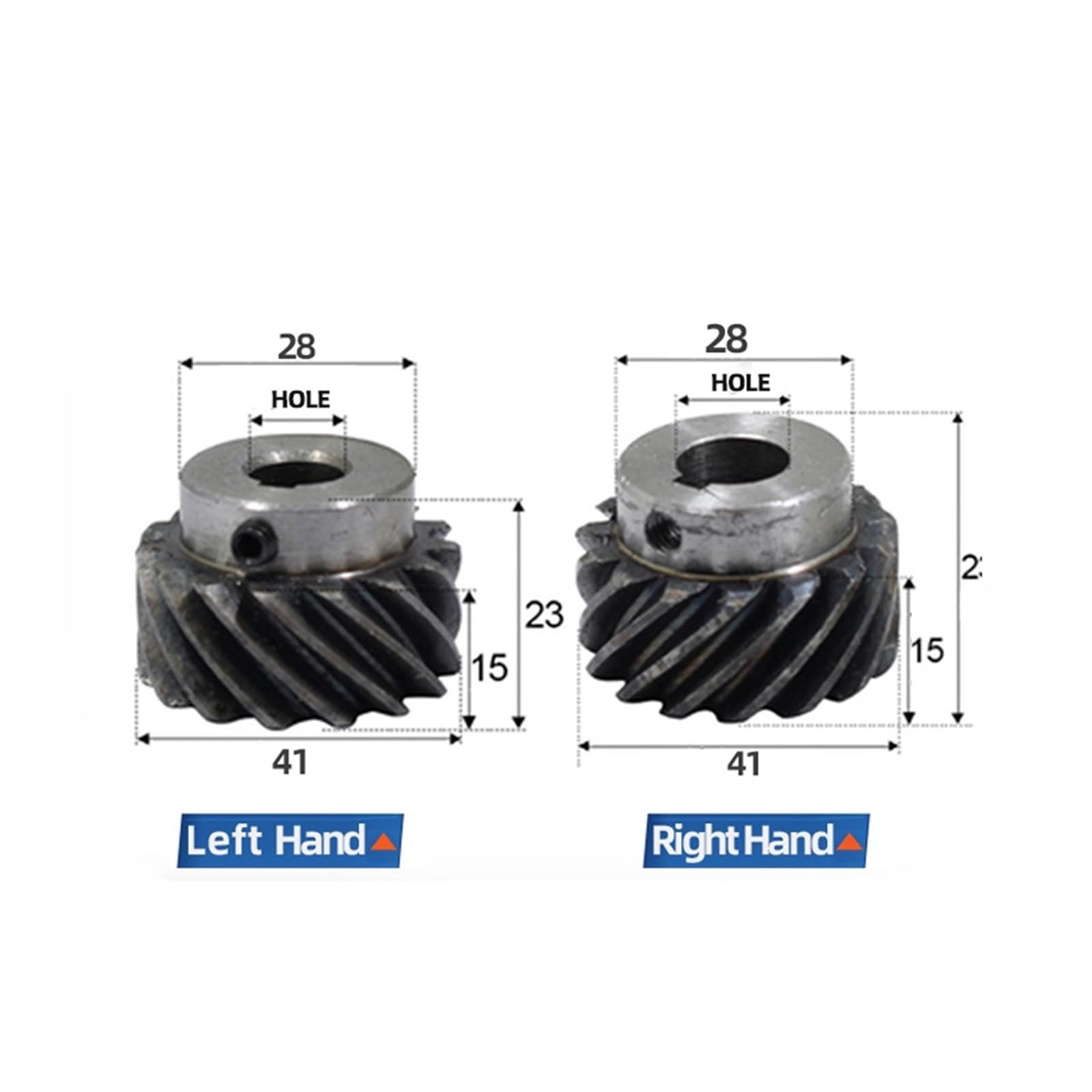
How to Source Left Hand Gear Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for left hand gear
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right left-hand gear can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexity of understanding gear orientation—whether in helical, bevel, or worm configurations—can impact operational efficiency and product performance. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into the various types of left-hand gears, their applications across industries, and critical considerations for supplier vetting. Buyers will find insights on cost structures, compatibility, and thrust load implications that are essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Germany and Vietnam) expand their manufacturing capabilities, the need for specialized gear solutions becomes paramount. This guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into the nuances of left-hand gear, ensuring they select the right products that meet their specific operational needs. From understanding the technical specifications to navigating the global supply chain, we aim to equip B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to optimize their procurement processes. By addressing the key challenges in sourcing left-hand gear, this guide will help businesses enhance their productivity and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
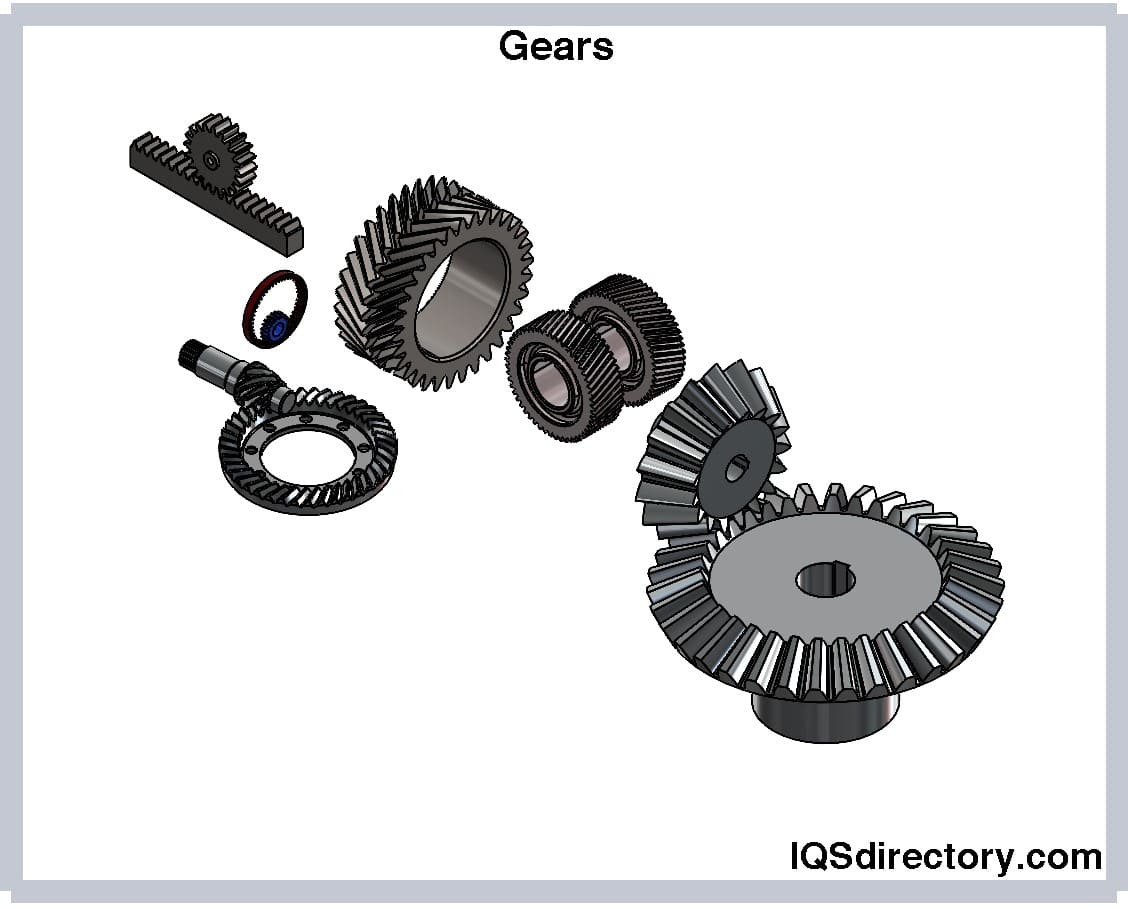
Understanding left hand gear Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helical Gears | Skewed teeth allowing for higher torque and quieter operation. | Machinery, automotive, and conveyors | Pros: Efficient torque transfer; Cons: Introduces thrust loads requiring careful bearing selection. |
| Spiral Bevel Gears | Angled teeth that enable the transmission of power between non-parallel shafts. | Gearboxes, automotive differentials | Pros: Compact design; Cons: Complex installation and alignment needed. |
| Worm Gears | Feature a screw-like design, ideal for high torque applications. | Lifts, conveyors, and rotary actuators | Pros: High reduction ratios; Cons: Low efficiency due to sliding contact. |
| Screw Gears | Can operate in pairs of the same or opposite hand; unique helix angle. | Robotics, conveyor systems | Pros: Versatile configurations; Cons: Thrust loads can complicate system design. |
| Spur Gears | Straight teeth aligned parallel to the axis; left-hand variants available. | General machinery and power transmission | Pros: Simple design and manufacturing; Cons: Noisy operation at high speeds. |
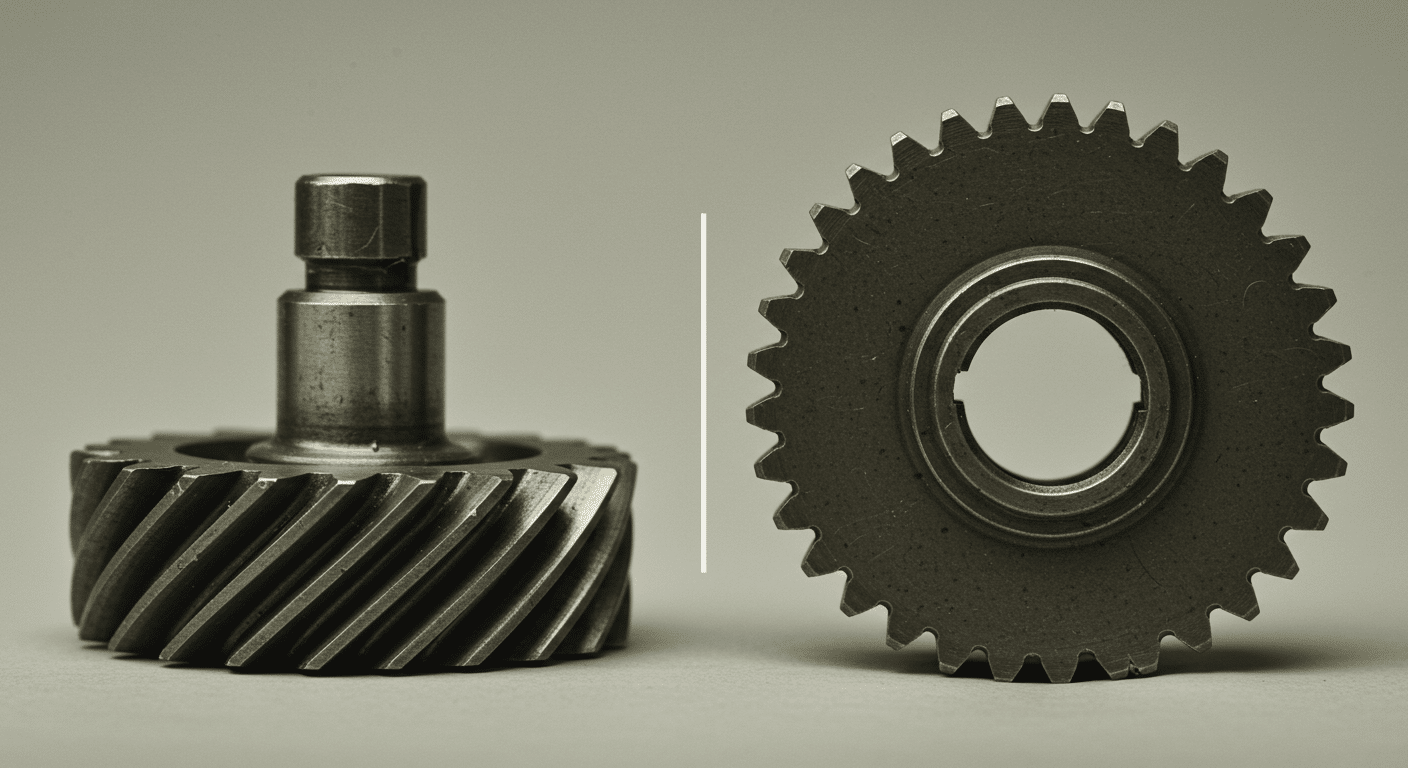
What Are Helical Gears and Their B2B Relevance?
Helical gears are characterized by their skewed teeth, which facilitate smoother operation and greater torque transmission compared to spur gears. In B2B applications, they are widely used in machinery, automotive systems, and conveyors where noise reduction and efficiency are paramount. Buyers should consider the additional thrust loads these gears introduce, necessitating the selection of appropriate bearings to ensure longevity and reliability.
How Do Spiral Bevel Gears Function in Industrial Settings?
Spiral bevel gears have angled teeth that enable efficient power transmission between non-parallel shafts, making them ideal for applications in gearboxes and automotive differentials. Their compact design is a significant advantage in space-constrained environments. However, buyers must account for the complexity of installation and alignment, which can increase overall project costs and timelines.
Why Choose Worm Gears for High Torque Applications?
Worm gears are distinguished by their screw-like design, providing high torque output with a compact footprint. They are commonly used in applications such as lifts, conveyors, and rotary actuators. While they offer high reduction ratios, buyers should be aware of their lower efficiency due to sliding contact, which can lead to increased wear and maintenance needs over time.
What Makes Screw Gears Unique in Gear Design?
Screw gears can operate in both left-hand and right-hand configurations, allowing for flexibility in design and installation. They are particularly useful in robotics and conveyor systems where precise motion is required. Buyers should note that, like helical gears, screw gears also generate thrust loads that must be managed carefully in system design to avoid premature failure.
Are Spur Gears Still Relevant in Modern Machinery?
Spur gears are one of the simplest gear types, featuring straight teeth aligned parallel to their axis. They are commonly used in general machinery and power transmission applications due to their straightforward design and ease of manufacturing. However, while they are cost-effective, buyers should consider their potential for noisy operation, particularly at high speeds, which may not be suitable for all applications.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
Key Industrial Applications of left hand gear
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of left hand gear | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision machinery for automotive assembly | Enhances torque handling and reduces noise during operation | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and standards |
| Marine Engineering | Propulsion systems in ships and submarines | Improves efficiency and reliability in harsh environments | Evaluate corrosion resistance and material specifications |
| Mining | Gear drives in conveyor systems and excavation equipment | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Assess load capacity and thrust bearing requirements |
| Renewable Energy | Gearboxes in wind turbines | Optimizes energy conversion and increases power output | Consider local regulations and environmental impact |
| Construction | Lifting equipment and cranes | Provides stability and precision in heavy lifting operations | Focus on safety certifications and load specifications |
How is Left Hand Gear Used in Manufacturing and What Problems Does it Solve?
In the manufacturing sector, left hand gears are commonly utilized in precision machinery for automotive assembly lines. These gears facilitate the smooth transfer of power between parallel shafts, improving torque handling and minimizing operational noise. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and South America, it is critical to ensure that these gears are compatible with existing machinery and adhere to local manufacturing standards. This compatibility not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces maintenance costs.
What Role Does Left Hand Gear Play in Marine Engineering?
In marine engineering, left hand gears are integral to propulsion systems in ships and submarines. The unique design allows for improved efficiency in power transmission, especially in challenging marine environments. This is particularly beneficial for buyers in the Middle East, where the harsh conditions can impact equipment longevity. When sourcing, it’s essential to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials used in left hand gears, ensuring they can withstand saltwater exposure and deliver reliable performance over time.
How are Left Hand Gears Applied in Mining Operations?
Mining operations leverage left hand gears in gear drives for conveyor systems and excavation equipment. These gears are designed to handle substantial loads, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. For buyers in Africa, where mining activities are often extensive, it is crucial to assess the load capacity and thrust bearing requirements of left hand gears. Ensuring these specifications meet the demands of heavy-duty applications can significantly impact productivity and operational costs.
Why are Left Hand Gears Important in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, left hand gears are used in gearboxes to optimize energy conversion. By improving the transfer of mechanical energy, these gears can increase the overall power output of turbines. International buyers, especially in regions focused on renewable energy initiatives, should consider local regulations and environmental impacts when sourcing left hand gears, ensuring compliance with sustainability standards while maximizing energy efficiency.
What is the Importance of Left Hand Gears in Construction Equipment?
In construction, left hand gears are critical components of lifting equipment and cranes, providing the necessary stability and precision for heavy lifting operations. This application is vital for construction projects in urban areas across Europe and South America, where safety and efficiency are paramount. Buyers should focus on sourcing gears that meet safety certifications and load specifications to ensure reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘left hand gear’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment and Compatibility Issues in Gear Systems
The Problem: One of the most common challenges faced by B2B buyers when dealing with left-hand gears is ensuring proper alignment and compatibility with existing systems. Many businesses may overlook the specific orientation of gears, leading to significant operational inefficiencies. For instance, if a manufacturer inadvertently uses a left-hand gear with a right-hand counterpart that is not designed to mesh correctly, it can result in increased wear, noise, and even catastrophic system failures. This misalignment often stems from a lack of clear communication between engineering teams and suppliers regarding the specifications needed for different gear orientations.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should establish a comprehensive specification document that clearly outlines the gear orientation requirements, including left-hand and right-hand designations. When sourcing left-hand gears, it’s essential to engage with reputable suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications and compatibility information. Utilizing 3D modeling software can also aid in visualizing how different gear configurations will fit within the existing machinery. Furthermore, conducting thorough compatibility tests before full-scale implementation can help identify potential issues early in the process.
Scenario 2: Increased Thrust Load Leading to System Overloads
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the increased thrust load associated with using left-hand gears, particularly in helical and bevel gear applications. This thrust load can lead to premature bearing failure and increased maintenance costs, causing disruptions in production schedules. Companies often underestimate the impact of thrust loads, resulting in inadequate thrust bearing selection or insufficient system support, which can compromise the entire gear assembly.
The Solution: To address the challenges posed by thrust loads, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application to understand the specific thrust forces generated by left-hand gears. This involves working closely with engineers to select appropriate thrust bearings that can accommodate these forces. Suppliers of left-hand gears should provide guidance on the necessary bearing types and load ratings. Additionally, investing in robust support structures and regular maintenance schedules can help mitigate the risks of overload and prolong the lifespan of the gear assembly.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Quality Left-Hand Gears in Global Markets
The Problem: Sourcing quality left-hand gears can be particularly challenging for international buyers, especially those operating in regions with varying manufacturing standards and quality control practices. Discrepancies in quality can lead to inconsistent performance, increased downtime, and ultimately, financial losses. B2B buyers may find it difficult to determine which suppliers can consistently deliver high-quality left-hand gears that meet their specific needs.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should conduct a thorough due diligence process when evaluating potential suppliers. This includes assessing the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality certifications, and customer reviews. Establishing long-term partnerships with manufacturers who specialize in left-hand gears can also provide a competitive edge. Furthermore, consider engaging in pilot projects or small-batch orders to evaluate quality before committing to larger purchases. Utilizing platforms that facilitate supplier comparisons based on quality metrics can also streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers make informed decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for left hand gear
What Are the Key Materials for Left Hand Gear in B2B Applications?
When selecting materials for left hand gear, it is essential to consider the specific properties that will affect performance, manufacturing, and application suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the production of left hand gears, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Left Hand Gear?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for high-load applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C and can withstand significant pressure, depending on the alloy used.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness and ability to handle heavy loads, which is crucial for gear applications. However, it can be prone to corrosion if not treated properly, which may necessitate additional coatings or treatments, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost.
Impact on Application: Steel gears are compatible with various media, including oils and lubricants, making them versatile for different environments. However, in corrosive environments, alternative materials may be more suitable.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial. Buyers from regions such as Europe or the Middle East should ensure that the steel grades meet local specifications.
What Advantages Do Aluminum Alloys Offer for Left Hand Gear?
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are lightweight and have excellent corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating typically around 150°C. They are also good at dissipating heat, which can enhance performance in high-speed applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum alloys makes them ideal for applications where weight savings are critical. However, they have lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit their use in high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gears work well in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in automotive or aerospace industries. They are generally compatible with various lubricants, but their lower strength may require careful application design.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 or DIN 1725. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality aluminum alloys can be a challenge, so verifying supplier credentials is essential.
How Do Plastic Composites Compare for Left Hand Gear Applications?
Key Properties: Plastic composites, such as nylon or polycarbonate, are known for their low weight and good chemical resistance. They can typically handle temperatures up to 100°C and are less likely to corrode than metal alternatives.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making them suitable for harsh environments. However, they generally have lower load-bearing capabilities compared to metals, which may limit their application in high-stress scenarios.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
Impact on Application: Plastic gears are often used in applications where noise reduction is a priority, such as in consumer electronics. Their compatibility with various chemicals makes them versatile, but they may not perform well under high loads.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 or ISO 527 is vital. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the materials meet specific performance criteria for their applications.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Left Hand Gear Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Bronze is known for its excellent wear resistance and low friction properties, making it suitable for gear applications. It can handle temperatures up to 300°C and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The wear resistance of bronze makes it ideal for high-friction applications, reducing the need for lubrication. However, it is generally more expensive than steel or aluminum, which can impact overall project costs.
Impact on Application: Bronze gears are particularly effective in marine applications due to their corrosion resistance in saltwater environments. They are also compatible with various lubricants, enhancing their performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B505 or DIN 1705 is essential. Buyers should also be aware of the higher costs associated with bronze, particularly in regions where sourcing may be limited.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Left Hand Gear
| Material | Typical Use Case for left hand gear | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-load mechanical applications | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum Alloys | Aerospace and automotive industries | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Consumer electronics and low-load applications | Corrosion resistant and low noise | Limited load-bearing capacity | Low |
| Bronze | Marine and high-friction applications | Excellent wear resistance | Higher cost | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used for left hand gears, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed decisions that align with specific application requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for left hand gear
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Left-Hand Gears?
The manufacturing process of left-hand gears, similar to other gear types, involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial in ensuring that the final product meets quality and performance standards.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for Left-Hand Gears?
The first step in manufacturing left-hand gears is selecting appropriate materials. Common materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, and specialized alloys like stainless steel, which provide strength and durability. For applications requiring high corrosion resistance, materials such as plastic or composites may also be utilized.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes treatment processes like annealing or hardening to enhance its mechanical properties. The preparation stage also involves cutting the material into appropriate shapes and sizes, often using advanced techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting to achieve precision.
How Are Left-Hand Gears Formed?
The forming stage includes several techniques, with machining being a predominant method. This involves processes like hobbing or shaping, where the gear teeth are created. For helical gears, including left-hand variants, the tooth profile is generated through a specialized hobbing process that ensures the correct helix angle.
In addition to hobbing, other forming techniques include forging and casting. Forging can produce stronger gears due to the alignment of the grain structure, while casting allows for more intricate designs. The choice of forming method often depends on the volume of production and specific application requirements.
What Does the Assembly Process for Left-Hand Gears Involve?
After the gears are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This involves integrating the left-hand gear with its mating components, such as right-hand gears or other mechanical parts, ensuring proper alignment and fit.
During assembly, it is crucial to use appropriate lubrication and consider thrust forces generated by the helical design. Careful attention to tolerances and fits during this stage minimizes wear and prolongs the lifespan of the gear.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used for Left-Hand Gears?
The finishing stage enhances the surface quality and prepares the gears for their operational environment. Common finishing techniques include grinding, polishing, and coating. Grinding is particularly important for achieving precise dimensions and surface finishes, reducing friction and wear during operation.
Coatings, such as anodizing or powder coating, may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction. This step is especially vital for gears used in harsh environments, which are common in industrial applications across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Left-Hand Gear Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that left-hand gears meet international and industry-specific standards. The implementation of QA begins with adherence to ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. This certification is particularly important for international buyers, as it provides assurance of consistent quality.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Are Relevant?
In addition to ISO 9001, other certifications such as CE marking and API standards may apply, depending on the application. For instance, gears used in oil and gas applications may require API certification, while those in the European market must meet CE standards for safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify any deviations or defects.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product, including dimensional checks and functional testing.
Common testing methods include non-destructive testing (NDT), dimensional inspections, and performance tests under simulated operational conditions. These tests help ensure that the gears can withstand the expected loads and environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Conducting audits is an effective way to assess a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and adherence to quality standards. During an audit, buyers can evaluate documentation, observe manufacturing practices, and review QC reports.
Illustrative image related to left hand gear
Requesting third-party inspection reports can provide additional assurance of product quality. Independent testing organizations can conduct inspections and provide certifications that validate the quality and compliance of the gears with relevant standards.
What Are the Nuances in QC/Certifications for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC and certifications is essential. Different regions may have varying regulations and expectations for gear manufacturing.
For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while Middle Eastern markets may have specific standards influenced by local regulations. Understanding these nuances ensures that buyers select suppliers who can meet the specific requirements of their market, facilitating smoother transactions and product acceptance.
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for left-hand gears are intricate and require a thorough understanding of materials, techniques, and standards. By engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance, B2B buyers can secure reliable components that meet their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘left hand gear’
To successfully procure left-hand gear, it is essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach that ensures the selection of high-quality products while minimizing risks. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps necessary for effective sourcing.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the left-hand gear you need. This includes understanding the specific type of gear (helical, bevel, or worm) and its application in your machinery or systems. Consider factors such as size, material, load capacity, and thrust requirements to ensure compatibility with your existing equipment.
- Key Considerations:
- Analyze the torque and speed requirements of your application.
- Determine any environmental factors that may affect gear performance, such as temperature or humidity.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in left-hand gear. Use industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors. Focus on those with a proven track record in your specific market.
- What to Look For:
- Supplier expertise in left-hand gear production.
- Reviews and testimonials from other B2B clients in your industry.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This evaluation should include assessing their production capabilities and quality assurance processes.
- Assessment Criteria:
- Certifications and compliance with international standards (ISO, etc.).
- Production capacity and lead times.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you narrow down your supplier options, request samples or prototypes of the left-hand gear. This step allows you to assess the quality, fit, and performance of the gear in real-world applications before making a bulk purchase.
- Why This Matters:
- Testing samples helps identify any potential issues early in the process.
- It provides insight into the supplier’s responsiveness and customer service.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and conditions for your procurement. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions. Clear agreements can help prevent misunderstandings later on.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be transparent about your budget and requirements.
- Consider long-term relationships for better pricing and terms.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Production
After agreeing on terms, finalize your order and maintain regular communication with the supplier during production. Monitoring the manufacturing process can help you ensure that quality standards are being met and that timelines are adhered to.
- Best Practices:
- Schedule regular updates and inspections, if possible.
- Establish a clear line of communication for addressing any issues that arise.
Step 7: Conduct Quality Assurance Upon Delivery
Upon receiving the left-hand gear, conduct a thorough quality assurance check to ensure that the products meet the specifications outlined in your initial order. Verify dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics before integrating them into your operations.
- Quality Check Checklist:
- Confirm that all items match the agreed specifications.
- Test the gear under operational conditions to verify performance.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes for left-hand gear, ensuring they select the right products from reputable suppliers while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for left hand gear Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Left-Hand Gears?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing left-hand gears, several components need to be considered:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials for left-hand gears include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys. The quality of these materials influences both the durability and performance of the gears. Buyers should request material certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. For instance, labor in regions with higher wages, such as Germany, will typically be more expensive than in parts of Africa or South America. Understanding local labor rates can help in evaluating total costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead and, consequently, the overall price of the gears.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for left-hand gears can be a significant upfront investment. The complexity and precision required for manufacturing can drive tooling costs higher. Companies should assess the impact of tooling on the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures is essential to ensure that the gears meet specifications. This process adds to the overall cost, but it can prevent expensive failures and returns in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can fluctuate based on distance and shipping methods. Incoterms also play a crucial role in determining who bears the transportation costs, which can further affect pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary widely among manufacturers, influenced by their market positioning and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Left-Hand Gears?
Several factors can influence the pricing of left-hand gears, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capabilities to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom gears designed to specific requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the potential for higher prices.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) justify higher prices but ensure better performance and reliability. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are essential for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes. Conducting due diligence on suppliers can mitigate risks and help in negotiating better prices.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects who pays for shipping and insurance. Understanding these terms can lead to more favorable pricing arrangements and clearer responsibilities during the transaction.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of Left-Hand Gears?
-
Negotiation: Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their needs and the market price range. Having multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with poor-quality gears.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Different regions have unique pricing dynamics. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic factors that can influence costs.
-
Request Quotes: Always obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers. This practice not only provides a clearer picture of the market but also allows for better comparison and negotiation.
-
Plan for Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers may offer discounts or priority service to repeat customers.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for left-hand gears can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing left hand gear With Other Solutions
In the realm of gearing solutions, particularly for industrial applications, selecting the right gear orientation can greatly influence performance and operational efficiency. While left-hand gears are a viable option, several alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or business needs. Below, we will explore how left-hand gears compare to two alternative solutions: right-hand gears and gear systems utilizing planetary gear mechanisms.
| Comparison Aspect | Left Hand Gear | Right Hand Gear | Planetary Gear System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for torque and noise reduction; requires pairing with right-hand gear for optimal use | Similar performance metrics as left-hand gears; must also be paired correctly | High torque density, compact design, and efficient power transmission |
| Cost | Generally comparable to right-hand gears | Similar cost structure; often interchangeable | Higher initial investment due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful pairing with right-hand gears; installation can be straightforward | Requires matching with left-hand gears for proper function; installation is similar | Installation can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and tools |
| Maintenance | Moderate; thrust loads require specific bearings | Similar maintenance requirements as left-hand gears | Typically lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts in some designs |
| Best Use Case | Applications requiring specific torque and noise considerations; ideal for parallel shaft configurations | Suitable for similar applications as left-hand gears; effective in standard gear setups | Best for applications needing compact designs and high torque; effective in automotive and aerospace sectors |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Right Hand Gears?
Right-hand gears are the most common alternative to left-hand gears. They exhibit similar performance characteristics, making them a reliable choice in many applications. The main advantage of right-hand gears is their widespread availability and compatibility with existing systems. However, they can require careful pairing with left-hand gears in applications where both orientations are needed, which may complicate inventory management and increase the chances of mismatched components.
How Do Planetary Gear Systems Compare?
Planetary gear systems present a more advanced alternative to traditional left-hand or right-hand gears. These systems consist of multiple gears arranged around a central sun gear, offering several advantages such as high torque capacity and compact design. The efficiency of power transmission is a significant benefit, allowing for more effective use of space and weight in applications like automotive and aerospace industries. However, the complexity of these systems can lead to higher initial costs and necessitate specialized installation and maintenance, which may not be feasible for all businesses.
Making the Right Choice: Which Gear Solution is Best for Your Needs?
When selecting between left-hand gears and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including application requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. If noise reduction and specific torque requirements are paramount, left-hand gears may be the best fit. Conversely, if ease of integration and widespread compatibility are more critical, right-hand gears could be the preferable option. For applications demanding high torque in compact spaces, investing in a planetary gear system may yield the best long-term benefits despite the initial costs. Ultimately, understanding the unique needs of your operations will guide you to the most effective gearing solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for left hand gear
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Left-Hand Gears?
1. Material Grade
Material selection is crucial for left-hand gears, as it directly impacts performance and durability. Common materials include steel, bronze, and plastic composites. Steel gears, often alloyed for enhanced strength, are preferred for high-load applications, while plastic gears may be used in lower-stress environments due to their lightweight and corrosion resistance. Understanding the appropriate material grade ensures that the gear can withstand operational demands and reduces the risk of premature failure.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a gear’s dimensions. For left-hand gears, maintaining precise tolerances is essential to ensure proper meshing with other gears. Standard tolerances are typically specified in terms of micrometers or thousandths of an inch. High precision is vital in applications requiring smooth operation and minimal backlash. Proper tolerancing reduces wear and tear, enhancing the overall longevity of the gear system.
3. Helix Angle
The helix angle determines the direction and angle at which the teeth are cut into the gear. For left-hand gears, this angle is critical for ensuring compatibility with right-hand counterparts in helical gear pairs. The standard helix angle can vary but is typically between 15 to 45 degrees. Correct helix angles allow for efficient torque transmission and contribute to quieter operation, making them essential in applications ranging from automotive to industrial machinery.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
4. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum load a gear can handle without failure. For left-hand gears, this is influenced by factors such as tooth design, material, and heat treatment. It is essential to match the load capacity with the specific application requirements to prevent gear failure, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs. Buyers should assess load ratings provided by manufacturers to ensure suitability for their specific use cases.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of left-hand gears affects friction, wear, and noise levels during operation. A smoother finish can lead to reduced friction and improved efficiency, while a rougher finish may increase wear and decrease lifespan. Surface treatments, such as hardening or coating, can also enhance durability. Choosing the right surface finish is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity in demanding applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Left-Hand Gear Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of left-hand gears, understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers sourcing components for assembly. OEMs often provide specialized products tailored to specific applications, ensuring compatibility and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For left-hand gears, MOQs can affect procurement strategies, especially for smaller companies or those with fluctuating demand. Understanding MOQs helps buyers effectively manage inventory and budget, ensuring they meet production needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific goods or services. When dealing with left-hand gears, issuing an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms. It is essential for comparing suppliers and ensuring that the selected gear meets both quality and cost requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms used in international shipping to define responsibilities between buyers and sellers. For left-hand gear suppliers, understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping costs, delivery timelines, and risk. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers make informed decisions regarding logistics and cost management.
5. Thrust Load
Thrust load refers to the axial force experienced by gears due to their operation, particularly in helical and bevel gears. For left-hand gears, understanding thrust loads is essential for selecting appropriate bearings and ensuring the stability of gear assemblies. Proper management of thrust loads prevents premature wear and enhances the reliability of mechanical systems.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing left-hand gears, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the left hand gear Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting Left Hand Gear Sourcing?
The global left hand gear market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, changing customer preferences, and regional market dynamics. Key trends include the increased adoption of automation and robotics, which necessitate precision engineering and innovative gear solutions. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand their manufacturing capabilities, the demand for left hand gears—particularly in applications requiring torque efficiency and noise reduction—continues to rise. Additionally, the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles in Europe and Asia is creating new opportunities for suppliers of left hand gears, as these vehicles often require specialized gearing systems for enhanced performance.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as predictive analytics and IoT integration, are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. These technologies enable manufacturers to optimize gear performance and maintenance schedules, thus reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency. International buyers should be aware of these advancements, as they can significantly influence procurement strategies. Collaboration with suppliers who leverage these technologies can provide a competitive edge in terms of cost efficiency and product reliability.
Furthermore, the globalization of supply chains presents both challenges and opportunities. Buyers must navigate varying regulations and quality standards across regions. Establishing relationships with local suppliers in target markets can mitigate risks associated with logistics and compliance, ensuring smoother operations.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into Left Hand Gear Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming an imperative in B2B sourcing, particularly in sectors like manufacturing where environmental impacts are significant. The left hand gear industry is no exception, as companies increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices. Sustainable sourcing involves selecting materials and suppliers that minimize environmental harm while promoting social responsibility.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, is on the rise among B2B buyers, who are keen to align their procurement strategies with corporate sustainability goals. Suppliers that utilize recyclable materials or employ energy-efficient manufacturing processes not only reduce their carbon footprint but also appeal to a growing base of environmentally-conscious clients.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are crucial for maintaining brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers should engage with suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices and adhere to fair labor standards. Conducting audits and requiring sustainability reports from suppliers can help ensure compliance with ethical practices. Ultimately, integrating sustainability into sourcing strategies not only addresses environmental concerns but also enhances competitive positioning in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
How Has the Left Hand Gear Industry Evolved Over Time?
The left hand gear sector has evolved significantly from its early mechanical origins to the highly specialized and technology-driven landscape we see today. Initially, gears were primarily used in simple machines, but advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of high-performance left hand gears suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
The introduction of helical gears, which provide smoother and quieter operation compared to traditional spur gears, marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of gearing technology. As industries demanded more efficient and reliable components, the focus shifted toward precision engineering and customization, allowing manufacturers to cater to specific application needs.
Today, the integration of digital technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation software, has further revolutionized the design and manufacturing processes. This evolution is critical for B2B buyers, as it underscores the importance of partnering with innovative suppliers who can offer advanced solutions tailored to the unique challenges of modern machinery and applications.
In summary, understanding market dynamics, prioritizing sustainability, and recognizing the historical context of left hand gears can significantly enhance sourcing strategies for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of left hand gear
-
1. How do I determine the correct orientation for left-hand gears?
To identify the correct orientation for left-hand gears, view the gear from the hub end through the bore. If the tooth trace follows a counterclockwise direction, it is designated as left-handed. It’s essential to ensure that when pairing helical gears, one must be left-handed and the other right-handed to achieve optimal torque and minimize noise. This orientation is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your machinery and ensuring efficient operation. -
2. What is the best type of left-hand gear for high-torque applications?
For high-torque applications, left-hand helical gears are often the best choice. They provide superior torque capacity and operate more quietly compared to spur gears of the same pitch and face width. The skewed tooth design allows for better load distribution, reducing wear and increasing the lifespan of the gear. When selecting a gear, consider the specific requirements of your application, including load capacity and noise levels. -
3. What are the key considerations when sourcing left-hand gears internationally?
When sourcing left-hand gears internationally, consider factors such as the supplier’s reputation, compliance with international quality standards, and production capabilities. It’s essential to verify certifications, request samples, and assess the supplier’s ability to meet your specifications. Additionally, factor in lead times, shipping logistics, and potential tariffs or duties that may apply, especially when importing from regions like Europe or Asia. -
4. How can I customize left-hand gears to fit my specific requirements?
Customization of left-hand gears can be achieved by discussing your specifications with the supplier during the initial inquiry. Most manufacturers can adjust parameters such as tooth design, material, and surface treatments based on your needs. Be prepared to provide detailed engineering drawings and discuss performance requirements. Keep in mind that custom orders may have higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) and longer lead times. -
5. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for left-hand gears?
Minimum order quantities for left-hand gears vary by manufacturer and specific gear type. Commonly, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the complexity of the design and the production process. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility regarding MOQs, especially if you’re a smaller business or testing a new product line. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard sizes or established products. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing left-hand gears?
Payment terms for sourcing left-hand gears typically include options such as upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. It’s common to negotiate terms based on order size and supplier policies. Ensure to discuss any potential risks, such as currency fluctuations or payment processing fees, especially when dealing with international transactions. Always secure a clear agreement in writing to avoid misunderstandings. -
7. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing left-hand gears?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing left-hand gears, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Implement a quality control plan that includes inspections at various production stages, and consider third-party inspections for critical components. Additionally, establish a clear return policy in case the gears do not meet specified standards. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the production process can also help mitigate quality issues. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing left-hand gears?
When importing left-hand gears, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including tariffs and duties that may apply. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process and ensure compliance with international shipping standards.
Top 4 Left Hand Gear Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gear Solutions – Helical, Bevel & Worm Gears
Domain: gearsolutions.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Left-hand and right-hand gears exist in helical, bevel, and worm gearing. Helical gears allow for more torque and lower noise compared to spur gears. The direction of hand is determined by viewing the gear from the hub end; counterclockwise indicates left-handed, and clockwise indicates right-handed. For helical gears on parallel shafts, one must be left-hand and the other right-hand. Screw gears,…
2. Lefty’s – Gifts & Kitchen Essentials for Left-Handers
Domain: leftyslefthanded.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Lefty’s the Left Hand Store offers a wide range of products specifically designed for left-handers, including:
1. **Gifts & Sets**: Top 20 gifts, gift certificates, and various gift sets for left-handed individuals, including kids and chefs.
2. **Kitchen Items**: Left-handed can openers, peelers, corkscrews, scoops, knives for preparation and cooking, measuring tools, BBQ mitts, and miscellaneous…
3. Maedler – Helical Spur Gears
Domain: maedlernorthamerica.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Spur Gears, Steel, Helical Tooth Right and Left Hand, Module 1
4. Tanhon – Right Hand Helical Gear
Domain: tanhon.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Right Hand Helical Gear: Cylindrical gear with teeth angled and twisted in a right-handed direction, allowing for smoother, quieter operation. Commonly used in high speed, high power transmission applications. Helix angle ranges from 15 to 45 degrees, with greater angles providing smoother operation and increased load capacity. Produces axial thrust load in opposite directions when meshed with ano…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for left hand gear
In the realm of left-hand gear sourcing, a strategic approach is paramount for international buyers navigating diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances of left-hand gear—such as its applications in helical, bevel, and worm gearing—is crucial for optimizing design and performance. Buyers must prioritize compatibility and thrust load considerations when integrating left-hand gears into their systems, ensuring that they select appropriate thrust bearings to enhance operational efficiency.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond mere procurement; it fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide quality left-hand gears tailored to specific applications. By engaging with manufacturers that emphasize innovation and quality control, businesses can gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage technological advancements and supplier networks to streamline sourcing processes. As market demands evolve, the proactive adaptation of sourcing strategies will be essential for success. Explore new partnerships and invest in research to stay ahead of the curve, ensuring your organization is equipped with the best solutions in left-hand gear technology.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to left hand gear
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.