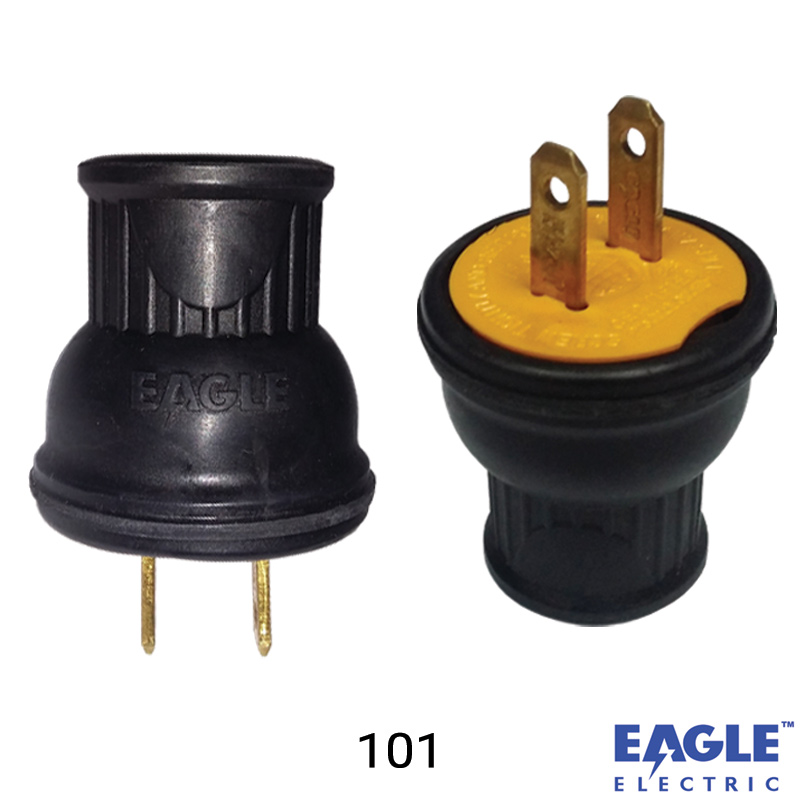
How to Source Parallel Plug Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parallel plug
In today’s interconnected global marketplace, sourcing the right parallel plug can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying plug types and standards, navigating the complexities of international electrical components can be daunting. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of parallel plugs, covering essential aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
By outlining the diverse applications of parallel plugs—from household appliances to industrial equipment—this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the technical specifications and compliance standards associated with parallel plugs is crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety in various environments.
Additionally, our insights into evaluating suppliers will help buyers mitigate risks and foster reliable partnerships. Whether you’re based in Vietnam, Nigeria, or elsewhere, this resource equips you with the knowledge necessary to confidently navigate the global market for parallel plugs, ensuring you select high-quality products that meet your business needs. As you explore this guide, you’ll find actionable strategies to enhance your sourcing process and optimize your supply chain, ultimately driving success in your operations.
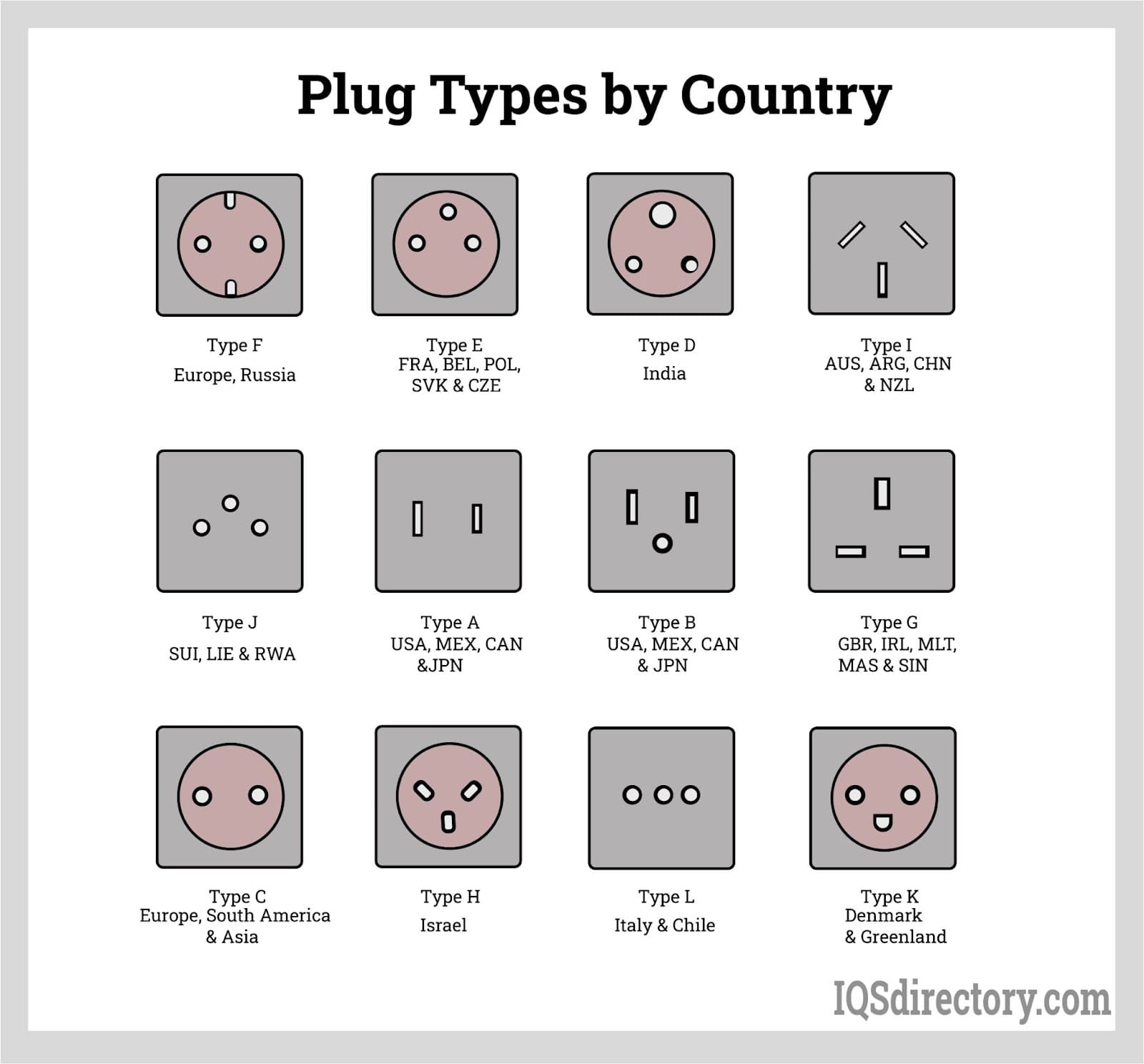
Understanding parallel plug Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Parallel Plug | Straight cylindrical design, typically with a flange | Electrical appliances, industrial equipment | Pros: Versatile, easy to install. Cons: Limited to specific hole sizes. |
| Heavy-Duty Parallel Plug | Thicker walls, designed for durability | Industrial machinery, construction | Pros: High durability, impact-resistant. Cons: Heavier, may be costlier. |
| Low-Temperature Parallel Plug | Made from materials that withstand low temps | Refrigeration, cold storage applications | Pros: Maintains integrity in cold environments. Cons: Limited to low-temp applications. |
| High-Temperature Parallel Plug | High-temperature resistant materials like silicone | Aerospace, automotive industries | Pros: Suitable for extreme conditions. Cons: Typically higher price point. |
| Water-Resistant Parallel Plug | Special coatings or materials to prevent water ingress | Outdoor equipment, marine applications | Pros: Protects against moisture damage. Cons: May require specific installation conditions. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Parallel Plugs?
Standard parallel plugs feature a straight cylindrical design, often equipped with a flange for easy handling. They are typically used in household appliances and light industrial equipment, where compatibility with specific electrical outlets is essential. When purchasing, buyers should consider the plug’s voltage and amperage ratings to ensure they meet their equipment’s requirements. Additionally, the standard plug’s versatility makes it a common choice across various sectors, although its fit is limited to specific hole sizes.
How Do Heavy-Duty Parallel Plugs Differ?
Heavy-duty parallel plugs are characterized by their thicker walls and robust construction, making them suitable for demanding environments such as industrial machinery and construction sites. Their durability ensures they can withstand impacts and harsh conditions, which is a significant advantage for B2B buyers looking for long-lasting solutions. However, the increased durability often comes with a higher price tag, and their weight may also be a consideration for transport and installation.
What Makes Low-Temperature Parallel Plugs Unique?
Low-temperature parallel plugs are specifically designed to maintain their integrity in cold environments, making them ideal for refrigeration and cold storage applications. These plugs are made from specialized materials that prevent brittleness and cracking at lower temperatures. When sourcing these plugs, buyers should evaluate the temperature range specifications to ensure suitability for their specific applications. Their ability to function effectively in low temperatures provides a critical advantage in preserving the performance of refrigeration equipment.
Why Choose High-Temperature Parallel Plugs?
High-temperature parallel plugs are constructed from materials like silicone that can endure extreme conditions, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and automotive. These plugs are essential for applications where high heat may cause standard plugs to fail. Buyers should consider the specific temperature ratings and the environment in which these plugs will be used. While they offer unparalleled performance under heat stress, their cost may be higher than standard options, which is an important factor for budget-conscious purchasers.
What Are the Benefits of Water-Resistant Parallel Plugs?
Water-resistant parallel plugs are engineered with special coatings or materials to prevent water ingress, making them suitable for outdoor equipment and marine applications. These plugs are crucial for protecting electrical connections in environments prone to moisture. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the level of water resistance required for their applications and ensure the plugs are compatible with their existing systems. While they provide excellent protection against moisture, installation conditions may vary, necessitating careful planning during procurement.
Key Industrial Applications of parallel plug
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Parallel Plug | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Manufacturing | Connecting heavy-duty machinery and equipment | Ensures reliable power supply, reducing downtime and maintenance costs | Compliance with regional electrical standards and voltage ratings |
| HVAC Systems | Powering commercial air conditioning units | Enhances energy efficiency and operational reliability | Compatibility with local outlet types and amperage requirements |
| Automotive | Wiring harness connections in vehicles | Improves electrical safety and performance in automotive systems | Durability against environmental factors and ease of installation |
| Construction | Temporary power connections on job sites | Facilitates efficient power distribution, enhancing productivity | Weather resistance and compliance with safety regulations |
| Renewable Energy | Connecting solar panels to inverters | Maximizes energy transfer efficiency and system reliability | Material quality for outdoor use and compatibility with existing systems |
How is Parallel Plug Used in Electrical Manufacturing?
In electrical manufacturing, parallel plugs are essential for connecting heavy-duty machinery and equipment. These plugs ensure a consistent and reliable power supply, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. By reducing downtime due to electrical failures, businesses can significantly cut maintenance costs. Buyers in this sector should consider compliance with regional electrical standards and the specific voltage ratings required for their equipment to avoid compatibility issues.
What Role Does Parallel Plug Play in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, parallel plugs are commonly used to power commercial air conditioning units. Their design allows for a secure connection that enhances energy efficiency and operational reliability. This is particularly important in regions with extreme temperatures, where consistent cooling is vital. Buyers should ensure that the plugs they source are compatible with local outlet types and meet the amperage requirements of their HVAC systems to guarantee optimal performance.
How is Parallel Plug Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry employs parallel plugs for wiring harness connections in vehicles. These plugs improve electrical safety and performance by providing secure connections that withstand vibrations and temperature fluctuations. For international buyers, sourcing durable plugs that can resist environmental factors is critical, as it affects the longevity and reliability of automotive systems. Additionally, ease of installation is a significant consideration to streamline assembly processes.
What Benefits Do Parallel Plugs Provide in Construction?
In construction, parallel plugs are used for temporary power connections on job sites, facilitating efficient power distribution among various tools and equipment. This enhances overall productivity and ensures that power is readily available where needed. Buyers must prioritize sourcing plugs that are weather-resistant to withstand outdoor conditions and ensure compliance with safety regulations to protect workers and equipment.
How Do Parallel Plugs Enhance Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, such as solar power systems, parallel plugs connect solar panels to inverters. This connection maximizes energy transfer efficiency and contributes to the overall reliability of the energy system. For businesses involved in renewable energy, it’s vital to consider the material quality of the plugs to ensure they can withstand outdoor conditions and are compatible with existing systems for seamless integration.

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parallel plug’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Compatibility Issues with Equipment and Outlets
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when trying to integrate parallel plugs with existing equipment or power outlets. Many facilities, especially in developing regions, may have older electrical systems that do not match the specifications of modern parallel plugs. This mismatch can lead to operational delays and increased costs due to the need for electrical upgrades or additional adapters, which can be both time-consuming and confusing to procure.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their existing electrical infrastructure before purchasing parallel plugs. This includes checking the voltage requirements, plug type, and amperage of both the equipment and the power outlets. When sourcing parallel plugs, look for products that offer clear specifications and compatibility guidelines. Engaging with suppliers who provide detailed product catalogs and technical support can also help ensure that the right products are chosen. For facilities facing significant compatibility issues, consider consulting with an electrical engineer who can recommend necessary upgrades or modifications to align with the new parallel plug standards.
Scenario 2: Quality and Reliability Concerns
The Problem: Another significant pain point for buyers is the concern over the quality and reliability of parallel plugs, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. Substandard plugs can lead to overheating, failures in electrical connections, and even safety hazards. This is especially critical in industries like manufacturing or energy, where equipment uptime is paramount, and any failure could result in costly downtime or even accidents.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing parallel plugs from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record of quality and safety compliance. Look for certifications that meet international safety standards, such as UL or CE marks. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence on suppliers, including requesting samples for testing, can help assess product quality before making bulk purchases. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who can provide warranties and after-sales support will also ensure reliability in the products used, thereby minimizing risks associated with poor-quality plugs.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Installation and Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter challenges during the installation and maintenance of parallel plugs. If the installation process is complicated or if the plugs require specific handling to maintain their integrity, it can lead to operational inefficiencies. This is particularly true for companies with limited technical expertise on staff or those operating in remote areas where skilled labor may not be readily available.

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
The Solution: To streamline installation and maintenance processes, it is essential to invest in training for personnel who will be handling parallel plugs. Suppliers often provide installation guides or even training sessions, which can be invaluable in ensuring correct usage. Additionally, buyers should look for parallel plugs designed for ease of installation, such as those with user-friendly features like color-coded connections or straightforward assembly instructions. For ongoing maintenance, creating a simple checklist or schedule can help staff monitor the condition of the plugs and ensure they are replaced or repaired as needed, thus minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parallel plug
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Parallel Plugs?
When selecting materials for parallel plugs, it is essential to consider their properties, including temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. The most commonly used materials for parallel plugs include Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Silicone. Each material offers unique advantages and limitations that can significantly impact performance in various applications.
How Does Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Perform in Parallel Plug Applications?
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a widely used material for parallel plugs due to its affordability and versatility. It provides basic protection against dust, dirt, and moisture, making it suitable for general-purpose applications. LDPE has a moderate temperature resistance, typically up to 80°C (176°F), which is adequate for many standard environments.
Pros: LDPE is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for high-volume production. Its lightweight nature also contributes to reduced shipping costs.
Illustrative image related to parallel plug
Cons: However, LDPE may not withstand high temperatures or harsh chemicals, limiting its use in more demanding environments. Its mechanical strength is lower compared to other materials, which may lead to wear over time.
Impact on Application: LDPE is ideal for applications requiring basic protection, such as in manufacturing and general storage. However, it may not be suitable for environments with high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
What Are the Benefits of Using Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) for Parallel Plugs?
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) is known for its excellent elasticity and durability, making it a robust choice for parallel plugs that need to withstand mechanical stress and environmental challenges. TPR has good temperature resistance, typically ranging from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F), which allows it to perform well in diverse conditions.
Illustrative image related to parallel plug
Pros: TPR is resistant to acids and provides a snug fit, ensuring effective sealing against dust and moisture. Its flexibility allows for easy installation and removal.
Cons: The primary drawback of TPR is its higher cost compared to LDPE. Additionally, while TPR is versatile, it may not be suitable for applications involving extreme temperatures or specific chemical exposures.
Impact on Application: TPR is suitable for applications in automotive and industrial sectors where flexibility and durability are critical. Buyers should consider TPR for environments with varying temperatures and moderate chemical exposure.
Why Choose Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) for Parallel Plugs?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another common material used for parallel plugs, particularly in applications requiring resistance to shredding and abrasion. PVC can typically withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F) and offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros: PVC is durable and cost-effective, providing a balance between performance and price. Its resistance to oils and greases makes it ideal for applications in environments where exposure to such substances is likely.
Cons: However, PVC has limitations in high-temperature applications and may become brittle over time if exposed to UV light. This can affect its longevity in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: PVC is well-suited for applications in manufacturing and construction, where durability and cost-effectiveness are essential. Buyers in regions with high UV exposure should consider additional protective measures for PVC plugs.
What Advantages Does Silicone Offer for Parallel Plugs?
Silicone is a premium material for parallel plugs, known for its high-temperature resistance and reusability. Silicone can withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F), making it ideal for demanding applications, such as those in the automotive or aerospace industries.
Pros: The primary advantage of silicone is its ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions. It is also reusable, providing long-term cost savings for businesses.
Cons: The downside is that silicone is significantly more expensive than other materials like LDPE or PVC, which may deter budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Silicone is ideal for high-temperature applications and environments where repeated plugging and unplugging occur. Buyers in industries requiring stringent temperature control should prioritize silicone for their parallel plugs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Parallel Plugs
| Material | Typical Use Case for parallel plug | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | General-purpose protection in manufacturing | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited temperature and chemical resistance | Low |
| TPR | Automotive and industrial applications | Excellent elasticity and durability | Higher cost compared to LDPE | Medium |
| PVC | Construction and manufacturing environments | Durable and resistant to oils | May become brittle over time | Low |
| Silicone | High-temperature industrial applications | High-temperature resistance and reusability | Higher cost than other materials | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in parallel plugs. Understanding these factors will assist in making informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific application needs and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parallel plug
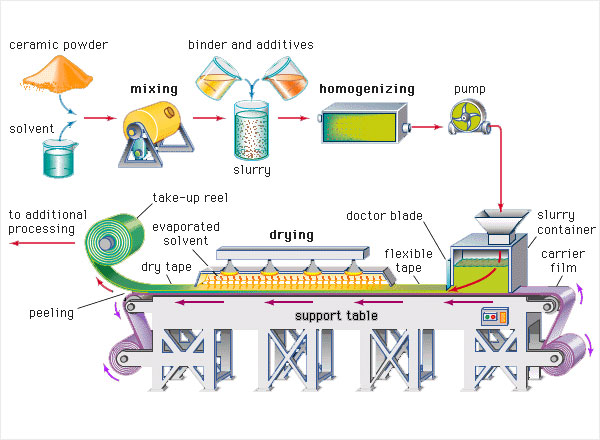
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Parallel Plugs?
The manufacturing process of parallel plugs involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Typically Used?
The first stage involves selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials for parallel plugs include thermoplastic rubber (TPR), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). These materials are chosen for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to various environmental factors like moisture, dust, and chemicals. The materials are sourced from certified suppliers to ensure consistency and quality. Quality checks are conducted at this stage to verify material properties, such as tensile strength and chemical resistance, ensuring they meet the specifications required for the intended application.
Illustrative image related to parallel plug
How Are Parallel Plugs Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This typically involves processes such as injection molding or extrusion. In injection molding, heated material is injected into molds that shape the parallel plugs. This method allows for high precision and repeatability, making it ideal for mass production. For plugs requiring a flange, specific mold designs facilitate this feature, enhancing the grip and fit. During this stage, temperature and pressure settings are carefully monitored to maintain consistent quality.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Parallel Plugs?
After forming, the assembly stage may involve integrating additional components, such as connectors or flanges. This stage can be automated or conducted manually, depending on the complexity of the plug design. Automated assembly processes often include robotic arms that ensure precise placement and assembly of parts, significantly reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Quality checks are performed during assembly to ensure all components fit correctly and function as intended.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted for Parallel Plugs?
The finishing stage involves processes such as trimming excess material, surface treatment, and packaging. Trimming ensures that the plugs meet the required dimensions and aesthetic standards. Surface treatments may include applying coatings for enhanced resistance to chemicals or UV exposure. Finally, packaging is done in a way that protects the plugs during transportation and storage. Each of these steps is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the specifications and quality expectations of B2B buyers.
What Are the International Standards and Quality Control Measures for Parallel Plugs?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of parallel plugs is vital for ensuring product reliability and safety. Various international standards govern the quality of electrical components, including ISO 9001 for quality management systems, CE marking for compliance with European standards, and API standards for products used in the petroleum industry.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers must provide documentation proving compliance with relevant standards. Tests conducted may include material analysis and dimensional inspections.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are performed to monitor production parameters and ensure consistency. This may include monitoring mold temperatures, pressure settings, and visual inspections for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the plugs undergo final inspections to verify that they meet all specifications. This stage may include functional testing, where plugs are tested for electrical conductivity and physical durability.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and safety of parallel plugs. These methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: This involves checking the electrical properties of the plugs to ensure they meet voltage and current specifications. Testing for insulation resistance and dielectric strength is also common.
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tests for tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to impact. Such tests help ensure that the plugs can withstand operational stresses.
-
Environmental Testing: Plugs may be subjected to conditions that simulate extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals to assess their durability and longevity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to robust quality control measures. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular supplier audits can help buyers assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place. This provides insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should request quality assurance reports that detail testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards. This documentation can provide assurance of product quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. These inspectors can conduct independent tests and evaluations.
-
Understand Certification Nuances: Different regions may have specific certifications that are required for electrical components. B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various challenges regarding quality control. Factors such as differing regulations, standards, and certifications can complicate procurement processes. Buyers should:
-
Stay Informed About Regional Standards: Understand the specific quality standards applicable in the regions of interest, such as CE marking in Europe or local certification requirements in Africa and South America.
-
Establish Clear Communication Channels: Maintain open communication with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly. This can help mitigate issues before they escalate.
-
Leverage Technology for Quality Monitoring: Implement digital tools for real-time monitoring of supplier performance and product quality. This can include software for tracking compliance and quality metrics.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for parallel plugs is crucial for B2B buyers. By being informed about the production stages, quality checkpoints, testing methods, and international standards, buyers can make educated decisions and ensure they procure reliable and compliant products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parallel plug’
To effectively source parallel plugs for your business needs, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps necessary to ensure you procure high-quality products that meet your specifications and standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the parallel plugs you need. This includes voltage ratings, amperage, and physical dimensions. Knowing the exact specifications will help you narrow down your options and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Illustrative image related to parallel plug
- Voltage Requirements: Determine if you need plugs for 208, 220, or 250 volts.
- Amperage Considerations: Identify the current requirements, such as 50 amps, to avoid potential hazards.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in parallel plugs. Utilize online marketplaces, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of candidates.
- Check Reviews and Ratings: Look for feedback from other B2B buyers to gauge supplier reliability.
- Industry Experience: Prefer suppliers with experience in your specific market sector.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure the supplier adheres to international standards relevant to electrical components.
- Product Quality Assurance: Ask about quality control processes to confirm product reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the parallel plugs for testing. This step allows you to evaluate the product quality firsthand and ensure it meets your specifications.
- Conduct Compatibility Tests: Use the samples in your existing systems to verify fit and performance.
- Assess Durability: Evaluate the materials used and their resistance to wear, moisture, and other environmental factors.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with your preferred suppliers to negotiate pricing and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and taxes, is vital for budgeting purposes.
- Bulk Order Discounts: Inquire about pricing breaks for larger orders to optimize your procurement costs.
- Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment options that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Confirm Delivery and Support
Before finalizing your order, confirm the delivery timelines and after-sales support offered by the supplier. Timely delivery is crucial to avoid disruptions in your operations.
- Warranty and Returns Policy: Understand the terms related to product returns and warranties in case of defects.
- Technical Support Availability: Ensure that the supplier provides support for installation and troubleshooting if needed.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Consider building a long-term partnership with your chosen supplier for ongoing needs. A reliable supplier can provide consistent quality and insights into new products or technologies.
- Regular Communication: Keep an open line of communication for future orders and feedback on product performance.
- Stay Updated: Engage with your supplier regarding industry trends and innovations that may benefit your operations.
By following these steps, you can streamline the sourcing process for parallel plugs and ensure that your procurement aligns with your operational needs and standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parallel plug Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Parallel Plug Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of parallel plug sourcing is critical for B2B buyers. The primary components influencing the overall cost include:

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials for parallel plugs include thermoplastic rubber (TPR), PVC, and LDPE. Each material has different cost implications based on its properties and availability. For instance, silicone, while more expensive, offers high-temperature resistance and durability, which may justify its cost for certain applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and Southeast Asia, may offer more competitive pricing. However, these savings may be offset by longer lead times or less stringent quality controls.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Companies with efficient production processes can pass savings on to buyers. It’s essential to assess a supplier’s operational efficiency to gauge potential cost benefits.
-
Tooling: Customization requires specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. For buyers needing unique specifications, understanding the tooling costs is vital for accurate budgeting.
-
Quality Control (QC): The level of quality assurance implemented during production affects pricing. Suppliers that emphasize rigorous QC protocols may have higher costs, but this can result in fewer defects and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Logistics: Shipping costs and lead times can significantly influence the total cost. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import duties should be considered, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up prices to ensure profitability. Understanding the industry standard margin can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Parallel Plug Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure for parallel plugs, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher purchase volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that maximize their order sizes to benefit from volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed plugs tailored to specific applications often come at a premium. Clearly defining needs upfront can help avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Material Selection: The choice between standard and high-performance materials affects pricing. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of more expensive materials against their immediate cost.
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers with industry-standard certifications (e.g., ISO) may charge more due to their commitment to quality. However, such certifications often correlate with reliability and reduced risk of failure.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but provide better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in the transaction can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Parallel Plug Purchasing?
International B2B buyers can benefit from several strategies to ensure cost-effective sourcing of parallel plugs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Buyers should engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially when committing to larger orders. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential failure costs in your decision-making process.
-
Assess Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, sourcing from suppliers in Africa or South America may present unique cost advantages due to lower labor costs but may also introduce logistical challenges.
-
Build Relationships: Developing long-term partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Trust and reliability often lead to more favorable negotiations.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, material costs, and technological advancements. Being informed can empower buyers to make better decisions and negotiate effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for parallel plugs can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. The examples provided are for illustrative purposes only and do not reflect current market conditions or specific supplier pricing. Always request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing aligned with your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parallel plug With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Parallel Plugs
When evaluating the best options for connecting electrical devices or protecting components, parallel plugs are just one of several solutions available. Understanding the alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in international markets where different standards and requirements may influence the choice of products. This analysis compares parallel plugs with two viable alternatives: tapered plugs and locking connectors, examining various aspects to help buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parallel Plug | Tapered Plug | Locking Connector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High stability and grip | Excellent sealing capabilities | Secure connection under load |
| Cost | Typically low ($21.95) | Moderate, varies by material | Higher due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation | Slightly more complex | Requires specific tools |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | General-purpose electrical use | Applications needing tight seals | High-vibration environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Tapered Plugs
Tapered plugs are designed with a conical shape that allows them to fit snugly into various hole sizes, making them ideal for applications requiring a tight seal. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to accommodate slight variations in hole dimensions, which is beneficial in manufacturing settings. However, the complexity of installation can be a drawback, as they may not be as straightforward to use as parallel plugs. While their cost is moderate, it can vary significantly based on the material used, such as silicone or EPDM.

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
Locking Connectors
Locking connectors provide a secure electrical connection that is particularly effective in environments subject to vibration or movement. They are designed to prevent accidental disconnection, making them ideal for heavy machinery or mobile equipment. While they offer superior performance in terms of stability, they come at a higher cost due to their more complex design. Installation can also require specialized tools, adding to the overall implementation effort. Additionally, maintenance is moderate, as regular checks are necessary to ensure the locking mechanism functions correctly.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate solution for your specific requirements, consider the nature of your application and the environment in which the product will be used. For general-purpose electrical connections, parallel plugs offer a cost-effective and easy-to-use option. If your application involves variable hole sizes or requires a tight seal, tapered plugs may be more suitable. In high-vibration scenarios, investing in locking connectors could provide the added security necessary for your operations. By evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgets.
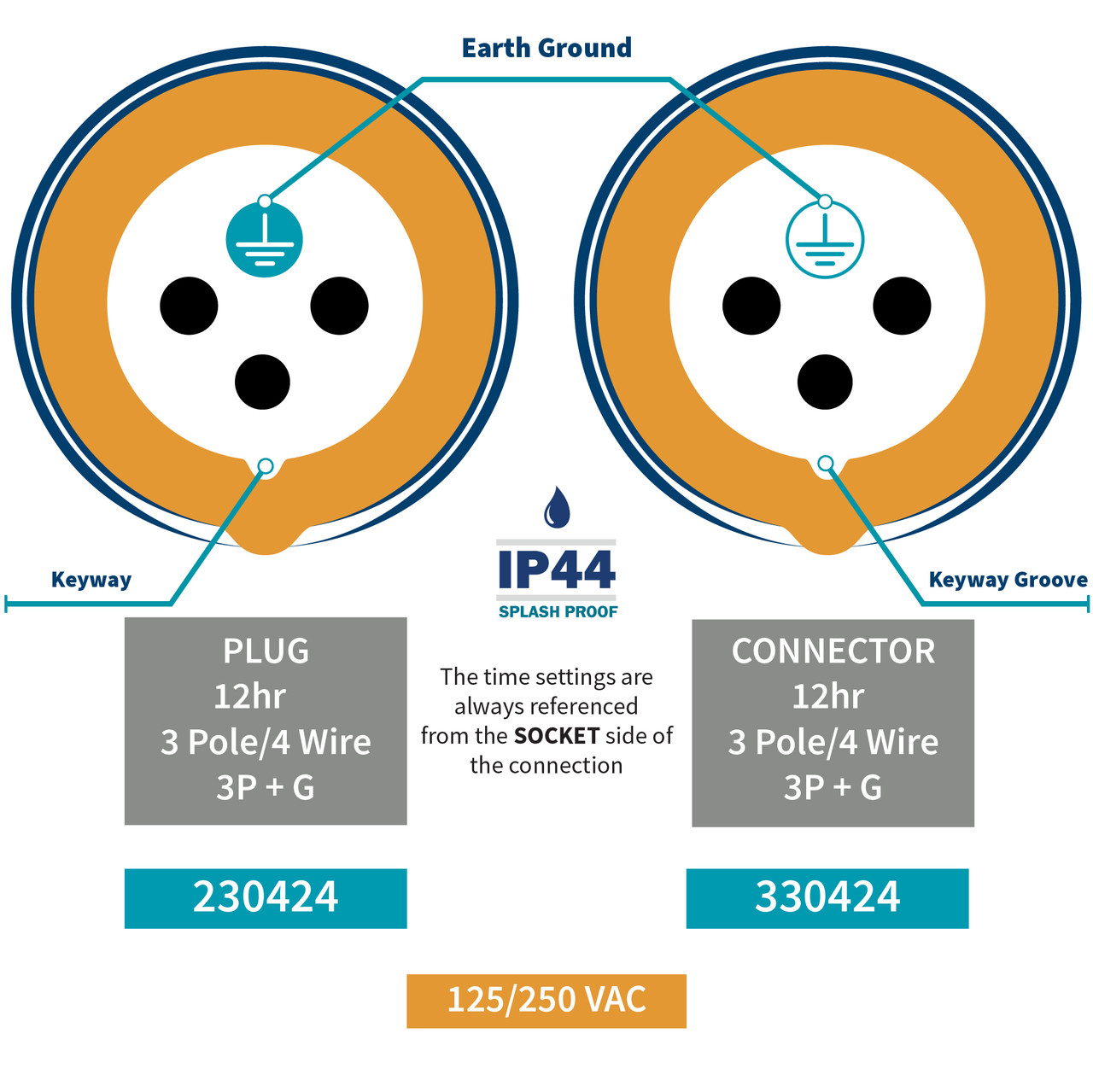
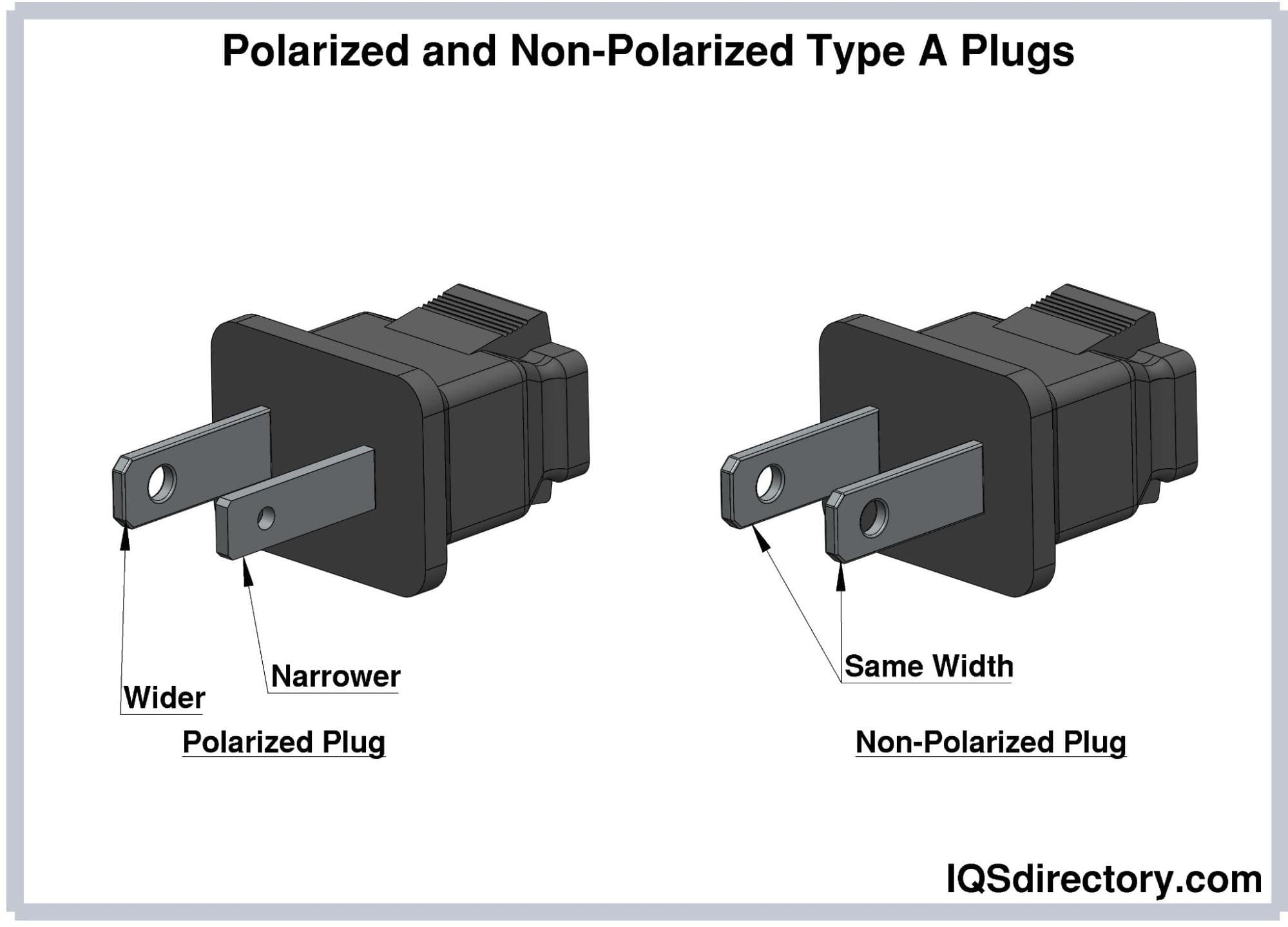
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parallel plug
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Parallel Plugs?
Understanding the technical properties of parallel plugs is essential for B2B buyers involved in electrical and mechanical applications. Here are the critical specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
-
Material Grade
– Parallel plugs are typically made from materials like thermoplastic rubber (TPR), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). The choice of material affects durability, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. For example, TPR is known for its acid resistance, while PVC offers high resistance to shredding, making it suitable for various applications. -
Voltage and Amperage Ratings
– Parallel plugs are designed to operate at specific voltage and amperage levels, such as 208V, 220V, or 250V with ratings like 50 Amps. Understanding these ratings is crucial for ensuring compatibility with electrical systems and avoiding overload, which can lead to equipment failure or safety hazards. -
NEMA Configuration
– The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) specifies configurations for plugs and receptacles, such as NEMA 6-30P or NEMA 6-50P. These configurations dictate the shape and pin arrangement of the plugs, ensuring proper fit and functionality in specific applications. Familiarity with NEMA standards is vital for compliance and safety. -
Tolerance Levels
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and performance of the plug. High tolerance levels ensure a snug fit, preventing dust and moisture ingress. Tighter tolerances are essential for applications requiring precise connections, such as in machinery or automotive components. -
Flange Design
– Many parallel plugs feature a flange, which provides a wider gripping surface for easier insertion and removal. The flange also enhances the plug’s sealing capabilities, protecting against contaminants. This design is particularly important in environments where dust and moisture can compromise electrical connections. -
Environmental Resistance
– Parallel plugs must be resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature extremes. Selecting plugs with appropriate environmental resistance ratings ensures longevity and reliability in various settings, from industrial to outdoor applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Parallel Plug Industry?
Familiarity with trade terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of parallel plugs, OEM specifications can dictate the quality and compatibility of the components being sourced. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially when sourcing parallel plugs in bulk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ for parallel plugs can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can aid in understanding shipping costs and responsibilities. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until its delivery. Knowing the lead time for parallel plugs is vital for project planning and ensuring timely availability of components. -
Certification Standards
– Certification standards, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne), indicate that a product meets specific safety and performance criteria. Ensuring that parallel plugs are certified can be crucial for regulatory compliance and customer trust.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing parallel plugs, ensuring compatibility and reliability in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parallel plug Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Parallel Plug Sector?
The parallel plug market is currently influenced by several global drivers, including the ongoing expansion of industrial and commercial infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe. This growth is largely fueled by increased urbanization, technological advancements, and a rising demand for energy-efficient appliances. The shift towards smart home technologies also drives the need for specialized electrical components such as parallel plugs, which are essential for connecting high-powered devices like air conditioners and electric dryers.
Emerging B2B tech trends are reshaping sourcing strategies in the parallel plug sector. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are streamlining the procurement process, making it easier for international buyers to access a wider range of products and suppliers. Additionally, automation in manufacturing is improving the quality and consistency of parallel plugs, catering to the growing demand for reliability and performance. Key sourcing trends include a focus on customization, where manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions to meet specific client needs, enhancing buyer engagement and satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
International B2B buyers should also be aware of market dynamics that include fluctuating raw material costs and geopolitical factors affecting supply chains. For instance, sourcing from regions with stable political climates can mitigate risks associated with disruptions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery of products, especially in fast-growing markets.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Parallel Plug Sector?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the parallel plug sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled materials or energy-efficient manufacturing techniques. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and labor conditions are fair. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are vital indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
In the parallel plug market, materials such as thermoplastic rubber (TPR), PVC, and LDPE are increasingly being evaluated for their environmental footprint. Eco-friendly alternatives, such as biodegradable plastics or materials with lower carbon emissions, are becoming more sought after. By prioritizing suppliers who offer these green certifications and materials, international buyers can contribute to a more sustainable industry while also meeting their compliance requirements.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Parallel Plugs in the B2B Context?
The evolution of parallel plugs can be traced back to the early 20th century, when electrical standards began to formalize to accommodate the growing demand for safe and reliable electrical connections. Initially used in household appliances, the design of parallel plugs evolved to meet the needs of industrial applications, particularly as machinery and high-powered devices became prevalent.
As international trade expanded, so did the need for standardized plugs that could accommodate various electrical systems across different regions. The introduction of NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) standards provided a framework for the safe use of parallel plugs, ensuring compatibility and safety in diverse applications. Today, parallel plugs are integral components in many industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction, reflecting the ongoing demand for high-quality electrical connections in a rapidly evolving market.
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, prioritizing sustainability, and recognizing the historical context of parallel plugs will empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both their operational needs and ethical considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parallel plug
-
How do I choose the right parallel plug for my application?
When selecting a parallel plug, consider the voltage and amperage requirements of your application. For instance, a 50 amp parallel plug typically operates at 208, 220, or 250 volts. Ensure compatibility with your existing receptacles and equipment. Also, assess the environmental conditions where the plug will be used; materials like thermoplastic rubber or PVC can offer additional resistance to moisture and chemicals. -
What is the best material for a parallel plug used in harsh environments?
For applications in harsh environments, silicone or thermoplastic rubber (TPR) are excellent choices for parallel plugs. Silicone offers high-temperature resistance and durability, making it suitable for repeated use in extreme conditions. TPR provides good acid resistance, making it ideal for applications involving chemical exposure. Always match the material properties with the specific requirements of your industry. -
What are the common applications for parallel plugs?
Parallel plugs are used in various applications, including connecting electrical appliances, air conditioning units, and industrial machinery. They provide a secure connection while protecting against dust, moisture, and damage. In manufacturing settings, they are often used to seal openings during production processes or for testing electrical equipment, ensuring operational integrity. -
How can I ensure quality when sourcing parallel plugs internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing parallel plugs, vet suppliers thoroughly by reviewing their certifications, production standards, and customer testimonials. Request samples to assess the product’s quality firsthand. Additionally, consider suppliers with ISO certifications or those that comply with international electrical standards, as this can indicate a commitment to quality and safety. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for parallel plugs?
Minimum order quantities for parallel plugs can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and your customization requirements. For bulk orders, negotiating lower MOQs may be possible, especially if you establish a long-term partnership with the supplier. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing parallel plugs?
Payment terms for sourcing parallel plugs can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments with balance due upon shipment, or net 30/60 terms after delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment conditions before placing an order to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection to mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing parallel plugs?
When importing parallel plugs, consider shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations in your country. Research freight options, such as air versus sea shipping, based on urgency and budget. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the process. -
How do I handle defects or quality issues with parallel plugs?
In the event of defects or quality issues with parallel plugs, promptly contact your supplier to report the problem. Document the issues with photos and detailed descriptions to support your claim. Most reputable suppliers will have a return policy or warranty in place. Ensure that you understand the terms of this policy before placing an order, so you know how to proceed if issues arise.
Top 9 Parallel Plug Manufacturers & Suppliers List
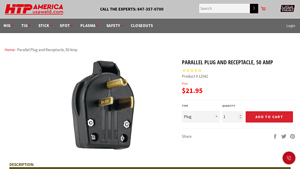
1. HTP AMERICA INC. – Parallel Plug and Receptacle, 50 Amp
Domain: usaweld.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Parallel Plug and Receptacle, 50 Amp”, “brand”: “HTP AMERICA INC.”, “product_number”: “12542”, “price”: “$21.95”, “type”: “Plug and Receptacle”, “voltage”: “208, 220, or 250 volts”, “description”: “Our 50 amp parallel plug, also known as a dryer plug, works with 208, 220, or 250 volts. The prongs on the plug look like a big, 100 volt plug, and can often be found in newer building…
2. GE Appliances – Room/Window Air Conditioners
Domain: products.geappliances.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Room / Window Air Conditioners have four different power cord plug styles: Parallel, Perpendicular, Tandem, and Large Tandem. Each plug type has specific voltage and amperage requirements. Users can check the product Specs & Details tab for specific models to find the plug type and refer to the Installation Instructions for the individual model’s plug type and amperage. It is essential to have the…
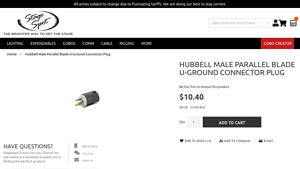
3. Hubbell – Male Parallel Blade U-Ground Connector Plug
Domain: stagespot.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hubbell Male Parallel Blade U-Ground Connector Plug, Price: $10.40, SKU: 5266CBLK, Warranty: 1 Year Limited Warranty
4. Metric MCC – 908 Steel Plain BSP Parallel Thread Socket Pipe Plug
Domain: metricmcc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “908 Steel Plain BSP Parallel Thread Socket Pipe Plug”, “material”: “Steel”, “finish”: “Plain”, “size”: “1BSP”, “stock_quantities”: {“GA”: 13, “IL”: 3, “NY”: 123, “RENO”: 46, “TX”: 0}, “certification”: “ISO 9001: 2015 Certified”}
5. Swagelok – Stainless Steel Pipe Plug
Domain: products.swagelok.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Product Type”:”Pipe Plug”,”Material”:”Stainless Steel”,”Size”:”1/2 in.”,”Thread Type”:”Male ISO Parallel Thread”,”Design”:”Straight Shoulder”}
6. DBI Plastics – Parallel Plugs Type (NC)
Domain: dbiplastics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, DBI Plastics – Parallel Plugs Type (NC), is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Vintage Outlet – Non-Polarized 20A
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Old ungrounded non-polarized 20amp outlet designed to accept either tandem or parallel plugs. It is from around 80 years ago, before standardization of plug types. The outlet may be wired for either 125V or 250V.
8. Harbor Freight – Predator 9500 Watt Inverter Generator
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Harbor Freight Predator 9500 Watt Inverter Generator
9. OMNI – Heavy Duty Parallel Plug 15A
Domain: omnionline.shop
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, OMNI – Heavy Duty Parallel Plug 15A, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parallel plug
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain for Parallel Plugs?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of international business, strategic sourcing of parallel plugs presents significant opportunities for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the distinct advantages offered by parallel plugs—such as their robust design, compatibility with various voltages, and ease of use—businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure product reliability.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only optimizes costs but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who can deliver quality components tailored to specific needs. This approach empowers businesses to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions while ensuring compliance with local and international standards.
As you consider your next procurement strategy, remember that the right sourcing decisions can lead to improved product performance and customer satisfaction. Engage with reliable suppliers who understand your market’s unique challenges and can provide innovative solutions.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality parallel plugs will continue to grow, driven by advancements in technology and infrastructure development. Now is the time to position your business for success by prioritizing strategic sourcing initiatives that align with your operational goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to parallel plug
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.