Notable Vehicle Uses: Suzuki Super Carry, Suzuki Celerio, Fuel Economy: 65 mpg, Transmission: 5-speed manual.
2. Kubota – Super Mini Series Diesel Engines
Domain: engine.kubota.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Kubota – Super Mini Series Diesel Engines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
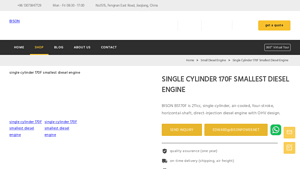
3. Bison – BS170F Diesel Engine
Domain: bison-machinery.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Model: BS170F (4HP)\nEngine Type: Single cylinder, 4-stroke, air-cooled, direct injection, diesel engine\nBore x Stroke: 70 x 55 mm\nDisplacement: 211 ml\nEngine Speed: 3000/3600 rpm\nCompression Ratio: 0.834\nRated Output Power: 2.5 kW (3.5 hp) at 3000 rpm\nMax Output Power: 2.8 kW (3.8 hp) at 3600 rpm\nFuel: 0# or 10# light diesel oil\nFuel Tank Volume: 2.5 liters\nFuel Consumption Rate: 280/288…
4. Facebook – Model Engines & Nano Technology
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Model Engines – Old and New, A BIT OF NANO TECHNOLOGY
5. Smokstak – Small Diesel Engines
Domain: smokstak.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Smallest engine that runs pure diesel: 60 pounds, approximately 4 hp. Lohmann Motor: 18cc, weighs under 60 lbs, can run on pure diesel or a mix of kerosene and diesel. R165 Changfa: water cooled, just over 3 hp, weighs around 50 lbs. Model airplane diesel engines: down to about 0.5 cc. Peri Diesel: 3 hp, weighs around 50 lbs, crank start, no glow plugs, splash lubrication. Petter engine: 3 hp, run…
6. Bison – 211cc BS170F Diesel Engine
Domain: slashgear.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
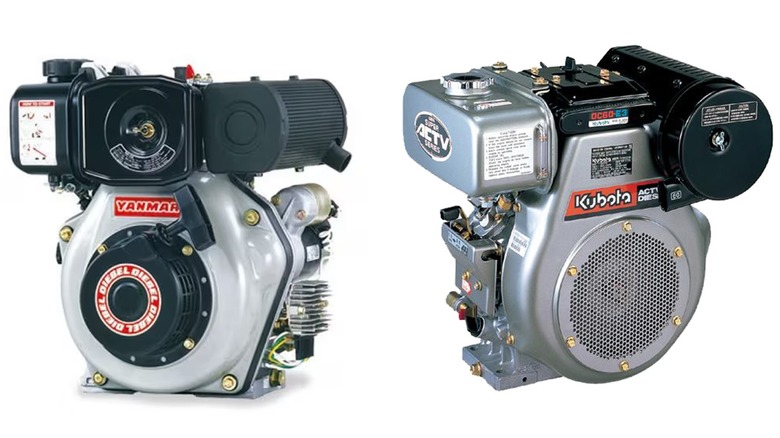
Introduction: Smallest Diesel Engines:
1. Bison 211cc BS170F Diesel Engine
– Power Output: 3-15 horsepower
– Dimensions: 18 x 14.7 x 19.2 inches
– Weight: 55 pounds
– Type: Four-stroke, single-cylinder
2. Kubota OC60-E4 Diesel Engine
– Dimensions: 15.9 x 18.1 x 18 inches
– Weight: 84 pounds
– Type: Single-cylinder
3. Yanmar L48N Diesel Engine
– Dimensions: 13 x 15 x 16.5 inches
– We…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for smallest diesel engine
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Diesel Engine Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of small diesel engines, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and innovation—exemplified by products like the BISON BS170F and YANMAR 3JH40—businesses can ensure they acquire engines that not only meet operational demands but also adhere to stringent environmental regulations. These engines offer significant advantages, including high fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and the versatility needed for a variety of applications, from agriculture to marine use.
Furthermore, leveraging partnerships with reputable manufacturers can enhance supply chain reliability and reduce lead times. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local market needs and infrastructure when making sourcing decisions.
As the demand for efficient and compact diesel solutions grows, staying ahead of technological advancements will be crucial. Investing in strategic sourcing today will position your business for success in the evolving landscape of small diesel engines. We encourage you to engage with trusted suppliers, explore innovative products, and capitalize on the opportunities that lie ahead.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.