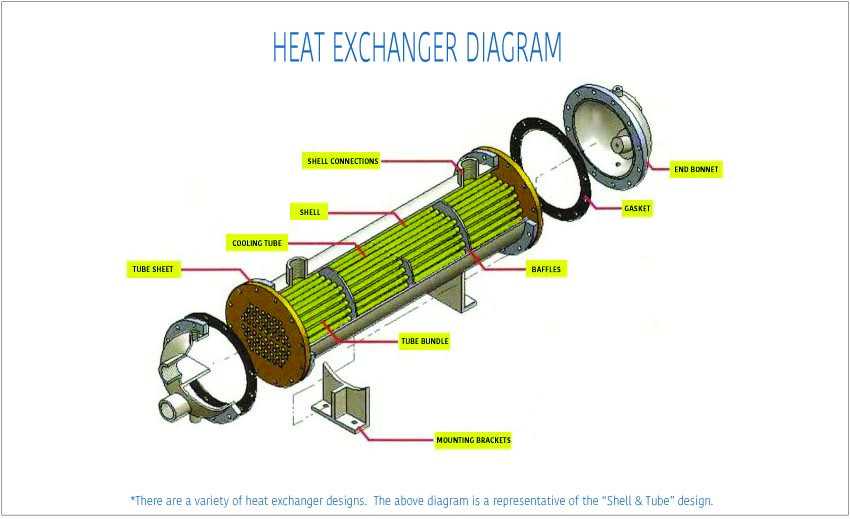
How to Source Heat Exchanger Parts Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat exchanger parts
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality heat exchanger parts presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The reliability and efficiency of heat exchangers are critical for various industries, from food processing to HVAC systems. Thus, understanding the nuances of the market—including types of heat exchanger parts, their specific applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting—becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of heat exchanger parts, offering insights into the diverse types available, including plate and shell-and-tube configurations, as well as the critical components such as gaskets, plates, and frame parts. It addresses common concerns regarding cost management and logistical challenges, providing actionable strategies for optimizing procurement processes.
By equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex market, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. Whether you are in Nigeria looking for reliable suppliers or in Vietnam assessing the best options for your manufacturing facility, the insights shared here will help streamline your sourcing efforts and enhance operational efficiency. With the right information at your fingertips, you can ensure that your heat exchanger systems perform optimally, ultimately driving productivity and profitability in your business.
Understanding heat exchanger parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plate Heat Exchanger Parts | Compact design, high surface area, customizable plates | Food & beverage, HVAC, chemical processes | Pros: Efficient heat transfer, space-saving. Cons: Susceptible to fouling, requires regular maintenance. |
| Gaskets | Essential for sealing, available in various materials | Used across all heat exchanger types | Pros: Prevent leaks, enhance efficiency. Cons: Material selection critical; improper choice can lead to failure. |
| Frame Parts | Structural components that support plates and gaskets | Industrial applications, power generation | Pros: Provides stability, customizable sizes. Cons: Can be costly to replace if damaged. |
| Tubular Heat Exchanger Parts | Cylindrical design, robust construction, lower pressure drop | Oil & gas, marine applications | Pros: Durable, suitable for high-pressure applications. Cons: Larger footprint, less efficient than plate types. |
| Finned Tube Parts | Enhanced surface area for heat transfer, often made of aluminum | HVAC, refrigeration | Pros: Increases heat transfer efficiency, lightweight. Cons: More prone to corrosion, may require specialized maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Plate Heat Exchanger Parts?
Plate heat exchanger parts are designed to maximize surface area while minimizing the overall footprint. This compact design allows for efficient heat transfer in various applications, including food and beverage processing, HVAC systems, and chemical manufacturing. When purchasing, consider the compatibility of plate configurations with existing systems, as well as the material used for plates, which can affect durability and maintenance needs.
Why Are Gaskets Critical in Heat Exchangers?
Gaskets play a vital role in ensuring that heat exchangers operate without leaks, maintaining efficiency and safety. They come in various materials such as NBR, EPDM, and FKM, each suitable for different temperature and chemical environments. Buyers should evaluate the operating conditions and select gaskets that will withstand the specific stresses of their applications, as improper selection can lead to significant downtime and operational inefficiencies.
How Do Frame Parts Contribute to Heat Exchanger Functionality?
Frame parts are essential in providing structural integrity to heat exchangers, particularly in plate and frame designs. They support the arrangement of plates and gaskets, ensuring proper alignment and function. When sourcing frame parts, businesses should consider the material strength and customization options to fit their specific heat exchanger configurations, as well as the potential costs associated with replacing damaged components.
What Are the Advantages of Tubular Heat Exchanger Parts?
Tubular heat exchanger parts are characterized by their robust cylindrical design, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as in the oil and gas industry. While they offer durability and reliability, they tend to have a larger footprint compared to other types. Buyers should assess the space available in their facilities and weigh the long-term investment against the operational benefits of increased durability.
How Do Finned Tube Parts Enhance Heat Transfer Efficiency?
Finned tube parts are designed to increase the surface area available for heat exchange, making them particularly effective in HVAC and refrigeration applications. Their lightweight construction allows for easier installation, but they may be more vulnerable to corrosion over time. B2B buyers should consider the environmental conditions where these parts will operate, and whether additional protective coatings or materials might be necessary to extend their lifespan.
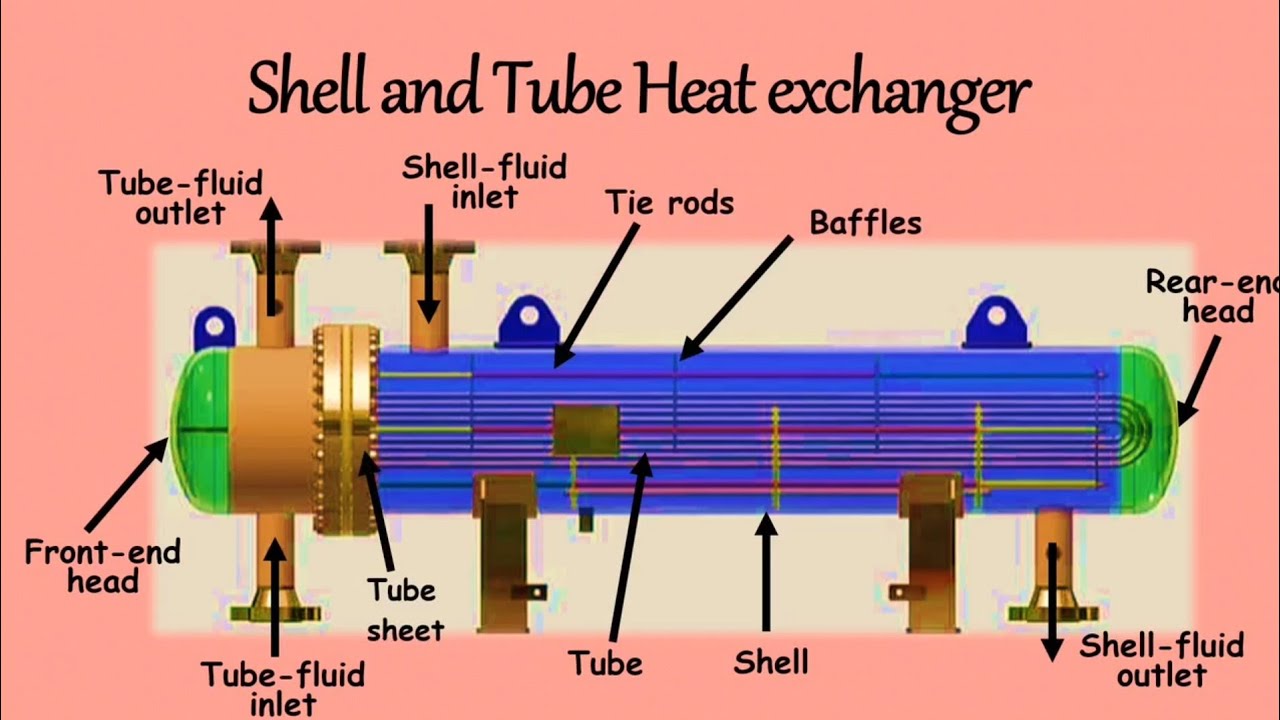
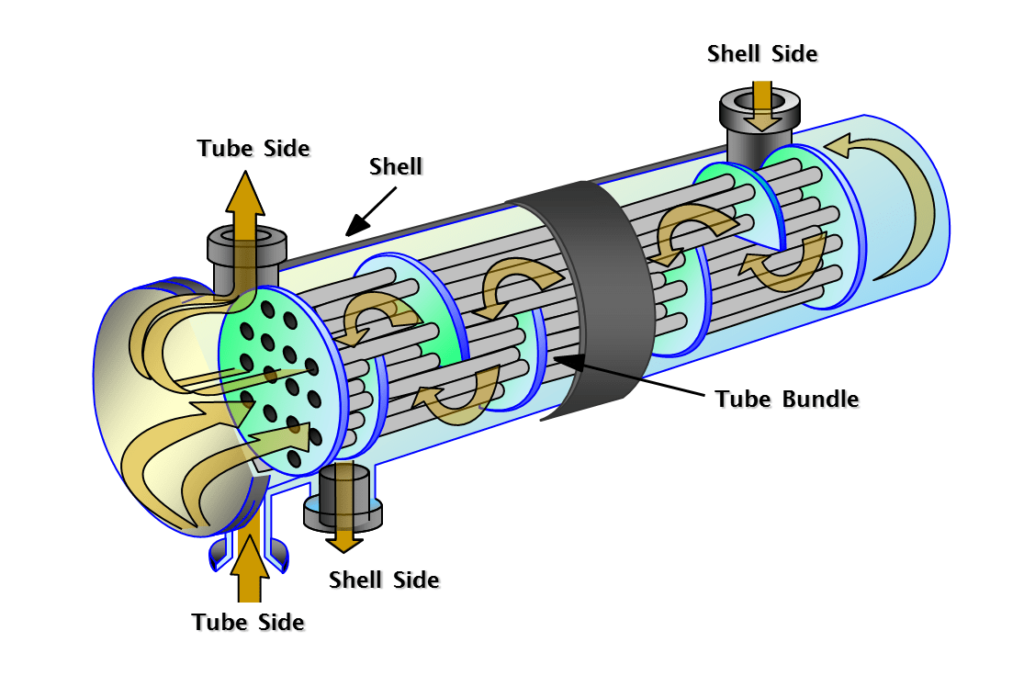
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
Key Industrial Applications of heat exchanger parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heat Exchanger Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Sanitary Heat Exchangers for Pasteurization | Ensures product safety and quality, compliance with health regulations | OEM compatibility, material certifications, rapid delivery |
| Chemical Processing | Heat Exchangers for Reaction Cooling | Maintains optimal reaction temperatures, improves yield and efficiency | Customization options, corrosion resistance, technical support |
| HVAC Systems | Heat Exchanger Parts for Climate Control Systems | Enhances energy efficiency, reduces operational costs | Availability of OEM parts, installation guidance, warranty terms |
| Oil & Gas | Heat Exchangers for Refining Processes | Increases energy recovery, reduces emissions | High-temperature resistance, compliance with industry standards, reliability |
| Power Generation | Heat Exchanger Parts in Steam and Gas Turbines | Improves thermal efficiency, extends equipment lifespan | Compatibility with various turbine models, expert installation support, fast shipping |
How Are Heat Exchanger Parts Utilized in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, heat exchanger parts are critical for processes like pasteurization, where sanitary heat exchangers ensure that products are heated to specific temperatures to eliminate harmful microorganisms. This application not only safeguards public health but also complies with stringent industry regulations. International buyers must prioritize sourcing OEM-compatible parts made from high-quality, food-grade materials to maintain product integrity. Additionally, rapid delivery options are essential to minimize downtime in production.
What Role Do Heat Exchanger Parts Play in Chemical Processing?
Heat exchangers in chemical processing are essential for controlling the temperatures of various reactions, particularly in exothermic reactions where excessive heat can lead to unsafe conditions. The right heat exchanger parts help maintain optimal temperatures, leading to improved reaction yields and overall process efficiency. Buyers in this sector should look for customization options that cater to specific chemical properties, as well as parts that offer corrosion resistance. Technical support during installation and operation is also crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency.
How Are Heat Exchanger Parts Beneficial in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, heat exchanger parts play a vital role in regulating indoor climates by transferring heat between air and fluids. This process enhances energy efficiency, leading to significant cost savings on energy bills. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality OEM parts is essential to ensure compatibility and performance. Additionally, having access to installation guidance and warranty terms can provide peace of mind, especially in regions with varying climatic conditions, such as Africa and the Middle East.
Why Are Heat Exchanger Parts Important in Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, heat exchanger parts are utilized in refining processes to recover energy and reduce emissions. These systems need to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, making material selection critical. Buyers should focus on sourcing parts that meet industry standards for high-temperature resistance and reliability. Ensuring that suppliers can provide technical documentation and compliance certifications is essential to uphold safety and operational efficiency in this sector.
How Do Heat Exchanger Parts Enhance Power Generation Efficiency?
Heat exchanger parts are integral to the efficiency of steam and gas turbines in power generation. They facilitate effective thermal energy transfer, which is crucial for maximizing the overall efficiency of power plants. International buyers should consider compatibility with various turbine models and seek suppliers who offer expert installation support. Fast shipping options are also vital to prevent delays in maintenance or upgrades, ensuring that power generation remains consistent and reliable.
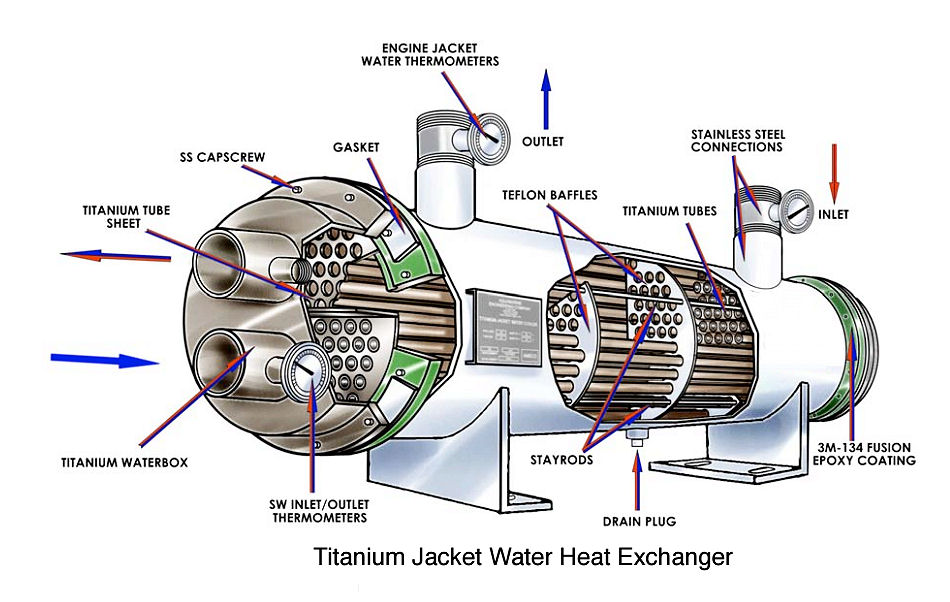
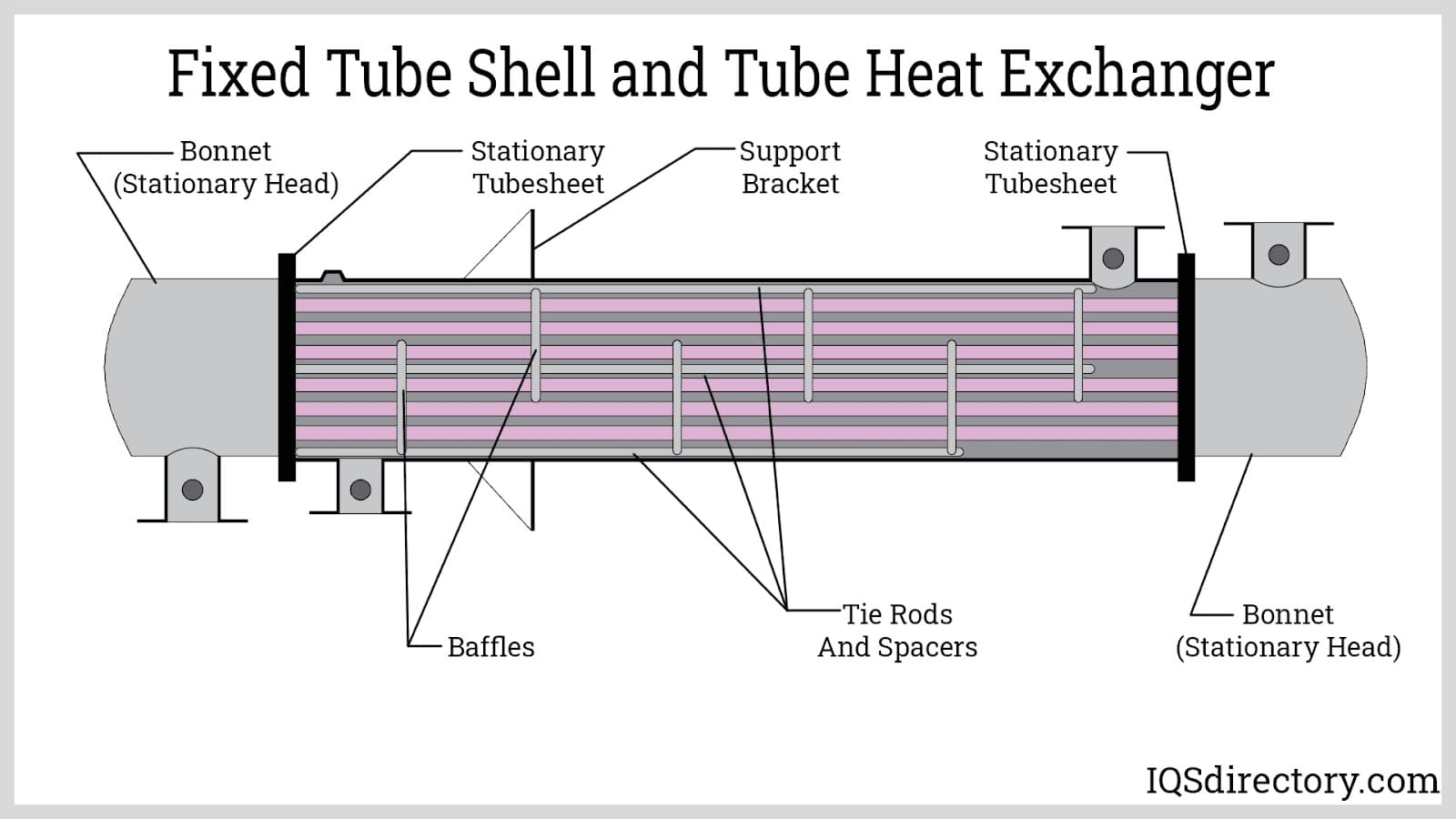
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heat exchanger parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays in Production Due to Downtime from Worn Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges when worn heat exchanger parts lead to unexpected downtime. For example, a manufacturing facility may experience a halt in production due to a failure in the heat exchanger, which can be attributed to aging gaskets or plates. Such incidents not only impact operational efficiency but also result in financial losses and strained client relationships. In regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less robust, the consequences can be even more pronounced as sourcing replacement parts becomes a race against time.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, it is essential for buyers to implement a proactive maintenance strategy that includes regular inspections and timely replacements of heat exchanger parts. Buyers should establish relationships with suppliers who can provide OEM parts and ensure rapid delivery. For instance, sourcing from vendors who offer overnight shipping for critical components, like gaskets and plates, can significantly reduce downtime. Additionally, maintaining an inventory of commonly replaced parts can provide a buffer against unexpected failures. Utilizing predictive maintenance tools can help monitor the condition of heat exchangers, allowing for preemptive action before failures occur.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Diverse Equipment Brands
The Problem: In many industrial settings, especially in regions with a mix of equipment from different manufacturers, compatibility issues can arise when sourcing heat exchanger parts. A B2B buyer may struggle to find suitable replacement parts for older or less common models, leading to frustration and delays. This scenario is particularly relevant in the Middle East and Europe, where equipment diversity is high due to multinational operations.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that carry a wide range of parts compatible with various brands and models of heat exchangers. When sourcing parts, it is crucial to provide detailed specifications, including model numbers and part types, to ensure compatibility. Buyers can also benefit from suppliers that offer customization options, such as tailored gaskets or plates designed to fit specific equipment. Engaging with suppliers who maintain comprehensive databases of parts and have expertise in cross-brand compatibility can streamline the sourcing process. Additionally, investing in training for maintenance staff on identifying compatible parts can enhance efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Maintenance Practices Leading to Increased Costs
The Problem: Inefficient maintenance practices can lead to increased operational costs for companies relying on heat exchangers. B2B buyers might experience issues such as improper installation of parts or inadequate cleaning procedures, resulting in reduced efficiency and higher energy consumption. In regions with high energy costs, such as Europe, this can significantly impact profitability.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should establish standardized maintenance protocols that emphasize proper installation and regular cleaning of heat exchangers. Collaborating with suppliers that provide training resources, installation guides, and expert support can enhance maintenance practices. For example, suppliers that offer installation services or consultations can help ensure that parts are fitted correctly, minimizing the risk of future issues. Implementing a Clean-in-Place (CIP) system can also streamline maintenance efforts, ensuring that heat exchangers operate at peak efficiency. Regular audits of maintenance practices can identify areas for improvement, ultimately reducing operational costs and enhancing system performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat exchanger parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Heat Exchanger Parts?
When selecting materials for heat exchanger parts, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they align with the specific requirements of various applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in heat exchangers, focusing on their performance attributes, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C or 1472°F). It also has good pressure ratings, making it suitable for various heat transfer applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can last for many years with minimal maintenance. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to fabricate, which may increase manufacturing complexity. Its suitability for high-temperature applications makes it ideal for industries such as oil and gas.
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it versatile across different sectors. However, it may not be the best choice for applications involving chloride environments, as it can lead to pitting corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A312 or DIN 17440. Understanding local corrosion challenges is vital for selecting the appropriate grade of stainless steel.
2. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for heat transfer. It can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 200°C or 392°F) and has good corrosion resistance when properly treated.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its superior thermal efficiency, which can lead to energy savings. However, its relatively lower strength compared to stainless steel can limit its use in high-pressure applications. Additionally, copper is more expensive than aluminum but less than high-grade stainless steel.
Impact on Application:
Copper is particularly well-suited for applications involving water and other non-corrosive fluids. However, its use in environments with aggressive chemicals or high chlorides should be avoided due to potential corrosion issues.
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for copper alloys in different regions. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B280 is essential, particularly in markets like South America where regulations may differ.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and is often used in applications requiring lightweight materials.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it an attractive option for portable heat exchangers. However, its lower strength and temperature limits compared to stainless steel can be a disadvantage in high-pressure applications. Additionally, aluminum is generally less expensive than stainless steel.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is best suited for applications involving air or water, but it may not perform well in environments with harsh chemicals. Its corrosion resistance is excellent in non-aggressive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B221. In markets like Europe, where lightweight materials are preferred for energy efficiency, aluminum may be a favored choice.

Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
4. Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in seawater and acidic environments. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 600°C or 1112°F) and has a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros & Cons:
Titanium’s primary advantage is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for extreme environments. However, it is one of the most expensive materials, and its fabrication can be complex, leading to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is suitable for applications in chemical processing and marine environments where corrosion is a significant concern. Its compatibility with a wide range of media makes it versatile, but its cost may limit its use in low-budget projects.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the stringent standards for titanium materials, such as ASTM B348. In regions like the Middle East, where high corrosion resistance is essential, titanium may be a preferred choice despite its cost.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Exchanger Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat exchanger parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper | Water and HVAC systems | Superior thermal conductivity | Lower strength in high-pressure settings | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight heat exchangers | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
| Titanium | Chemical processing and marine environments | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High cost and complex fabrication | High |
This guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in selecting the right materials for heat exchanger parts, ensuring they make informed decisions aligned with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat exchanger parts
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Heat Exchanger Parts?
Manufacturing heat exchanger parts involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and efficiency.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-grade materials, typically stainless steel or high-nickel alloys, known for their corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Suppliers often pre-treat these materials to remove impurities, enhancing their performance. Material specifications must meet international standards, which can include ASTM and EN standards, ensuring they are suitable for the intended application.
-
Forming: This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired forms. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and laser cutting are employed to create plates, gaskets, and other components. Advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining offer precision and repeatability, which are crucial for the intricate designs often found in heat exchangers.
-
Assembly: Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into complete units. This phase may include welding, bolting, or using adhesives, depending on the design and materials involved. Automated assembly systems are increasingly utilized to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves finishing processes such as surface treatment, cleaning, and inspection. Techniques like passivation enhance corrosion resistance, while polishing improves aesthetics and performance. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the parts meet the rigorous demands of their operational environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Heat Exchanger Part Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that every part meets stringent performance standards.
-
Adherence to International Standards: Many manufacturers comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Industry-specific standards, such as CE marking for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications, are also critical. These certifications not only ensure compliance but also enhance the credibility of suppliers in the international market.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Manufacturers implement multiple quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the production process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial check verifies the quality of raw materials upon receipt. Suppliers may be required to provide material test certificates to validate compliance with specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks ensure that processes remain within defined parameters. This may include monitoring machine settings and conducting random inspections of parts.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that the final product meets all specifications. This may involve dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing. -
Common Testing Methods: Testing methods such as non-destructive testing (NDT), pressure testing, and thermal cycling tests are commonly used. NDT techniques, including ultrasonic and radiographic testing, help identify flaws without damaging the parts, while pressure tests ensure the integrity of the heat exchanger under operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for mitigating risks associated with product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and the presence of robust quality management systems.
-
Quality Reports and Certifications: Requesting quality reports, including inspection records and certification documents, can help verify a supplier’s commitment to quality. Buyers should also check for third-party certifications that validate the supplier’s adherence to industry standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies to evaluate suppliers can add an extra layer of assurance. These agencies can conduct independent assessments of manufacturing processes, materials, and finished products, ensuring they meet specified standards.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges and nuances in quality control that require careful consideration:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the regulatory environment and cultural practices of suppliers in different regions is crucial. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and practices to ensure compliance and facilitate smooth operations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The complexity of international logistics can impact quality. Buyers must account for potential delays, damage during transport, and other logistical challenges that may affect the quality of heat exchanger parts upon arrival.
-
Communication and Relationship Management: Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers is vital. Regular updates, feedback, and collaborative problem-solving can help ensure that quality standards are maintained throughout the manufacturing and delivery process.
Conclusion
Manufacturing heat exchanger parts is a meticulous process that requires a strong focus on quality assurance. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of QA, and how to verify supplier quality control, B2B buyers can make informed decisions. This not only enhances operational reliability but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers, ensuring that their heat exchanger systems operate efficiently and effectively across various industries.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heat exchanger parts’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure heat exchanger parts. Given the critical role these components play in industrial processes, ensuring you follow a structured approach to sourcing can lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced downtime, and overall cost savings.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by detailing the exact specifications of the heat exchanger parts you need. This includes dimensions, material composition, and compatibility with existing systems. Clear technical specifications help in communicating your needs to suppliers and ensure that the parts will function correctly within your equipment.
- Consider OEM Standards: Ensure the parts meet Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) standards for quality and compatibility.
- Identify Performance Requirements: Specify operational parameters like temperature and pressure ratings to avoid mismatches.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in heat exchanger parts. Use industry directories, trade shows, and online marketplaces to compile a list of potential candidates.
- Check for Industry Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality.
- Evaluate Geographic Reach: Given the global nature of your procurement, consider suppliers who can meet your shipping and delivery needs efficiently.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and quality assurances. This is crucial for maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
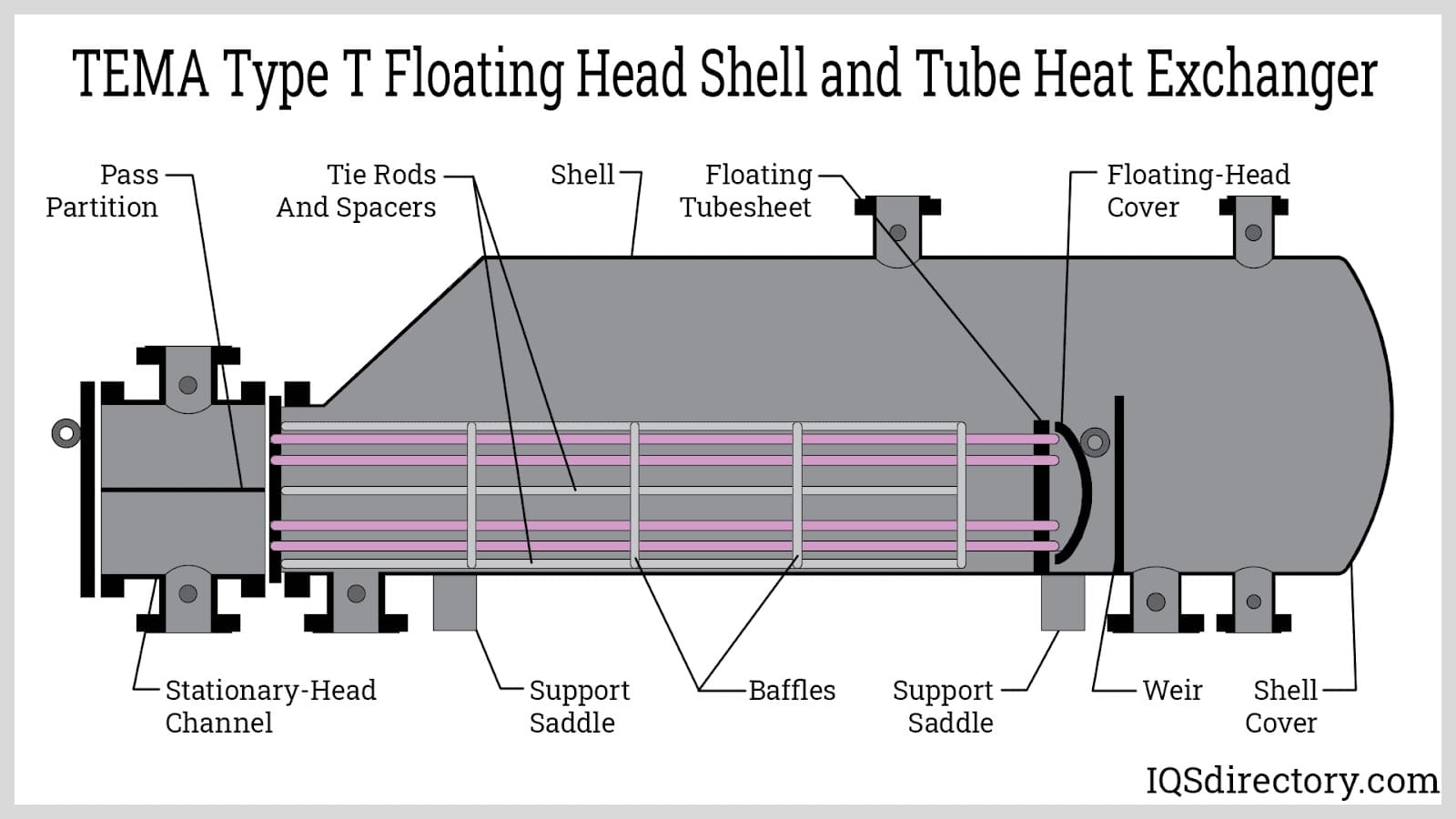
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
- Request Documentation: Ask for copies of ISO certifications or any relevant quality management system documentation.
- Investigate Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers adhere to local and international safety and environmental regulations.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Inventory
Assess the capabilities of potential suppliers, including their inventory levels and lead times for parts. A supplier with a robust inventory can help you avoid delays in production due to unexpected breakdowns.
- Inquire About Customization Options: If your needs are unique, check if the supplier can provide customized solutions.
- Assess After-Sales Support: Evaluate the level of support offered for installation and maintenance, as this can significantly impact operational efficiency.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes. Comparing pricing should go beyond just the cost of parts; consider shipping costs, lead times, and payment terms as well.
- Look for Volume Discounts: Many suppliers offer reduced rates for bulk purchases, which can lead to significant savings.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in the expected lifespan and warranty of the parts to determine the best overall value.
Step 6: Conduct Final Due Diligence
Before making a purchase, perform final checks on your selected supplier. This involves confirming references and possibly visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible.
- Seek Testimonials from Similar Industries: Contact previous clients to gain insights into their experiences with the supplier.
- Review Contract Terms: Ensure all aspects of the agreement are clear, including delivery schedules and return policies.
Step 7: Place Your Order and Monitor Delivery
After selecting the supplier, place your order, and closely monitor the delivery process. Effective communication is vital during this stage to ensure that everything proceeds smoothly.
- Establish a Point of Contact: Designate a representative from your company to liaise with the supplier for any queries or issues.
- Track Shipping and Delivery: Use tracking tools to stay informed about the shipment status and ensure timely arrival.
Following this structured checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing heat exchanger parts, ultimately supporting your operational efficiency and success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat exchanger parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Heat Exchanger Parts?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing heat exchanger parts, several critical components come into play:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences cost. Common materials include stainless steel, high-nickel alloys, and specialized gaskets made from EPDM or NBR. Prices fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and the specific properties required for the application.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass not only the wages of the workforce involved in production but also the skilled labor required for installation and maintenance. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but the need for specialized training can increase overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance of equipment. Manufacturers often allocate a percentage of these overheads to the cost of each part, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can represent a significant upfront investment. For buyers requiring unique specifications or modifications, these costs must be factored into the total price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet stringent quality standards involves costs associated with testing and certification. For international buyers, especially in regulated industries, compliance with local and international standards can add to expenses.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary widely depending on the origin, destination, and mode of transport. International buyers need to consider tariffs, taxes, and potential delays in logistics, particularly when sourcing from different continents.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to their costs, which can vary based on market competition, demand, and the exclusivity of the parts offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heat Exchanger Parts Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat exchanger parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Ordering in bulk often leads to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may provide discounts for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts generally incur higher costs due to the added complexity in design and manufacturing. Buyers should assess whether standard components meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) can increase prices but often lead to better performance and longevity, which is vital for reducing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to perceived quality and service levels, but they can also offer advantages like better support and faster delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the overall cost structure.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Secure Better Prices?
International buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance their purchasing outcomes:
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms. Long-term partnerships often result in preferential treatment.
-
Leverage Market Knowledge: Familiarize yourself with market trends and pricing benchmarks. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations, helping them recognize fair prices and identify potential overcharging.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Instead of solely considering the initial purchase price, evaluate the long-term costs associated with maintenance, downtime, and replacement. This comprehensive view can justify higher upfront costs if they lead to savings down the line.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If possible, being open to alternative materials or standard parts can yield significant savings. Suppliers often have excess inventory on standard items that can be sold at a discount.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, making it a viable option for many buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
Buyers should remain cautious about indicative pricing, as costs can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. Fluctuations in material prices, changes in shipping rates, and unexpected tariffs can all influence the final price. Therefore, obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers and regularly reviewing contracts is essential for ensuring competitive pricing and securing the best value for heat exchanger parts.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heat exchanger parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Heat Exchanger Parts
In the realm of industrial applications, heat exchangers play a pivotal role in optimizing energy efficiency and thermal management. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can achieve similar objectives. This section explores how heat exchanger parts compare with other solutions, such as cooling towers and thermal storage systems. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their unique operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Exchanger Parts | Cooling Towers | Thermal Storage Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; effective heat transfer | Good for large-scale cooling | Stabilizes temperature fluctuations |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing maintenance | High installation costs; low operating costs | High upfront costs; long-term savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation | Complex setup; requires skilled labor | Requires space and infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Regular checks and part replacements | Requires water treatment and cleaning | Minimal maintenance once installed |
| Best Use Case | Industrial processes requiring precise temperature control | Large facilities needing extensive cooling | Applications with fluctuating heat loads |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cooling Towers?
Cooling towers are designed to remove heat from water used in industrial processes, making them an effective alternative in applications where large-scale cooling is necessary. Their primary advantage is their ability to handle significant heat loads at a lower operational cost compared to heat exchangers. However, cooling towers can be expensive to install and require ongoing maintenance, including water treatment and cleaning to prevent fouling. They are best suited for facilities such as power plants and large manufacturing plants where cooling demands are substantial.
How Do Thermal Storage Systems Compare?
Thermal storage systems utilize stored thermal energy to manage temperature fluctuations, particularly in buildings or processes with varying heat loads. One of the main benefits is their ability to reduce peak energy demand, which can lead to lower energy costs over time. However, thermal storage systems often require a significant initial investment and a dedicated space for installation. They are ideal for applications where there is a need to balance energy consumption, such as in district heating systems or large commercial buildings.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right thermal management solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term objectives. If precise temperature control and efficient heat transfer are paramount, investing in quality heat exchanger parts may be the best option. Conversely, if the application involves significant heat loads and cooling requirements, cooling towers might be more suitable. For facilities experiencing fluctuating heat demands, thermal storage systems can provide a strategic advantage in energy management. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s operational goals, financial considerations, and maintenance capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat exchanger parts
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Heat Exchanger Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of heat exchanger parts is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications not only impact performance but also influence procurement decisions and long-term operational efficiency.
1. Material Grade
Heat exchanger components are often made from various materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or high-nickel alloys. The material grade affects thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and pressure handling. For instance, stainless steel is commonly used in food and beverage applications due to its resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. Selecting the right material ensures the longevity of the equipment and compliance with industry standards.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the manufacturing process. In heat exchangers, tight tolerances are critical for ensuring proper fit and function of parts like gaskets and plates. Misalignment can lead to inefficiencies, leaks, or even catastrophic failures. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess the quality and reliability of the components they are procuring.
3. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum operating pressure a component can withstand. It is essential for ensuring safety and reliability in high-pressure applications, such as in industrial settings. Components must be matched to the system’s pressure requirements to avoid failures. Buyers should inquire about pressure ratings to ensure that the heat exchanger parts can safely handle their specific operational conditions.
4. Thermal Efficiency
This property measures how effectively a heat exchanger transfers heat between two fluids. Higher thermal efficiency translates to better performance and energy savings. It is vital for buyers to consider thermal efficiency when evaluating different heat exchanger designs and materials, as it directly impacts operational costs and energy consumption.
5. Surface Treatment
Surface treatments, such as coatings or finishes, enhance corrosion resistance and improve cleanability. This is especially important in industries like food processing where hygiene is paramount. Buyers should look for parts with appropriate surface treatments that align with their operational requirements and regulatory compliance.
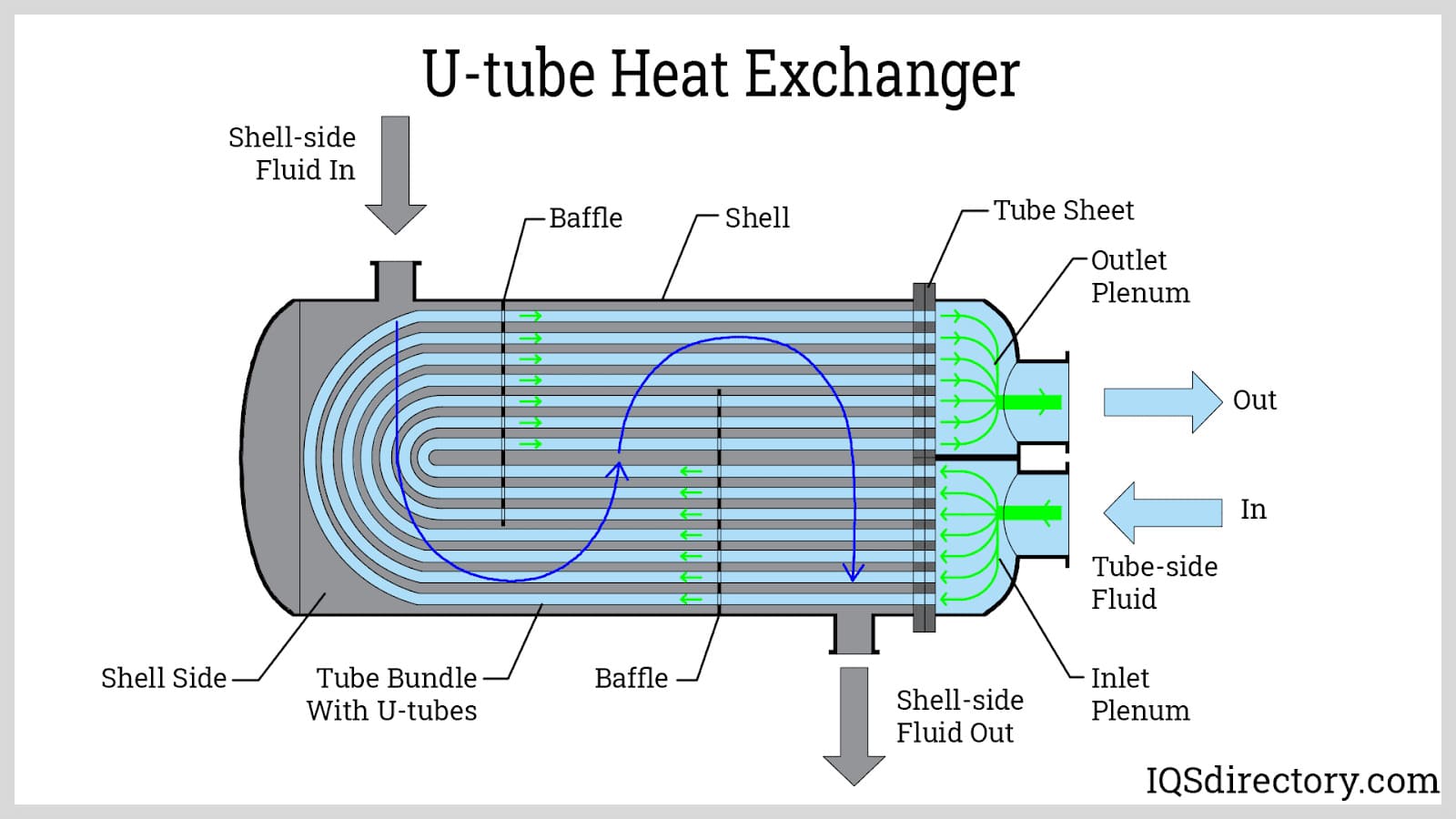
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Heat Exchanger Parts Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace for heat exchanger parts.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat exchangers, OEM parts are specifically designed to fit and function in original equipment. Buyers should prioritize OEM parts to ensure compatibility and maintain warranty protections.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when sourcing specialized heat exchanger parts, as it can impact inventory management and budgeting. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and availability of specific products. In the heat exchanger market, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and terms from different suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and risk transfer. Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers to negotiate favorable terms and avoid misunderstandings during shipping and delivery.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. In the heat exchanger parts market, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the part and the supplier’s capacity. Buyers should inquire about lead times to plan for maintenance and avoid production delays.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, enhance their procurement strategies, and improve operational efficiencies in their heat exchange systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heat exchanger parts Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Heat Exchanger Parts Sector?
The heat exchanger parts market is experiencing notable growth driven by various global factors. Increasing industrialization, especially in developing regions like Africa and South America, is enhancing demand for efficient thermal management solutions. Emerging markets are also witnessing a surge in energy efficiency regulations, pushing manufacturers to upgrade their existing systems and source reliable parts. Furthermore, the rise in renewable energy applications, such as solar and geothermal systems, is creating new opportunities for heat exchanger parts suppliers.
In terms of technology, digital transformation is reshaping how B2B buyers source heat exchanger parts. Advanced supply chain management software and e-commerce platforms are streamlining procurement processes, enabling faster decision-making and reducing lead times. Additionally, the integration of IoT technologies is improving the monitoring and maintenance of heat exchangers, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing downtime, which is crucial for industries like oil and gas, food and beverage, and HVAC systems.
International buyers are also increasingly focusing on vendor reliability and service quality. They seek suppliers who not only offer a broad range of OEM parts but also provide expert installation support and timely delivery. This trend emphasizes the importance of building strong relationships with suppliers who understand the unique challenges faced by various industries across different regions, including Europe, the Middle East, and emerging markets in Asia.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Heat Exchanger Parts Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the heat exchanger parts sector, influenced by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impacts associated with production and disposal of heat exchanger parts. This has led to a growing emphasis on sourcing from suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and using eco-friendly materials.

Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with businesses recognizing the value of transparent supply chains. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and certifications, such as ISO 14001 or similar green certifications. These certifications assure buyers that their suppliers are committed to minimizing their ecological footprint while maintaining high-quality standards.
Moreover, the use of recyclable materials and the development of “green” heat exchanger parts are gaining traction. Innovations in materials science, such as high-nickel alloys and stainless steel, not only improve efficiency but also enhance the longevity of components, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This aligns with the growing trend of circular economy principles, where the focus is on maximizing resource use and minimizing waste throughout the product lifecycle.
What Is the Historical Context of Heat Exchanger Parts Sourcing?
Historically, heat exchangers have been integral to various industrial processes, with their origins dating back to the early 19th century during the industrial revolution. The evolution of heat exchanger technology has paralleled advancements in manufacturing and materials science, leading to more efficient designs and enhanced performance. Initially, sourcing parts was a localized process, limited to regional suppliers. However, globalization has transformed the landscape, enabling international buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers.
As industries expanded, the need for reliable and standardized parts became evident. This led to the establishment of OEMs and the development of comprehensive parts catalogs, allowing buyers to source components with greater ease. The advent of digital platforms and e-commerce has further revolutionized sourcing in recent years, enabling B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Vietnam and Nigeria, to connect with suppliers worldwide. This historical context underscores the ongoing shift toward a more interconnected and efficient marketplace for heat exchanger parts, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands.
Illustrative image related to heat exchanger parts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat exchanger parts
-
How do I solve issues with worn heat exchanger parts?
To address issues with worn heat exchanger parts, start by conducting a thorough inspection of your equipment. Identify any signs of leaks, reduced efficiency, or unusual noises. Replace worn components promptly with high-quality OEM parts to ensure optimal performance. Partnering with suppliers that offer fast shipping can minimize downtime. Additionally, consider implementing a preventive maintenance schedule to regularly check and replace parts before they lead to significant operational issues. -
What is the best type of gasket material for my heat exchanger?
The best gasket material for your heat exchanger depends on the operating conditions and the fluids involved. Common options include NBR, which is suitable for temperatures up to 140°C, and EPDM, which can withstand up to 170°C. For more demanding environments, consider high-performance materials like FKM or HNBR. It’s crucial to consult with your supplier to ensure compatibility with your specific heat exchanger model and application requirements. -
How can I ensure the quality of heat exchanger parts when sourcing internationally?
To ensure the quality of heat exchanger parts from international suppliers, conduct thorough due diligence. Verify the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, and request product samples before placing bulk orders. Utilize third-party inspection services to assess the quality of parts upon delivery. Establish clear quality assurance protocols and maintain open communication with your supplier to address any concerns promptly. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for heat exchanger parts?
Minimum order quantities for heat exchanger parts can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs range from a few units for standard components to larger quantities for specialized parts. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer or looking to test new parts. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for initial orders or provide bulk pricing incentives. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing heat exchanger parts internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers. Common terms include upfront payment, net 30 or net 60 days, and letters of credit. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and purchasing strategy. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to protect your transaction. Always clarify payment terms in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I customize heat exchanger parts to fit my specific needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for heat exchanger parts, such as tailored dimensions, materials, and designs. To initiate the process, provide detailed specifications and application requirements to your supplier. Collaborate closely during the design phase to ensure that the customized parts meet your operational needs. Keep in mind that custom orders may involve longer lead times and potentially higher costs, so plan accordingly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing heat exchanger parts internationally?
When sourcing heat exchanger parts internationally, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling industrial components. Ensure that the supplier provides clear shipping timelines and tracking information. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes that may apply to your shipments to avoid unexpected costs. Planning for potential delays in customs can help maintain your supply chain’s efficiency. -
How can I vet suppliers for heat exchanger parts effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers for heat exchanger parts, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and references from other businesses. Request certifications and documentation to verify their compliance with quality standards. Conduct site visits if possible, or utilize video conferencing to assess their facilities. Establishing a relationship with suppliers through trial orders can also help you evaluate their reliability and product quality.
Top 10 Heat Exchanger Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HVAC Parts Shop – HVAC Repair Parts
Domain: hvacpartsshop.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: HVAC Parts Shop offers a wide range of HVAC repair parts and accessories, including furnace parts, air conditioning parts, and HVAC controls. Key product categories include:
– Air Conditioning Parts: A/C Cabinet Parts, Crankcase Heaters, Condenser Coils, Compressors, Evaporator Coils, Fan Motors, and more.
– Furnace Parts: Gaskets, Blower Motors, Burners, Electric Heat Kits, Flame Sensors, Gas Val…
2. AGC – Plate Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: agcheattransfer.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Plate Heat Exchanger Parts Supply from AGC Heat Transfer Products includes ProFlow Series Plates, Hydraulic Frames, Twin Spindle Frames, Stainless Tie-Bar Frames, Powder Coated Mild Steel Tie Bar Frames, “Matched” Hot Water Sets, Pilot Scale Heat Exchangers, Pulsation Dampeners, SA Frames, and other OEM Equipment. Services offered include Plate Checks, PHE 101 Training Course, Installation Supervi…
3. Noritz – Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: support.noritz.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Noritz Heat Exchanger Parts include various components for tankless water heaters. Key products listed are:
– BWCD098-B Thermistor – Heat Exchanger ($36.62)
– EHWL003 Gasket – Secondary Heat Exchanger ($12.82)
– ELRD001 Pipe – Main Flow Sensor to Heat Exchanger ($164.78)
– ELRD003 Pipe – Heat Exchanger to Main Water Servo ($164.78)
– ELVD051 Pipe – Flow Sensor to Heat Exchanger ($73.23)
– EM…
4. Tranter – Plate Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: tranter.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Tranter provides parts and accessories for plate heat exchangers, including gasketed plate and frame, shell and plate, and welded block heat exchangers. Key offerings include:
– **Plates and Gaskets**: Customized plate assemblies with pre-attached gaskets and full plate packs for various brands.
– **Gaskets**: Standard gaskets available in NBR (max temperature 140°C / 284°F) and EPDM (max tempera…
5. Aramsco – Heat Exchangers & Heater Parts
Domain: aramsco.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Aramsco – Heat Exchangers & Heater Parts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Sen-Dure – Heat Exchanger Gasket & End Cover Kit
Domain: marineengineparts.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Sen-Dure – Heat Exchanger Gasket & End Cover Kit, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Atlas Bronze – Heat Exchanger Parts
Domain: atlasbronze.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Heat Exchanger Parts Diagram | Heat Exchanger Components. Heat exchangers transfer heat between fluids, used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural gas processing, and sewage treatment. Industries include waste water treatment, refrigeration, wine and beer-making, petroleum refining, and nuclear power….
8. WCRHX – Heat Exchangers and Replacement Parts
Domain: wcrhx.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Replacement Parts – WCRHX HEAT EXCHANGERS includes Plate Heat Exchangers, Immersion Plates, and Refurbished/Used Heat Exchangers. Key offerings include Heat Exchanger Plates and Heat Exchanger Gaskets, with over 200,000 plates and 600,000 gaskets in stock for immediate shipment. WCR provides OEM-quality specified plates and gaskets for all makes and models of plate heat exchangers. The company pro…
9. Thermopedia – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thermopedia.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are popular for their flexibility in handling a wide range of pressures and temperatures. They are categorized into two main types: those used in the petrochemical industry (covered by TEMA standards) and those used in the power industry (like feedwater heaters and condensers). The main components include: 1. Front Header (Stationary Header) – where fluid enters the …
10. CPE Systems – Flow Gaskets and Port Gaskets
Domain: cpesystems.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Flow Gasket for CPE60H’, ‘price’: ‘$16.00’, ‘sku’: ‘HX/CPE60H-FLOW GASKET’}, {‘name’: ‘Flow Gasket for CPE30H’, ‘price’: ‘$12.00’, ‘sku’: ‘HX/CPE30H-FLOW GASKET’}, {‘name’: ‘Port Gasket for CPE60H’, ‘price’: ‘$14.00’, ‘sku’: ‘HX/CPE60H-PORT’}, {‘name’: ‘Port Gasket for CPE30H’, ‘price’: ‘$12.00’, ‘sku’: ‘HX/CPE30H-PORT-EPDM’}, {‘name’: ‘Flow Plate with Gasket for CPE60H’, ‘price’: ‘$47….
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat exchanger parts
In the competitive landscape of heat exchanger parts, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for success. By leveraging a diverse supplier network, international B2B buyers can ensure access to high-quality OEM parts, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Prioritizing reliable suppliers with a proven track record in fast shipping and comprehensive support services allows businesses to maintain seamless production processes, especially in critical industries such as food and beverage, HVAC, and energy.
Moreover, the customization of components like gaskets and plates tailored to specific operational needs can significantly improve system performance and longevity. Buyers should also consider the importance of technical documentation and installation support to mitigate risks associated with part replacements.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and sustainable heat exchanger solutions will continue to grow. By investing in strategic sourcing practices today, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can position themselves for future success. Engage with trusted suppliers to optimize your procurement processes and stay ahead of industry trends—it’s an investment that will pay dividends in operational reliability and cost savings.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.