How to Source Industrial Powder Blender Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial powder blender
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right industrial powder blender can present a formidable challenge for B2B buyers. With diverse applications spanning industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemicals, the complexity of selecting a suitable blending solution is compounded by varying powder characteristics and production requirements. This guide aims to demystify the intricacies of the industrial powder blender market, providing insights into the different types of mixers available, their specific applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Vietnam and Germany—will find this resource invaluable. It empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions by outlining critical factors such as cost analysis, hygiene standards, and customization options. By navigating through comprehensive sections on technology innovations, best practices for blending, and case studies from various industries, readers will gain the knowledge necessary to optimize their operations and enhance product quality.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a strategic tool for B2B buyers to streamline their sourcing processes, ensuring they select the most efficient and effective industrial powder blending solutions tailored to their unique needs.
Understanding industrial powder blender Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ribbon Mixer | Uses a helical ribbon to move material; efficient for bulk blending | Food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals | Pros: Cost-effective, simple design; Cons: Less effective for fine powders. |
| Paddle Mixer | Features flat blades for mixing; suitable for viscous materials | Plastics, food, and chemical industries | Pros: Versatile for different materials; Cons: May require longer mixing times. |
| Plow Mixer | Incorporates plow-shaped blades to lift and fold materials; high shear mixing | Food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical sectors | Pros: Excellent for agglomeration; Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Conical Mixer | Cone-shaped design allows for gentle blending; minimizes segregation | Pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals | Pros: High blend uniformity; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
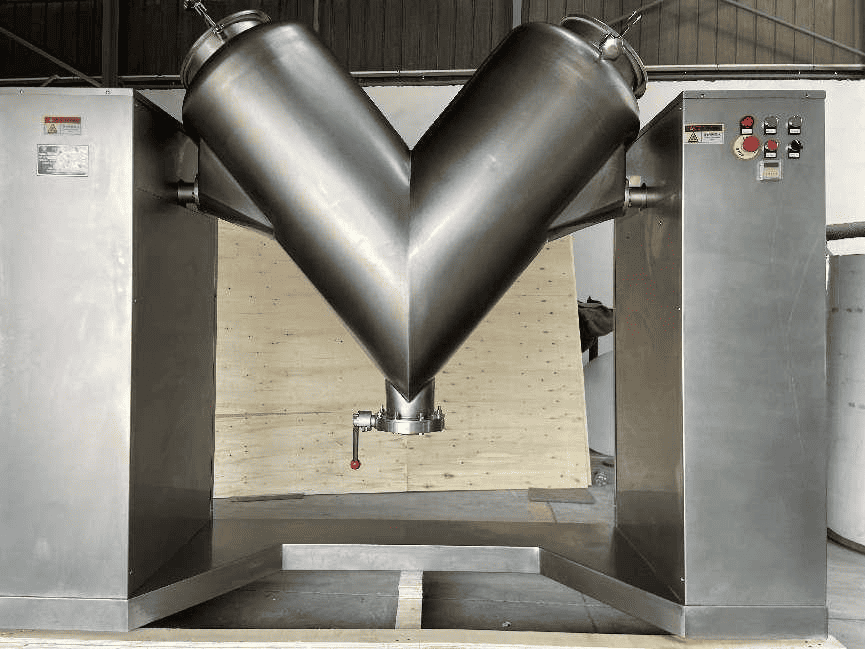
| V-Blender | Features a V-shaped chamber for efficient mixing of powders; ideal for dry powders | Nutraceuticals, food, and chemicals | Pros: Minimal cross-contamination; Cons: Limited capacity for larger batches. |
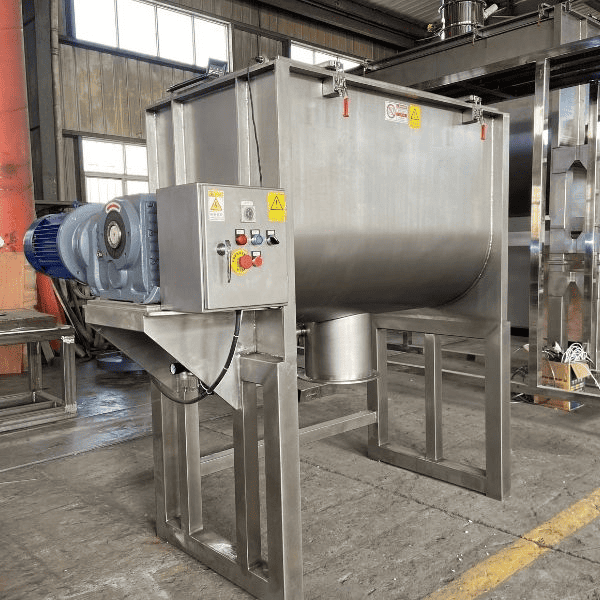
What are the Characteristics of Ribbon Mixers?
Ribbon mixers are designed with a helical ribbon that moves materials in a continuous flow, ensuring a thorough blend of bulk powders. They are particularly effective in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, where large volumes of ingredients need to be mixed uniformly. When considering a ribbon mixer, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific particle characteristics of the powders being mixed, as this type may not perform optimally with fine or sticky powders. Additionally, the simplicity of the design allows for easier maintenance, making it a cost-effective option for many businesses.
How Do Paddle Mixers Differ from Other Types?
Paddle mixers utilize flat blades that mix materials in a gentle folding motion, making them suitable for both dry and wet ingredients, particularly in the plastics and food industries. Their versatility allows them to handle a range of material viscosities, but buyers should be aware that mixing times may be longer compared to other mixer types. When purchasing, consider the mixer’s capacity and the nature of the materials involved, as these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency.
Why Choose a Plow Mixer for Your Operations?
Plow mixers are equipped with plow-shaped blades that agitate and fold materials, making them ideal for applications requiring high shear mixing, such as in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. Their design allows for effective agglomeration, which can enhance product consistency. However, B2B buyers should note that these mixers typically consume more energy and may not be the best choice for lighter powders. Evaluating the energy costs versus the benefits of improved product quality will be crucial in the purchasing decision.
Illustrative image related to industrial powder blender
What Benefits Do Conical Mixers Offer?
Conical mixers feature a cone-shaped design that promotes gentle blending, reducing the risk of segregation and ensuring high uniformity in the final product. They are commonly used in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical applications where precision is paramount. While they deliver excellent mixing performance, the initial investment can be higher than other types. Buyers should assess their production requirements and budget to determine if the enhanced blending capabilities justify the cost.
How Do V-Blenders Minimize Contamination Risks?
V-blenders utilize a V-shaped chamber to efficiently mix dry powders while minimizing the risk of cross-contamination. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries such as nutraceuticals and food, where product purity is essential. However, their capacity may be limited for larger batch sizes, which could impact production throughput. Buyers should weigh the benefits of contamination control against the potential need for multiple units to meet volume demands, ensuring that their investment aligns with production goals.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial powder blender
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial powder blender | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Mixing of dry ingredients for baked goods and snacks | Ensures consistent product quality and flavor | Compliance with food safety standards and hygienic design |
| Pharmaceuticals | Homogenizing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Enhances bioavailability and efficacy of drugs | Precision in blending to avoid segregation and contamination |
| Chemical Processing | Creating uniform mixtures of polymers and additives | Improves product performance and stability | Equipment compatibility with various chemical properties |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care | Formulating powders for makeup and skincare products | Guarantees consistent texture and application | Consideration of ingredient sensitivity and regulatory compliance |
| Agriculture and Animal Feed | Blending feed ingredients for livestock nutrition | Optimizes nutrient delivery and feed efficiency | Ability to handle bulk materials and ensure uniformity |
How is Industrial Powder Blender Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, industrial powder blenders are essential for mixing dry ingredients such as flour, sugar, and spices for baked goods and snacks. These blenders ensure that the ingredients are uniformly distributed, which is crucial for maintaining consistent flavor and quality across batches. Buyers should prioritize equipment that meets food safety standards and offers hygienic designs to prevent contamination during the blending process.
What Role Does Industrial Powder Blender Play in Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceuticals, industrial powder blenders are used to homogenize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with excipients, ensuring that the final product is effective and safe for consumption. This blending process enhances the bioavailability of drugs, directly impacting their efficacy. Buyers should focus on precision blending capabilities to avoid segregation and contamination, as well as compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
How is Industrial Powder Blender Beneficial in Chemical Processing?
The chemical processing industry relies on industrial powder blenders to create uniform mixtures of polymers, additives, and other chemical components. These blenders help improve the performance and stability of the final products, which is vital for maintaining competitive advantage. When sourcing blenders, businesses must consider the compatibility of the equipment with various chemical properties to ensure safe and efficient processing.
How is Industrial Powder Blender Used in Cosmetics and Personal Care?
In the cosmetics and personal care sector, industrial powder blenders are critical for formulating powders used in makeup and skincare products. These blenders ensure a consistent texture and application, which is essential for customer satisfaction. Buyers should consider equipment that can handle sensitive ingredients and comply with cosmetic regulations to avoid any adverse reactions.
What is the Importance of Industrial Powder Blender in Agriculture and Animal Feed?
In agriculture, industrial powder blenders are employed to blend feed ingredients for livestock, ensuring optimal nutrient delivery and feed efficiency. This application is crucial for improving the health and productivity of animals. Buyers should look for blenders capable of handling bulk materials while maintaining uniformity in the final feed products, which is vital for achieving desired nutritional outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial powder blender’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Mixing Leading to Product Inconsistency
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of ensuring product consistency across batches when using industrial powder blenders. Variability in powder characteristics, such as particle size and moisture content, can lead to uneven mixing. This inconsistency not only affects product quality but also damages brand reputation, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals where strict compliance with quality standards is mandatory. Furthermore, inadequate mixing techniques may require additional time and resources for rework, leading to increased operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should consider investing in advanced mixing technologies that cater to specific powder characteristics. For instance, employing blenders with adjustable settings can allow for tailored mixing processes, accommodating various powder types—from fine to coarse. Buyers should consult with manufacturers to understand the capabilities of different models, such as ribbon mixers for bulk solids or high-shear mixers for powders that require intensive blending. Additionally, implementing a quality control system that includes regular testing of mixed batches can help identify inconsistencies early in the production cycle, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
Scenario 2: Downtime Due to Cleaning and Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant downtime associated with cleaning and maintaining industrial powder blenders. In industries with stringent hygiene standards, such as food production and pharmaceuticals, the need for frequent cleaning can disrupt production schedules. Moreover, traditional cleaning methods may not adequately prevent cross-contamination, leading to potential recalls and compliance issues. This can be particularly problematic in facilities that operate under tight deadlines and require a quick turnaround between different product batches.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should explore blenders designed for easy clean-in-place (CIP) operations. Equipment that utilizes hygienic designs, such as stainless steel construction and accessible mixing chambers, can significantly reduce cleaning times and enhance safety. Additionally, investing in IBC (Intermediate Bulk Container) blenders allows for seamless switching between batches without the need for extensive cleaning, as each batch is contained within its own vessel. Implementing a scheduled maintenance plan that includes regular inspections can also help preempt issues before they lead to costly downtime.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Blender for Specific Applications
The Problem: The diversity of available industrial powder blenders can overwhelm buyers, making it challenging to select the right equipment for their specific applications. With numerous options—ranging from paddle mixers to vacuum dryers—buyers may struggle to identify which type best suits their production needs. This confusion can lead to misallocation of resources, purchasing equipment that doesn’t meet their operational requirements, and ultimately, poor return on investment.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage in a thorough needs assessment before making a purchase. This process should include a detailed analysis of the powders being processed, including their flow properties and any unique handling requirements. Collaborating with experienced suppliers who offer consultation services can provide valuable insights into the most suitable blending technologies. Additionally, utilizing pilot plants or testing facilities that allow for real-world trials of different mixers can help buyers make informed decisions based on practical outcomes rather than theoretical specifications. By investing time in this evaluation process, buyers can ensure they choose a blender that aligns with their production goals, leading to enhanced efficiency and profitability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial powder blender
When selecting materials for industrial powder blenders, it is crucial to consider the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This analysis focuses on four common materials used in the construction of industrial powder blenders: stainless steel, carbon steel, plastic, and ceramic. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact performance, durability, and compliance with international standards.
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in Industrial Powder Blenders?
Stainless steel is widely regarded for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. It typically comes with a temperature rating of up to 500°C and can handle pressures of up to 10 bar, making it suitable for various applications, including food and pharmaceutical industries.

Illustrative image related to industrial powder blender
Pros: Its durability ensures a long lifespan, while its non-reactive nature prevents contamination of sensitive materials. Stainless steel also meets stringent hygiene standards, which is essential for compliance in many industries.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other materials, which may be a concern for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, makes it a preferred choice in industries requiring high hygiene standards.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare as a Material for Industrial Powder Blenders?
Carbon steel is another common material used in industrial powder blenders. It offers good strength and is generally more cost-effective than stainless steel. It can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, typically up to 300°C and 5 bar, respectively.
Pros: Its affordability makes it attractive for manufacturers looking to optimize costs. Carbon steel is also relatively easy to fabricate, allowing for quick production and customization.
Cons: However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion and may require protective coatings, which can add to maintenance costs. It is less suitable for applications involving moisture or corrosive powders.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is best suited for dry powders or non-corrosive materials, making it a viable option for industries like construction or bulk material handling.
What are the Advantages of Using Plastic in Industrial Powder Blenders?
Plastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are increasingly being used in industrial powder blenders, particularly for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant options. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 100°C and pressures of around 2 bar.
Pros: The main advantages of plastic include its low weight, resistance to corrosion, and lower manufacturing costs. Additionally, plastics can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility.
Cons: However, plastics have lower strength and temperature resistance compared to metals, which may limit their use in high-stress applications. They can also be susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic blenders are ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications where hygiene is a priority, but they may not be suitable for heavy-duty industrial uses.
Why Choose Ceramic for Industrial Powder Blenders?
Ceramic materials are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. They can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,600°C) and are chemically inert, making them suitable for highly abrasive or corrosive powders.
Pros: The primary advantage of ceramics is their durability and ability to maintain performance in extreme conditions. They are also non-reactive, ensuring product purity.
Cons: The main limitation is their brittleness, which makes them prone to cracking under mechanical stress. Additionally, ceramics can be costly and complex to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are ideal for specialized applications in industries such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals, where abrasive materials are common.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Powder Blenders
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial powder blender | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction and bulk material handling | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Prone to corrosion, requires coatings | Medium |
| Plastic | Food and pharmaceutical applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength and temperature limits | Low |
| Ceramic | Chemical and pharmaceutical industries | Exceptional hardness and chemical inertness | Brittle and costly to manufacture | High |
In conclusion, the choice of material for industrial powder blenders should be guided by the specific application requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with regional standards. Understanding the properties and limitations of each material can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial powder blender
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Industrial Powder Blenders?
The manufacturing process of industrial powder blenders is a multi-stage operation that requires precision and attention to detail. Each stage contributes significantly to the final product’s performance and quality.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing materials, which typically include various grades of stainless steel, motors, and electronic components. Suppliers should be vetted based on their ability to provide high-quality materials that meet industry standards. In many cases, materials undergo testing for chemical composition and mechanical properties to ensure they meet the necessary specifications for durability and safety.

Illustrative image related to industrial powder blender
Forming Techniques
After preparation, the next step is forming the components. This can involve several techniques, including:
- CNC Machining: This precision method is crucial for creating parts with tight tolerances, such as mixing blades and housing.
- Welding: High-quality welding techniques are employed to join metal parts, ensuring structural integrity.
- Casting or Forging: Some components may be cast or forged, depending on their design and the required mechanical properties.
Each technique has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the specific requirements of the blender design.
Assembly Processes
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage typically involves:
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller components are first assembled into sub-units, which can then be integrated into the main unit.
- Main Assembly Line: Skilled technicians or automated systems put together the main body of the blender, ensuring all parts fit correctly and function as intended.
Quality checks are integrated into the assembly process, focusing on alignment, fitting, and function.
Finishing Touches
The final stage involves finishing processes such as surface treatment, painting, and polishing. These not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve resistance to corrosion and wear. Additional testing may be performed at this stage to verify that the surface finishes meet industry-specific standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Powder Blenders?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that industrial powder blenders meet both safety and performance standards. Various international and industry-specific certifications play a vital role in this process.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the relevant quality standards is essential. The most notable include:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that manufacturers have a quality management system in place that consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for pharmaceutical applications, API standards ensure that the blenders meet stringent criteria for safety and efficacy.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring during the manufacturing process to ensure components are being produced within specified tolerances.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to confirm it meets all specifications before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance for industrial powder blenders often includes several testing methods:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that the blender operates according to design specifications, including mixing efficiency and operational speed.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates the blender’s performance under various load conditions, ensuring it can handle the intended production volume.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the longevity of the materials and components, often involving stress tests and wear simulations.
These testing methods help ensure that the blenders are reliable and effective in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is critical. Here are actionable steps to take:
- Request Documentation: Ask for quality management certifications, test reports, and compliance documents. This documentation can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Conduct Audits: Arrange for on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This firsthand observation can reveal much about the supplier’s operations.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices, ensuring compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing from different regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Understanding these can help avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Quality perceptions can vary based on regional practices. Engaging local experts can bridge these gaps.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Be aware of potential supply chain disruptions that can affect quality. Establishing a robust logistics plan can mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance is essential for B2B buyers in sourcing industrial powder blenders. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside a robust quality assurance framework, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial powder blender’
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, sourcing an industrial powder blender requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of selecting the right equipment for your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your powder blending process. This includes understanding the types of powders you will be blending, their characteristics (e.g., flowability, particle size), and the desired blend uniformity. Having specific technical specifications helps ensure that the equipment you select can efficiently handle your unique materials and processes.
Step 2: Assess Production Capacity Needs
Determine the production volume you expect from your blending operations. Consider both the batch sizes and the frequency of production. This step is critical to ensure that the chosen blender can meet your output demands without compromising quality or efficiency.
- Batch vs. Continuous Production: Decide if you require a batch or continuous mixing system based on your production flow.
- Scalability: Ensure the equipment can scale with your business growth.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Expertise and Reputation
Investigate potential suppliers to gauge their expertise in the industry and the reliability of their products. Look for companies with a proven track record and positive customer testimonials, particularly from businesses in similar sectors or regions.
- Request Case Studies: Ask for examples of successful implementations that align with your needs.
- Check Certifications: Ensure they meet relevant industry standards and regulations, especially in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals.
Step 4: Examine Equipment Features and Technology
Analyze the specific features of the powder blenders being offered. Modern blenders often come equipped with advanced technologies that enhance blending efficiency and product quality.
- Mixing Techniques: Consider if the blender uses ribbon, paddle, or plow mixing techniques, and how these align with your powder characteristics.
- Hygiene Standards: For industries requiring strict hygiene, look for features such as easy cleaning protocols and food-grade materials.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before making a purchase, it is prudent to request demonstrations or trials of the equipment. This allows you to observe the blending process firsthand and evaluate the machine’s performance with your specific materials.
- Testing Facilities: Some suppliers may offer the opportunity to test your powders in their facilities, providing valuable insights into how the machine handles your specific requirements.
Step 6: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Evaluate the total cost of ownership beyond the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance costs, energy consumption, and the potential need for future upgrades or modifications.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure the supplier provides robust support and warranty terms that cover both the equipment and ongoing service needs.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for blenders that offer lower energy consumption to reduce long-term operational costs.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract with Clear Terms
Once you have selected a supplier and equipment, ensure that the contract outlines all terms clearly. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, installation support, and service agreements.
- Negotiate Terms: Be clear about your expectations to avoid misunderstandings later on.
- Review Terms for Compliance: Ensure that all equipment meets the necessary compliance standards for your industry.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial powder blenders, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial powder blender Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Powder Blender Manufacturing?
When sourcing industrial powder blenders, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly influences the cost. High-quality stainless steel and specialized alloys may incur higher expenses but enhance durability and hygiene, critical for food and pharmaceutical applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary by region, with skilled labor often more expensive in developed countries. In contrast, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs may reduce overall expenses but could introduce challenges in quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can mitigate these costs, making it essential for buyers to assess the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for unique blender designs can add to initial costs. However, investing in the right tooling can enhance product quality and reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Quality Control: Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the blenders meet industry standards, which can increase upfront costs but reduce the risk of defects and recalls.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must be factored into the total cost, especially for international shipments. Tariffs, customs duties, and delivery times can all impact the final pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure business sustainability. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Industrial Powder Blender Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of industrial powder blenders, making it crucial for buyers to navigate these effectively.
-
Volume/MOQ: The Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) significantly affects pricing. Larger orders often come with volume discounts, making it advantageous for companies with high production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized blenders designed for specific applications will generally cost more than standard models. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and required certifications (e.g., FDA, CE) can substantially impact prices. Buyers should ensure that the materials used meet the necessary quality standards relevant to their industry.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and financial stability can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate who bears shipping costs and risks. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Industrial Powder Blender Prices?
Negotiating the best price for industrial powder blenders requires strategic planning and understanding of market dynamics.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on upfront costs, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. This approach often reveals that higher initial investments can lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough market research to compare suppliers not just on price but on the value they provide, including quality, service, and reliability.
-
Negotiate Terms: Be prepared to negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties. Flexible terms can lead to cost savings and better cash flow management.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local economic conditions can affect pricing. Factor these elements into your budget.
-
Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: Obtain quotes from several manufacturers to identify competitive pricing and assess the range of offerings available in the market.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for industrial powder blenders can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. This analysis serves as a guide for B2B buyers, and it is advisable to seek tailored quotes from suppliers to obtain the most accurate and relevant pricing information for specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial powder blender With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Industrial Powder Blenders
In the quest for efficient powder mixing solutions, industrial powder blenders are a popular choice among manufacturers. However, other alternatives may also meet specific production needs effectively. This section evaluates industrial powder blenders against two viable alternatives: Tumble Blenders and Continuous Mixers. Understanding the differences in performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases will aid B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Powder Blender | Tumble Blender | Continuous Mixer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and uniformity in blends; suitable for various powder characteristics. | Gentle mixing; ideal for fragile powders but may lack consistency with heavier materials. | Excellent for large volumes; maintains constant flow, reducing mixing time. |
| Cost | Typically higher initial investment but offers long-term efficiency gains. | Generally lower cost; limited to specific applications. | Moderate to high cost; justifiable for high-output operations. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful setup and calibration; may need operator training. | Simple setup; user-friendly operation. | Complex installation; may require integration with existing processes. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; cleaning can be time-consuming depending on design. | Minimal maintenance; easier to clean, especially with batch operations. | Requires consistent upkeep; potential downtime for cleaning and maintenance. |
| Best Use Case | Versatile applications across food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. | Best for delicate powders in batch processes like food or nutraceuticals. | Ideal for large-scale operations requiring continuous production, such as in bulk chemicals or plastics. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Tumble Blenders
Tumble blenders are designed for gentle mixing of powders, making them suitable for fragile materials. They operate by rotating a cylindrical drum, allowing the contents to tumble and mix without excessive force. The primary advantage of tumble blenders is their simplicity and lower cost compared to more complex systems. However, they may not provide the consistency needed for heavier or more cohesive powders, making them less versatile than industrial powder blenders.
Continuous Mixers
Continuous mixers are engineered for high-volume production, allowing for a steady flow of materials through the mixing chamber. This technology is particularly beneficial for industries where large quantities of product need to be mixed efficiently, such as in bulk chemicals or food manufacturing. While continuous mixers can reduce overall production time and increase throughput, their initial setup can be complex and costly. Additionally, they may require integration with other systems, which could lead to higher maintenance demands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Production Needs
When selecting the appropriate mixing solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific production requirements, including the nature of the powders, desired output, and operational constraints. Industrial powder blenders offer versatility and precision, making them ideal for diverse applications. In contrast, tumble blenders provide a cost-effective solution for delicate materials, while continuous mixers excel in high-output scenarios. Evaluating these factors will help manufacturers choose the best blending technology to enhance their production efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial powder blender
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Industrial Powder Blenders?
When selecting an industrial powder blender, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring it meets your production needs. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material of construction, often stainless steel, is critical for durability and hygiene. Stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 are common, with 316 offering better corrosion resistance, which is vital in food and pharmaceutical applications. Selecting the right grade ensures longevity and compliance with industry standards. -
Mixing Capacity
The blending capacity, usually measured in liters or cubic meters, indicates the volume of powder that can be processed in one batch. This specification is essential for aligning the blender’s output with your production requirements, allowing for efficient scaling of operations without compromising quality. -
Mixing Speed and Time
This specification refers to the RPM (revolutions per minute) and the duration of mixing. Different materials require varying speeds for optimal blending. Understanding the required mixing time helps in planning production schedules and ensuring consistent product quality. -
Discharge Efficiency
Discharge efficiency is the percentage of material that can be effectively removed from the blender after mixing. High discharge efficiency minimizes waste and reduces cleaning time, which is critical for maintaining productivity in high-volume operations. -
Hygiene Standards
Compliance with hygiene standards, such as FDA or GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), is crucial, especially in food and pharmaceutical industries. Equipment designed for easy cleaning and minimizing contamination risks is essential for maintaining product integrity and safety. -
Power Consumption
The energy efficiency of the blender can significantly impact operating costs. Understanding the power requirements and selecting energy-efficient models can lead to substantial savings in long-term operational expenses.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Industrial Powder Blender Market?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of industrial powder blenders, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess product quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for budget planning and inventory management, especially for businesses looking to scale their production. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. Crafting a detailed RFQ helps buyers receive accurate quotes and compare different suppliers effectively, ensuring the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, covering aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps in understanding shipping costs and liabilities, which is crucial for budgeting and risk management. -
CIP (Cleaning in Place)
CIP refers to a method of cleaning equipment without disassembly. Understanding CIP capabilities is essential for industries where hygiene is paramount, as it ensures that production can resume quickly without compromising cleanliness. -
Batch vs. Continuous Mixing
This terminology differentiates between two mixing processes. Batch mixing processes handle fixed quantities of material, while continuous mixing allows for ongoing production without interruption. Knowing the differences helps businesses choose the right mixing system based on their production needs.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make informed decisions when selecting an industrial powder blender, ensuring it aligns with your operational goals and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial powder blender Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Industrial Powder Blenders?
The industrial powder blender market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient and versatile mixing solutions across various sectors, including food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Globalization and the rise of e-commerce have amplified competition, prompting manufacturers to invest in advanced blending technologies to enhance product quality and reduce operational costs. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a noticeable shift toward automation and the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI. These innovations facilitate real-time monitoring and control of blending processes, ensuring consistency and quality in production.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of customization in blending equipment. As businesses seek to differentiate their products, demand for tailored powder mixing solutions that accommodate specific powder characteristics—such as particle size and flow properties—has surged. The rise of sustainable practices is another key driver, with manufacturers increasingly focusing on energy-efficient and environmentally friendly blending technologies. Additionally, the ongoing supply chain disruptions have prompted international buyers to seek reliable and flexible sourcing strategies, fostering the need for strong partnerships with equipment manufacturers who can offer both quality and support.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Industrial Powder Blenders?
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration in the sourcing of industrial powder blenders. Environmental impact assessments are now a standard part of the procurement process, as companies aim to minimize their carbon footprints and comply with stricter regulations. Buyers are increasingly looking for equipment that is not only energy-efficient but also constructed from recyclable or sustainably sourced materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to green building standards are becoming essential benchmarks for evaluating suppliers.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, with businesses prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate responsible labor practices and supply chain transparency. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical concerns can significantly influence purchasing decisions. By opting for suppliers with a commitment to sustainable practices and ethical sourcing, companies can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Adopting ‘green’ certifications can also serve as a competitive advantage in the marketplace, positioning businesses as leaders in sustainability within their respective industries.
What Is the Evolution of Industrial Powder Blending Technology?
The evolution of industrial powder blending technology dates back to the early 20th century when basic mechanical mixers were used for simple blending tasks. As industries expanded and the complexity of products increased, the need for more sophisticated blending solutions became apparent. The introduction of powered mixers in the mid-20th century marked a significant advancement, allowing for greater efficiency and consistency in mixing processes.
Illustrative image related to industrial powder blender
In recent decades, innovations such as the development of high-shear mixers and IBC (Intermediate Bulk Container) blending systems have transformed the landscape. These technologies enable manufacturers to achieve precise blending results while minimizing contamination risks and reducing cleaning times between batches. The advent of smart blending technologies, which incorporate sensors and automation, has further revolutionized the industry by providing real-time data analytics and process optimization. This ongoing evolution reflects the industry’s response to growing demands for efficiency, customization, and sustainability, shaping the future of powder blending equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial powder blender
-
How do I solve mixing inconsistencies in my powder blending process?
To address mixing inconsistencies, first assess the characteristics of the powders being blended, such as particle size, flowability, and moisture content. Choose an appropriate mixer type—like a ribbon or paddle mixer—based on your specific needs. Implement regular maintenance and calibration of your equipment to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, consider conducting pilot tests to refine your mixing parameters and validate the results before full-scale production. -
What is the best industrial powder blender for my specific application?
The best industrial powder blender depends on your unique requirements, including the types of powders, batch sizes, and desired mixing outcomes. For fragile powders, a tumble blender may be ideal, while high-shear mixers work well for more vigorous blending. Consult with manufacturers to evaluate your production needs, and consider trialing different models to determine which offers the best efficiency and consistency for your application. -
What should I consider when sourcing an industrial powder blender internationally?
When sourcing internationally, evaluate potential suppliers based on their experience, certifications, and the quality of their products. Ensure they have a robust supply chain and can provide support in your region. Additionally, investigate their compliance with international safety and quality standards relevant to your industry. Establish clear communication regarding delivery timelines, warranty terms, and after-sales support to avoid potential issues. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for industrial powder blenders?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for customized solutions, while others may require larger orders for standard models. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and explore options for trial orders or samples, especially if you are unsure about committing to a larger purchase initially. -
How can I ensure the quality of the powder blender I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications, certifications, and performance data from the supplier. Look for manufacturers that offer warranties and after-sales service, as this can indicate confidence in their products. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or request a demonstration of the blender. Engaging in third-party quality assurance assessments can also provide added assurance regarding the equipment’s reliability and efficiency. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing an industrial powder blender?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, often influenced by the order size and the buyer’s relationship with the manufacturer. Common practices include upfront deposits (20-50%), with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms in advance and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations are important for importing industrial powder blenders?
When importing, factor in shipping costs, customs duties, and potential delays in transit. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial equipment to ensure safe and timely delivery. Prepare all necessary documentation, including import permits and compliance certifications, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, consider the local infrastructure and delivery capabilities to ensure that the blender can be efficiently installed and integrated into your production line. -
How can I customize my industrial powder blender to fit my specific production needs?
Customization options for industrial powder blenders often include adjustments to size, mixing speed, and specific features like vacuum capabilities or high-shear mixing. Engage with manufacturers early in the design process to discuss your requirements, including the types of materials you will be blending and any industry-specific regulations you must adhere to. Many suppliers offer pilot testing to help validate custom solutions before full-scale production.
Top 5 Industrial Powder Blender Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PerMix – Industrial Powder Mixers
Domain: permixmixers.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: PerMix Powder Mixers include a variety of industrial mixers and mills such as: PerMix Ribbon Mixer, PerMix Paddle Mixer, PerMix Plow Mixer, PerMix Vacuum Mixer & Dryer, PerMix Fluidized Zone Mixer, PerMix High Speed Granulator Mixer, PerMix Conical Mixer, PerMix V-Blender Mixer, PerMix Double Cone Mixer, PerMix 3D Mixer, PerMix Drum Mixer, and PerMix Vertical Paddle Mixer. Additionally, they offer…
2. Matcon – IBC Blenders & Powder Mixers
Domain: matconibc.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Efficient, effective, flexible IBC Blenders & Industrial Powder Mixers. In-bin blending for flexibility and agility, no need for clean down between batches. Tumble blending for gentle mixing of fragile powders, with high shear mixing option available. Matcon Blending Range includes IBC Blender & NIR for mixing efficiencies, Pilot Scale Blender for testing & small volumes, Blending With High Shear …
3. Hosokawa Micron – Industrial Powder Mixers
Domain: hosokawa-micron-bv.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Industrial Powder Mixers from Hosokawa Micron include a range of technologies designed for efficient mixing of powders and bulk solids. Key products include: Nauta® Conical Screw Mixers for gentle, low-shear mixing; Ribbon Screw Blenders for cohesive and free-flowing powders; Paddle Mixers for mid- to high-shear blending; Continuous Mixers for fast, consistent blending in continuous operations. Th…
4. Palamatic Process – Industrial Mixers and Blenders
Domain: palamaticprocess.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Industrial mixers and blenders designed for uniform and efficient mixing across various sectors. Key products include: 1. Monorotor batch belt mixer 2. Biorotor batch pellet mixer 3. Vertical mixer – ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications with hygienic design 4. Sanitary ribbon blenders 5. Plow and blade mixers – offer fast batch mixing and consistent reproducibility. Features include: – C…
5. TOTE® – Dry Powder Blender
Domain: totesystems.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, TOTE® – Dry Powder Blender, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial powder blender
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial powder blending, strategic sourcing is paramount for B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By investing in the right blending technologies—such as IBC blenders, ribbon mixers, and high-shear systems—companies can significantly improve their mixing processes, reduce downtime, and minimize cross-contamination risks. Understanding the unique characteristics of your powders and production requirements is essential in selecting the most suitable equipment, which can lead to increased productivity and cost savings.
As international markets become increasingly interconnected, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-quality industrial powder blenders can provide a competitive edge. Collaborating with trusted suppliers who offer customization options and robust testing facilities can help ensure that your blending equipment meets stringent industry standards while accommodating varying batch sizes and formulations.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and efficient blending solutions will continue to grow. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in the powder blending sector. Engaging with industry experts and leveraging comprehensive sourcing strategies will be key to optimizing your blending operations and driving long-term success in your markets.

Illustrative image related to industrial powder blender
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.