How to Source Pneumatic Cylinder Components Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic cylinder components
Navigating the global market for pneumatic cylinder components can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially when it comes to sourcing reliable suppliers and ensuring product quality. With diverse applications spanning industries from manufacturing to automotive, the demand for pneumatic cylinders is on the rise. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of pneumatic cylinder components, offering insights into various types, applications, and critical factors to consider when selecting the right products for your needs.
In this comprehensive resource, we will explore the different categories of pneumatic cylinders, including single-acting and double-acting options, and delve into their specific applications across sectors such as robotics, packaging, and material handling. Additionally, we will address essential considerations for supplier vetting, including quality assurance, pricing structures, and logistical challenges that may arise in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational requirements and budget constraints. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, understanding the nuances of pneumatic cylinder components will enhance your procurement strategy and ultimately drive your business forward in a competitive global market.
Understanding pneumatic cylinder components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Acting Cylinder | Operates in one direction; uses a spring return. | Clamping, lifting, and pushing applications. | Pros: Cost-effective, simple design. Cons: Limited force direction; lower efficiency in some applications. |
| Double-Acting Cylinder | Operates in both directions; uses compressed air. | Automation, packaging, and assembly processes. | Pros: Greater control and efficiency. Cons: More complex and higher initial cost. |
| Compact Cylinder | Space-saving design; typically lighter and shorter. | Restricted spaces in manufacturing and robotics. | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces; versatile. Cons: May have lower force output compared to standard cylinders. |
| Rodless Cylinder | No external rod; uses internal mechanisms for motion. | Applications requiring long strokes with limited space. | Pros: Space-efficient; smooth operation. Cons: More complex design may lead to higher maintenance needs. |
| Tandem Cylinder | Two cylinders working in unison; increased force. | Heavy-duty applications in manufacturing. | Pros: High force output; versatile. Cons: Requires more space and can be more expensive. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Single-Acting Cylinders?
Single-acting cylinders are characterized by their ability to exert force in one direction only, utilizing a spring mechanism to return to their original position. This design is particularly suitable for applications where the load is only moved in one direction, such as clamping and lifting tasks. When purchasing, buyers should consider the required force, speed, and the specific application context. While they are cost-effective and simple, their limitations in directionality and efficiency may not meet the needs of more complex operations.
Why Choose Double-Acting Cylinders for Your Business?
Double-acting cylinders are distinguished by their capability to exert force in both directions, powered by compressed air on both the extension and retraction strokes. This versatility makes them ideal for various automation, packaging, and assembly processes. When selecting a double-acting cylinder, businesses should assess the required force, speed, and cycle frequency. Although they offer greater control and efficiency, they come with a more complex design and higher initial costs, which could impact budget considerations.
How Do Compact Cylinders Benefit Space-Constrained Applications?
Compact cylinders are designed to save space while maintaining functionality, making them particularly advantageous in environments where installation space is limited. They are commonly used in manufacturing and robotics applications where footprint is a concern. Buyers should evaluate the force output in relation to the specific requirements of their application. While compact cylinders are versatile and lightweight, they may provide less force compared to standard cylinders, which is an important consideration in demanding applications.
What Makes Rodless Cylinders Unique in Pneumatic Systems?
Rodless cylinders are unique due to their internal mechanisms that allow for linear motion without an external rod, making them ideal for applications requiring long strokes in confined spaces. They are often used in scenarios where traditional cylinders would be obstructed. When considering a rodless cylinder, it is essential to factor in the stroke length and load requirements. Although they offer smooth operation and efficient space usage, their more complex design may lead to increased maintenance needs.
When Should You Consider Tandem Cylinders for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Tandem cylinders consist of two cylinders operating together to deliver increased force, making them suitable for heavy-duty tasks in manufacturing. They are often employed in applications that require significant lifting or pushing capabilities. Buyers should assess their specific force requirements and available installation space when considering tandem cylinders. While they provide high output and versatility, they typically require more space and can incur higher costs, which should be factored into the overall project budget.
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic cylinder components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic cylinder components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Automated assembly lines for car parts | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Consider reliability, response time, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Packaging | Movement control of packaging materials and products | Enhances throughput and accuracy in packaging processes | Ensure the cylinders can handle the specific weights and sizes of materials. |
| Food and Beverage | Filling, sealing, and packaging processes | Maintains hygiene and speeds up production cycles | Look for corrosion-resistant materials and compliance with food safety standards. |
| Manufacturing | Material handling and sorting systems | Improves operational efficiency and reduces waste | Evaluate the operating pressure and space constraints in the production line. |
| Medical Equipment | Operation of surgical robots and prosthetic devices | Provides precision and reliability in critical applications | Prioritize precision engineering and compliance with medical device regulations. |
In the automotive sector, pneumatic cylinder components are integral to automated assembly lines, where they precisely position and manipulate car parts during production. This automation leads to increased efficiency and significant labor cost reductions. Buyers should focus on sourcing reliable cylinders that offer fast response times and are compatible with existing machinery to ensure seamless integration.
In the packaging industry, pneumatic cylinders control the movement of materials and products, facilitating the packaging process. This application enhances throughput and accuracy, allowing businesses to meet higher production demands. When sourcing, it is crucial to ensure that the cylinders can accommodate the specific weights and sizes of the packaging materials being used.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
The food and beverage sector utilizes pneumatic cylinders in filling, sealing, and packaging processes. These components help maintain hygiene standards while speeding up production cycles. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing cylinders made from corrosion-resistant materials and ensure they comply with food safety regulations to avoid contamination.
In manufacturing, pneumatic cylinders are employed in material handling and sorting systems, improving operational efficiency and reducing waste. This application is particularly vital in high-volume environments where speed and precision are essential. Buyers should evaluate the operating pressure and space constraints when selecting pneumatic cylinders to fit their production lines.
In the medical equipment field, pneumatic cylinders play a crucial role in the operation of surgical robots and prosthetic devices. They provide the precision and reliability necessary for critical applications. Buyers must prioritize sourcing options that feature precision engineering and adhere to stringent medical device regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness in their applications.
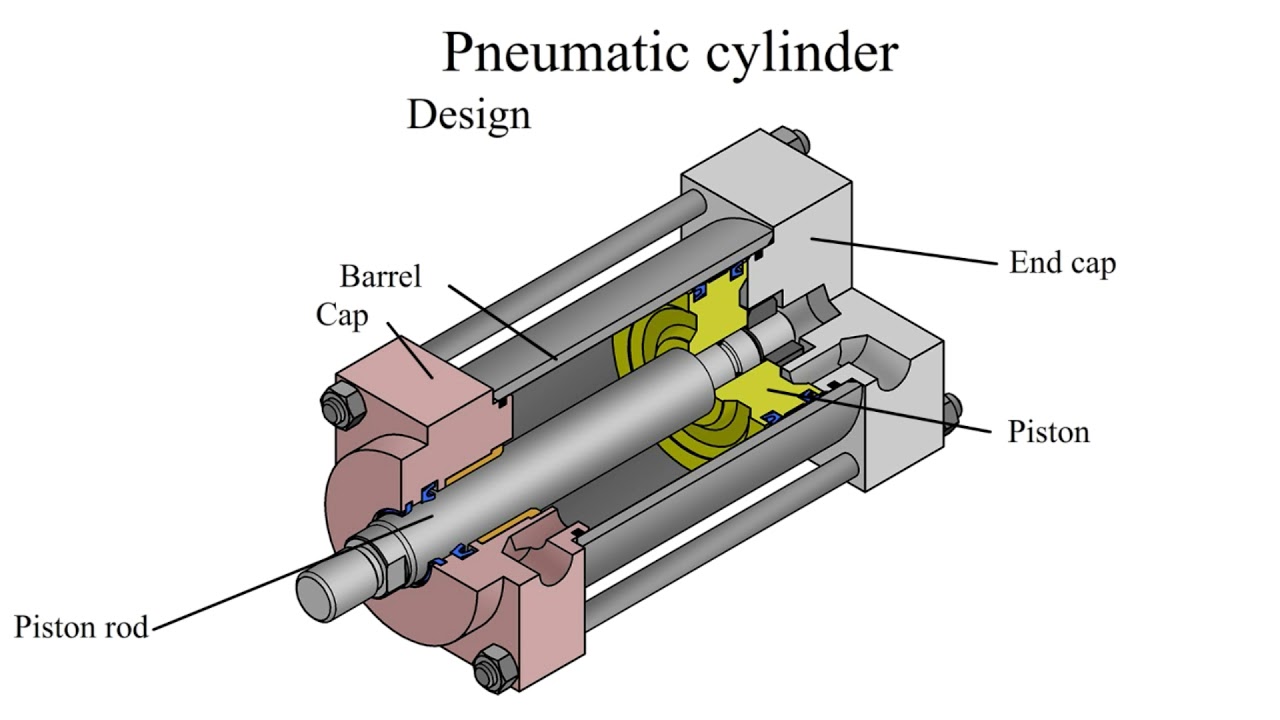
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pneumatic cylinder components’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Performance in Automated Systems
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter issues with pneumatic cylinder components that do not deliver consistent performance. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, such as improper selection of cylinder types, inadequate maintenance, or fluctuations in air pressure. For instance, in an automated assembly line, a pneumatic cylinder that fails to maintain its force or speed can lead to production delays, increased waste, and ultimately, higher operational costs. This is particularly problematic in industries like automotive manufacturing, where precision and reliability are crucial.
The Solution:
To address performance inconsistencies, it is vital for buyers to thoroughly assess their application requirements before selecting pneumatic cylinder components. This includes considering the operating environment, load requirements, and the frequency of use. Buyers should opt for double-acting cylinders for applications requiring bidirectional force, while single-acting cylinders can be suitable for simpler tasks. Furthermore, regular maintenance schedules must be established to check for wear and tear, air leakage, and ensure proper lubrication. Leveraging data from performance monitoring tools can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Existing Systems
The Problem:
Another significant challenge faced by B2B buyers is the compatibility of new pneumatic cylinder components with existing systems. As companies evolve and upgrade their machinery, the integration of new components can lead to complications, particularly if they do not match existing specifications or interfaces. This often results in costly downtime, as companies may need to redesign systems or revert to older, less efficient technology to accommodate the new components.
The Solution:
To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough compatibility analysis prior to procurement. This involves reviewing the specifications of existing pneumatic systems, including cylinder sizes, mounting styles, and connection types. Engaging with manufacturers or suppliers who offer customization options can also provide tailored solutions that fit seamlessly into existing setups. Additionally, investing in modular components can facilitate easier upgrades in the future, allowing for flexible adaptations as operational needs change.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Frequent Failures
The Problem:
Frequent failures of pneumatic cylinder components can lead to high replacement costs, significantly impacting a company’s bottom line. This issue may arise from using low-quality components, inadequate maintenance practices, or operating under conditions that exceed the component’s specifications. For instance, in harsh environments such as food processing or chemical manufacturing, exposure to contaminants can accelerate wear and lead to premature failures, forcing companies to frequently replace their components.
The Solution:
To reduce replacement costs associated with failures, it is essential for buyers to invest in high-quality pneumatic cylinder components designed for specific environmental conditions. This includes selecting components made from durable materials resistant to corrosion and wear, such as stainless steel or special coatings for added protection. Implementing a robust maintenance program that includes regular inspections, cleaning, and timely replacements of seals and filters can extend the life of the cylinders. Furthermore, training staff on the proper operation and handling of pneumatic systems can minimize the risk of user-induced damage, ultimately leading to a decrease in overall costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic cylinder components
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
When selecting materials for pneumatic cylinder components, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and composite materials, focusing on their relevant properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Pneumatic Cylinder Applications?
Aluminum is widely used in pneumatic cylinder components due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can withstand moderate pressures, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, easy to machine, and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. Its low weight contributes to energy efficiency in pneumatic systems.
Cons: However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-pressure applications beyond its limits and can be less durable than steel in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with most pneumatic media, but care should be taken with corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to minimize costs and ensure quality.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Stainless steel is another common material, known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 400°C and high pressures, making it suitable for demanding environments.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to wear and corrosion make stainless steel ideal for applications in the automotive and food processing industries.
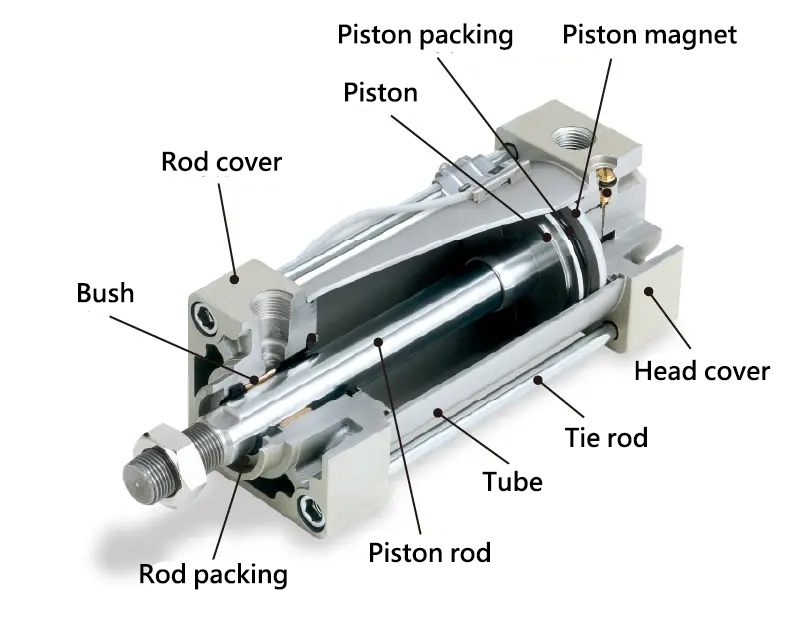
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to aluminum, along with increased manufacturing complexity due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive fluids, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM, especially in regions like South America and Africa, where regulatory compliance can vary significantly.
Why Choose Brass for Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Brass is often used for fittings and connectors in pneumatic systems due to its excellent machinability and good corrosion resistance. It operates effectively at temperatures up to 300°C and can handle moderate pressures.
Pros: Brass is cost-effective and provides good sealing capabilities, making it ideal for small-scale applications.
Cons: However, brass is not as strong as aluminum or stainless steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is generally compatible with air and non-corrosive fluids but may not be suitable for aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of brass, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Composite materials are increasingly being used in pneumatic cylinders due to their lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. They can withstand temperatures up to 150°C and moderate pressures.
Pros: Composites are resistant to corrosion and can be tailored for specific applications, providing design flexibility.
Cons: The main limitation is their higher manufacturing complexity and cost compared to traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Composites can be used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace or automotive sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composite materials meet local and international standards, as the technology and regulations around composites can differ widely across regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pneumatic Cylinder Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for pneumatic cylinder components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | General-purpose pneumatic cylinders | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited high-pressure use | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty applications in automotive and food processing | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Brass | Fittings and connectors in pneumatic systems | Good machinability and sealing | Limited strength | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and customizable | High manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide equips B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in pneumatic cylinder components, enabling informed decision-making tailored to their specific application needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic cylinder components
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
The manufacturing process of pneumatic cylinder components involves several crucial stages that ensure the creation of high-quality products. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials for pneumatic cylinder components include aluminum, stainless steel, and various polymers. These materials are chosen for their strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties.
During material preparation, raw materials undergo processes such as cutting, machining, and surface treatment to achieve the desired specifications. For instance, aluminum may be anodized to enhance its corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Quality control begins at this stage, where materials are inspected for consistency, defects, and compliance with specified standards.
How Are Pneumatic Cylinder Components Formed?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage commences. This involves various techniques such as machining, extrusion, and forging. Machining is particularly prevalent for creating precise features and tolerances essential for the functionality of pneumatic cylinders. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often utilized to achieve the necessary precision.
In addition to machining, extrusion processes may be employed for producing specific shapes and profiles, particularly for cylinder bodies. Forging can also be used for components that require enhanced strength, as it aligns the grain structure of the metal.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail for Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form a complete pneumatic cylinder. This involves the integration of various parts such as the cylinder body, piston, rod, and seals. During assembly, it is crucial to ensure that all components fit together correctly and operate smoothly.
Assembly techniques vary depending on the design of the cylinder. Some manufacturers utilize automated assembly lines for higher efficiency, while others may rely on skilled technicians for more complex configurations. Quality checks are performed at this stage to identify any misalignments or fitting issues that could affect performance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
The finishing stage encompasses various surface treatments that enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of pneumatic cylinder components. Common techniques include painting, anodizing, and powder coating. These processes not only improve appearance but also provide additional protection against environmental factors such as moisture and corrosion.
Finishing also includes the application of lubricants and sealants, which are essential for the optimal functioning of pneumatic cylinders. The final products undergo rigorous inspections to ensure that they meet all specified standards before being packaged for distribution.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for pneumatic cylinder components, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. This involves adhering to quality management systems such as ISO 9001, which sets out the criteria for a quality management system.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Control in Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturing?
In addition to ISO 9001, other industry-specific standards may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, API standards for oil and gas applications, and various safety standards relevant to specific industries. Compliance with these standards not only enhances product credibility but also facilitates international trade.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. The main checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on raw materials and components to verify their compliance with specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring and testing components at various stages to identify any deviations from standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the completed pneumatic cylinders for functionality, safety, and adherence to specified standards before they are dispatched.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Several testing methods are commonly utilized to ensure the performance and reliability of pneumatic cylinder components. These include:
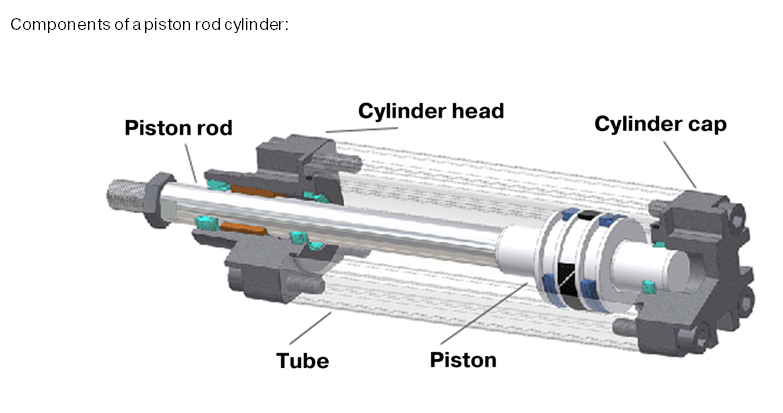
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
-
Leak Testing: Ensures that there are no air leaks, which could compromise the cylinder’s functionality.
-
Pressure Testing: Verifies the cylinder’s ability to withstand operational pressures without failure.
-
Functional Testing: Assesses the overall operation of the cylinder, including speed, response time, and movement accuracy.
These tests are essential for confirming that the products can perform reliably in their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Their Suppliers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
What Steps Should Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate the quality management systems in place. Buyers should request access to the supplier’s production facilities and quality control documentation. During the audit, key areas to focus on include:
- Compliance with international standards (ISO, CE, API, etc.)
- Quality control checkpoints and testing procedures
- Maintenance of equipment and machinery
How Can Buyers Use Reports and Certifications to Assess Supplier Quality?
Buyers should request quality reports and certifications from suppliers to verify compliance with relevant standards. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s quality assurance processes and their commitment to maintaining high standards. Look for certifications that demonstrate adherence to international quality management systems.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of production, offering additional assurance that the products meet specified standards. Third-party inspectors can also provide detailed reports that highlight any potential issues, allowing buyers to make informed decisions.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Vary for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control that can differ by region. Understanding local regulations, market expectations, and cultural differences is crucial. For instance, certain markets may have stricter regulations regarding environmental impact or safety standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
By taking a proactive approach to understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain reliability and product performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pneumatic cylinder components’
In the competitive landscape of industrial automation and machinery, sourcing pneumatic cylinder components requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the foundation of effective sourcing. Determine the type of pneumatic cylinders you need—single-acting or double-acting—based on your application. Consider specifications such as stroke length, bore size, operating pressure, and environmental conditions to ensure compatibility with your machinery.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in pneumatic cylinder components. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential candidates. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry, as this often correlates with reliability and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier choices, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Additionally, check for compliance with regional regulations, especially if you are sourcing from international markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
To assess the quality and suitability of components, request samples along with technical documentation. This should include product specifications, installation guidelines, and maintenance instructions. Analyzing these documents helps you understand the component’s performance and longevity, ensuring it meets your operational demands.
Step 5: Inquire About Customization Options
Depending on your application, you may require customized pneumatic cylinder components. Engage potential suppliers about their ability to modify components to suit specific needs, such as unique sizes or additional features like cushioning devices or integrated sensors. A supplier’s flexibility can significantly enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed pricing information and payment terms. Compare costs across various suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership, including shipping, installation, and potential maintenance costs. Favorable payment terms can also enhance cash flow management, especially for larger orders.
Step 7: Check References and Customer Reviews
Finally, before making a purchase, reach out to other customers or industry peers for references. Inquire about their experiences with the supplier, focusing on product quality, delivery timelines, and customer service. Online reviews and case studies can also provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability and support capabilities.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they make informed decisions when sourcing pneumatic cylinder components, ultimately leading to enhanced operational performance and reliability in their applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic cylinder components Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
When sourcing pneumatic cylinder components, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials. Prices can vary based on market conditions and the specific requirements of the application, such as corrosion resistance or weight considerations.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to higher prices for components, making it essential to consider the location of your suppliers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds required for production can represent a significant upfront investment. These costs may be amortized over large production runs, which can lead to lower per-unit costs as volumes increase.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that components meet specific quality standards often requires additional resources for testing and inspection. Investing in robust QC processes can prevent costly defects and returns, but it may also increase initial costs.
-
Logistics: Transporting components from suppliers to your facility incurs logistics costs, which can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and customs clearance processes. Understanding the logistics landscape in your region is crucial for managing these expenses effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a markup to cover their costs and profit margin. This can vary widely depending on the supplier’s market position, the demand for specific components, and their overall pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pneumatic Cylinder Component Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of pneumatic cylinder components, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it essential to assess your needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized components or those with specific technical requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can increase costs but may provide long-term benefits, such as improved performance and reduced maintenance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can also reduce the risk of costly delays and defects.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for calculating total landed costs. Different Incoterms can affect responsibility for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, impacting the overall price you pay.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers Sourcing Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies are essential:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may lead to higher costs later.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Gather market intelligence on pricing trends and competitor offerings. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and help justify your budget.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers may offer more favorable conditions to loyal customers.
-
Be Transparent: Communicate your needs clearly and discuss your budget constraints. This openness can foster trust and help suppliers propose more tailored solutions.
-
Evaluate Shipping Options: Explore different shipping options and routes to find the most cost-effective solution. Working with logistics experts can help you minimize these expenses.
Conclusion: Understanding Costs and Prices in Pneumatic Cylinder Component Sourcing
Navigating the complexities of sourcing pneumatic cylinder components requires a thorough understanding of cost structures and pricing influencers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with their budgetary constraints. It’s essential to remember that prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, and engaging in strategic negotiations can lead to significant savings and enhanced supplier relationships. Always consider the total cost of ownership to ensure the best long-term value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pneumatic cylinder components With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Pneumatic Cylinder Components
In the realm of industrial automation and mechanical systems, pneumatic cylinder components are widely utilized due to their simplicity and reliability. However, various alternative technologies can also achieve similar objectives, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. This analysis compares pneumatic cylinders with electric actuators and hydraulic cylinders, focusing on key performance aspects that B2B buyers should consider when selecting the best solution for their applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Pneumatic Cylinder Components | Electric Actuators | Hydraulic Cylinders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate speed, limited precision | High precision and speed | High force output, slower speed |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate to high cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install and operate | Requires electrical setup | More complex installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but requires air supply | Low maintenance, no air needed | Higher maintenance due to fluid management |
| Best Use Case | General automation tasks | Applications requiring precise control | Heavy lifting and high-force applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Actuators?
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making them an excellent alternative for applications requiring high precision and speed. They offer advantages such as a cleaner operation (no compressed air required), lower energy consumption in some cases, and precise control over positioning. However, the initial investment can be significantly higher compared to pneumatic cylinders, and they may not be suitable for environments with extreme temperatures or where explosive gases are present.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
How Do Hydraulic Cylinders Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Hydraulic cylinders utilize fluid pressure to generate motion and can produce much higher force compared to pneumatic cylinders. They are ideal for heavy lifting applications, such as in construction and industrial machinery. While they provide impressive power and can operate in demanding environments, they also come with a higher cost and require more complex maintenance to manage hydraulic fluids and potential leaks. Additionally, their speed is generally slower than pneumatic systems, which could be a drawback in applications needing rapid movement.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
When selecting between pneumatic cylinder components, electric actuators, and hydraulic cylinders, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific application requirements. Consider factors such as the required precision, speed, force output, and operational environment. Pneumatic cylinders may be more suitable for general automation tasks with lower budgets and maintenance needs. In contrast, electric actuators excel in precision applications, while hydraulic cylinders are best for heavy-duty tasks. By aligning the technology with application needs, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic cylinder components
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Understanding the essential technical properties of pneumatic cylinder components is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and reliability in various applications. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material used in pneumatic cylinders typically includes aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials. Each material offers different advantages, such as corrosion resistance, weight, and strength. For instance, aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective, making it suitable for many industrial applications, while stainless steel provides enhanced durability in harsh environments. Selecting the right material is vital for ensuring the longevity and functionality of the cylinder in specific operational conditions. -
Operating Pressure
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the cylinder can handle, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. Understanding the operating pressure is essential for matching the pneumatic cylinder to the requirements of your system. Choosing a cylinder with the appropriate pressure rating can prevent premature failure and ensure safety during operation. -
Bore Size
The bore size refers to the internal diameter of the cylinder and directly impacts the force output. A larger bore size allows for greater force generation but may require more space and power. For B2B buyers, understanding bore size is crucial for aligning the cylinder’s capabilities with the intended application, such as lifting, pushing, or clamping. -
Stroke Length
Stroke length is the distance the piston travels within the cylinder. This specification is critical for determining how much movement is required in a particular application. Selecting the correct stroke length ensures that the cylinder can perform its intended function without requiring additional components or modifications. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In pneumatic cylinders, maintaining tight tolerances is vital for ensuring proper sealing and preventing air leaks, which can compromise efficiency and performance. Understanding tolerance levels helps B2B buyers assess the quality and suitability of components for their specific applications. -
Sealing Mechanisms
The type of sealing mechanism used in a pneumatic cylinder, such as O-rings or lip seals, plays a significant role in preventing air leakage and protecting internal components from contaminants. Proper sealing is crucial for maintaining efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the cylinder, making it an essential consideration for buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly streamline communication and procurement processes. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of pneumatic cylinders, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can affect quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. It can also influence purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies that may not require large quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process used by buyers to invite suppliers to submit price quotes for specific products or services. For pneumatic cylinder components, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and detailed specifications tailored to their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding Incoterms is essential for managing shipping costs and responsibilities, which can significantly impact the overall procurement process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is critical for planning production schedules and maintaining operational efficiency, especially in industries with tight deadlines. -
Pneumatic Actuator
A pneumatic actuator is a device that converts compressed air into mechanical motion. This term is often used interchangeably with pneumatic cylinders, but it encompasses a broader range of devices. Understanding the differences can aid in selecting the right component for specific applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing pneumatic cylinder components, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring product compatibility.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pneumatic cylinder components Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Pneumatic Cylinder Components Sector?
The pneumatic cylinder components market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. The rise of automation across industries, particularly in manufacturing and packaging, has increased the demand for pneumatic solutions that offer reliability, speed, and efficiency. Additionally, the ongoing trend towards Industry 4.0 is influencing the adoption of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled pneumatic systems that allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. These advancements enable international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to optimize operational efficiencies and reduce downtime.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced materials and smart actuators, are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly seeking components that not only meet performance specifications but also offer enhanced durability and reduced environmental impact. For instance, the integration of proportional solenoid valves and electric actuators is becoming more common, offering precise control over pneumatic systems. Moreover, as industries expand into new markets like Brazil and Vietnam, sourcing strategies are adapting to local regulations and market demands, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about regional trends.
In summary, the pneumatic cylinder components sector is characterized by a strong push towards automation and smart technology integration, compelling international buyers to rethink their sourcing strategies to align with these evolving market dynamics.
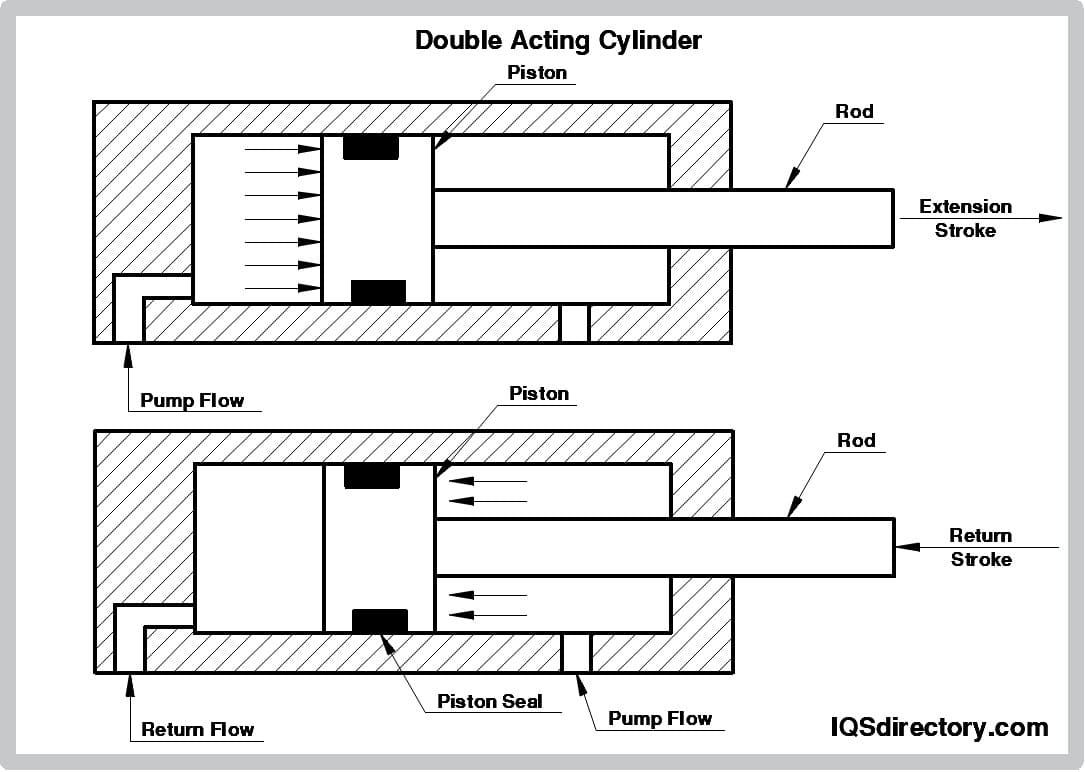
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Pneumatic Cylinder Components Market?
The importance of sustainability in the pneumatic cylinder components market cannot be overstated. As global awareness of environmental issues grows, businesses are increasingly pressured to adopt sustainable practices. The manufacturing processes of pneumatic components can have a significant environmental impact, from energy consumption to waste generation. Therefore, international B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly practices and materials.
Ethical sourcing has also become a critical component in supplier selection. Buyers are looking for manufacturers that adhere to ethical labor practices and have transparent supply chains. This is particularly important in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain integrity can be a concern. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming key indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of pneumatic cylinder components, such as recyclable plastics or low-emission metals, is gaining traction. Suppliers that invest in sustainable technologies and materials not only help mitigate environmental impact but can also enhance their competitiveness in the global market, appealing to conscious buyers looking for responsible sourcing options.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Development of Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
The evolution of pneumatic cylinder components dates back to the early 20th century when the industrial revolution propelled the need for efficient automation solutions. Initially, pneumatic systems were rudimentary, relying on basic mechanical designs. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering led to the development of more sophisticated pneumatic cylinders that could handle higher pressures and offer greater reliability.
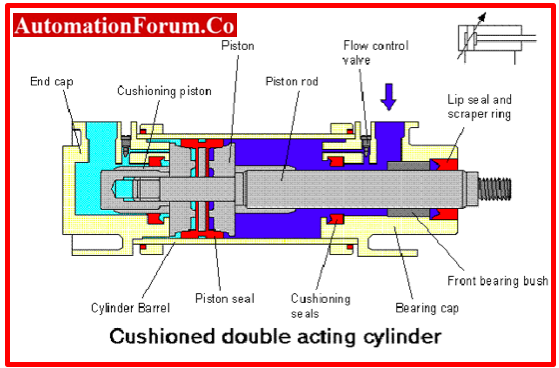
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components
By the mid-20th century, pneumatic technology began to gain traction in manufacturing, particularly in automotive and packaging industries. The introduction of double-acting cylinders and various actuator types expanded application possibilities, enhancing the overall efficiency of production processes. Today, the industry is on the cusp of a new era, marked by digital transformation and the integration of smart technologies, which are set to redefine how pneumatic systems operate and are sourced globally.
In conclusion, understanding the historical context of pneumatic cylinder components provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, highlighting the technological advancements that have shaped the current market landscape and the potential for future innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic cylinder components
-
How do I solve issues with pneumatic cylinder performance?
To address performance issues with pneumatic cylinders, begin by checking for air leaks in the system, as they can significantly reduce efficiency. Inspect seals and fittings for wear or damage and ensure that the air supply is clean and at the correct pressure. Regular maintenance, including lubrication and cleaning, can also help prevent performance degradation. If issues persist, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or seek expertise from a qualified technician to assess the system’s design and compatibility with your application. -
What is the best type of pneumatic cylinder for heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty applications, double-acting cylinders are typically the best choice due to their ability to exert force in both directions, providing greater versatility and control. Additionally, consider cylinders with robust construction materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel, to withstand high pressures and harsh environments. Look for features like cushioning mechanisms to absorb shock and extend cylinder life. Tailor your selection based on specific operational demands, such as load weight, speed, and cycle frequency. -
How can I verify the credibility of a pneumatic cylinder supplier?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, conduct thorough research, including checking their business history, customer reviews, and industry certifications. Request references from previous clients to assess their experience and reliability. Additionally, evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures, ensuring they comply with international standards. Engaging in direct communication with the supplier can also provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to meet your specific requirements. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic cylinder components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic cylinder components can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units for standard components to hundreds for specialized or custom items. When sourcing, inquire directly with potential suppliers about their MOQs, as many are willing to negotiate based on your needs or offer flexibility for first-time orders. This can be particularly beneficial for startups or companies testing new products in their operations. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing pneumatic cylinder components internationally?
Payment terms in international trade can vary, but common options include upfront payment, partial payment before shipment with the balance upon delivery, or payment upon receipt of goods. Letters of credit are also a secure option for larger transactions. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreements to avoid misunderstandings. It’s advisable to utilize secure payment methods and consider currency exchange implications, especially when dealing with suppliers in different regions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for pneumatic cylinder components?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications such as ISO 9001. Conduct factory audits if possible, or use third-party inspection services to evaluate production standards. Additionally, specify testing requirements for the components, such as pressure testing and performance evaluations, before shipment. Establishing clear quality expectations in the contract can help mitigate risks associated with defective products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pneumatic cylinder components?
When importing pneumatic cylinder components, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial components to navigate international shipping complexities. Factor in potential delays at customs and ensure all documentation, such as bills of lading and commercial invoices, is accurate and complete. Additionally, assess the total landed cost, including tariffs and taxes, to accurately budget for your procurement. -
Can pneumatic cylinders be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for pneumatic cylinders to meet specific application requirements. Customizations may include variations in size, stroke length, mounting configurations, and materials. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and application scenarios to facilitate the design process. Engaging in early discussions about customization can also help identify potential challenges and ensure that the final product aligns with your operational demands.
Top 9 Pneumatic Cylinder Components Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
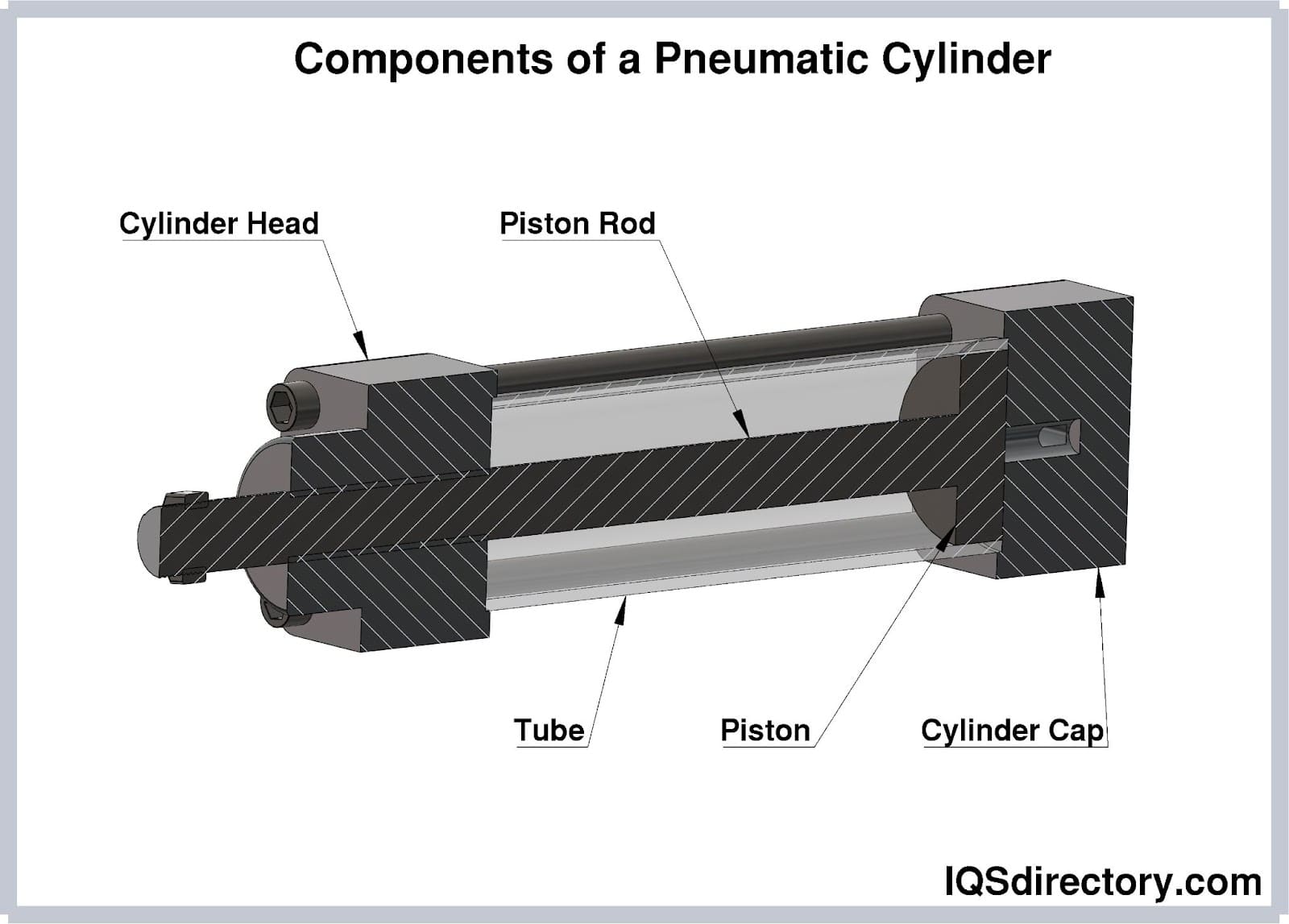
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical systems that produce force using compressed air. Key components include: 1. Bore: Main body housing internal components, precision-machined for air-tightness. 2. Piston: Movable barrier dividing the cylinder chamber, enabling linear motion. 3. Piston Rod: Transmits force from the piston to external loads, with stroke length influencing motion range. 4. Piston Cus…
2. Compact Automation – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: compactautomation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical devices that utilize compressed air to generate linear force and motion. They are categorized into single-acting and double-acting cylinders. Key components include the cylinder body, piston, and rod, with sealing elements to prevent air leakage. Enhancements can include accessories like cushioning devices and position sensors. Proper installation and maintenance…
3. Yates Cylinders – Pneumatic Cylinder Parts & Repairs
Domain: yatesind.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Yates Cylinders offers a wide variety of pneumatic cylinder parts, including accessories such as brackets, couplers, and pins. They provide cylinder repairs and rebuilds with 24/7 emergency service. Regular maintenance is recommended for maximum reliability, including checking for air leaks, inspecting air filters, lubricating components, and checking seals for damage. Pneumatic cylinder parts inc…
4. Trimantec – Free Delivery & Returns
Domain: trimantec.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: This company, Trimantec – Free Delivery & Returns, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Omchele – Pneumatic Cylinders and Valves
Domain: omchele.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic Cylinders: Standard Cylinders, Mini Cylinders, Guided Cylinders, Compact Cylinders, Rodless Cylinders; Pneumatic Grippers; FRL Units: Air Regulators, Air Filter Regulators, Filter Regulator Lubricators, Compressed Air Filters, Air Lubricators; Pneumatic Valves: Pneumatic Solenoid Valves, Flow Control Valve; Fitting & Tubing & Accessories: Air Hoses, Quick Connectors, Stainless Steel Fitt…
6. CKD – Air Cylinders
Domain: ckd.co.jp
Introduction: Air cylinders are devices that utilize compressed air as a power source, converting compressed air energy into linear or reciprocating motions. Key components include:
– Cylinder tube: Forms the cylinder chamber and guides the piston.
– Cover: Houses supply and exhaust ports, split into head and rod covers.
– Tie Rod: Connects the cylinder tube to the cover.
– Piston: Moves within the cylinder…
7. Festo – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: festo.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are components that perform movement using compressed air, also known as compressed air cylinders. They are cost-effective solutions for various applications, characterized by simple commissioning and speeds ranging from 10 mm/s to 3 m/s. There are two main types: single-acting cylinders, which generate movement in one direction using compressed air and an internal spring for r…
8. SMC – Air Cylinders
Domain: smcworld.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Air Cylinders: Standard Air Cylinders (Round Type), Standard Air Cylinders (Square Cover), Compact Air Cylinders, Environment Resistant Cylinders, Stainless Steel Made to Order, Water Resistant Cylinder, Dust Resistant Cylinder, Mechanically Jointed Rodless Cylinders, Magnetically Coupled Rodless Cylinders, Table Cylinders, Guide Cylinders, Dual Rod Cylinders, Lock Cylinders/Cylinder with An End L…
9. AutomationDirect – Pneumatic Air Cylinders
Domain: automationdirect.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic air cylinders from AutomationDirect, featuring various types, sizes, and specifications suitable for different applications. Key features include durability, reliability, and a range of options for stroke lengths, mounting styles, and bore sizes. Products are designed for efficient operation in automated systems.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic cylinder components
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Strategic sourcing of pneumatic cylinder components is paramount for enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring product reliability. Buyers must consider the specific requirements of their applications, such as actuation type, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs. Understanding the diverse range of pneumatic cylinders—single-acting, double-acting, and various configurations—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production processes.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Optimize Your Supply Chain?
By prioritizing relationships with reputable suppliers, buyers can secure high-quality components that reduce downtime and operational costs. Additionally, embracing modern technologies, such as automation and data analytics, allows for real-time monitoring of supply chain activities, further optimizing procurement strategies. This proactive approach not only fosters innovation but also positions businesses to adapt to emerging market trends.
What’s Next for International Buyers of Pneumatic Cylinder Components?
Looking ahead, the global market for pneumatic cylinder components is poised for growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increasing demand across various sectors. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to explore partnerships with leading manufacturers to leverage these opportunities. Investing in high-quality pneumatic components today will pave the way for enhanced productivity and competitive advantage tomorrow. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy and connect with trusted suppliers to elevate your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
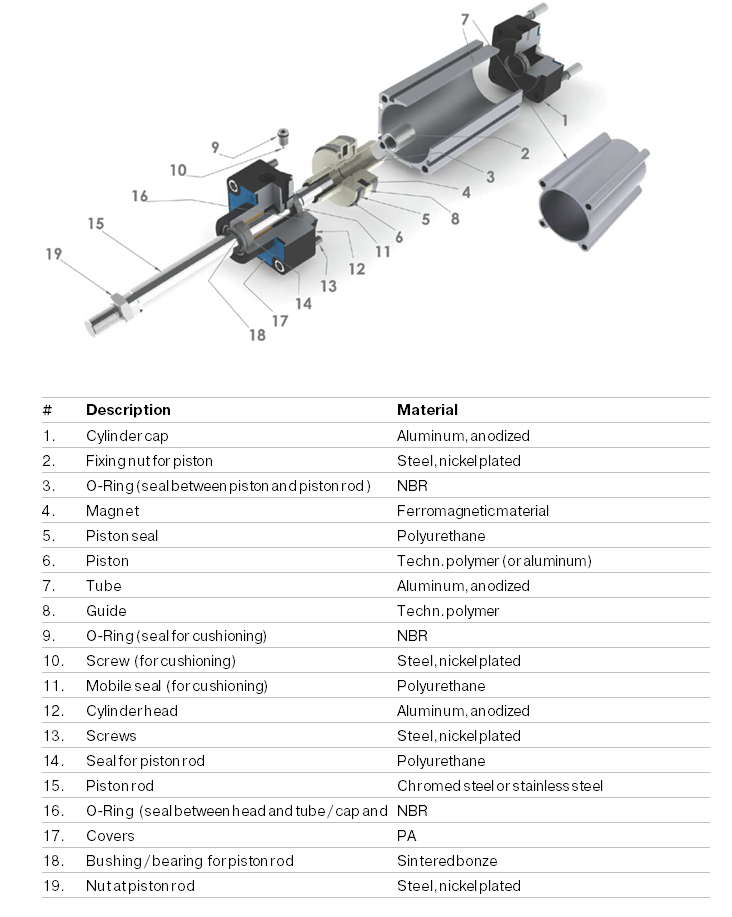
Illustrative image related to pneumatic cylinder components