How to Source Halt Chamber Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for halt chamber
In today’s fast-paced global market, sourcing a highly effective HALT chamber can present a significant challenge for businesses aiming to enhance product reliability and accelerate time to market. As manufacturers increasingly rely on Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) to identify design flaws and optimize product performance, the demand for advanced testing systems continues to rise. This comprehensive guide addresses the myriad complexities associated with selecting the right HALT chamber, including types of chambers, their various applications across industries, and critical supplier vetting processes.
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Nigeria and Germany—will find actionable insights tailored to their unique market conditions and regulatory environments. This guide not only delves into the technical specifications and operational efficiencies of different HALT systems but also provides a thorough analysis of costs, potential return on investment, and the importance of post-purchase support.
By equipping decision-makers with knowledge on the latest technological advancements and supplier capabilities, this resource empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their strategic goals. Whether you are a procurement manager or a quality assurance specialist, understanding the nuances of HALT chambers will enable you to elevate your product development processes and ultimately drive business success in a competitive landscape.
Understanding halt chamber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard HALT | Combines temperature cycling with vibration testing | Electronics, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited to standard testing conditions. |
| High-Temperature HALT | Supports extreme temperature ranges up to 250°C | Defense, energy, and high-performance sectors | Pros: Ideal for high-temp applications. Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| HALT with Vibration Table | Features advanced vibration technology with 6DOF | Complex assembly testing in various industries | Pros: Comprehensive stress testing. Cons: Complex setup and calibration required. |
| Modular HALT Systems | Customizable configurations for specific testing needs | R&D, product development in diverse sectors | Pros: Flexibility in design. Cons: Potentially longer lead times for customization. |
| Benchtop HALT | Compact design suitable for limited spaces | Smaller electronics and components manufacturers | Pros: Space-efficient and cost-effective. Cons: Limited testing capacity compared to larger models. |
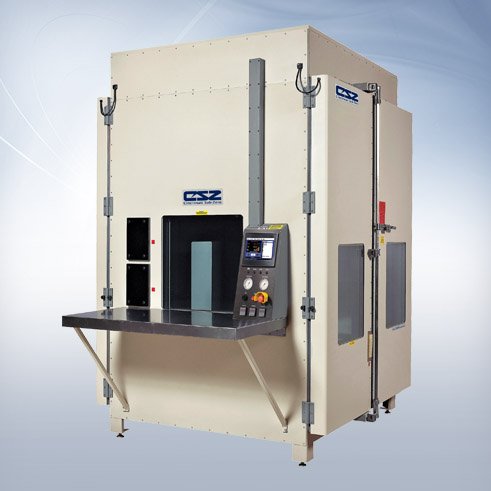
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Standard HALT Systems?
Standard HALT systems are the cornerstone of accelerated reliability testing, effectively combining temperature cycling and vibration testing to identify potential design flaws in products. These chambers are particularly suitable for sectors such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where reliability is paramount. Buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness and availability of these systems, but be aware that they may be limited in their ability to accommodate extreme testing conditions.
Why Choose High-Temperature HALT Chambers for Specialized Applications?
High-Temperature HALT chambers extend the testing range to extreme temperatures, reaching up to 250°C. This capability is essential for industries such as defense and energy, where products must endure harsh conditions. While these systems provide critical insights for high-performance applications, buyers should factor in the higher operational costs associated with their use, as well as the need for specialized maintenance.
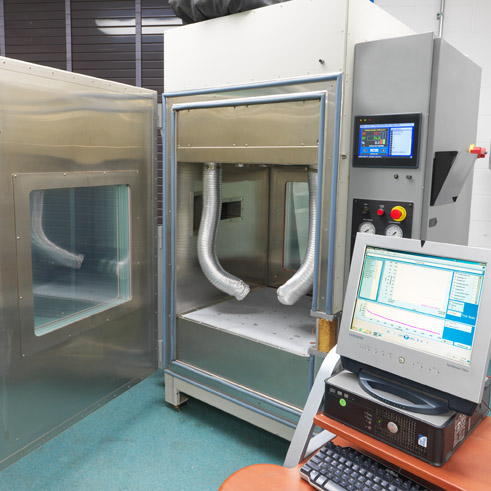

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
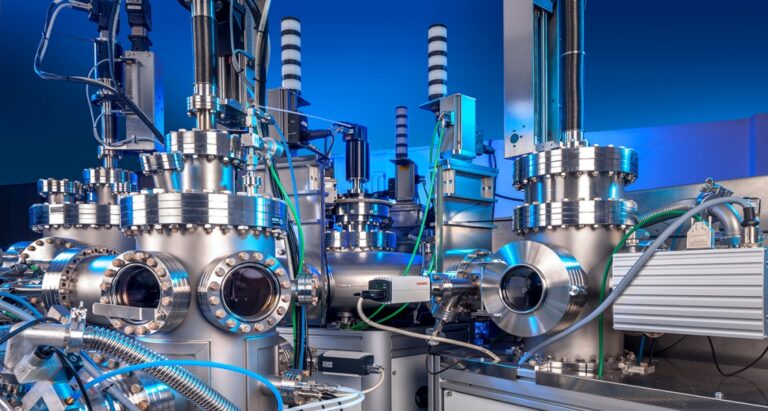
How Does a HALT Chamber with Vibration Table Enhance Testing Capabilities?
HALT systems equipped with advanced vibration tables utilize six degrees of freedom (6DOF) to simulate complex stress scenarios. This feature is crucial for testing intricate assemblies found in various industries. While the comprehensive nature of this testing provides valuable data, the setup and calibration can be complex, requiring skilled personnel to operate effectively.
What Benefits Do Modular HALT Systems Offer for Custom Testing?
Modular HALT systems are designed for flexibility, allowing businesses to customize configurations to meet specific testing requirements. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for research and development teams across diverse sectors. However, potential buyers should be prepared for longer lead times due to customization processes, which may impact project timelines.
When Should You Consider Benchtop HALT Chambers for Your Testing Needs?
Benchtop HALT chambers are an excellent choice for companies with limited space or smaller products, such as electronic components. Their compact design allows for efficient use of space while still delivering reliable testing results. Buyers should weigh the benefits of cost-effectiveness and space efficiency against the limited testing capacity, ensuring it meets their specific operational needs.
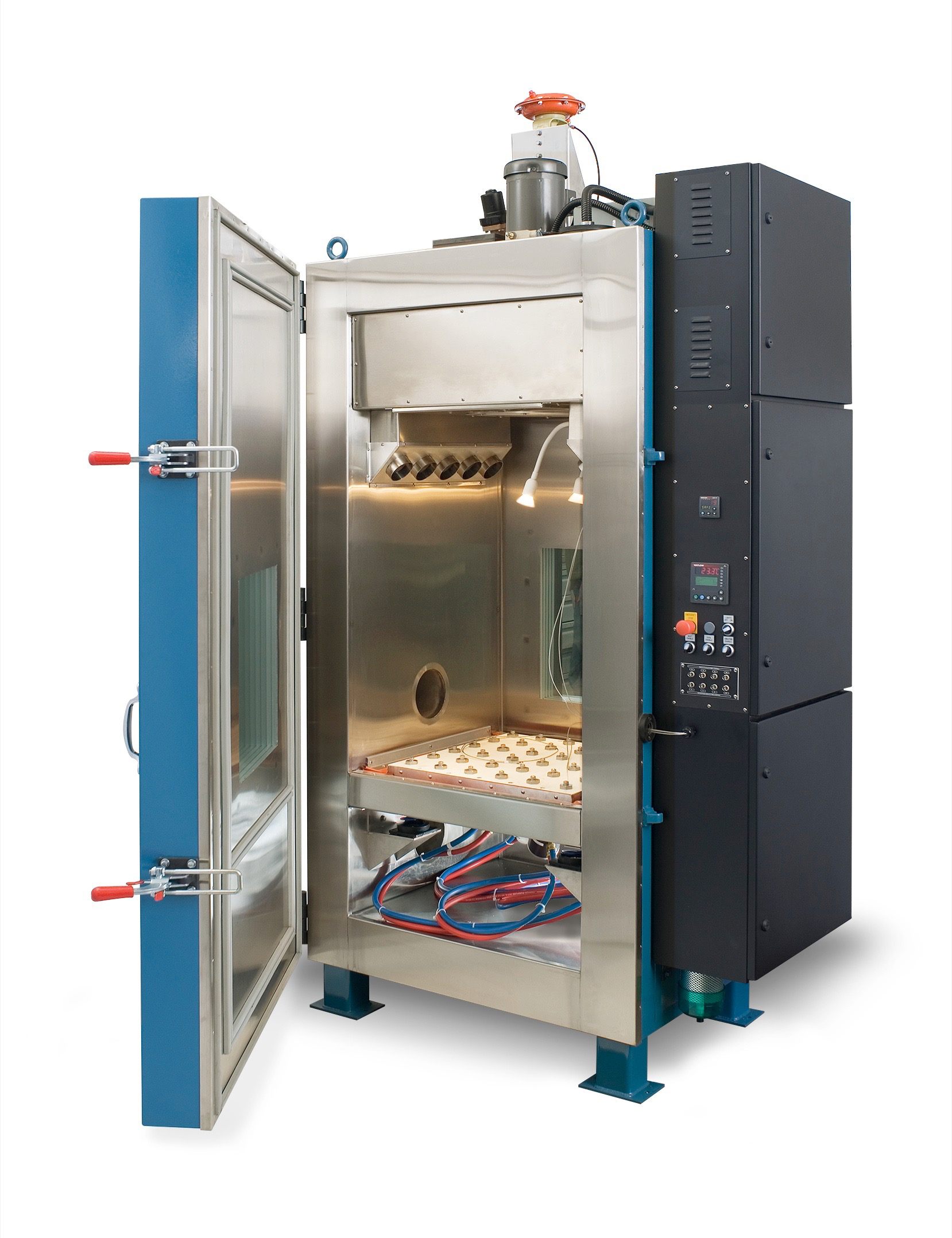

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
Key Industrial Applications of halt chamber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of halt chamber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Testing avionics and electronic components | Enhances reliability and safety of critical systems, reducing failures in the field. | Certification compliance, temperature range, vibration levels. |
| Automotive | Evaluating automotive electronics and components | Accelerates product development cycles, minimizing warranty costs and recalls. | Size and capacity, energy efficiency, integration with existing systems. |
| Consumer Electronics | Assessing durability of mobile devices | Improves product longevity and customer satisfaction, reducing returns. | Testing protocols, software compatibility, local support services. |
| Industrial Equipment | Reliability testing for machinery components | Identifies design flaws early, leading to cost savings and enhanced performance. | Customization options, maintenance support, scalability of testing. |
| Renewable Energy | Testing solar panels and wind turbine components | Ensures performance under extreme conditions, enhancing market competitiveness. | Environmental compliance, energy consumption, adaptability to local conditions. |
How is HALT Chamber Used in Aerospace & Defense Testing?
In the aerospace and defense sectors, HALT chambers are crucial for testing avionics and electronic components. These systems undergo extreme temperature and vibration conditions to identify potential failures before deployment. By simulating real-world stresses, companies can ensure the reliability and safety of their systems, which is essential for mission-critical operations. Buyers in this sector must consider certification compliance and the chamber’s ability to replicate specific temperature ranges and vibration levels.
What Role Does HALT Play in Automotive Development?
Automotive manufacturers utilize HALT chambers to evaluate the reliability of electronic components and systems in vehicles. This testing accelerates product development cycles, allowing manufacturers to identify design flaws early, which can significantly reduce warranty costs and recalls. When sourcing HALT chambers, automotive companies should focus on size and capacity, energy efficiency, and the ability to integrate testing systems into existing workflows.
How Does HALT Testing Benefit Consumer Electronics?
Consumer electronics companies use HALT chambers to assess the durability of products like smartphones and tablets. By subjecting devices to extreme conditions, manufacturers can enhance product longevity and customer satisfaction, ultimately reducing return rates. Key considerations for international buyers include the specific testing protocols employed, software compatibility for data analysis, and the availability of local support services for maintenance.
Why is HALT Important for Industrial Equipment Reliability?
In the industrial equipment sector, HALT chambers are essential for reliability testing of machinery components. By identifying design flaws early in the development process, manufacturers can achieve significant cost savings and enhance the overall performance of their products. Buyers should consider customization options to meet specific testing requirements, as well as maintenance support and the scalability of testing solutions to accommodate varying production volumes.
How is HALT Chamber Used in Renewable Energy Testing?
Renewable energy companies leverage HALT testing to ensure the performance of solar panels and wind turbine components under extreme environmental conditions. This testing is critical to validating product durability and enhancing competitiveness in a growing market. When sourcing HALT chambers, companies should prioritize environmental compliance, energy consumption efficiency, and the adaptability of testing setups to local climatic conditions.
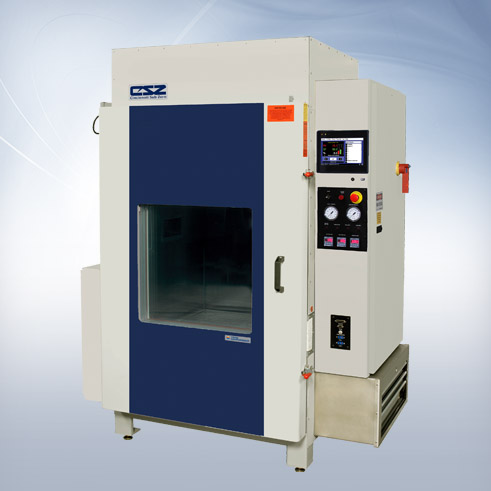

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘halt chamber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Long Testing Cycles
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of extended testing cycles when using traditional testing methods. This can lead to significant delays in product development, affecting time-to-market and overall competitiveness. In industries where rapid innovation is key, such as electronics or automotive, slow testing processes can result in missed opportunities and increased costs. Buyers are often frustrated by the inability to identify design flaws early, leading to costly recalls and warranty claims down the line.
The Solution: To combat long testing cycles, B2B buyers should invest in a Highly Accelerated Life Test (HALT) chamber. These chambers significantly reduce testing time by simulating extreme conditions, allowing for quicker identification of product weaknesses. Buyers should look for chambers equipped with advanced features such as rapid temperature cycling and simultaneous vibration testing. For instance, models that offer ramp rates of 60-100°C per minute enable faster thermal transitions, which can accelerate the testing process. Additionally, integrating data logging and monitoring systems allows for real-time analysis and quicker adjustments, thereby streamlining the overall testing workflow.
Scenario 2: Managing High Operational Costs
The Problem: Operational costs are a major concern for B2B buyers, especially in regions where energy prices are high. The inefficient use of resources during testing can lead to inflated costs, impacting the budget for research and development. Buyers often find that traditional testing chambers consume excessive energy, resulting in higher operational expenses and diminishing returns on investment.
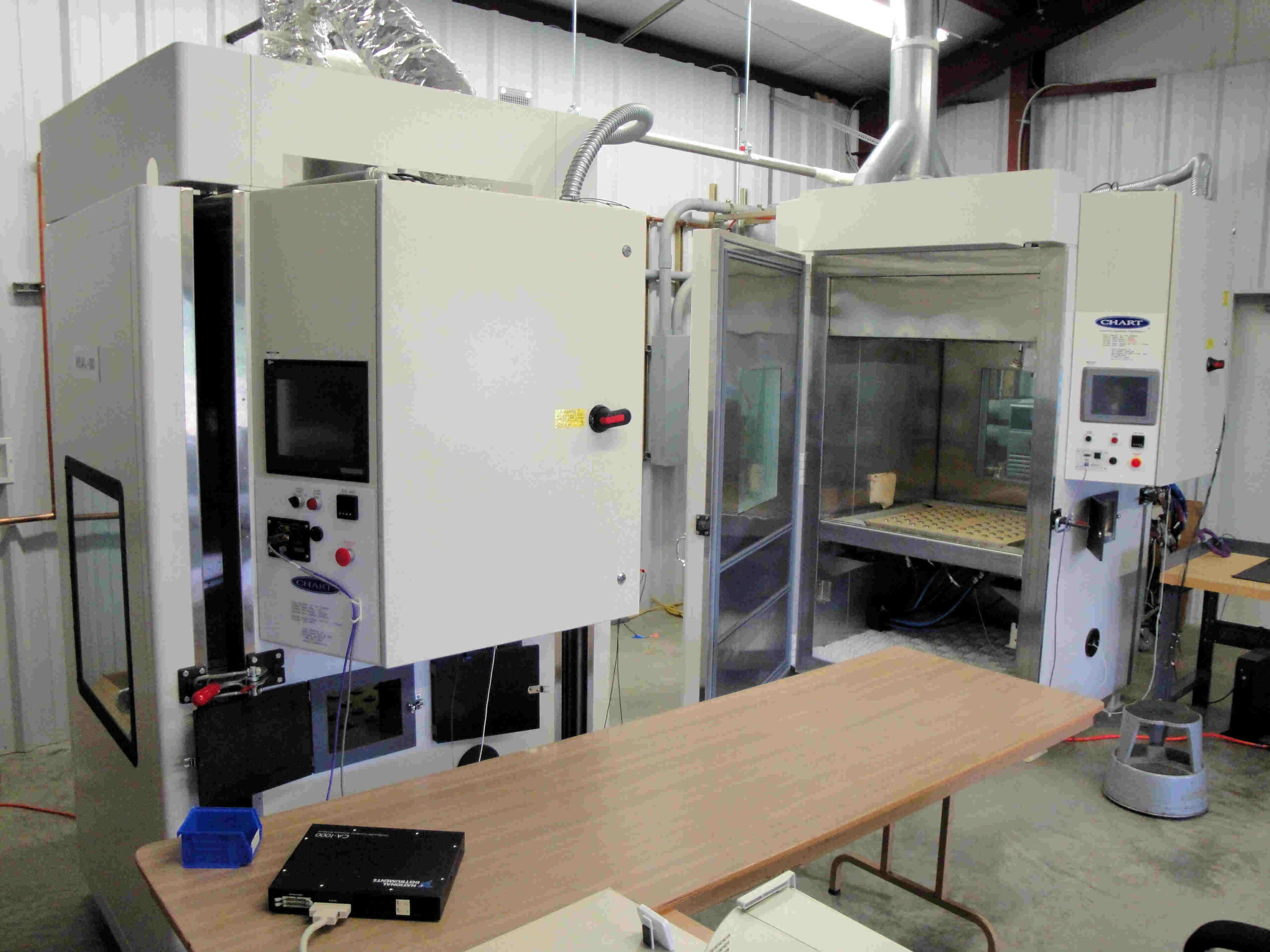

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
The Solution: Buyers should consider HALT chambers designed for energy efficiency. Opting for models that utilize vacuum-jacketed liquid nitrogen cooling systems can drastically reduce energy consumption and eliminate issues like condensation and dripping water. These systems not only maintain consistent temperatures but also enhance safety and reduce maintenance costs. Additionally, buyers should evaluate suppliers who offer customizable features that align with their specific needs, such as proportional control systems that optimize liquid nitrogen usage. Investing in energy-efficient HALT chambers not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to sustainability initiatives, making it a smart choice for modern businesses.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Reliable Data and Testing Accuracy
The Problem: Inaccurate data from testing processes can lead to flawed product designs and ultimately, market failures. B2B buyers often struggle with the reliability of data obtained from conventional testing methods, where environmental factors and equipment limitations can skew results. This unreliability can erode trust with stakeholders and complicate compliance with industry standards.
The Solution: To ensure reliable data and testing accuracy, buyers should opt for HALT chambers with advanced control systems and instrumentation. Look for chambers equipped with PLC-based controls and LabVIEW-based operation for precise monitoring of thermal and vibrational profiles. The inclusion of multiple accelerometers and thermocouples can provide comprehensive data, enhancing the accuracy of the results. Moreover, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer robust software tools for data analysis and integration with automated test equipment (ATE). This enables a more thorough evaluation of test results and fosters better decision-making. Regular maintenance agreements can also help ensure that the testing equipment remains calibrated and functioning optimally, further enhancing data reliability.
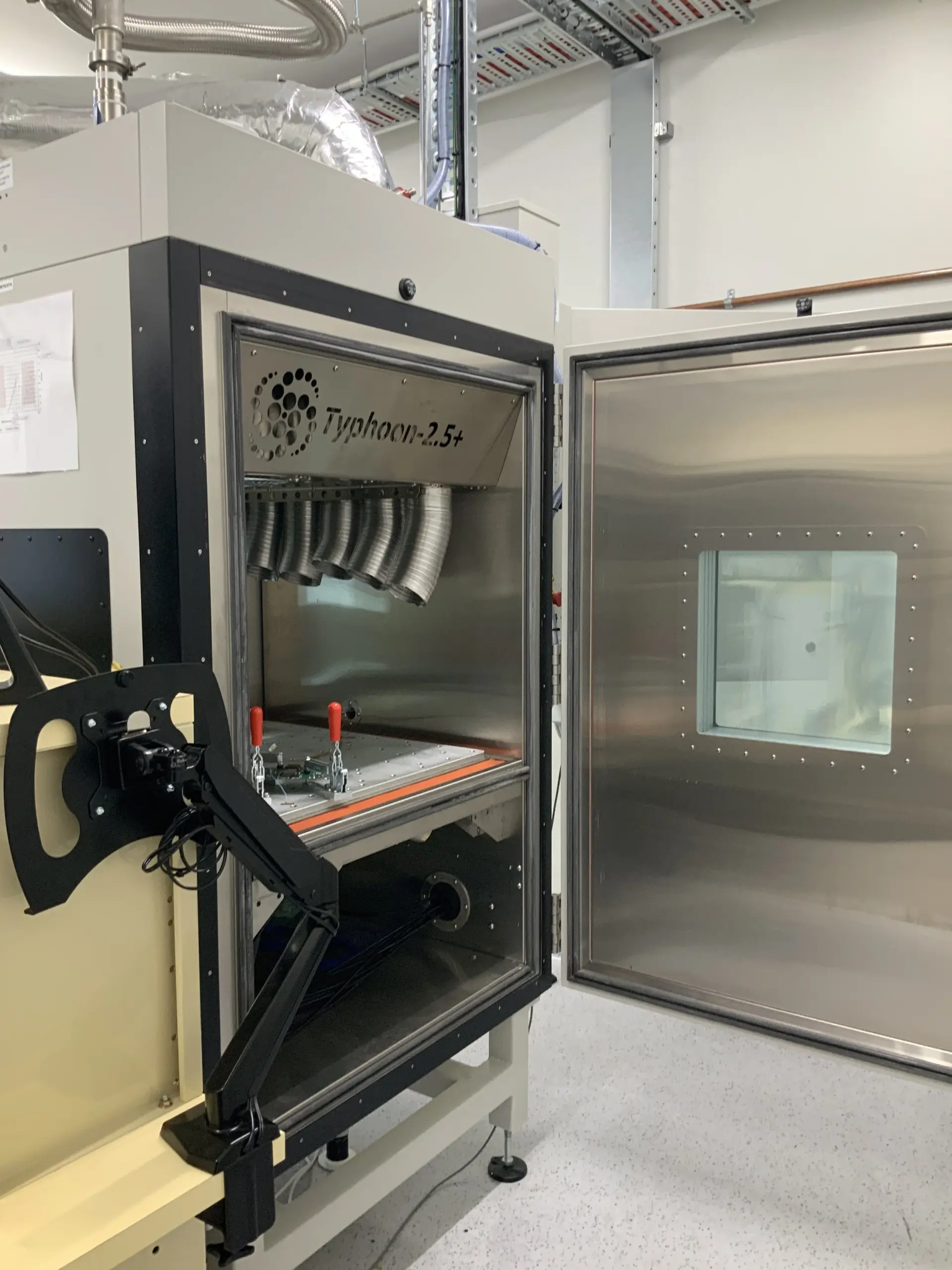

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
By addressing these common pain points with targeted solutions, B2B buyers can improve their testing processes, reduce costs, and ultimately bring more reliable products to market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for halt chamber
What are the Key Materials Used in HALT Chambers?
When selecting materials for HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing) chambers, several factors influence the decision-making process, including thermal performance, durability, and compatibility with various testing environments. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of HALT chambers, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in HALT Chamber Applications?
Stainless steel is a widely used material in HALT chambers due to its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperature variations, making it ideal for environments that require rapid heating and cooling. Stainless steel also offers high structural integrity and durability, ensuring long-term performance under rigorous testing conditions.
Pros: It is durable, easy to clean, and resistant to rust and corrosion. Its strength allows for the construction of robust chamber designs capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than other materials. Additionally, stainless steel can be difficult to machine, leading to increased manufacturing complexity.

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various media and its ability to maintain structural integrity under thermal cycling make it suitable for a wide range of testing scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used meets the required specifications for their specific applications.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in HALT Chamber Design?
Aluminum is another common material used in HALT chambers, particularly for structural components and heat exchangers. It is lightweight yet strong, offering good thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum facilitates easier handling and installation. It is also more cost-effective than stainless steel, which can help reduce overall project budgets.
Cons: While aluminum is corrosion-resistant, it may not perform as well as stainless steel in extreme environments. It can also be less durable under high-stress conditions, leading to potential deformation over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal properties make it suitable for applications requiring rapid temperature changes, but its lower strength may limit its use in high-pressure scenarios.
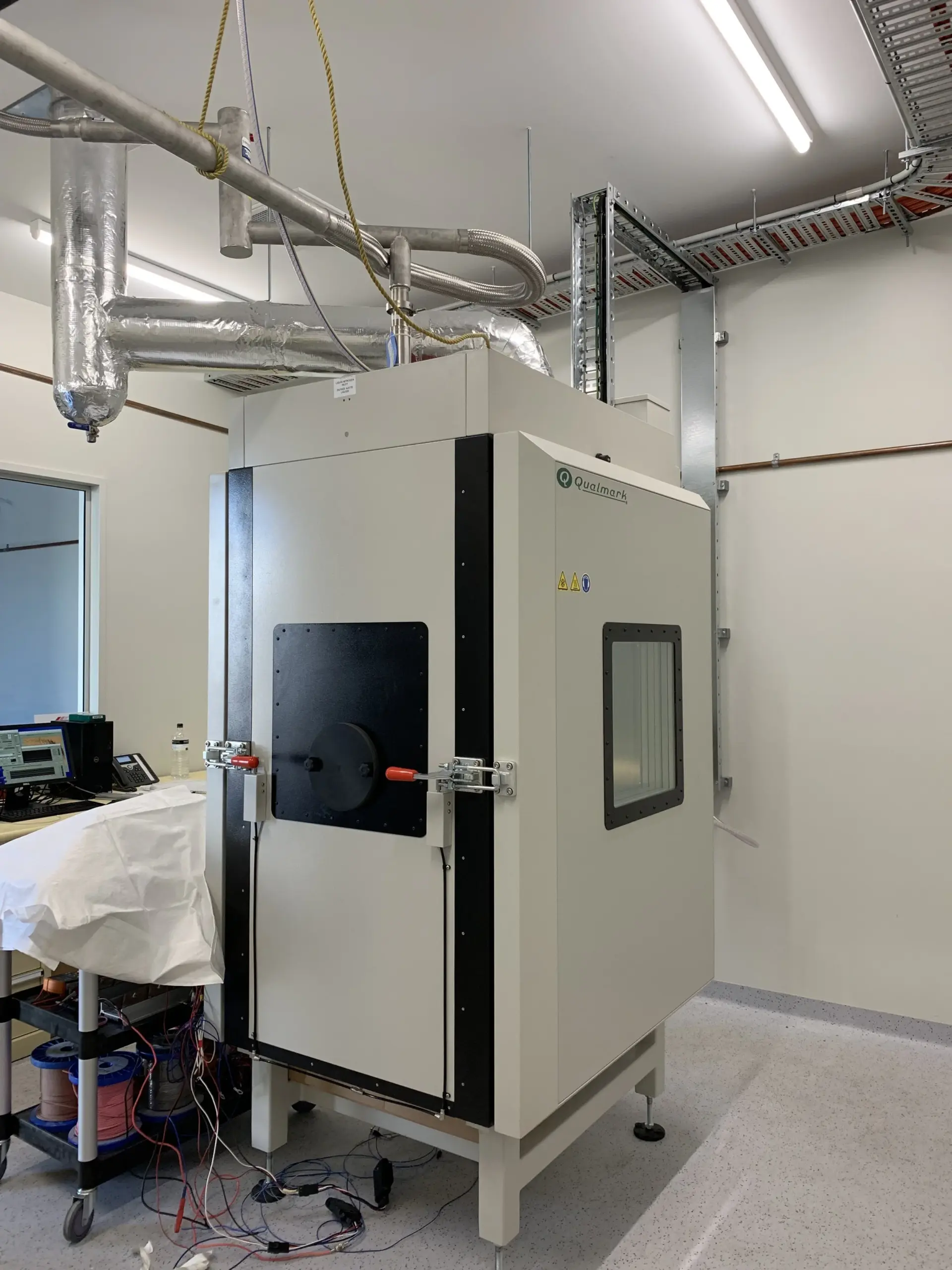

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet relevant international standards, especially in regions with strict regulatory requirements.
How Does Composite Material Enhance HALT Chamber Functionality?
Composite materials, often a combination of polymers and metals, are increasingly used in HALT chambers for their excellent thermal insulation properties and lightweight characteristics. They can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros: Composites offer superior thermal insulation, reducing energy costs associated with heating and cooling. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be engineered to specific requirements.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly. Additionally, their long-term durability under extreme conditions may not match that of metals.
Impact on Application: Composites can be particularly beneficial in applications where thermal efficiency is paramount, but their suitability for high-stress environments should be evaluated carefully.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the certification of composite materials against international standards to ensure compliance and performance reliability.
What Advantages Does Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) Offer for HALT Chambers?
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) is increasingly being utilized in HALT chambers due to its lightweight and high-strength characteristics. GRP is particularly effective in environments where thermal insulation is critical.
Pros: GRP provides excellent thermal insulation and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various testing environments. Its lightweight nature also simplifies installation.
Cons: The primary limitation is its lower structural integrity compared to metals, which may affect its performance under extreme stress conditions.
Impact on Application: GRP is ideal for applications requiring effective thermal insulation but may not be suitable for high-pressure testing scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that GRP meets necessary international compliance standards, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for HALT Chambers
| Material | Typical Use Case for halt chamber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Structural components and interiors | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Heat exchangers and structural parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength under high stress | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Insulation and specialized components | Excellent thermal insulation | Complex manufacturing and potential durability issues | Medium |
| Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) | Insulation and lightweight structures | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower structural integrity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers considering HALT chambers. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can significantly influence the performance and longevity of testing equipment in various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for halt chamber
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a HALT Chamber?
The manufacturing process of Highly Accelerated Life Test (HALT) chambers involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards, ultimately delivering reliable testing solutions for B2B clients.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing HALT chambers is the careful selection and preparation of materials. High-grade stainless steel is often used for the chamber’s interior due to its corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. The material is cut to size and inspected for quality before moving to the forming stage. This stage may involve processes like laser cutting and CNC machining to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances.
Forming Techniques
In the forming stage, the components of the HALT chamber are shaped and fabricated. Techniques such as bending, welding, and assembling components like the vibration table and thermal conditioning systems are employed. Advanced technologies such as robotic welding can enhance precision and reduce manufacturing time, ensuring that the chambers are robust and capable of withstanding the stresses they will encounter during testing.
Assembly Process
The assembly of the HALT chamber is a critical phase that combines all previously manufactured components. Technicians meticulously fit the thermal and vibration systems, ensuring that all connections are secure and meet the necessary specifications. Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the assembly process to catch any defects early, thereby minimizing the risk of issues later on.
Finishing Touches
Once assembled, the HALT chamber undergoes a finishing process. This includes surface treatments, painting, and applying insulation to enhance energy efficiency. The final assembly is also tested for leaks and structural integrity before being prepared for shipment. Proper finishing not only improves the aesthetics of the chamber but also contributes to its performance and longevity.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into HALT Chamber Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in the manufacturing of HALT chambers, ensuring that every unit meets international standards and specific customer requirements. This involves adhering to various quality management systems and industry-specific certifications.
What International Standards Are Relevant to HALT Chambers?
Manufacturers of HALT chambers typically comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, compliance with CE marking requirements indicates that the product meets European safety and environmental standards, which is particularly important for buyers in Europe.
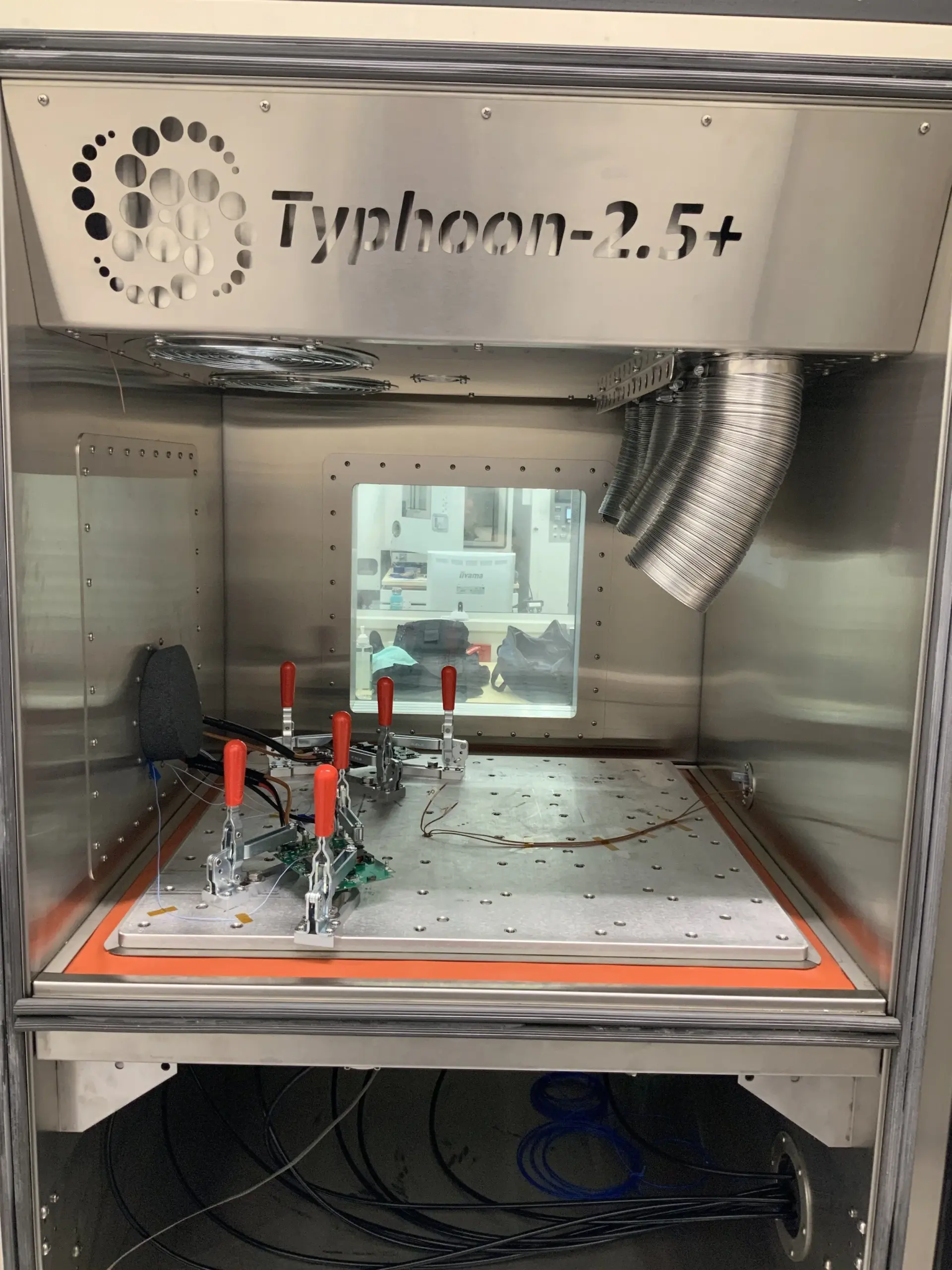
Illustrative image related to halt chamber
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control is integrated at multiple stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor processes and identify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive evaluation of the completed HALT chamber is performed, including functional testing and performance validation.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in HALT Chamber Production?
Testing methods for HALT chambers are crucial to verify their performance and reliability. Common methods include:
- Thermal Cycling Tests: These tests evaluate the chamber’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes, ensuring that it can accurately simulate extreme conditions.
- Vibration Tests: The vibration system is tested to ensure it can deliver the required frequency and amplitude, which is vital for effective HALT testing.
- Functional Testing: Each chamber is subjected to operational tests to confirm that all systems work as intended, including temperature control and vibration mechanisms.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential to ensure they receive reliable products. Here are several strategies:
Conducting Audits
Buyers can perform on-site audits of manufacturing facilities to assess quality control processes firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality management systems and observing production practices.
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality assurance reports, including data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. This transparency builds trust and allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Employing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can verify compliance with international standards and ensure that the HALT chambers meet specified requirements.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances when sourcing HALT chambers. These include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards relevant to their markets.
- Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is crucial in the B2B space. Buyers should consider suppliers who can provide documentation and support in languages they understand.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality control does not end at manufacturing. Buyers should assess the supplier’s logistics capabilities to ensure that products are delivered in good condition and on time.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for HALT chambers is vital for B2B buyers seeking reliable testing solutions. By focusing on the manufacturing stages, quality control standards, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can make informed decisions and build successful partnerships with suppliers in this critical industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘halt chamber’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure a Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) chamber. Designed to enhance product reliability and performance, HALT chambers are crucial in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This guide will help you navigate the procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your organizational needs.
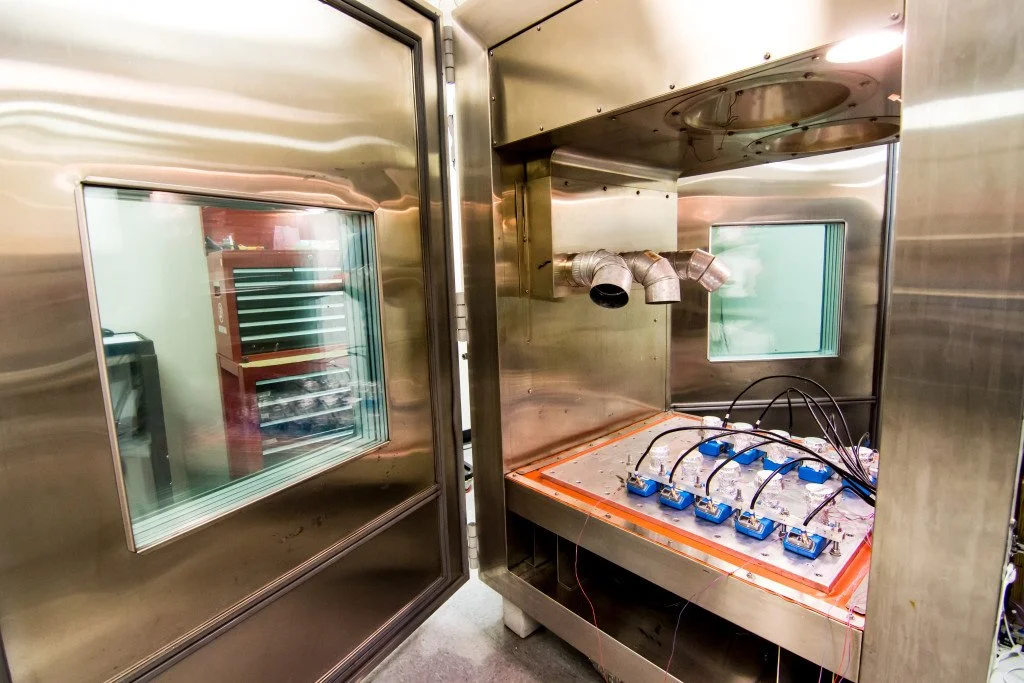

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital before initiating the procurement process. Determine the required temperature range, vibration capabilities, and chamber size based on the products you intend to test. Consider factors such as:
- Temperature and Vibration Requirements: Specify the extremes your products will endure to ensure the chamber can replicate these conditions accurately.
- Size and Capacity: Assess the dimensions of the products to be tested to ensure they fit comfortably within the chamber.
Step 2: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing HALT chambers. Look for companies that specialize in environmental testing equipment and have established a strong presence in your target markets. Key aspects to consider include:
- Industry Experience: Favor suppliers with extensive experience in your specific industry, as they will better understand your unique testing needs.
- Customer Reviews and Case Studies: Request testimonials or case studies from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; consider:
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure the supplier meets international standards such as ISO certifications, which signify quality and reliability.
- Product Demonstrations: If possible, arrange for demonstrations to observe the chamber’s functionality and performance firsthand.
Step 4: Assess Technical Support and Training
Technical support and training are essential components of your HALT chamber investment. Evaluate the supplier’s offerings in this area to ensure you receive adequate assistance. Consider:
- Training Programs: Inquire about training sessions for your team on how to operate the chamber effectively.
- Ongoing Support: Assess the availability of customer support and maintenance services post-purchase to address any operational challenges.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline all costs associated with the purchase. This step is critical for financial planning and budget alignment. Pay attention to:
- Pricing Transparency: Ensure that the quotation includes costs for optional features, installation, and potential shipping fees.
- Lead Times: Confirm the expected delivery timelines to align with your project schedules.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Service Agreements
A robust warranty and service agreement can provide peace of mind and protect your investment. Carefully review the terms offered by each supplier, focusing on:
- Warranty Duration: Check the length and coverage of the warranty to ensure it meets your operational needs.
- Service Agreements: Evaluate the terms of any maintenance or service agreements that may be available to support long-term functionality.
Conclusion
By following this step-by-step checklist, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of procuring a HALT chamber. This structured approach ensures that you make informed decisions, ultimately enhancing your product testing capabilities and driving reliability in your offerings.

Illustrative image related to halt chamber
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for halt chamber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for HALT Chamber Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Test) chambers is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-grade stainless steel is commonly used for the interior to ensure durability and thermal efficiency, while insulation materials can vary in cost based on performance specifications. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in superior materials versus lower-cost options.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Customization and advanced technology integration often require skilled labor, which can drive up costs. Understanding the local labor market dynamics can help buyers gauge potential labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead costs encompass all indirect expenses associated with production, such as utilities and facility maintenance. Tooling costs, particularly for specialized components, can significantly affect the overall price, especially for custom or high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure that each chamber meets rigorous standards. The costs associated with testing and certification, especially for international markets, should be factored into the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the destination and shipping method. Buyers must consider Incoterms and potential tariffs, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Supplier Margin: The supplier’s margin varies based on market positioning, brand reputation, and the level of customer support offered. Established brands with a strong track record may command higher prices due to perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect HALT Chamber Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of HALT chambers, making it essential for buyers to understand these nuances.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer better pricing for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate favorable terms, especially if they anticipate future needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as advanced control systems or unique temperature ranges can significantly affect price. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these features against their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Chambers that comply with international quality standards or have specific certifications may incur higher costs. However, these certifications often ensure reliability and longevity, which can lead to cost savings in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and relationship with logistics partners can impact pricing. Long-standing suppliers may offer better terms due to established operational efficiencies.
-
Incoterms and Shipping Considerations: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Costs can vary depending on whether the buyer or supplier is responsible for shipping and handling.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Secure Better Pricing?
Negotiating effectively can lead to substantial savings. Here are some strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to purchase multiple units, use this as a negotiation point to secure better pricing.
-
Discuss Long-Term Partnerships: Expressing interest in a long-term partnership can encourage suppliers to offer more favorable terms.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of costs. This transparency can aid in negotiations and help identify areas for potential savings.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also ongoing costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If a supplier’s terms do not meet your budget, be ready to explore other options. This stance can often lead to improved offers.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several unique factors can influence pricing:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of how currency rates can affect the final cost, especially for international purchases.
-
Import Tariffs and Taxes: Research potential import duties that may apply, as these can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Local Regulations: Compliance with local standards may necessitate additional features or certifications, impacting pricing.
-
Logistics Challenges: Consider the reliability of logistics providers in your region and how this may affect shipping times and costs.
Conclusion
In summary, the sourcing of HALT chambers involves a complex interplay of cost components and price influencers. By understanding these factors and employing effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and ensure they receive the best value for their investment. Always seek detailed quotes and be informed about all associated costs to make a well-rounded decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing halt chamber With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in HALT Testing Solutions
In the realm of reliability testing, the Highly Accelerated Life Test (HALT) chamber is a sophisticated tool designed to identify product weaknesses through extreme temperature and vibration conditions. However, various alternatives exist that may suit specific needs or budgets of B2B buyers. Understanding these alternatives can help organizations make informed decisions when investing in testing solutions.
| Comparison Aspect | Halt Chamber | Environmental Stress Screening (ESS) | Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High performance in identifying design flaws rapidly. | Effective for long-term reliability predictions but less aggressive than HALT. | Similar to HALT, but often less intense; focuses on specific failure modes. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment but cost-effective in reducing recalls and warranty claims. | Generally lower upfront costs, but may incur additional long-term testing expenses. | Moderate costs, but can vary widely based on specific methodologies and equipment. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized knowledge for setup and operation. | Easier to implement as it often uses existing test setups. | Can be straightforward, but the complexity depends on the testing protocols employed. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance; parts can be costly. | Lower maintenance requirements; typically uses simpler equipment. | Maintenance varies based on equipment complexity; generally manageable. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for products needing rapid design validation and failure analysis. | Best suited for ongoing reliability testing in production environments. | Effective for early-stage product development and pre-production testing. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Environmental Stress Screening (ESS)
ESS employs a combination of temperature and humidity cycling to evaluate product reliability under stress. While it is a cost-effective alternative, it is not as aggressive as HALT testing. The primary advantage of ESS is its ease of implementation, as it can often utilize existing equipment and processes. However, it may not uncover all potential design flaws as thoroughly as HALT, leading to possible late-stage failures in the field.
Accelerated Life Testing (ALT)
ALT focuses on simulating the aging process of products through controlled environmental conditions, often involving temperature and humidity variations. This method is particularly useful for predicting product longevity and identifying failure modes early in the design phase. While ALT can be less intense than HALT, it provides valuable insights into product durability. The main drawback is that it may not reveal immediate design flaws as effectively, potentially resulting in higher long-term costs due to product failures post-launch.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a testing solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including budget constraints, the urgency of product development, and the criticality of reliability in their industry. HALT chambers offer unparalleled performance for rapid flaw identification, making them ideal for high-stakes applications where product reliability is paramount. In contrast, alternatives like ESS and ALT may provide cost-effective solutions for organizations focusing on long-term reliability without the immediate pressures of market introduction. Ultimately, the choice should align with the organization’s strategic goals and risk management strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for halt chamber
What Are the Key Technical Properties of HALT Chambers?
Understanding the technical specifications of HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing) chambers is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance product reliability and reduce time-to-market. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Temperature Range
The operational temperature range of a HALT chamber typically spans from -100°C to 250°C. This range allows for extensive testing under extreme conditions, helping to identify potential design flaws. For international buyers, selecting a chamber with the appropriate temperature range ensures that the products can withstand the environmental extremes they may encounter in different markets, such as the harsh climates found in parts of Africa or South America. -
Change Rate
Change rates refer to how quickly the chamber can alter temperatures, often ranging from 60°C to 100°C per minute. High change rates are essential for simulating rapid environmental shifts, which can accelerate the identification of weaknesses in product designs. This capability is particularly valuable for industries where time-to-market is critical, as it allows for quicker iterations and refinements. -
Vibration Specifications
HALT chambers often feature advanced vibration technology, capable of providing multi-frequency excitation (e.g., from 10 Hz to over 5,000 Hz). This ability is vital for testing complex assemblies that experience various vibrational stresses during their lifecycle. Understanding the vibration specifications helps businesses ensure that their products can withstand operational stresses, reducing the risk of premature failures. -
Cooling System Efficiency
Many HALT chambers utilize a vacuum-jacketed liquid nitrogen (LN2) cooling system. This design not only minimizes energy consumption but also enhances temperature stability and reduces safety hazards associated with condensation. For B2B buyers, selecting a chamber with an efficient cooling system can lead to significant operational cost savings over time. -
Control System Capabilities
A sophisticated control system, often based on Windows platforms and featuring LabVIEW integration, is essential for precise monitoring and data logging during tests. This capability allows businesses to analyze performance metrics comprehensively, leading to better-informed decisions and optimizations. -
Material and Build Quality
The interior of HALT chambers is typically constructed from stainless steel, ensuring durability and ease of maintenance. The build quality is crucial for maintaining consistent performance over long periods, which is particularly important for organizations that rely on extensive testing.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the HALT Chamber Market?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms associated with HALT chambers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for ensuring that the HALT chambers meet specific standards and specifications required by your business. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest order size that a supplier is willing to accept. For international buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory planning, ensuring that you meet supplier requirements while optimizing purchasing costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services. Crafting a precise RFQ for HALT chambers can help buyers receive accurate pricing and lead times, facilitating smoother procurement processes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international buyers, as it impacts total landed costs and delivery timelines. -
HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screening)
HASS is a follow-up process to HALT, focusing on identifying defects in production units by applying stress testing. Understanding HASS can help businesses implement quality control measures that prevent early product failures. -
Dew Point
Dew point is a critical measurement in environmental testing, indicating the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture. For HALT testing, maintaining appropriate dew point levels is essential to avoid condensation, which can compromise testing outcomes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right HALT chamber for their needs while navigating the complexities of international procurement.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the halt chamber Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Halt Chamber Sector?
The halt chamber market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for reliable product testing across various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and automotive. As businesses strive to minimize product failures and enhance quality assurance, HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing) and HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screening) technologies are becoming essential. The integration of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI in testing chambers allows for real-time monitoring and data analytics, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions quickly. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where the emphasis on product quality and reliability is paramount.
Emerging markets are increasingly adopting HALT/HASS systems to meet global standards. For instance, countries in Africa and South America are recognizing the value of these testing methodologies to enhance their competitive edge in the global marketplace. Additionally, energy efficiency and sustainability are key considerations for modern buyers. As manufacturers look to optimize operational costs, investing in energy-efficient chambers that reduce energy consumption without compromising performance is becoming a priority.
The market is also seeing a shift towards modular and customizable solutions that cater to specific testing needs, allowing businesses to scale their operations effectively. As such, B2B buyers are advised to stay informed about the latest innovations and choose suppliers that offer flexible solutions tailored to their unique requirements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into the Halt Chamber Supply Chain?
In today’s B2B landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing are not just trends; they are crucial components of a responsible supply chain. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including those related to halt chambers, is under scrutiny as businesses aim to minimize their carbon footprint. This has led to an increased demand for suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing waste during production.
B2B buyers should seek partners with certifications that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems. Additionally, suppliers who utilize green technologies in their manufacturing processes can provide a competitive advantage. For instance, halt chambers designed with energy-efficient cooling systems not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to a smaller environmental impact.
Moreover, the importance of transparency in the supply chain cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who openly communicate their sourcing practices and the environmental implications of their operations. This alignment with ethical sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters trust with consumers increasingly concerned about sustainability.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Halt Chambers in the B2B Context?
The evolution of halt chambers dates back to the early 1990s when the need for accelerated reliability testing became evident in various industries. Initially, these chambers were basic thermal shock devices. However, as technology advanced, the capabilities of HALT and HASS systems expanded significantly. Today, these testing chambers integrate complex functionalities, such as simultaneous temperature cycling and vibration testing, allowing for comprehensive assessments of product durability.
The introduction of automated controls and data logging systems has further transformed the landscape, enabling manufacturers to conduct tests more efficiently and accurately. As global markets became more competitive, the role of HALT testing evolved from a luxury to a necessity for businesses aiming to meet stringent quality standards and reduce the risk of product recalls. This historical context highlights the importance of HALT chambers as essential tools for modern manufacturers looking to enhance product reliability while navigating the complexities of global supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of halt chamber
-
How do I choose the right HALT chamber for my testing needs?
Choosing the right HALT chamber involves evaluating your specific testing requirements, such as temperature range, vibration frequency, and sample size. Consider the types of products you will be testing and the stresses they will encounter in real-world conditions. Review the technical specifications of different models to ensure they align with your needs. Additionally, consult with manufacturers to discuss your application and seek recommendations based on their experience with similar products. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering a HALT chamber?
Lead times for HALT chambers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, model, and any customization required. Generally, standard models may have a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks, while custom configurations can take longer. It’s advisable to communicate with your supplier early in the purchasing process to get a precise timeline, as factors such as production schedules and shipping logistics can also impact delivery. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by HALT chamber suppliers?
Payment terms for HALT chamber purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit of 30-50% upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. Always clarify payment details and any associated costs, including shipping and installation, to avoid unexpected expenses. -
How can I ensure the quality of the HALT chamber I purchase?
To ensure quality, source HALT chambers from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record in reliability testing. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request documentation of the chamber’s testing capabilities and performance metrics. Additionally, consider asking for references from other customers in your industry to gain insights into their experiences with the product and the supplier’s customer support. -
Are customization options available for HALT chambers?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for HALT chambers to meet specific testing requirements. Customizations may include adjustments to temperature ranges, vibration profiles, and interior sizes. It is essential to discuss your particular needs with the supplier during the initial consultation phase. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications to ensure the custom chamber meets your testing objectives effectively. -
What should I know about logistics and shipping for HALT chambers?
Logistics and shipping for HALT chambers can be complex due to their size and sensitivity. Ensure your supplier has experience with international shipping and understands the regulations in your country. Discuss shipping costs and options, including insurance and customs clearance. It’s also important to confirm how the chamber will be handled upon arrival, including installation and setup, to ensure it operates correctly from the start. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for HALT chambers?
Minimum order quantities for HALT chambers typically depend on the manufacturer and the model. While some suppliers may have a MOQ of one unit, others might require larger orders for specific models or custom configurations. Always inquire about MOQs during initial discussions and consider how this impacts your budget and testing timeline. -
How do I evaluate potential suppliers for HALT chambers?
When evaluating potential suppliers for HALT chambers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Request information about their product warranty and after-sales support. Additionally, assess their responsiveness and willingness to engage in discussions about your specific testing needs, as this can indicate their commitment to customer service and satisfaction.
Top 7 Halt Chamber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HALT and HASS Chambers – Time Compressor Series
Domain: haltandhass.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: HALT and HASS Chambers: Designed for accelerated reliability testing, these chambers combine high and low vibration levels with fast temperature change rates to enhance defect detection. Key products include: 1. Time Compressor 2.0 2. Time Compressor 2.5 3. Time Compressor 3.0 4. Time Compressor 4.0 5. Benchtop Vibration Table – Ideal for compact products and electronics, can be used for vibration…
2. Thermotron – HALT HASS Chamber
Domain: thermotron.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: HALT HASS Chamber – Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) and Highly Accelerated Stress Screening (HASS) utilize temperature and vibration to identify design issues, enhance product quality, and eliminate early product failures. The chamber determines product operating and destruct limits while functionally testing and continuously monitoring the product. Key benefits include quicker market intro…
3. CSZ Industrial – HALT & HASS Chambers
Domain: cszindustrial.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: HALT & HASS Chambers – Accelerated Stress Testing. Time Compressor® chambers provide extreme temperature & vibration capabilities for product design and manufacturing cycles. HALT techniques uncover design weaknesses; HASS techniques find manufacturing defects. Performance: temperature ramp rates >90ºC/min (194 ºF/min), vibration levels 1 to 90 GRMS. Low sound levels, liquid nitrogen consumption, …
4. MPI Thermal – Halt Test Chamber
Domain: mpi-thermal.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Halt Test Chamber | Highly Accelerated Life Testing | Highly Accelerated Stress Screening | Product Line: TA-5000A, TA-5000A with Glass Cap Thermal Head & Stand, TA-5000 with Hood, TA-5000A with Clamshell & Flex Hose, TA-5000B Flex Hose & Features, TA-5000B with Clamshell & Flex Gas Hose, TA-3000A, TA-3000B, TA-1000A, TA-1000B, TC-100 Chiller | Temperature Testing Range: -80°C to +200°C | Applicat…
5. Weiss – Vibration Test Chambers
Domain: weiss-na.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: HALT & HASS and AGREE Vibration Test Chambers provide combined testing for temperature, humidity, and vibration to identify product design and production defects. Features include customizable options such as LN2 cooling and thermal limit door interlocks. They can function as stand-alone chambers for temperature and humidity testing. The chambers utilize LEEF and LOW GWP technologies for up to 40%…
6. Environmental Test Chambers – HALT HASS Solutions
Domain: environmentaltestchambers.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: HALT HASS test chambers are used to test the reliability and lifespan of products through Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) and Highly Accelerated Stress Screening (HASS). HALT identifies design flaws during the product design phase by exposing prototypes to extreme conditions such as temperature, vibrations, humidity, and radiation. HASS, on the other hand, is used during the production phas…
7. ACSTestChambers – Halt and Hass Test Chambers
Domain: acstestchambers.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Halt and Hass test chambers are designed for accelerated environmental testing, applying high environmental stress through triaxial vibration, rapid climate cycles, and humidity control. Key benefits include reduced production costs, timely corrective actions for design issues, lower engineering and warranty costs, and faster market placement of products. The chambers feature an inspection window,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for halt chamber
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for HALT chambers is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance product reliability and accelerate time-to-market. By investing in advanced testing solutions such as those offered by Qualmark and Thermotron, organizations can effectively identify design flaws and reduce the risk of costly recalls and warranty claims. The innovative features of modern HALT systems, including energy-efficient designs and comprehensive data acquisition capabilities, not only streamline the testing process but also empower manufacturers to meet stringent quality standards across diverse markets.
As buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider their options, the importance of selecting a trusted supplier cannot be overstated. Building strong relationships with reputable manufacturers ensures access to the latest technology and support services, facilitating a smoother implementation of HALT testing protocols.
Looking ahead, the demand for reliable testing solutions will continue to rise as industries evolve and consumer expectations grow. International buyers are encouraged to explore the offerings of leading HALT chamber manufacturers and leverage their expertise to drive innovation and quality in their product lines. Invest in HALT technology today to secure a competitive edge for tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to halt chamber