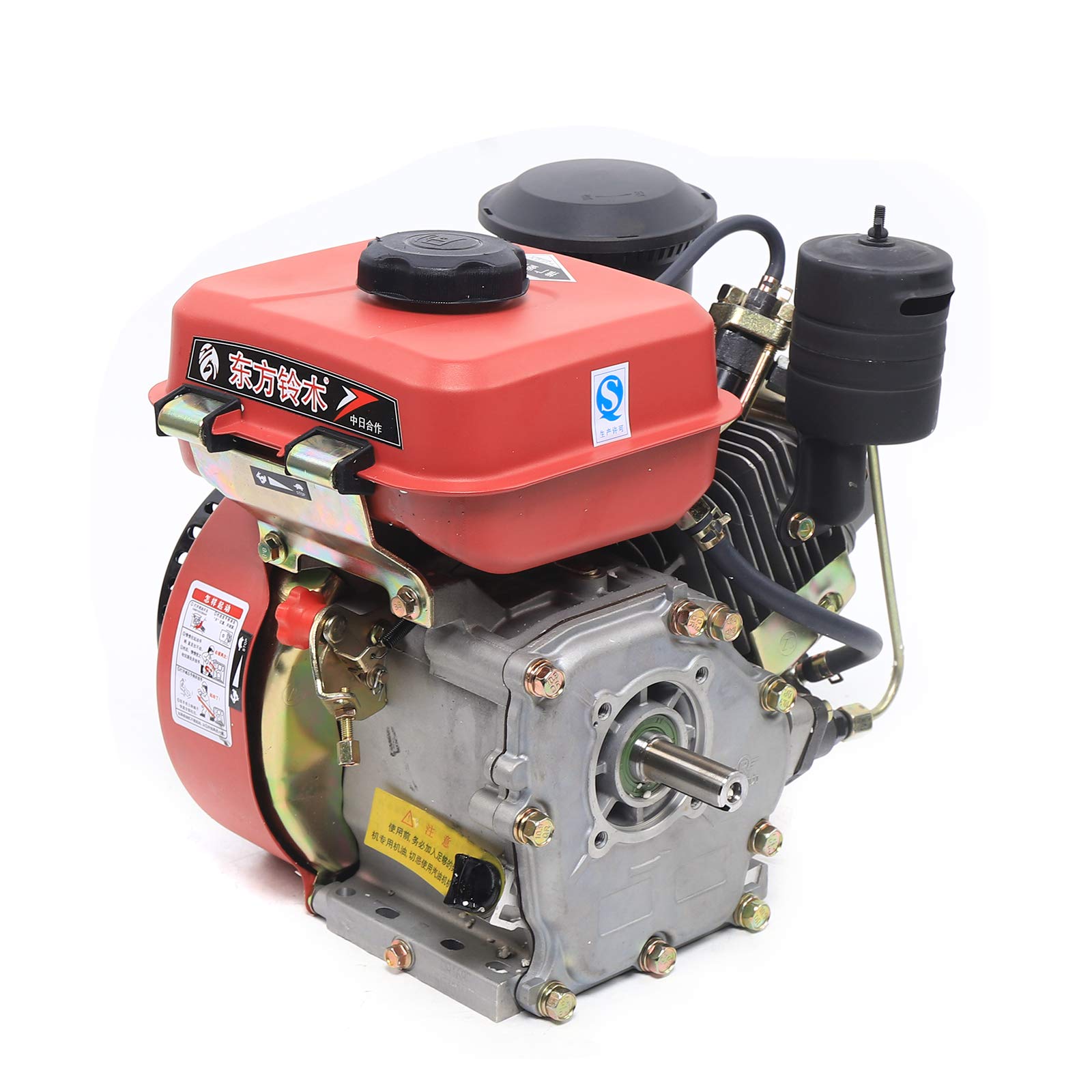
How to Source Small Diesel Engines Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small diesel engines
Navigating the global market for small diesel engines presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary hurdles is sourcing reliable engines that meet specific operational demands while ensuring compliance with regional regulations. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of small diesel engines, including various types, their applications across industries, and critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
In addition to detailed specifications and performance metrics, we delve into essential topics such as cost analysis, supplier vetting processes, and installation considerations. By addressing these elements, we aim to empower international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their unique business needs.
Whether you are looking for robust engines for agricultural machinery in Brazil, durable options for construction equipment in Vietnam, or efficient power solutions for transportation in the Middle East, this guide is designed to enhance your understanding of the small diesel engine market. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you will be equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing and implementing small diesel engines effectively, ensuring that your investments yield optimal returns.
Understanding small diesel engines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Diesel Engines | Small size, lightweight, often turbocharged | Small construction equipment, generators | Pros: High power-to-weight ratio, fuel-efficient. Cons: Limited torque at low RPMs. |
| Marine Diesel Engines | Designed for marine environments, corrosion-resistant materials | Boats, ships, and offshore equipment | Pros: Durable, designed for continuous operation. Cons: Higher maintenance costs due to harsh conditions. |
| Industrial Diesel Engines | Robust construction, high torque output | Manufacturing, heavy machinery | Pros: Long-lasting, can handle heavy loads. Cons: Typically more expensive, larger footprint. |
| Portable Diesel Engines | Mobile, often equipped with a frame for easy transport | Construction sites, outdoor events | Pros: Versatile, easy to move. Cons: May sacrifice power for portability. |
| Repower Diesel Engines | Engine kits for retrofitting older vehicles, often factory-built | Vehicle restoration, fleet upgrades | Pros: Modern technology in older platforms, emissions compliant. Cons: Installation complexity, may need additional components. |
What Are the Characteristics of Compact Diesel Engines for B2B Buyers?
Compact diesel engines are characterized by their lightweight design and high power output relative to size. They are often turbocharged, providing enhanced efficiency and performance. These engines are commonly used in small construction equipment and portable generators, making them ideal for businesses that require reliable, mobile power solutions. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should assess the engine’s fuel efficiency and power delivery characteristics, particularly how it performs at varying RPMs.
Why Are Marine Diesel Engines Essential for B2B Applications?
Marine diesel engines are specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions of marine environments, featuring corrosion-resistant materials and robust construction. They are widely used in boats, ships, and offshore equipment, where reliability and durability are paramount. Buyers should consider the long-term maintenance costs and the engine’s ability to operate continuously under load, ensuring it meets the demands of their marine applications.
How Do Industrial Diesel Engines Support Heavy Machinery Operations?
Industrial diesel engines are known for their durability and high torque output, making them suitable for applications in manufacturing and heavy machinery. These engines are built to last and can handle substantial loads, which is crucial for businesses that rely on consistent performance in demanding environments. B2B buyers should evaluate the engine’s lifespan and operational costs, as well as its compatibility with existing machinery.
What Advantages Do Portable Diesel Engines Offer for Construction?
Portable diesel engines are designed for mobility and versatility, often featuring a frame for easy transport. They are commonly used at construction sites and outdoor events where power is needed away from traditional sources. While they offer significant flexibility, buyers must weigh the trade-off between portability and power, ensuring the engine meets the specific demands of their operations without compromising performance.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Repower Diesel Engines?
Repower diesel engines are factory-built kits designed for retrofitting older vehicles, allowing businesses to modernize their fleets with updated technology. These engines are often emissions compliant, making them suitable for various regulatory environments. Buyers should consider the complexity of installation and the potential need for additional components, as well as the benefits of integrating modern engine technology into older platforms to enhance performance and efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of small diesel engines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of small diesel engines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Tractors and agricultural equipment | Enhanced power and fuel efficiency for field operations | Engine durability, fuel type compatibility, and service support |
| Construction | Generators and construction machinery | Reliable power supply for tools and equipment on-site | Emission standards, maintenance availability, and load capacity |
| Transportation & Logistics | Delivery trucks and light commercial vehicles | Improved torque for heavy loads and better fuel economy | Engine size, weight, and integration with existing vehicle systems |
| Mining | Haul trucks and excavators | Robust performance in harsh environments and low fuel costs | Engine cooling systems, maintenance schedules, and warranty terms |
| Marine | Small vessels and fishing boats | Efficient power for propulsion and onboard systems | Saltwater resistance, engine weight, and regulatory compliance |
How Are Small Diesel Engines Used in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, small diesel engines power tractors and various farming equipment, facilitating essential tasks such as plowing, planting, and harvesting. Their high torque and fuel efficiency enable farmers to operate machinery effectively, even in challenging terrains. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should consider engine durability and the availability of local service support to minimize downtime during peak agricultural seasons.
What Role Do Small Diesel Engines Play in Construction?
Small diesel engines are integral to construction machinery, such as generators and compact excavators. They provide a reliable power source for tools and equipment, ensuring consistent productivity on construction sites. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe must prioritize compliance with local emissions standards and consider the maintenance availability of these engines to ensure long-term operational success.
How Are Small Diesel Engines Beneficial in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics industry, small diesel engines are commonly used in delivery trucks and light commercial vehicles. Their design offers improved torque, making them suitable for carrying heavy loads over long distances while maintaining better fuel economy. B2B buyers from regions like Brazil should focus on engine size and weight, ensuring compatibility with existing vehicle systems to optimize fleet performance.
Why Are Small Diesel Engines Essential in Mining?
Mining operations rely on small diesel engines for powering haul trucks and excavators, where robust performance is crucial in harsh conditions. These engines are designed to provide efficient power while minimizing fuel costs, which is vital for the profitability of mining operations. When sourcing engines for mining applications, buyers should evaluate cooling systems, maintenance schedules, and warranty terms to mitigate operational risks.
How Do Small Diesel Engines Enhance Marine Applications?
In the marine sector, small diesel engines are utilized in small vessels and fishing boats, providing the necessary power for propulsion and onboard systems. Their efficiency and reliability are key for commercial fishing operations that depend on consistent performance in variable sea conditions. Buyers in this industry should consider factors such as saltwater resistance and regulatory compliance to ensure the longevity and legality of their marine engines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small diesel engines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible Components for Small Diesel Engines
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing compatible components for small diesel engines. When purchasing an engine, critical components such as fuel pumps, filters, and electrical harnesses may not be included. This can lead to compatibility issues, increased downtime, and unexpected costs as buyers scramble to find the right parts from different suppliers. Additionally, the lack of clear guidance on compatibility can result in misalignment between engine specifications and the auxiliary systems they need to integrate with, causing further complications during installation.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is essential to work with a trusted engine manufacturer that provides a comprehensive package that includes all necessary components. For instance, choosing suppliers like Cummins that offer a complete engine kit can simplify the procurement process. These kits typically come with installation guides and customer support to ensure compatibility with vehicle-specific components. Additionally, buyers should leverage online tools or consult with technical experts to verify compatibility and specifications before making a purchase. Establishing a relationship with a reliable distributor who can offer ongoing support and access to OEM parts will also streamline the sourcing process and reduce the risk of installation errors.
Scenario 2: Navigating Emission Compliance Regulations for Small Diesel Engines
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in regions with stringent emission regulations often encounter significant challenges when it comes to ensuring compliance for small diesel engines. Different countries and states have varying requirements, and failing to meet these can lead to legal issues, fines, and a damaged reputation. For instance, buyers may purchase an engine that is not compliant with local laws, only to find themselves unable to use it in their applications, resulting in wasted investment and operational delays.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers must conduct thorough research on the specific emission standards applicable in their region before making a purchase. This includes understanding both national and local regulations, as well as any potential changes on the horizon. Working with suppliers who provide clear documentation regarding compliance and emissions testing is critical. Buyers should also consider engines that are designed with flexibility for emissions control, such as those that can accommodate after-treatment systems. Engaging with regulatory consultants or industry associations can provide additional insights into compliance strategies, ensuring that the engines selected meet all necessary requirements and minimize the risk of future penalties.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Scenario 3: Ensuring Efficient Maintenance and Support for Small Diesel Engines
The Problem: Once a small diesel engine is operational, maintaining its performance and longevity can become a daunting task for B2B buyers. Many encounter difficulties in accessing parts for maintenance or finding qualified technicians who understand the intricacies of diesel engines. This can lead to prolonged downtimes and increased operational costs, as businesses struggle to keep their equipment running smoothly in demanding environments.
The Solution: Establishing a proactive maintenance plan is crucial for optimizing the performance of small diesel engines. Buyers should choose engines from manufacturers that offer extensive support networks, including easy access to spare parts and service manuals. For example, opting for brands that provide online resources, like Cummins, can be beneficial as they often have dedicated support teams and comprehensive documentation available. Additionally, training internal staff or partnering with certified service providers can enhance maintenance capabilities. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program that includes regular inspections, oil changes, and filter replacements will not only improve engine reliability but also extend its lifespan, ultimately saving costs in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small diesel engines
What Are the Key Materials Used in Small Diesel Engines?
When selecting materials for small diesel engines, it is crucial to consider properties that directly affect performance, durability, and overall efficiency. Here, we analyze four common materials: cast iron, aluminum alloys, stainless steel, and composite materials. Each material has unique properties and implications for international buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Cast Iron Benefit Small Diesel Engines?
Cast iron is a traditional choice for engine blocks due to its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Key properties include high tensile strength and good thermal conductivity, which help manage engine heat.
Pros: Cast iron is durable and cost-effective, making it suitable for mass production. Its ability to absorb vibrations contributes to smoother engine operation.
Cons: The weight of cast iron can be a drawback, affecting the overall vehicle weight and fuel efficiency. Additionally, its manufacturing complexity can lead to higher production costs in some regions.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with various engine media, including oil and fuel, but may require protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers should also consider local manufacturing capabilities and the availability of cast iron components in their regions.
What Advantages Do Aluminum Alloys Offer for Engine Components?
Aluminum alloys are increasingly popular in small diesel engines for components like cylinder heads and pistons due to their lightweight nature and good thermal properties. Key properties include a lower density compared to cast iron and excellent corrosion resistance.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Pros: The reduced weight of aluminum alloys enhances fuel efficiency and performance. They also allow for better heat dissipation, which is vital for engine longevity.
Cons: While aluminum is less expensive than some advanced materials, it can be more costly than cast iron. Additionally, aluminum components may require more complex manufacturing processes, which could impact lead times.
Impact on Application: Aluminum alloys are compatible with various fuels and lubricants but may not be suitable for high-stress applications without additional treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards for quality and performance. Regions with high humidity or saltwater exposure may require specific aluminum grades to prevent corrosion.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Exhaust and Fuel Systems?
Stainless steel is commonly used for exhaust systems and fuel lines due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance. Key properties include high tensile strength and resistance to oxidation.
Pros: Stainless steel offers durability and longevity, reducing maintenance costs. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it a preferred choice for visible components.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel can be a barrier for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various exhaust gases and fuels, making it a versatile choice for engine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding emissions is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of stainless steel components in their local markets.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Engine Performance?
Composite materials, including carbon fiber and reinforced plastics, are emerging in small diesel engines, particularly for non-structural components. Key properties include lightweight characteristics and high strength-to-weight ratios.
Pros: Composites can significantly reduce weight, improving fuel efficiency and performance. They also offer design flexibility, allowing for complex shapes that can enhance aerodynamics.
Cons: The cost of composite materials can be significantly higher than traditional materials, and their manufacturing processes can be complex and time-consuming.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in components that require high strength but low weight, such as intake manifolds.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the availability of composite materials in their regions and any specific regulations regarding their use in automotive applications.
Summary Table of Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for small diesel engines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks, crankshafts | Durable and cost-effective | Heavy and complex manufacturing | Low |
| Aluminum Alloys | Cylinder heads, pistons | Lightweight and good heat dissipation | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Exhaust systems, fuel lines | Corrosion-resistant and durable | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Composite Materials | Intake manifolds, non-structural parts | Lightweight and design flexibility | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for small diesel engines, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small diesel engines
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Small Diesel Engines?
The manufacturing process for small diesel engines consists of several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the engine’s performance, durability, and compliance with international standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Small Diesel Engines?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically aluminum and cast iron, which are essential for the engine block and cylinder heads. Advanced techniques such as metallurgical analysis and chemical testing are used to verify the composition and strength of these materials. After selection, materials are cut to size, cleaned, and treated to remove impurities, ensuring optimal performance during the engine’s lifecycle.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Small Diesel Engine Components?
Forming processes include casting, machining, and forging. For instance, the engine block may be produced through sand casting, which allows for intricate designs and shapes. Once cast, components undergo precision machining to achieve exact tolerances, ensuring proper fit and function. Forging is often employed for critical components like crankshafts and connecting rods, enhancing their strength and fatigue resistance. These processes are essential for achieving the high-performance standards expected from small diesel engines.
How Is the Assembly of Small Diesel Engines Conducted?
During the assembly phase, components are meticulously put together following strict protocols. Each engine is assembled in a clean environment to minimize contamination risks. Teams of skilled technicians utilize specialized tools and fixtures to ensure precision in alignment and torque specifications. The assembly process may include the installation of critical components such as fuel injectors, turbochargers, and electronic control units. A systematic approach is essential to maintain consistency and quality across production batches.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Small Diesel Engines?
Finishing processes involve surface treatments, painting, and final inspections. Components may undergo processes such as anodizing or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance. These treatments not only improve aesthetics but also contribute to the longevity of the engine. Final inspections, including visual checks and measurements, are conducted to ensure that all specifications have been met before the engines are packaged and shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Small Diesel Engines?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of small diesel engines, ensuring reliability and compliance with international standards. The most commonly recognized standard is ISO 9001, which establishes guidelines for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that a manufacturer adheres to rigorous quality control processes and is committed to continuous improvement.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO certifications, B2B buyers should look for industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European safety and environmental regulations, and API certifications for performance and emissions standards. These certifications serve as a testament to the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and adherence to international norms.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process, encompassing In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), Incoming Quality Control (IQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Tests may include dimensional checks and material composition analysis to ensure compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, IPQC monitors critical processes to ensure that each step meets predefined quality standards. This can include real-time measurements and adjustments during machining and assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection stage involves comprehensive testing of the completed engine, including performance tests, emissions checks, and durability assessments. This step ensures that the engine meets all operational and regulatory requirements before leaving the facility.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Small Diesel Engines?
Common testing methods for small diesel engines include dynamometer testing, where the engine’s performance is measured under various load conditions. Emissions testing is also critical, particularly for compliance with environmental regulations. Additionally, non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, such as ultrasonic or X-ray inspections, are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take a proactive approach to verify supplier quality control practices. Conducting audits of manufacturing facilities is an effective way to assess compliance with quality standards and certification requirements. Additionally, requesting quality assurance reports, inspection records, and certifications can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Supplier Verification?
Engaging third-party inspection services adds an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct thorough evaluations of manufacturing processes, materials, and finished products. Their reports can validate the supplier’s claims regarding quality and compliance, giving buyers confidence in their purchasing decisions.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of regional regulations and compliance requirements that may vary significantly between markets. For instance, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may face different emissions standards and safety regulations. Understanding these nuances is crucial for ensuring that the engines purchased meet local regulations and can be operated legally and efficiently in their respective markets.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for small diesel engines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, industry standards, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small diesel engines’
Introduction
Sourcing small diesel engines requires a strategic approach to ensure that your procurement aligns with your operational needs and regulatory requirements. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for international B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of engine specifications, supplier evaluations, and compliance considerations. By following these steps, you can make informed purchasing decisions that will enhance your operations.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Identify the specific power output, torque requirements, and displacement needed for your applications. Consider factors such as engine weight, size, and intended use—whether for vehicles, industrial equipment, or power generation.
- Power Requirements: Determine the horsepower and torque needed for optimal performance.
- Engine Type: Decide between naturally aspirated or turbocharged engines based on your performance needs.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Certification Standards
Understanding compliance and certification standards is critical when sourcing diesel engines, especially in different regions. Ensure that the engines meet local emissions regulations and industry standards to avoid legal complications.
- Emissions Regulations: Check for compliance with EPA or CARB standards, depending on your region.
- Certification Documentation: Request copies of certifications to validate compliance with local and international standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Review their company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This step ensures that the supplier is reliable and capable of meeting your needs.
- Supplier History: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the diesel engine market.
- Customer Reviews: Assess feedback from other B2B buyers to gauge supplier performance and service quality.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
After-sales support can significantly impact your operational efficiency. Review the warranty terms and the level of technical support provided by the supplier to ensure that you have recourse in case of issues.
- Warranty Coverage: Understand what the warranty covers, including labor and parts.
- Technical Support Availability: Confirm the supplier’s responsiveness and availability of technical assistance post-purchase.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline all costs involved. This should include the price of the engine, shipping, taxes, and any additional components or services.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the quotation provides a clear breakdown of all associated costs.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly impact your budget.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Evaluate potential risks associated with the procurement process, including supplier reliability, market volatility, and logistical challenges. This assessment will help you identify and mitigate risks before finalizing your purchase.
- Contingency Planning: Develop contingency plans for potential supply chain disruptions.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends that may affect pricing and availability.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Monitor Delivery
Once you are satisfied with your supplier and terms, finalize the purchase. Monitor the delivery process closely to ensure that the engines arrive on time and in the expected condition.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
- Delivery Schedule: Confirm the expected delivery date and any potential delays.
- Quality Checks: Plan for quality inspections upon receipt to ensure compliance with your specifications.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the procurement process for small diesel engines, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and reduced risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small diesel engines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Small Diesel Engines?
When analyzing the cost structure for small diesel engines, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
Materials represent the most significant portion of the cost. High-quality steel, aluminum, and specialized components like fuel injectors and turbochargers contribute to this expense. Suppliers often source materials in bulk, which can lead to cost reductions; however, fluctuations in raw material prices can impact overall pricing.
Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor involved in the manufacturing process. This includes assembly, quality inspection, and administrative tasks. Labor rates can vary significantly based on geographical location, which is particularly relevant for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses not directly tied to the production process, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. This is often a fixed cost that can be spread over larger production volumes, influencing the price per unit.
Tooling costs are associated with the equipment necessary for production. Custom tooling for specialized engine designs can increase initial costs but can be amortized over larger production runs.
Quality Control (QC) is critical in the engine manufacturing process. Rigorous testing and compliance with international standards ensure reliability and performance. Investing in QC may raise upfront costs but can lead to reduced warranty claims and increased customer satisfaction.
Logistics costs are incurred in transporting engines from the manufacturing facility to the buyer’s location. This includes shipping, customs duties, and insurance. The choice of Incoterms can significantly influence these costs, with options like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affecting overall pricing.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Profit margin is the final component, which varies by manufacturer based on their market positioning, brand reputation, and sales strategy. Understanding these components helps buyers anticipate the total cost of ownership beyond the initial purchase price.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Small Diesel Engine Pricing?
Pricing for small diesel engines is heavily influenced by order volume and customization requests. Suppliers often provide tiered pricing, where the cost per unit decreases as order quantities increase. This is particularly advantageous for businesses looking to source engines for multiple units or large-scale projects.
Customization, such as specific engine specifications or additional features, can also impact pricing. While tailored solutions may meet specific operational needs, they typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
What Role Do Quality Certifications and Supplier Factors Play in Pricing?
Quality certifications, such as ISO or EPA compliance, can significantly influence pricing. Engines that meet stringent environmental standards often command higher prices due to the additional costs associated with compliance. Buyers should inquire about certifications to ensure that the engines meet local regulations, especially in regions with strict emissions standards.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Supplier factors, including their reputation, experience, and after-sales support, also play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge higher prices but offer better warranties and customer service, which can be invaluable for long-term operational success.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Negotiate Better Prices for Small Diesel Engines?
International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should employ strategic negotiation techniques to achieve cost-efficient sourcing of small diesel engines.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, fuel efficiency, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Leverage Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can create competitive pressure, leading to better pricing and terms.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce immediate financial strain, which can be a critical factor for businesses in developing markets.
-
Explore Local Assembly Options: Sourcing engines closer to the point of use can reduce logistics costs. Some suppliers may offer local assembly or support, which can further optimize expenses.
-
Be Aware of Currency Fluctuations: For international transactions, currency exchange rates can affect costs. Consider hedging options or negotiating prices in a stable currency.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind About Pricing Nuances for International Transactions?
International buyers must navigate various pricing nuances, including tariffs, import duties, and customs regulations that can affect the final cost of small diesel engines. It’s essential to research these factors thoroughly to avoid unexpected expenses.
Furthermore, understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, impacting the overall cost structure.
Finally, always seek a detailed breakdown of costs from suppliers to ensure transparency and to facilitate informed decision-making. This approach will help buyers establish a solid foundation for successful negotiations and sourcing strategies in the competitive landscape of small diesel engines.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small diesel engines With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Small Diesel Engines
In the quest for efficient power solutions, small diesel engines have been a popular choice across various industries. However, as technology evolves and sustainability becomes a priority, it is crucial for B2B buyers to consider alternative power sources. This analysis compares small diesel engines with electric motors and gasoline engines, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Comparison Aspect | Small Diesel Engines | Electric Motors | Gasoline Engines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, suitable for heavy loads and rugged terrains. | Instant torque, ideal for urban applications with lower load. | Good acceleration and performance, but less efficient under heavy loads. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; lower fuel costs over time. | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs. | Generally lower upfront cost; higher fuel costs and maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation and adaptation for vehicles. | Often easier to integrate with existing systems; requires charging infrastructure. | Widely understood technology; easy to implement in many existing systems. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance; parts may be costly. | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts lead to reduced downtime. | Moderate maintenance; parts are relatively affordable and widely available. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for heavy-duty applications like construction and agriculture. | Best for urban environments and light-duty applications. | Suitable for personal vehicles and light commercial use. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Electric Motors
Electric motors are gaining traction as a viable alternative to small diesel engines, particularly in urban settings where emissions are a concern. They provide instant torque and are highly efficient for light-duty applications. The operational costs are lower due to minimal maintenance needs and the absence of fuel expenses. However, the initial investment can be significant, and businesses must consider the availability of charging infrastructure. Additionally, electric motors may not perform as well under heavy loads compared to diesel engines.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Gasoline Engines
Gasoline engines offer a more traditional alternative, often with lower upfront costs than diesel engines. They are relatively easy to implement in existing systems, making them a popular choice for personal vehicles and light commercial use. While they provide good acceleration, their efficiency diminishes under heavy loads, making them less suitable for demanding applications. Furthermore, gasoline engines typically incur higher operational costs over time due to fuel consumption and maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing the right power solution involves assessing the specific needs of your business. Consider factors such as the intended application, operational costs, and maintenance capabilities. Small diesel engines are ideal for heavy-duty tasks requiring robust performance, while electric motors may serve urban environments where emissions and efficiency are top priorities. Gasoline engines offer a middle ground but may not be as efficient in demanding scenarios. By evaluating these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small diesel engines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Small Diesel Engines?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of small diesel engines is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating options for various applications. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Horsepower (HP)
Horsepower indicates the engine’s power output. This measurement is vital for determining whether an engine can meet the operational demands of specific applications, such as agricultural machinery or small commercial vehicles. A higher horsepower rating typically translates to better performance and efficiency, making it essential for buyers to match the horsepower to their operational requirements. -
Torque
Torque measures the rotational force produced by the engine, expressed in pound-feet (lb-ft) or Newton-meters (N•m). This specification is particularly important for applications requiring heavy lifting or towing capabilities. Understanding the torque curve can help buyers assess how well the engine will perform under load, influencing decisions related to vehicle design and operational efficiency. -
Displacement
Engine displacement, measured in liters (L) or cubic inches, refers to the total volume of all the cylinders in the engine. Displacement is directly related to the engine’s power output and fuel efficiency. For buyers, knowing the displacement helps in selecting engines that balance power needs with fuel consumption, especially in markets sensitive to fuel costs. -
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio indicates how much the engine compresses the air-fuel mixture before ignition. A higher compression ratio often leads to improved efficiency and power output. Buyers should consider this specification as it affects fuel choice, combustion efficiency, and overall engine performance. -
Aspiration Type
The aspiration type, whether naturally aspirated or turbocharged, significantly impacts engine performance and efficiency. Turbocharged engines can produce more power from a smaller displacement, making them attractive for applications where space and weight are considerations. Understanding the aspiration type helps buyers evaluate the suitability of engines for their specific use cases. -
Fuel System
The fuel system type—mechanical or electronic—affects the engine’s efficiency, emissions, and maintenance needs. Electronic fuel systems generally offer better fuel management and emissions control, which can be a decisive factor for buyers concerned about regulatory compliance and long-term operating costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Small Diesel Engine Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the small diesel engine market. Here are several key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of small diesel engines, OEMs are critical for ensuring compatibility and quality. Buyers often prefer OEM parts for reliability and performance, especially in regulated markets. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are not overcommitting resources. Negotiating MOQs can lead to cost savings, especially for bulk purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specified products. It is a standard practice in B2B procurement, allowing buyers to compare offers and make informed decisions. Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline the purchasing process and enhance supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is crucial for effective supply chain management. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and the completion of the product. For buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and inventory management, especially in industries where engine availability can directly impact production schedules. -
Warranty
A warranty is a manufacturer’s promise to repair or replace a product if necessary within a specified period. Knowing the warranty terms is essential for buyers, as it affects long-term operational costs and risk management, particularly in markets with stringent reliability standards.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their supply chains, and ensure they are investing in the right small diesel engines for their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small diesel engines Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Small Diesel Engines Sector?
The small diesel engines sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by global demand for efficiency and sustainability. Key market dynamics include a growing preference for diesel engines due to their superior fuel efficiency and torque characteristics compared to gasoline engines. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing regions such as Africa and South America, where diesel engines are essential for agriculture, transportation, and industrial applications.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping sourcing strategies. The integration of advanced telematics and IoT in engine monitoring systems allows for improved performance tracking and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Furthermore, international buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces to source engines and components, enhancing accessibility and streamlining procurement processes.
Additionally, geopolitical factors and trade agreements impact sourcing strategies. Buyers must navigate tariffs and import regulations, which can vary significantly by region, affecting pricing and availability. Countries in the Middle East and Europe are focusing on localizing supply chains to mitigate risks associated with global supply disruptions. This trend emphasizes the need for international buyers to establish strong partnerships with reliable suppliers that can provide consistent quality and support.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Small Diesel Engines Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of small diesel engines. As environmental regulations tighten globally, manufacturers are under pressure to reduce emissions and improve the overall environmental impact of their products. International buyers are increasingly seeking engines that comply with stringent emissions standards, which not only ensures regulatory compliance but also enhances their brand reputation in environmentally conscious markets.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for suppliers that prioritize responsible sourcing practices, including fair labor conditions and sustainable materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming vital for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, the use of recycled materials in engine components is gaining traction, enabling manufacturers to minimize waste and reduce their carbon footprint.
By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with consumer preferences for greener solutions, thus enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Small Diesel Engines in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of small diesel engines dates back to the late 19th century, with significant advancements occurring throughout the 20th century. Initially, these engines were predominantly used in industrial and agricultural applications due to their durability and efficiency. The post-World War II era saw a surge in demand as economies expanded, leading to innovations in engine design and manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener technologies. The introduction of common rail fuel injection systems and turbocharging has significantly improved performance metrics, making small diesel engines more attractive for a wider range of applications, including light-duty vehicles and commercial equipment.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the technological advancements that have shaped the current market landscape, guiding them in making informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small diesel engines
-
How do I ensure the quality of small diesel engines from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking their certifications, production capacity, and quality assurance processes. Request samples or visit their facilities if possible. It’s also wise to seek references from other B2B buyers who have previously sourced from them. Additionally, consider implementing a third-party inspection service to verify the quality before shipment. Establish clear quality standards in your contracts to safeguard your interests. -
What are the key specifications to look for when sourcing small diesel engines?
Key specifications include horsepower, torque, engine size, and fuel efficiency. Ensure that the engine meets your specific application requirements, such as weight capacity and emissions standards. Consider additional features like turbocharging, electronic control systems, and compatibility with existing machinery. It’s also important to review warranty terms and after-sales support options, as these can significantly impact the overall value and usability of the engine. -
What is the best way to negotiate payment terms with suppliers for small diesel engines?
When negotiating payment terms, prioritize establishing a mutually beneficial agreement. Common practices include a deposit upfront with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Consider using letters of credit to mitigate risk. Always clarify the implications of payment delays on delivery timelines and discuss potential discounts for bulk orders. Flexibility in payment terms can strengthen your relationship with the supplier and may lead to better pricing and service. -
How can I customize small diesel engines to fit my specific needs?
Customization options often depend on the manufacturer’s capabilities. Discuss your specific requirements, such as power output, size, and additional features like integrated cooling systems or emissions modifications. Be clear about your application to help the manufacturer recommend the best configuration. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions, but ensure that any modifications comply with local regulations to avoid compliance issues later. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for small diesel engines?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, often influenced by production capabilities and market demand. Typically, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs due to their production processes, while smaller or more niche suppliers may accommodate lower orders. When negotiating, communicate your needs clearly and explore options for flexibility, especially if you are a new buyer. Establishing a good relationship with the supplier can also lead to more favorable terms. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing small diesel engines?
Logistics involves several factors, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping regulations, especially concerning heavy machinery. Be prepared for potential delays in customs and ensure all necessary documentation is in order to avoid fines or confiscation. Consider the total landed cost, including shipping, tariffs, and insurance, to accurately assess the investment. -
How do I handle warranty claims for small diesel engines sourced internationally?
Handling warranty claims internationally can be complex. Start by reviewing the warranty terms provided by the supplier, including the process for filing claims. Maintain detailed records of your purchase, including invoices and communication with the supplier. If a claim arises, contact the supplier directly with all necessary documentation. Be aware of the logistics involved in returning defective products, which may include shipping costs and potential delays. -
What should I know about compliance with international regulations for small diesel engines?
Compliance varies by region and is crucial for legal operation. Research the specific emissions standards and certifications required in your target market, such as EPA or CARB regulations in the U.S. or EU standards in Europe. Ensure that the engines you source meet these requirements to avoid penalties and operational issues. Discuss compliance with the supplier and request documentation to confirm adherence to relevant regulations before making a purchase.
Top 6 Small Diesel Engines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carroll Stream – Small Gas and Diesel Engines
Domain: carrollstream.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Carroll Stream Motor Company offers a wide selection of small gas and diesel engines suitable for various applications, including lawn mowers, generators, water pumps, and pressure washers. Key features include:
– Fast shipping: Most orders ship same day if ordered before 1 PM EST.
– Free shipping on most engines.
– Engine types: Gasoline and diesel options, with benefits tailored to specific need…
2. Rehlko – Diesel Engines
Domain: engines.rehlko.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Diesel Engines | Rehlko Engines | 34 Results | Kohler Engines is now Rehlko | Parts & Service | Global Parts Lookup | Diesel Parts | Genuine Parts | Extended Warranty (US only) | Diesel Engine Fluids (US only) | Digital Solutions | Customer Support | Find a Dealer | Become a Dealer | Dealer Training | Rehlko Merchandise | About Us | Leadership Team | Press Room | Careers | Sustainability Report
3. Cummins – 4BT, VW – 1.9 TDI, Isuzu – 4FB1
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Cummins 4BT: A small, old-school, all-mechanical diesel engine. Popular for diesel-swapping applications.
2. VW 1.9 TDI: Known for reliability, fuel efficiency, and capability of making reasonable power with modifications.
3. Isuzu 4FB1: Produces around 50hp, known for reliability and longevity, with some users reporting over 800k miles.
4. Isuzu 2.2 liter: Larger variant of Isuzu engines, a…
4. Suzuki – E08A Diesel Engine
Domain: carbuzz.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Product Name: E08A Diesel Engine
Engine Type: 0.8L turbo-diesel I2
Power Output: 32-47 hp
Torque: 55-95 lb-ft
Bore x Stroke: 3.03 x 3.35 inches
Compression Ratio: 15-16:1
Production Years: 2016-2020
Primary Market: India, with some sales in the Philippines
Applications: Suzuki Super Carry, Suzuki Celerio
Fuel Economy: Up to 65 mpg (for Celerio)
Transmission: 5-speed manual
Engine Features: Four-st…
5. Yanmar – Air-Cooled Diesel Engines
Domain: yanmarengines.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Yanmar’s air-cooled diesel engines are single-cylinder, direct injection engines that comply with EPA and CARB exhaust emission standards. They feature a counter-balancing system for smooth high-speed operation and offer multiple PTO shaft options along with electric or recoil starting. The engines are categorized into three series: LN Series (Export Only), LV Series (EU Stage 5), and LW Series (E…
6. Kubota – Super Mini Series Diesel Engines
Domain: engine.kubota.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Kubota – Super Mini Series Diesel Engines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small diesel engines
As the demand for small diesel engines continues to rise globally, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing has become essential for B2B buyers. By leveraging reliable suppliers and understanding market dynamics, businesses can secure high-quality engines that meet their operational needs while optimizing costs. The importance of choosing the right engine cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts performance, fuel efficiency, and overall project success.
Investing in engines like the Cummins R2.8 Turbo Diesel illustrates the value of sourcing products that come with comprehensive support and installation resources. This not only minimizes downtime but also enhances the potential for successful integration into various applications, from commercial vehicles to industrial equipment.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer robust customer support and technical resources. By doing so, they can ensure that their sourcing strategies align with the evolving needs of their markets. Engage with suppliers today to explore the best options for your business and drive future growth in the competitive landscape of small diesel engines.

Illustrative image related to small diesel engines
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.