How to Source Lube System Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lube system
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable lubrication systems is critical for businesses aiming to maximize operational efficiency and minimize maintenance costs. The global market for lube systems presents unique challenges, especially for B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying regulations and product availability can complicate procurement processes. This comprehensive guide serves as your essential resource for navigating the complexities of lubrication systems, addressing diverse types—including automatic and manual systems—applications across multiple industries, and best practices for supplier vetting.
Throughout this guide, you will find detailed insights into key components, installation techniques, and maintenance strategies that can significantly impact the longevity and performance of your machinery. We delve into cost considerations, helping you understand pricing structures and potential ROI, ensuring that you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business goals. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge and resources, this guide empowers you to confidently source lubrication systems that meet your operational needs and enhance productivity, regardless of your geographic location.
Prepare to explore the myriad options available and discover how the right lube system can transform your maintenance approach and drive your business forward.
Understanding lube system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Lubrication Systems | Requires operator intervention; lower initial cost | Small workshops, light machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, simple setup. Cons: Labor-intensive, inconsistent application. |
| Automatic Lubrication Systems | Delivers precise lubrication automatically; reduces downtime | Heavy machinery, construction, mining | Pros: Increased uptime, reduced labor costs. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex maintenance. |
| Centralized Lubrication Systems | Distributes lubricant to multiple points from a single source | Manufacturing, automotive assembly | Pros: Efficient, minimizes waste. Cons: Installation complexity, higher upfront costs. |
| Oil Mist Lubrication Systems | Uses fine oil mist for lubrication; effective in harsh environments | High-speed machinery, turbines | Pros: Reduces friction, extends equipment life. Cons: Potential for oil mist contamination, requires specialized equipment. |
| Grease Lubrication Systems | Utilizes grease for lubrication; ideal for heavy loads | Construction, agriculture, transportation | Pros: Excellent for high-load applications, seals out contaminants. Cons: Grease can harden, requiring more maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Manual Lubrication Systems?
Manual lubrication systems are the most traditional form of lubrication, relying on operators to apply lubricants at regular intervals. This type of system is often characterized by its simplicity and low initial cost, making it an attractive option for small workshops or light machinery settings. However, the labor-intensive nature of manual systems can lead to inconsistent application and increased downtime, as operators may forget or delay lubrication tasks. B2B buyers should consider the operational demands of their equipment and the availability of skilled labor before opting for manual solutions.
Illustrative image related to lube system
Why Choose Automatic Lubrication Systems for Heavy Machinery?
Automatic lubrication systems are designed to deliver precise amounts of lubricant automatically, which significantly enhances equipment uptime and productivity. These systems are particularly beneficial in environments where machinery operates continuously, such as in construction or mining. While the initial investment for automatic systems can be higher, the long-term savings in reduced labor costs and maintenance make them a worthwhile consideration for B2B buyers. Additionally, these systems can be customized to meet the specific lubrication needs of different machinery, ensuring optimal performance.
How Do Centralized Lubrication Systems Work?
Centralized lubrication systems distribute lubricant from a single source to multiple lubrication points, making them highly efficient for large manufacturing or automotive assembly operations. These systems minimize waste and ensure that all parts receive consistent lubrication, which can enhance the lifespan of machinery. However, the complexity of installation and the higher upfront costs can be a barrier for some businesses. Buyers should evaluate their operational scale and the long-term benefits of centralized systems against the initial investment.
What Are the Benefits of Oil Mist Lubrication Systems?
Oil mist lubrication systems use a fine mist of oil to lubricate machinery, offering effective lubrication in harsh environments where traditional methods may fail. This approach is particularly suited for high-speed machinery and turbines, where reduced friction can lead to enhanced performance and longevity. However, potential contamination and the need for specialized equipment can deter some buyers. B2B purchasers should assess the operational environment and the specific needs of their machinery when considering oil mist systems.
When to Use Grease Lubrication Systems?
Grease lubrication systems are ideal for applications involving heavy loads, such as in construction and agriculture. These systems utilize grease to create a protective barrier against contaminants, which can prolong equipment life. While grease lubrication offers excellent performance under heavy-duty conditions, it can harden over time and may require more frequent maintenance. Buyers should consider their machinery’s operational demands and maintenance capabilities when deciding on grease lubrication solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of lube system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lube system | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Automatic lubrication for heavy machinery | Reduces downtime, enhances equipment lifespan | Compatibility with machinery, ease of installation, and maintenance support |
| Food Processing | Centralized lubrication for conveyor systems | Ensures hygiene, increases operational efficiency | Compliance with food safety standards, material durability, and ease of cleaning |
| Mining | Lubrication for drilling and excavation rigs | Minimizes wear and tear, enhances operational uptime | Robustness in harsh environments, temperature tolerance, and service availability |
| Automotive | Lubrication in assembly lines | Increases production speed, reduces maintenance costs | Customization for specific machinery, reliability, and availability of spare parts |
| Energy (Oil & Gas) | Lubrication for compressors and pumps | Increases equipment efficiency, reduces energy consumption | Adaptability to extreme conditions, efficiency ratings, and supplier reliability |
How is ‘lube system’ utilized in the construction industry to enhance operations?
In the construction sector, automatic lubrication systems are critical for heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. These systems ensure that equipment is continuously lubricated, significantly reducing downtime caused by manual lubrication. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing systems that are compatible with a variety of machinery brands and models is crucial. Additionally, considering the availability of local maintenance support can mitigate operational disruptions.
What role does lubrication play in food processing applications?
In food processing, centralized lubrication systems are employed to maintain conveyor belts and machinery, ensuring that operations remain hygienic and efficient. These systems help prevent contamination, which is vital in food production environments. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that comply with food safety standards and offer materials that withstand cleaning processes. The ability to customize systems to fit specific equipment layouts is also an important consideration.
How does lubrication impact mining operations?
In the mining industry, lubrication systems are essential for equipment used in drilling and excavation. They reduce wear and tear on critical components, thereby enhancing the operational uptime of rigs and other machinery. For businesses sourcing these systems, it is important to select products designed to perform reliably in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures and dust. Additionally, understanding the local supply chain for parts and maintenance services can be advantageous for minimizing downtime.
Why is lubrication essential in automotive assembly lines?
Automotive manufacturers utilize lubrication systems in assembly lines to ensure that machinery operates smoothly and efficiently. These systems help to speed up production processes while minimizing maintenance costs associated with equipment failures. Buyers should focus on sourcing lubrication systems that can be easily integrated into existing machinery and offer reliable performance. The availability of spare parts and technical support is also a key factor in maintaining operational efficiency.
What benefits do lubrication systems bring to the energy sector?
In the energy sector, particularly in oil and gas, lubrication systems are crucial for the efficient operation of compressors and pumps. They help to enhance equipment efficiency and reduce energy consumption, which can lead to significant cost savings. When sourcing these systems, it is essential for buyers to consider the adaptability of the lubrication solutions to extreme operational conditions. Supplier reliability and the efficiency ratings of the lubrication products are critical factors that should be evaluated to ensure long-term performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lube system’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Lubrication Leading to Equipment Downtime
The Problem: A manufacturing facility in Nigeria faces frequent equipment breakdowns due to inadequate lubrication practices. Operators are using manual lubrication methods, which often result in inconsistent application. This inefficiency leads to significant downtime, production delays, and increased maintenance costs as machinery components wear out faster than expected. The facility struggles to maintain productivity while also managing the operational costs associated with these failures.
The Solution: Implementing an automatic lubrication system can drastically improve efficiency and reduce downtime. B2B buyers should evaluate and select systems that offer precise lubrication at consistent intervals, even when machinery is in motion. This not only ensures optimal lubrication but also prolongs the life of equipment. When sourcing these systems, consider factors such as compatibility with existing machinery, ease of installation, and the ability to monitor lubrication levels through digital interfaces. Investing in high-quality components, such as pumps and controllers, will further enhance the reliability of the lubrication process, ensuring that each component receives the correct amount of lubricant without the risk of over- or under-lubrication.
Scenario 2: Contamination Issues in Lubrication Systems
The Problem: A construction company in South America is experiencing contamination issues with its lubrication systems. Dust and debris from the environment are infiltrating the lubrication lines, leading to reduced lubricant effectiveness and causing excessive wear on the machinery. This scenario not only affects performance but also results in costly repairs and replacements, straining the company’s budget and project timelines.
The Solution: To combat contamination, it is essential to invest in a lube system that features filtration and sealing technologies designed for harsh environments. B2B buyers should focus on systems that utilize high-quality filters to remove contaminants before they reach the machinery. Additionally, implementing a centralized lubrication system can minimize the number of connection points where contamination can occur. Regular maintenance checks and the use of protective covers for lubrication points can also help maintain system integrity. Suppliers should be selected based on their ability to provide comprehensive solutions, including customized filtration options tailored to the specific environmental challenges faced by the construction industry.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Manual Lubrication
The Problem: An industrial plant in the Middle East is dealing with high operational costs stemming from its reliance on manual lubrication methods. Workers must frequently stop machinery to apply lubricants, which not only disrupts workflow but also increases labor costs and reduces overall productivity. The plant manager is looking for a way to streamline operations without sacrificing equipment reliability.
The Solution: Transitioning to an automatic lubrication system is a key strategy to reduce operational costs. Buyers should consider systems that can integrate with existing machinery to facilitate a seamless transition. Moreover, investing in training for staff on how to operate and maintain these systems can maximize their benefits. By automating the lubrication process, the plant can ensure that lubrication occurs during operation, thus eliminating downtime and reducing labor hours. Additionally, monitoring systems that provide real-time data on lubricant usage can help in optimizing lubricant consumption, further driving down costs. Collaborating with suppliers who offer robust customer support and training programs will ensure that the plant maximizes the return on investment in the new lubrication system.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lube system
What Are the Key Materials Used in Lubrication Systems?
When selecting materials for lubrication systems, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact system performance, reliability, and overall maintenance costs. Here, we analyze four common materials used in lubrication systems: stainless steel, brass, plastic, and rubber.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Lubrication Systems?
Stainless steel is a popular choice for lubrication system components due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 1,200°F (649°C) and can withstand high pressures, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to rust and corrosion, and can handle extreme temperatures and pressures. It also has a long lifespan, which reduces the frequency of replacements.
Illustrative image related to lube system
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, as stainless steel is more expensive than other materials. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can be higher due to the need for specialized machining and welding.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of lubricants and fluids, including oils and greases. Its robustness makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications in industries such as mining and construction.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can be harsh, stainless steel’s corrosion resistance is particularly advantageous.
What Role Does Brass Play in Lubrication Systems?
Brass is another commonly used material, particularly for fittings and connectors in lubrication systems. It offers good corrosion resistance and is typically rated for moderate temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Brass is relatively easy to machine and offers good thermal conductivity. It is also less expensive than stainless steel, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications.

Illustrative image related to lube system
Cons: While brass is resistant to corrosion, it is not as robust as stainless steel and may not perform well in high-pressure environments. Its lower temperature tolerance (around 400°F or 204°C) can also limit its use in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Brass is suitable for lubricants that do not contain aggressive chemicals. It is often used in low-pressure systems, such as those found in automotive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of brass, especially in food and beverage applications. Compliance with standards like JIS is essential in regions such as Japan and other parts of Asia.
How Do Plastics Compare in Lubrication Systems?
Plastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are increasingly being used in lubrication systems due to their lightweight and cost-effective properties. They can handle a range of temperatures, typically up to 200°F (93°C).
Pros: Plastics are resistant to many chemicals and are lightweight, which can reduce overall system weight. They are also less expensive and can be manufactured easily.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastics is their lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals. They may also degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are suitable for non-aggressive lubricants and are often used in automotive and light industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local environmental regulations, especially in regions where plastic waste management is a concern. Standards such as ASTM for plastic materials should be considered.
What Advantages Does Rubber Provide in Lubrication Systems?
Rubber is commonly used for seals and gaskets in lubrication systems due to its flexibility and excellent sealing properties. It can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 121°C).

Illustrative image related to lube system
Pros: Rubber provides excellent sealing capabilities, preventing leaks and contamination. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to replace.
Cons: Rubber can deteriorate over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals. Its lifespan may be shorter compared to metal components.
Impact on Application: Rubber is ideal for sealing applications in lubrication systems, ensuring that lubricants remain contained and effective.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that rubber materials meet specific industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO, to ensure compatibility with various lubricants and environmental conditions.
Summary of Material Selection for Lubrication Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for lube system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Low-pressure automotive fittings | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Medium |
| Plastic | Lightweight automotive components | Lightweight and resistant to chemicals | Lower temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets in lubrication systems | Excellent sealing properties | Shorter lifespan under extreme conditions | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for lubrication systems requires careful consideration of the specific application, environmental conditions, and compliance with international standards. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each material can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that enhance system performance and longevity.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lube system
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Lube Systems?
The manufacturing process of lube systems involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Lube Systems?
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves the preparation of raw materials. High-quality metals such as stainless steel and aluminum are commonly used for components like reservoirs, pumps, and tubing due to their corrosion resistance and durability. Additionally, various grades of plastic may be utilized for certain parts that require lightweight properties. Suppliers typically source materials from reputable vendors to ensure they meet international standards. Buyers should inquire about the origin and certifications of these materials to assess their quality.
How Are Components Formed in Lube Systems?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes such as machining, casting, and injection molding.
-
Machining: This process involves cutting and shaping materials to create precise components. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed to enhance accuracy and reduce waste.
-
Casting: For complex shapes, casting techniques may be used, allowing manufacturers to create intricate designs without extensive machining.
-
Injection Molding: Commonly used for plastic components, this method ensures uniformity and allows for mass production.
These forming techniques are critical as they directly impact the performance and reliability of the lube system. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities and the technologies they employ.
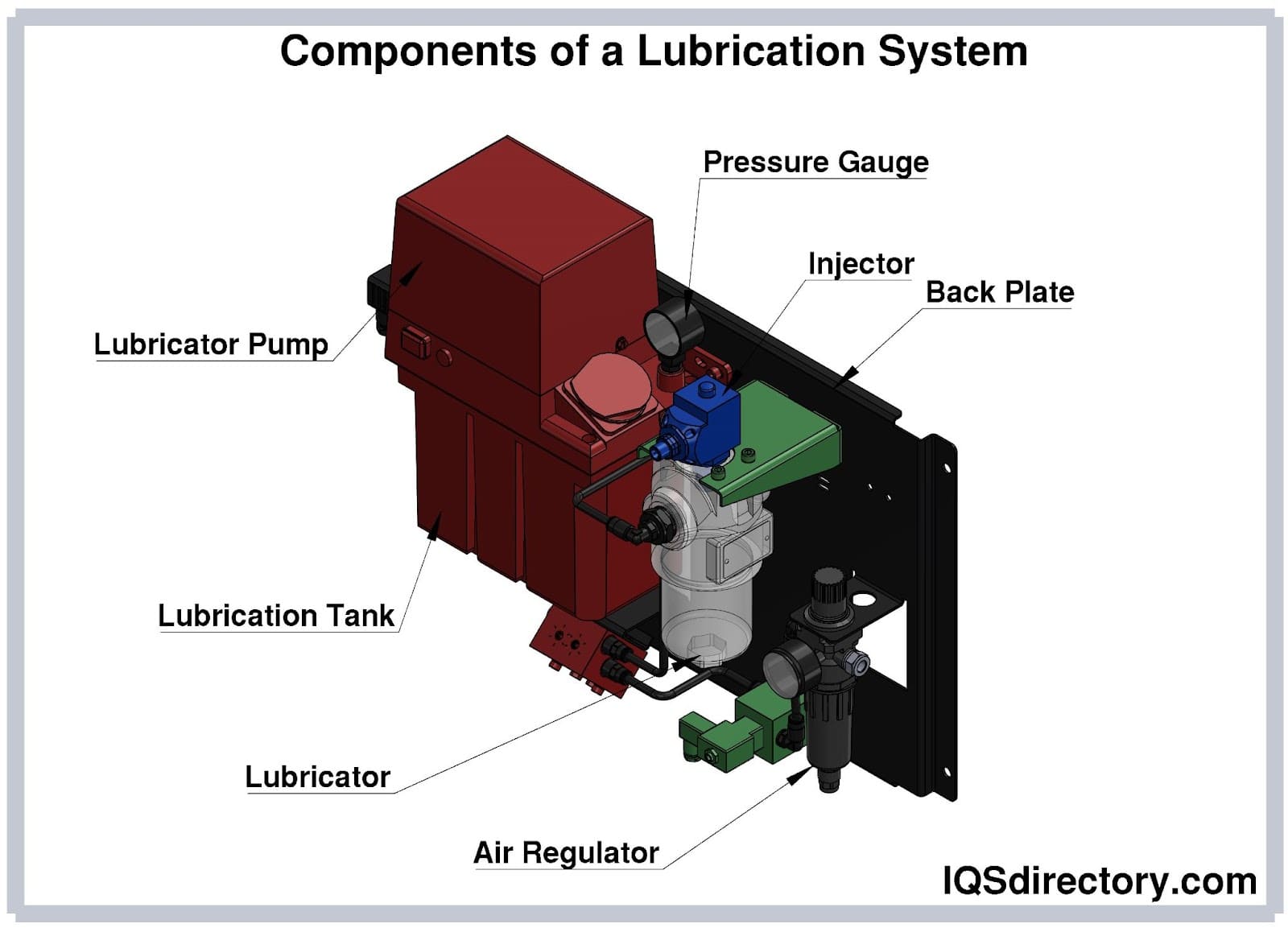
Illustrative image related to lube system
What Is the Assembly Process for Lube Systems?
The assembly stage brings together the formed components to create the complete lube system. This stage involves:
-
Component Integration: Each part, including pumps, hoses, and fittings, is assembled according to a detailed blueprint.
-
Quality Checks: During assembly, manufacturers often conduct preliminary quality checks to ensure that components fit correctly and function as intended.
-
Testing for Leaks: After assembly, systems may undergo leak tests to verify their integrity before moving to the finishing stage.
Buyers should ask potential suppliers about their assembly protocols and any specific machinery used, as this can affect the reliability of the final product.
How Are Lube Systems Finished and Prepared for Delivery?
The finishing stage involves applying coatings, surface treatments, or protective finishes to enhance durability and aesthetics.
-
Coatings: Applying corrosion-resistant coatings can significantly extend the lifespan of lube systems, especially in harsh environments.
-
Labeling and Packaging: Proper labeling for identification and safe packaging for transport are also crucial in this stage.
Once finishing is complete, the systems are prepared for shipping, with quality assurance checks ensuring compliance with specifications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of lube systems to ensure reliability and performance. Key international standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, ensuring that suppliers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) has specific standards for lubrication products that ensure their effectiveness and safety.
B2B buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to these standards, as they reflect a commitment to quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Lube System Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks raw materials against specifications before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing, this stage involves monitoring processes and products to identify any defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly and finishing are complete, FQC ensures that the final product meets all specifications before shipment.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC processes used by suppliers to ensure comprehensive oversight throughout manufacturing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that a supplier meets quality standards, B2B buyers can take several actions:
-
Request Audits and Reports: Buyers can ask for copies of quality audits and reports to assess a supplier’s adherence to industry standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors to evaluate manufacturing facilities and processes can provide an unbiased view of a supplier’s quality control measures.
-
Certifications: Buyers should verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) and that these are up to date.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific nuances in quality control that can differ by region. For example:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding regional manufacturing practices can help buyers set realistic expectations and communicate effectively with suppliers.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be aware of local regulations that may affect product specifications and quality standards.
-
Logistics and Transport Considerations: Quality control does not end at the factory. Buyers must consider how products will be transported and stored, as these factors can also impact quality.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers in the lube system market. By focusing on these areas, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce the risk of equipment failure.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lube system’
When sourcing lubrication systems, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of options, specifications, and suppliers. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your procurement process, ensuring that you secure a system that meets your operational needs while optimizing costs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific lubrication needs is paramount. Identify the type of equipment requiring lubrication, the lubricant type (oil or grease), and the necessary delivery method (manual or automatic). This clarity will help you select systems that are compatible with your machinery and operational requirements.
- Consider equipment type: Different machines may require tailored lubrication solutions.
- Assess environmental conditions: Operating conditions, such as temperature and exposure to contaminants, influence lubricant selection.
Step 2: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before choosing a supplier, ensure they hold relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Certifications like ISO or industry-specific recognitions can indicate reliability and quality in manufacturing practices.
- Verify production standards: Look for suppliers who adhere to stringent quality control measures.
- Check for sustainability certifications: As environmental concerns grow, consider suppliers committed to eco-friendly practices.
Step 3: Assess Product Range and Customization Options
A reputable supplier should offer a variety of lubrication systems and components. This diversity allows you to select solutions that can be customized to fit your specific operational needs, enhancing efficiency and performance.
- Look for modular systems: These can be tailored to different equipment and can adapt as your operations evolve.
- Inquire about availability of spare parts: Ensure that replacement parts are readily available to minimize downtime.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
Gather comprehensive information about the lubrication systems you are considering. This should include technical specifications, installation guidelines, and maintenance requirements.
- Ask for data sheets: These documents provide essential insights into system capabilities.
- Seek user manuals: Understanding installation and maintenance processes will help you assess the total cost of ownership.
Step 5: Compare Costs and Value Propositions
While price is a crucial factor, it shouldn’t be the sole consideration. Analyze the total cost of ownership, including initial investment, maintenance expenses, and potential downtime costs.
- Consider long-term savings: Systems that require less maintenance or provide greater uptime may justify a higher initial cost.
- Evaluate warranty and support services: Robust support can significantly reduce operational risks and costs.
Step 6: Solicit References and Case Studies
Before finalizing your decision, request references from past clients or case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s success in similar industries. This can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability and customer service.
- Reach out to existing customers: Their experiences can highlight potential issues or advantages not mentioned in sales pitches.
- Look for industry relevance: Ensure the references relate closely to your industry for more applicable insights.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Review and Decision Making
Once you have gathered all necessary information, conduct a final review of your options. Compare all factors, including technical specifications, supplier reliability, and total costs, before making a decision.
- Involve key stakeholders: Engage team members from different departments to ensure all perspectives are considered.
- Prepare for negotiation: Be ready to discuss terms and conditions to secure the best deal.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing lubrication systems, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lube system Sourcing
When sourcing lubrication systems, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the various cost components, pricing influencers, and practical tips to optimize purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lube System Manufacturing?
The cost structure of lubrication systems typically comprises several key components:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used—such as metals, plastics, and specialized lubricants—significantly impact costs. High-quality materials may be more expensive but can enhance system performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor may demand higher wages, influencing the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, making products more competitively priced.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific lube systems can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs are justified by the expected return on investment through enhanced efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure reliability and performance. While these processes add to the cost, they are crucial for maintaining high standards, especially in industries where equipment failure can lead to significant downtime.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing can add considerable expenses, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import duties should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. Understanding a supplier’s cost structure can aid in negotiating favorable terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Lube System Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the lube system market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their usage patterns to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed systems tailored to specific applications typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against standard options.
-
Materials and Certifications: Systems made from premium materials and those that meet international certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may have higher upfront costs but can provide long-term savings through enhanced durability and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and service levels of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can impact overall costs significantly.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Lube System Prices?
To ensure cost-efficiency in sourcing lube systems, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. A clear understanding of your requirements can empower you in negotiations.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance costs, potential downtime, and the lifespan of the system to gauge the true value of your investment.
-
Research Market Prices: Benchmark against multiple suppliers to understand standard pricing. Use this data to negotiate better terms or identify suppliers who offer more competitive pricing.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to labor costs, material availability, and economic conditions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should tailor their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Final Note on Pricing
Prices for lube systems can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. It’s essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and engage in strategic negotiations to secure the best deals. Keep in mind that the prices listed in product catalogs or websites are indicative and may fluctuate based on market conditions, currency fluctuations, and supplier pricing strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lube system With Other Solutions
When considering lubrication solutions for industrial machinery, it’s crucial to evaluate the available options to determine the best fit for specific operational needs. The traditional lube system offers numerous advantages, but alternatives may provide unique benefits that could align better with a company’s requirements. This analysis will compare the lube system with two viable alternatives: manual lubrication systems and centralized lubrication systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Lube System | Manual Lubrication System | Centralized Lubrication System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; continuous lubrication while equipment operates | Inconsistent; depends on human application | Consistent; automated and precise delivery of lubricant |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs due to reduced downtime | Low initial cost, higher long-term costs due to labor and potential equipment failure | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective for large operations over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires trained personnel for installation and setup | Simple to implement; minimal training needed | More complex setup; requires planning and potential downtime during installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; regular monitoring needed | High maintenance; frequent checks needed for effectiveness | Low maintenance; regular checks for system integrity required |
| Best Use Case | High-demand environments with continuous operation | Small-scale operations or low-demand environments | Large facilities with multiple lubrication points and high machinery usage |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Lubrication Systems?
Manual lubrication systems are straightforward, requiring minimal investment and low-tech solutions. They work well in smaller operations where equipment does not run continuously. However, their primary drawback is the inconsistency and potential for human error in applying lubricant, which can lead to equipment failure and increased downtime. In high-demand settings, relying on manual lubrication may not meet the necessary performance standards, often resulting in higher long-term costs due to maintenance and repairs.
How Do Centralized Lubrication Systems Compare to Lube Systems?
Centralized lubrication systems automate the lubrication process, ensuring consistent and precise application across multiple lubrication points. This can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs, making them ideal for large operations with many machines. However, they typically require a higher upfront investment and more complex installation. While they are more efficient than manual systems, they may not be as cost-effective in smaller operations where the scale does not justify the investment.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Lubrication Solution?
Choosing the right lubrication solution hinges on a thorough understanding of operational needs, machinery usage, and budget constraints. For businesses operating in high-demand environments, a lube system or centralized lubrication solution may offer the best efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run. Conversely, companies with less demanding lubrication needs might find manual systems sufficient, especially if they seek to minimize initial costs. Ultimately, evaluating the specific context and requirements will guide B2B buyers in selecting the most appropriate lubrication method for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lube system
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Lube System?
When selecting a lubrication system, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Below are key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of components, such as tubing and fittings, directly impacts the durability and longevity of the lubrication system. High-grade materials like stainless steel or specialized polymers resist corrosion and wear, making them ideal for harsh environments. This is particularly important for industries operating in humid or abrasive conditions, where equipment failure can lead to costly downtime.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In lubrication systems, precise tolerances ensure proper fit and function of components like pumps and valves. Tight tolerances prevent leaks and ensure efficient lubricant delivery, which is essential for maintaining machinery performance. For B2B buyers, selecting components with appropriate tolerances can significantly reduce maintenance costs over time.
3. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure a component can safely handle. In lubrication systems, this is critical for ensuring that lubricants are delivered effectively to all necessary points without risk of system failure. For industries using high-pressure applications, it’s vital to choose components rated for those pressures to avoid catastrophic failures.
4. Flow Rate
Flow rate measures the volume of lubricant that can be delivered in a specific period. It is essential for matching the lubrication system to the specific requirements of machinery, especially in high-demand environments like manufacturing or heavy equipment. Understanding the required flow rate helps buyers select the right system to maintain optimal lubrication and prevent equipment wear.
5. Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the ambient temperatures in which the lubrication system can function effectively. Lubricants can degrade at extreme temperatures, leading to reduced effectiveness and potential equipment damage. Buyers must consider the operating environment of their machinery to ensure that the selected lubrication system can withstand those conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Lube Systems?
Familiarity with industry terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process more effectively. Here are several important terms:
Illustrative image related to lube system
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of lubrication systems, understanding OEM components is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance. Buyers should look for OEM parts to maintain warranty protections and ensure the quality of their systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. If the MOQ is too high, it may lead to excess stock and increased costs, particularly for smaller operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing information from suppliers. Providing detailed RFQs allows buyers to compare costs and terms across different suppliers, ensuring they get the best value for their investment in lubrication systems.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid unexpected costs and ensure smooth transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
5. Lubricant Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. In lubrication systems, selecting the appropriate viscosity is critical for ensuring that lubricants can effectively coat and protect machinery components. Buyers must consider the operating conditions to choose the right lubricant viscosity for their applications.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding lubrication systems that enhance equipment performance and reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lube system Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Lube System Sector?
The global lube system market is undergoing significant transformations driven by various factors, including technological advancements, increasing demand for automation, and the imperative for enhanced operational efficiency. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking automatic lubrication systems that ensure optimal performance and reduce maintenance costs. Innovations in smart lubrication technologies, such as IoT-enabled systems, are emerging to provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, thereby enhancing uptime and productivity.
Moreover, the demand for environmentally friendly lubrication solutions is rising, with buyers prioritizing suppliers that offer sustainable products. For instance, systems that minimize waste and enhance lubricant efficiency are gaining traction. Buyers are also looking for suppliers who can deliver comprehensive service packages, including installation, training, and ongoing support, to ensure seamless integration into their operations. This shift toward a service-oriented approach allows manufacturers to build long-term relationships with clients and differentiate themselves in a competitive marketplace.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing in the Lube System Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the lube system sector. The environmental impact of lubricants, particularly in terms of pollution and waste, has prompted companies to seek out ethical sourcing practices. Buyers are increasingly focused on suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications and eco-friendly materials, which not only reduce environmental harm but also align with corporate social responsibility goals.
The trend toward sustainability also extends to the entire supply chain. Buyers are interested in understanding the sourcing practices of their suppliers, including the use of renewable resources and the energy efficiency of production processes. This focus on ethical sourcing is not merely a regulatory compliance measure; it is a strategic advantage that can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Companies that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability are likely to gain a competitive edge in the international market.
What Is the Evolution of the Lube System Sector?
The lube system sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from manual lubrication methods to sophisticated automatic systems. Historically, lubrication processes were labor-intensive, relying on manual application that often resulted in inconsistent results and equipment wear. The introduction of automatic lubrication systems revolutionized the industry by ensuring precise delivery of lubricants at optimal intervals, thus extending the life of machinery and reducing downtime.
As technology advanced, the integration of digital solutions, such as IoT and data analytics, has further transformed the landscape. These innovations enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing companies to optimize their operations. Today, the lube system sector is characterized by a strong emphasis on efficiency, reliability, and sustainability, reflecting the changing needs of B2B buyers in a rapidly evolving marketplace.

Illustrative image related to lube system
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lube system
-
1. How do I solve lubrication issues in heavy machinery?
To effectively solve lubrication issues in heavy machinery, it’s essential to assess the specific lubrication needs of each equipment type. Implementing an automatic lubrication system can ensure consistent application of the right lubricant at appropriate intervals, reducing wear and tear. Additionally, regularly scheduled maintenance checks can help identify potential lubrication failures before they lead to costly downtimes. Partnering with a reliable supplier who offers quality lubricants and supports installation can further enhance the reliability of your machinery. -
2. What is the best automatic lubrication system for industrial applications?
The best automatic lubrication system for industrial applications depends on the specific machinery and operational environment. Systems like Graco’s automatic lubrication solutions are designed for various industrial applications, offering features like precise lubrication delivery and real-time monitoring. It’s important to consider factors such as system compatibility with existing equipment, ease of installation, and maintenance requirements. Consulting with suppliers who provide tailored solutions can help ensure you choose the most effective system for your needs. -
3. How can I customize a lubrication system to fit my specific machinery?
Customization of a lubrication system can be achieved by collaborating closely with your supplier. Identify the unique lubrication points, types of lubricants required, and the operational conditions of your machinery. Many suppliers offer bespoke solutions that include tailored components such as pumps, hoses, and fittings designed to meet your specific operational demands. Engaging in a detailed discussion about your requirements will allow the supplier to design a system that maximizes efficiency and minimizes downtime. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for lube systems when sourcing internationally?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for lube systems can vary significantly among suppliers and regions. Typically, MOQs are established based on production costs, shipping logistics, and supplier capabilities. For international buyers, it’s advisable to inquire directly with suppliers for their specific MOQs, as some may offer flexibility, especially for new customers or bulk orders. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ will help you plan your procurement strategy effectively and ensure you meet your operational needs without excessive inventory costs. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing lube systems internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of lube systems can vary widely depending on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms (like 30, 60, or 90 days). It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Make sure to clarify any additional costs, such as shipping and customs fees, which could impact the total payment amount. Transparent communication with suppliers will facilitate smoother transactions. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for lube systems from international suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance for lube systems sourced internationally, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your suppliers. Conducting factory audits or requesting samples for testing can also provide insight into the quality of their products. It’s beneficial to establish a clear QA process that includes regular inspections and performance assessments of the lubrication systems upon receipt. Building a strong relationship with your supplier will foster trust and encourage adherence to quality standards. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing lubrication systems?
When importing lubrication systems, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Selecting a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international trade can simplify the shipping process and ensure compliance with local laws. Additionally, factor in the costs of transportation, insurance, and potential tariffs. Understanding the end-to-end logistics will help you plan more effectively and avoid unexpected delays or expenses during the import process. -
8. How do I evaluate and vet suppliers of lubrication systems?
Evaluating and vetting suppliers of lubrication systems involves several key steps. Start by researching the supplier’s reputation, including customer reviews and case studies. Request references from current clients to gauge satisfaction and reliability. It’s also advisable to assess their experience in the industry, product range, and after-sales support. Consider visiting their facilities if possible, or conducting a video conference to discuss your requirements and gauge their responsiveness and expertise. This thorough vetting process will help ensure you partner with a trustworthy supplier.
Top 5 Lube System Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Lube Technologies – BSP Thread Lubrication System Parts Kit
Domain: lubetechnologies-shop.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Featured Products: 1. SKU: LT-BSPPK – BSP Thread Lubrication System Parts Kit for Heavy Equipment (Komatsu, John Deere, Hitachi, Volvo) – Price: $489.51 2. SKU: LT-SWTPK – Street Sweepers / Trucks Parts Kit for Automatic Lubrication Systems – Price: $685.41 3. SKU: LT-LNPK – Lincoln™ Replacement Parts Kit For Automatic Lubrication Systems – Price: $627.92 4. SKU: LT-HEPK – Heavy Equipment Parts Ki…
2. LUBE Corporation – Advanced Lubrication Systems
Domain: lube-global.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: LUBE Corporation offers a variety of lubrication systems and products including: 1. World standard LHL system grease lubrication system 2. Battery drive grease kit 3. Main pipe decompression system 4. Multi-Port Centralized Lubrication System 5. LUBE Original Grease 6. Oil lubrication system 7. Air driven dispensing system 8. Piping Parts 9. Oil pump 10. Consumables.
3. Graco – Automatic Lubrication Systems
Domain: graco.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Graco Automatic Lubrication systems provide the proper amount of lubrication on a more frequent basis, enhancing uptime and productivity while reducing maintenance costs. Key components include Auto Lube Accessories, Auto Lube Controllers, Automatic Grease & Oil Pumps, Automatic Grease & Oil Systems, Flow Divider Valves, and Grease & Oil Injectors. These systems are designed for various applicatio…
4. Timken – Lubricants and Lubrication Systems
Domain: timken.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Timken offers lubricants and lubrication systems designed to maximize performance, productivity, and uptime. Key products include:
– Groeneveld-Beka Lubrication Systems
– Single-Point Lubricators
– Des-Case Filtration Products
– Industrial Grease (Premium All-Purpose, Construction and Off-Highway, Ball Bearing Pillow Block, Mill, Food Safe, Synthetic Industrial, Multi-Use Lithium, Automotive, …
5. Lubecore – Automated Lubrication Systems
Domain: lubecore.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Lubecore offers next generation automated lubrication systems designed for various industries including agriculture, construction, mining, municipal, ports and terminals, small equipment, stationary equipment, transportation, and waste and recycling. Their systems are produced in Canada and focus on quality and ease of use, aiming to reduce equipment failure caused by improper greasing, which acco…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lube system
In the rapidly evolving landscape of lubrication systems, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal driver for international B2B buyers. By leveraging high-quality automatic lubrication solutions, companies can enhance equipment reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and significantly improve operational efficiency. The integration of advanced systems not only ensures precise lubrication but also minimizes waste and downtime, leading to substantial long-term savings.
As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, the demand for innovative lubrication technologies will only grow. Buyers should focus on suppliers that offer comprehensive solutions, including parts kits and customizable systems, to meet the diverse needs of their operations.
Looking ahead, the commitment to strategic sourcing in lubrication systems will empower organizations to navigate challenges effectively and capitalize on emerging opportunities. B2B buyers are encouraged to assess their current lubrication practices and consider transitioning to automatic systems that promise enhanced productivity and lower operational risks. The future of lubrication is not just about keeping machinery running; it’s about optimizing performance and driving business success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.