How to Source Sealed Bearing Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sealed bearing
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing high-quality sealed bearings can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse and demanding environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Sealed bearings play a crucial role in machinery performance and longevity, offering superior protection against contaminants while minimizing maintenance needs. However, navigating the global market requires a keen understanding of the different types available, their specific applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of sealed bearings, exploring various types such as contact and non-contact seals, and their suitability for different operational contexts. We will also cover key considerations in supplier selection, cost factors, and best practices for ensuring long-term reliability and performance of your bearings. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Whether you are in Vietnam, Brazil, or any other region, understanding the nuances of sealed bearings will enable you to optimize your procurement strategy and ensure your machinery operates at peak performance, regardless of the environmental challenges you face.
Understanding sealed bearing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Sealed | Seals make light contact with the inner ring for maximum protection | Heavy machinery, outdoor equipment | Pros: Superior contamination protection. Cons: Slightly increased friction. |
| Non-Contact Sealed | No physical contact between the seal and inner ring, reducing friction | Electric motors, precision instruments | Pros: Lower friction and heat generation. Cons: Moderate contaminant protection. |
| Dual Sealed | Features seals on both sides for enhanced protection | Agricultural equipment, automotive parts | Pros: Excellent sealing from both ends. Cons: Slightly higher cost. |
| Single Sealed | One seal for applications needing protection on one side | Gearboxes, conveyor systems | Pros: Cost-effective solution with decent protection. Cons: Limited sealing capability. |
| Shielded Sealed | Incorporates a metal shield along with a seal for added protection | Fans, pumps, and appliances | Pros: Balances protection and low friction. Cons: Less effective against fine dust and moisture. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Contact Sealed Bearings?
Contact sealed bearings are designed with seals that make light contact with the inner ring, providing maximum protection against contaminants like dust and moisture. They are ideal for heavy machinery and outdoor equipment, where exposure to harsh environments is common. Buyers should consider the slightly increased friction and heat generation, which may impact energy efficiency in high-speed applications. However, the enhanced sealing capability often outweighs these concerns, particularly in demanding conditions.
How Do Non-Contact Sealed Bearings Differ?
Non-contact sealed bearings utilize seals that do not touch the inner ring, allowing for lower friction and heat generation. This design is particularly beneficial in electric motors and precision instruments, where efficiency is critical. Buyers should note that while these bearings provide excellent operational smoothness, their contaminant protection is moderate compared to contact seals. Therefore, they are best suited for cleaner environments or applications where lubrication is consistently maintained.
When Should You Consider Dual Sealed Bearings?
Dual sealed bearings come with seals on both sides, offering enhanced protection against contaminants. These bearings are well-suited for agricultural equipment and automotive parts, where exposure to dirt and moisture is prevalent. While the cost may be higher than single-sealed options, the increased durability and reliability can justify the investment, especially in demanding applications where equipment downtime is costly.
What Advantages Do Single Sealed Bearings Offer?
Single sealed bearings feature one seal, making them a cost-effective choice for applications that only require protection on one side, such as gearboxes and conveyor systems. They provide decent protection against contaminants while keeping costs down. Buyers should consider the limitations of this design, as it offers less sealing capability compared to dual sealed options. However, for many standard applications, single sealed bearings present a balanced solution.
Why Choose Shielded Sealed Bearings?
Shielded sealed bearings combine a metal shield with a seal, offering a good balance between protection and low friction. This type is commonly used in fans, pumps, and household appliances, where a mix of efficiency and contamination protection is necessary. Buyers should be aware that while shielded sealed bearings provide decent protection against larger particles, they may not be as effective against fine dust or moisture compared to fully sealed options. This makes them suitable for less demanding environments.
Key Industrial Applications of sealed bearing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Sealed Bearing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery (e.g., tractors, harvesters) | Enhanced durability in harsh environments, reduced downtime | Ensure compatibility with equipment, resistance to dirt and moisture, and maintenance-free operation. |
| Automotive | Wheel hubs and electric motors | Improved reliability and longevity, lower maintenance costs | Look for high-quality seals to prevent contamination and ensure performance under varying loads. |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems and robotic automation | Increased efficiency and reduced operational disruptions | Consider load capacity, speed ratings, and environmental conditions affecting the bearings. |
| Construction | Heavy machinery (e.g., excavators, bulldozers) | Longer service life and reduced maintenance needs | Assess the operating environment and the bearing’s ability to withstand heavy loads and contaminants. |
| Food and Beverage | Processing equipment (e.g., mixers, conveyors) | Compliance with hygiene standards and enhanced reliability | Verify food-grade materials and seals to prevent contamination, ensuring safety and compliance. |
How Are Sealed Bearings Used in Agriculture?
Sealed bearings are integral to agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, which operate in challenging environments filled with dirt, moisture, and debris. These bearings protect internal components from contaminants, ensuring reliable operation and reducing the frequency of maintenance. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America where agricultural practices are vital, sourcing sealed bearings that can withstand harsh conditions is crucial. Buyers should focus on bearings that offer durability and maintenance-free operation, which can significantly reduce downtime and repair costs.
What Role Do Sealed Bearings Play in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, sealed bearings are commonly found in wheel hubs and electric motors. Their design prevents dirt and moisture ingress, which is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity in vehicles. B2B buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe should prioritize high-quality sealed bearings that can handle varying loads and provide consistent performance over time. Ensuring that these bearings are properly sourced can lead to lower maintenance costs and improved reliability, which are critical for automotive manufacturers and suppliers.
How Are Sealed Bearings Beneficial in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing environments often rely on conveyor systems and robotic automation, where sealed bearings play a pivotal role in ensuring smooth operation. These bearings help minimize operational disruptions by providing reliable performance and reducing the need for frequent maintenance. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, it is essential to consider load capacity, speed ratings, and the specific environmental conditions in which these bearings will operate. Selecting the right sealed bearings can enhance efficiency and productivity in manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Why Are Sealed Bearings Important for Construction Machinery?
Heavy machinery used in construction, such as excavators and bulldozers, benefits significantly from sealed bearings due to their ability to withstand harsh operating conditions. These bearings provide extended service life and reduce maintenance requirements, which is vital for construction projects that demand high uptime. Buyers in regions with active construction markets, like Brazil and parts of Africa, should evaluate the load-bearing capacity and the seals’ ability to resist environmental contaminants. Investing in quality sealed bearings can lead to substantial cost savings and operational efficiency.
How Do Sealed Bearings Contribute to the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, sealed bearings are essential for processing equipment, such as mixers and conveyors, where hygiene and reliability are paramount. These bearings prevent contamination from food particles and liquids, ensuring compliance with health standards. For international buyers, particularly those in Europe, sourcing food-grade sealed bearings made from suitable materials is crucial. Ensuring that bearings meet hygiene standards can enhance product safety and operational reliability, which are vital for maintaining consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sealed bearing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Type of Seal for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with choosing between various types of seals when sourcing sealed bearings. With options such as contact seals and non-contact shields, the confusion can lead to selecting a bearing that either underperforms or fails prematurely. For instance, in environments with high exposure to dirt and moisture, a contact seal might be necessary, but if a buyer mistakenly opts for a non-contact shield, they risk contamination, leading to increased maintenance costs and equipment downtime. This decision can significantly impact the operational efficiency and reliability of machinery.
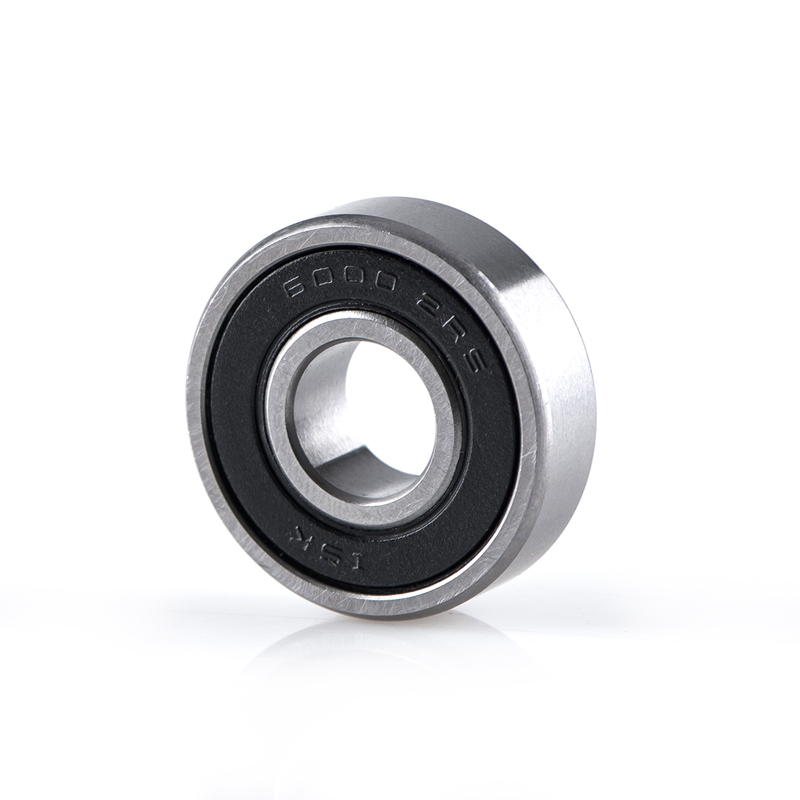
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their specific application requirements, considering factors such as operating environment, expected loads, and speed. It is crucial to collaborate with bearing manufacturers or suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and recommendations based on the intended use. For example, if the application involves outdoor machinery exposed to dust and water, specifying sealed bearings with contact seals (like those marked as “2RS”) will offer superior protection. Additionally, buyers should request samples or trial bearings for testing to ensure that the selected type performs optimally in real-world conditions.
Scenario 2: Unexpected Bearing Failures and Their Impact on Operations
The Problem: Buyers frequently face unexpected failures of sealed bearings, which can lead to significant operational disruptions. These failures often stem from incorrect installation, inadequate lubrication, or the use of bearings that do not meet the specific environmental conditions. In industries like manufacturing or agriculture, such failures can halt production lines, causing costly delays and affecting overall business productivity.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
The Solution: To reduce the risk of bearing failures, it is essential to implement a comprehensive maintenance and monitoring program. Buyers should invest in proper training for their maintenance teams to ensure that bearings are installed correctly and that the sealing integrity is maintained. Utilizing condition monitoring tools can provide real-time data on bearing performance, allowing for timely interventions before failures occur. Furthermore, establishing a relationship with a trusted supplier can provide access to technical support and guidance in selecting bearings that are best suited for specific environmental challenges, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Scenario 3: Balancing Cost and Quality in Sealed Bearings
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are often caught between the dilemma of cost versus quality when procuring sealed bearings. While lower-cost options may seem appealing, they can lead to poor performance, higher failure rates, and increased maintenance costs. This is particularly true for industries operating in harsh environments, where the longevity and reliability of bearings are crucial. Buyers may find themselves paying more in the long run due to frequent replacements and repairs, negating the initial savings.
The Solution: To effectively balance cost and quality, buyers should adopt a value-based procurement strategy. This involves assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront purchase price. Buyers should evaluate supplier reputations, warranty offerings, and the expected lifespan of the bearings based on real-world applications. Engaging in discussions with suppliers about the specific conditions in which the bearings will operate can also lead to recommendations for higher-quality products that may have a higher upfront cost but will ultimately reduce maintenance needs and extend service life. Additionally, consider bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing on high-quality bearings that meet performance requirements. This strategic approach ensures that operational efficiency is maximized while managing costs effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sealed bearing
What Are the Key Materials Used in Sealed Bearings?
When selecting sealed bearings for various applications, the choice of material is critical. Different materials offer distinct properties that can significantly impact performance, durability, and overall suitability for specific environments. Below, we analyze four common materials used in sealed bearings, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Typically, it can operate effectively in environments ranging from -50°C to 200°C, depending on the specific grade used.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel bearings are durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments, such as marine or chemical applications. However, they can be more expensive than other materials, and their manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application:
These bearings are ideal for applications that involve exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, such as in food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or JIS. The availability of stainless steel bearings may vary, so sourcing from reliable suppliers is essential.
2. Chrome Steel
Key Properties:
Chrome steel is characterized by its high hardness and wear resistance. It typically operates effectively in temperatures up to 120°C and can handle moderate loads.
Pros & Cons:
Chrome steel bearings are less expensive than stainless steel and provide excellent performance in clean environments. However, they lack corrosion resistance, making them unsuitable for applications exposed to moisture or corrosive substances.
Impact on Application:
These bearings are commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery applications where cost-effectiveness and performance in clean environments are priorities.
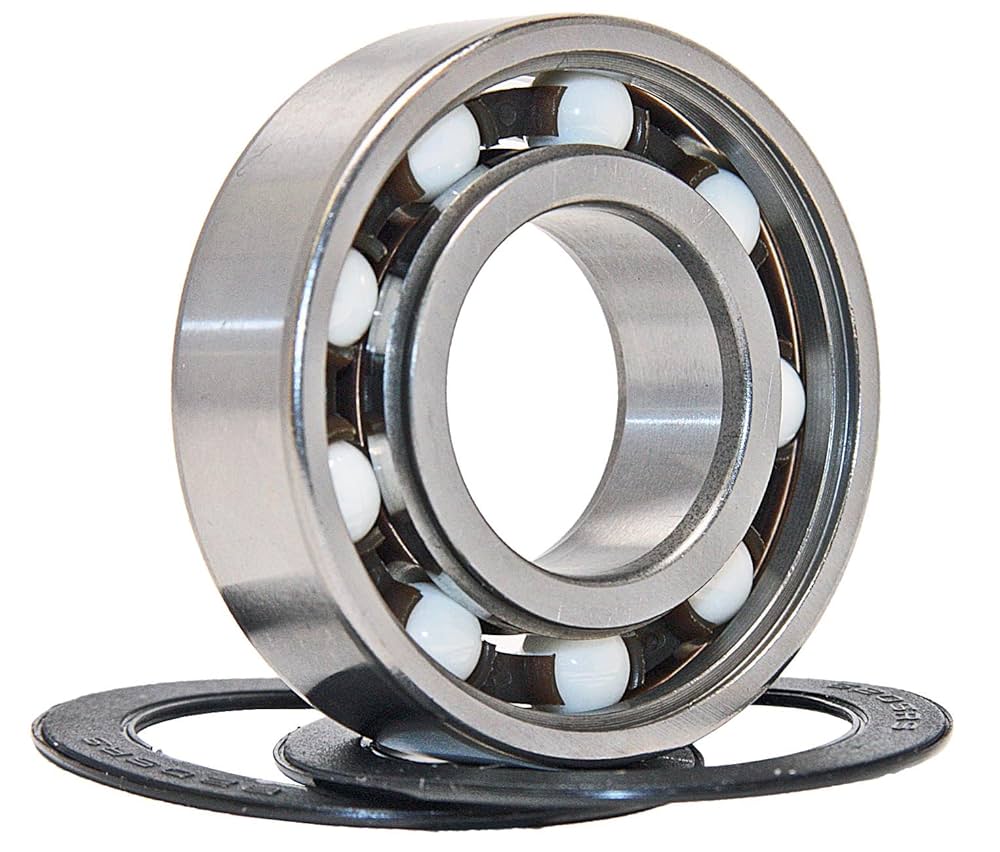

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the need for proper lubrication to prevent rusting, especially in humid regions like the Middle East. Compliance with relevant standards is also crucial for ensuring quality.
3. Polymer
Key Properties:
Polymer materials, such as nylon or PTFE, offer lightweight properties and excellent chemical resistance. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C.
Pros & Cons:
Polymer bearings are cost-effective, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. However, they may not handle high loads as effectively as metal bearings, and their temperature limits are lower.
Impact on Application:
These bearings are well-suited for applications in the food industry, medical devices, and environments where weight reduction is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific chemical compatibility of the polymer with the application media. Additionally, they should verify compliance with food safety standards when used in food processing.
4. Ceramic
Key Properties:
Ceramic materials are known for their high hardness, low density, and excellent wear resistance. They can withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 200°C, and are also non-magnetic.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Pros & Cons:
Ceramic bearings are extremely durable and can operate in corrosive environments without degradation. However, they are brittle and can be more expensive than traditional materials, leading to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
These bearings are ideal for high-speed applications and environments where chemical exposure is a concern, such as in aerospace or high-performance automotive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should evaluate the cost versus performance benefits, especially in regions where high-performance applications are common. Compliance with aerospace or automotive standards may be necessary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Sealed Bearings
| Material | Typical Use Case for Sealed Bearing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Chrome Steel | Automotive, industrial machinery | Cost-effective and durable | Lacks corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Polymer | Food industry, medical devices | Lightweight and chemically resistant | Limited load capacity | Low |
| Ceramic | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | High durability and temperature resistance | Brittle and high cost | High |
This material selection guide aims to empower international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when selecting sealed bearings, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sealed bearing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Sealed Bearings?
The manufacturing process of sealed bearings involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers and their capabilities.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used for Sealed Bearings?
The first stage in manufacturing sealed bearings begins with material selection. Typically, high-carbon chromium steel is used for the bearing rings and rolling elements due to its excellent hardness and wear resistance. Other materials, such as stainless steel or ceramic, may also be used depending on the application and environmental conditions.
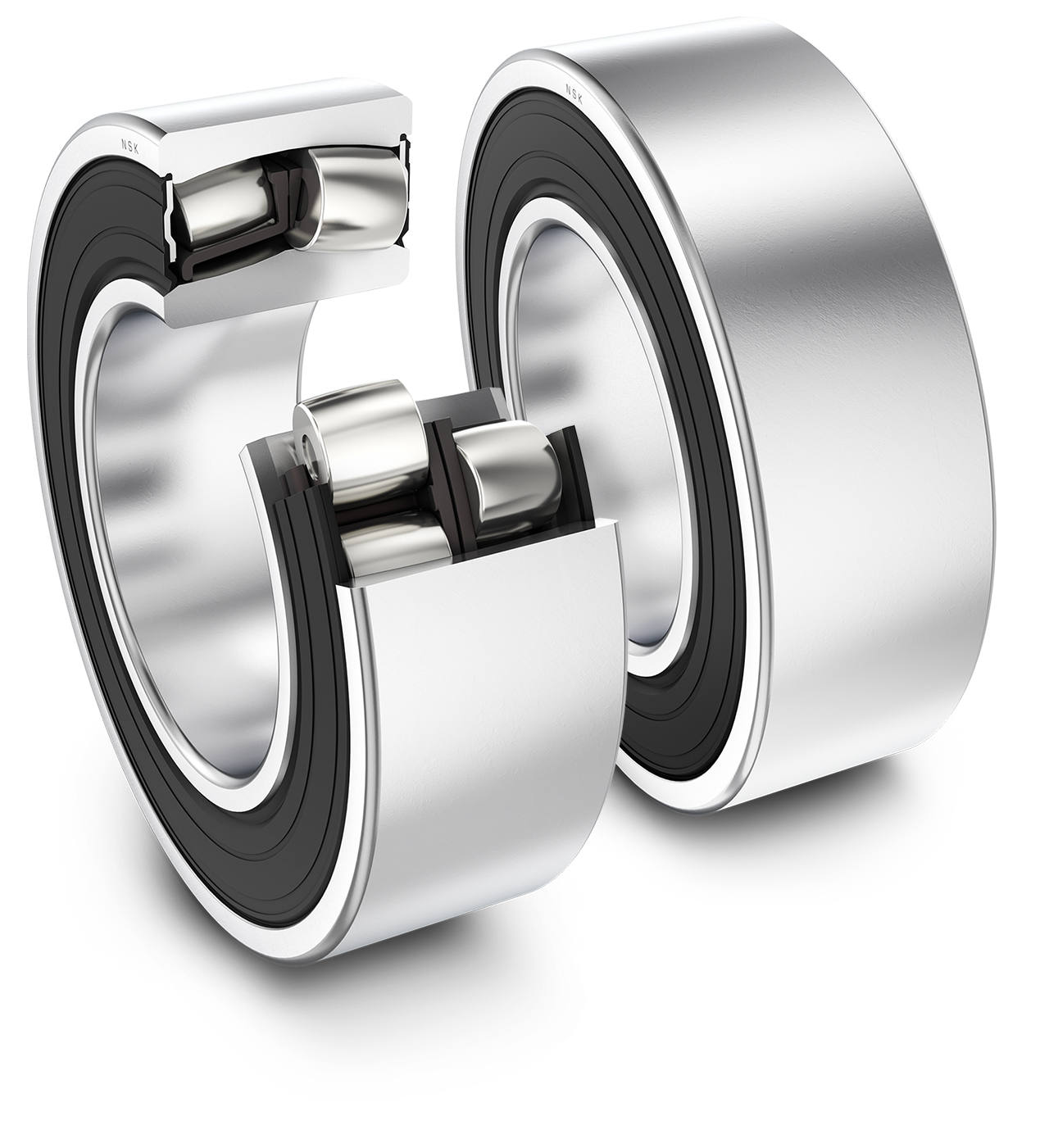

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove any contaminants that could affect performance. This may involve chemical cleaning or ultrasonic cleaning methods, ensuring the raw materials are free from oils, dust, or other residues.
How Are Sealed Bearings Formed During Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the steel into the necessary components—inner and outer rings, and rolling elements (balls or rollers). This is typically achieved through processes such as:
- Forging: A method that involves deforming the material under high pressure to create the desired shape. This process enhances the material’s grain structure, improving strength.
- Machining: Precision machining follows forging to achieve the exact dimensions and surface finishes required. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their accuracy.
- Heat Treatment: This step involves heating the components to specific temperatures and then cooling them to enhance hardness and durability. Heat treatment is critical to achieving the necessary mechanical properties for bearing performance.
What Techniques Are Used in the Assembly of Sealed Bearings?
After forming, the assembly stage begins. This typically includes the following steps:
- Greasing: Sealed bearings are pre-lubricated with grease before assembly. This grease is carefully selected based on the application requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
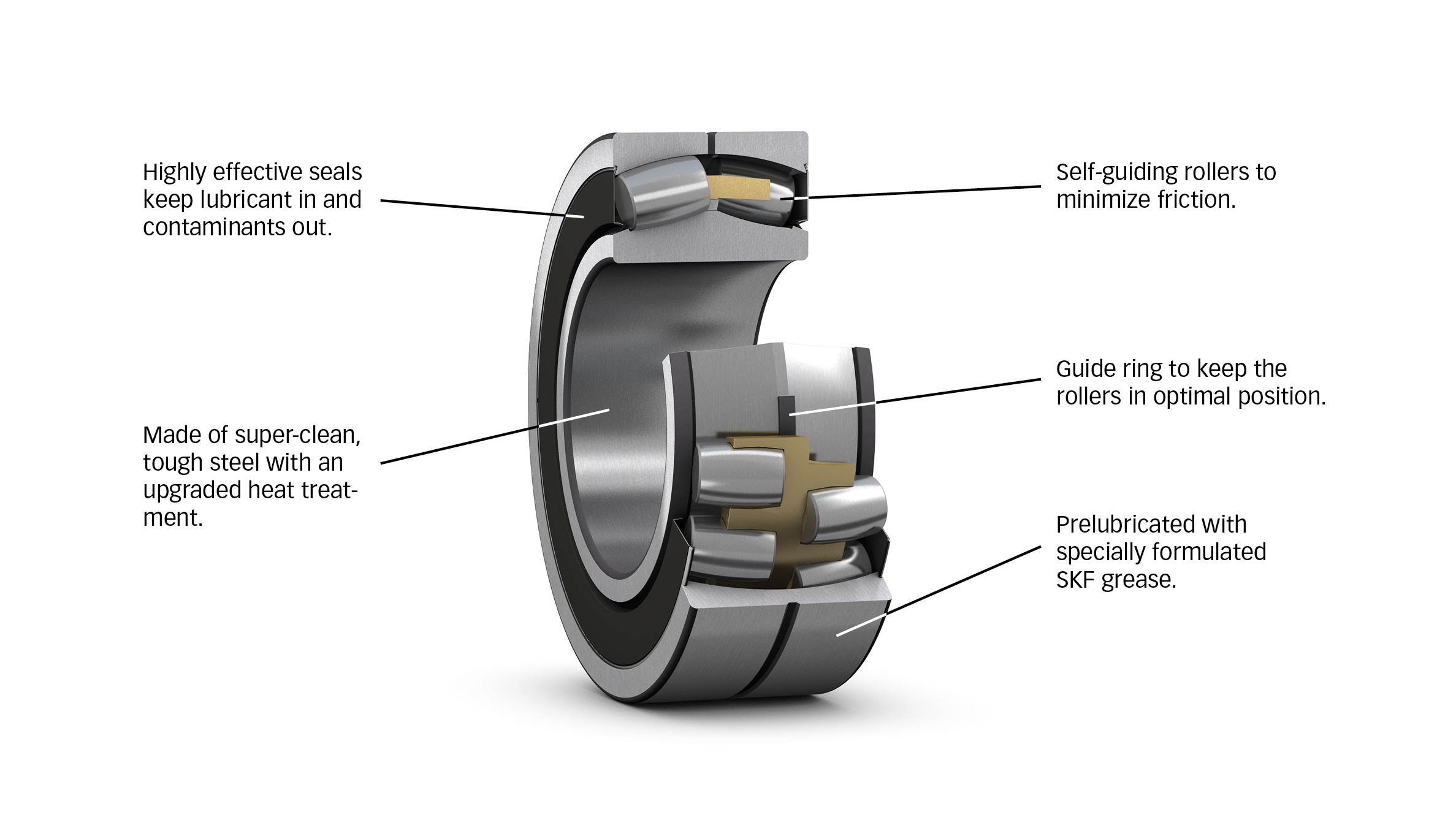
- Seal Installation: The seals, usually made from rubber or polymer, are installed on one or both sides of the bearing. The design of the seal is crucial, as it must effectively prevent contaminants from entering while retaining the lubricant.
- Final Assembly: The inner and outer rings are joined with the rolling elements, ensuring precise alignment and fit. This is often done in a clean room environment to minimize contamination risks.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Sealed Bearings?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for sealed bearings, where reliability is paramount. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QC measures.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Sealed Bearing Quality Assurance?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards ensures that products meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for applications in the oil and gas sector, may also be relevant. These certifications indicate that the bearings meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Sealed Bearing Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that any defects are identified and addressed promptly. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or reprocessed.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random samples are tested at various stages to ensure that dimensions, materials, and assembly processes comply with quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, finished bearings undergo comprehensive testing to verify their performance. This includes checking for dimensional accuracy, seal integrity, and lubrication retention.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Sealed Bearings?
Several testing methods are utilized to assess the quality and performance of sealed bearings:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using precise measuring tools, manufacturers verify that all dimensions fall within specified tolerances.
- Performance Testing: Bearings may be subjected to dynamic testing under load to evaluate their performance characteristics, such as friction, temperature rise, and noise levels.
- Seal Integrity Testing: This ensures that the seals function correctly and do not allow contaminants to enter or lubricant to escape. Common methods include pressure decay tests and immersion tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are several strategies:
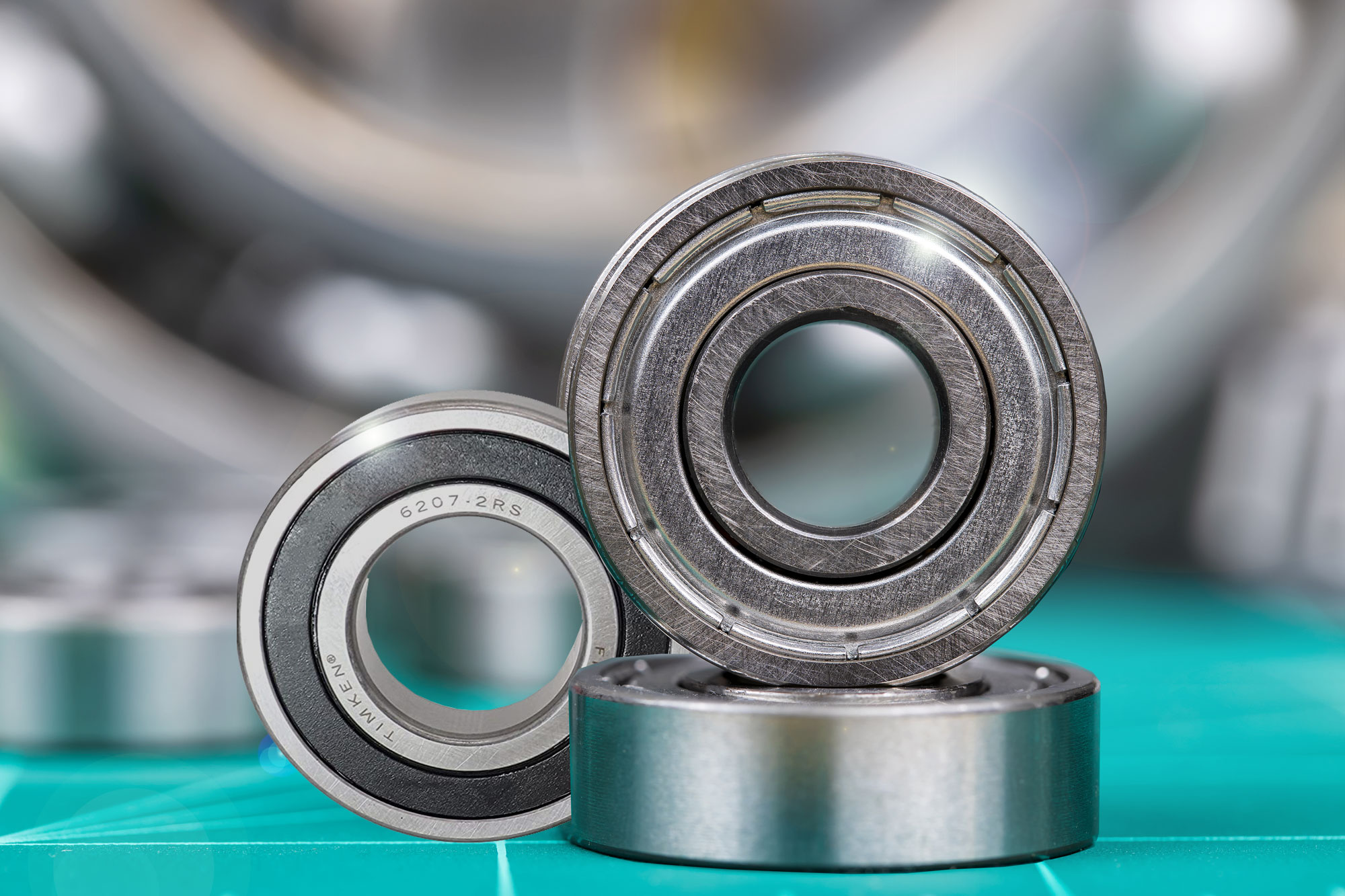

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can include both on-site inspections and reviewing their quality management documentation.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control measures, including test results and compliance with international standards. This transparency can build trust and confidence in the supplier’s capabilities.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These services can validate that the bearings meet specified standards before shipment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various certification requirements and quality expectations that may vary by region. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification for compliance with EU regulations, while buyers in the Middle East may focus on adherence to local standards.
Understanding these nuances is essential for successful international procurement. Buyers should engage in thorough research and maintain open communication with suppliers to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and standards.
In conclusion, by comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for sealed bearings, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality components for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sealed bearing’
In the competitive landscape of international sourcing, acquiring sealed bearings requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers streamline the procurement process, ensuring they make informed decisions while securing reliable components for their operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. Identify the specific dimensions, load capacities, and environmental conditions in which the sealed bearings will operate. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that you receive the right products tailored to your needs.
- Key Considerations:
- Load ratings and speed requirements.
- Operating temperature and exposure to contaminants.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in sealed bearings. Look for companies with a robust reputation in the industry, particularly those with experience in your region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Reliable suppliers can provide insights into product availability and lead times.
- Action Points:
- Use online directories and trade platforms.
- Attend industry trade shows or conferences to meet suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verifying supplier certifications is a critical step in ensuring quality and reliability. Check for industry-standard certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. This can significantly reduce the risk of procurement errors and enhance the integrity of your supply chain.
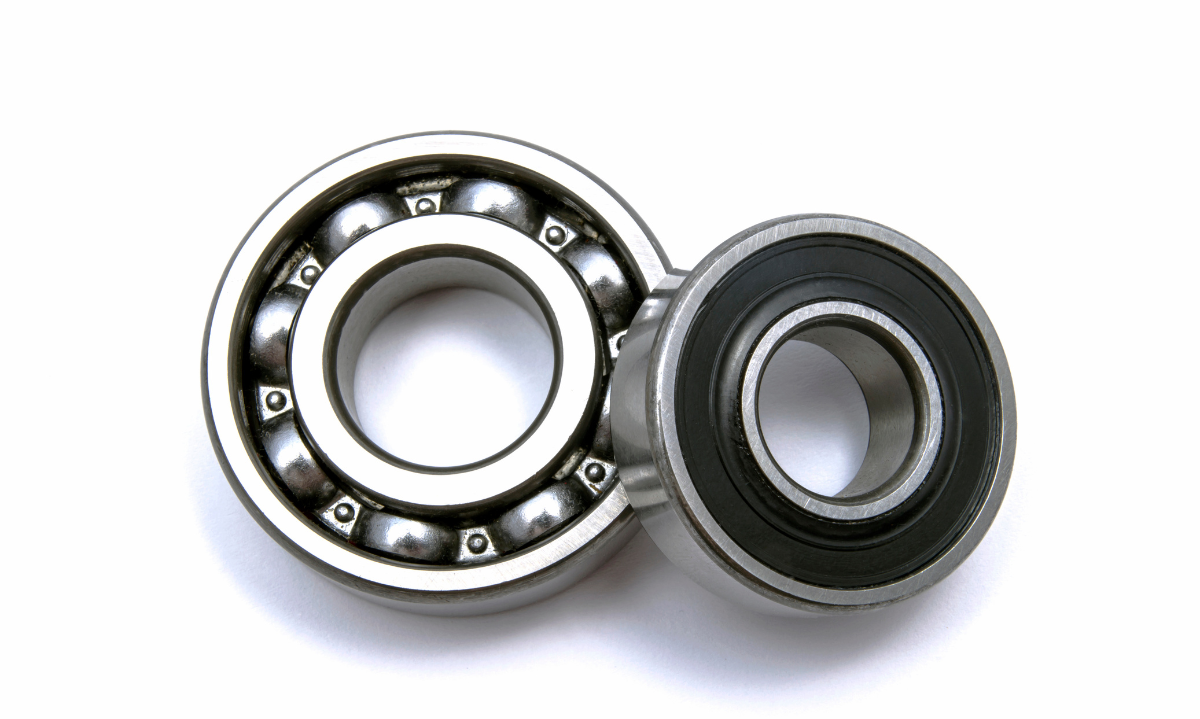

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
- What to Look For:
- Quality assurance processes.
- Compliance with international standards.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the sealed bearings for testing. This allows you to evaluate their performance under real-world conditions and verify that they meet your specifications. Testing can help identify any issues before mass procurement, saving time and resources.
- Testing Criteria:
- Lubrication retention and sealing effectiveness.
- Performance under expected load and speed conditions.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. While cost is a significant factor, also consider the overall value, including warranty terms, delivery schedules, and customer support. A slightly higher price might be justified by better service and product reliability.
- Key Factors to Analyze:
- Total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential downtime.
- Flexibility in payment terms and conditions.
Step 6: Negotiate Contracts Carefully
Engage in negotiations with selected suppliers to ensure mutually beneficial terms. Pay attention to delivery timelines, payment schedules, and after-sales support. A well-negotiated contract can protect your interests and foster a long-term partnership.
- Important Aspects:
- Clearly define penalties for non-compliance or delays.
- Establish communication protocols for ongoing support.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
After placing your order, set up a quality assurance process to monitor the performance of the sealed bearings throughout their lifecycle. This includes regular assessments and feedback loops with your supplier to address any issues promptly.
- Monitoring Techniques:
- Implement routine inspections and performance metrics.
- Maintain open communication with the supplier for continuous improvement.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing sealed bearings effectively, ensuring they select the right products from reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sealed bearing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sealed Bearing Sourcing?
When sourcing sealed bearings, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in sealed bearings typically include high-grade steel, polymers for seals, and lubricants. The quality of these materials directly influences both performance and cost. For instance, bearings made from advanced alloys or those with specialized coatings may command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. This includes the assembly of bearings, quality control (QC), and any specialized processes such as heat treatment or surface finishing. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to balance this with quality considerations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses associated with production. Efficient manufacturing practices can help reduce overhead costs, which in turn can lower the overall price of the bearings.
-
Tooling: The costs related to the machinery and tools necessary for producing sealed bearings are significant. Custom tooling for unique specifications can add to the upfront costs but may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that sealed bearings meet specific standards requires investment in quality control processes. This may involve testing for performance, durability, and adherence to certifications, which can affect the final pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are significant, especially for international shipments. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can influence the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences Pricing for Sealed Bearings?
Several factors can influence the pricing of sealed bearings, particularly in international markets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts based on the volume purchased, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed bearings tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the benefits of customization justify the extra expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Bearings that require higher quality materials or possess specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may be priced higher due to the rigorous standards met during production.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide greater assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for pricing. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) or FOB (Free on Board) can significantly impact the total landed cost.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs and Pricing for Sealed Bearings?
-
Negotiation Tips: Engaging in open discussions with suppliers about pricing can yield better terms. Highlighting your potential for repeat business or larger future orders can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Cost-Efficiency Strategies: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) instead of just the purchase price. Evaluate factors such as maintenance costs, lifespan, and performance to find the best overall value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market conditions and currency fluctuations is essential. Leveraging local suppliers or negotiating currency terms can help mitigate risks.
-
Due Diligence on Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, considering their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and customer feedback. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure a reliable supply chain.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for sealed bearings can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotations from multiple suppliers to establish a competitive benchmark. Always consider the context of your specific requirements and local market conditions when evaluating prices.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sealed bearing With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Sealed Bearings
When considering bearing solutions for industrial applications, it’s essential to evaluate various options to determine the best fit for specific operational needs. Sealed bearings are known for their durability and maintenance-free operation, but alternatives such as shielded bearings and open bearings may also provide suitable solutions depending on the environment and requirements. This analysis will compare sealed bearings with these two alternatives to highlight their respective advantages and drawbacks.
| Comparison Aspect | Sealed Bearing | Shielded Bearing | Open Bearing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent contamination protection; longer life expectancy due to lubrication retention. | Good dust protection; lower friction than sealed bearings. | Minimal friction; relies on external lubrication. |
| Cost | Generally low production costs; slight premium for sealing technology. | Similar to sealed, often slightly lower due to simpler design. | Typically the lowest cost option; no seals or shields. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install; no need for frequent maintenance. | Straightforward installation; requires occasional re-lubrication. | Simple installation; dependent on external lubrication systems. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance-free; sealed for life. | Requires periodic maintenance to re-grease. | Requires regular lubrication and maintenance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for harsh, dirty environments where maintenance is challenging. | Suitable for moderately clean environments with high-speed requirements. | Best for clean, well-lubricated conditions; commonly used in machinery with continuous oil supply. |
Pros and Cons of Shielded Bearings
Shielded bearings utilize metal shields that partially enclose the internal components. They offer a balance between protection and efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring low friction and moderate contaminant protection. The main advantage of shielded bearings is their ability to operate in environments where some exposure to dirt and debris exists without significantly increasing friction. However, they do require periodic maintenance, as the lubrication can dry out over time, necessitating re-greasing to ensure optimal performance.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Pros and Cons of Open Bearings
Open bearings are designed without any seals or shields, making them the simplest and most cost-effective option. They provide minimal friction, which can be advantageous in high-speed applications where low torque is critical. However, open bearings are highly susceptible to contamination from dirt, dust, and moisture, making them unsuitable for environments that lack consistent lubrication. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure they remain operational, as they rely on an external lubrication system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When selecting the right bearing solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific operating environment, maintenance capabilities, and performance requirements of their applications. Sealed bearings are an excellent choice for harsh conditions where contamination is a concern and maintenance schedules are limited. In contrast, shielded bearings offer a good balance of protection and performance for cleaner environments, while open bearings are best suited for applications where continuous lubrication is assured and cost is a primary concern. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can choose the most suitable bearing solution that meets their operational needs effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sealed bearing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sealed Bearings?
When evaluating sealed bearings, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here are some key properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in sealed bearings, typically steel or stainless steel, determine the bearing’s durability and resistance to corrosion. Stainless steel bearings, for instance, are ideal for applications in humid or corrosive environments, while standard steel bearings might be more cost-effective for indoor use. Choosing the right material is essential for maximizing service life and minimizing replacement costs.
2. Load Rating
Load ratings indicate the maximum load a bearing can handle without failure. This specification is divided into dynamic and static load ratings. Understanding the load requirements of your application ensures that you select a bearing capable of withstanding operational stresses, which is critical for preventing premature wear and failure.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from the nominal dimensions of the bearing components. High-precision tolerances are vital in applications requiring smooth operation and minimal vibration, such as in motors or high-speed machinery. Selecting bearings with the appropriate tolerance levels can enhance overall machinery performance and reduce maintenance needs.
4. Sealing Type
The type of seal (contact or non-contact) significantly affects the bearing’s performance. Contact seals provide superior protection against contaminants but can introduce more friction, while non-contact seals minimize friction but offer less protection. Buyers must assess their operational environment and maintenance capabilities to select the most suitable sealing type.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the environments in which a bearing can function effectively. Sealed bearings designed for extreme temperatures are essential in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where temperature fluctuations can be significant. Proper selection based on temperature tolerance can prevent failure and enhance reliability.
6. Lubrication Type
Sealed bearings often come pre-lubricated, typically with grease, which allows for maintenance-free operation. Understanding the type of lubricant used and its expected life span is important for ensuring that the bearing performs optimally throughout its service life. This can lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer operational periods.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Sealed Bearing Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions involving sealed bearings. Here are some common terms:
Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are marketed by another company. In the context of bearings, OEM parts are designed to meet specific performance standards and specifications set by the machinery manufacturers. Understanding OEM relevance helps buyers ensure compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for buyers looking to manage inventory and costs effectively. Knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and assessing whether a supplier aligns with your purchasing strategy.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications of the products needed. Properly crafting an RFQ ensures that you receive accurate pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better comparison and negotiation.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for clarifying shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with the delivery of sealed bearings, ensuring smooth international trade operations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the products. This is a critical factor for inventory management and production planning. Knowing the lead time helps businesses anticipate supply chain needs and avoid production delays.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the length of time a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their bearing products. Understanding warranty terms helps buyers assess the risk involved in their purchase and the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when procuring sealed bearings, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sealed bearing Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global sealed bearing market is witnessing a robust growth trajectory driven by several key factors. As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and reliability, the demand for sealed bearings—known for their low maintenance and extended lifespan—continues to rise. Notably, sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery are leading this trend, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. For instance, Brazil’s growing automotive sector and Vietnam’s expanding manufacturing base are contributing to a surge in demand for high-performance sealed bearings.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies within this sector. Digital platforms for procurement are enhancing transparency and efficiency, allowing buyers to compare products and suppliers more effectively. Additionally, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology in machinery is prompting a shift towards predictive maintenance, further emphasizing the need for durable, sealed solutions that minimize downtime. This trend is particularly relevant in regions with challenging environmental conditions, where the robustness of sealed bearings can significantly impact operational efficiency.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and supply chain challenges. International buyers must navigate fluctuations in material costs and availability, particularly for high-quality polymers and lubricants used in seal manufacturing. As a result, establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and timely delivery is essential for B2B buyers looking to maintain their competitive edge.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, the sealed bearing sector is adapting to meet these demands. The environmental impact of bearing production, from raw material extraction to manufacturing processes, necessitates an emphasis on ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes, such as recyclable polymers and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to conscientious B2B buyers. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation in increasingly competitive markets.
In addition, the trend towards circular economy practices is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers that offer take-back programs for used bearings, facilitating recycling and reducing waste. By prioritizing suppliers with sustainable practices, international B2B buyers can align their procurement strategies with broader environmental goals, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future while ensuring product reliability.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of sealed bearings can be traced back to the early 20th century when engineers began recognizing the need for improved lubrication and protection from environmental contaminants. Initially, bearings were open and required frequent maintenance, which was impractical for many applications. The introduction of seals and shields marked a significant advancement, allowing for longer service intervals and enhanced reliability.
Over the decades, advancements in materials science have led to the development of high-performance polymers and lubricants that have further improved the efficiency and lifespan of sealed bearings. Today, sealed bearings are integral to numerous applications across diverse industries, reflecting a continuous drive for innovation and quality in the B2B market. As technology progresses, the future of sealed bearings will likely focus on enhanced performance and sustainability, catering to the evolving needs of global buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sealed bearing
-
How do I choose the right sealed bearing for my application?
Selecting the appropriate sealed bearing requires an understanding of your application’s specific conditions. Consider factors like operating environment (dust, moisture), load capacity, and speed requirements. For harsh environments, opt for sealed bearings with contact seals to maximize contamination protection. If your application involves high speeds but lower contamination risk, non-contact seals may be more suitable. Always consult with suppliers to ensure that the bearing specifications align with your operational needs. -
What are the benefits of sourcing sealed bearings from international suppliers?
Sourcing sealed bearings internationally can provide access to a broader range of products, competitive pricing, and advanced manufacturing technologies. Many suppliers in regions like Europe and Asia specialize in high-quality bearings and may offer customized solutions to meet specific requirements. Additionally, international suppliers often have robust logistics networks, ensuring timely delivery. However, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure quality standards and reliability. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for sealed bearings?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize factors such as manufacturing certifications (ISO), product quality, and industry experience. Request samples to assess the bearing’s performance and durability. Check customer reviews and case studies to gauge the supplier’s reliability and service quality. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain practices and lead times to ensure they can meet your demands consistently. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for sealed bearings?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs for sealed bearings range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the manufacturer and product specifications. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard products, while customized or specialized bearings may require higher quantities. Always clarify MOQs before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing sealed bearings internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and your relationship with them. Common terms include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Ensure to discuss and negotiate payment options that suit your cash flow needs. Be aware of any additional fees, such as currency conversion and international transaction fees, which may impact overall costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for sealed bearings I purchase?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing sealed bearings. Request documentation of quality control processes from your supplier, including ISO certifications and test results for batch samples. Consider implementing incoming inspection protocols upon receipt of goods to verify compliance with your specifications. Establishing a quality agreement can also help maintain standards and clarify responsibilities regarding defects or issues. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping of sealed bearings?
Logistics play a vital role in international procurement. Consider shipping options, lead times, and customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Choose a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial products to navigate complexities effectively. Additionally, factor in shipping costs and insurance to protect your investment during transit. Clear communication with your supplier about logistics can help prevent delays and ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize sealed bearings for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for sealed bearings to meet specific application requirements. Customizations can include variations in size, seal types, lubrication methods, and materials. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria to your supplier. Keep in mind that custom orders may involve longer lead times and higher MOQs, so plan accordingly to avoid production disruptions.
Top 7 Sealed Bearing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bearings Direct – Ball Bearings Supplier
Domain: bearingsdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Ball Bearings Supplier – Free Shipping On Orders $100+ – In Stock in Glendale CA – Contact: 818-545-1900 – Categories: Metric Ball Bearings, Extra Light Duty Ball Bearings (6000 Series), Light Duty Ball Bearings (6200 Series), Medium Duty Ball Bearings (6300 Series), Thin High Speed Ball Bearings (6700 Series), Extra Thin High Speed Bearings (6800 Series), Thin High Speed Light Duty Bearings (6900…
2. VXB – Sealed Ball Bearings
Domain: vxb.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Sealed Ball Bearing – Wide Selection, Free Shipping to All US States on All Non-Freight Orders, $10 Minimum Order, Address: 2165 S. Dupont Dr Ste F Anaheim CA 92806 US.
3. McMaster – Sealed Bearings
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Sealed Bearings, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. PIB Sales – Bearings Comparison Guide
Domain: pibsales.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Sealed, Open and Shielded Bearings Comparison: 1. Open Bearings: – No built-in seals or shields, exposing internal components. – Used in clean, well-lubricated environments (e.g., gearboxes). – Rely on machine lubrication, cannot prevent contaminants. 2. Shielded Bearings: – Metal shields on one or both sides partially enclose internal components. – Suitable for moderately clean environments (e.g….
5. Reddit – Sealed vs Unsealed Bearings
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Sealed bearings are generally more weatherproof and require less adjustment. They wear out over time and cannot be repaired internally, but can be replaced with new cartridges. Unsealed bearings offer better serviceability, allowing for easier maintenance and repair, but require more attention. High-end unsealed bearings may have slightly less drag, but the difference is minimal in performance. Se…
6. Machinery Lubrication – Sealed vs. Shielded Bearings
Domain: machinerylubrication.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Sealed and shielded bearings differ in lubrication methods; sealed bearings should not be regreased, while shielded bearings can be. Bearings are identified using AFBMA or SKF coding systems, where the shields or seals section indicates if a bearing is sealed. AFBMA codes may include ‘EE’ for sealed bearings, while SKF codes use ‘2RSI’. A bearing without a purge path does not necessarily mean it i…
7. VeneerSupplies – Double-Sealed Ball Bearing
Domain: veneersupplies.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Double-Sealed Ball Bearing”, “Regular Price”: “$12.40”, “Vendor”: “VeneerSupplies.com”, “Species”: “Ziricote”, “Condition”: “New”, “Weight”: “Not specified”, “Lead Time”: “Ships on Monday”, “Customer Rating”: “Not specified”, “Shipping”: “Not specified”, “Current Stock”: “Not specified”, “Gift Wrapping”: “Not specified”, “Minimum Order”: “Not specified”, “Quantity Discounts”: “Av…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sealed bearing
In the rapidly evolving landscape of sealed bearing procurement, strategic sourcing stands as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. By understanding the unique advantages of sealed bearings—such as their contamination protection, lubrication retention, and maintenance-free operation—companies can optimize their supply chains while enhancing the longevity and reliability of their machinery. The cost-effectiveness and versatility of sealed bearings make them an attractive option across diverse industries, from manufacturing to agriculture.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to significant savings and improved operational efficiency. Prioritizing partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand local market dynamics and global standards can further enhance procurement outcomes.
As we look to the future, the demand for high-performance sealed bearings will likely continue to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing focus on sustainability. Now is the time to assess your sourcing strategies, explore innovative suppliers, and ensure that your organization is equipped to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Engage with trusted partners today to secure a competitive edge in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to sealed bearing
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.