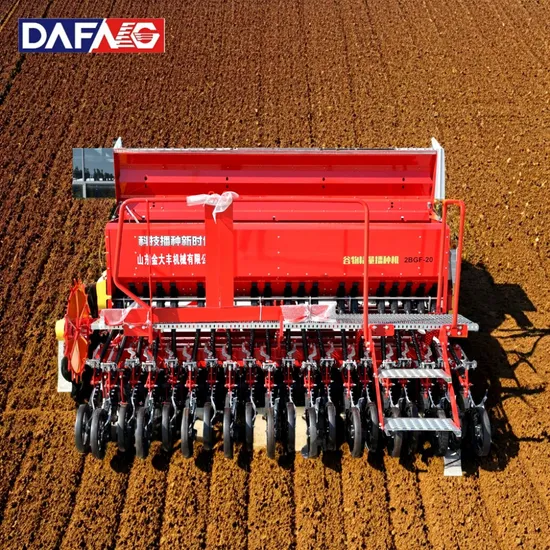
How to Source Rice Seeder Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rice seeder
As global agricultural demands escalate, the challenge of sourcing efficient rice seeders becomes increasingly critical for B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The right rice seeder not only enhances planting efficiency but also ensures optimal seed placement, directly impacting yield and profitability. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the rice seeder market, detailing various types of seeders, their applications across different terrains, and essential features that enhance their performance.
International buyers will gain valuable insights into supplier vetting processes, enabling them to identify reliable manufacturers and assess product quality. Furthermore, this guide addresses cost considerations and potential return on investment, equipping decision-makers with the knowledge to make informed purchases. From understanding the functionality of mechanical and pneumatic seeders to exploring advanced features like precision depth control and modular designs, this resource serves as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of the rice seeder market.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategic recommendations, this guide aims to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that agricultural enterprises are well-equipped to meet the challenges of modern rice cultivation efficiently and effectively.
Understanding rice seeder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Rice Seeder | Utilizes a mechanical system for seed distribution; various opener types available | Small to medium-sized farms for efficient sowing | Pros: Cost-effective, simple operation. Cons: Limited precision compared to pneumatic systems. |
| Pneumatic Rice Seeder | Employs air pressure for precise seed placement; modular design for adaptability | Large-scale operations requiring high accuracy | Pros: High precision, adaptable for various crops. Cons: Higher initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| Direct Seed Rice Seeder | Designed for both wet and dry field conditions; features adjustable depth control | Versatile applications in diverse soil conditions | Pros: Multi-crop capability, efficient in varied environments. Cons: Complexity in setup and operation. |
| Walking Rice Seeder | Manual operation; smaller footprint; suitable for small plots | Ideal for smallholder farmers and tight spaces | Pros: Affordable, easy to transport. Cons: Labor-intensive, slower operation. |
| Riding Rice Seeder | Tractor-mounted; capable of covering larger areas quickly | Commercial farming operations with extensive fields | Pros: High efficiency, reduces labor costs. Cons: Requires a tractor, higher upfront investment. |
What Are the Characteristics of Mechanical Rice Seeders?
Mechanical rice seeders are designed to operate with a straightforward mechanical system that facilitates seed distribution through various types of openers. They are particularly suitable for small to medium-sized farms where budget constraints are a priority. Buyers should consider their operational simplicity and cost-effectiveness; however, they may sacrifice precision compared to more advanced seeding technologies. This type of seeder is ideal for farmers looking to enhance their sowing efficiency without significant upfront investments.
How Do Pneumatic Rice Seeders Stand Out?
Pneumatic rice seeders utilize air pressure to ensure precise seed placement, making them highly effective for large-scale agricultural operations. Their modular design allows for flexibility, enabling farmers to adapt them for various crops beyond rice. While they offer high accuracy and reduced seed wastage, buyers should be prepared for a higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. These seeders are particularly beneficial for operations that prioritize precision agriculture and seek to optimize yield.
What Benefits Do Direct Seed Rice Seeders Provide?
Direct seed rice seeders are engineered to perform well in both wet and dry field conditions, featuring adjustable depth control that enhances planting accuracy. Their versatility allows for application in diverse soil types, making them suitable for a range of crops, including legumes and cereals. Buyers should weigh the advantages of their multi-crop capabilities against the complexity of setup and operation. This type of seeder is excellent for farmers looking to maximize their planting efficiency across different growing conditions.
Why Choose Walking Rice Seeders for Small Farms?
Walking rice seeders are manually operated machines that are ideal for small plots and tight spaces. Their compact design and affordability make them an excellent choice for smallholder farmers who may not have access to larger machinery. However, they require more labor and can be slower in operation. Buyers should consider their operational capacity and labor availability when opting for this type of seeder, as it provides a cost-effective solution for small-scale agricultural activities.
What Makes Riding Rice Seeders Ideal for Commercial Operations?
Riding rice seeders are designed to be mounted on tractors, allowing for rapid coverage of large agricultural areas. This type of seeder is particularly advantageous for commercial farming operations that require efficiency and reduced labor costs. While they significantly enhance productivity, buyers must consider the need for a compatible tractor and the higher upfront investment. These seeders are best suited for operations focused on maximizing output while minimizing labor demands.
Key Industrial Applications of rice seeder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rice seeder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Large-scale rice cultivation | Increased efficiency in planting, reduced labor costs, and uniform crop establishment | Compatibility with local tractor models and soil types, availability of spare parts, and after-sales support |
| Agro-technology | Precision seeding for diverse crops | Enhanced yield through precise seed placement and reduced seed waste | Technology integration with existing farm equipment and ease of operation for local farmers |
| Food Processing | Supply chain enhancement for rice producers | Consistent quality and quantity of rice supply, leading to better processing efficiency | Reliability of the seeder under varying weather conditions and adaptability to different field types |
| Export and Trade | Facilitating export quality rice production | Meeting international quality standards and increasing market competitiveness | Compliance with export regulations, machine certifications, and local agricultural practices |
| Research and Development | Testing new rice varieties | Accelerated research outcomes through efficient planting methods | Access to data analytics tools for monitoring growth and seed performance, and collaboration opportunities with local agricultural universities |
How is rice seeder utilized in large-scale agriculture?
In large-scale rice cultivation, rice seeders play a pivotal role by automating the planting process, which significantly reduces labor costs and increases operational efficiency. These machines ensure uniform seed distribution, minimizing the risk of over- or under-seeding that can lead to inconsistent crop yields. For international buyers, it is essential to consider the compatibility of seeders with local tractor models, soil conditions, and the availability of after-sales support to maintain equipment efficiency.
What are the benefits of precision seeding in agro-technology?
In the agro-technology sector, rice seeders equipped with precision seeding technology can handle not only rice but also various crops like soybeans and peanuts. This versatility allows for enhanced crop yields through accurate seed placement and reduced waste. Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing seeders that integrate seamlessly with existing farm equipment and are user-friendly for local farmers, ensuring they can maximize productivity while minimizing the learning curve.
How does a rice seeder enhance food processing operations?
For food processing businesses, the consistent quality and quantity of rice produced by efficient seeders directly impact processing efficiency and product quality. By ensuring that rice is planted uniformly, seeders help maintain optimal growth conditions, leading to better harvests. When sourcing seeders, businesses should consider the reliability of equipment under varying environmental conditions to ensure uninterrupted supply chains and maintain quality standards.
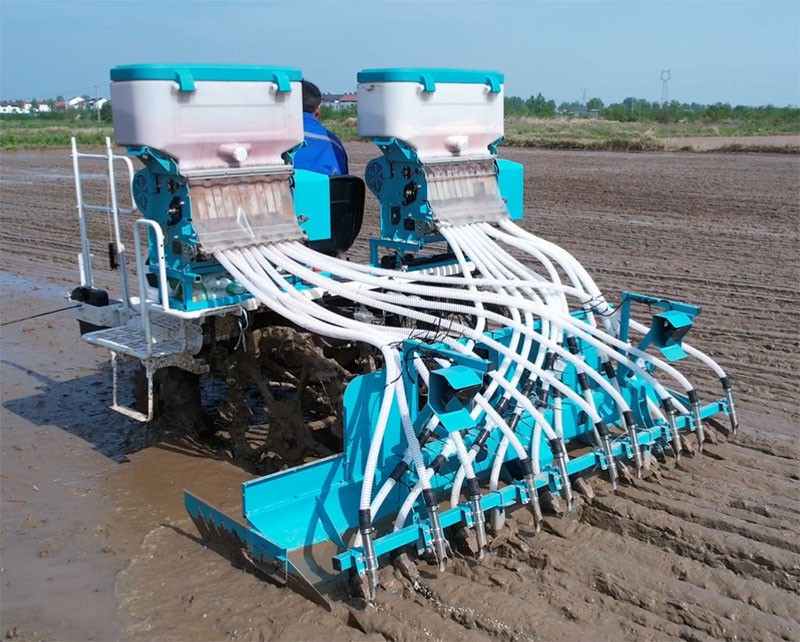

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
In what ways does rice seeder support export and trade?
Rice seeders are crucial for producing high-quality rice that meets international standards, thereby enhancing market competitiveness for exporters. By utilizing advanced seeding techniques, producers can ensure a consistent product that is attractive to global buyers. International buyers should look for seeders that comply with local agricultural practices and export regulations, as well as those that come with necessary certifications to facilitate smoother trade processes.
How does rice seeder contribute to research and development in agriculture?
In research and development, rice seeders enable agricultural scientists to test new rice varieties and planting techniques efficiently. By using these machines, researchers can accelerate the planting process and gather data on crop performance more effectively. Buyers in this sector should consider seeders that offer advanced data analytics capabilities to monitor growth and seed performance, fostering collaboration with local agricultural universities and enhancing research outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rice seeder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Seed Depth and Distribution in Rice Planting
The Problem: B2B buyers in the agricultural machinery sector often encounter issues with inconsistent seed depth and distribution when using rice seeders. This inconsistency can lead to uneven crop emergence and growth, resulting in lower yields and increased competition from weeds. Farmers may experience frustration when they invest in expensive machinery only to find that their seeding practices do not yield the expected results. Moreover, variations in soil conditions and moisture levels can exacerbate these challenges, leading to further complications in crop management.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize seeders equipped with advanced seed metering and depth control mechanisms. For instance, choosing a rice seeder with a pneumatic seeding system, like those offered by APV, allows for precise control over seed placement and depth, ensuring uniformity across the field. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate the specifications of the seeder, such as its adjustable row openers and pneumatic technology, which can adapt to various soil conditions. Regular maintenance and calibration of the seeder before planting seasons can also help maintain optimal performance. Additionally, training for operators on the proper setup and adjustments can greatly enhance the effectiveness of the equipment, leading to improved crop establishment and yield.
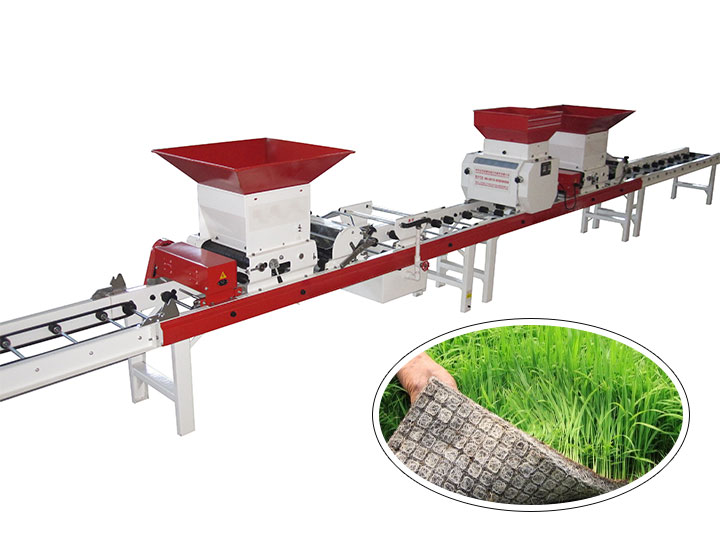

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Transitioning Between Wet and Dry Conditions
The Problem: In regions where rice is cultivated in both wet and dry conditions, B2B buyers often face the challenge of using a single seeder for varying soil types and moisture levels. This lack of adaptability can lead to inefficiencies in planting operations, as equipment that works well in one condition may not perform adequately in another. Buyers may find that they need to invest in multiple machines or face reduced planting efficiency and crop performance due to improper equipment for the conditions.
The Solution: Buyers should consider modular rice seeders that offer interchangeable components designed for both wet and dry seeding. For instance, seeders like the APV DSR can be configured with specific modules tailored to wet or dry fields, allowing for seamless transitions without the need for multiple machines. When selecting a rice seeder, it’s crucial to assess its modularity and compatibility with various attachments. Furthermore, investing in training for staff on how to quickly switch between configurations can improve operational efficiency. This flexibility not only saves costs but also maximizes the effectiveness of planting operations across diverse environmental conditions.
Scenario 3: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Maintenance costs and potential downtime associated with rice seeders can be significant pain points for B2B buyers. Frequent repairs and the need for replacement parts can strain budgets, especially for smaller agricultural enterprises. Buyers may struggle with understanding the long-term reliability of the equipment they purchase, leading to uncertainty about the total cost of ownership over time.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance concerns, buyers should conduct thorough research into the durability and reliability of the seeders they are considering. Opting for machines from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and after-sales support can significantly reduce long-term costs. Additionally, buyers should inquire about warranties and service agreements that cover parts and repairs. Establishing a proactive maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations can help identify potential issues before they escalate, thus minimizing downtime. Investing in training for operators on the correct use and routine maintenance of the seeder can also extend the lifespan of the equipment, ensuring that it operates efficiently throughout its intended lifecycle.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rice seeder
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Rice Seeders and Why?
When selecting materials for rice seeders, it’s essential to consider properties that affect performance, durability, and cost. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the construction of rice seeders, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Rice Seeder Construction?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for components that experience significant wear and tear, such as frames and seed metering devices. It generally has a temperature tolerance of up to 400°C and can withstand various pressures.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness, which ensures longevity and reliability in harsh agricultural environments. However, it is prone to corrosion if not treated properly, which can lead to maintenance challenges. The manufacturing process can be complex due to welding and machining requirements, potentially increasing production costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various agricultural applications, but its susceptibility to rust necessitates protective coatings, especially in humid or wet environments commonly found in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers should also consider the availability of corrosion-resistant treatments to enhance longevity, particularly in regions with high moisture levels.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Rice Seeder Design?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, with a melting point around 660°C. It is often used in components where weight reduction is beneficial, such as in seeders designed for mobility.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its resistance to rust and lightweight nature, which can improve maneuverability. However, it is less durable than steel, making it more susceptible to deformation under heavy loads. The cost of aluminum can also be higher compared to steel, affecting overall pricing.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for seeders used in regions with high humidity or saline conditions, where rust could be a significant issue. Its compatibility with various crops makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet standards like JIS H 2000 for wrought aluminum alloys. The cost implications of using aluminum should be weighed against the benefits of reduced weight and corrosion resistance.
How Does Plastic Enhance Rice Seeder Functionality?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, are lightweight and resistant to chemicals and moisture. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs in seeders. However, they may not withstand high mechanical stress as effectively as metals, leading to potential durability issues over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are ideal for seed boxes and covers, where moisture resistance is essential. Their lightweight nature can also contribute to overall machine efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use is important, especially in Europe. Buyers should also consider the long-term sustainability of plastic components in their sourcing decisions.
What Advantages Does Composite Material Offer for Rice Seeders?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can endure a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: Composites are highly durable and resistant to chemical degradation, making them suitable for various agricultural applications. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in components that require both strength and lightweight characteristics, such as seed metering devices and structural elements in seeders.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composites meet relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. The initial cost may be higher, but the long-term benefits of durability and reduced maintenance can justify the investment.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rice Seeders
| Material | Typical Use Case for rice seeder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Frame, seed metering devices | High durability and strength | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Less durable under heavy loads | High |
| Plastic | Seed boxes, covers | Cost-effective and lightweight | May deform under stress | Low |
| Composite | Structural elements, metering devices | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher production costs | High |
This guide provides essential insights into the material selection process for rice seeders, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rice seeder
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rice Seeders?
The manufacturing process of rice seeders involves several critical stages that ensure the machines meet the required quality and performance standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques to guarantee that the final product is reliable and efficient for agricultural use.
How Is Material Prepared for Rice Seeder Production?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing of rice seeders. This stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as steel and aluminum, which are essential for the structural integrity of the seeder. Suppliers must provide certification for these materials to ensure compliance with international standards.
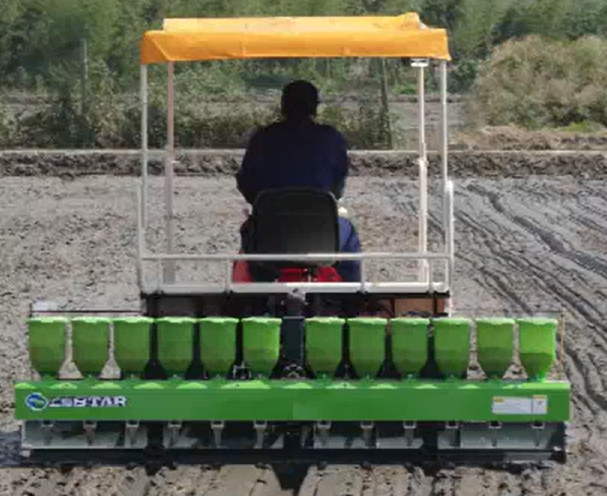

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Once sourced, materials undergo cutting and shaping to create the components needed for the seeder. Advanced technologies such as laser cutting and CNC machining are often employed for precision. This ensures that each part fits together seamlessly during assembly, which is crucial for optimal machine performance.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Rice Seeder Components?
The forming stage involves transforming the prepared materials into specific components of the rice seeder. This can include processes like stamping, bending, and welding. For instance, the frame of the rice seeder may be constructed using welding techniques that ensure a strong and durable assembly.
In addition, forming techniques may vary depending on the design and functionality of the seeder. For example, pneumatic components that require precise air pressure management will undergo specialized forming processes to ensure airtight seals and reliable operation. Manufacturers should utilize advanced forming technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
How Is the Assembly of Rice Seeders Conducted?
The assembly stage is critical in the manufacturing process, as it involves bringing together all the individual components into a fully functional rice seeder. This process typically follows a systematic approach, often guided by detailed assembly manuals and quality control checklists.
During assembly, skilled technicians or automated systems will integrate components such as the seed metering device, openers, and the control system. It is essential to adhere to best practices to ensure that each part functions harmoniously. For instance, the calibration of the seed metering device must be precise to ensure even seed distribution, which directly impacts crop yield.
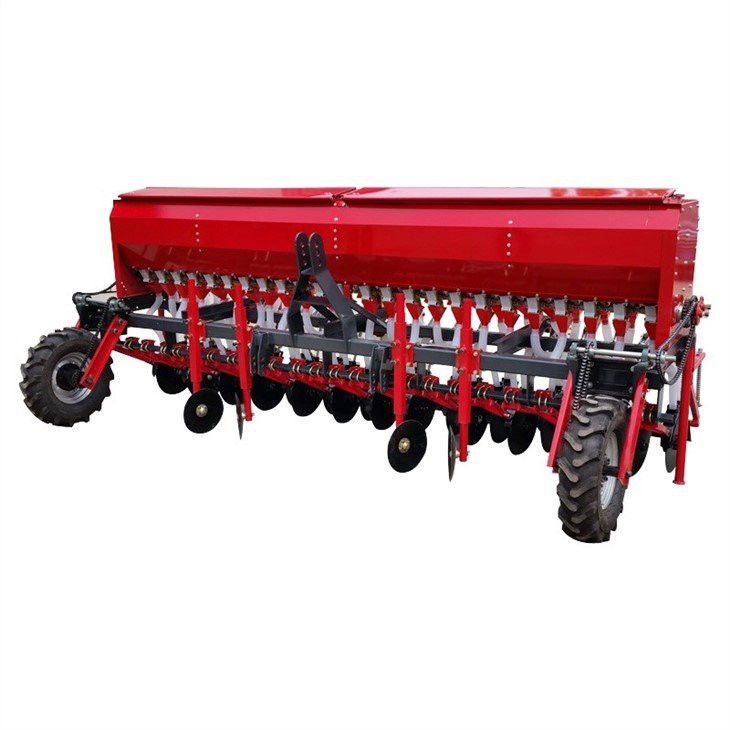

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
What Are the Finishing Processes for Rice Seeders?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of rice seeders. This stage may involve painting, powder coating, or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear during field use. A high-quality finish not only extends the machine’s lifespan but also improves its marketability.
Quality assurance during the finishing process is vital. Manufacturers should conduct visual inspections and tests for finish quality, ensuring there are no defects that could compromise performance. This attention to detail can differentiate a manufacturer in the competitive agricultural machinery market.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of rice seeders. B2B buyers should be familiar with various international standards and industry-specific certifications that signify a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. The most notable among these is ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS).
How Do International Standards Like ISO 9001 Impact Rice Seeder Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 certification ensures that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management system that consistently produces products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. For rice seeder manufacturers, adhering to these standards means implementing continuous improvement processes and maintaining documentation that can be audited.
In addition to ISO 9001, other certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for specific agricultural applications may also be relevant. These certifications affirm compliance with safety and environmental regulations, making them crucial for international buyers.
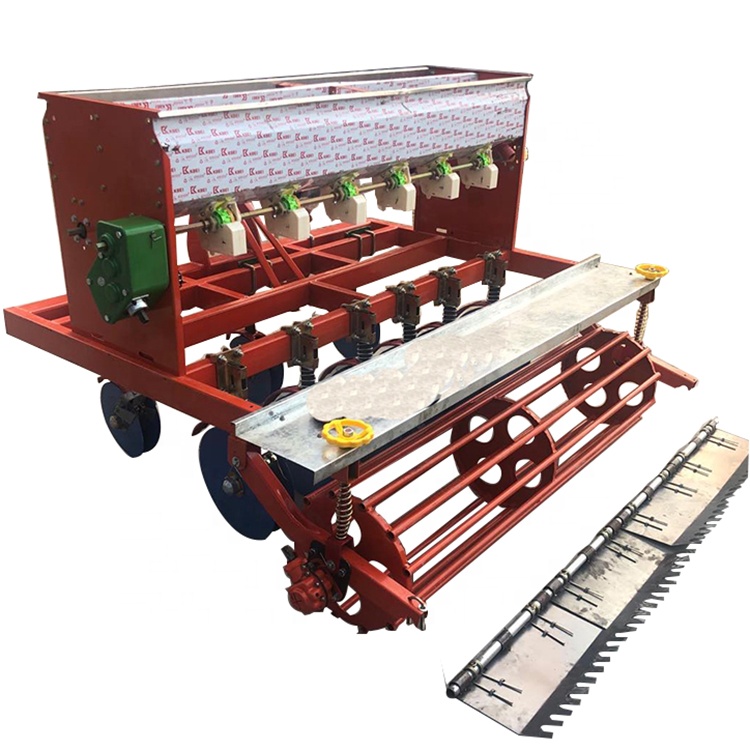

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Rice Seeder Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process of rice seeders. These checkpoints ensure that every stage of production meets established standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival. It ensures that all materials meet the required specifications before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various tests and inspections are conducted at different stages to monitor the quality of components. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and functionality of parts as they are assembled.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the rice seeder is fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes functionality tests, performance assessments, and safety checks to ensure the seeder operates as intended.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Rice Seeder Quality Assurance?
Testing methods employed in the quality assurance of rice seeders vary but typically include:
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that all components, such as seed metering devices and openers, operate correctly under simulated field conditions.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting the seeder to various environmental conditions to assess its resilience and lifespan.
- Precision Testing: Measuring the accuracy of seed placement and depth control, which are critical for effective planting.
These testing methods provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of the seeder, allowing manufacturers to make necessary adjustments before the final product reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to verify a supplier’s quality control practices. This can be achieved through:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for documentation related to their quality assurance processes, including test results and inspection reports.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to assess the quality of products before shipment can provide an additional layer of assurance.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control practices can significantly impact procurement decisions. It is advisable to establish long-term relationships with manufacturers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and transparency.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for rice seeders are critical components that determine the effectiveness and reliability of these agricultural machines. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing rice seeders, ensuring that they invest in high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs. Establishing partnerships with manufacturers that adhere to international standards and maintain rigorous quality control measures will ultimately lead to better outcomes in agricultural productivity.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rice seeder’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of rice seeders, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist. This structured approach will help ensure that you make informed decisions, securing machinery that meets your operational needs and enhances productivity.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is essential to outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the type of rice you will be planting, field conditions (wet or dry), and the desired seeding method (direct seeding or transplanting). This clarity will help you narrow down options and ensure that the seeder you choose is compatible with your farming practices.
Step 2: Research Supplier Reputation
Investigating potential suppliers is crucial for a successful purchase. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in the agricultural machinery sector, particularly those specializing in rice seeders. Read customer reviews, seek testimonials, and examine case studies to assess their reliability and product performance in similar environments.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Features
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, delve into the specific features of their rice seeders. Key aspects to consider include:
– Seed metering technology: Look for advanced metering systems that ensure precise seed placement, which can significantly enhance crop yields.
– Adjustability: Choose models that offer flexibility in row spacing and seeding depth to accommodate varying field conditions and crop types.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the rice seeders meet local and international agricultural standards. This verification is essential not only for operational efficiency but also for compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Ask for certifications and documentation that confirm adherence to quality and safety standards.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, arrange for product demonstrations or trial periods. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the machine’s performance in real-world conditions. Pay attention to ease of operation, maintenance requirements, and how well the seeder adapts to your specific agricultural practices.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Reliable after-sales support is vital for minimizing downtime and ensuring long-term satisfaction. Inquire about the warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and the responsiveness of the supplier’s customer service team. A supplier that offers robust support can make a significant difference in your overall operational efficiency.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Finally, compare the pricing structures of different suppliers. Look beyond the initial purchase price to consider total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential financing options. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment plans or financing solutions that can ease budget constraints.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for rice seeders, ensuring that they choose equipment that meets their agricultural needs while providing reliability and efficiency in the field.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rice seeder Sourcing
When sourcing rice seeders for international markets, understanding the cost structure and pricing factors is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis delves into the various components that contribute to the overall cost of rice seeders and the influences that can impact pricing, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rice Seeder Manufacturing?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in rice seeders include high-grade steel for the frame, durable plastics for seed boxes, and various components such as pneumatic systems and seeding mechanisms. The choice of materials directly affects the durability and efficiency of the seeder, influencing both upfront costs and long-term maintenance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in assembly, quality control, and testing. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to ensure that quality is not compromised, as this can lead to higher maintenance costs later.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and general administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can reduce overhead per unit, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for customized seeders. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has existing molds for standard models or if new tooling will be required for specific customizations.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that seeders meet international standards and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it significantly reduces the risk of defects and enhances the product’s reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are vital, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can substantially impact the total cost. Incoterms chosen by the buyer can also influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover their risks and ensure sustainability. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better margins.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rice Seeder Sourcing?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should evaluate their needs and consider negotiating for better pricing based on volume commitments.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized seeders may incur additional costs due to specialized materials or unique functionalities. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Seeders that comply with international quality standards (ISO, CE, etc.) may come at a premium but offer peace of mind regarding performance and reliability. Buyers should weigh the benefits against the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging manufacturers may offer lower prices to penetrate the market.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who bears the risk and cost at various points in the shipping process. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage costs effectively.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Rice Seeder Prices?
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the prevailing market rates and supplier capabilities can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, repairs, and operational efficiency. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a good rapport can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable conditions.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Solicit proposals from various suppliers to compare prices and terms. This not only provides leverage in negotiations but also helps identify the best overall value.
Conclusion
Sourcing rice seeders involves navigating a complex landscape of cost components and pricing influencers. By understanding these factors and employing strategic negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions, ensuring they acquire quality equipment that meets their agricultural needs while managing costs effectively. Always remember that prices may vary based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, so thorough due diligence is essential for achieving the best deal.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rice seeder With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Rice Seeders for Effective Planting
In the quest for efficient rice cultivation, understanding the available alternatives to traditional rice seeders is crucial for B2B buyers. Various technologies and methods can offer distinct advantages depending on specific farming conditions, crop types, and operational goals. This analysis compares rice seeders with two viable alternatives: manual broadcasting and drone seeding, providing insights into their effectiveness, cost, and implementation.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
| Comparison Aspect | Rice Seeder | Manual Broadcasting | Drone Seeding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in seed placement; ensures uniformity and spacing, leading to better yields. | Inconsistent seed distribution; higher risk of uneven growth and lower yields. | High precision; capable of covering large areas quickly with minimal labor. |
| Cost | Medium initial investment; long-term savings through improved yields and reduced labor costs. | Low initial cost; however, potential for lower yield may incur higher costs in the long run. | High initial investment; ongoing operational costs for drone maintenance and battery replacement. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training for operators; may need additional tractor equipment. | Simple and requires no specialized training; can be done manually by workers. | Requires skilled operators and adherence to regulatory guidelines for drone operation. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance; parts may require replacement over time. | Minimal maintenance; mainly involves manual labor. | Regular software updates and battery maintenance; potential technical issues with drones. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale commercial farming where precision is critical; effective in diverse soil conditions. | Suitable for small-scale or subsistence farming where cost is a primary concern. | Effective for large, flat areas with easy access; beneficial for precision agriculture with multiple crop types. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Manual Broadcasting
This traditional method involves spreading seeds by hand or using simple tools. While it requires minimal investment and can be easily implemented by local labor, it often leads to inconsistent seed placement. This inconsistency can result in uneven growth and lower overall yields, particularly in competitive agricultural markets. Thus, while it may be suitable for small-scale or subsistence farmers, it may not meet the demands of larger operations aiming for efficiency and productivity.
Drone Seeding
Utilizing drones for seed distribution is an innovative approach gaining traction in modern agriculture. This method allows for precise seed placement over large areas quickly, making it ideal for expansive fields. However, the initial investment in drone technology can be substantial, and ongoing operational costs may deter some farmers. Additionally, drone operation requires skilled personnel and adherence to aviation regulations, which can complicate implementation. Nevertheless, for those seeking to integrate advanced technology into their farming practices, drone seeding represents a forward-thinking solution.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Planting Solution
When selecting the appropriate planting solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific agricultural needs, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. Rice seeders offer precision and efficiency, making them suitable for large-scale operations, while manual broadcasting may suffice for smaller farms with budget limitations. Drone seeding presents a cutting-edge alternative that maximizes efficiency but requires significant investment and expertise. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their agricultural objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rice seeder
What Key Technical Properties Should B2B Buyers Consider in Rice Seeders?
When evaluating rice seeders, several technical specifications are vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of rice seeders significantly influences durability and resistance to wear and tear. High-grade steel or corrosion-resistant materials are preferred as they withstand harsh agricultural environments, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs. -
Seeding Depth Control
Precision in seeding depth, typically ranging from 1.0 cm to 5.0 cm, is essential for optimal crop growth. Adjustable depth control mechanisms allow for flexibility depending on soil type and moisture content. This feature is crucial for ensuring uniform seed placement, which directly impacts crop yield and quality. -
Row Spacing and Configuration
The ability to adjust row spacing is critical for maximizing land use and accommodating various crop types. Rice seeders that offer multiple row configurations (e.g., 8 to 16 rows) enable farmers to optimize planting density, which can enhance productivity and resource management. -
Seeding Rate Adjustment
A variable seeding rate capability (e.g., 0.5 to 250 kg/ha) allows for customized planting based on crop requirements and field conditions. This feature is particularly valuable for B2B buyers looking to maximize efficiency and reduce seed wastage, leading to better cost control. -
Pneumatic Seed Distribution System
A reliable pneumatic system ensures accurate seed placement and minimizes seed loss. This technology is essential for achieving consistent crop emergence and reducing the risk of over-seeding or under-seeding, which can adversely affect yields. -
Modular Design
A modular approach allows for future upgrades and adaptability to different crops beyond rice. This flexibility is attractive to buyers aiming to diversify their operations without investing in entirely new machinery.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Purchasing Rice Seeders?
Navigating the agricultural machinery market requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are some common terms that can aid in the purchasing process:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure they are purchasing high-quality machinery that meets industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is critical for buyers, especially when planning budgets and inventory levels. This can also affect negotiations and pricing strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from potential suppliers. This process helps buyers compare costs and services, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management and ensuring timely planting seasons. -
Warranty and After-Sales Support
Warranties and the availability of after-sales support are critical factors for B2B buyers. A robust warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in their product, while reliable support ensures any issues can be resolved quickly, minimizing downtime.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in rice seeders, ultimately enhancing their agricultural operations and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rice seeder Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Rice Seeder Sector?
The global rice seeder market is influenced by several key drivers, including the increasing demand for rice as a staple food, advancements in agricultural technology, and the push for higher yields amidst a growing population. In regions like Africa and South America, where rice consumption is rising, the adoption of mechanized seeding solutions is becoming critical for improving productivity and efficiency. Emerging technologies such as precision seeding and direct seeding methods, like those offered by modular systems, are gaining traction. These innovations not only enhance planting accuracy but also reduce seed wastage and improve crop establishment.
Moreover, international B2B buyers are increasingly looking for equipment that offers versatility across different crops. For instance, seeders that can handle various crops, including legumes and cereals, present an attractive option for farmers seeking to diversify their production. In markets like Europe, particularly Germany, there is a noticeable shift towards automated and smart farming solutions, including seeders equipped with IoT capabilities for real-time monitoring and adjustment of seeding parameters.
As the agricultural sector becomes more competitive, sourcing trends are also evolving. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who can provide robust after-sales support and maintenance services, ensuring that equipment remains operational and effective throughout its lifespan. Additionally, regional sourcing strategies are becoming prevalent, as buyers seek to minimize logistics costs and improve supply chain resilience.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Rice Seeder Industry?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of the agricultural machinery industry, with B2B buyers placing greater emphasis on the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. The rice seeder sector is no exception, as manufacturers are pressured to adopt eco-friendly practices and materials in their production processes. This includes utilizing sustainable materials, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring that manufacturing processes adhere to stringent environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, as buyers are more conscious of the social implications of their purchasing decisions. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical labor practices can affect local communities. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can enhance a supplier’s credibility and appeal to buyers focused on responsible sourcing.
Furthermore, the incorporation of green technologies in rice seeders, such as energy-efficient motors and recyclable components, can serve as a competitive differentiator. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that not only meet their operational needs but also align with their values regarding sustainability and ethical practices. This alignment can foster long-term partnerships and contribute to a positive brand image in a market that is progressively leaning towards environmentally conscious farming practices.
How Has the Rice Seeder Technology Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of rice seeder technology has been remarkable, transitioning from manual sowing methods to sophisticated mechanized solutions. Historically, rice planting was a labor-intensive process, reliant on manual labor to scatter seeds across fields. As agricultural practices advanced, the introduction of simple mechanical seeders marked the beginning of a new era in rice cultivation.
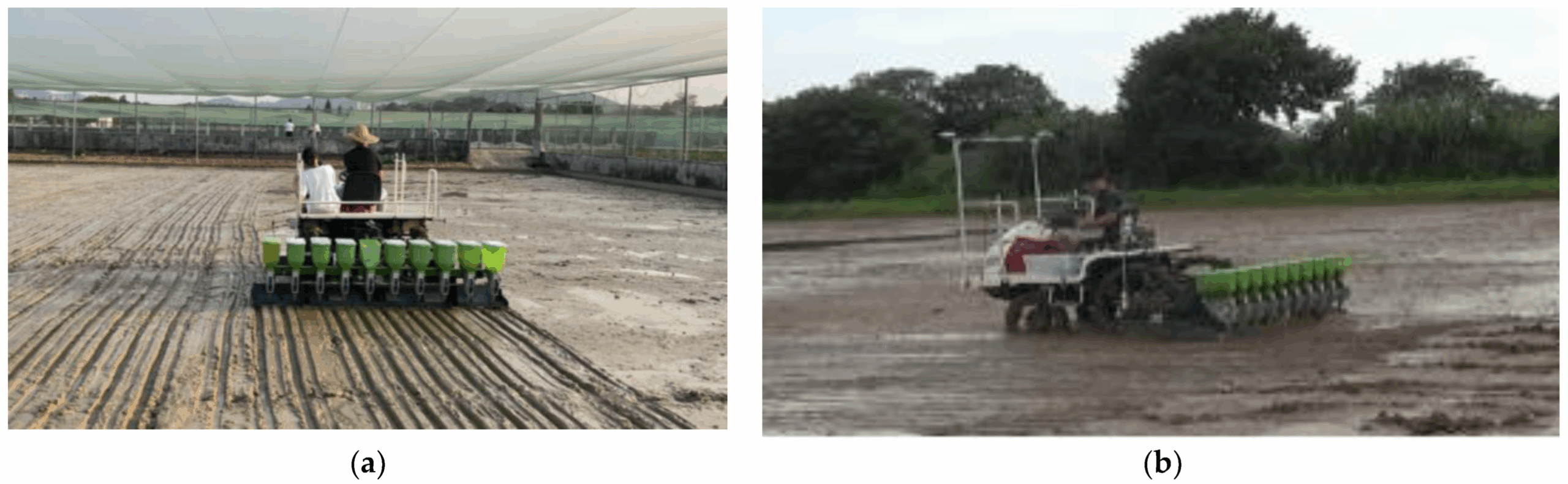

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
In the late 20th century, the development of more complex seeding machines, such as pneumatic and direct seeding systems, revolutionized the way rice was planted. These innovations not only improved planting efficiency but also addressed issues related to seed depth and spacing, leading to better crop yields. Today, modern rice seeders are equipped with advanced technologies, including GPS for precise navigation and automated systems for optimal seed placement.
The focus on multi-crop functionality has also expanded the utility of rice seeders, allowing farmers to use a single machine for various crops. This versatility is especially beneficial in regions where crop rotation is practiced, providing both economic and operational efficiencies. As technology continues to evolve, the rice seeder sector is poised to embrace further advancements that will enhance productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rice seeder
-
How do I solve issues with uneven seed distribution when using a rice seeder?
Uneven seed distribution can significantly impact crop yields. To address this issue, ensure that the seed metering device is calibrated correctly according to the seed type and desired planting density. Regular maintenance of the seeder, including checking for blockages in the seed tubes and ensuring the openers are functioning properly, is essential. Additionally, utilizing row markers can help maintain consistent spacing, reducing the likelihood of uneven distribution. -
What is the best rice seeder for varying soil conditions?
For diverse soil conditions, consider a modular rice seeder that can adapt to both wet and dry fields. Models like the APV DSR Seeder offer customizable attachments for different soil types, ensuring optimal seed placement and coverage. Features such as adjustable working widths and depth control mechanisms allow for precise operation in various environments, making them versatile choices for international B2B buyers. -
What are the key features to look for in a rice seeder?
When sourcing a rice seeder, prioritize features such as seed metering accuracy, depth control, and the ability to handle different soil types. Look for models with robust construction for durability and ease of maintenance. Additionally, seeders with modular designs allow for future upgrades, while those equipped with advanced monitoring systems can improve operational efficiency by providing real-time feedback during planting. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing rice seeders in international trade?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the transaction size. Common terms include a 30% upfront deposit with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms, including letter of credit arrangements or installment payments, especially for larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties and to ensure clear communication regarding any potential additional costs. -
How can I vet suppliers of rice seeders effectively?
Vetting suppliers is critical to ensure reliability and quality. Start by checking their business credentials, including registration, certifications, and industry experience. Request references from previous clients and review their performance history. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or arranging virtual tours to assess production capabilities. Platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources can also provide supplier ratings and customer feedback, aiding in your decision-making. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for rice seeders?
The MOQ for rice seeders varies by manufacturer and product type. Generally, larger suppliers may have an MOQ ranging from 5 to 10 units, while smaller manufacturers might accommodate smaller orders. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers, as some may be flexible with MOQs for first-time buyers or trial orders. Always confirm any potential additional costs associated with smaller orders. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing rice seeders?
To ensure quality assurance, look for suppliers that provide detailed product specifications and compliance with international agricultural standards. Request samples or visit their manufacturing facility to inspect the production processes. Establish clear quality expectations in your contract, including warranties or guarantees. Additionally, consider third-party inspection services before shipment to verify product quality and adherence to agreed specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing rice seeders?
When importing rice seeders, consider shipping methods, transit times, and customs regulations in your country. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with agricultural equipment to ensure safe and timely delivery. Additionally, factor in duties and taxes that may apply upon import. It’s wise to plan for potential delays and have contingency measures in place, such as insurance coverage for high-value shipments.
Top 4 Rice Seeder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. FM World Agri – Rice Seeder
Domain: fmworldagri.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: The rice seeder is a planting machine designed for sowing small seeds such as grains, vegetables, and pastures. Key characteristics include: 1. Seeding Wheel: Driven by the walking wheel to rotate and discharge seeds from the seed box into the seeding pipe. 2. Opener: Creates grooves for seed placement. 3. Compaction Device: Compacts the soil over the seeds after sowing. 4. Seed Metering Devices: …
2. APV – Modular DSR Seeder
Domain: en.apv.at
Introduction: Modular DSR Seeder for Direct Seeding of Rice and Other Crops. Capable of seeding in wet (DSR W) and dry (DSR D) fields. High-capacity row seeding (up to 16 rows). Precise depth control (1.0 cm – 5.0 cm). Lightweight and durable design. Adjustable working widths: 1.50 m, 2.0 m, 2.5 m. DSR W module features a floating leveling board and depth-adjustable row openers. DSR D module includes specially …
3. KEIBUNTECH – Semi-Automatic Seeding Machine K-6ST
Domain: japan-agritrading.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: KEIBUNTECH Semi-Automatic Seeding Machine for Paddy Rice with a Brush K-6ST
4. iHarvester – Rice Seeder
Domain: iharvester.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Rice Seeder:
– Also known as paddy seeder machine or precision seeder.
– Designed to mechanize the process of sowing rice seeds directly into the field.
– Key Features:
– Precision Planting: Ensures consistent seed spacing and depth for better crop management.
– Time and Labor Efficiency: Reduces manual labor and speeds up planting.
– Cost-Effective: Saves costs on seed wastage and lab…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rice seeder
In today’s competitive agricultural landscape, the strategic sourcing of rice seeders is vital for enhancing productivity and ensuring food security. By investing in high-quality, innovative seeding technology, businesses can achieve more efficient planting, reduce labor costs, and improve crop yields. Key considerations for international buyers include the adaptability of seeders for different soil types, precision planting capabilities, and the potential for multi-crop functionality, which can significantly enhance operational flexibility.
Moreover, leveraging relationships with reputable manufacturers can provide access to advanced technology and reliable after-sales support, essential for maintaining equipment performance in diverse agricultural environments. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for efficient and sustainable farming practices will only grow.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
Looking forward, B2B buyers are encouraged to explore the latest advancements in rice seeder technology to meet the changing needs of their operations. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves for success in a rapidly advancing agricultural sector, ensuring they remain competitive while contributing to global food security. Take the next step in enhancing your agricultural capabilities by investing in the right rice seeder solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to rice seeder
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.