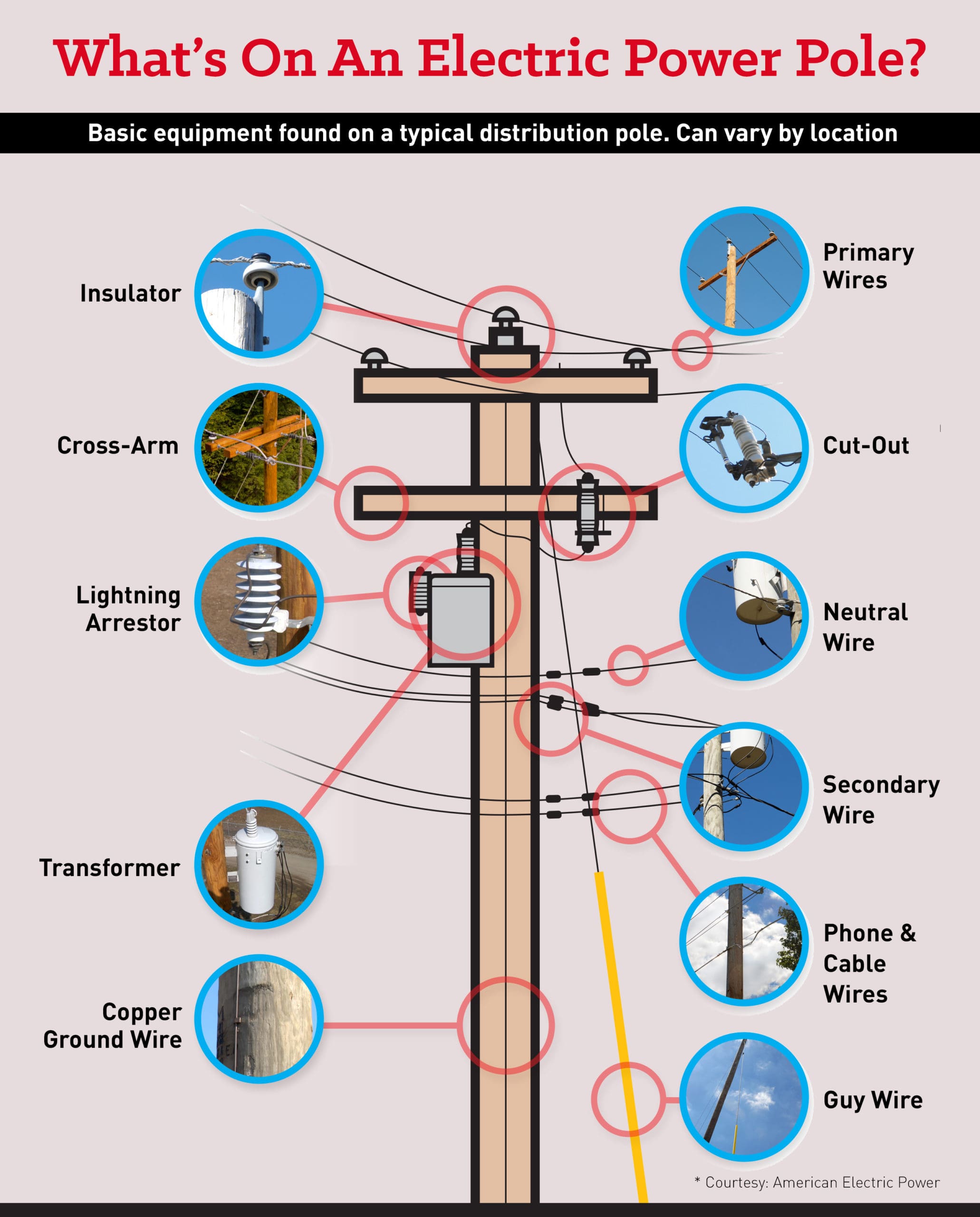
How to Source Power Line Parts Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power line parts
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing reliable power line parts poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. From Africa to South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of these components is crucial for ensuring efficient energy transmission and distribution. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of power line hardware—such as insulators, connectors, and grounding solutions—while highlighting their various applications across industries, including telecommunications and utilities.
As the demand for efficient and sustainable energy solutions grows, it becomes imperative for businesses to navigate the complexities of supplier vetting and cost considerations. This guide equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions by outlining essential criteria for evaluating suppliers, understanding material properties, and recognizing the importance of adherence to international standards.
With actionable strategies and expert recommendations, this resource serves as a vital tool for companies looking to enhance their procurement processes. By empowering buyers with the knowledge to select high-quality power line parts that meet specific operational needs, we aim to foster greater confidence in their purchasing decisions, ultimately contributing to improved infrastructure and energy reliability in their respective markets.
Understanding power line parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Cross Arm | Provides structural support for overhead lines; made of steel | Utility poles, transmission lines | Pros: Durable, supports heavy loads. Cons: Heavier than alternatives, may require specialized installation. |
| Power Line Insulator | Non-conductive material preventing electrical leakage | Transmission and distribution lines | Pros: High resistance to environmental factors. Cons: Can be costly if specialized types are needed. |
| Lightning Arrester | Protects equipment from voltage spikes caused by lightning | Utility infrastructure, telecommunications | Pros: Essential for safety, mitigates damage. Cons: Needs regular inspection and maintenance. |
| Guy Wire and Thimble | Used for stabilization of poles; connects to anchors | Pole stabilization, telecommunications | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install. Cons: Requires proper tensioning for effectiveness. |
| Transformer | Converts voltage levels; essential for power distribution | Electrical grids, residential areas | Pros: Versatile, crucial for safe power delivery. Cons: Bulkier and requires maintenance. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Steel Cross Arms in power line infrastructure?
Steel cross arms are vital components used to support overhead power lines, particularly in utility poles and transmission towers. Their robust construction allows them to bear significant loads, making them suitable for high-voltage applications. When purchasing steel cross arms, buyers should consider factors such as weight capacity, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Proper installation is crucial, as the weight may necessitate specialized handling and equipment.
How do Power Line Insulators contribute to electrical safety and efficiency?
Power line insulators are essential for ensuring the safe transmission of electricity by preventing current from leaking to the ground or other structures. Made from materials like porcelain or composite polymers, these insulators withstand environmental stressors such as wind and rain. B2B buyers should evaluate the insulator’s dielectric strength, mechanical properties, and resistance to environmental degradation. Selecting the right insulator is critical, as improper choices can lead to costly outages and safety hazards.
Why are Lightning Arresters important for protecting power infrastructure?
Lightning arresters are designed to safeguard electrical equipment from voltage surges caused by lightning strikes. By diverting excess voltage safely to the ground, these devices are indispensable for maintaining the integrity of power systems. Buyers should assess the arrester’s response time, energy absorption capacity, and installation requirements. Regular inspections are necessary to ensure functionality, making it imperative for businesses to factor in maintenance costs when considering these components.
What role do Guy Wires and Thimbles play in stabilizing power poles?
Guy wires and thimbles are critical for the stabilization of utility poles, especially in areas prone to high winds or seismic activity. These components provide lateral support, ensuring that poles remain upright and secure. When sourcing guy wires, buyers should focus on material strength, corrosion resistance, and installation ease. Proper tensioning is vital for effectiveness; thus, understanding the environmental conditions and load requirements is essential for optimal performance.
How do Transformers facilitate power distribution in electrical grids?
Transformers are crucial for adjusting voltage levels within electrical grids, ensuring that power is safely transmitted from generation points to end-users. They can be found in various configurations, including pole-mounted and ground-based units. B2B buyers should consider factors such as capacity, efficiency ratings, and maintenance needs when selecting transformers. Given their role in power quality and reliability, investing in high-quality transformers is critical for any business involved in energy distribution.
Key Industrial Applications of power line parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of power line parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Installation of solar and wind energy connections | Enhances energy reliability and supports sustainable initiatives | Quality assurance, local regulations, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Telecommunications | Infrastructure for fiber optic and data transmission | Facilitates high-speed communication and connectivity | Durability, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards |
| Mining and Resource Extraction | Power supply for remote operations | Ensures uninterrupted power for operational efficiency | Heavy-duty materials, resistance to extreme conditions, and local sourcing options |
| Construction and Infrastructure | Support structures for utility poles and lines | Provides safety and compliance with electrical standards | Availability, lead times, and adherence to local building codes |
| Agriculture | Electrification of irrigation systems | Increases productivity and efficiency in farming practices | Weather resistance, ease of installation, and local service support |
How Are Power Line Parts Used in Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, power line parts are crucial for connecting solar panels and wind turbines to the grid. Components such as insulators and connectors ensure that energy generated can be transmitted safely and efficiently. International buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, must consider local climate conditions, as parts need to withstand high temperatures and humidity. Additionally, sourcing durable and corrosion-resistant materials is essential to maintain system reliability over time.
What Role Do Power Line Parts Play in Telecommunications Infrastructure?
Power line parts are integral to telecommunications, where they support the infrastructure for fiber optic and data transmission lines. Items such as crossarms and insulators secure cables to poles, ensuring stable connectivity. For businesses in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with telecommunications standards is critical, as is sourcing materials that can endure environmental stressors. Reliable suppliers who understand local regulations can provide significant advantages in maintaining service quality.
How Are Power Line Parts Essential for Mining and Resource Extraction?
In mining operations, power line parts facilitate the electrification of remote sites, providing the necessary energy for machinery and equipment. Components like grounding anchors and heavy-duty connectors are essential for ensuring safety and operational efficiency. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who offer high-strength materials that can withstand harsh conditions, including dust and moisture, to prevent failures that can lead to downtime.
What Importance Do Power Line Parts Have in Construction and Infrastructure Projects?
Construction projects rely heavily on power line parts for the installation of utility poles and the associated electrical infrastructure. Properly designed components like pole bands and anchor rods ensure compliance with safety and electrical standards. Buyers in Europe must pay attention to local building codes and sourcing options to ensure timely delivery and quality assurance. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in local regulations can streamline the procurement process.
How Do Power Line Parts Support Agricultural Electrification?
In agriculture, power line parts are vital for electrifying irrigation systems, which enhance efficiency in farming operations. Components such as surge arresters protect equipment from electrical surges, ensuring consistent power delivery. Buyers, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather, must consider sourcing parts that offer high resistance to environmental factors. Selecting suppliers with a track record in agricultural applications can help ensure the longevity and reliability of the systems in place.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power line parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays Due to Inadequate Inventory Management
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant delays in project timelines due to inadequate inventory management of power line parts. When essential components like insulators or crossarms are out of stock, it can halt construction or maintenance projects, leading to increased costs and lost revenue. This is particularly critical for international buyers who may face longer shipping times and customs delays, making it imperative to have the right parts available when needed.
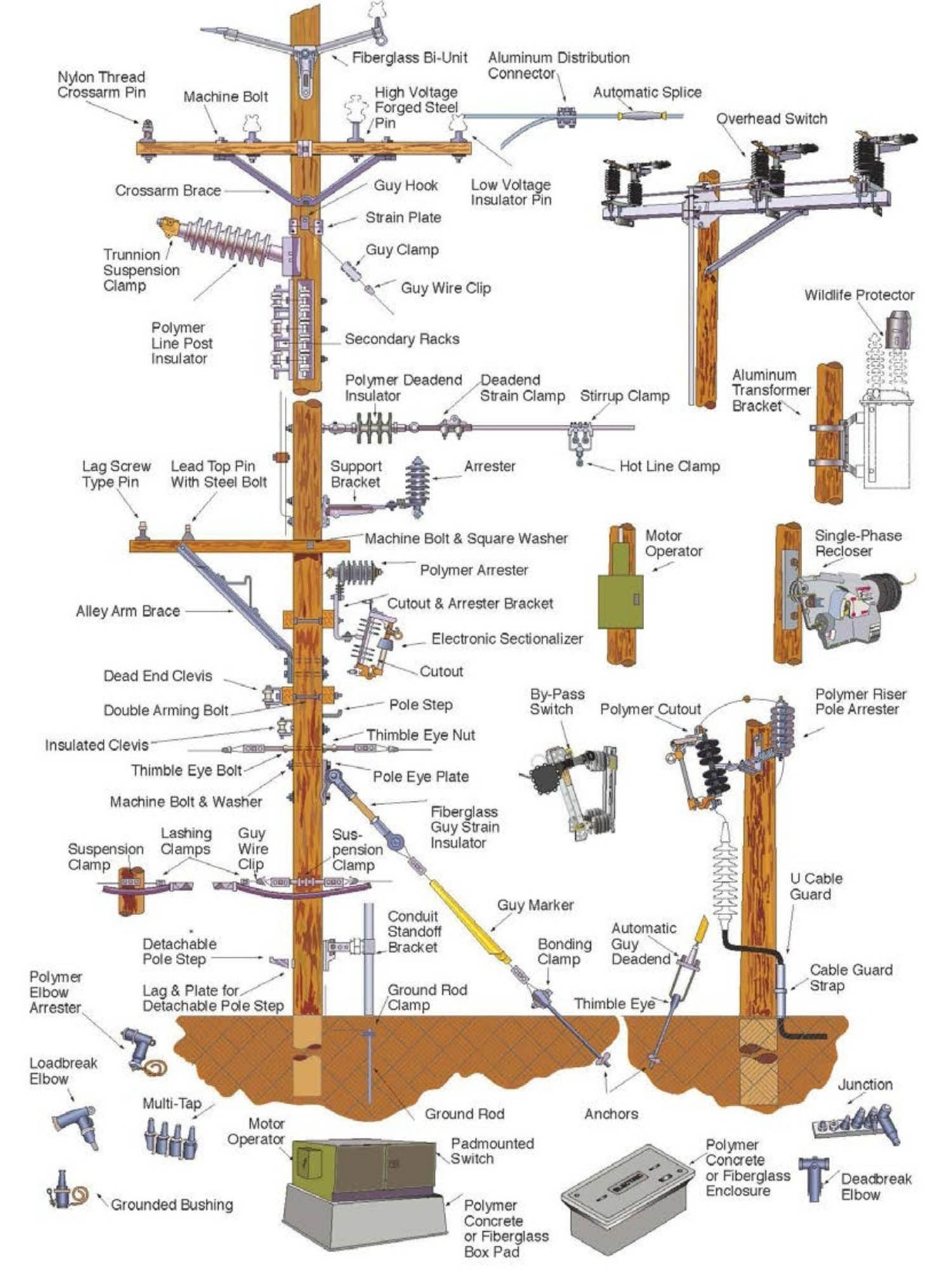
Illustrative image related to power line parts
The Solution: To mitigate these delays, businesses should implement a robust inventory management system that tracks the availability of power line parts in real-time. Establishing strong relationships with multiple suppliers can provide backup options when primary sources are unavailable. Additionally, adopting a just-in-time (JIT) inventory approach ensures that components arrive precisely when needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of stockouts. Regularly reviewing and adjusting inventory levels based on demand forecasts and project timelines can also enhance operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Sourcing Quality Components
The Problem: The quality of power line parts can vary significantly across suppliers, leading to potential safety issues and operational inefficiencies. Buyers may find themselves dealing with components that do not meet international standards or have subpar durability, resulting in frequent failures and the need for replacements. This is particularly concerning in regions with harsh environmental conditions, where the integrity of power line parts is critical to maintaining a reliable electricity supply.
The Solution: To ensure quality, buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to established industry standards and certifications. Conducting thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, including reviewing their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and past customer feedback, is essential. Additionally, implementing a testing protocol for incoming components can help verify their reliability before installation. Leveraging technology such as blockchain for supply chain transparency can also provide traceability of the parts, ensuring that only high-quality components are utilized in projects.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Understanding Technical Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the technical specifications of power line parts, which can lead to incorrect purchases and project delays. For instance, misunderstanding the load capacity of a particular pole or the insulation rating of an insulator can result in using components that are inadequate for the intended application. This not only jeopardizes project timelines but also poses safety risks and increases liability.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should invest in training programs for their procurement teams to enhance their understanding of the technical specifications relevant to power line parts. Additionally, collaborating closely with engineers and technical experts during the sourcing process can ensure that the right components are selected. Creating a comprehensive specification guide that outlines the critical parameters for each type of part can serve as a valuable reference. Furthermore, engaging with manufacturers for technical support or clarification can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that the correct specifications are met for each project.

Illustrative image related to power line parts
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power line parts
What are the Key Materials Used in Power Line Parts?
When selecting materials for power line components, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials is crucial for ensuring reliability and compliance. Here, we analyze four prevalent materials: steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and composite materials.
How Does Steel Perform in Power Line Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in power line hardware due to its high strength and durability. Key properties include excellent tensile strength and resistance to deformation under load, making it suitable for components like cross arms and pole fittings. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced through hot-dip galvanization, which is essential for outdoor applications.
Pros: Steel offers high load-bearing capacity and is relatively cost-effective compared to other metals. Its availability and ease of manufacturing make it a preferred choice for many applications.
Cons: The main drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in certain applications where lighter materials may be preferable.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various environmental conditions, making it suitable for regions with extreme weather. However, international buyers must consider local corrosion rates and treatment standards.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Power Line Parts?
Aluminum is another popular choice for power line components, particularly in overhead lines. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, which is critical for longevity in harsh environments.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. It also does not corrode as easily as steel, making it ideal for coastal or humid regions.
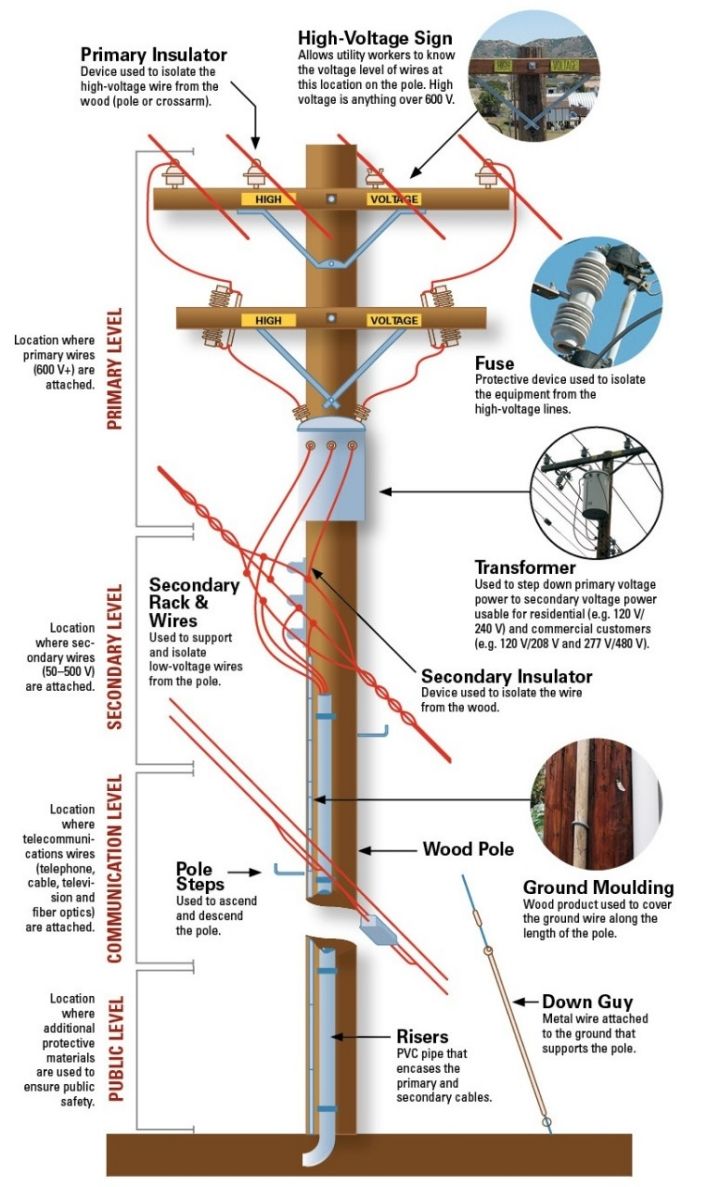
Illustrative image related to power line parts
Cons: The primary limitation of aluminum is its lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may necessitate larger or more frequent supports in certain applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for high-voltage transmission lines where weight is a critical factor. Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards for aluminum alloys, such as ASTM B221.
How Does Fiberglass Compare in Power Line Hardware?
Fiberglass is increasingly used in power line applications due to its non-conductive properties and resistance to environmental degradation. Key properties include high tensile strength and excellent insulation capabilities, making it suitable for insulators and cross arms.
Pros: Fiberglass is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for areas with high humidity or salt exposure. Its non-conductive nature enhances safety in electrical applications.
Cons: The main drawback is the higher cost of fiberglass compared to metals, which can impact budget considerations for large projects. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Fiberglass is particularly effective in applications requiring electrical insulation. International buyers should verify compliance with standards such as IEC 61109 for insulators.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Power Line Parts?
Composite materials, often a combination of fiberglass and resins, are becoming popular for power line components due to their unique properties. These materials provide excellent strength, lightweight characteristics, and superior corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and are resistant to environmental factors, making them suitable for various climates. They also require minimal maintenance over their lifespan.
Cons: The cost of composite materials can be significantly higher than traditional materials like steel and aluminum, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for innovative applications where traditional materials may not suffice. Buyers must ensure that composite products meet local and international standards, such as ASTM D3039.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Power Line Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for power line parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Cross arms, pole fittings | High strength and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Overhead lines | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength than steel | Medium to High |
| Fiberglass | Insulators, cross arms | Non-conductive and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Composite | Innovative applications | High strength-to-weight ratio and low maintenance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in power line parts, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power line parts
What Are the Key Stages of Manufacturing Power Line Parts?
Manufacturing power line parts involves several critical stages that ensure the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and composites, each chosen for their specific properties, such as strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. The materials undergo inspection for quality assurance, ensuring they meet the required specifications before moving to the next stage.
-
Forming Techniques: Forming is where raw materials are shaped into components. Various techniques such as forging, casting, and machining are employed depending on the complexity of the part. For instance, steel cross arms may be fabricated through hot rolling, while insulators are often molded using advanced polymer techniques. Precision in this stage is crucial, as any deviation can lead to compromised performance in the field.
-
Assembly of Components: Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into finished products. This process may involve welding, bolting, or using specialized fasteners to ensure strong, reliable connections. Each assembly is conducted under strict guidelines to maintain consistency and integrity.
-
Finishing Processes: The final stage includes surface treatments such as galvanizing, painting, or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetic appeal. This step is vital, especially for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Quality checks are performed after finishing to ensure that the protective layers are uniform and effective.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Power Line Parts Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for power line parts, ensuring that products are reliable and safe for use. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA practices.
-
International Standards: Adhering to standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to quality management systems. This certification involves regular audits and continuous improvement processes that help maintain high production standards.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the region and application, additional certifications may be required. For instance, CE marking is crucial for European markets, indicating compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Similarly, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply for components used in oil and gas industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch any defects early. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense where raw materials are inspected upon arrival. Testing for dimensions, material properties, and compliance with specifications helps prevent defective materials from entering production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, components are subjected to various checks to ensure they meet specified tolerances. Techniques such as visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional tests are commonly employed. Advanced manufacturers may use automated systems for real-time monitoring.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, a thorough inspection is conducted. This includes tests for electrical properties, mechanical strength, and environmental durability. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspections, may be used to assess the integrity of critical components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing practices and quality control systems firsthand. This can help buyers understand the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports can give insights into the frequency of defects and the effectiveness of their quality management systems.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality practices. These inspectors can conduct tests and assessments that align with international standards, offering additional assurance to buyers.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers should be aware of various nuances that can affect quality control and certification processes:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards for manufacturing and certification. For example, while ISO certifications are globally recognized, specific regions may require additional certifications like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for electrical safety in North America or SANS (South African National Standards) for products sold in South Africa.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural approaches to quality and compliance is essential. For instance, suppliers in some regions may prioritize cost over quality, impacting their adherence to international standards. Open communication regarding expectations and standards can help mitigate these risks.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should ensure that their suppliers maintain transparency throughout the supply chain. This includes understanding where materials are sourced, the processes used, and any third-party certifications that may apply. Transparency can enhance trust and ensure that the products meet the necessary quality standards.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for power line parts are critical to ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards. For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions, understanding these processes and actively verifying supplier practices can lead to more informed purchasing decisions and successful project outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power line parts’
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing power line parts effectively is crucial for ensuring reliable electricity transmission and distribution. This guide provides a practical checklist for international B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of procurement and ensure that you select the best components for your needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is the first step in sourcing power line parts. Clearly outline the types of components needed, such as insulators, cross arms, or connectors, and their technical specifications, including material, size, and load capacity. This clarity will help in communicating with suppliers and ensuring that the parts meet your operational standards.
2. Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry and those that specialize in power line hardware. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry associations to compile a list of potential partners.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Ensure that the suppliers adhere to relevant quality and safety standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. This step is crucial to avoid sourcing subpar products that could compromise your infrastructure.
4. Request Samples and Product Specifications
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the components you intend to procure. Assess the quality and suitability of the samples against your specifications. Additionally, obtain detailed product specifications and datasheets, which should include mechanical properties, material composition, and electrical characteristics.
5. Understand the Supply Chain and Lead Times
Discuss the supply chain logistics with your suppliers to understand lead times, delivery schedules, and any potential bottlenecks. Knowing how long it will take to receive your order is essential for planning and avoiding project delays. Also, inquire about their inventory management practices to ensure they can meet your demand consistently.
6. Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and warranties. Don’t hesitate to negotiate to achieve favorable conditions that align with your budget and project timelines. Ensure that you understand the total cost of ownership, including shipping, taxes, and potential tariffs, especially for international transactions.
7. Establish a Quality Assurance Protocol
Before finalizing your order, establish a quality assurance protocol that includes inspection and testing of the components upon arrival. This step is vital to ensure that the parts meet your specifications and are free from defects. Consider implementing a feedback mechanism for continuous improvement and communication with your suppliers.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing power line parts more effectively, ensuring that they procure high-quality components that will support their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power line parts Sourcing
Understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing dynamics of power line parts is vital for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize procurement strategies. This analysis dissects the key cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for navigating the sourcing landscape effectively.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Power Line Parts?
When evaluating the cost structure of power line parts, several components are critical:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Components like steel, aluminum, and specialized insulating materials vary in price based on market conditions, availability, and quality. Galvanization processes to prevent corrosion also add to the material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality assurance. Regions with higher labor costs may influence overall pricing, making it essential to consider the labor market of the supplier’s location.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized parts. Buyers should account for these costs, particularly when engaging suppliers for bespoke solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures product reliability and safety, which is crucial for power line applications. However, these processes can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary widely based on distance, weight, and shipping methods. Incoterms play a crucial role here, affecting who bears the logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that can vary based on market competition, demand, and the buyer’s negotiation leverage.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power Line Parts Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of power line parts, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing minimum order quantities (MOQs) can be a strategic way to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components tailored to specific needs can significantly increase costs. Standardized parts usually offer cost advantages due to streamlined production.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) tend to command higher prices. However, they can also ensure greater reliability and longevity, reducing total ownership costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for proven quality and service guarantees.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is critical. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine cost responsibilities and can affect total landed costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Power Line Parts Pricing?
Negotiation is a crucial aspect of securing favorable pricing for power line parts. Here are actionable tips for B2B buyers:
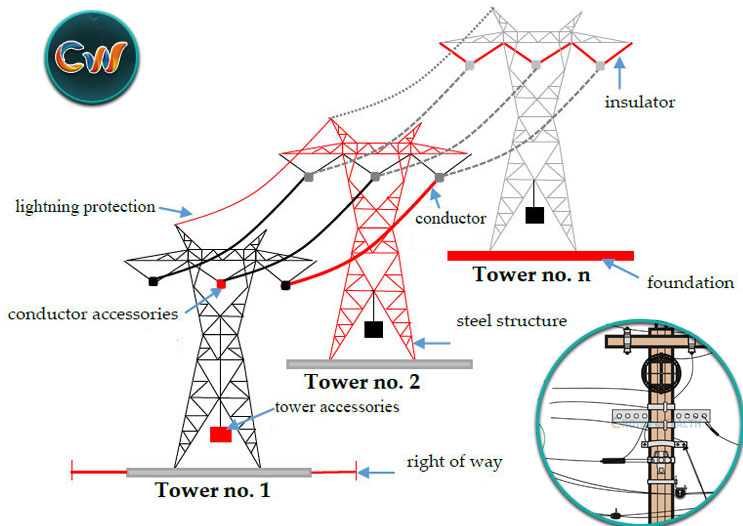
Illustrative image related to power line parts
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs, including maintenance, failure rates, and replacement costs. This holistic view can justify higher upfront investments in quality parts.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Engage suppliers about pricing tiers based on order volumes. Committing to larger purchases can yield significant savings.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate your specifications and requirements. This helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and reduces the likelihood of costly misunderstandings later.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Solicit quotes from various suppliers to gauge market rates. This competitive approach not only aids in price negotiation but also provides insights into supplier capabilities.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can minimize logistics costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
Conclusion
In the competitive landscape of power line parts sourcing, understanding cost structures, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By employing these insights, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and reliability in their power line infrastructure investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power line parts With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Power Line Parts
In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical infrastructure, the need for efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solutions is paramount. While traditional power line parts play a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electricity, various alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar goals. This analysis compares power line parts with two viable alternatives: underground cabling and wireless power transmission systems. Understanding these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional contexts.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Power Line Parts | Underground Cabling | Wireless Power Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and load capacity | Excellent for urban areas; less vulnerable to weather | Limited range; efficiency varies with distance |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; maintenance costs can add up | High installation costs; lower maintenance over time | High initial investment; ongoing R&D costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes and materials | Requires extensive excavation and planning | Complex technology; regulatory hurdles |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections needed | Minimal once installed | Requires periodic upgrades and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Rural and suburban areas; high voltage transmission | Urban environments; areas prone to extreme weather | Applications needing mobility or temporary setups |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Underground Cabling
Underground cabling is increasingly adopted in urban areas where space is limited and aesthetics are a concern. Its primary advantage lies in its resilience to environmental factors such as storms and vandalism, significantly reducing power outages. However, the initial installation cost can be prohibitive due to the need for extensive excavation and specialized labor. Once installed, maintenance is minimal compared to overhead lines, making it a long-term cost-effective solution for cities facing space and aesthetic challenges.
Wireless Power Transmission
Wireless power transmission, while still in its nascent stages, presents an innovative alternative, especially for applications that demand mobility or temporary setups. This technology eliminates the need for physical connections, allowing for more flexible deployment. However, its range is currently limited, and efficiency decreases with distance, which can pose challenges for large-scale applications. Additionally, the high initial investment and ongoing research and development costs can deter many businesses from adopting this technology. Nevertheless, it holds promise for specific sectors such as transportation and remote energy delivery.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right solution for power transmission and distribution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their operational requirements, budget constraints, and the specific challenges of their geographical location. Power line parts remain a reliable choice for many applications, particularly in rural areas where high-voltage transmission is necessary. However, alternatives like underground cabling may be better suited for urban environments, while wireless power transmission could be explored for niche applications requiring flexibility. By assessing the pros and cons of each option, businesses can align their energy infrastructure investments with their long-term strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power line parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power Line Parts?
Understanding the technical properties of power line parts is critical for B2B buyers seeking to ensure reliability, safety, and efficiency in electrical installations. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of power line components, such as insulators and conductors, determines their strength and durability. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and composite materials. High-grade materials resist corrosion and fatigue, ensuring a longer lifespan, which is particularly important in harsh environments like those found in Africa and South America.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension of power line parts. Accurate tolerances ensure that components fit correctly and function as intended. For B2B buyers, tight tolerances can reduce installation time and costs, minimizing the risk of equipment failure due to improper fittings.
3. Breaking Load Capacity
This property indicates the maximum load that a component can withstand before failure. For example, conductors and hardware must be able to support the weight of ice, wind, and other environmental factors. Understanding breaking load capacities is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with local regulations, especially in areas prone to extreme weather.
4. Electrical Insulation Properties
Insulation materials must have high dielectric strength to prevent electrical breakdown. Insulators used in power line fittings should exhibit low conductivity and high resistance to environmental stressors. This property is vital for minimizing energy loss and ensuring the safety of the electrical grid.
5. Galvanization
Galvanization is a process that coats steel components with a layer of zinc to prevent rust and corrosion. This is particularly important for outdoor applications where exposure to moisture and other elements is common. For B2B buyers, selecting galvanized components can lead to lower maintenance costs and prolonged equipment life.
6. Design Specifications
Design specifications cover the geometric and structural characteristics of power line parts, including size, shape, and weight. Proper design is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and for optimizing performance. Buyers should assess design specifications to ensure they meet the requirements of their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Power Line Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are some commonly used terms in the power line parts industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the power line industry, OEMs often provide specialized components that meet specific design and performance standards, making them crucial for quality assurance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. It can also influence the decision to source from different suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer requesting pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. Submitting RFQs allows buyers to compare options and negotiate favorable terms, ensuring they receive the best value for their investments.

Illustrative image related to power line parts
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is crucial when sourcing components globally.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time that elapses from the placement of an order until its delivery. For power line parts, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and ensuring timely installation, especially in regions with longer supply chains.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to the qualifications and compliance measures that products must meet to ensure safety and quality. Common standards include IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). Buyers should ensure that components meet relevant certification standards to mitigate risk and ensure reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the power line industry can make informed decisions that enhance project outcomes and operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to power line parts
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power line parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Power Line Parts Sector?
The global power line parts market is experiencing significant evolution, driven by several factors. The increasing demand for reliable electricity infrastructure in developing regions, particularly in Africa and South America, is a primary catalyst. These regions are investing heavily in energy distribution networks to support economic growth, which translates to increased sourcing of power line hardware. Additionally, the ongoing transition towards renewable energy sources is reshaping the market, as traditional power line components are adapted for compatibility with solar and wind energy systems.
Emerging technologies are also influencing sourcing trends. Automation and smart grid technologies are becoming integral in power line management, prompting buyers to consider advanced components that support these innovations. Digital platforms for procurement are gaining traction, allowing international buyers to streamline sourcing processes and enhance transparency. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce in B2B transactions is enabling buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East to access a wider range of suppliers, thus fostering competition and better pricing.
Market dynamics are characterized by a focus on quality and reliability. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate robust testing and quality assurance processes. The emphasis on high breaking load capacities and resistance to environmental factors is crucial, particularly in regions prone to severe weather conditions. As a result, international buyers are encouraged to develop strong relationships with manufacturers who meet these stringent requirements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Power Line Parts Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the power line parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, pushing buyers to seek suppliers who adopt eco-friendly practices. This includes using recyclable materials and minimizing waste during production. As global awareness of climate change grows, companies that prioritize sustainability can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, as buyers are increasingly aware of the implications of sourcing decisions. Ensuring fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials is essential. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices. Buyers should look for these certifications when evaluating potential partners.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials into power line parts is a growing trend. For instance, manufacturers are exploring alternatives to traditional steel and aluminum, such as composites that offer lighter weight and better resistance to corrosion. These advancements not only contribute to sustainability goals but also enhance the durability and performance of power line components.
What Is the Evolution of the Power Line Parts Sector?
The power line parts sector has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from rudimentary fittings to sophisticated components designed for modern electrical grids. Early power line hardware primarily consisted of basic insulators and conductors, which were sufficient for the less demanding infrastructure of the past. As electricity demand surged in the mid-20th century, the need for more reliable and efficient components became apparent.
The introduction of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques in the late 20th century marked a turning point. Innovations such as hot-dip galvanization improved the corrosion resistance of components, while modular designs facilitated easier installation and maintenance. Today, the sector is witnessing a convergence of technology and sustainability, with smart components that integrate seamlessly into modern energy systems. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting suppliers who not only understand the legacy of power line infrastructure but are also forward-thinking in their approach to design and manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power line parts
-
How do I choose the right power line parts for my project?
Selecting the appropriate power line parts requires a thorough understanding of your specific application and requirements. Consider factors such as the type of electrical infrastructure (overhead or underground), voltage levels, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards in your region. It’s also essential to evaluate the mechanical and electrical properties of the components, ensuring they are suitable for your intended use. Collaborating with experienced suppliers can provide insights and recommendations tailored to your project needs. -
What is the best material for power line hardware in high-corrosion environments?
For high-corrosion environments, galvanized steel or stainless steel is often the best choice for power line hardware. Galvanization provides a protective layer against rust and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Stainless steel, while more expensive, offers superior resistance to corrosive elements and is ideal for areas with high humidity or exposure to chemicals. When sourcing materials, ensure compliance with international standards for durability and safety. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for power line components?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, manufacturing capabilities, and quality certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in producing power line components that meet international standards. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their ability to customize products to meet your specific requirements. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities and support for international shipping, especially if you are sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, or Europe. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power line parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power line parts can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of component. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen for smaller items to several hundred for larger, custom-made parts. It’s advisable to discuss your project needs with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and project timeline. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or bulk purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of power line parts can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and consider using secure payment methods that offer protection against fraud. Additionally, understand any applicable taxes, tariffs, or fees that could impact the overall cost of your purchase. -
How can I ensure the quality of power line parts before shipment?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications and certifications for the power line parts you are purchasing. Many reputable suppliers offer quality assurance processes, including factory audits and third-party inspections. Consider implementing a pre-shipment inspection to verify that the components meet your specifications and compliance standards. This step is particularly crucial when dealing with international suppliers to minimize risks associated with product quality. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing power line components?
Logistics for importing power line components involve understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling electrical components to navigate international shipping complexities. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country, and ensure all documentation is in order to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, factor in lead times for manufacturing and shipping when planning your project schedule. -
Are there customization options available for power line parts?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for power line parts to meet specific project requirements. Customization can include alterations in design, size, material, and finish. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and any relevant standards that must be met. Be prepared for potential lead times associated with custom orders, as these may require additional manufacturing processes and quality checks.
Top 6 Power Line Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. TTF Power – Power Line Hardware
Domain: ttfpower.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Power line hardware includes various components essential for power and communication projects, such as: ACSR Cable, Drop-Out Fuse, Cutout, Electrical Insulator, Formed Wire, Guy Wire, Ground Anchor, Surge Arrester, Suspension Clamp, ADSS/OPGW Accessories, Distribution Box & Enclosure, Conductor Hardware, Formed Wire Lug & Terminal, Splice Connector, Load Break Cutout, Link Break Cutout, Grounding…
2. HB Jinyong – Overhead Power Line Solutions
Domain: hbjinyong.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Overhead power lines are groups of suspended cables and wires used to transport electrical power between locations. They are supported by utility poles or steel towers to maintain safe height and ground clearance. Types of power lines include transmission lines (high-voltage primary power) and distribution lines (lower voltage for public use). Power lines can be classified by voltage (low, medium,…
3. Hubbell Power Systems – Line Construction Hardware
Domain: hubbell.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Line Construction Hardware for electric utility and communications outside plant grid construction. Hubbell Power Systems, Inc. offers a breadth of products, quality, and availability required to keep jobs moving. Customer service is available for inquiries.
4. Line Power – Longwall Control Systems
Domain: linepower.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1. Parts and Rebuild 2. Longwall Control Systems 3. High Capacity Longwall Power Center 4. Outdoor Substations 5. High Voltage Grounding Resistors 6. High Voltage Splice Box 7. XP Electrical Enclosure 8. Distribution Vacuum Circuit Breaker 9. High Voltage Couplers 10. Series 64 Low Voltage Coupler 11. Series 67 Low Voltage Coupler 12. Series 68 Low Voltage Coupler 13. Series 69 Low Voltage Coupler…
5. Graybar – Pole Line Hardware
Domain: graybar.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Key product categories include Pole Line Hardware, Pole Line Anchors, and Pole Line Accessories. Major manufacturers featured are Hubbell Power Systems, Maclean Power Systems, and Preformed Line Products, among others. The products are available in various lengths, including 18 in., 12 in., 24 in., and 8 ft. The country of origin for many products includes the United States, Mexico, China, and Ind…
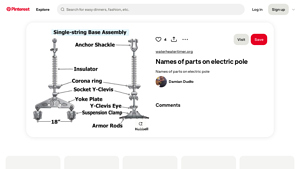
6. Pinterest – Electric Pole Components Guide
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Names of parts on electric pole, Transmission line, Basic electrical wiring, Electronic circuit design, Electric Pole Components, Electric Pole Parts Names, Parts Of A Power Pole, Parts Of A Power Pole Diagram, Parts Of A Utility Pole, Types Of Electric Poles
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power line parts
In summary, effective strategic sourcing of power line parts is essential for optimizing supply chains and ensuring the reliability of electrical infrastructure. Key components such as conductor hardware, insulators, and grounding systems are vital for maintaining safety and performance in power transmission. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, transparency, and technical expertise, as these factors directly impact the longevity and efficacy of power line systems.
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, so does the importance of sourcing high-quality materials that can withstand environmental challenges, particularly in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By forging strong partnerships with reputable manufacturers and distributors, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to assess their sourcing strategies and explore innovative solutions that align with global energy trends. Engage with suppliers who are not only equipped to meet current demands but are also poised to adapt to future challenges in the power line sector. Embrace this opportunity to strengthen your supply chain and ensure the resilience of your electrical infrastructure.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.